Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Inorganic Chemistry
1/484
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
485 Terms
Liberation
Active drug molecule released from dosage form.
Absorption
Movement of drug into the bloodstream.
Bioavailability
Amount of drug reaching bloodstream from dose.
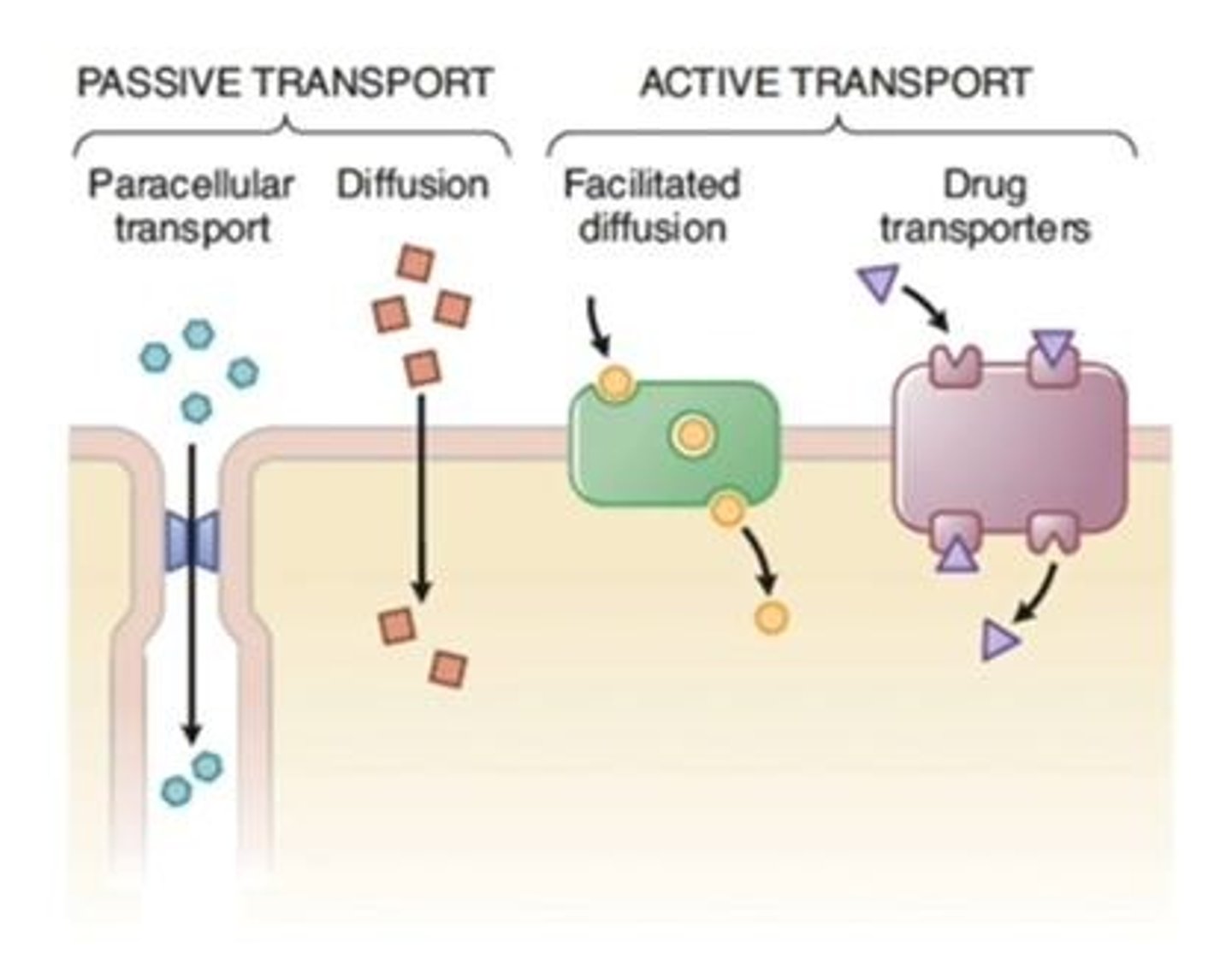
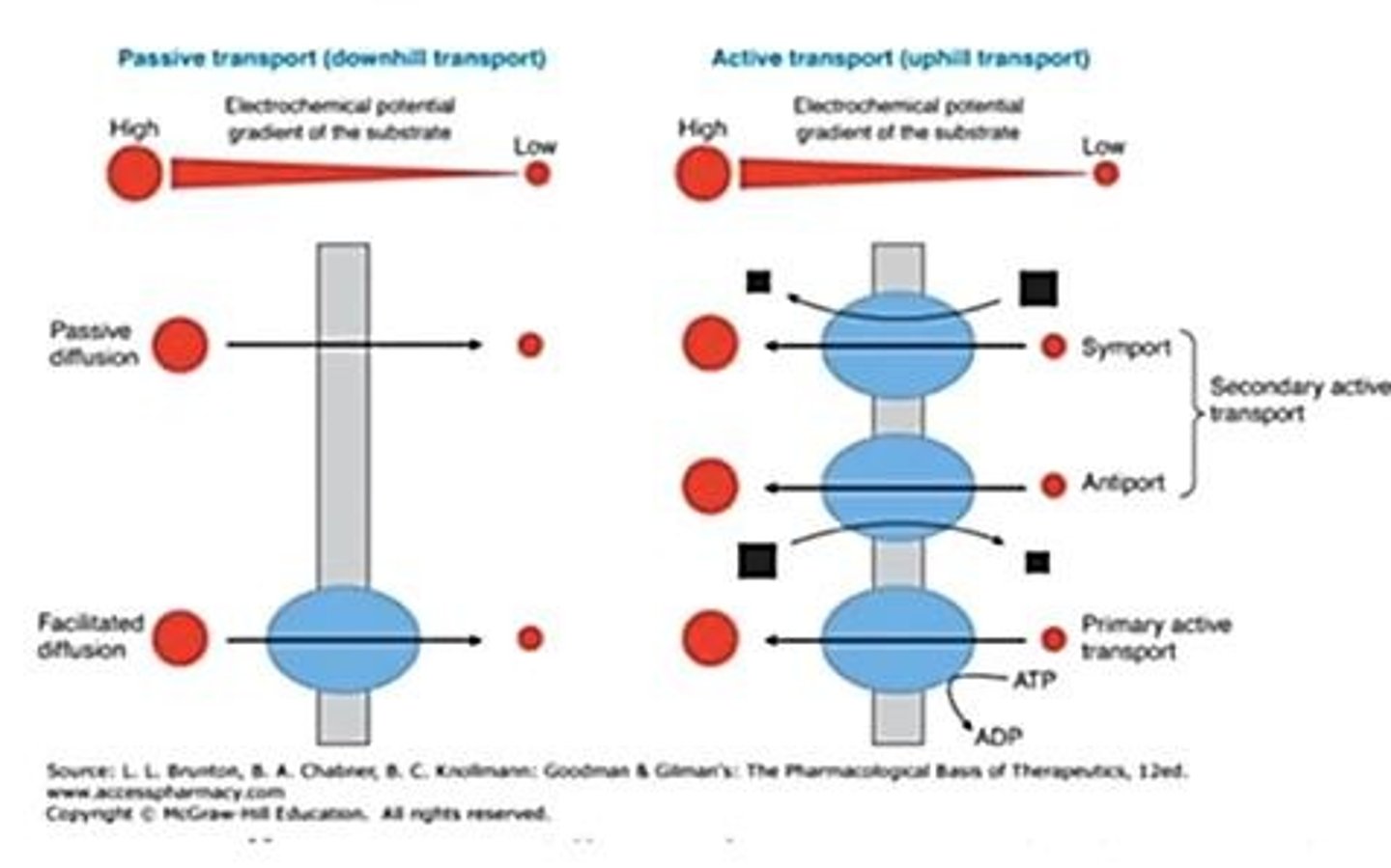
Passive Transport
Movement across membranes without energy.
Endocytosis
Process of cellular intake via membrane engulfing.
Exocytosis
Process of cellular secretion via membrane fusion.
Active Transport
Energy-requiring movement of molecules across membranes.
Distribution
Transport of drug molecules through blood vessels.
Therapeutic Site of Action
Desired location where drug exerts effects.
Reservoir
Storage site for drugs, not actively used.
Unwanted Site of Action
Location where drug causes undesired effects.
Free Drug
Drug not bound to proteins or tissues.
Pharmacodynamics
Effects of drug on the body.
