Foundations of Bio 1 - Midterm 1
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
pH equation
pH = -log[H+]
[H+] = 10^-pH
dsDNA vs. ssDNA (& RNA)
-double stranded: A-T/A-U & C-G concentrations are the same concentration, 2 strands in helix
-single stranded: bases not in same concentrations, 1 stranded helix
Peptide bonds
-link amino acids together to make polypeptides (proteins)
phosphodiester bonds
connect sugar-phosphate backbone
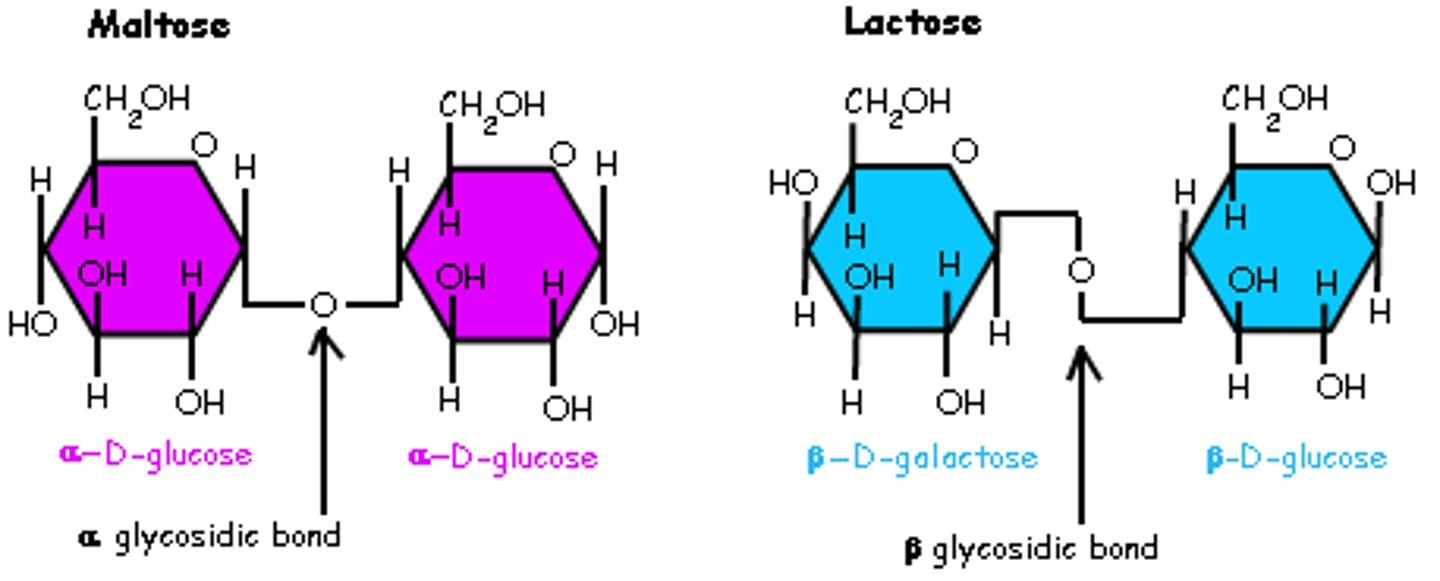
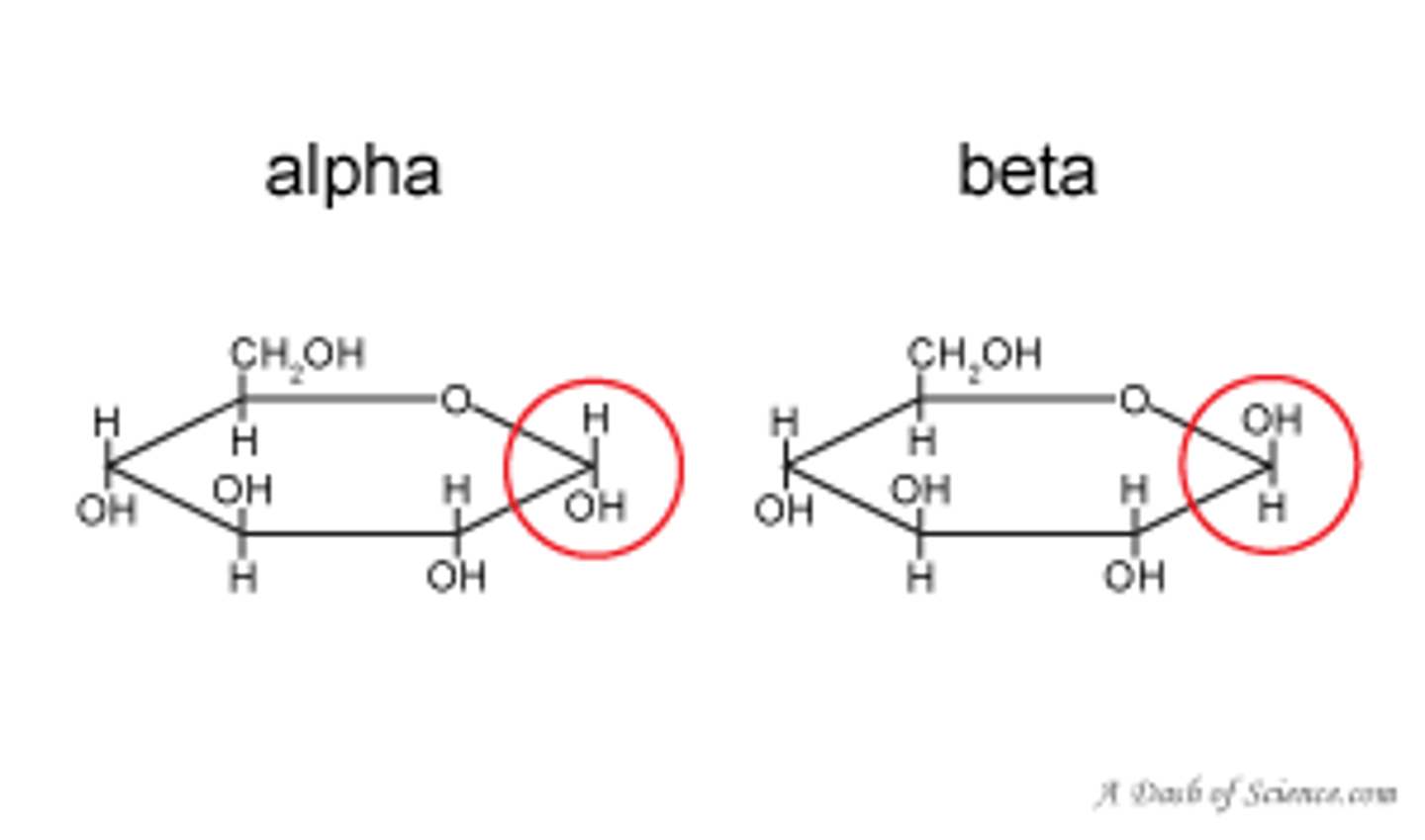
alpha glycosidic linkage
-covalent bond that connects glycogen and starch
-2 H both on top react w/ O
-is what breaks down carbs during digestion
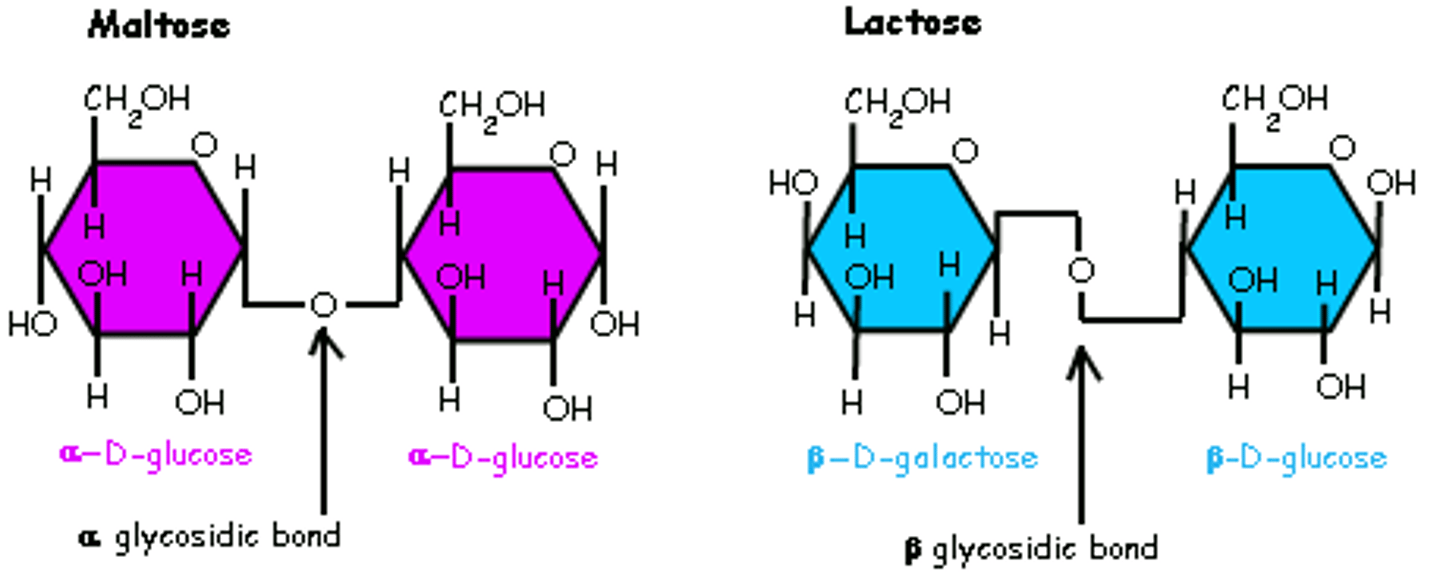
beta glycosidic linkage
-found in cellulose
-2 H, one on top other on bottom bond w/ O
structural isomers
differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms, but same formula
cis-trans isomers
differ in spatial arrangements, but same molecules
optical isomers
mirrored structures of molecules
most resistant to denaturation
proteins with many internal disulfide bonds
primary structure (proteins)
