AP Biology Unit 2 Test
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Cells
The basic unit of structure and function in all living things
all cells are/contain:
bound by a plasma membrane
contain cytosol
contain chromosomes
contain ribosomes
Prokaryotes
domains bacteria and archea
DNA in nucleoid region
smaller
eukaryotes
Protists (unicellular), fungi, animals, and plants
DNA in nucleus
membrane-bound organelles
bigger
Organelles
membrane-enclosed structures within eukaryotic cells
endomembrane organelles
1. Nuclear envelope
2. Endoplasmic reticulum
3. Golgi complex
4. Lysosomes
5. Vesicles/vacuoles
6. Plasma membrane
energy organelles
1. Mitochondria
2. Chloroplasts
Compartmentalization
-allows for different metabolic reactions to occur in different locations
-increases surface area for reactions to occur
-prevents reactions interfering with each other
Unique Cell Components of Plants
1. chloroplasts
2. central vacuole
3. cell wall
4. plasmodesmata
Unique Cell Components in Animals
1. Lysosomes
2. Centrosomes
3. Flagella
Nucleus
-Contains chromosomes
-enclosed by nuclear envelope (double membrane)
-Nuclear pores (regulate entry/exit of materials)
-contains nucleolus
nucleolus/ribosome formation
- dense region of nucleus where rRNA is synthesized
-rRNA+proteins= ribosomes
-subunits exit nuclear pores-> assemble into ribosomes
Ribosomes
-translate messages found on mRNA into primary proteins
-RNA+proteins
-2 locations:
Cytosol (aka free ribosomes)
Rough ER or nuclear envelope (proteins can be secreted from cell, in transport vesicles)
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
-synthesizes membranes
-compartmentalize the cell to separate rough ER proteins and free ribosome proteins
Rough ER
contains ribosomes for protein synthesis bound to ER membrane
Smooth ER
-Contains no ribosomes
-Synthesizes lipids, metabolizes carbohydrates, and detoxifies the cell
Golgi Complex
-Contains flattened membranous sacs called cisternae (not connected)
-seperate sacs from cytosol
-directionality:
Cis face- receives vesicles from ER
Trans face-sends vesicles back out into cytosol or plasma membrace for secretion
Golgi Complex Functions
- Receives transport vesicles with materials from the ER
- Modifies the materials
- Sorts the materials
- Adds molecular tags
- Packages materials into new transport vesicles that exit the membrane via exocytosis
Lysosomes
-membranous sac with hydrolytic enzymes
-hydrolyzes macromolecules in animal cells
-Autophagy
Autophagy
-lysosomes recycle their own cell's organic materials
-allows cell to renew itself
-break into (ex. CHO) and uses elsewhere
Peroxisomes
-similar to lysosomes
-membrance bound metabolic compartment
-catalyze reactions that produce H2O2
-enzymes in peroxisomes that break down the H2O2 to H2O
What are vacuoles?
Large vesicles that stem from the ER and Golgi.
Food vacuole
Forms via phagocytosis and is then digested by lysosomes.
Contractile vacuoles
Maintain water level in cell
Central vacuole
A vacuole found in plants that contains inorganic ions and water, important for turgor pressure (without it, plants shrink)
Protein Synthesis Steps
1. Transcription (Nucleus)- mRNA copied
2. Translation (ribosomes)- mRNA read->polypeptide chain
3. Modification (Golgi app)- packaged
4. Secretion (plasma membrane)- deliver out or in specific cell locations
Endosymbiont Theory
-similarities of mitochondria and chloroplasts have to prokaryotes- might have been enveloped a long time ago
evidence: x2 membrane, ribosomes, circular DNA, capable of independant function
mitochondria
-site of cellular respiration
-Contains: enzymes for cellular respiration and and produce ATP, mitochondrial DNA, Ribosomes
-# of mitochondria in cells correlates with metabolic activity
cells with high metabolic activity=more mitochondria (ex. muscles)
mitochondria membrane
-x2 membrane
-outer=smooth
-inner=folds called christae
- divides mitochondria into 2 internal compartments and increases surface area
intermembrane- space between inner and outer membrane
mitochondrial matrix
-enclosed by inner membrane
-location for Krebs Cycle (producing ATP)
-Contains: enzymes for cellular respiration and and produce ATP, mitochondrial DNA, Ribosomes
Chloroplast
-Organelles in Photosynthetic organisms
-site of photosynthesis
-contains green pigment chlorophyll
Thylakoids and stroma
-inside x2 membrane
-thylakoid- membranous sacs that organize into stacks called grana
light dependent reactions occur
Stroma- fluid around thylakoids
-location for Calvin Cycle (glucose)
- contains chloroplast DNA, ribosomes, enzymes
Cytoskeleton
-network of fibers through cytoplasm
-gives structure and support
-anchors organelles
-allows for movements of vesicles and organelles within cell/whole cell
3 types of fibers in cytoskeleton
1. Microtubules
2. Microfilaments
3. Intermediate filaments
Microtubules
-hollow, rod-like structures made of protein tubulin
-grow from centrosome
-assist in microtubule assembly
-serve as structural support for movement of orgtanelles
-seperate chromosomes during cell division
-cell motility
microfilaments
-thin, solid rods made of protein actin
-maintain cell shape (bear tension)
-Assist in muscle contraction and cell motility
-actin works with myosin to cause contraction
-division of animal cells (contractile ring of cleavage furrow)
Intermediate filaments
-fibrous proteins made up of subunits
-permanent structural elements of cells
-maintain cell shape
-anchor nucleus and organelles
-form nuclear lamina (lines nuclear envelope)
Cellular Metabolism depends on...
Size
-cellular waste must leave
-dissipates thermal energy
-Nutrients/chemicals must enter
cell size dictates...
function
Cells need a _______ surface area-to-volume ratio to optimize the exchange of material through the plasma membrane
high
Cells tend to be...
Small.
