Disorders of the Skeletal System: Trauma, Infections, & Neoplasms
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What are the most common causes of Musculoskeletal Injury in each age group?
Childhood:
Falling, bicycles & sports
Adults under 45:
Trauma (motor vehicle accidents)
Adults over 65:
Falling
Acute Sports Injuries
Sudden trauma
Injuries to soft tissue and/or bone
Overuse Sports Injuries
Chronic & repetitive
High levels of stress without sufficient recovery time
Contact Sports Injuries
Brain, Neck, Spine injuries
Growth Plates if a child is before puberty
Extrinsic Risk Factors: training methods, equiptment
How do you diagnose a skeletal (bone) injury?
X-Ray
How do you diagnose a soft tissue injury?
MRI or CAT Scan
Contusions
Soft Tissue Injury
Muscle bruises
Etiol: skin over injury is fine, ruptured blood vessels & damaged muscle cells
S/S: Eccymotic (black & blue), swelling, inflammation
Tx: MICE
Hematomas
Soft Tissue Injury
WORSE than contusions (wider area & deeper injury)
S/S: pain and swelling take longer to subside
Tx: MICE
What is a Joint?
Where two bones meet
Strains
Tendons (muscle-tendon units)
stretching or partial tear
Etiol: inflammatory response
S/S: decreased muscle function, pain, swelling, stiffness
Tx: M.I.C.E
Sprains
Ligaments (bone to bone)
WORSE than Strain (less blood flow than tendon)
Ankle is most common, Knee 2nd
Etiol: abnormal or excessive movement of joint
S/S: rapid swelling, discoloration, limitation of function
Tx: MICE
Congenital Dislocation
Dislocation at hip or knee
Traumatic Dislocation
Caused by falls, blows, or rotational injuries
Pathologic Dislocation
Caused by Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Neuromuscular Disease (ND), or Paralysis