only peptide bonds, amino acid monomers -> polypeptides
secondary structure (proteins)
hydrogen bonds, alpha helices or beta pleated sheets
tertiary structure (proteins)
-hydrogen bonds
-disulfide bridges
-hydrophobic interactions
-folding of polypeptides, creation of shapes
-influences distribution of hydrophobic/phillic interactions (pH/ionic strength can alter)
quaternary structure (proteins)
-hydrogen bonds
-disulfide bridges
-hydrophobic interactions
-ionic interactions
-2+ polypeptides form larger proteins
hydrogen bonds
-non covalent
-2nd+ protein structures
polar molecules
-unequal distribution and pull of charges
-one side of molecule is more neg, other more pos
-electronegativity between 0.5-1.7
-same elements bonded, asymmetrical
nonpolar molecules
-equal sharing of electrons
-elements w/ similar electronegativity
-no partial charges
-symmetrical; polar bonds cancelled out
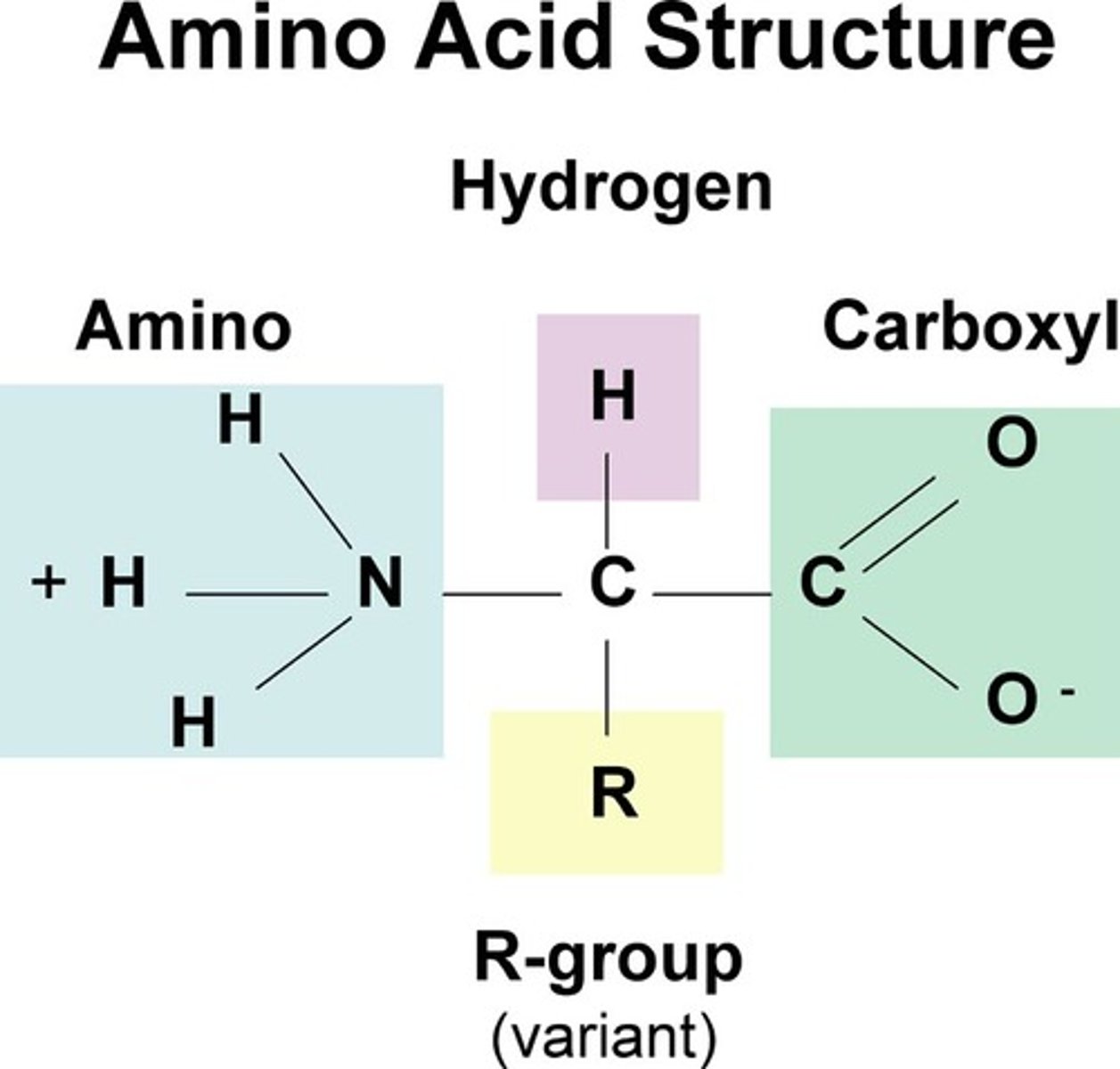
protein structure
N terminus -> C terminus
amino acid end -> carboxyl end
alpha 1,2 glycosidic linkage
-glucose + fructose = sucrose