Small cells have high SA:V Ratio
Optimizes exchange of materials
larger cells have a _______ SA:V ratio
Lower
-lose efficiency in exchanging materials
-more storage
-cellular demand for resources increases
-rate of heat exchange decreases
Phospholipid structures
Hydrophilic head: Phosphate and Glycerol
Hydrophilic tail: Unsaturated/Saturated fatty acids
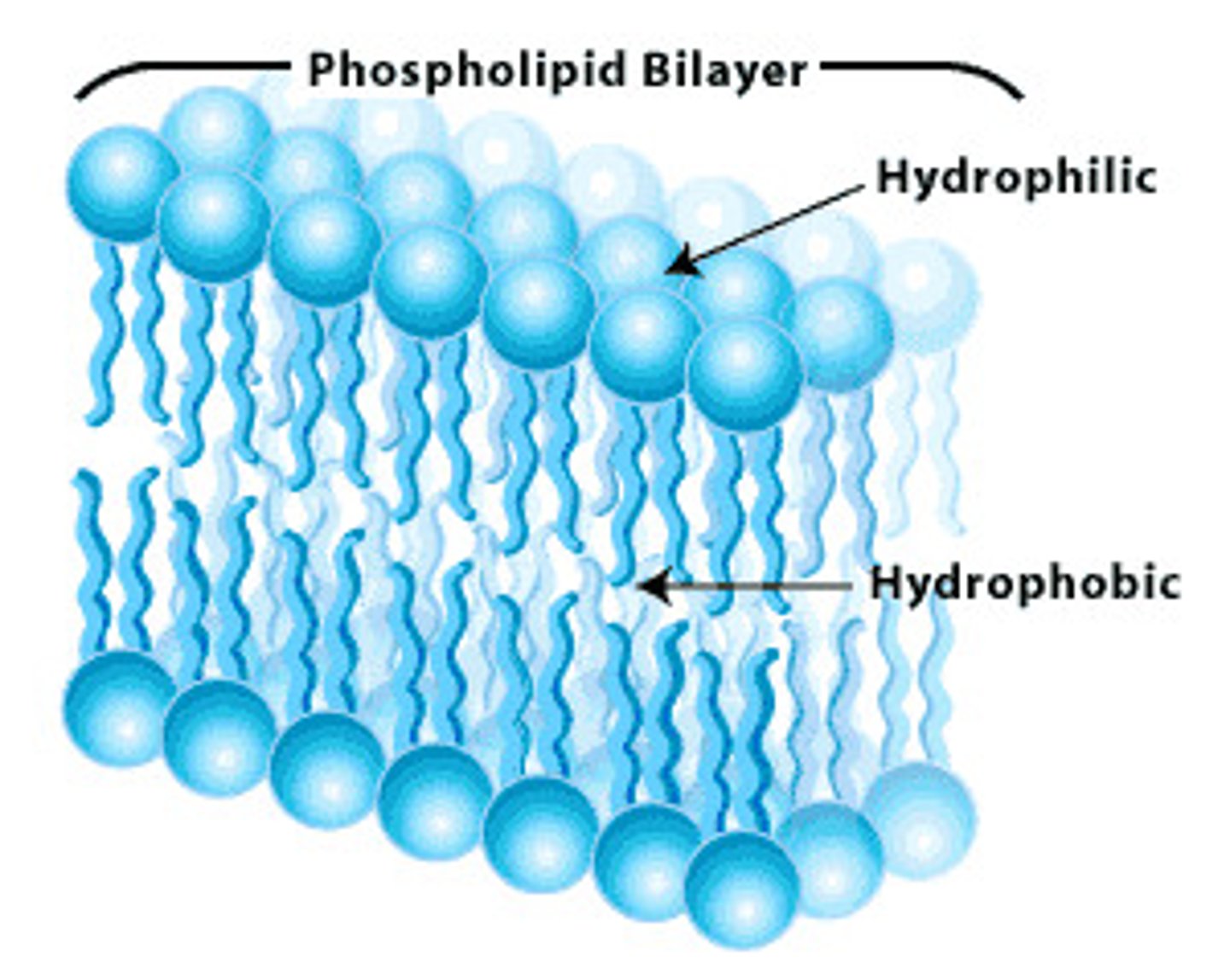
plasma membrane
-separates internal cell environment
-composed mostly of phospholipids
Amphipathic
-hydrophobic head and hydrophilic tails
-forms a bilayer
Selective Permeability
- regulate which substances enter and exit
Easy passage through membranes:
-Small, nonpolar, hydrophobic molecules
-ex. hydrocarbons, gases (CO2, O2, N2)
Difficult or assisted passage through membranes:
-Hydrophilic, polar, large molecules- and ions
-ex. sugars, water, amino acids, Na+, K+
Phospholipid Orientation
- Hydrophilic heads- toward aqueous environments
-Hydrophobic tails- face inward, away from ater
Fluid Mosaic Model- Fluid
-membrane held together by weak hydrophobic interactions- can move and shift
- temperature affects fluidity
