18 - gravitational fields
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what causes gravitational fields?
what do gravitational fields give rise to?
what is the range of a gravitational field?
for any object placed in a gravitational field, what force is acting on it?
- all objects with mass create a gravitational field around them
- gravitational fields give rise to a force
- field is infinite but negligible at large distances
- any object with mass placed in a gravitational field will experience an attractive force toward the centre of mass of the object, creating the field
what does a gravitational field look like around a spherical mass?
radial field lines
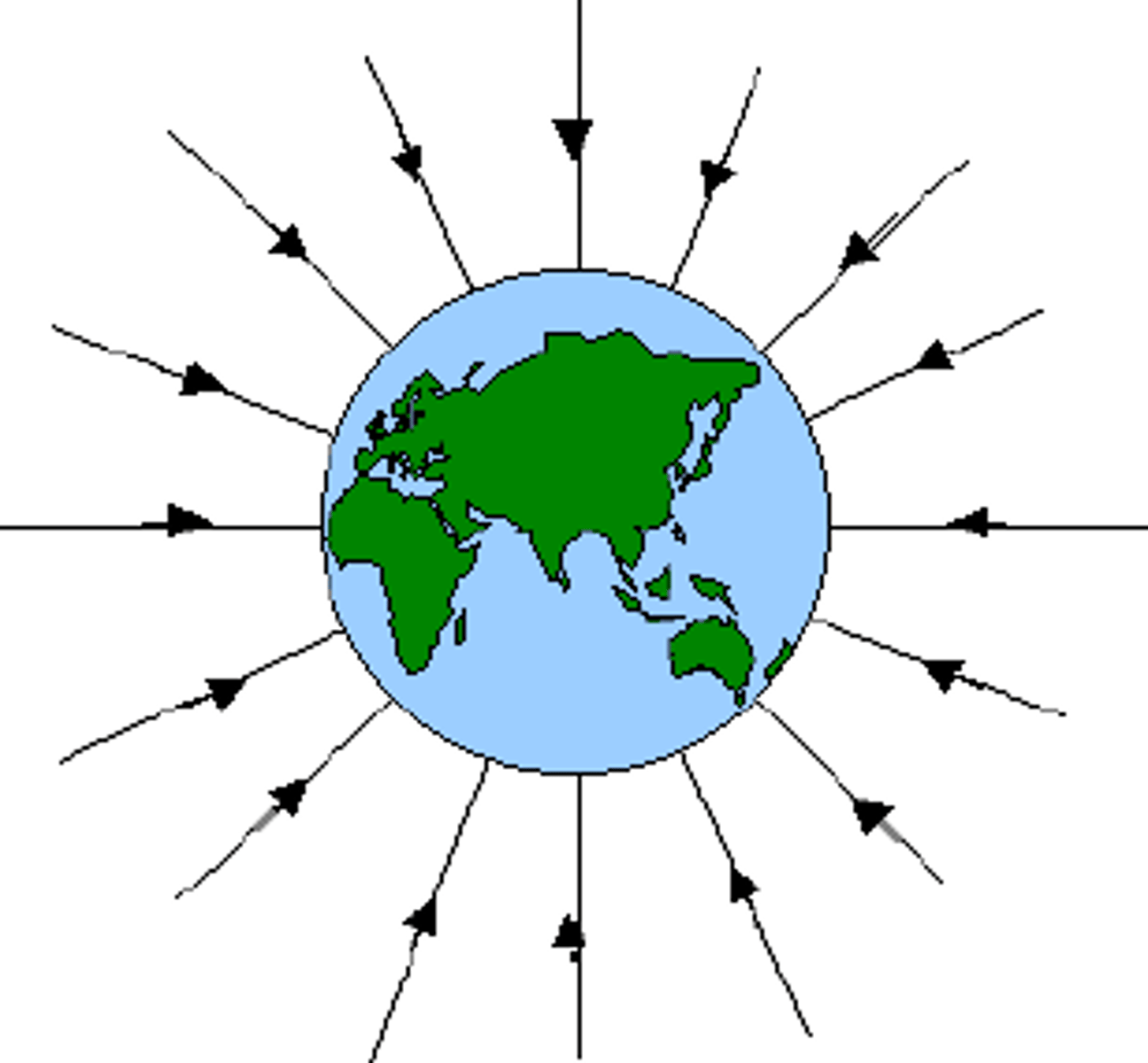
what does gravitational field look like on the surface of a planet?
define gravitational field strength
why must the object be small?