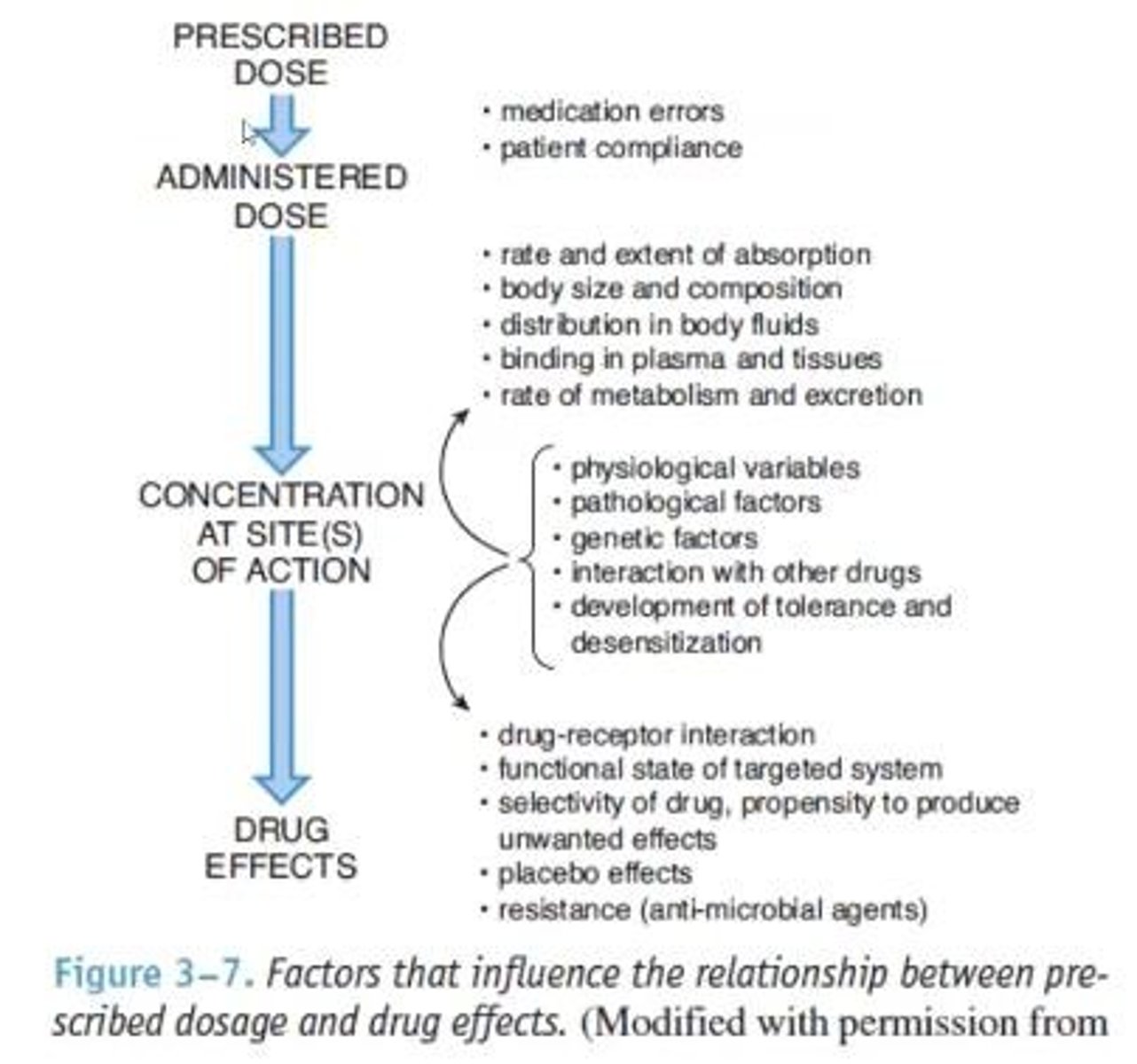
Pharmacokinetics
Body's processes affecting drug absorption and elimination.