- unsaturated tails maintain fluidity at low temps
-kinked tails prevent tight packing
fluid mosaic model: Mosaic
-Membrane comprised of many macromolecules
Membrane proteins
-Integral and Peripheral
Integral proteins
-embedded into bilayer
-aka transmembrane proteins
-amphipathic- the hydrophobic part is attached to the membrane, but the inside is hydrophilic to allow for facilitated transport
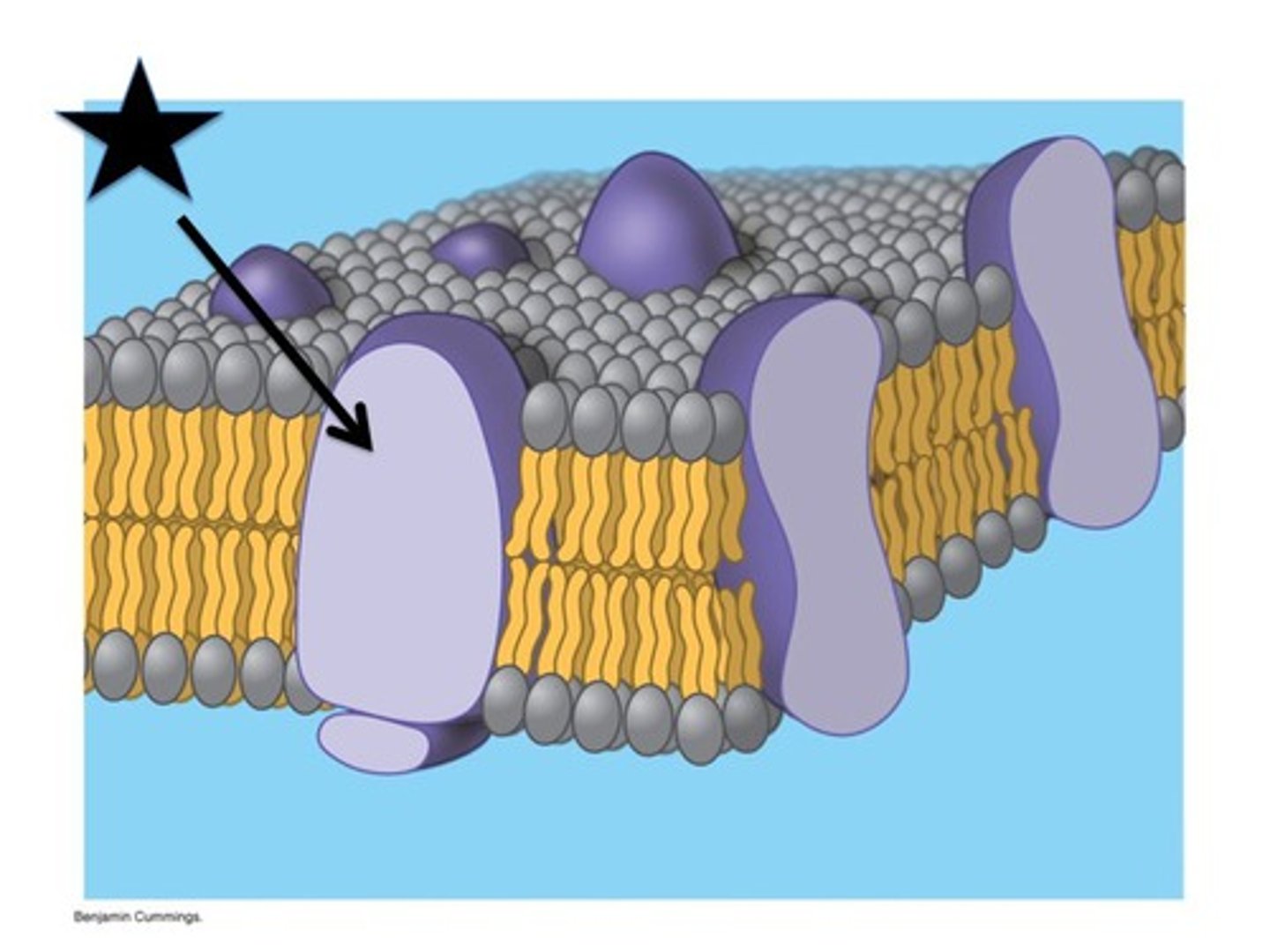
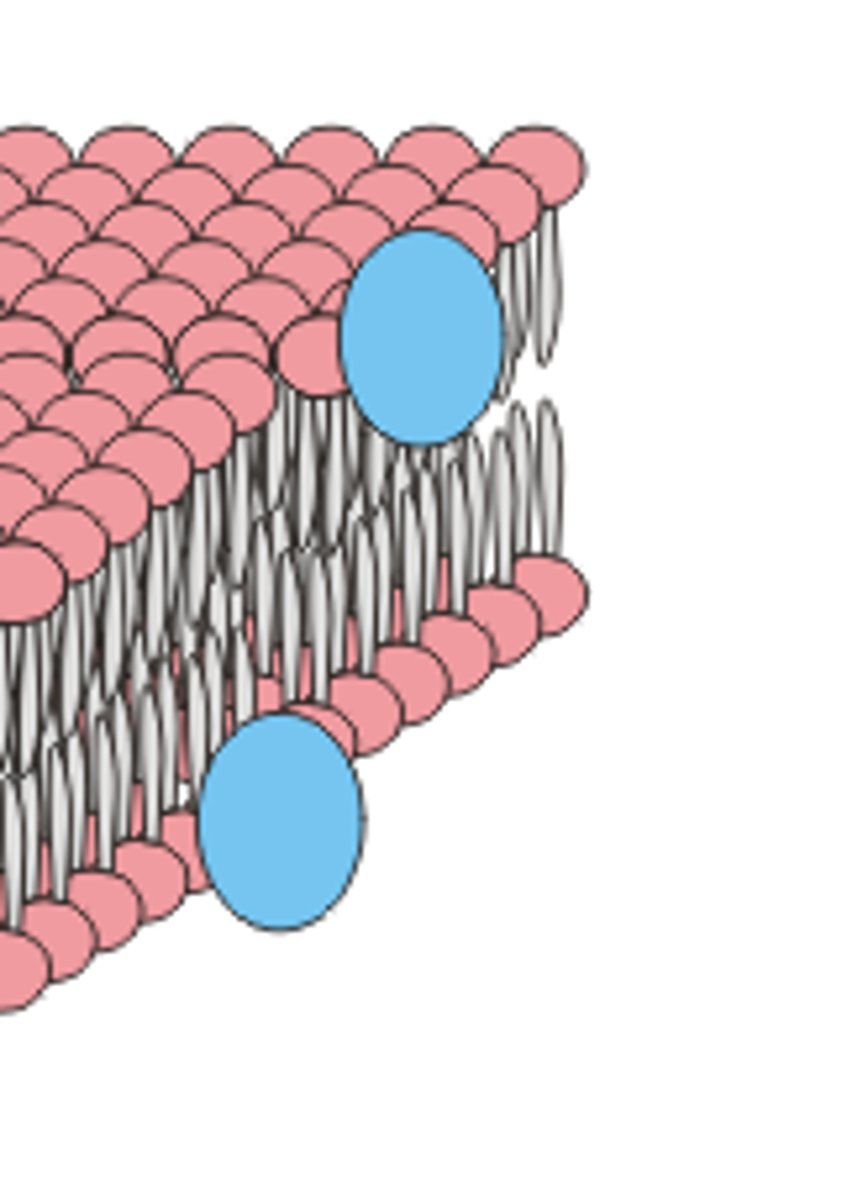
Peripheral Proteins
- not embedded into lipid bilayer
-loosely bonded to surface
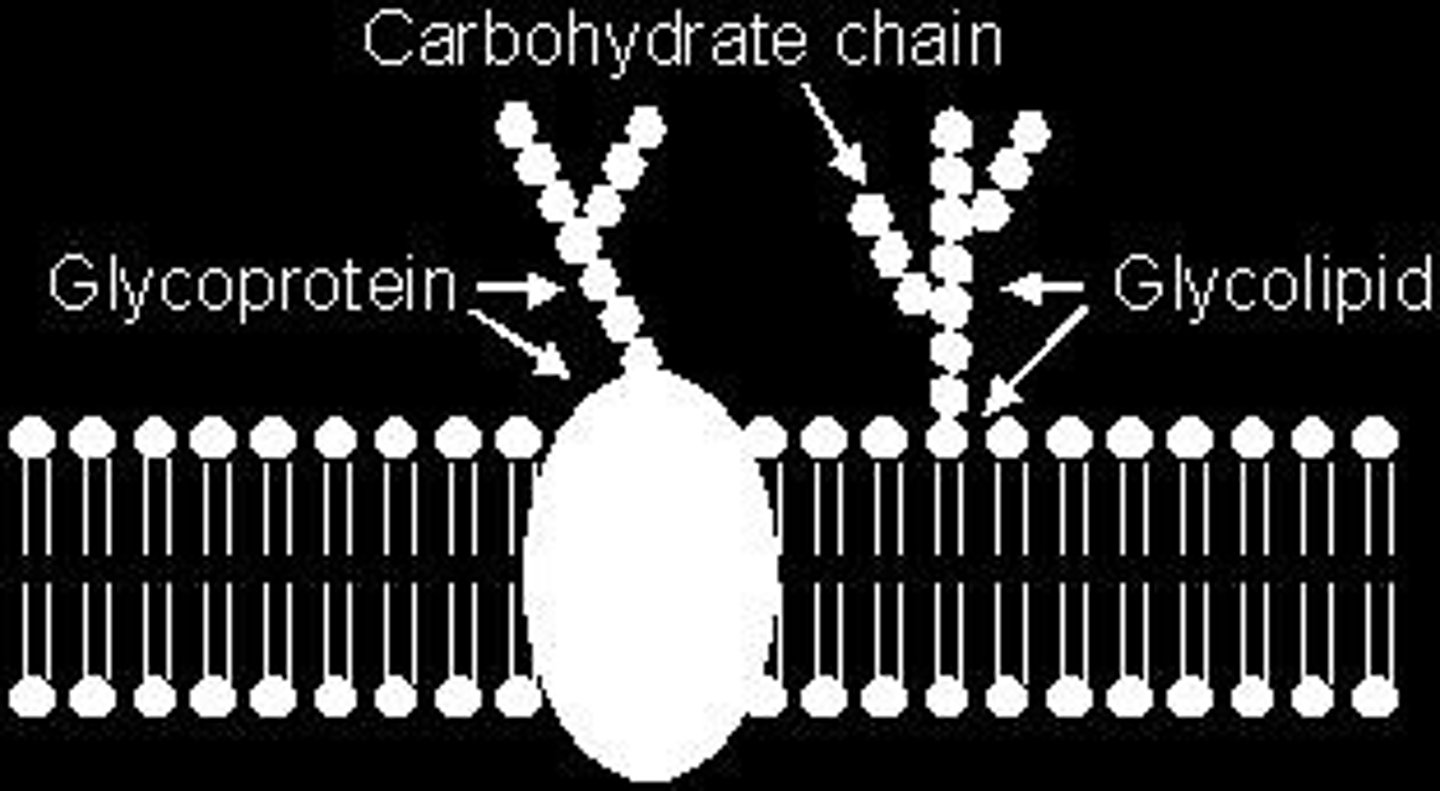
Membrane Carbohydrates
-important for cell to cell recognition
- glycolipids- carbohydrates bonded to lipids
-glycoproteins- carbs bonded to proteins
Plant cell membrane structure
- have a cell wall that covers plasma membrane
-protects cell and regulates water intake
-cell wall composed of cellulose
Plasmodesmata
-Hole like structures in the cell wall filled with cytosol that connect adjacent cells
-transfer materials and messages
Types of transport across membranes
passive and active
Passive Transport