gravitational field strength, g, is defined as the gravitational force exerted per unit mass on a small object placed in that field
- g = F/m
- so objects gravitational field is negligible compared to external gravitational field
what is Newton's law of gravitation?
what is the equation for gravitational force?
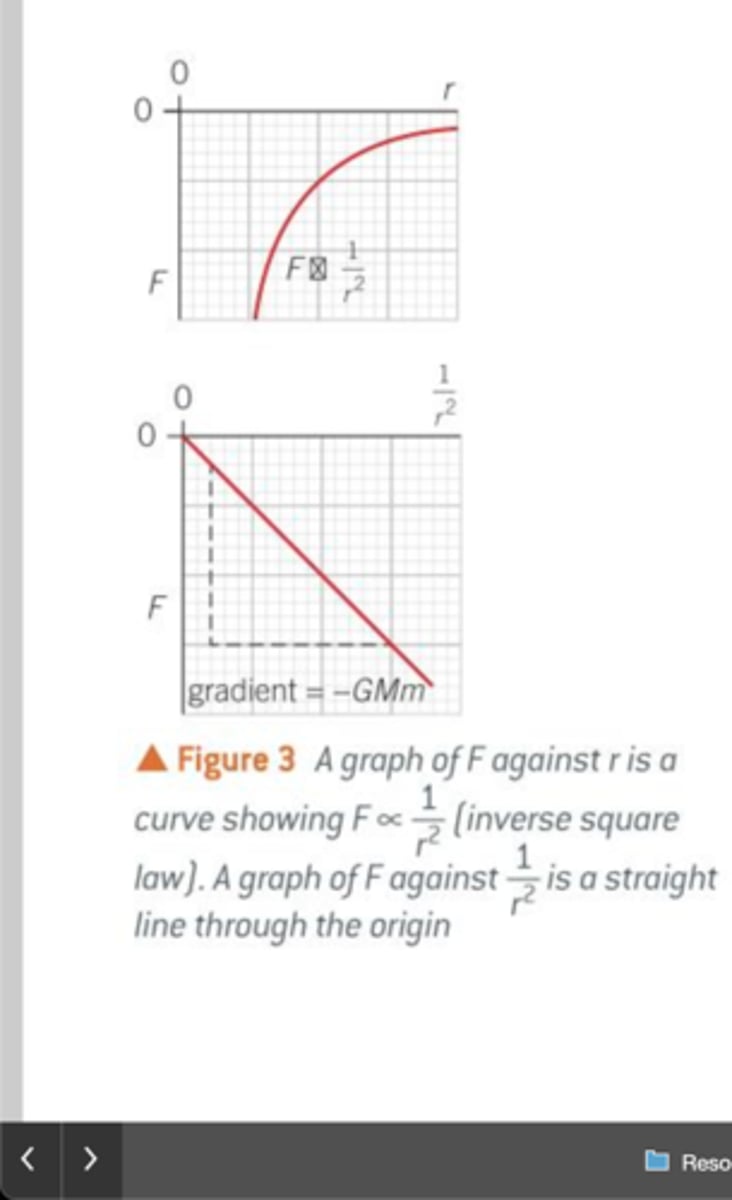
The force between two point masses is directly proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the separation between them
- f ∝ Mm
- F ∝ 1/r²
- F = - GMm/r²
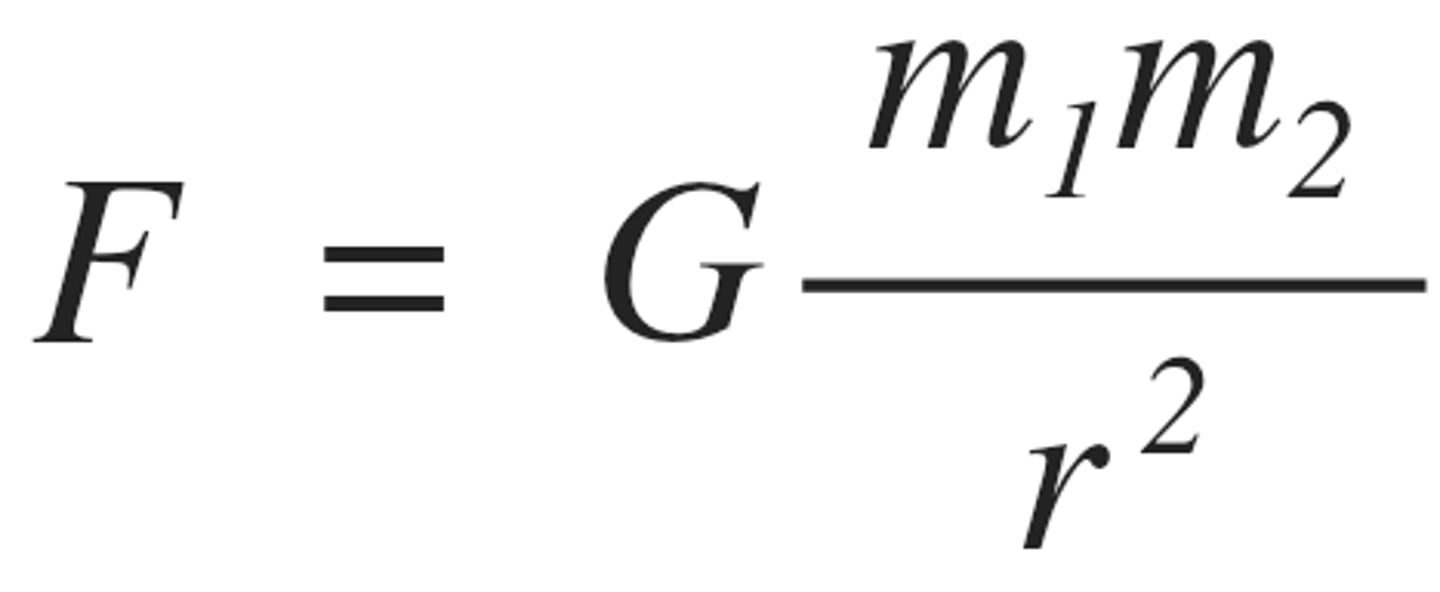
why is there a negative sign for the equation for the gravitational force?
force is a vector - for, F = - GMm/r², the positive direction is from the mass M towards the mass m
∴ the force on m is negative
graph for F against radius
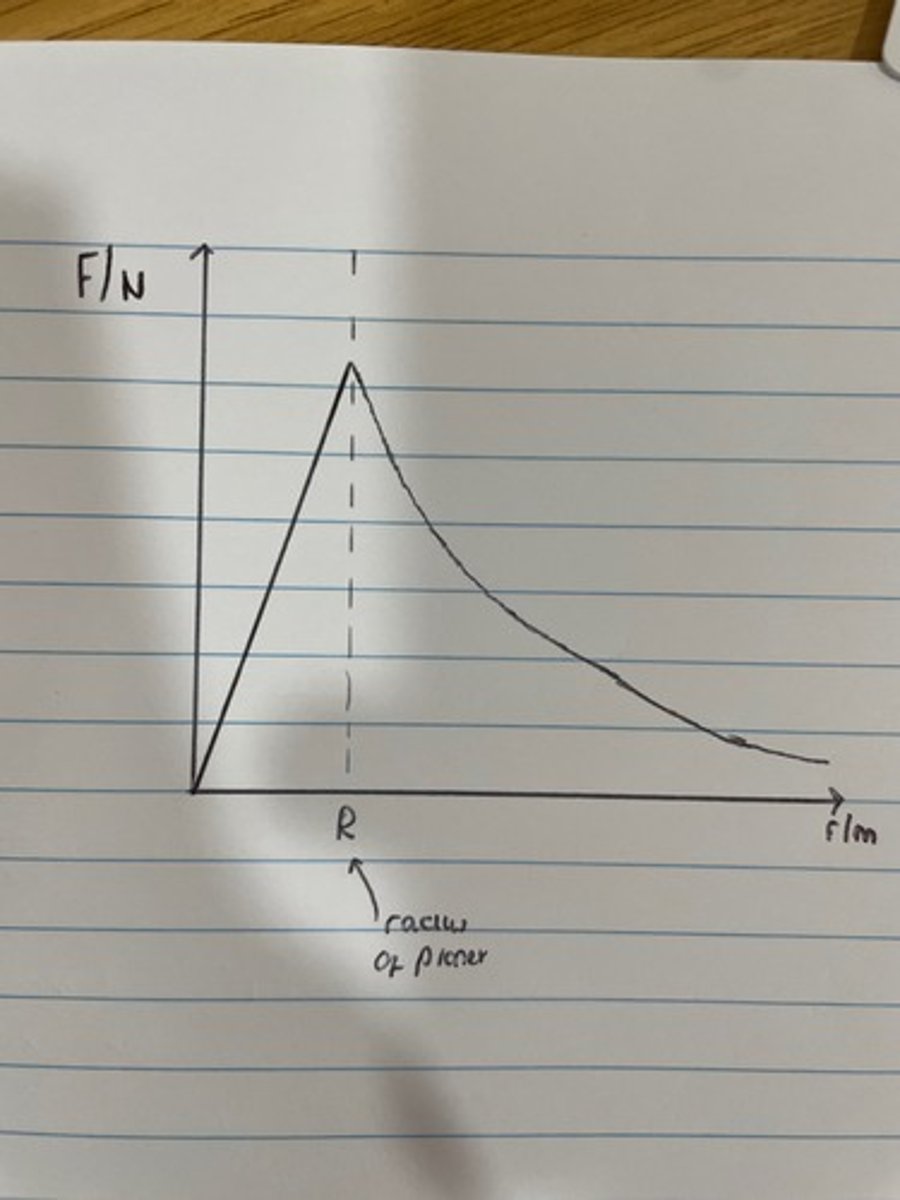
graph for F againts 1/r²
formula for gravitational field strength in a radial field
what does it show about the field strength?