-linkage between glucose's hexagonal structure (1) & fructose's pentagonal structure (2)
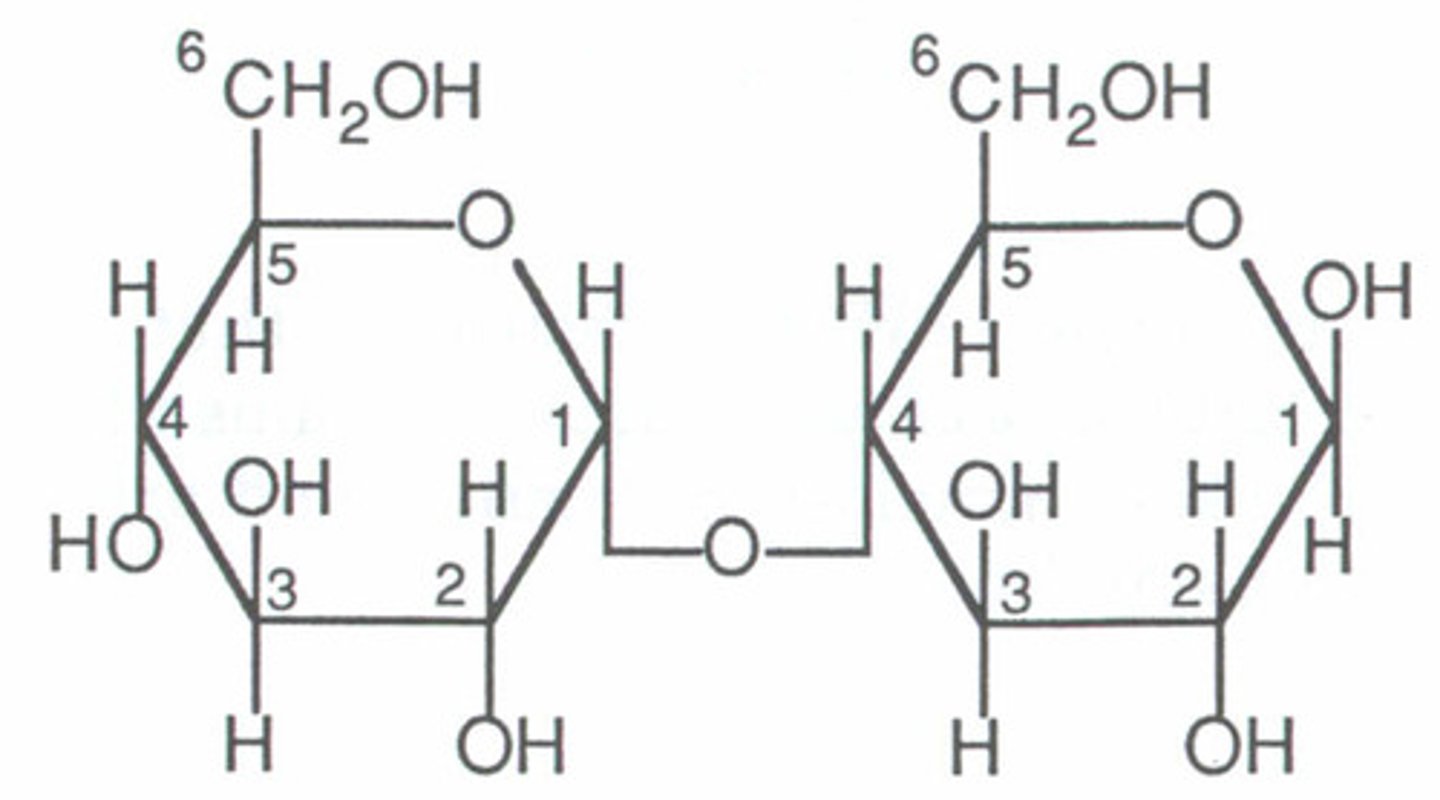
alpha 1,4 glycosidic linkage
-the number 1 carbon in one monosaccharide is bound to the number 4 carbon in another monosaccharide
-(points of hexagon right next to each other)
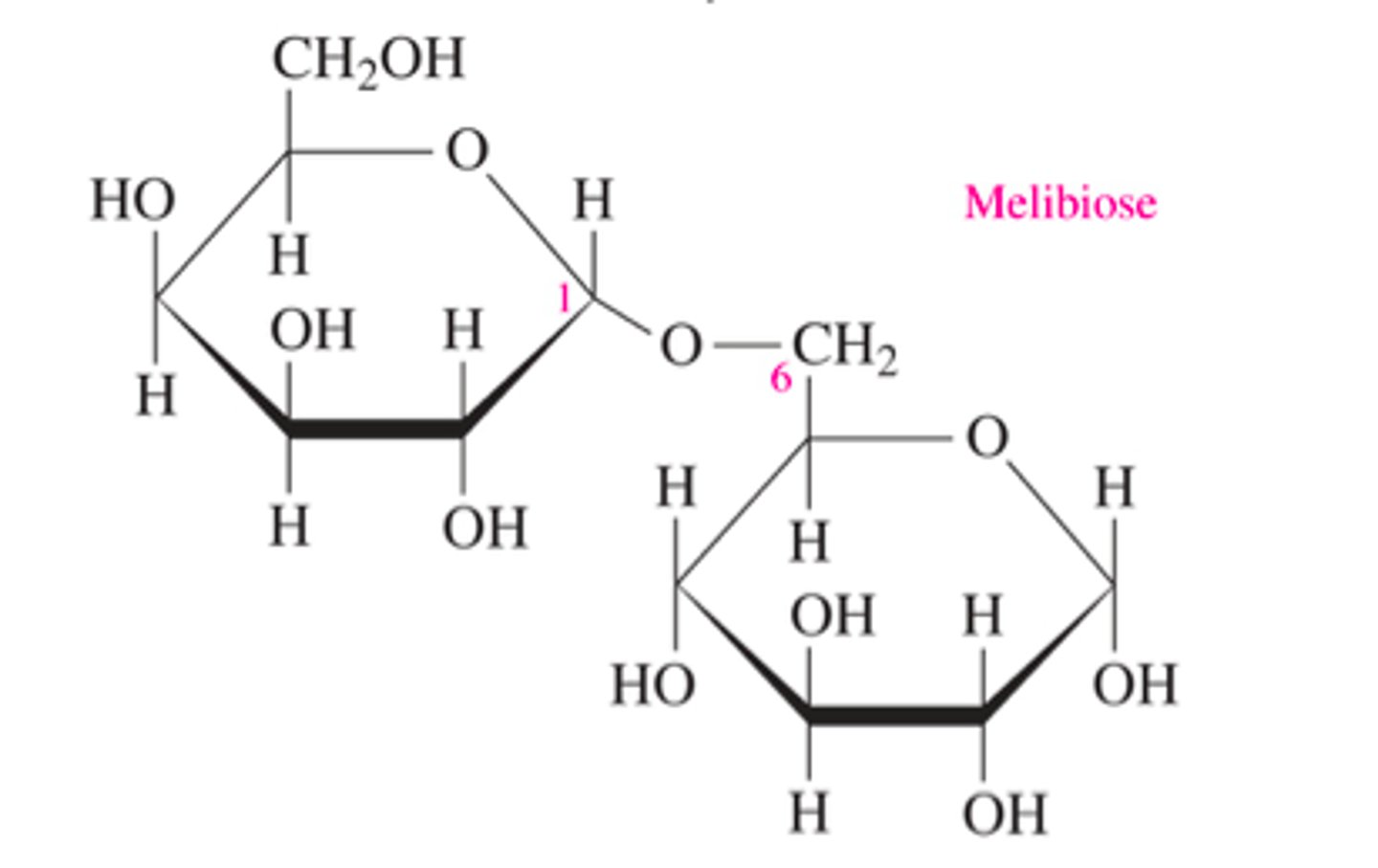
alpha 1,6 glycosidic linkage
a branch point in glycogen (1 of first monosaccharaide + top left of 2nd monosaccharide)
cellulose
-polysaccharide of glucose monomers w/ beta 1,4 glycosidic linkages (more reinforcement)
-structural, rigid
-linear chains via hydrogen bonds = rigidity
starch
-polysaccharides of glucose monomers w/ alpha glycosidic linkages
-main form of energy storage 4 plants
-branching limits hydrogen bonds, causing less stable structure (less grouped)
glycogen
-glucose polysaccharide
-highly branched & dense
-solid deposits more compact than starch
-found in liver & muscles of animals
-if none present = no energy storage
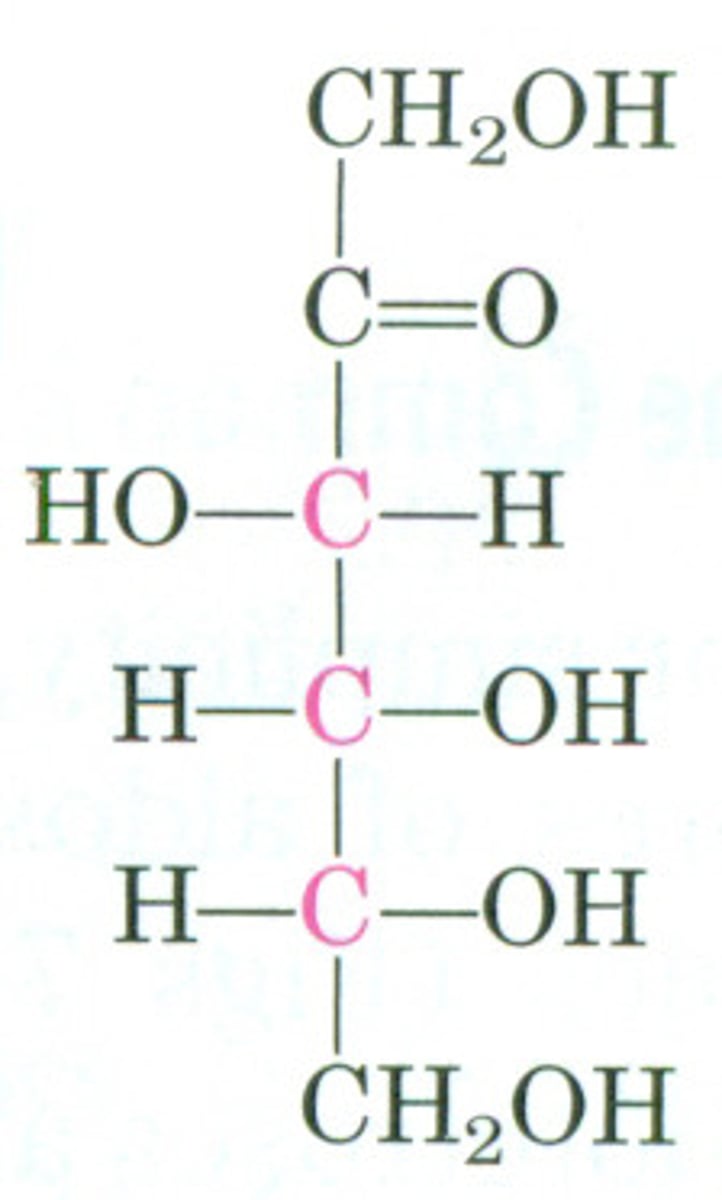
glucose
-C6H12O6, the "blood" sugar
-source of energy via glycolysis & cellular respiration
-alpha = 1st carbon has H>OH (HOH!)