-transport of a molecule that does not require energy from the cell because a molecule is moving with its concentration or electrochemical gradient
-involved in the import of materials and export of waste
Examples of passive transport
-Diffusion
-Osmosis
-Facilitated diffusion
Diffusion
-spontaneous process resulting from the constant motion of molecules
- substances move from a high to low concentration
-move down the concentration gradient
-molecules diffuse directly across the membrane
-different rates of diffusion for different molecules
Osmosis
-diffusion of H2O down its concentration gradient across a selectively permeable membrane
-aka diffusion of H2O from areas of low solute concentration to high solute concentration
Facilitated Diffusion
- diffusion via transport proteins
-increases rate of diffusion for small ions, water, carbs
-2 categories: channel and carrier- specific for substances it can facilitate movement for
Channel Proteins
-provide a channel for molecules and ions to pass
-channel is hydrophilic
-many channels are gated- only allow when there is a stimulus
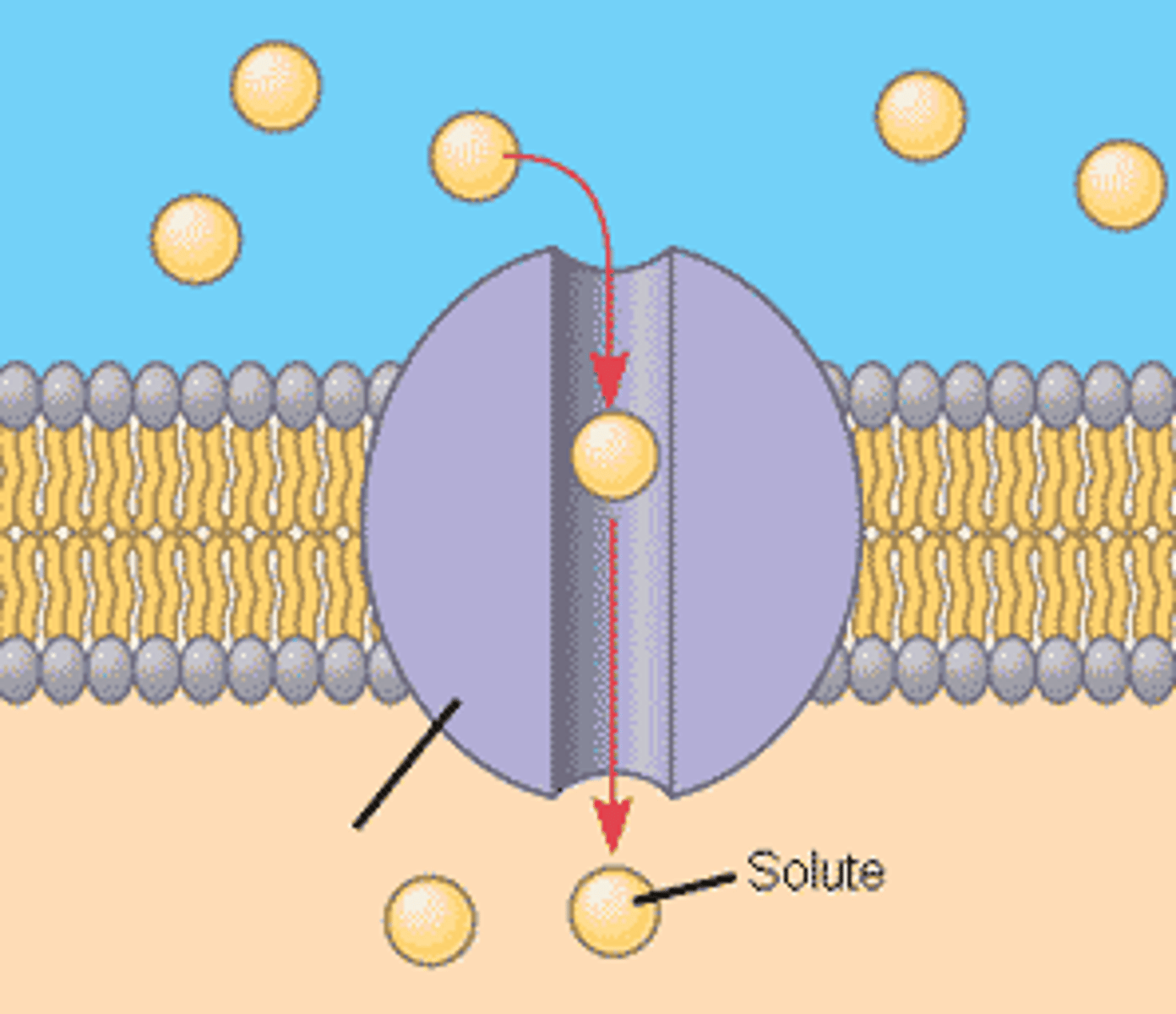
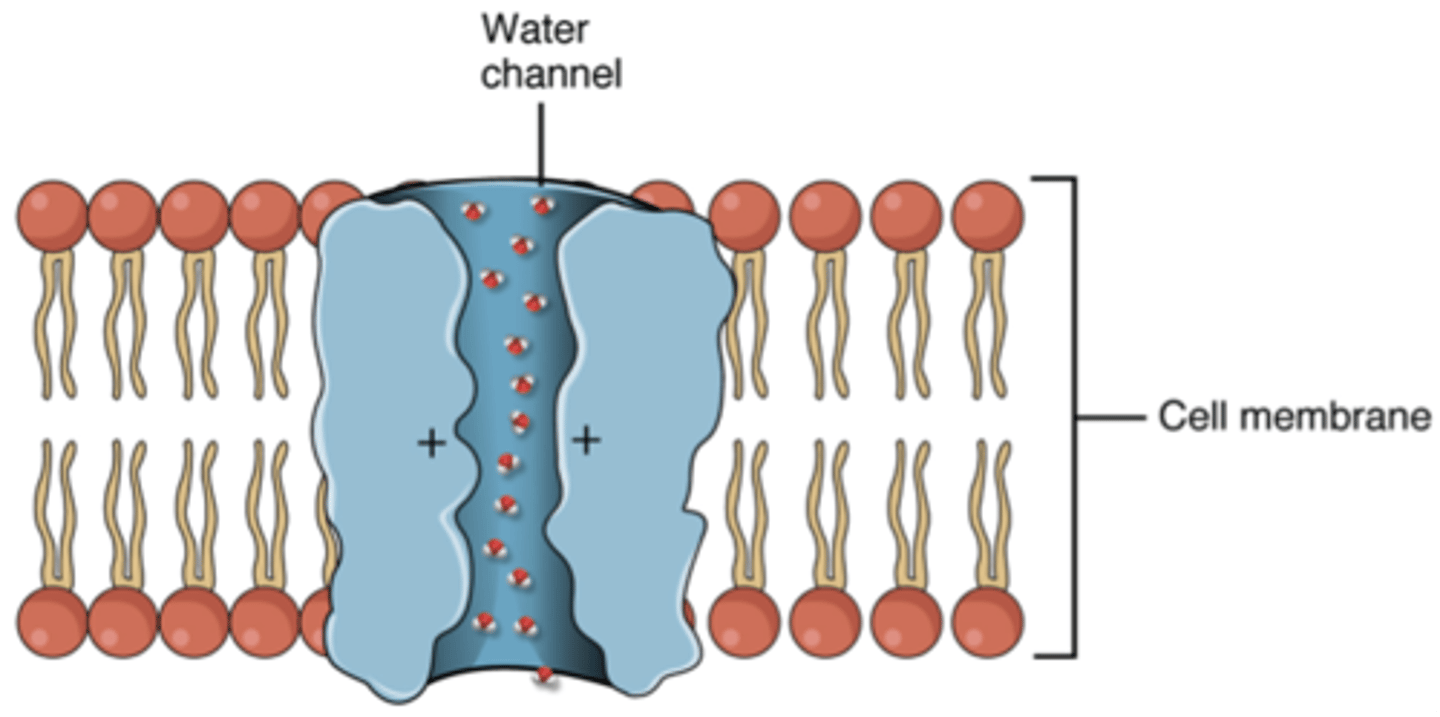