Dislocation
Bones have separated at a joint
Dx: X-ray (bone)
S/S: Deformity, pain, limited movement
Tx: Manipulation (return bone to correct position), Closed surgery (doesn’t break skin), Open surgery (breaks skin)
Shoulder & Rotator Cuff Injury
(“Pitcher’s Arm”)
Overuse Injury
Etiol: overuse or direct trauma
Dx: MRI
S/S: pain, tenderness, difficulty abducting or rotating arm
Tx: Anti-Inflammatories, Corticosteroid Injections, PT, Surgical repair
Ligamentous Injuries (Knee)
WORST - MOST SERIOUS
Pop or tearing sensation + sudden pain
S/S: inability to bear weight, pain, swelling
Tx: MICE + immobilization, ROM, surgical repair
Meniscus Injury (Knee)
Rotational injury from sudden or sharp pivot
S/S: swelling, pain, knee instability/locking
Tx: Immobilization, quad exercises, Surgery (if torn)
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
(“Runners Knee”)
Most common cause of anterior knee pain
Etiol: Imbalances in forces controlling patella
S/S: Pain
Tx: Rest, PT
Hip Dislocation
LIFE THREATENING
Etiol: severe trauma
S/S: severe pain, inability to move lower extremeties
Tx: Reduction surgery to repair dislocation (closed first, then open)
Hip Fracture
Mostly caused by falls (proximal femur is usually involved)
Risk Factors: age, muscular atrophy (physical inactivity), Osteoporosis
Dx: X-ray
S/S: severe pain, inability to move, swelling & bruising
Tx: Surgery, Biphosphonates (increases osteoblasts - heals bone)
Greenstick Fracture
Bone only breaks on one side
COMMON IN KIDS (10 & under)
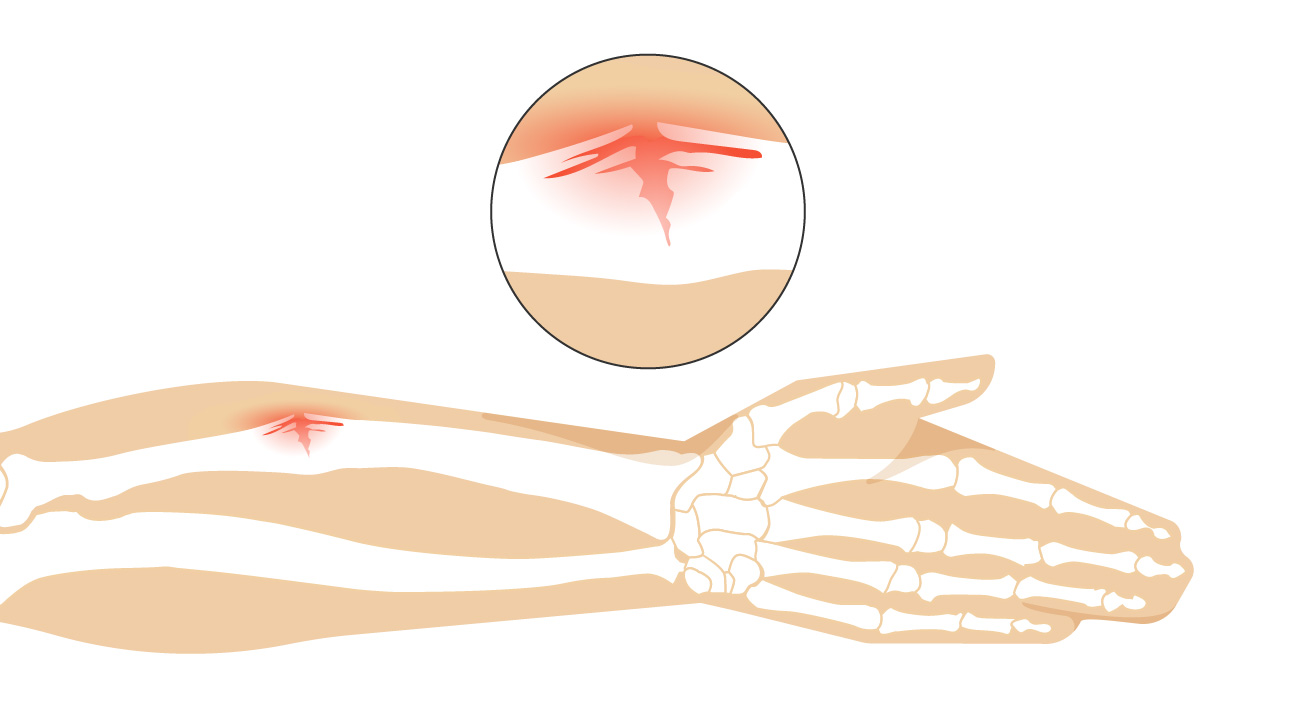
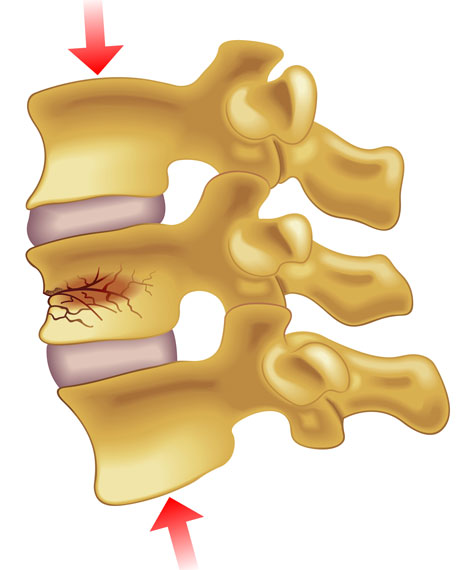
Compression Fracture
Vertebrae of spine collapses
COMMON IN OLD WOMEN
Cause: Osteoporosis