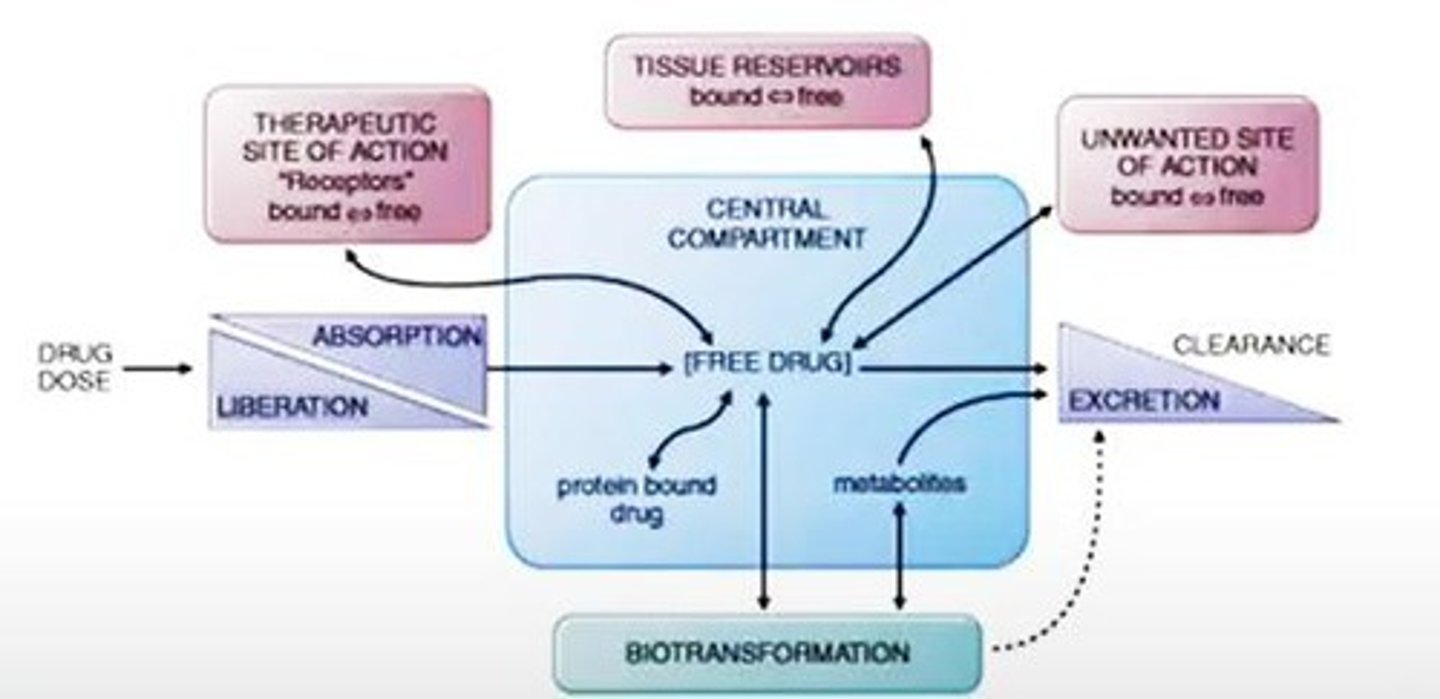
Biotransformation
Conversion of drug into more excretable forms.
Excretion
Elimination of drugs from the body.
Renal Excretion
Elimination of drugs via the kidneys.
Capillary Excretion
Storage of drugs in bile for elimination.
Pulmonary Excretion
Elimination of drugs through the lungs.
Paracellular Transport
Transport occurring between adjacent cells.
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration.
LADME
Processes: Liberation, Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion.
Concentration Gradient
Difference in concentration across a membrane.
Electrochemical Gradient
Combined effect of concentration and charge.
Osmosis
Water movement from high to low concentration.
Fick's Law of Diffusion
Rate of diffusion proportional to concentration difference.
Permeability Coefficient
Measure of a membrane's permeability to a substance.
Sodium-Potassium ATPase
Pump maintaining sodium and potassium gradients.
Villi
Intestinal projections increasing surface area for absorption.
Ionization
Degree to which a substance dissociates into ions.