-beta = 1st carbon has OH>H (OHHHHH)
-more stable ring forms
fructose
-hexose fruit sugar
-L & D forms
-forms 1,2 alpha glycosidic linkage w/ glucose
-covalent bond during cyclization = between carbons 2 & 5
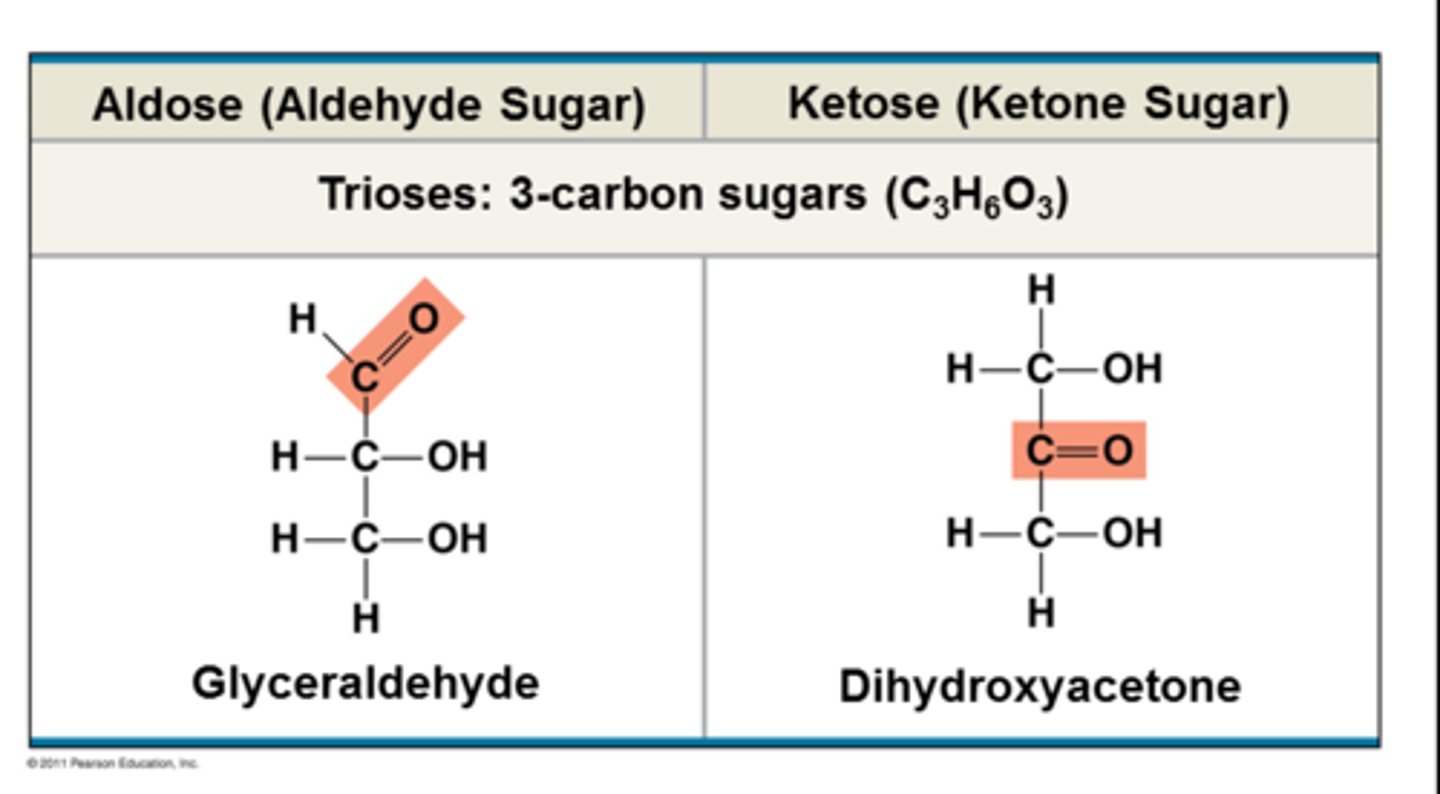
trioses
-3 carbon sugar
-glyceraldehyde more reactive bc of availability of O (at end of chain)
-pic = chemically diff structures
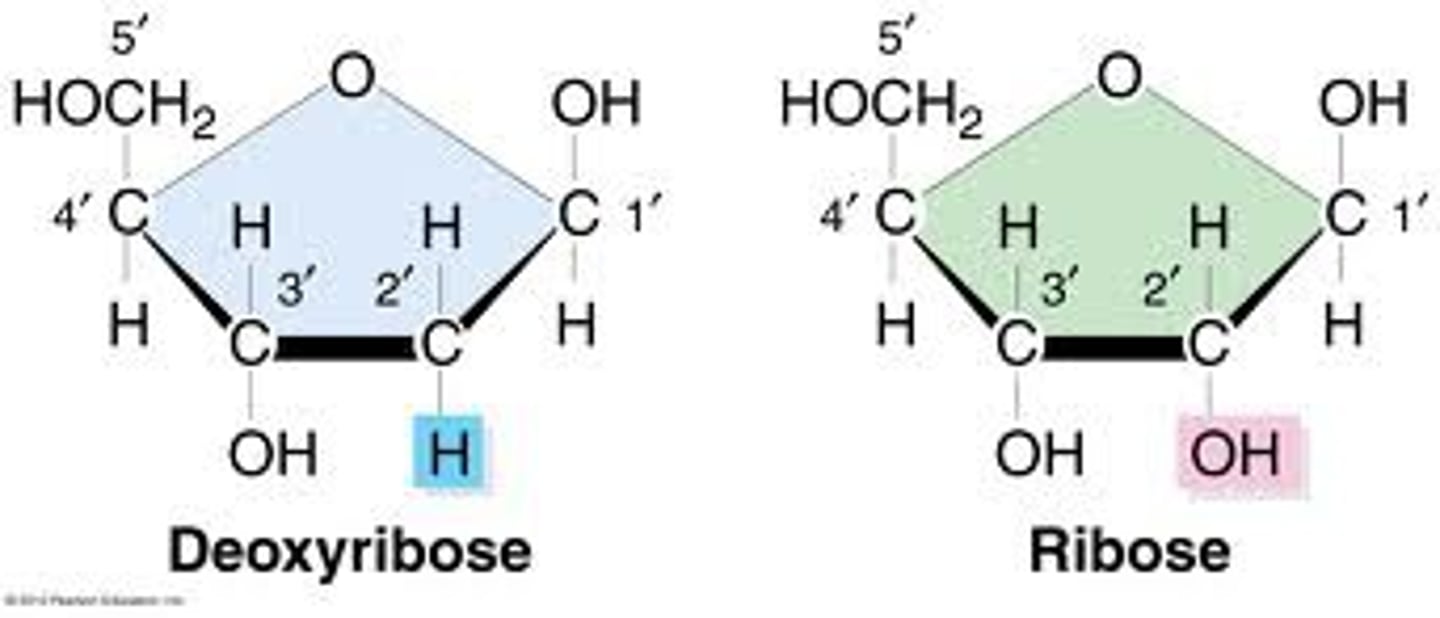
pentose
-5 carbon sugar
-deoxyribose & ribose (OH at 2',bottom right)
-SHAPE DOES NOT MATTER, COUNT CARBONS TO DETERMINE IF PENT/HEXOSE
hexose
-6 carbon sugar
-liner = not stable in aqueous environments
-circular = more energetically stable in aqueous env.
-α-glucose, α-mannose, α-galactose, fructose
L vs. D isomers
-L isomers more predominant bc more recognized during evolution,
Condensation/Dehydration Synthesis
-process used to make a polymer and you REMOVE H2O
-glycosidic linkages to bond monosaccharides
Sugar Phosphate
-fructose 1,6-biphosphate = extra phosphate group (bi)
-potential energy raised to yield ATP
-intermediate in energy metabolism
Amino Sugars