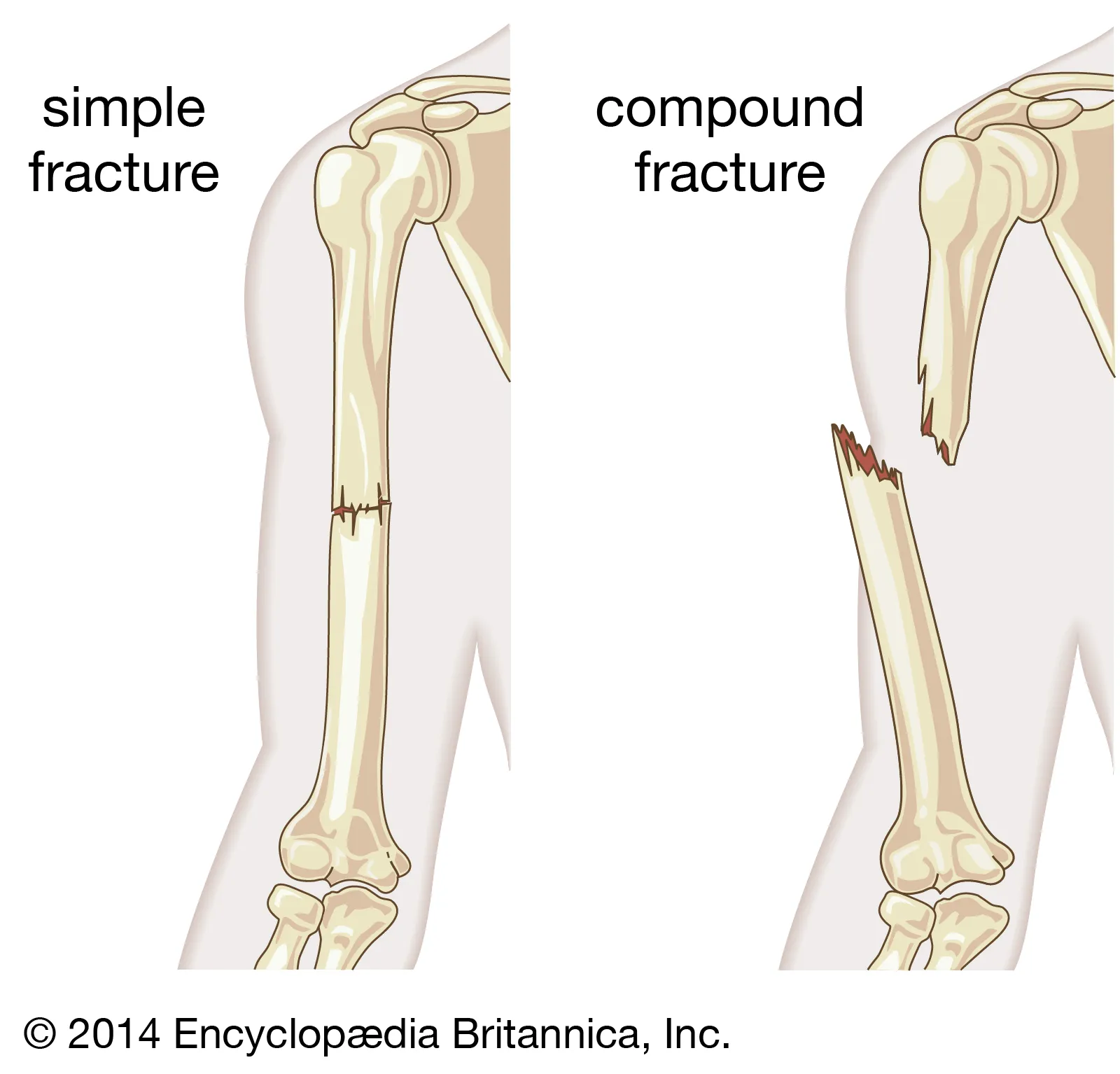
Fractures
Broken Bone
S/S: pain & tenderness, swelling, loss of function/mobility
Dx: X-ray
Tx: Splint, Reduction with Fixation Device (closed or open), Immobilization, rehab
Local Shock
Temporary window that fracture can be Reduced with little to no pain
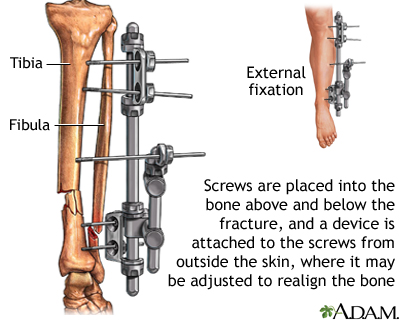
30 minutes from time of fracture
Fixation Device
Used to realign a fracture (broken bone)
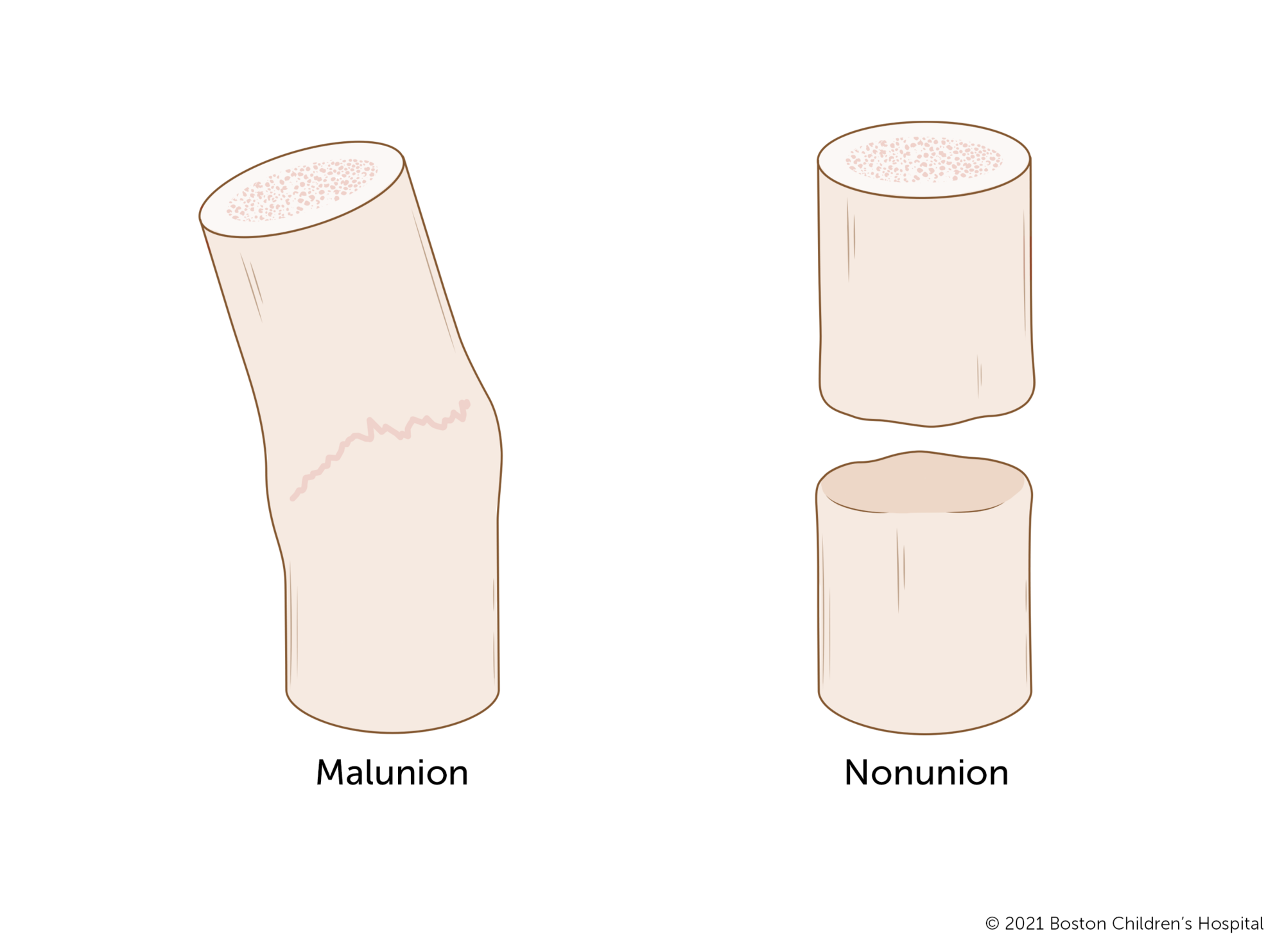
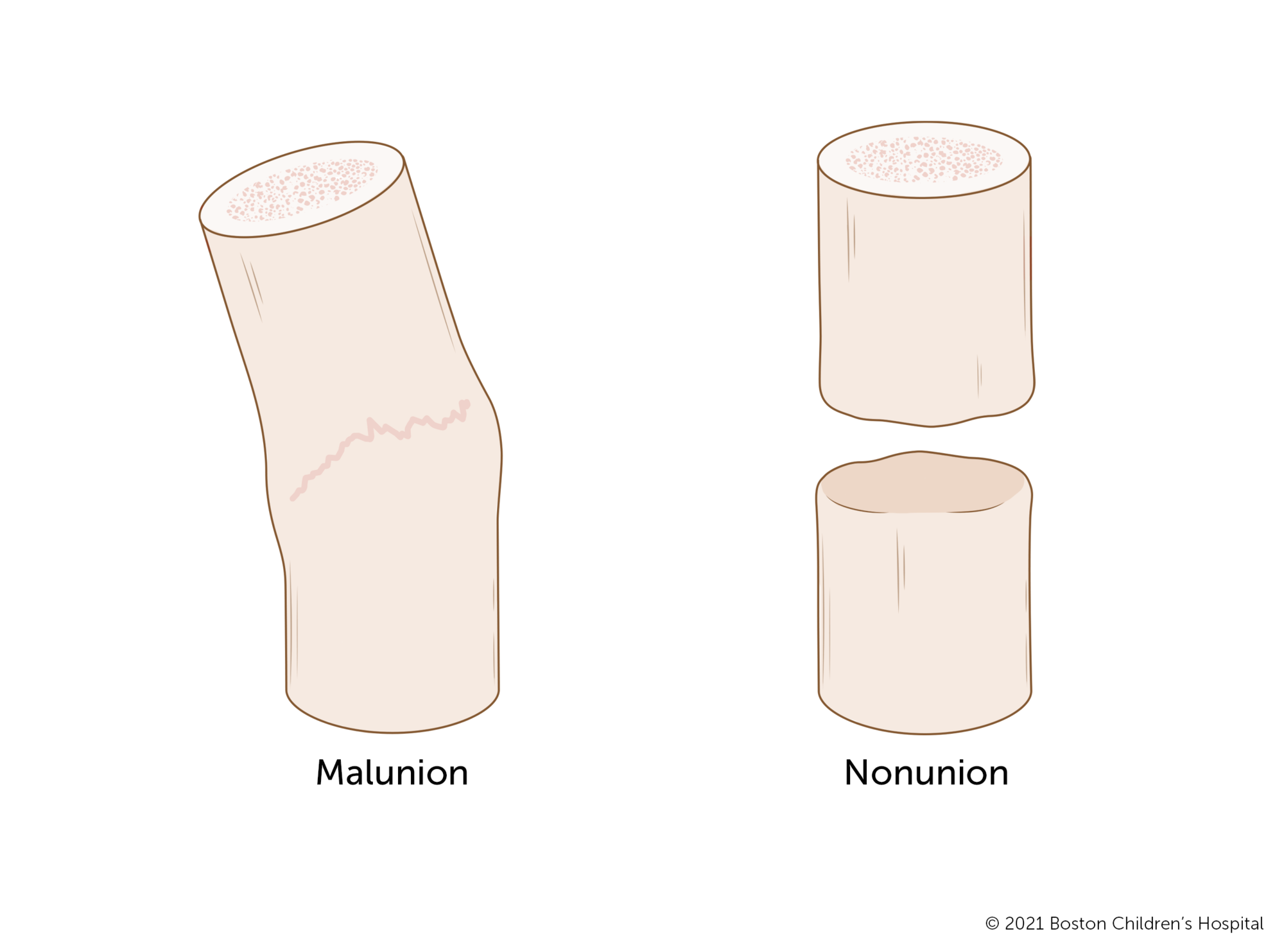
Malunion
Bone Healing with deformity (improper alignment)
Tx: Bone Grafts, Electrical Stimulation (stimulates osteoblasts)
Delayed Union
Failure of bone to heal within the normal time period
Tx: Bone Grafts, Electrical Stimulators (stimulates osteoblasts)
Nonunion
Bone stopped healing & never fully repaired
Tx: Bone Grafts, Electrical Stimulation (stimulates osteoblasts)
