L5 vaccination
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Variolation
inject patients with active small pox
disease that have been globally eliminated
disease poised for global elimination
small pox (1980)
rinderpest (2011)
poised (one reservoir, one source — human)
polio
measles
guinea worm
Natural adaptive immunity
acquired as part of normal life experience, NO MEDICAL INTERVENTION
type:
natural passive immunity
natural active immunity
artificial adaptive immunity
acquired through a medical procedure (i.e. vaccine)
type:
artificial passive immunity
artificial active immunity
natural passive immunity
transfer of preformed antibodies from mother to fetus (placental → IgG) or newborn child (milk)
natural active immunity
development of immunity by naturally contracting the disease
artificial passive immunity
definition
advantage
disadvantage
transfer of preformed antibodies from a vaccinated individual (or animal) to a recipient
used in immunocompromised individuals or cases in which immediate effects are required (snake bites, tetanus)
advantage
simple process, act immediately
disadvantage
short term (2-3 months)
does not create memory
consists only a transferred element (Ab) with SINGLE moa
no evolution of immunity to greater strength and specificity
artificial active immunity
definition
advantage
disadvantage
inject recipient with antigen (s) that stimulate production of antibodies or reactive cells → create memories, takes time, and is lasting
advantage
long term effects, elicit memory
stimulate multi-component response (ab and cell mediated immunity
evolution of response toward greater strength and specificity
disadvantage
more complex process
takes time to develop immunity (cuz we are stimulating 1˚ response)
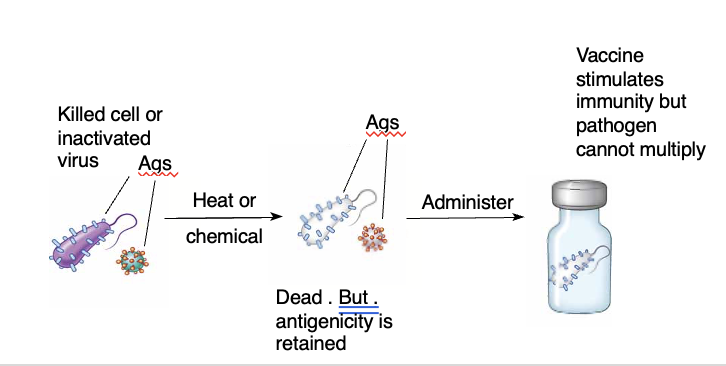
Killed or inactivated vaccines
cultivate desired strain, treat it with formalin or other agent that kills the strain but does not destroy its antigenicity
often require a larger dose and more booster to be effective
ex. SALT polio
Live attenuated cells or viruses
use process that substantially lessen or negates the virulence of viruses or bacteria, but alive
usually pass virus to cell they not use to
ex. Sabin vaccine - polio thru monkey - once adapted to monkey → don’t do well in human
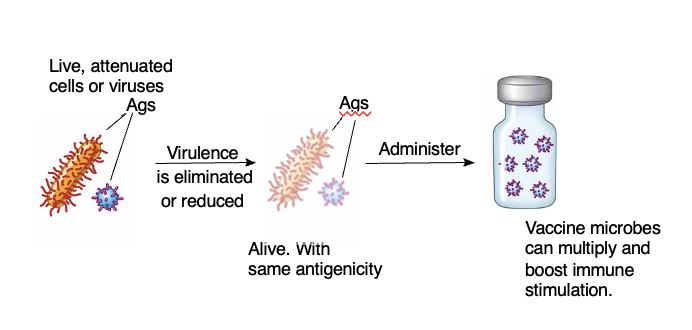
advantage and disadvantage of live preparation of live attenuated vaccine
Think sabin polio vaccine
Advantages of live preparations are:
–Can multiply and produce limited infection (but not disease) like the natural pathogen
–They often confer greater and longer-lasting protection
–Usually require fewer doses and boosters
Disadvantages of live preparations include:
–Sometimes require special storage
–Can potentially be transmitted to other people
–Can conceivably mutate back to virulent strain
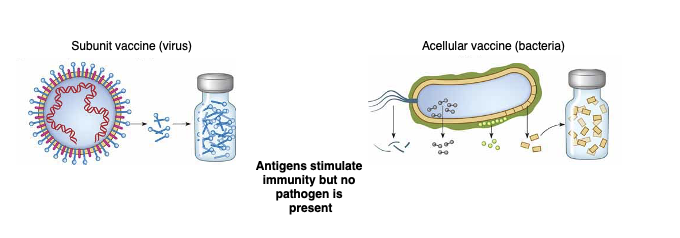
Acellular or subcellular vaccine (subunit - if a virus)
antigens stimulate imunity but no pathogen is present
exact antigenic determinants can be used when known:
capsules - pneumococcus, meningococcus
surface protein - anthrax, hep B
exotoxin - diphtheria, tetanus
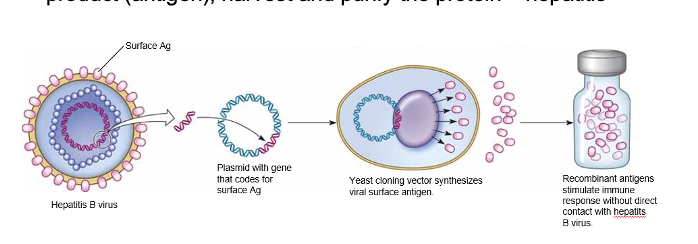
Genetically engineered vaccines
insert genes for pathogen’s antigen into plasmid vector → clone them in an appropriate host → stimulate the clone host to synthesize and secrrete a protein product (antigen) → harvest and purify the protein.
