U1 AOS 2 - Neuroimaging technology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
what is neuroimaging
technique that captures a picture of the brain ; non invasive (can be used without entering brain)
neuroimaging techniques
structural neuroimaging - techniques that produce images or scans (eg MRI, CT scan)
functional neuroimaging - provides view for particular aspect of brain (PET and fMRI)
Computerised Technology (CT) - STRUCTURAL
x ray equipment that scans the brain at diff angles
creates horizontal cross section of brain
needs ‘contrast’ to highlight blood vessels
limitations : not as detailed as other scanners
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - STRUCTURAL
magnetic fields vibrate atoms in brain to make an image
produces more clearer,detailed images
can detect small changes (e.g. cancerous and non cancerous tissues)
positron emission tomography (PET) - FUNCTIONAL
Produces colour images (shows brains structure, activity,function)
records level of activity in brain areas during tasks
less detailed than MRI
color code indicates activity levels: violet, blue, green, yellow, and red (highest).
Functional Magnetic Resonance (fMRI) FUNCTIONAL
Detects + records brain activity by measuring oxygen consumption. (Identifies brain areas by detecing changes in blood ox levels)
gives better images than PET, gives detailed images in quick time.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
Detects, amplifies, and records general patterns of electrical activity in the brain.
used to study states of consciousness (awake, sleeping) + brain disorders (epilepsy, parkinsons)
other functional neuroimaging btechniques
Magnetoencephalography (MEG).
Near infra-red spectroscopy (NRIS).
Diffuse optical tomography (DOT).
Major brain reigions
hindbrain ; medulla, pons, cerebellum
midbrain : reticular formation, substantial nigra
forebrain : hypothalamus, thalamus, cerebrum.
Hindbrain
basic survival functions
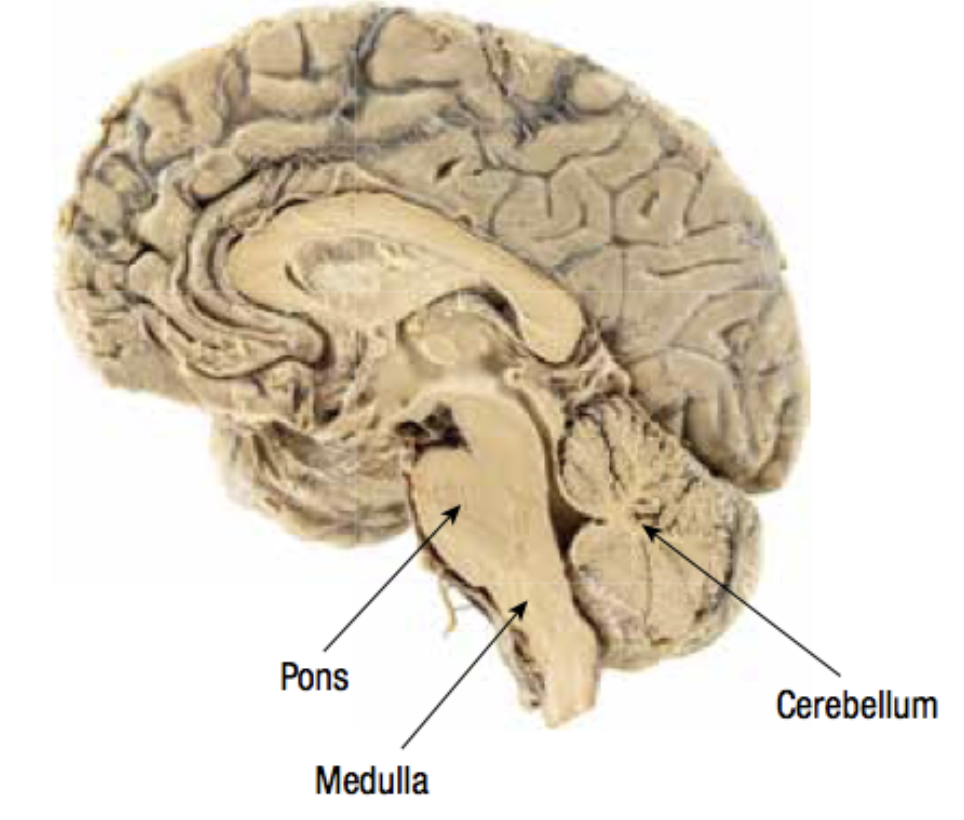
Hindbrain : Medulla
control vital functions (breathing, heart rate) CONNECTS SPINAL CORD TO BRAIN
Hindbrain : Pons
involved in sleep, dreaming, coordination
Hindbrain : Cerebellum
coordinates voluntary movements and balance.
midbrain
sensory processing and arousal
Reticular Formation: filters sensory info, consciousness, sleep-wake cycle.
Reticular Formation : Midbrain
Reticular Formation: filters sensory info, consciousness, sleep-wake cycle.
Forebrain
involved in thinking and emotions
Hypothalamus - Forebrain
regulates body functions (hunger, thirst, hormones).
Thalamus - Forebrain
sensory relay station (except smell), attention, arousal.
Cerebrum - forebrain
complex thought, emotion, memory, learning.
limbic system
generally controls emotional behaviour
interconnected group of forebrain structures : includes amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus.
cerebral cortex
STRUCTURE
Outer layer of the cerebrum.
Divided into left & right hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum.
FUNCTIONS
Higher mental functions: thinking, planning, decision-making.
Divided into sensory, motor, and association areas.
Cortical Lobes
frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe
frontal love
Planning, decision-making, personality.
Primary Motor Cortex: voluntary movements.
Broca’s Area: speech production (left hemisphere).
parietal lobe
Sensory processing, spatial awareness.
Primary Somatosensory Cortex: touch sensations.
Occipital Lobe
Visual processing.
Primary Visual Cortex: interprets info from eyes.
Temporal lobe
Memory, hearing, facial recognition.
Primary Auditory Cortex: processes sound.
Wernicke’s Area: speech comprehension (left hemisphere)