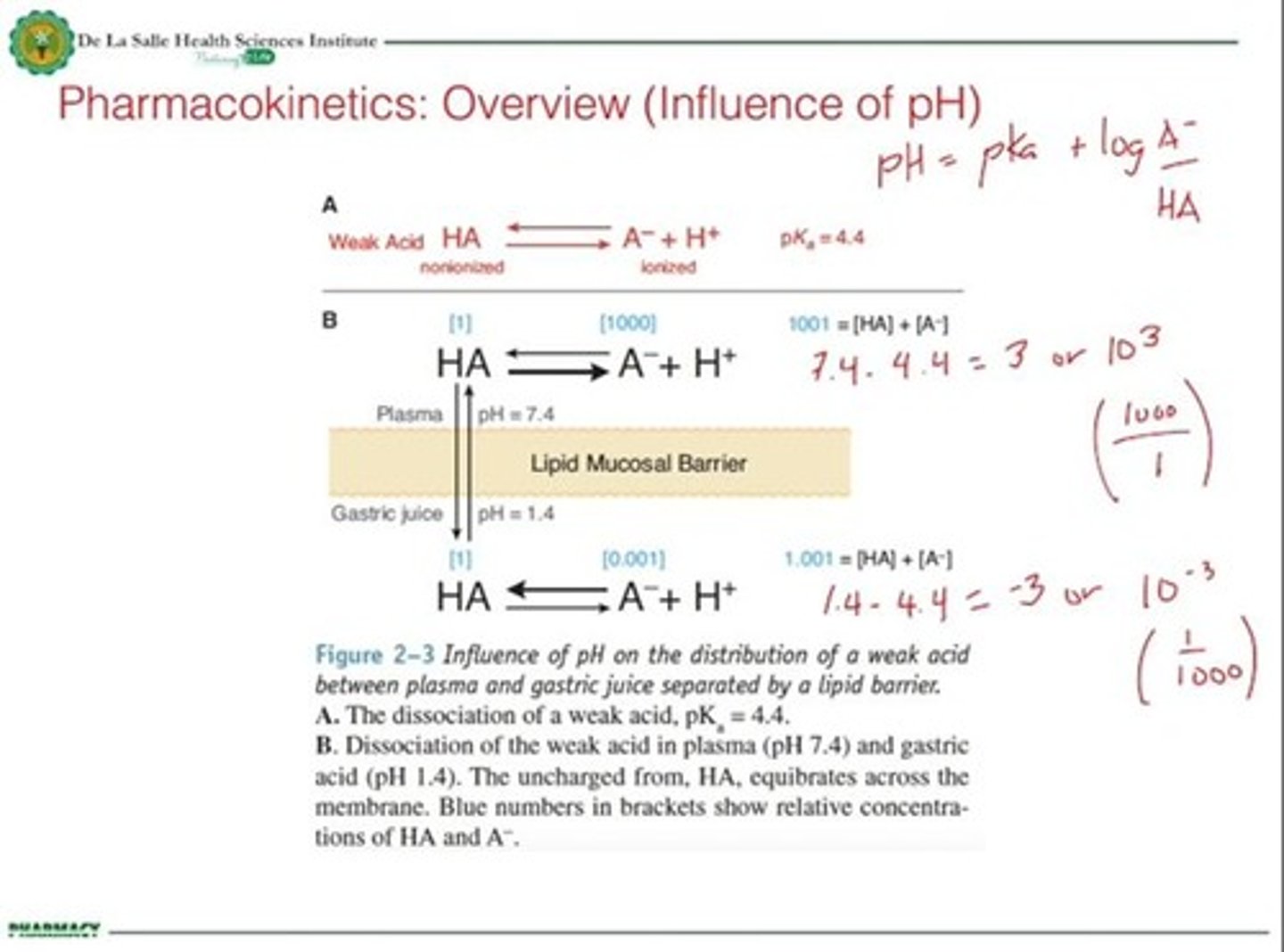
Henderson Hasselbalch Equation
Calculates pH based on ionization states.
Amphipathic Molecules
Molecules with both polar and nonpolar parts.
Cotransport
Simultaneous transport of multiple substances.
Symport
Transport of two substances in the same direction.
Antiport
Transport of two substances in opposite directions.
Solubility
Ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent.
Surface Area
Area available for diffusion processes.
Unionized State
Form of a molecule not carrying a charge.
Lipid Mucosal Barrier
Membrane barrier affecting drug absorption.
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive transport using channel proteins along gradient.
Pinocytosis
Cellular uptake of liquid substances.
Phagocytosis
Cellular uptake of large solid particles.
Receptor-mediated Endocytosis
Specific uptake via receptor binding.
Carrier-mediated Transport
Transport using specific proteins or channels.
Reversible Vesicle Transport
Bidirectional transport of receptors and proteins.
Primary Active Transport
Direct use of ATP to move substances.
Secondary Active Transport
Indirect use of ATP, involves symport or antiport.
Gated Channels
Channels that open under specific conditions.
Voltage-gated Channels
Open in response to electrical changes.
Ligand-gated Channels
Open when a specific molecule binds.
Mechanically-gated Channels
Open due to physical changes or pressure.
Metabolism
Biotransformation of substances for easier excretion.
Tissue Reservoirs
Storage sites for minerals and nutrients.
Drug Receptors
Molecules where drugs bind to elicit responses.