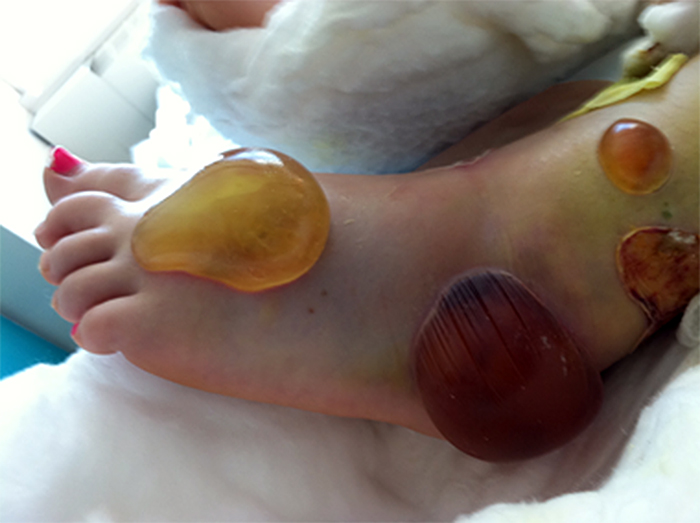
Fracture Blisters
Skin overlying fractured bone
places with less scar tissue (tattoos hurt the most)
Tx: soft dressings, surgery
DO NOT POP
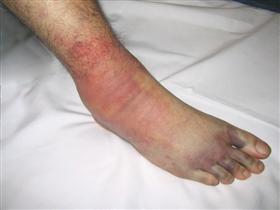
Compartment Syndrome
Cast is placed before inflammation has stopped
Compresses blood vessels (low BF)
May lead to Necrosis
S/S: severe pain beyond initial injury
Tx: Remove cast, Fasciotomy to cut surrounding tissue (last resort)
Fat Embolism Syndrome
Fat from bone marrow enters bloodstream & blocks blood vessels
Follows long bone trauma
S/S: rash, dyspnea (shortness of breath), altered mental state
Tx: treat symptoms util fat is reabsorbed
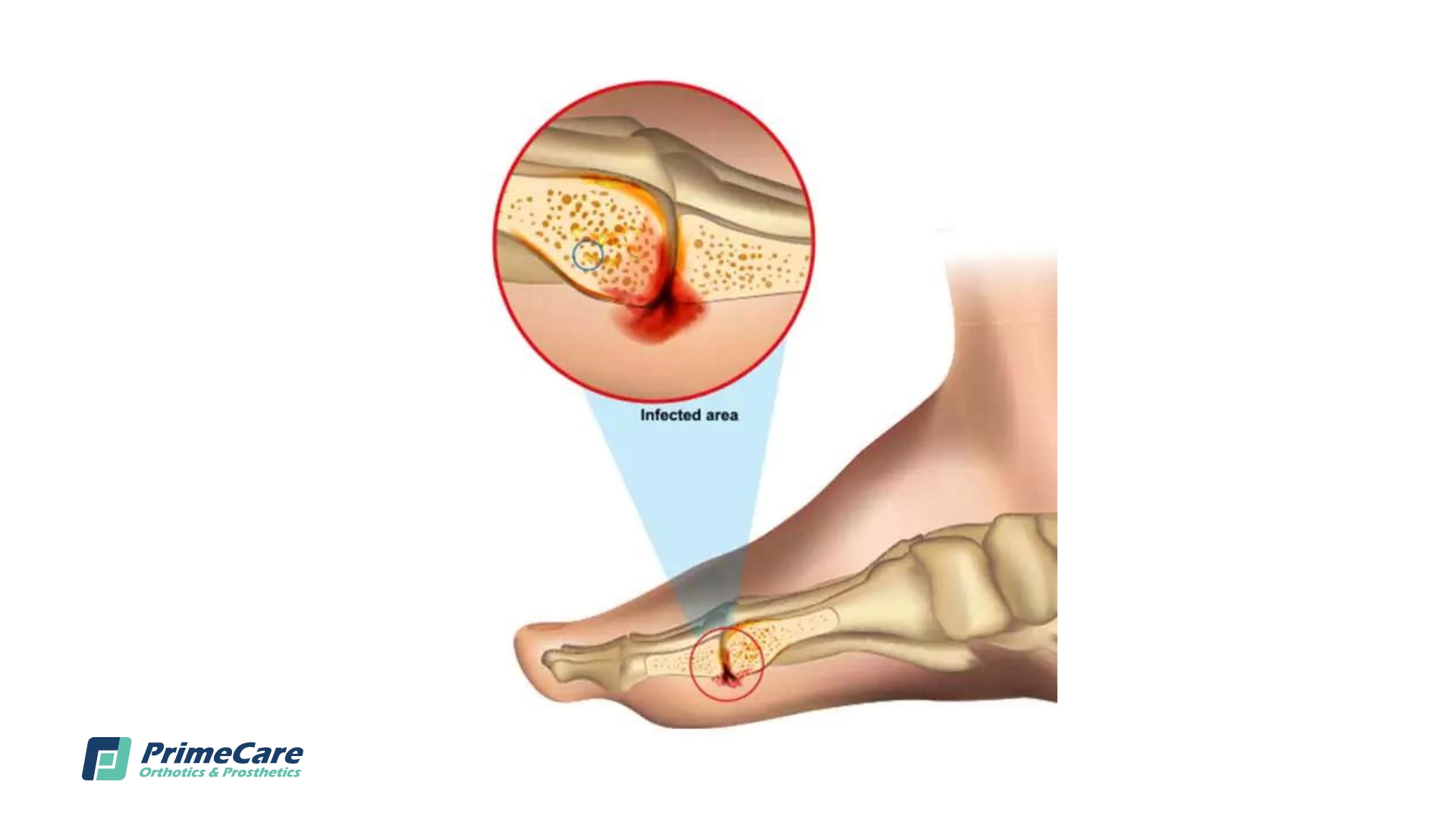
Osteomyelitis
Abscess on bone
Etiol: Bacterial (staph) or Fungal (open wounds, bone fractures)
Dx: MRI shows abscess