-contain an amino group in place of a hydroxyl group at 2'
-monosaccharides found in extracellular matrix
-flexibility (ex: cartilage)
Chitin
-N containing polysaccharide that forms exoskeletons/shells of insects, crustaceans, & cell wall in fungi
-contains acetyl group
Lipids
-nonpolar hydrocarbons (aggregate together away from water)
-insoluble in water (prevent water evaporation, waxes)
-store energy, form cell membrane structure, thermal/electrical insulation
-can be pigments, hormones, vitamins
Triglycerides
-long nonpolar hydrocarbon chains w/ 3 fatty acids + glycerol (H & C both similar electronegativities = hydrophobic)
-fats & oils
-can differ in number of chains and their length, & amount of double bonds
Ester Linkage
-3 dehydration synth reactions between fatty acid carboxyl & glycerol's hydroxyl
-3 single covalent bonds
Saturated Fatty Acid (Fats)
-solid at room temp w/out double bonded carbon
-many H atoms, but more cannot be added to long chains
-interact mainly w/ nonpolar/hydrophobic (allows for tight package)
-high melting point
Unsaturated Fatty Acids (oils)
-liquid at room temp w/ double bonded carbons
-loosely packed bc kinks from double bond
-low melting points
-identified by position of 1st double bonded carbon (omega carbon) being opposite end of hydroxyl
Fatty Acid
-carboxyl group + hydrocarbon tails
-bottom, hydrophobic part of triglycerides
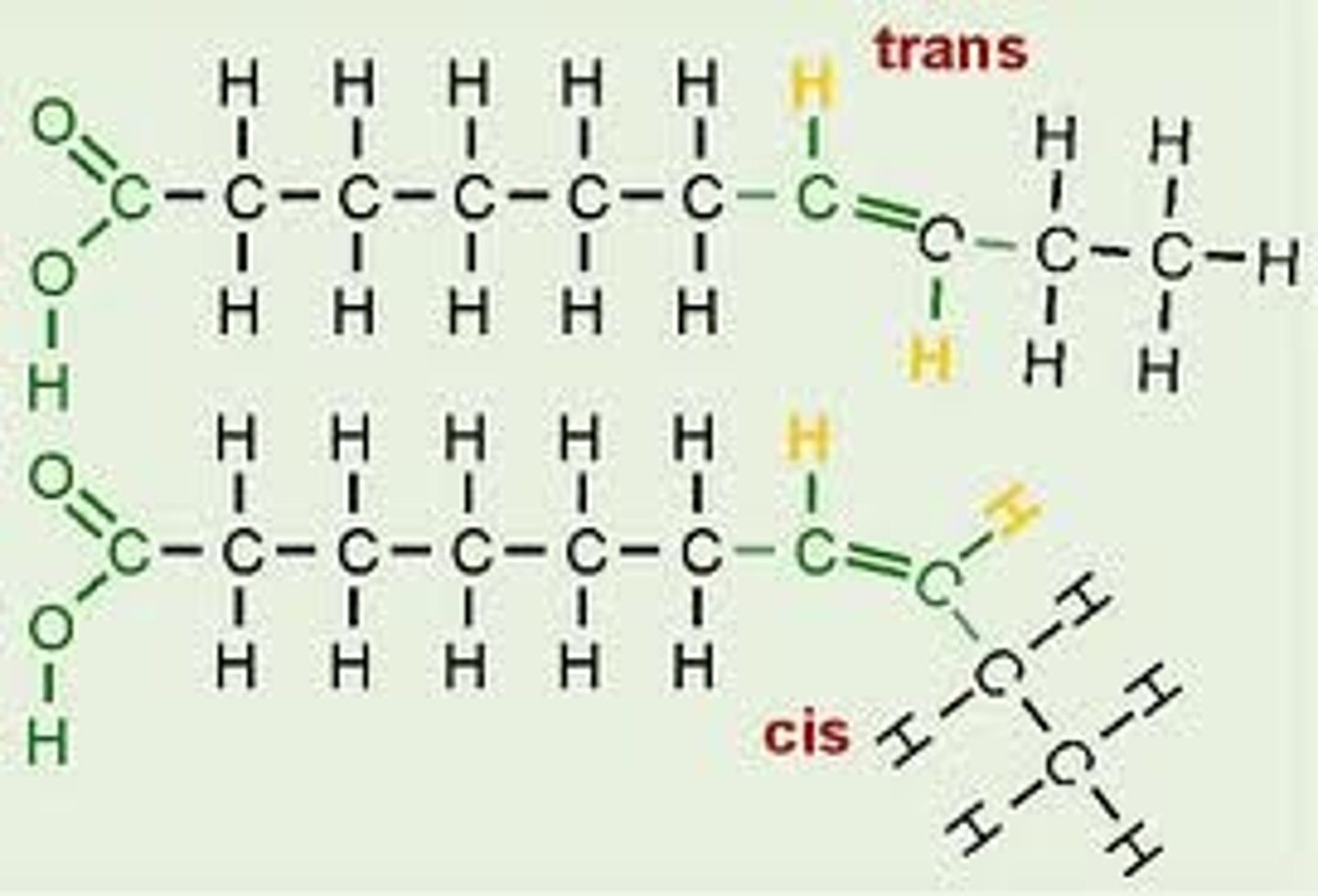
Trans Fats
-unsaturated fat, formed artificially during hydrogenation of oils
Spidroin
-protein of spider silk
-helices allow for flexible proteins and breakage resistance
-has a polished surface for hydrogen bonds w/ H2O

Hydroxyl
-bond between an O and an H
-polar, forms hydrogen bonds via condensation
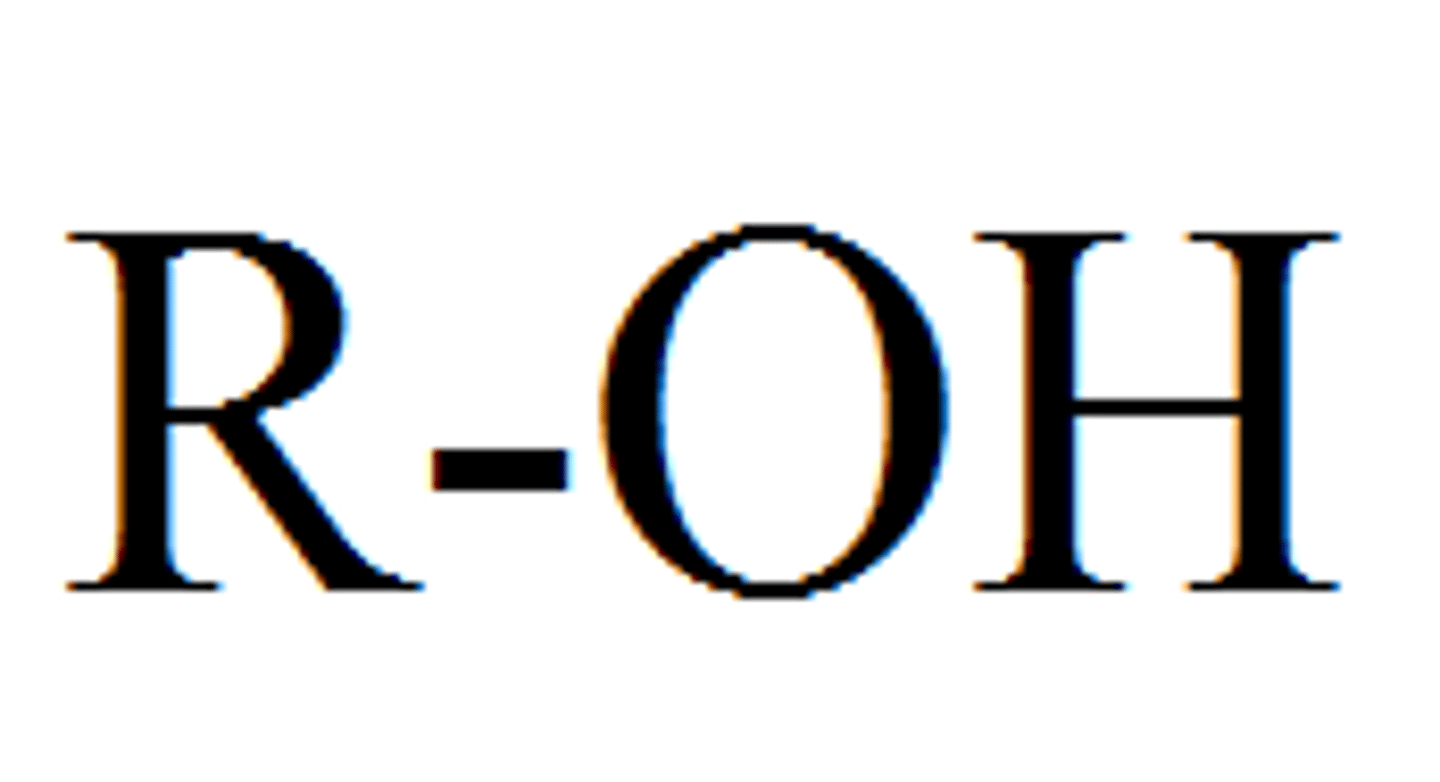
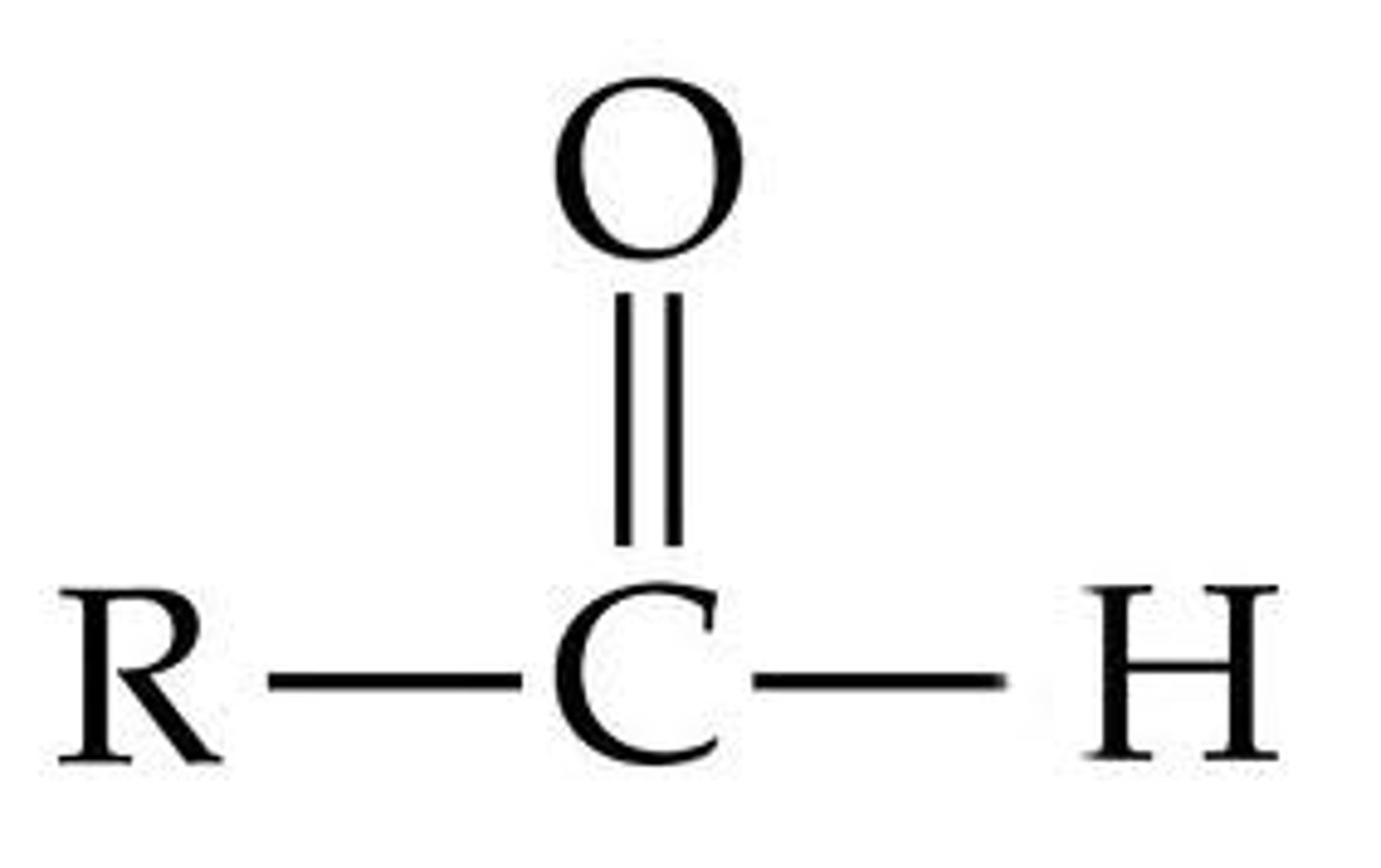
Aldehyde
-polar
-C=O is very reactive
-energy releasing reactions
Keto
-C=O between two R chains
-polar
-important in carbs & energy reactions

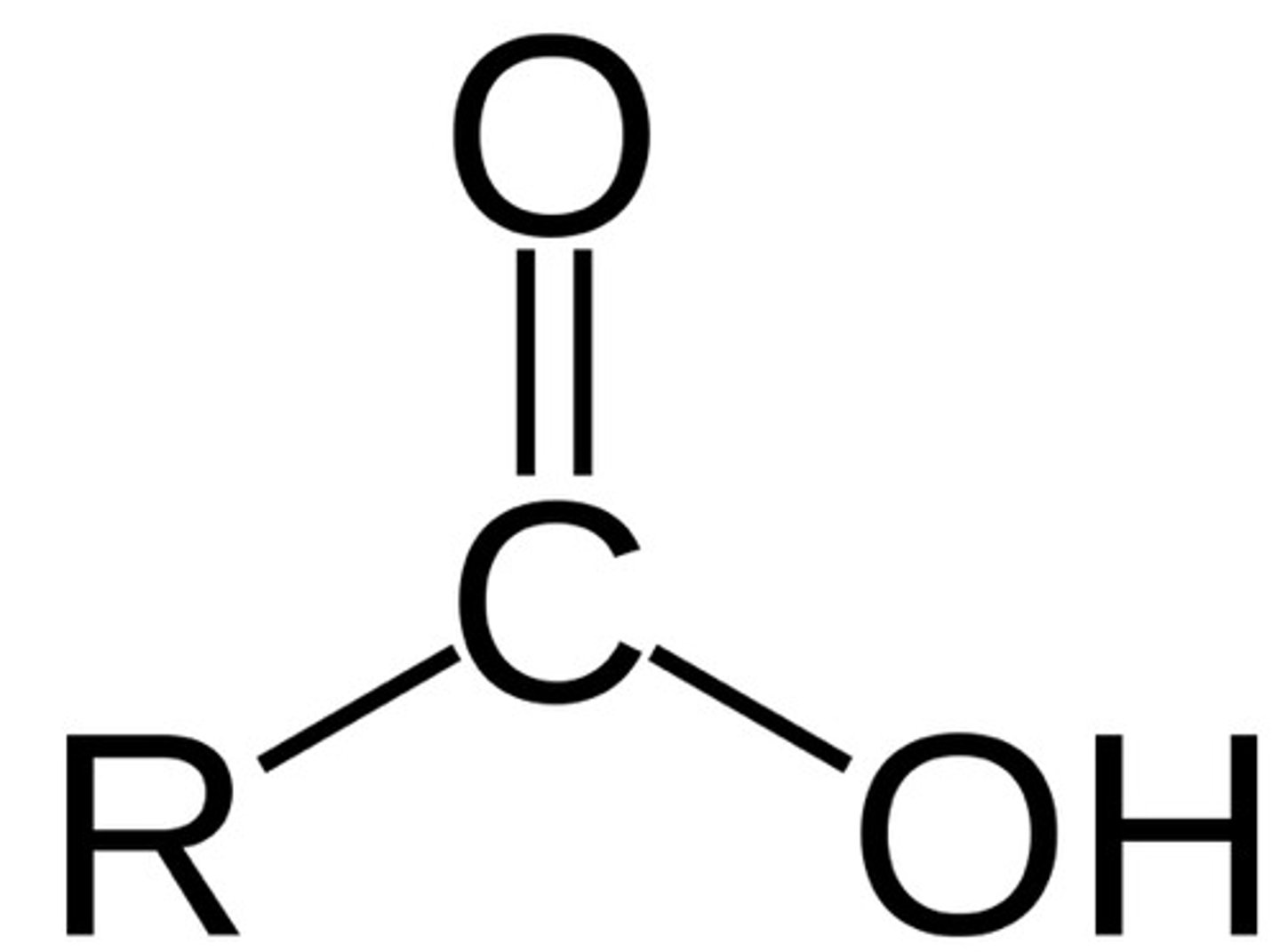
Carboxyl
-COOH (or OH-C=O)
-forms COO- & H+ (charged molecule)
-condensation = gives up OH
-energy releasing reactions
Amino
-H-N-H
-charged, basic (N is highly electronegative)
-accepts H+ to form NH3+
-gives up H+ to condensate