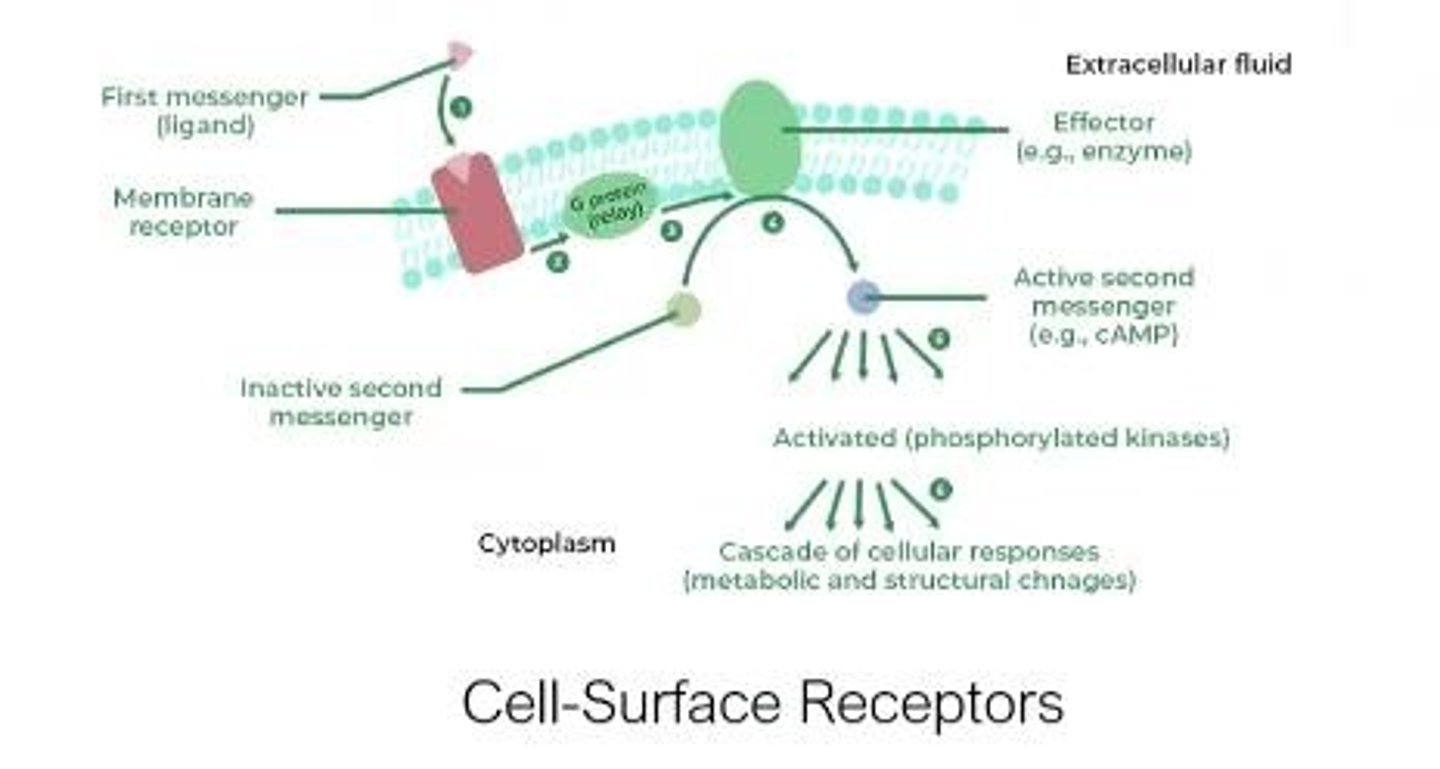
GPCR
G-protein coupled receptors; integral membrane proteins.
Signal Transduction
Conversion of signals into cellular actions.
Ligand
Molecule that binds to a receptor.
Transmembrane Receptors
Proteins spanning the plasma membrane.
Nuclear Receptors
Receptors located inside the cell nucleus.
Intracellular Receptors
Receptors within the cytoplasm of cells.
Autocrine Signaling
Cell signals itself as target.
Juxtacrine Signaling
Cell signaling to adjacent cells.
Paracrine Signaling
Cell signaling to nearby cells.
Endocrine Signaling
Cell signaling to distant target cells.