S/S: Edema (swelling from fluid), Erythema (redness), warmth
Tx: Antibiotics (bacterial, Antifungals (Fungal), Surgical drainage or Debridement (remove dead tissue), Bone Graft, Amputation
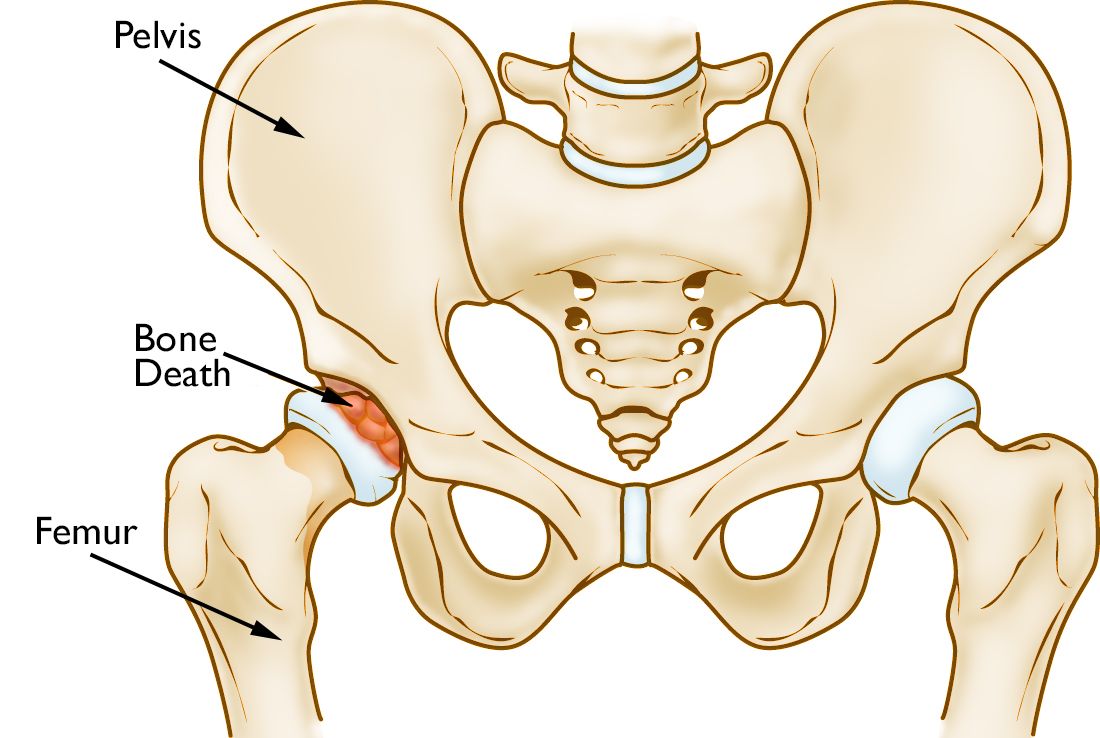
Osteonecrosis
Dead bone tissue from lack of blood supply
Etiol: Ischemia (low BF) or Infarction (no BF) to bone, Fat Embolism
S/S: Asymptomatic (early), Pain (late)
Tx: Joint Replacement (must replace)
Bone Tumors
Benign & Malignant neoplasms can develop from:
Chrondogenic (cartilage)
Osteogenic (bone)
Fibrogenic (supporting elements)
3 S/S: Pain, Mass, Impaired function
Benign Bone Tumor
Slow-growing
Doesn’t disrupt surrounding tissue
Tx: Surgery or radiation
Malignant Bone Tumor
Osteosarcoma (most common)
Starts in bone & moves elsewhere
S/S: pain, localized swelling, fractures (tumor will grow)
Tx: Cancer treatment (chemo, radiation, etc.)