Aquaporins
specific channel protein for water
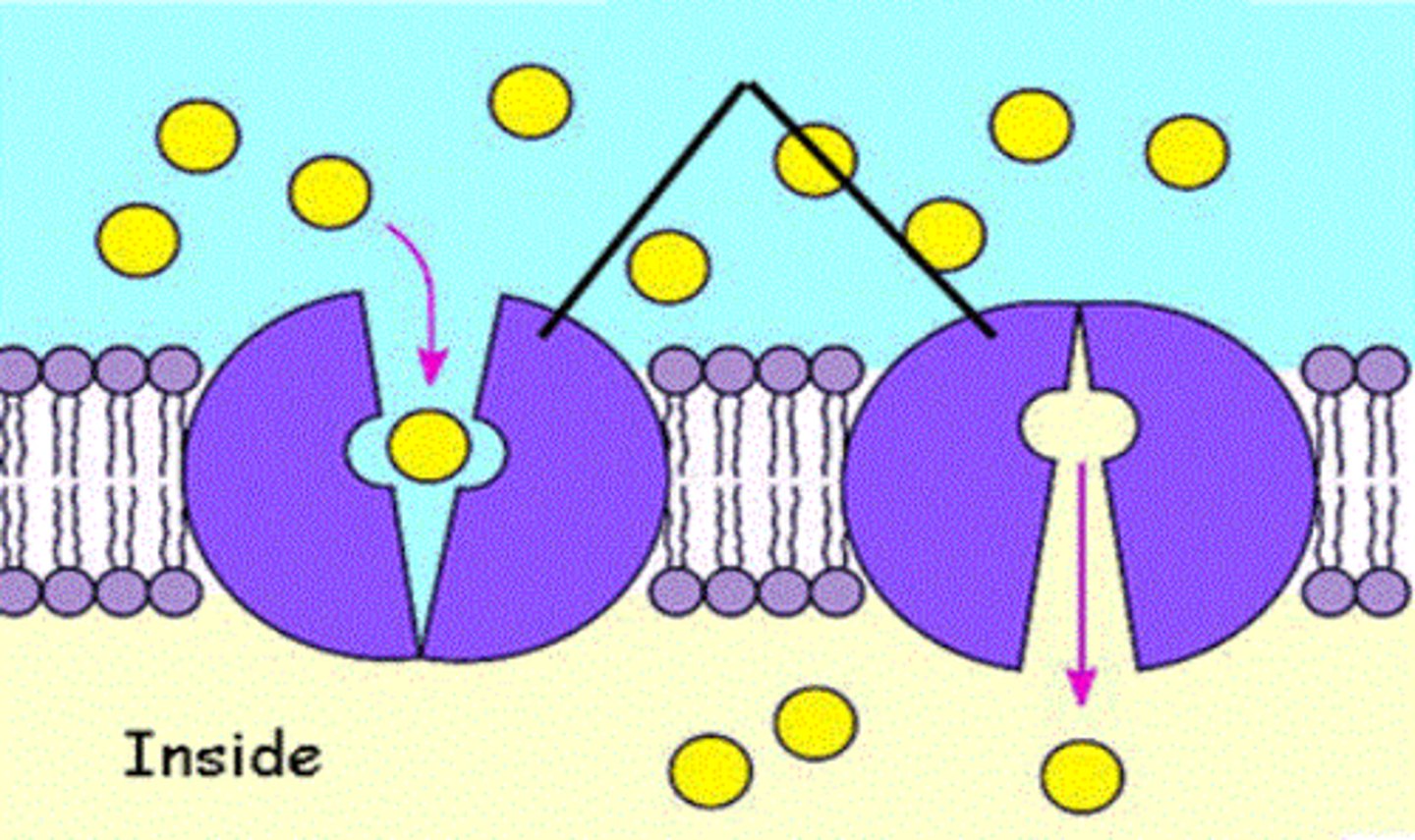
Carrier Proteins
undergo conformational changes for substances to pass
Active transport
transport of a molecule that requires energy because it moves the solute against its concentration gradient
Types of active transport
-pumps
-cotransport
-exocytosis
-endocytosis
Adenosine triphosphate
-energy source used by cells
-ATP can transfer the terminal phosphate group to the transport protein, which changes its shape (and function) to better move a substance
Pumps
-maintain membrane potential
Membrane potential
-unequal concentrations of ions across the membrane results in an electrical charge (electrochemical gradient)
-cytoplasm relatively negative compared to extracellular fluid
-energy stored in electrochemical gradients
Electrogenic pumps
-proteins that generate voltage across membranes, which can be used later as an energy source for cellular processes
Sodium Potassium Pump
-animal cells regulate concentrations of Na+ and K+
-3 Na+ pumped out of cell
-2 K+ get pumped into cell
-results in a +1 net charge to the extracellular fluid