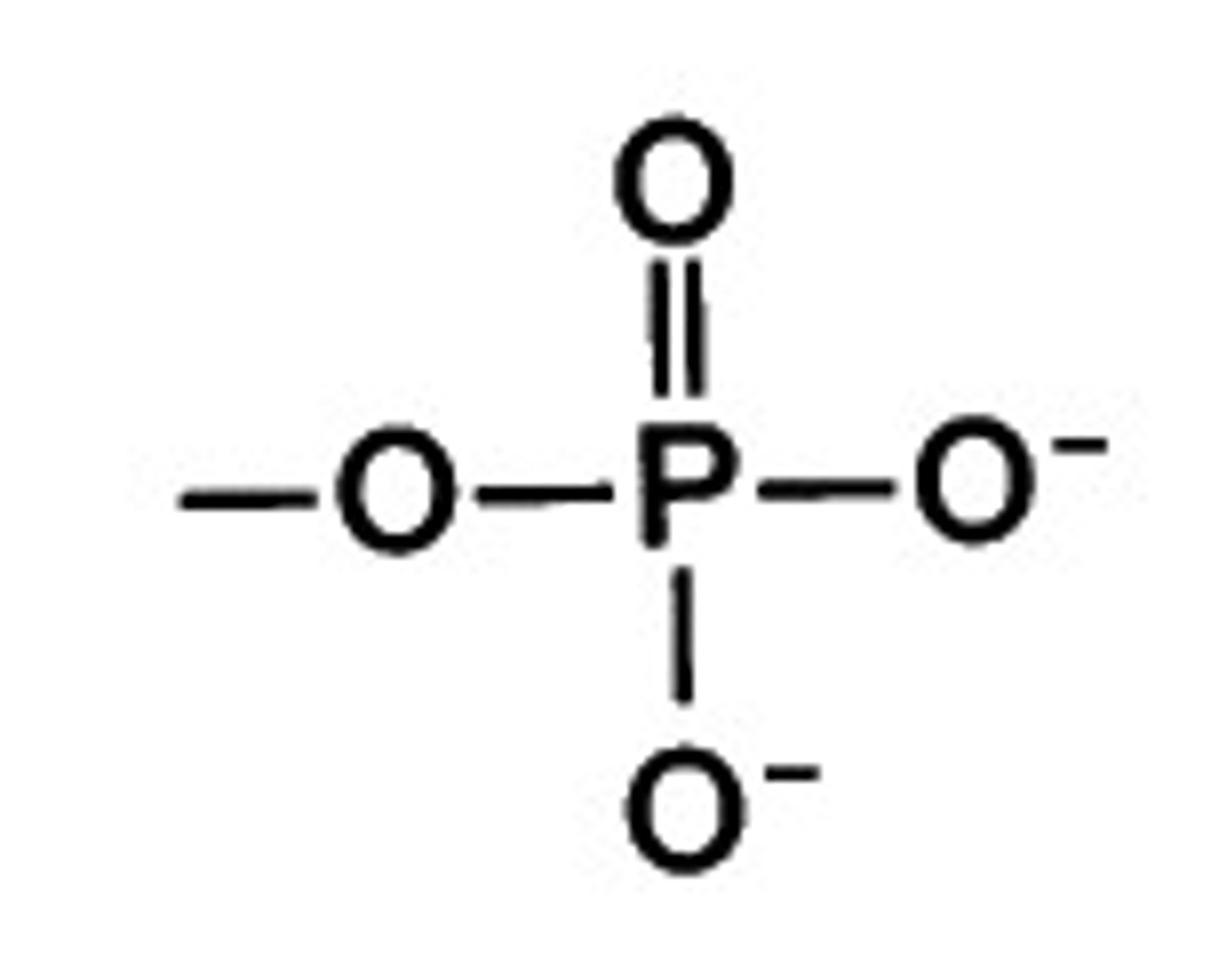
Phosphate
-PO4, 3-
-charged, acidic
-gives up OH -> condensation
-hydrolysis when bonded to another PO4 = lots of energy released
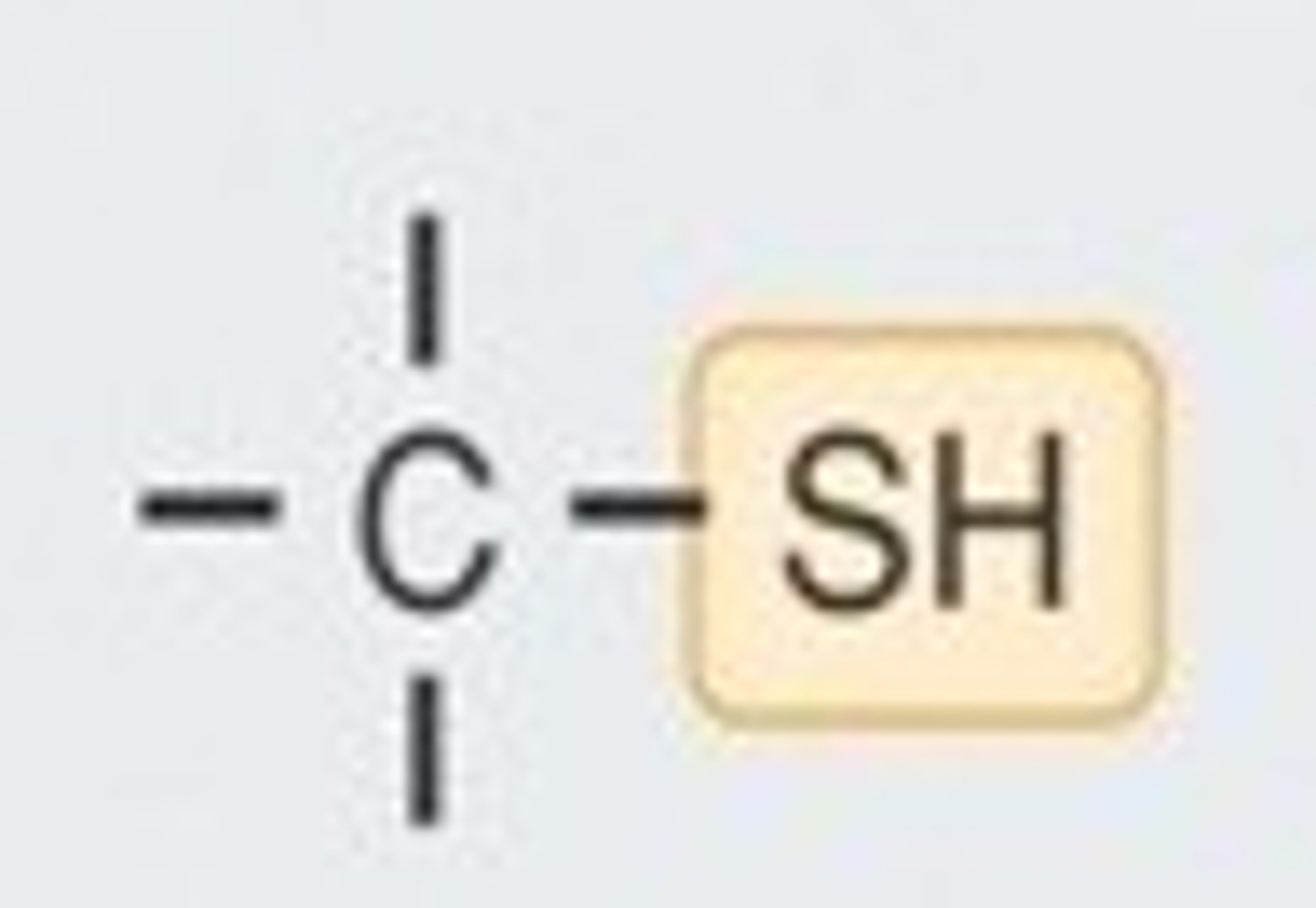
Sulfhydryl
-SH
-forms disulfide bridges by giving up H
-stabilizes protein structure
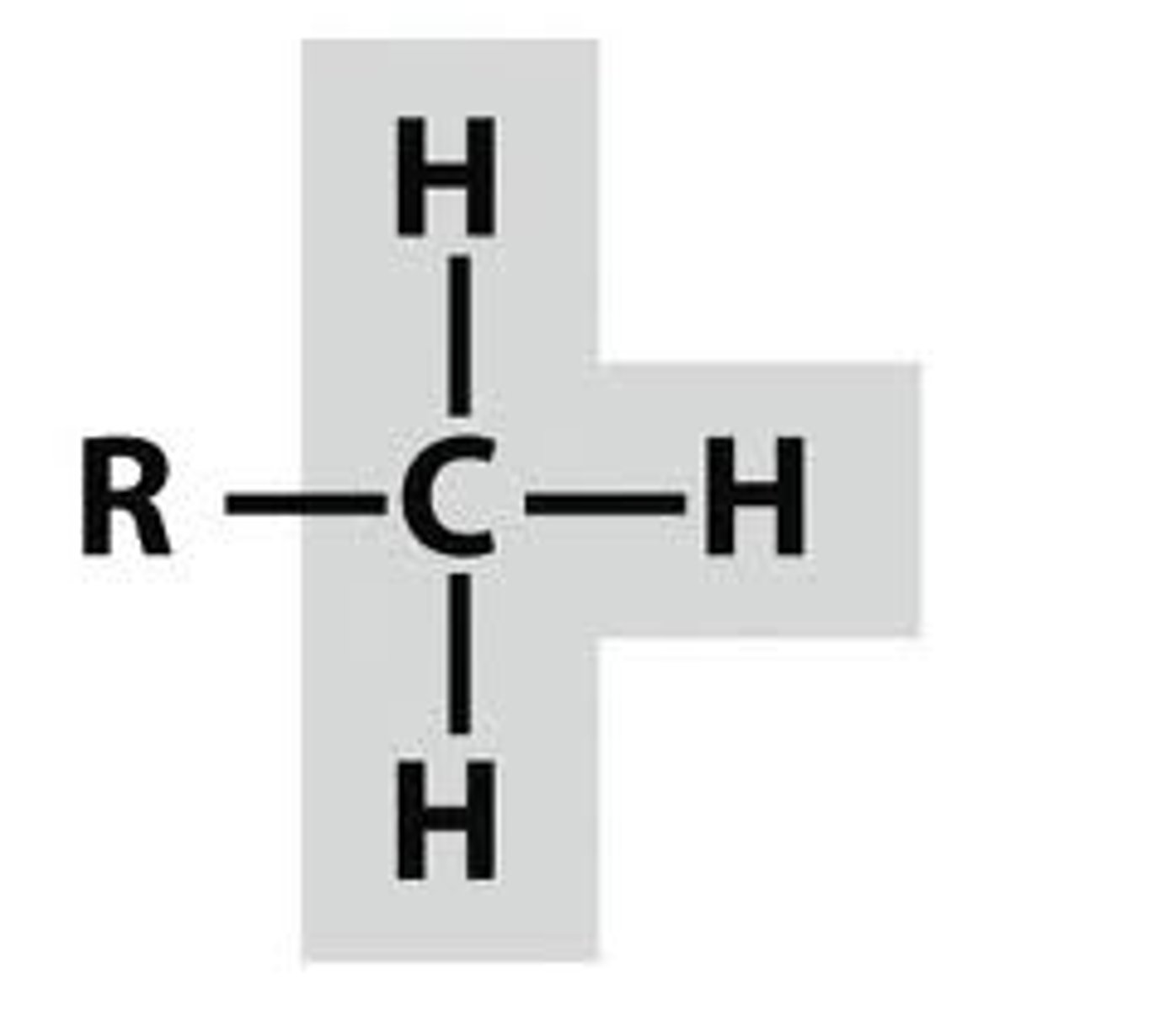
Methyl
-nonpolar
-interacts w/ other nonpolar molecules
-energy transfer
Esterification
-linkages need a carboxyl
Phosphodiester Bond
Amphipathic
-part hydrophillic, part hydrophobic
abiogenesis
-provided evidence that life could originate from inoraganic compounds
-miller urey experiment
cyanobacteria
-first photosynthesizing bacteria
-showed that photosynthesis was possible in early evolution
anaerobic metabolism
-anoxygenic photosynthesis/cellular respiration w/out oxygen (causes sulfates to make sulfur)
-reduces nitrate, sulfate, CO2, etc.
-low ATP yield
aerobic metabolism
-uses O2 as electron accepter
-more efficient, higher ATP yield
-(metabolism = water oxidizes & releases O2)
LUCA
-last universal common ancestor
-produced bacteria & archaea, then prokaryotes & etc.