- field strength is independent of the mass in orbit
- only the mass of the planet creating the gravitational field affects the field strength and the distance between a point in the radial field and the planet
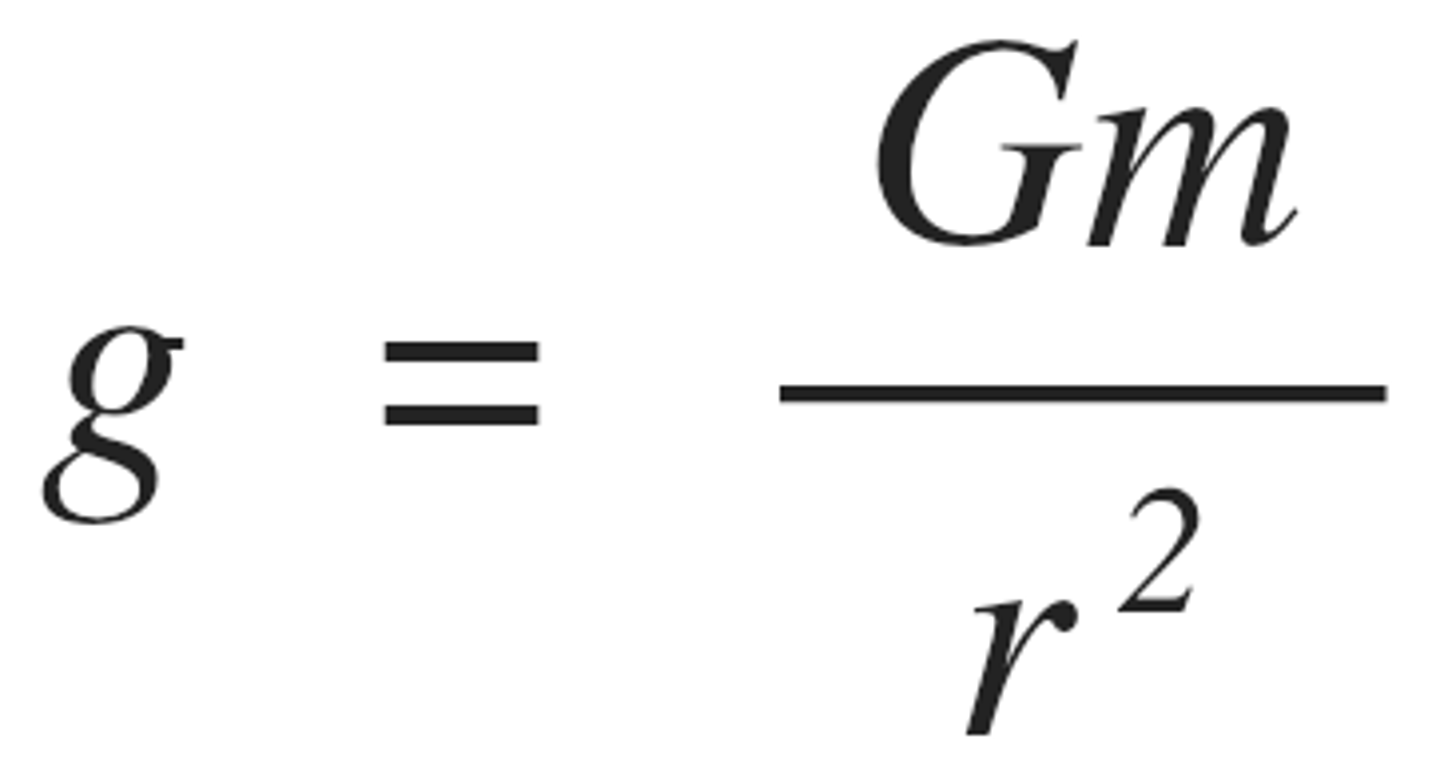
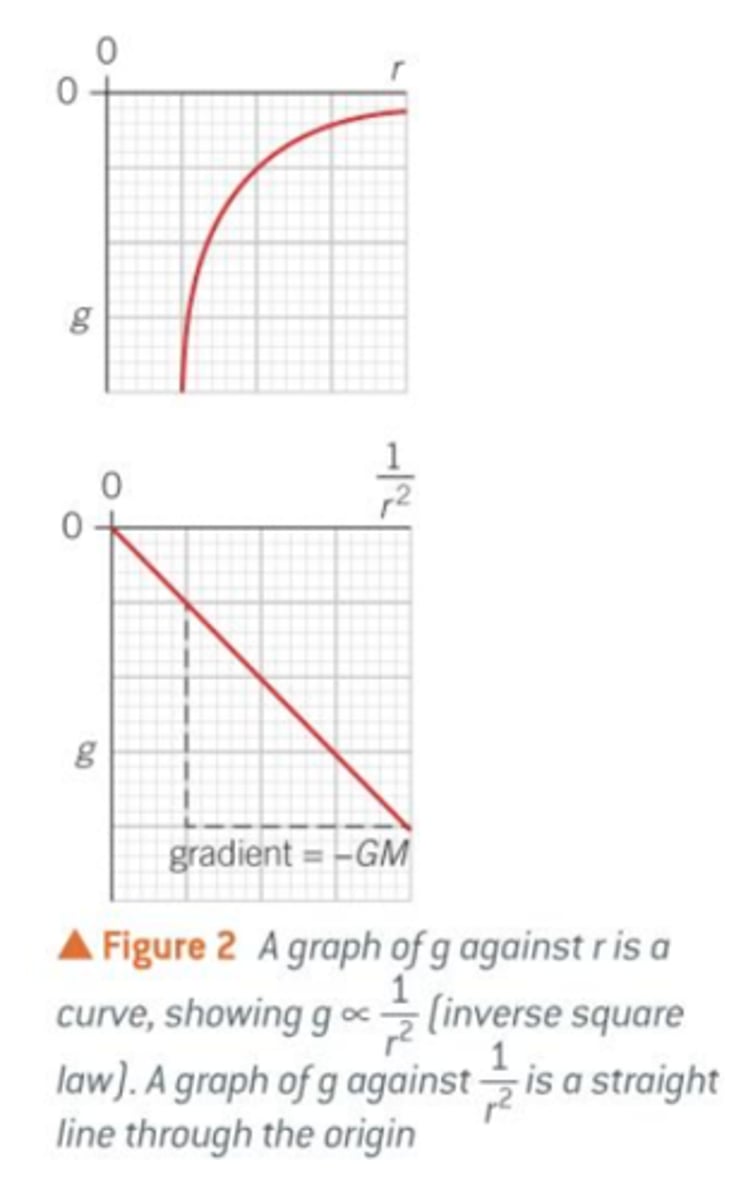
what conclusions can we draw for the gravitational field strength at any point in a radial field?
graph for the conclusions?
- g is proportional to the mass creating the gravitational field
- g is inversely proportional to 1/r²
What is Kepler's first law?
