Chapter 13 meiosis and sexual life cycles
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Meiosis
Most cells never undergo meiosis
Results in four unique haploid gametes
* no longer in cell cycle
Occurs only and gonads the the balls and the ovaries
Heredity
The transformation of traits through generations, and along with inherited similarity, there is variation
Gene
Unit of heredity and only classified as a gene if it is able to produce a functional product.
DNA is also the molecule of inheritance.
Linear sequence of nucleotides its location is a locus.
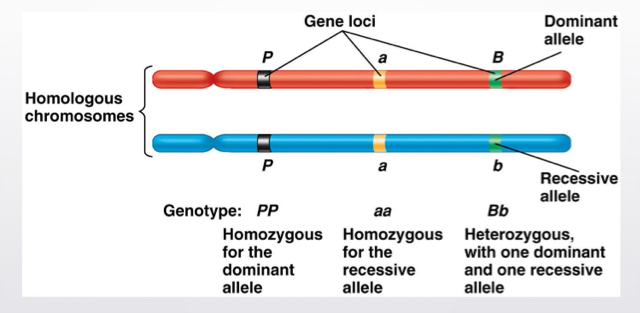
Homologous chromosomes
In diploid cells, pairs of chromosomes containing same genes, not same alleles
Sex chromosomes
Determine the sex of the individual and are called X andY in mammals.
human females have a homologous pair of X chromosomes
Human males have one x and one Y chromosome
The remaining 22 pairs of chromosomes are called autosomes
Types of reproduction
Asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction has no fusion of gametes one parent contributes offspring, genetically identical to parent essentially clones, and it uses mitosis to make duplicate budding and binary vision dividing in half.
Sexual reproduction is the fusion of two parents must contribute offspring are not identical parents and it uses meiosis. It’s all about variation.
Life cycle
Lifecycle is the generation to generation sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism
Fertilization is the union of gametes
Zygotes produce somatic cells develop into an organism
Meiosis one and Meiosis two
Meiosis one separates the members of each homologous pair and produces two dollar sales each with one set of chromosomes
Meiosis two essentially the same as mitosis and each of the cells, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate
Variation
Demonstrated by the differences in appearance that offspring show from parents and siblings
Crossing over
Crossing over, occurs in meiosis one during prophase in which exchange of corresponding genes between non sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes
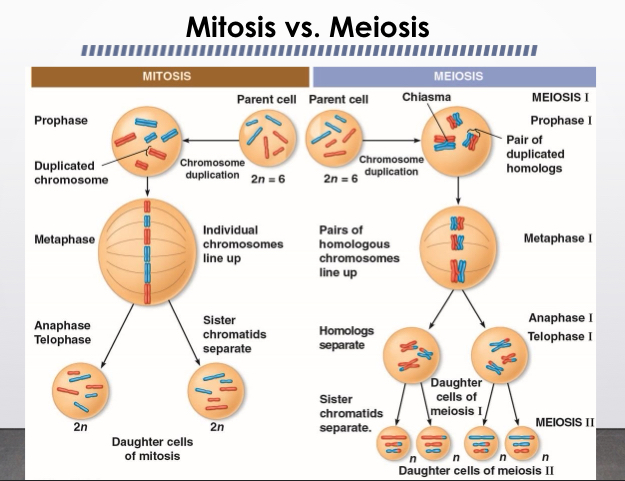
Mitosis versus meiosis
Summary of mitosis
Occurs in both diploid and haploid cells. Occurs during interface before mitosis begins. The number of divisions is only one the synopsis of homologous chromosomes that does not occur. The number of cells and genetic composition is two each genetically identical to the parent cell with the same number of chromosomes and rule animal or plant body that enables multicellular animal or plant to arise from a single cell produces self for growth repair, and in some species asexual reproduction produces gametophyte plant.
Summary of meiosis
Meiosis can only occur in diploid cells. Occurs during interphase before meiosis one begins. The number of divisions is two. The synapsis of homologous chromosomes occurs during prophase one along with crossing over between non sister chromatids, resulting in chiasmata. The number of daughter cells in genetic composition is four each haploid genetically different from the parent cell and from each other produces gam meets in animals or spores and plants reduces number of chromosomes sets by half an introduces, genetic variability among the gametes or spores
Nondisjunction.
A member of a chromosome pair fails to separate at anaphase with abnormal numbers of chromosomes appears to be involved in 10 to 30% of human conceptions and is the main reason for pregnancy loss. Failure tip of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis one also is the failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis two.