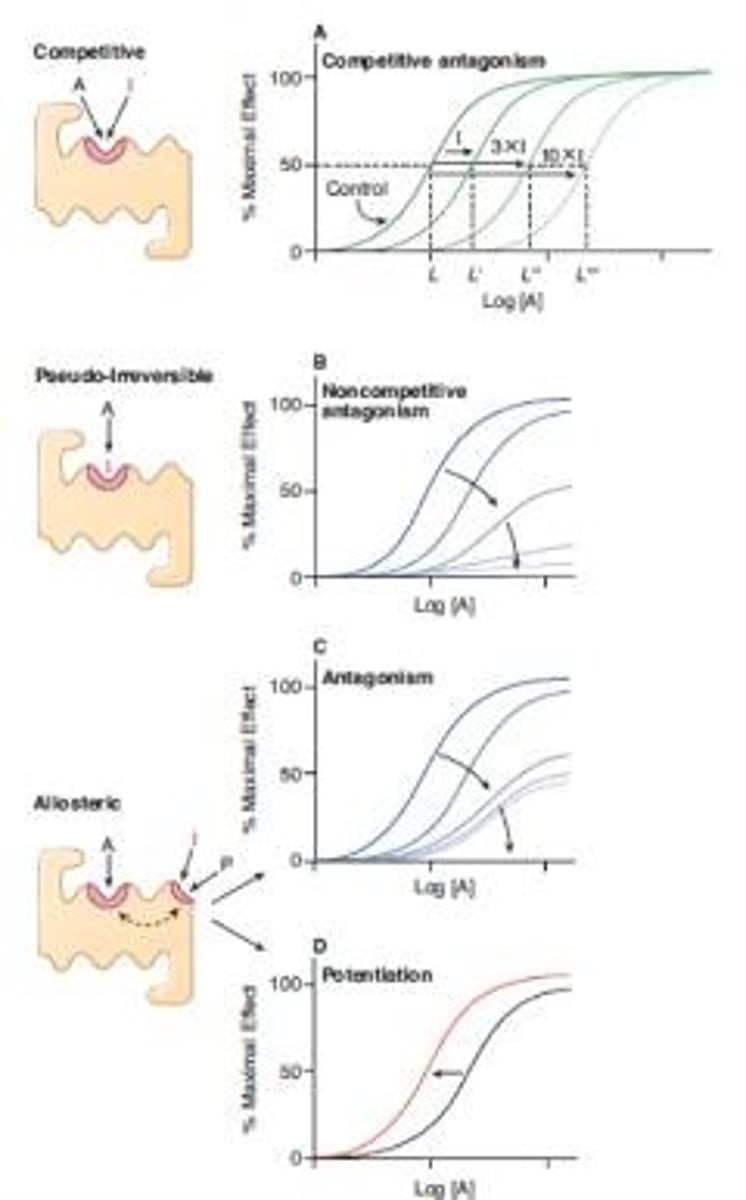
Antagonism
Binding that produces opposite effects.
Endogenous Ligands
Molecules produced by the body for receptors.
Exogenous Ligands
External molecules interacting with body receptors.
Competitive Inhibition
Ligands compete for the same receptor.
Pseudo-Irreversible Inhibition
Inhibitor permanently blocks receptor binding.
Allosteric Modulation
Binding alters receptor shape and function.
Affinity
Strength of binding between ligand and receptor.
Efficacy
Ability of a drug to produce an effect.
Potency
Concentration required to achieve a desired effect.
Transmembrane Non-Enzymatic Proteins
Proteins without enzymatic activity across membranes.
Intracellular Enzymes
Enzymes located within organelles of cells.
Agonism
Mimics endogenous ligands to produce effects.
Antagonistic Effect
Opposes or nullifies the effect of a ligand.
Lead Toxicity
Causes anemia through antagonistic effects.
Cortisol
Endogenous ligand affecting various physiological processes.
Prednisone
Exogenous ligand mimicking cortisol's effects.
Agonist
Substance producing the same effect as another.
Compound A
Binds receptor X to induce heartbeats.
Compound B
Also binds receptor X, causing heartbeats.
Dose Variability
Effects change based on dosage and administration.
Receptors
Proteins that bind ligands to trigger cellular responses.
Ion Channels
Facilitate ion movement across cell membranes.
Ligand-gated Ion Channels
Open in response to ligand binding.
Voltage-gated Ion Channels
Open based on membrane voltage differences.