Proton pump
-integral membrane protein that builds up a proton gradient across the membrane
-used by plants, fungi, and bacteria
-pumps H+ out of cell
Favorable vs. Unfavorable movement
- favorable: downhill diffusion
- unfavorable: uphill transport
Cotransport
-the coupling of a favorable movement of one substance with an unfavorable movement of another substance
-uses energy stored in electrochemical gradients (generated by pumps) to move against gradient
-plants use for sugars and amino acids (ex. sucrose and H+)
Exo and endocytosis
transport of large molecules
Exocytosis
-secretion of molecules via vesicles that fuse to plasma membrane
-vesicles can fuse to the membrane by forming a bilayer
-once fused-> release to extracellular fluid
endocytosis
-uptake of molecules from vesicles fused from the plasma membrane
-phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor mediated
Phagocytosis
-a cell engulfs particles to be later digested by lysosomes
- cell surrounds particle with pseuopodia
- particle packaged into food vacuole- fuses to lysosome
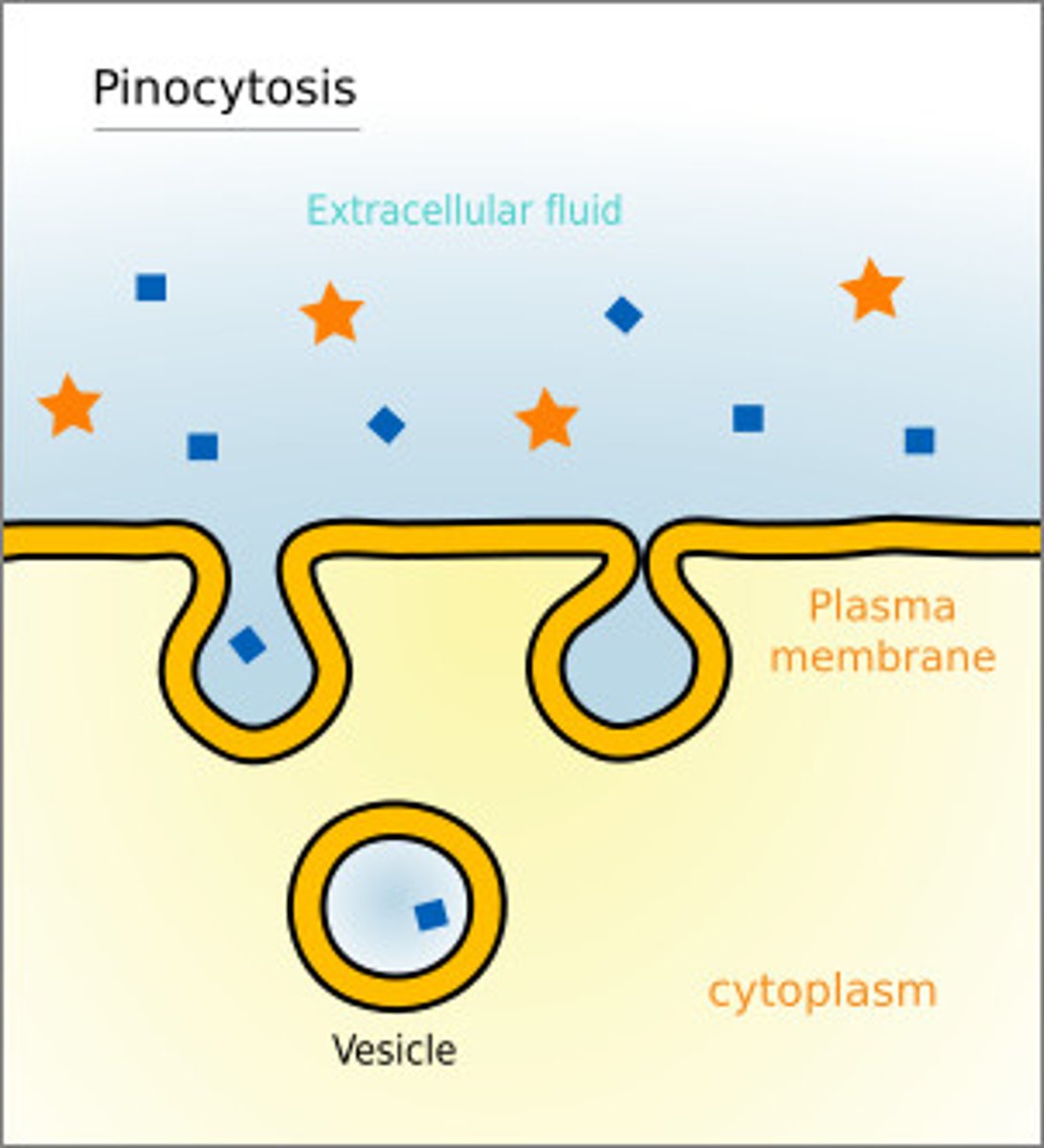
Pinocytosis