The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci
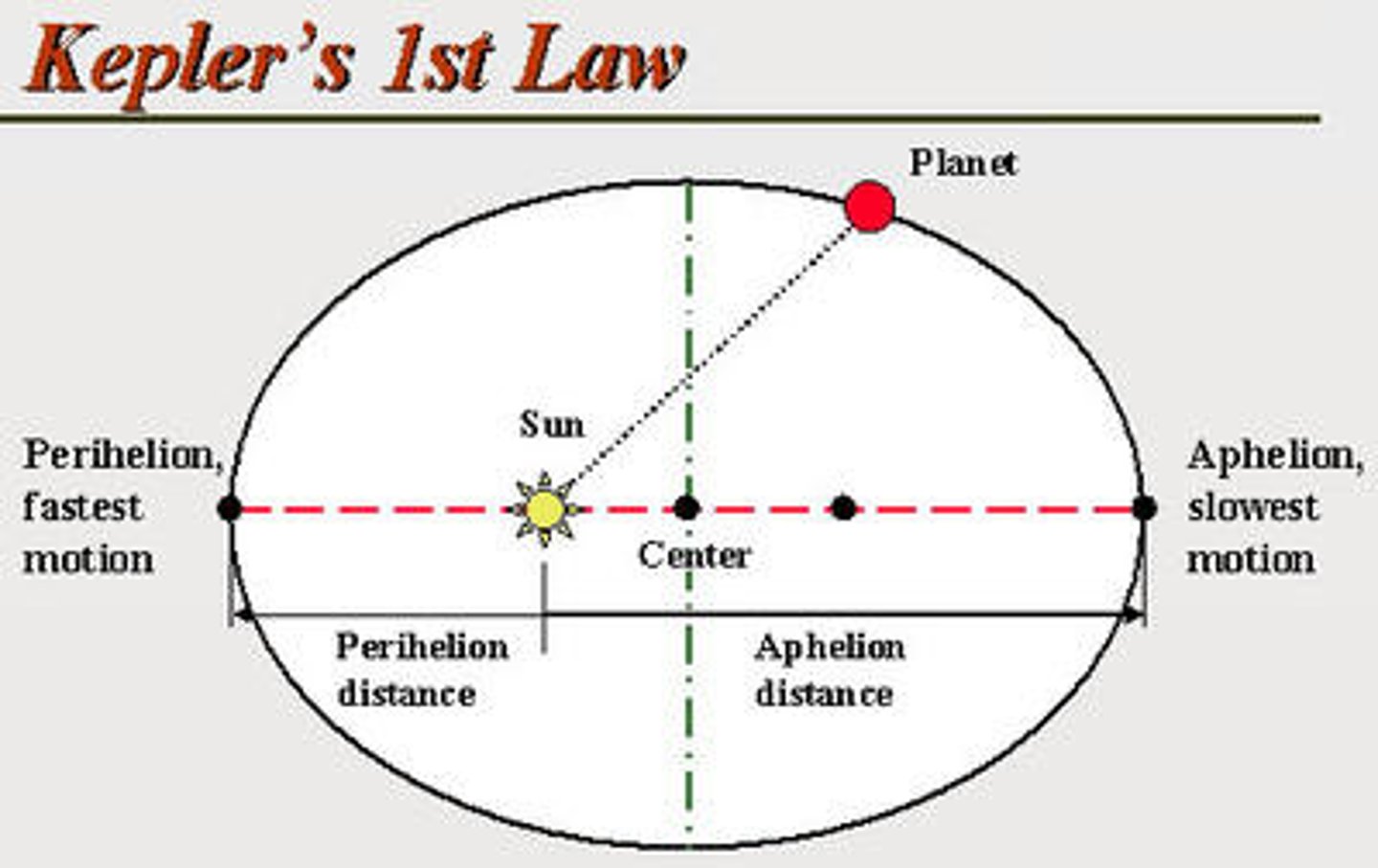
What is aphelion?
the point in the orbit of a planet, asteroid, or comet at which it is furthest from the sun.
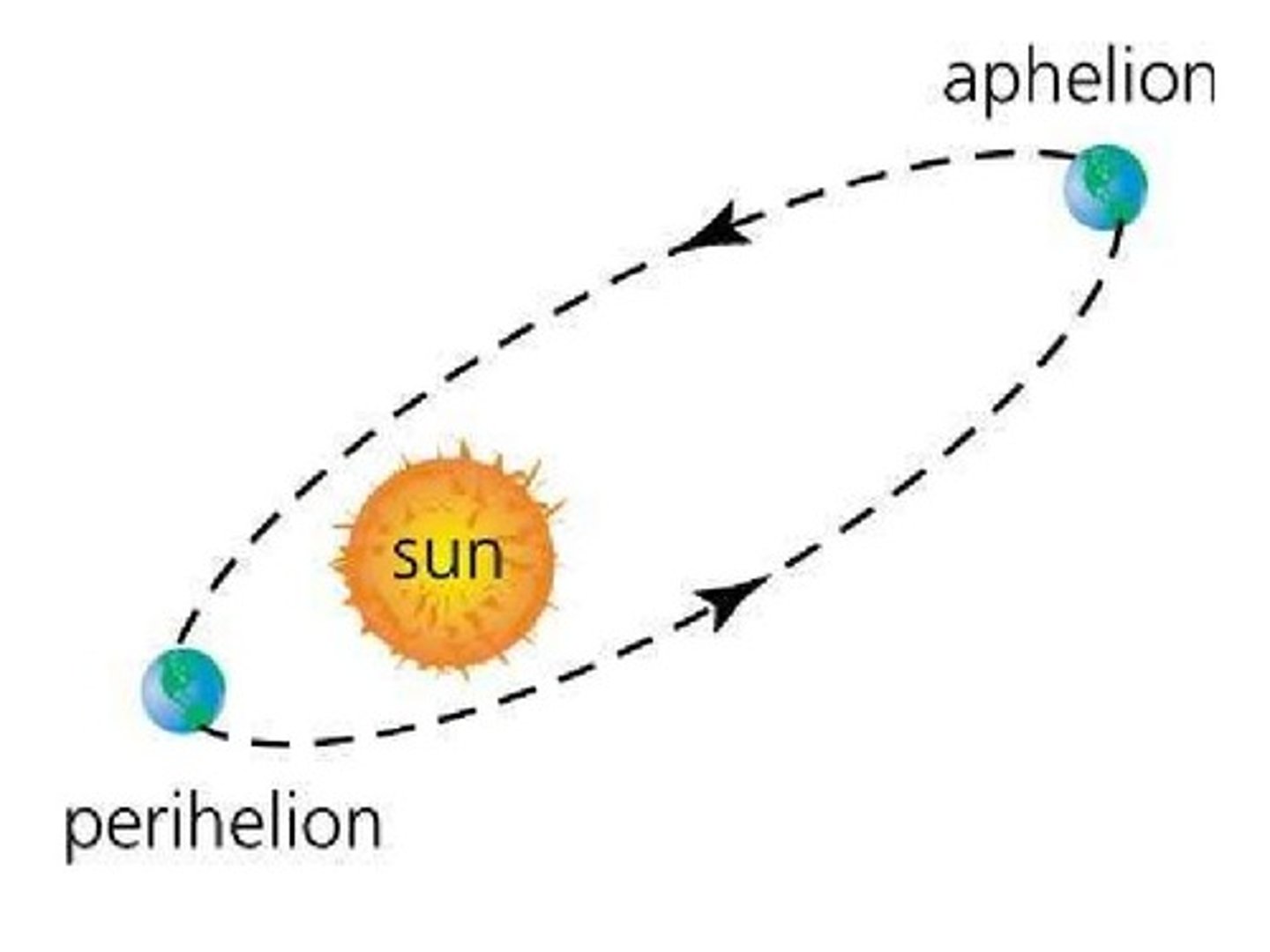
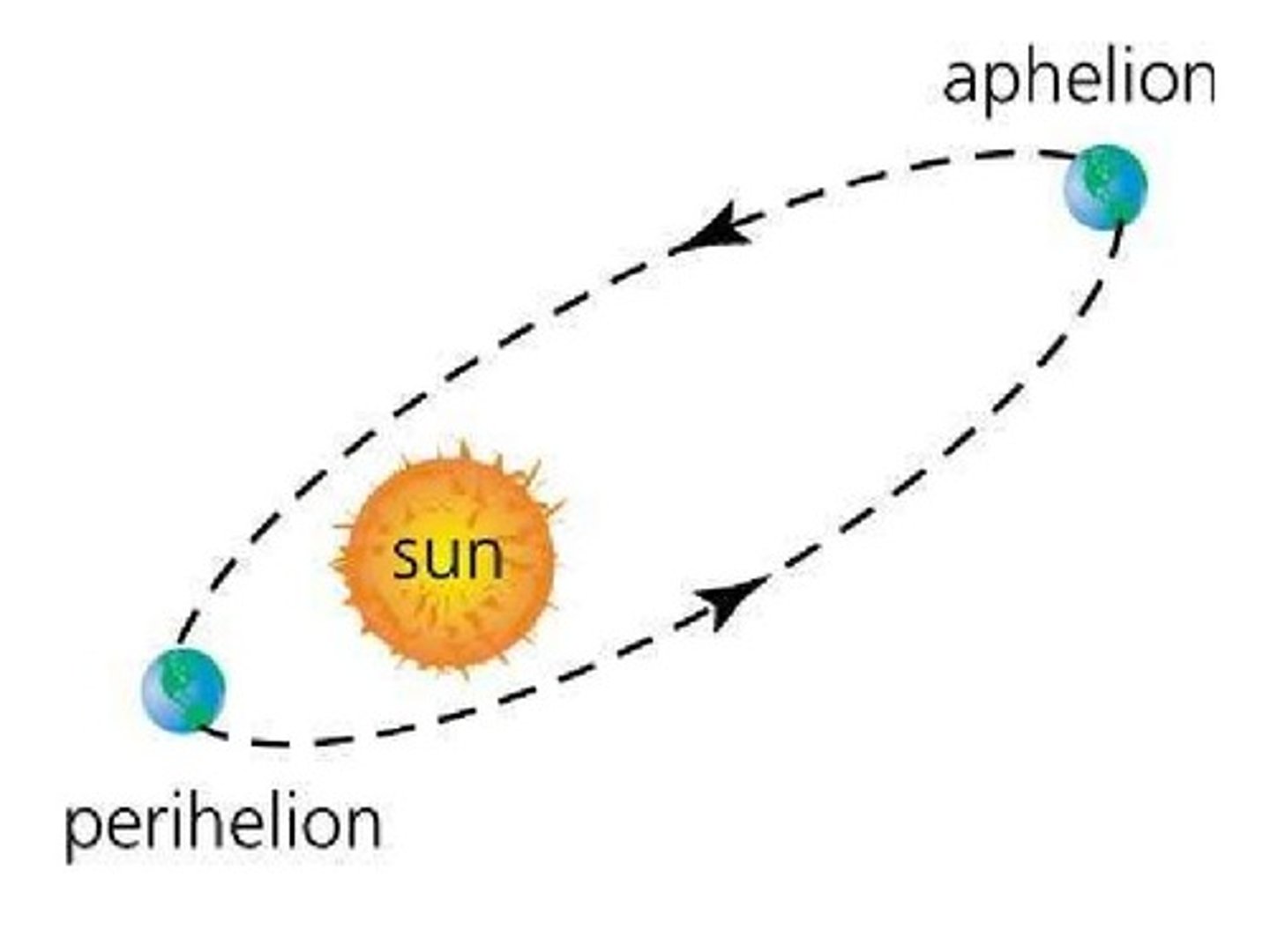
What is perihelion?
the point in the orbit of a planet, asteroid, or comet at which it is closest to the sun.
