L36 Evolution and Medicine
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards about HIV/AIDS, sequence changes, phylogenetic trees, and evolution in the context of medicine, based on lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Lentivirus
A type of retrovirus, such as HIV, characterized by a long incubation period.
Sequencing virus
HIV is a virus with a genome, which is inserted into human genome in infected cells. Using PCR we can isolate viral genomes or pieces of viral genomes from patients.
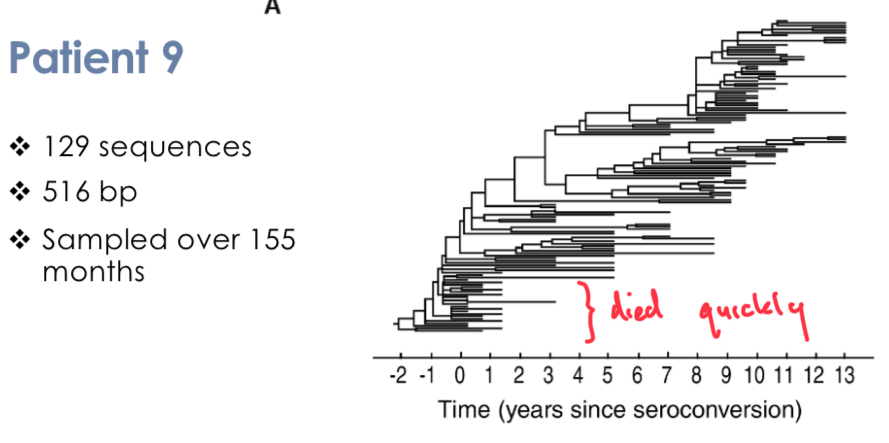
Tree of HIV sequence
Multiple sequences come from each patient, and these sequences are more closely related within a patient than between patients.

Infections from multiple viruses (1st theory why within rather than between)
Each patient may have more than one viral sequence due to infection of multiple viruses. Maybe because, multiple sequences, infection from a ‘bulk source’. But no because doesn’t explain the pattern of the tree.
The viruses are changing (2nd theory why within rather than between)
The multiple sequences may be due to virus changing within patient. Maybe becausepattern of tree suggests single point of entry of virus, then diversification. However patient 91 has virus in two parts of the tree.
Proving theory 2
If the viruses are changing then if we sample a patient successively then we should see different viral sequences appearing. (which was observed)
Mechanism of change (proximate)
HIV is a lentivirus (sort of retrovirus), with an RNA genome, and infects and damages immune system cells.
What is causing the change? (ultimate)
Reverse transcription? Shitty enzyme with no proof reading, mutations occur.
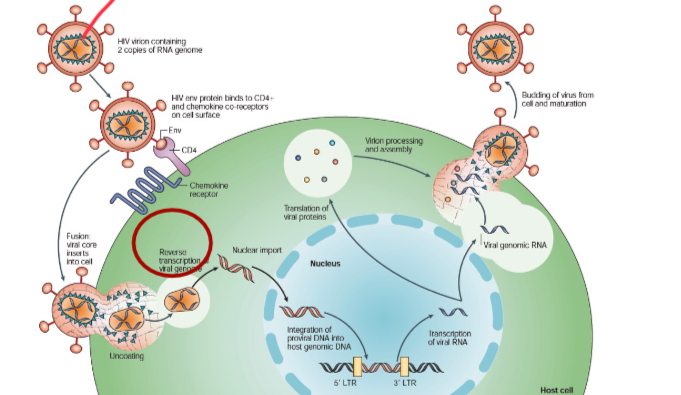
Reverse Transcriptase
An enzyme that synthesizes DNA from an RNA template to insert into genome, it is error-prone leading to many viral variants.
Reverse Transcription
The process of converting RNA sequence back into DNA, carried out by reverse transcriptase.
Is the change in sequence simply mutation?
We do not find inactivating mutations, all the variants found encode active, working viruses. So is the cause evolution?
Evolution HIV
It meets all the requirements for natural selection, looks like HIV evolves. Can test that theory by changing selective pressure= different outcome.
Do viruses evolve differently when patient takes anti-retroviral drugs?
Yes, AIDS viruses from patients on anti-retrovirals have a different pattern of variation from those that are not.
Concequences of HIV evolving
Has the fastest rate of evolving we know of, is proportional to the rate of mutation. So patients don’t just have a virus, they have heaps of viral variants. Causing rapid resistence to therapy (even complex), so making effective vaccines is very hard.
HIV
Human Immunodeficiency Virus, a retrovirus that attacks the immune system, leading to AIDS if untreated.
HIV armada
Somewhere out there is a virus thats evolved against any vaccine

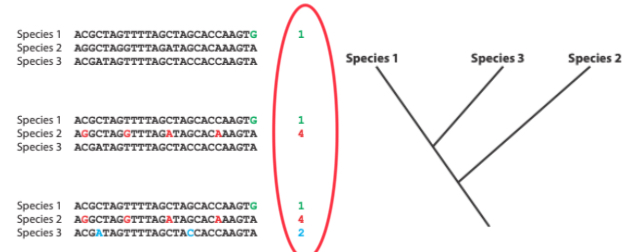
Phylogenetic Trees for HIV
Using sequenced genome, we can reconstruct the evolutionary history of HIV, and draw relationships. Made from alignment of DNA sequence.
Is HIV evolution an isolated case?
No, many pathogens evolve within host the same way. Antibiotic resistence spreading through a population of bacteria is also an evolutionary process. Our own genome evolves in response to pathogens too.
Evolution and medicine
Evolutionary thinking can help us understand and better respond to pathogens like HIV. Evolution is a key-way that pathogens respond to hosts and therapy.