-nonspecific uptake of extracellular fluid containing dissolved molecules
-cell takes in dissolved molecules in protein coated vesicle
-protein coat helps mediate transport of molecules
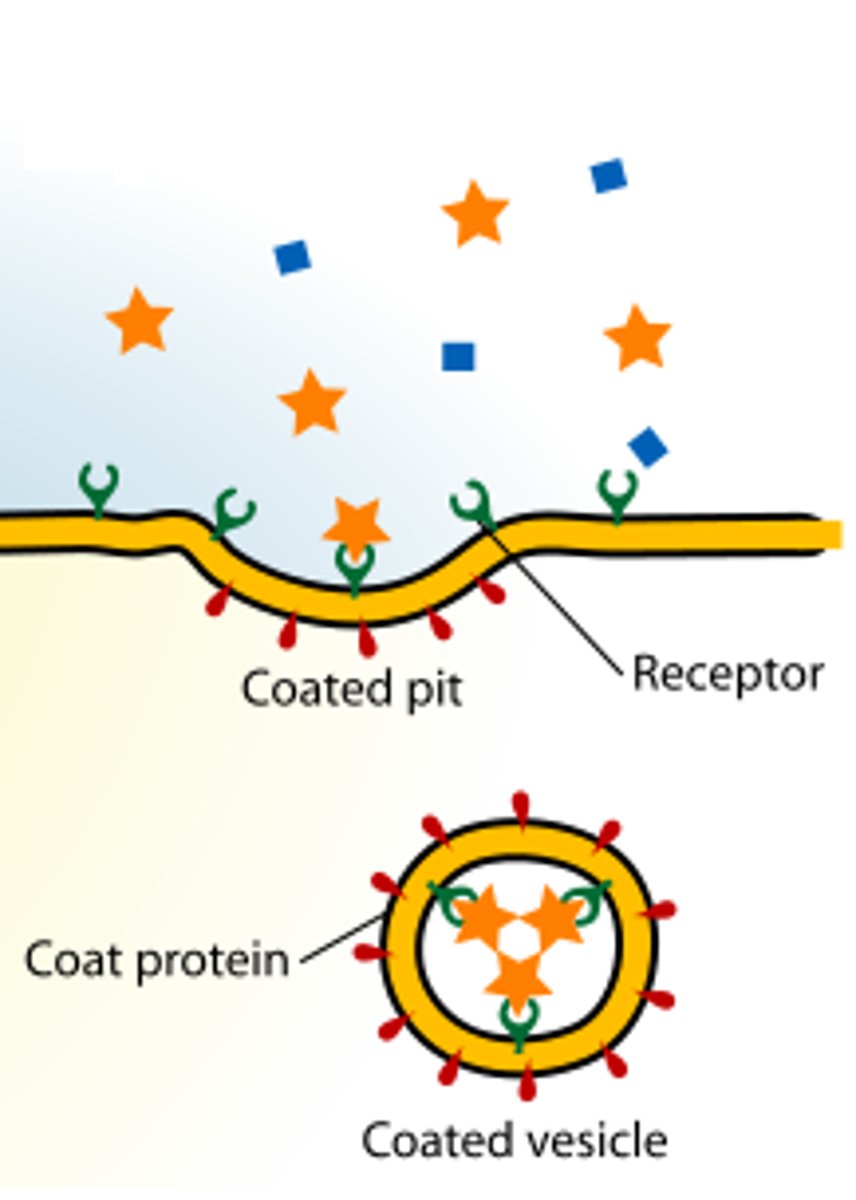
receptor-mediated endocytosis
-Specific uptake of molecules via solute binding to receptors on the plasma membrane
-allows cell to take up large quantities of specific substance
-when solutes bind to receptors->cluster in coated vesicles to be taken into cell
Tonicity
-the ability of an extracellular solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
-depends on concentration of solutes that cannot pass through cell membrane
3 types of solutions cells can be in:
Isotonic- happy cell
Hypertonic- raisin
Hypotonic- fat hippo
Osmoregulation
-cells must be able to regulate their solute concentrations and maintain water balance
-(animal cells react differently than cells with cell walls)
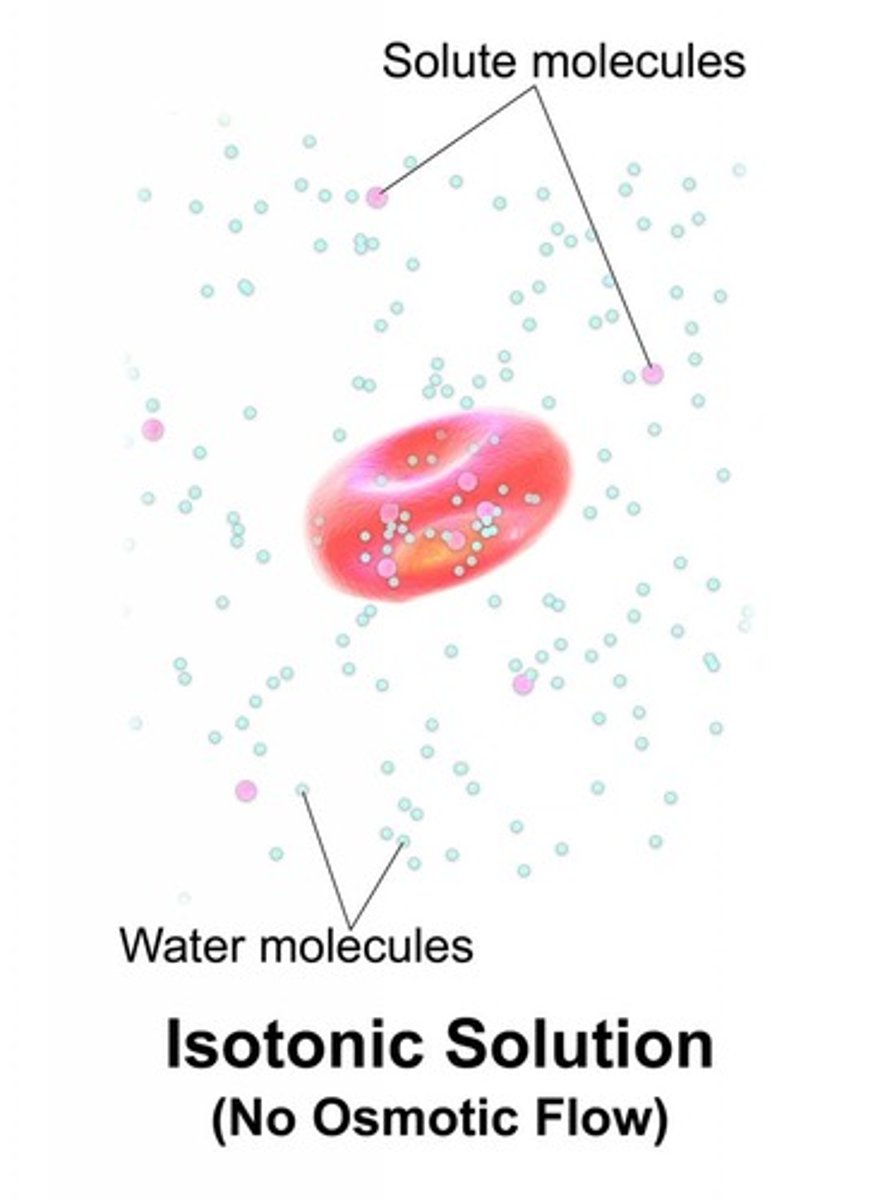
Isotonic Solutions
-have no net movement of H2O
-concentration of solutes equal inside and outside of cell
-water diffuses into and out of cell at same rate
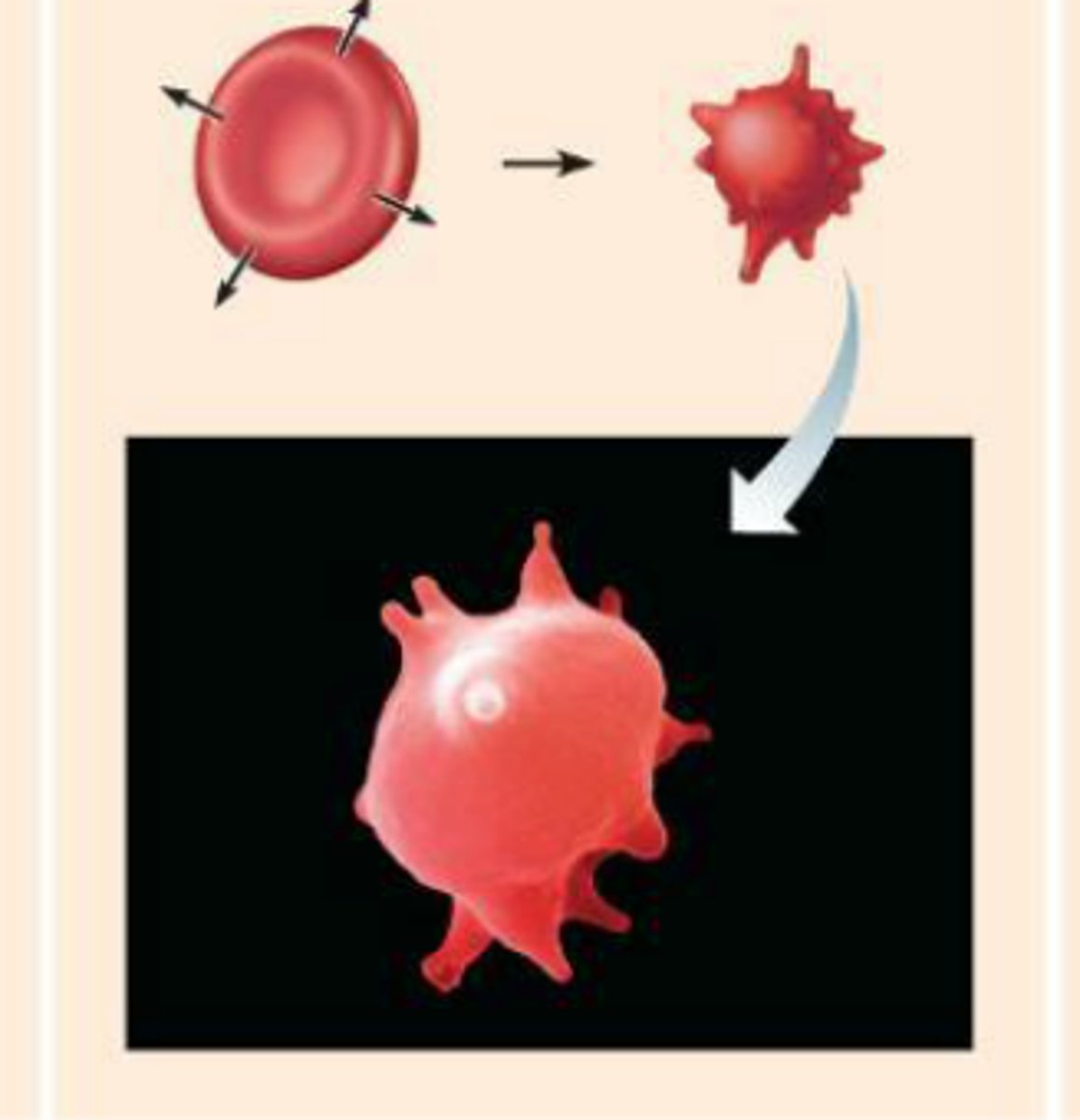