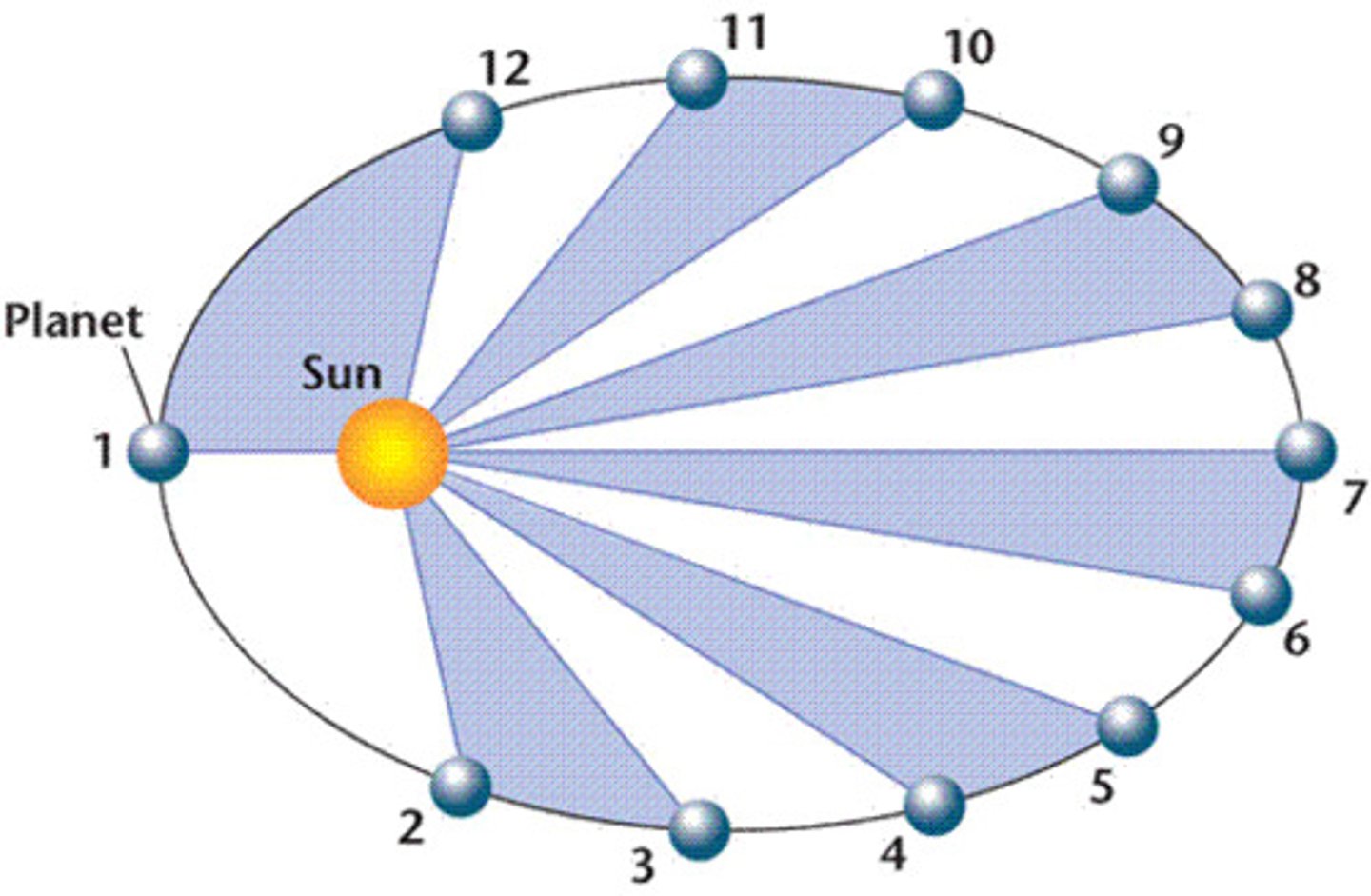
What is Kepler's second law?
A line joining a planet and the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time
What is Kepler's third law?
the square of the orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of its average distance from the sun
- T² ∝ r³
what is the equation from Kepler's third law?
is the constant universal?
