Physics
electricity
prescence and flow of electric charges
electric current
flow of charged particles or current
1/83
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
electricity
prescence and flow of electric charges
electric current
flow of charged particles or current
current in metal
due to movement of electrons
ammeter
used to measure currents
rate of flow of charge
ammeter measures what
electric potential
electric current is only present if there is ____ between two points
electric current in a wire
the net amt of charge that passes through the wire’s full cross section at any point per unit time
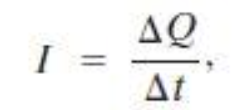
Q = charge; t = time interval
current formula
direct current
if the charges move around the circuit in the same direction at all times
ex: batteries
Alternating current
if the charges move first one way and then the opposite way
changes its direction each half-cycle
ex: household current
electric circuit
conducting path that allows a charge to flow from one terminal to another
purpose of battery
produce potential difference, which can make charges move
Resistance
measure of the opposition it offers to the flow of electric current
SI unit is Ohm
resistor
wire or electrical device that offers resistance to electrical flow
resistance
what causes electrical energy to be converted into heat
Resistance
depends on the conductor’s
length
cross-sectional area
type of material
temp
resistivity
property of the conductor to which it offers resistance to the flow of current through it
resistance
the better the conductor the less its?
Ohm-meter
SI unit for resistivity
resistor
electrical component that limits or regulates the flow of an electrical current in an electronic unit
brown
1% tolerance
red
2% tolerance
Gold
5 % tolerance
Silver
10 % tolerance
no color
20% tolerance
black
number 0; multiplier 1
brown
1
red
2
orange
3
yellow
4
green
5
blue
6
violet
7
gray
8
white
9
gold
-1
silver
-2
Ohm’s law
the higher the electric potential difference or voltage, the more charges can move
George Ohm
discovered Ohm’s law
voltage
aka electromotive force
voltage
quantitative expression of the potential difference in charge between two points in an electrical field
resistance
hindrance to the flow of charge
Current
Unit of measurement: Ampere
Volatage
Unit of measurement: Volt
Resistance
Unit of measurement: Ohm
electric power
rate at which electric energy is converted into another form such as mechanical energy, heat, or light
Electric Power
equal to the product of the current and voltage
power
energy per unit time (watt)
energy
power x time (ex: kWh)
electric circuits
any path along which current and electrons can flow
electromotive force (EMF)
maximum potential difference across the terminals is provided and maintained
direct current circuit
mostly used in low voltage applications.
resistor is main component
series circuits
Two or more loads are linked across a single loop of wire
The current is the same at all points
Total resistance to current in this circuit is the sum of the individual resistances along the path.
parallel circuits
different loads are situated on different wire loops.
• Junctions
parallel circuits
Components connected all have the same voltage.
Each path operates independently of the other paths.
Total current in this circuit equals the sum of the currents
As the number of branches is increased, resistance of the circuit is decreased
parallel circuits
these types of circuits are prone to overloading
Mild tingling sensation
0.001 A
Muscle spasms (“can’t let go”)
0.01-0.02 A
Fatal (heart fibrillation)
0.2A
120 volts
household current voltage that can stop one’s heart
extension cords
may not be used as permanent wiring and should be removed after temporary use for an activity or event.
surge suppressors with built in circuit breakers
may be used long-term and are available with three, six and 15 foot-long cords.
work
done when there is motion (scalar quantity)
Joule
work is measured in
work against inertia
applying force to cause change in motion
ex: throwing/ kicking a ball
W = Fd = mgh
work against gravity
involves height
W = mgh
Gravitational Potential Energy
stored as the result of the gravitational attraction of the earth for the object
mgh
directly proportional to both mass and height
kinetic energy
energy of an object in motion
once object at rest starts moving
Work-Energy Theorem
states that the net change in KE of a particle is equivalent to the sum of work done by all types of external forces
KE increases as a result of the amt of work. work done on an object transfers energy to the object
mechanical energy
energy that is possessed by an object due to its motion or due to its position
mechanical energy
sum of KE and PE of an object
potential energy
as an object is falling what decreases?
kinetic energy
as an object is falling what increases?
conservation of energy
PE lost during motion is converted to KE
constant
mechanical energy stays?
law of conservation of energy
energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but can only be converted from one form to another
4186 joules
1 Kcal =?
food
type of chemically stored energy
in kilocalories
power
rate at which work is done and energy is expended
1KW
1000 Watts
1MW
1 × 10^6 Watts
1 HP
746 watts
1 HP
0.746 KW
1 HP
550 ft-lb of w/s