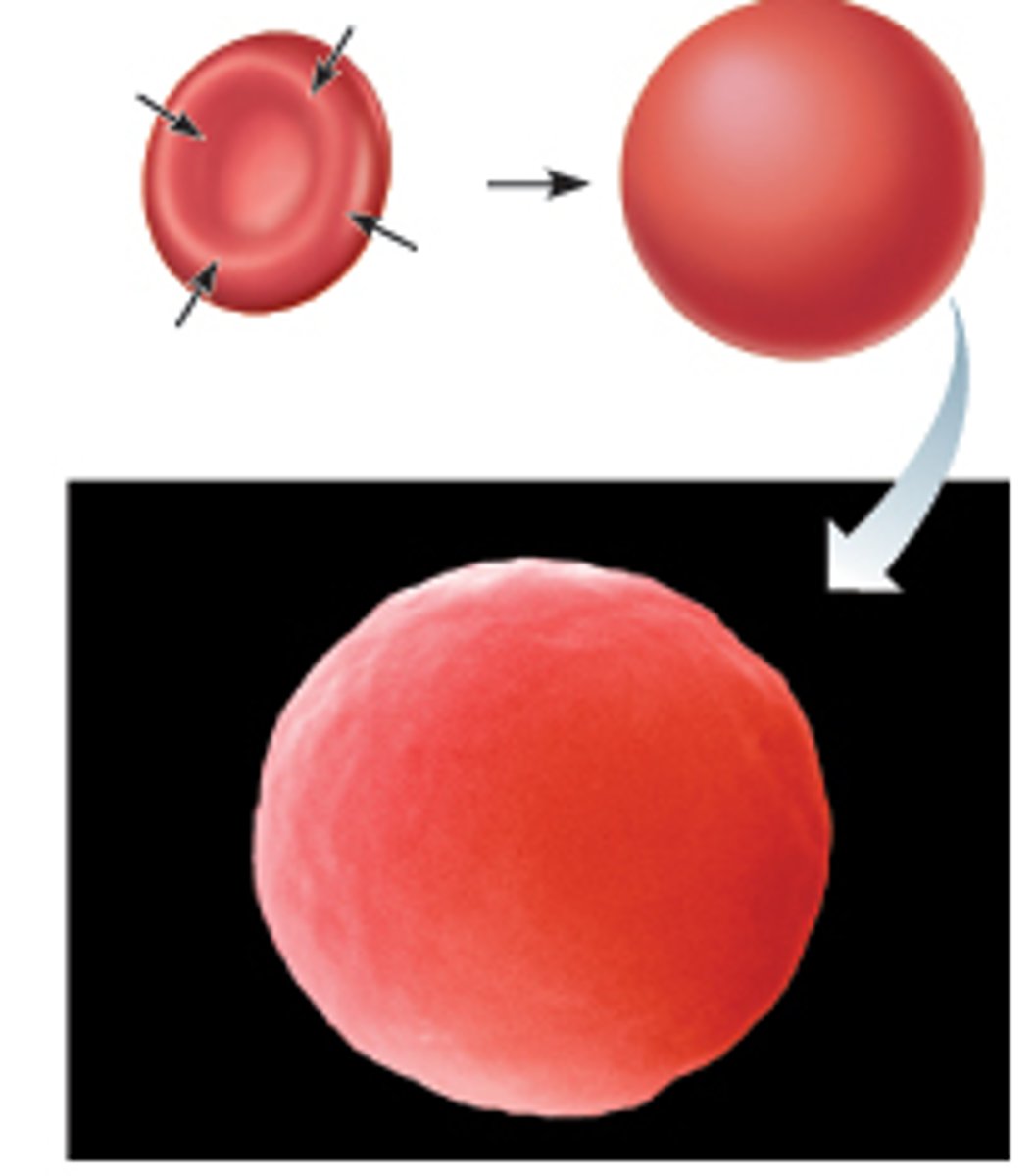
Hypertonic solutions
-loses water to its surroundings
-concentration of solutes is higher outside of cell
-water moves to extracellular fluid
-cells shrivel and die
Plasmolysis
vacuole shrinks and plasma membrane pulls away from cell wall
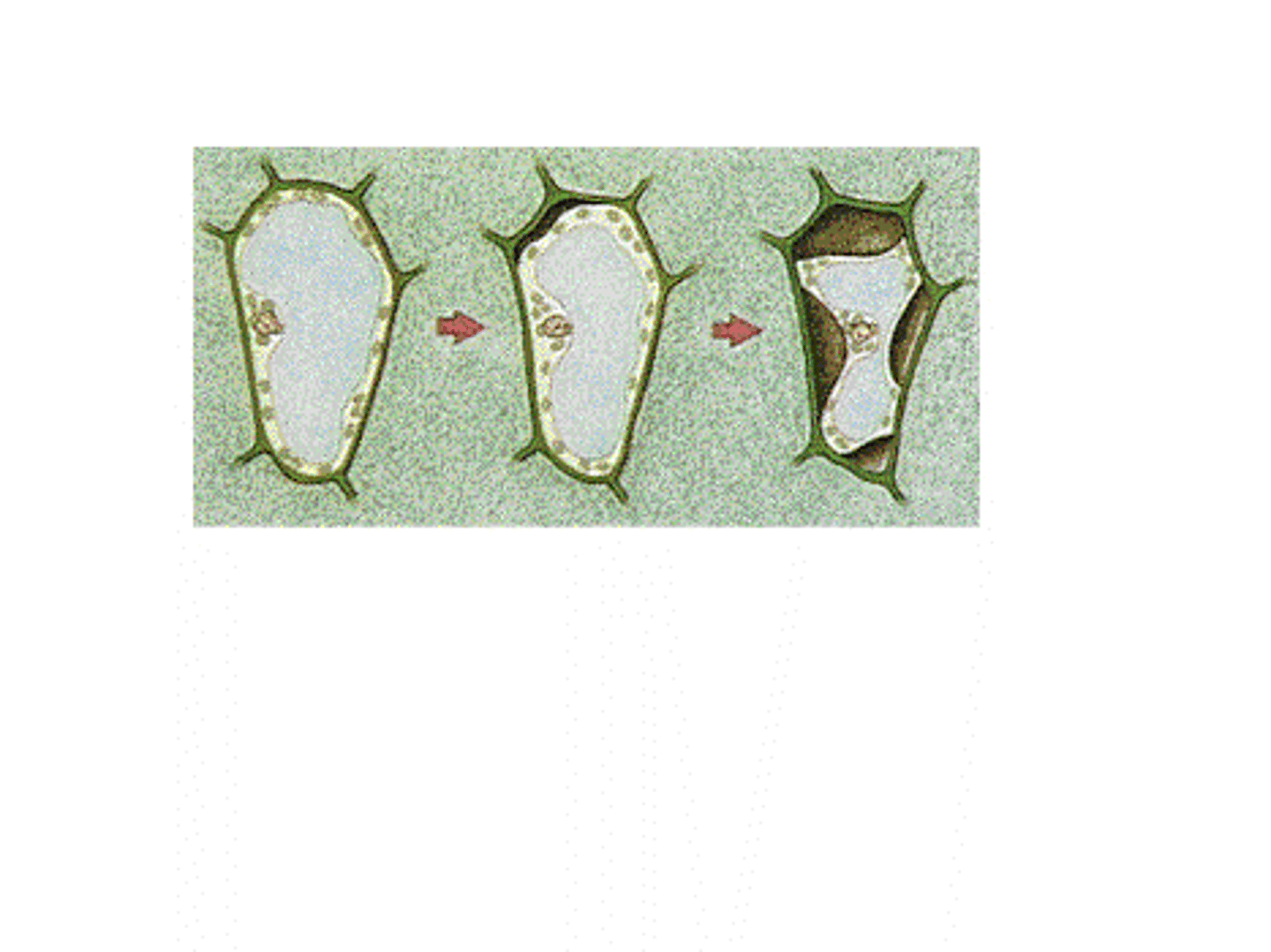
Hypotonic solutions
-gain water from surroundings
-concentration of solutes lower outside the cell
-cell will gain water-> cells swell and lyse (burst)
-plant cells work OPTIMALLY (maintain turgor pressure)
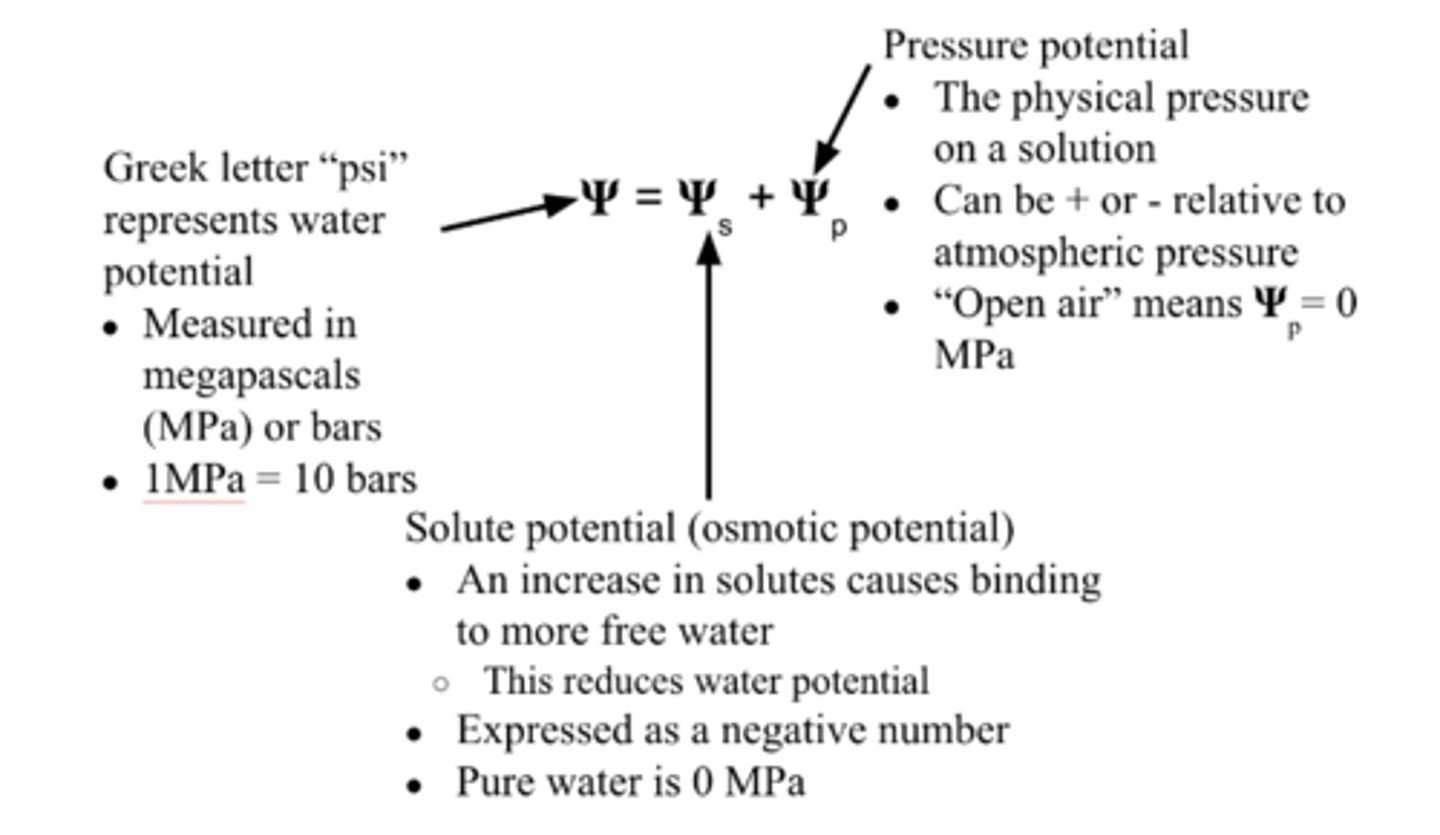
Water potential
-a physical property that predicts the direction water will flow
-includes the effects of solute concentration and physical pressure
Water will flow from areas of:
- high water potential to low water potential
-low solute to areas of high solute concentration
-high pressure to areas of low pressure
Unit for water potential
megapascals (MPa) or bars
water potential formula
solute potential formula
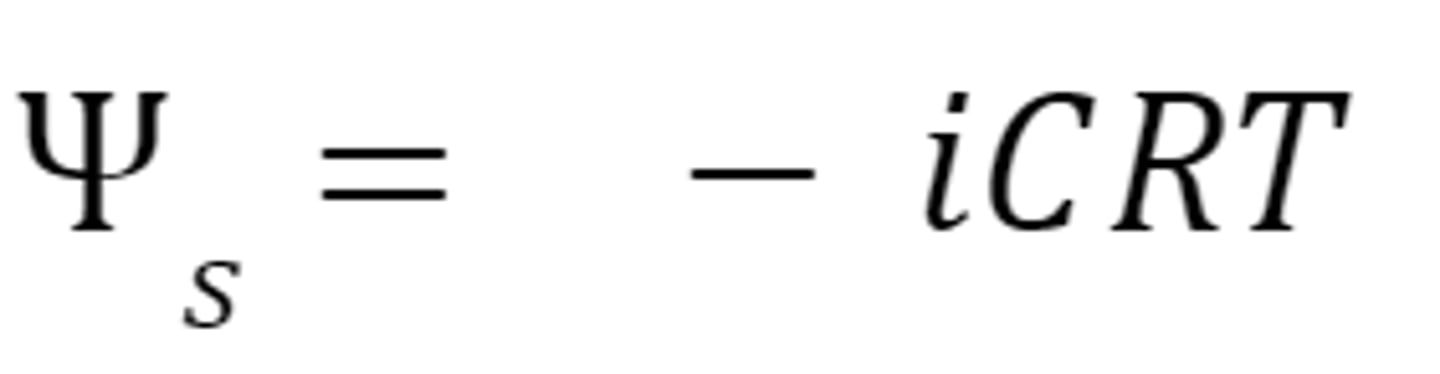
Ionization constant
-if no ions are formed the constant is one (basically all covalent bonds)
-ionic bonds= 2