- no, this constant is only works for the Sun
- in another solar system, T² ∝ r³ will be true but with another constant
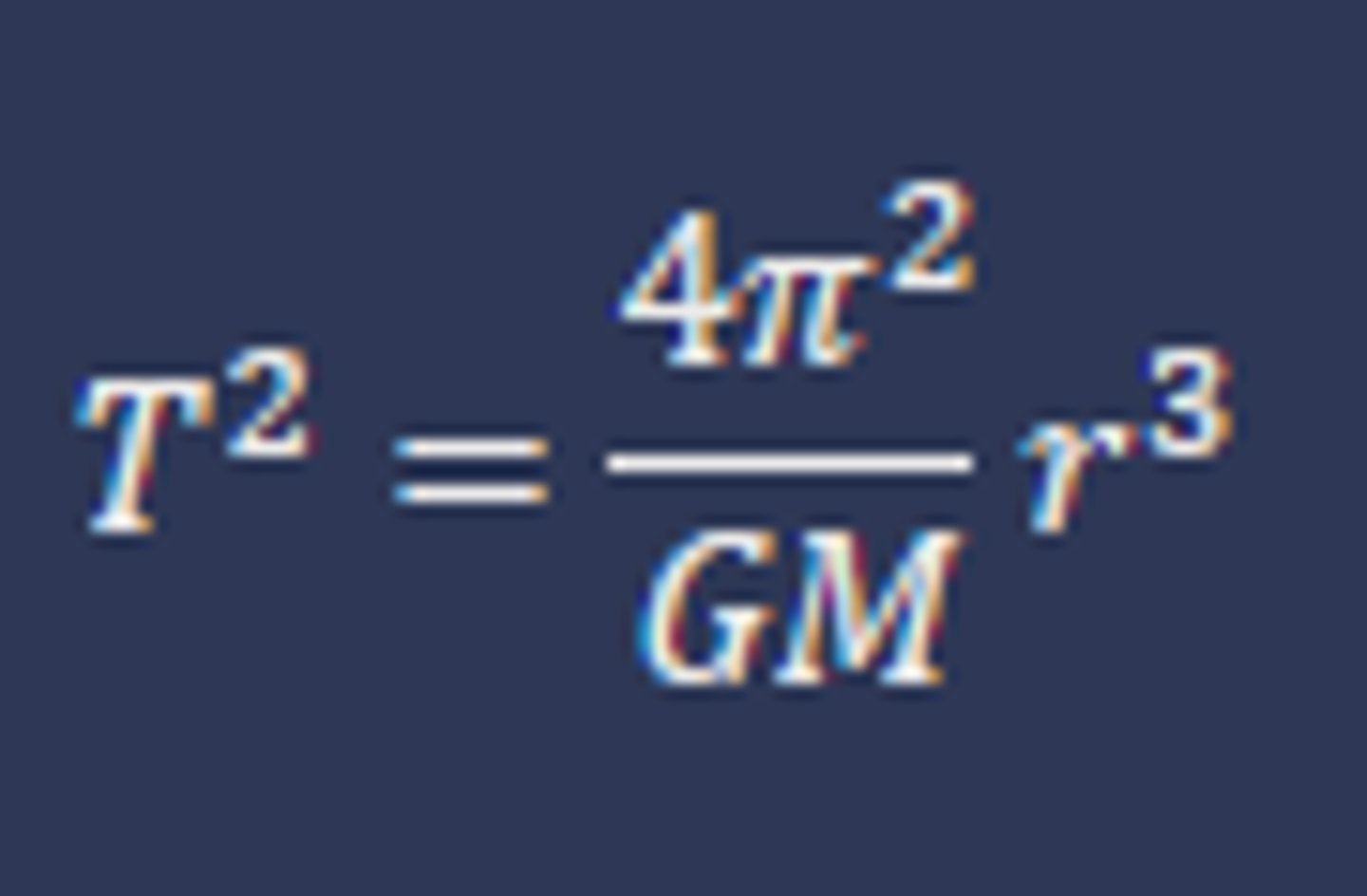
Derivation of Kepler's Third Law
what is the first step?
what is the assumption being made?
centripetal force is equal to gravitational force on the planet in orbit
- the orbit of the planet is being modelled as circular due to the low eccentricity orbit

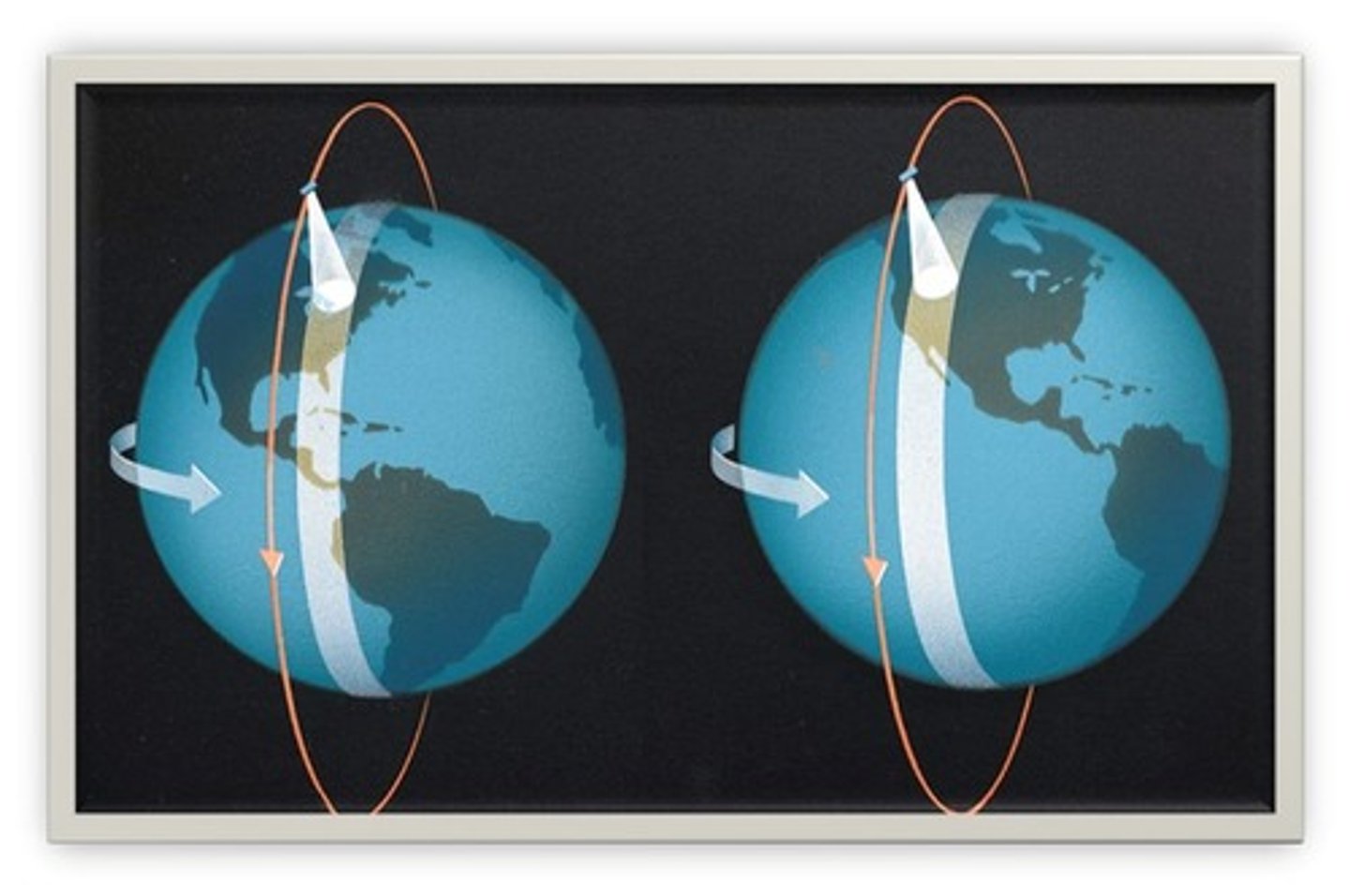
What is a polar orbitting satellite?