ex. hep B
Genetic engineered vaccine: “trojan horse” vaccine
genetic material from a pathogen is inserted into a live carrier nonpathogen → recombinant expresses the foreign gene
currently in experimental stage
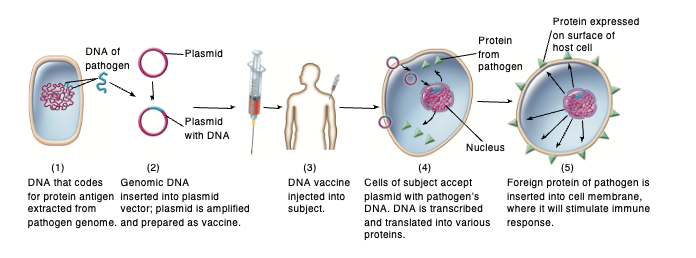
Genetically engineered vaccine: DNA vaccines
naked DNA or microbial DNA inserted into plasmid vector
human cells will pick up the DNA plasmid and express the microbial DNA as protein → cause B and T cells to respond, be sensitized, form memory cell
currently in experimental stage
Genetically Engineered vaccines: RNA vaccines
same idea as DNA, but use RNA to induce production of desired antigen in host cells
COVID
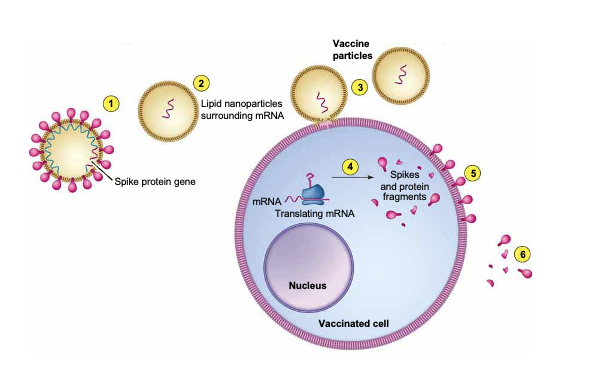
Advantages and disadvantages of RNA vaccine
Advantages
Directly translated in cytoplasm -- no need for nuclear uptake, no alteration of host genome
Modified nucleoside forms available that avoid degradation
Can be engineered for optimal translation in various organisms/tissues
Standardized and scalable methods for synthesis, manufacturing and delivery
Disadvantages
Can elicit cellular antiviral response (interferon) that will destroy the vaccine RNA
Can lead to inflammatory reactions and, potentially, immune hypersensitivities
Thimerosal (mercury) in vaccines
mercury-based preservative once added to some vaccines and injectables.
safe and effective, with no link to autism or other diseases
It was removed from most vaccines over 25 years ago out of caution,
kept in some influenza vaccines to allow safe use of multidose vials and lower cost during mass immunizations.
never used in MMR vaccines, and the CDC’s Advisory Committee has recently voted to remove it from all influenza vaccines as well.
Aluminum in vaccine
False claim: ingredient in vaccines responsible for inducing allergies, depression and autism
adjuvant to enhance the immune response → allowing lower doses and fewer boosters, especially in killed or subunit vaccines.
It is not used in live vaccines like MMR.
very well studied, with an excellent safety record backed by billions of doses.
Infants up to 6 months in the U.S. receive about 4 mg of aluminum from vaccines.
In comparison: much lower than daily intake of aluminum.
Guillan-Barre syndrome
complication of several vaccine, especially influenza
1/100,000 vaccines
neurological condition - destruction of peripheral neuronal myelin sheath → weakness and sensory loss
due to autoimmune reaction elicited by viral proeins
most patient recover but some get chronic GBS and some die