Mechanisms of Evolution
-natural selection
-sexual selection (breeding/mating patterns)
-genetic drift (random fluctuation in frequencies of various genes due to chance events, ex natural disaster kills off certain species)
-genetic flow (flow of genes due to im/migration)
-mutations
Mendel
-breeding experiments
-theory of inheritance (pea plants & alleles)
Darwin & Wallace
-evolution by natural selection
-species found on various areas before pangea broke apart
relative atomic weight
-used to measure how abundant an isotope is
-shows the average of mass numbers in representative sample of atoms within an element
-ratio of the average mass per atom
-dimensionless, unitless number
carbon-14 dating
-determines age of various organic sediments (wood, charcoal, shells, bones, fossils, etc)
-half life + where they were found on earth = when they were alive
-14C is unstable & decays to 14N (half life = 5700 years)
-forms as result of cosmic radation
electronegativity
-attractive force that nucleus exerts on electrons (how much atom wants electrons)
-depends on # of positive charges & distance between nucleus & electrons in valence
-less valence electrons = more electronegativity bc closer to nucleus & more reactive
DNA process
-DNA > DNA polymerase transcribes into mRNA > mRNA translated by ribosome in cytoplasm > nucleotide
-phosphate group = 5'
-OH = 3' (where new nucleotides are attached)
phosphodiester bond
-strong covalent bonds that link sugar phosphate dna backbone together
disulfide bridges
-formed by oxidation between 2 sulfhydryls of 2 cysteines
-most resistant to denaturation
oleic acid
-monounsaturated fatty acid with one double bond
stearic acid
-saturated fatty acid, waxy, colorless solid
elaidic acid
-monounsaturated trans fatty acid
-trans isomer of oleic acid
phosphorylation
-the addition of a phosphate group to a molecule
-reverse reaction can occur w/ hydrolysis
-if added to protein = disruption in structure & nonpolarity (phosphates are polar)
-if added to protein = full control & regulation of processes (can create on/off switch for enzymatic activity)
cyclization
-the process of a straight form molecule connecting into 2/3d
GTP (guanine triphosphate)
-energy source in protein synthesis
-signaling pathways
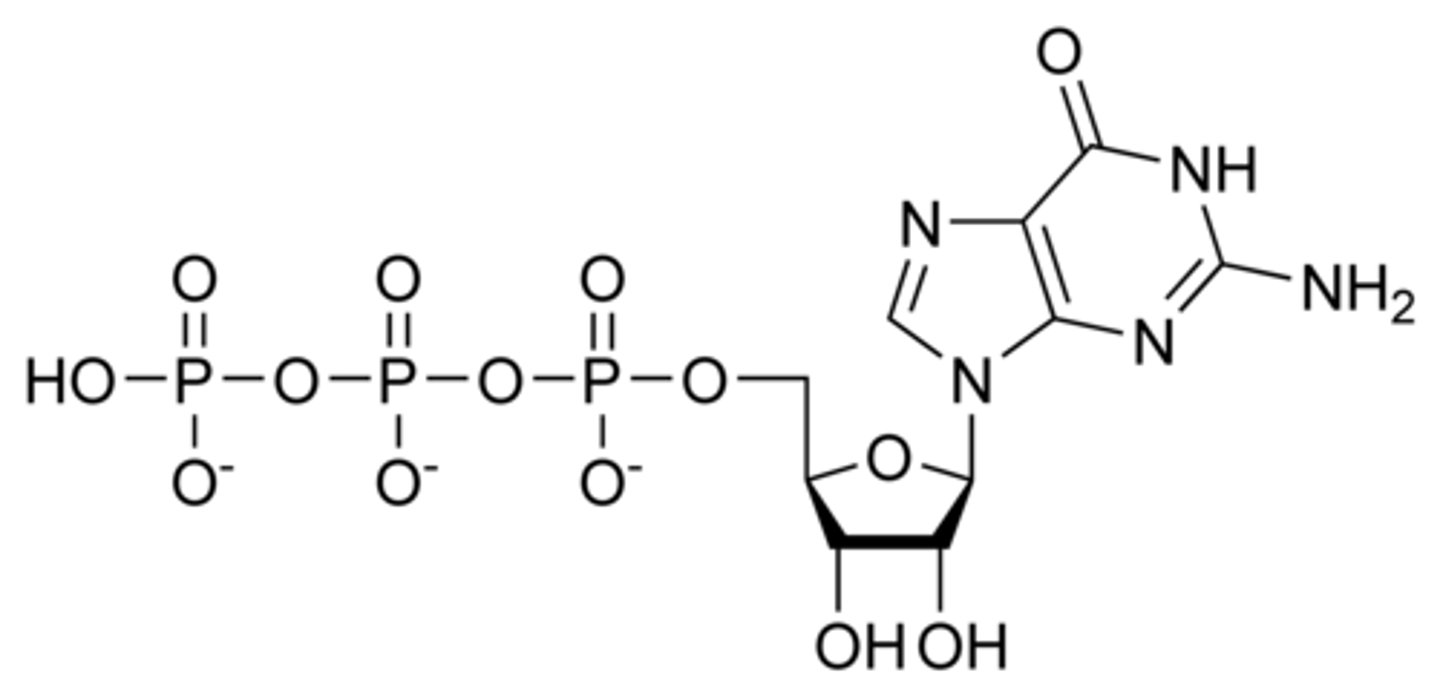
cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate)
-hormone signaling
-gene expression
-nervous stimulation transmission
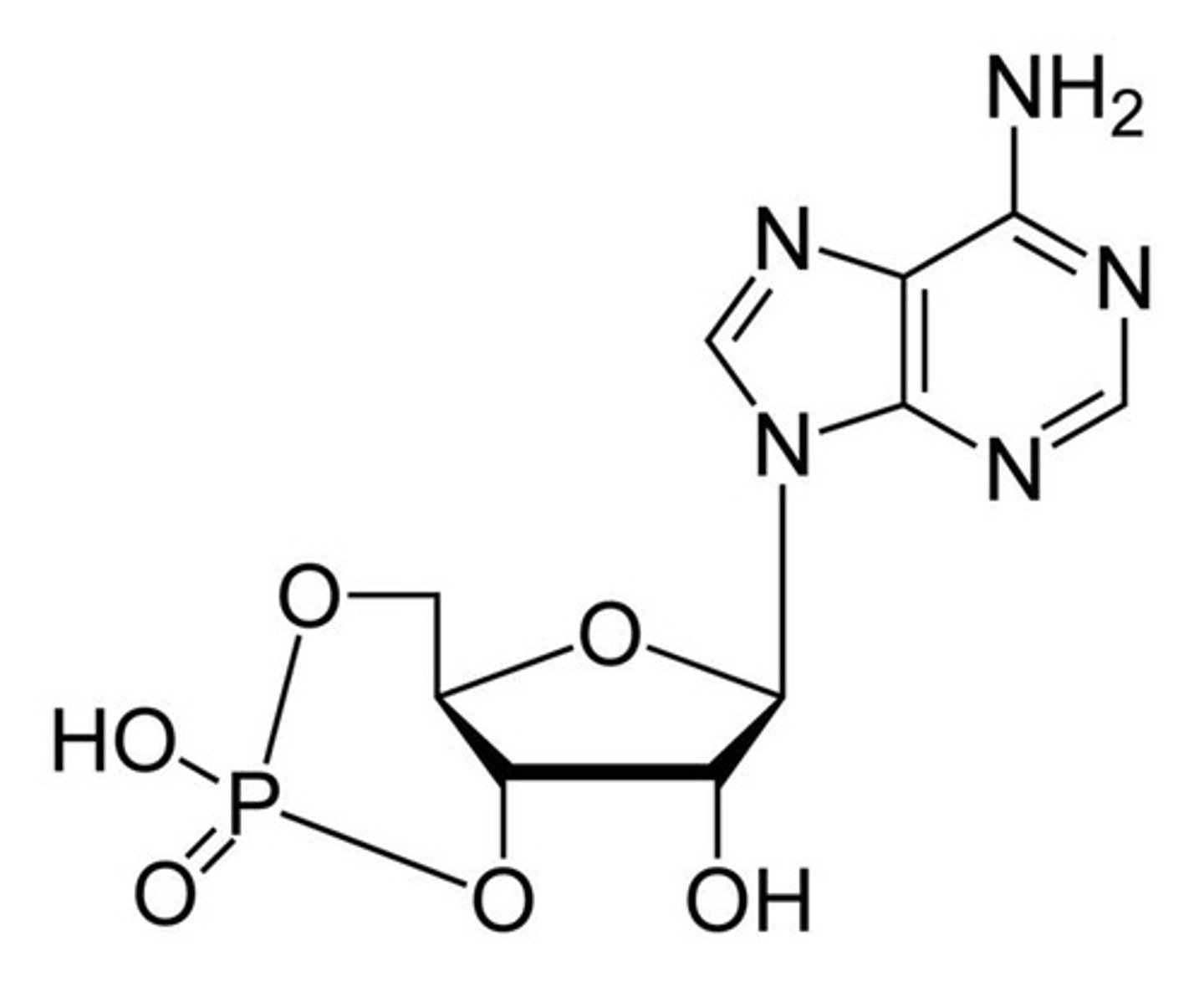
purines
-adenine & guanine
-2 ring structure w/ one penta, one hexa
pyrimidines
-thymine, uracil, cytosine
-single 6 membered ring
steroids
-lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings
-classified as lipids bc amphipathic (both hydrophobic & phillic)
why primary structure determines tertiary structure
-the order of amino acids influences reactions within the polypeptides
-acids at opposite ends can react with each other
-R groups can exert influence on neighboring and distant amino acids
carbohydrate functions
-source of energy & structure (ex cell walls)
-source of carbon for other molecules
-molecular structure (backbone of nucleic acids, deoxy/ribose)
-cell identity/recognition (glycoproteins)
alpha helix vs. beta plated
-alpha helix = ribbon like structure
-beta plated sheet = flat sheet w/ minor ridges
-formed in secondary structure, seen in tertiary
high vs. low melting point
-higher = packed tightly due to hydrophobic interactions, solid at room temp
-low melting point = double bonds in carbon cause less tight packing, reduces energy required to turn molecule into liquid
nucleotide vs. nucleoside
-nucleoside = nitrogenous base + sugar, no phosphate group
-nucleotide = nitrogenous base + sugar + 1-3 phosphate groups