why is it usefu?
polar orbits orbit the poles
- as the earth rotates, they offer a complete view of the Earth over a given period
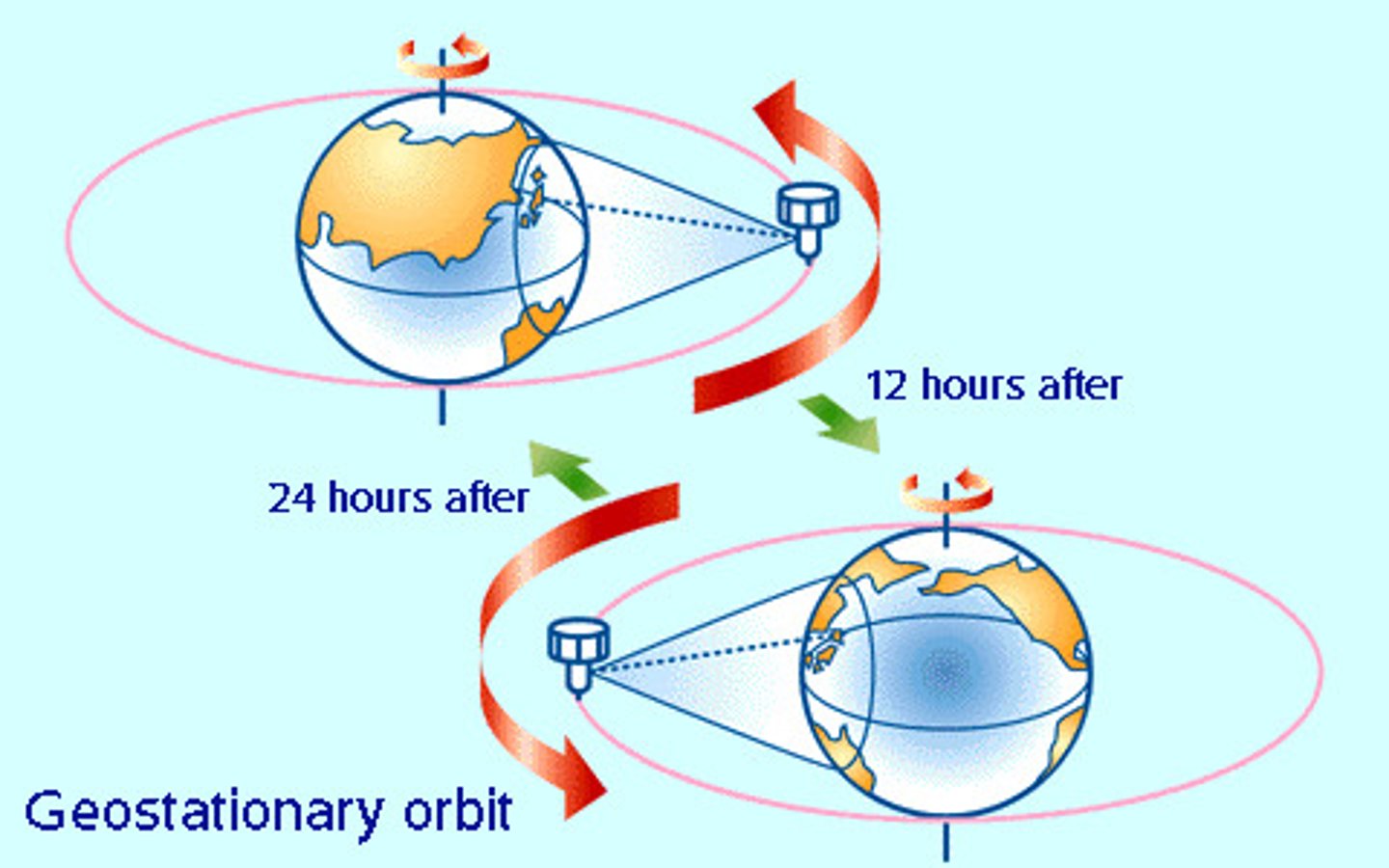
what is a geostationary satellite?
what is its time period of orbit in hours?
what line must the orbit follow and what direction?
A satellite that is placed in a geostationary orbit is one that remains above the same point of the Earth whilst it rotates
- 24hrs
- must orbit above the earths equator
- must rotate in the same direction as the earth, west to east
what is a geostationary satellite used for?
- telecommunications
- weather monitoring
for a satellite in a stable orbit, how do we find the speed it is travelling?
so what does the velocity of a satellite depend on?
gravitational force = centripetal force
rearrange for v
v = √(GM/r)
the mass of the planet it is orbiting and the height it is orbiting at
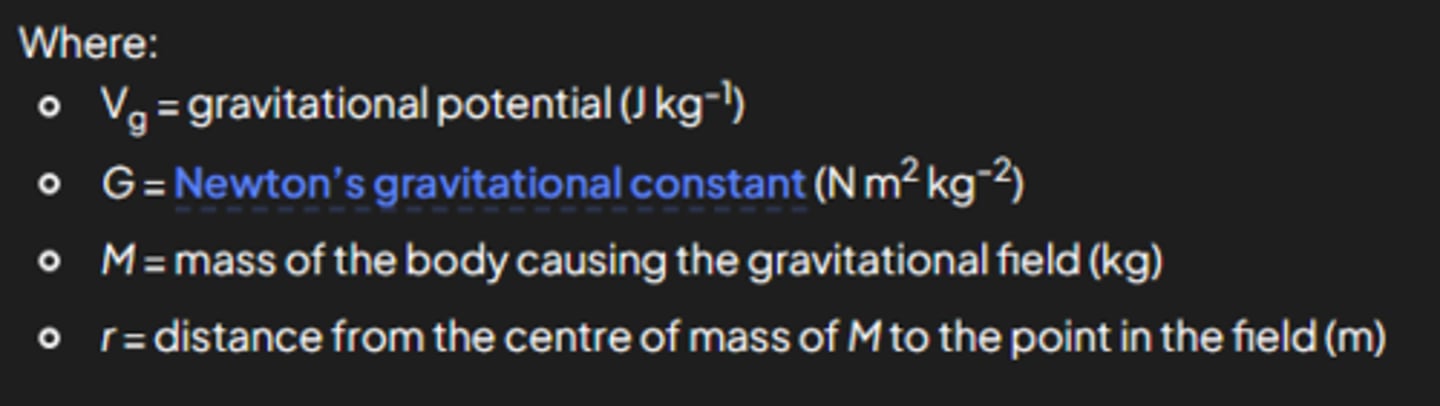
Define gravitational potential (Vg) at a point in a gravitational field
the work done per unit mass in bringing a small test mass from infinity to the point
what is the gravitational potential at infinity?