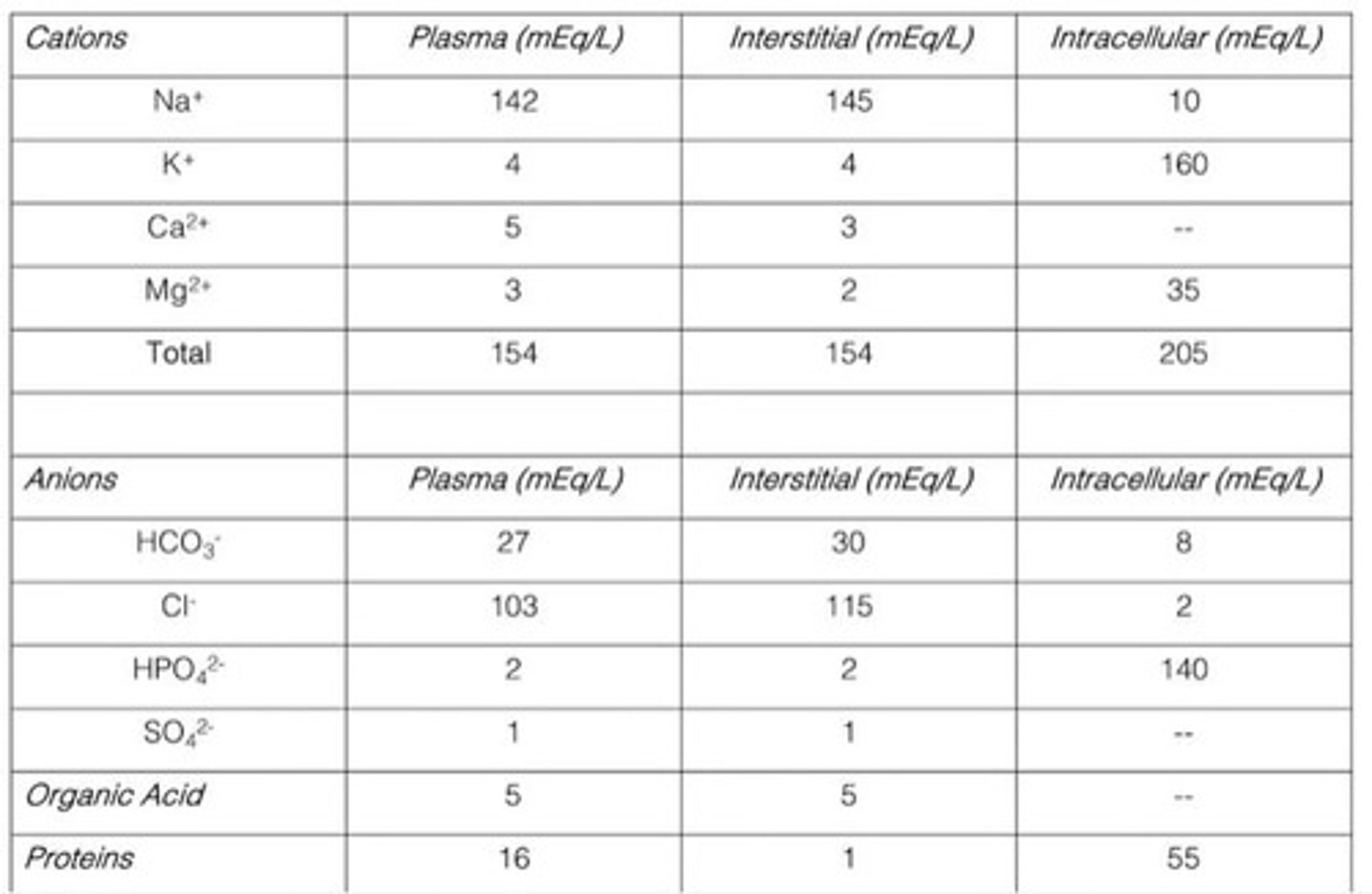
Electrolytes
Maintain pH, ionic, and osmotic balance in the body.
Steady-State Balance
Dynamic equilibrium of input and output in systems.
Tonicity
Effect of solute concentration on cell volume.
Molarity
Concentration of solute in a solution.
Osmolarity
Total solute concentration in a solution.
Osmolality
Solute concentration per kilogram of solvent.
Positive Balance
Excess input overwhelms body's capacity.
Negative Balance
More output than input leads to deficiency.
Gatorade
Electrolyte drink developed for athlete performance.
Dr. Cade
Created Gatorade to address athlete hydration needs.
Electrolyte Levels
Measured through student sweat analysis.
Blood Sugar Levels
Low levels indicate potential health issues.