Vg max = 0
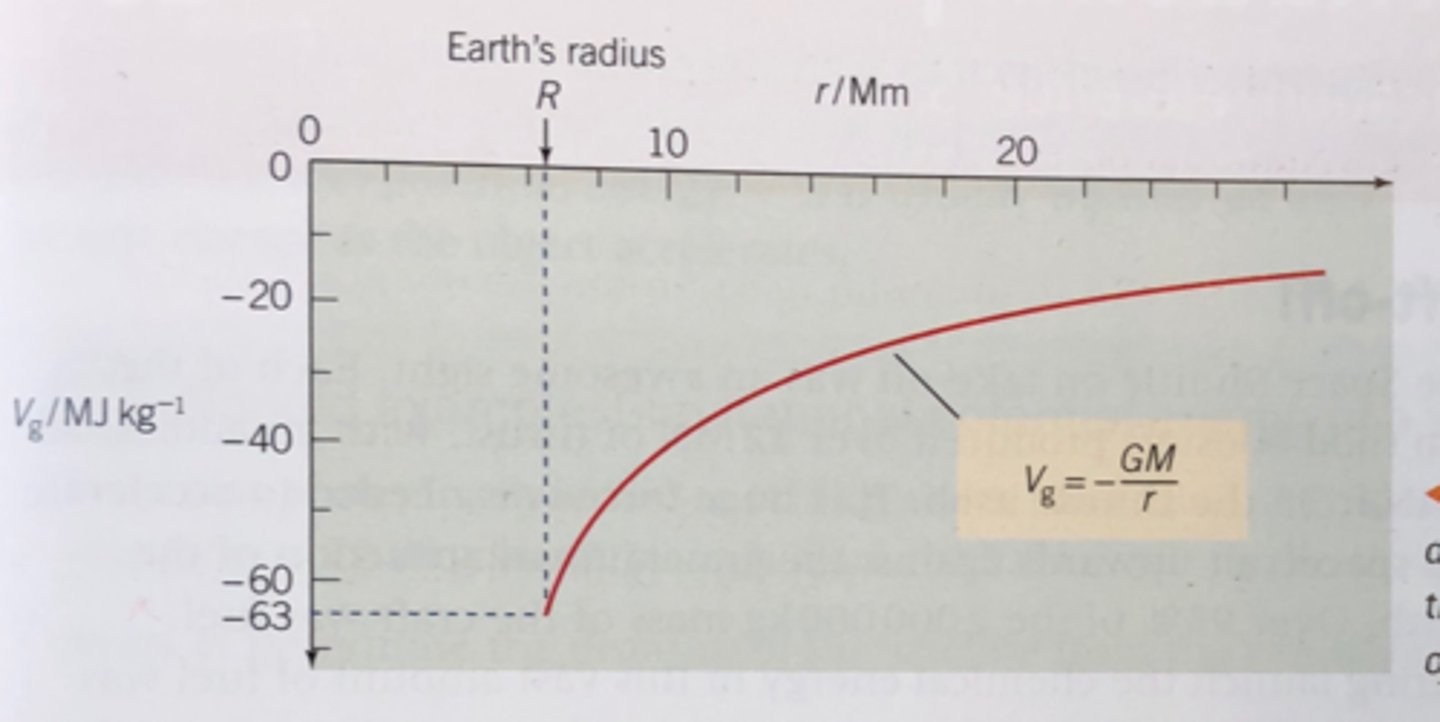
what is the formula for gravitational potential, Vg?
what are the proportionalities
-GM/r
Vg ∝ M
Vg ∝ 1/r
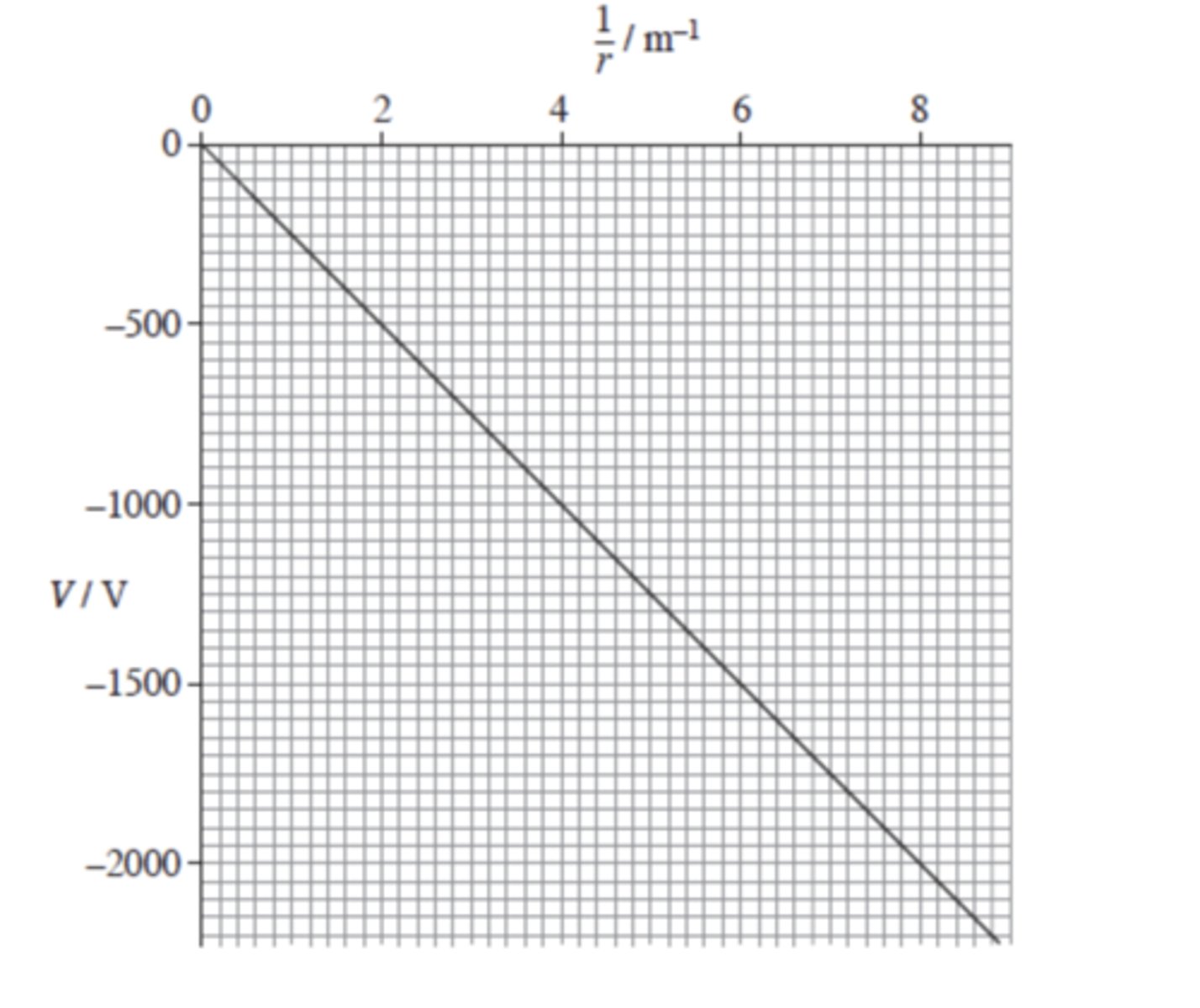
Graph of Vg against r
graph of Vg against 1/r
gradient?
m = -GM
Define gravitational potential energy
how to get from Vg to GPE ?
The work done to move a mass from infinity to a point in a gravitational field
E=MVg
formula for gravitational potential energy in a radial field
E = -GMm/r

in order to get the escape velocity, what should the minimum energy supplied to it be equal to?
to escape the gravitational field of a mass, an object must be supplied with energy equal to the gain in GPE needed to lift it out of the field
1/2m² = GMm/r
does escape velocity vary depending on the mass trying to escape
no, only on the mass creating the gravitational field and the distance of the object from the centre of the mass