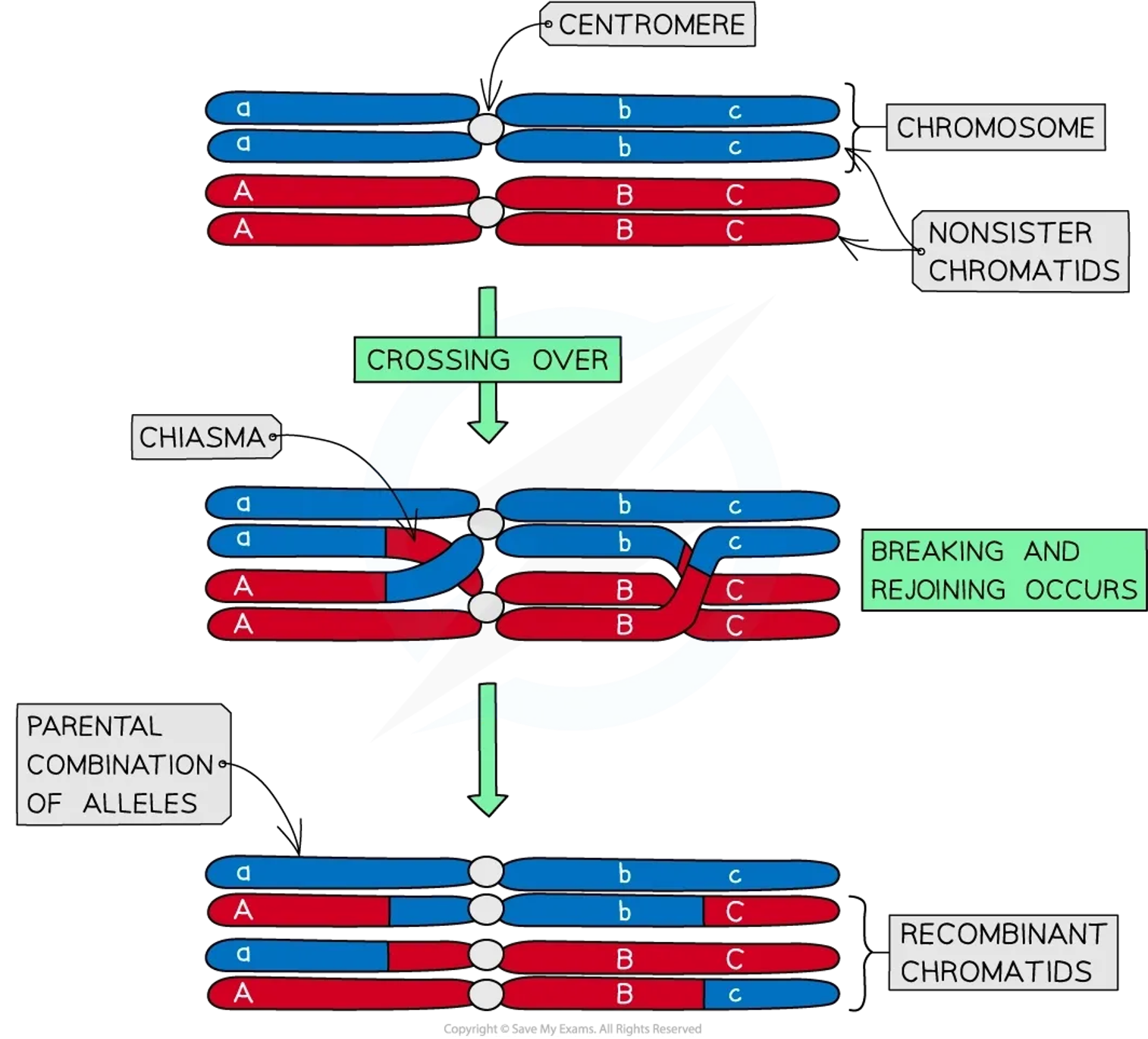
Crossing over + recombination T3 W4
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
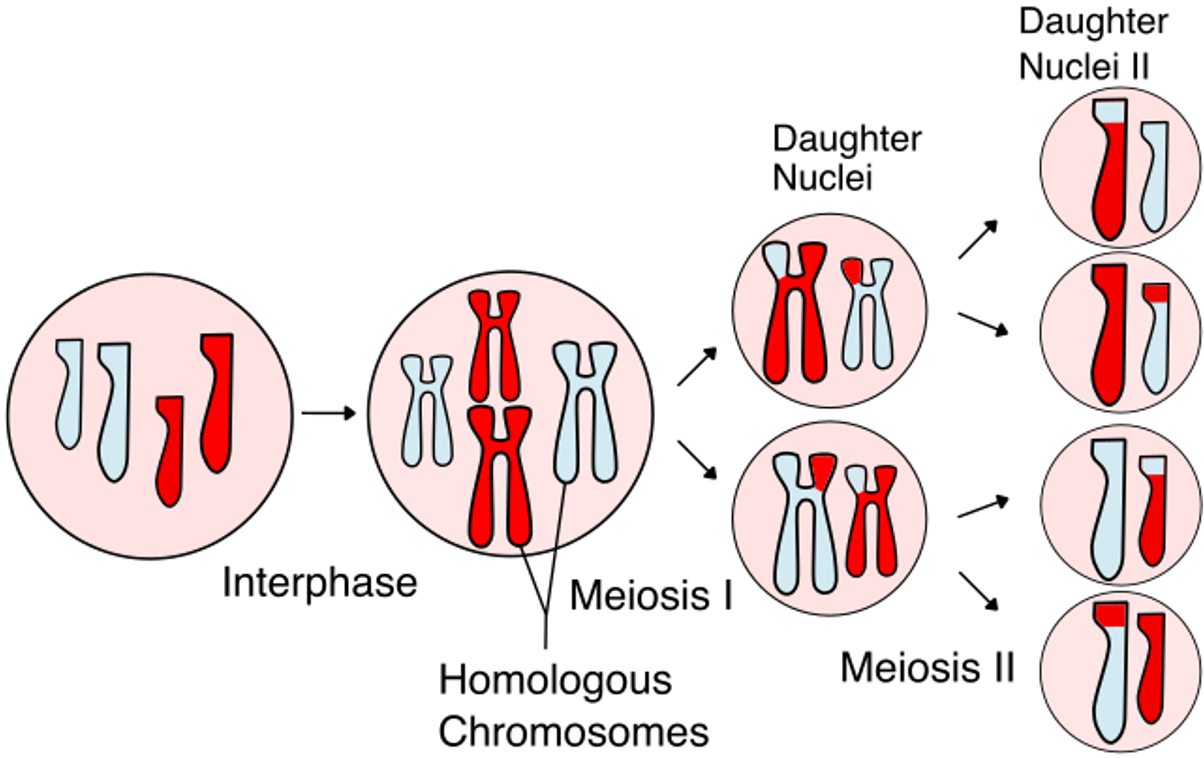
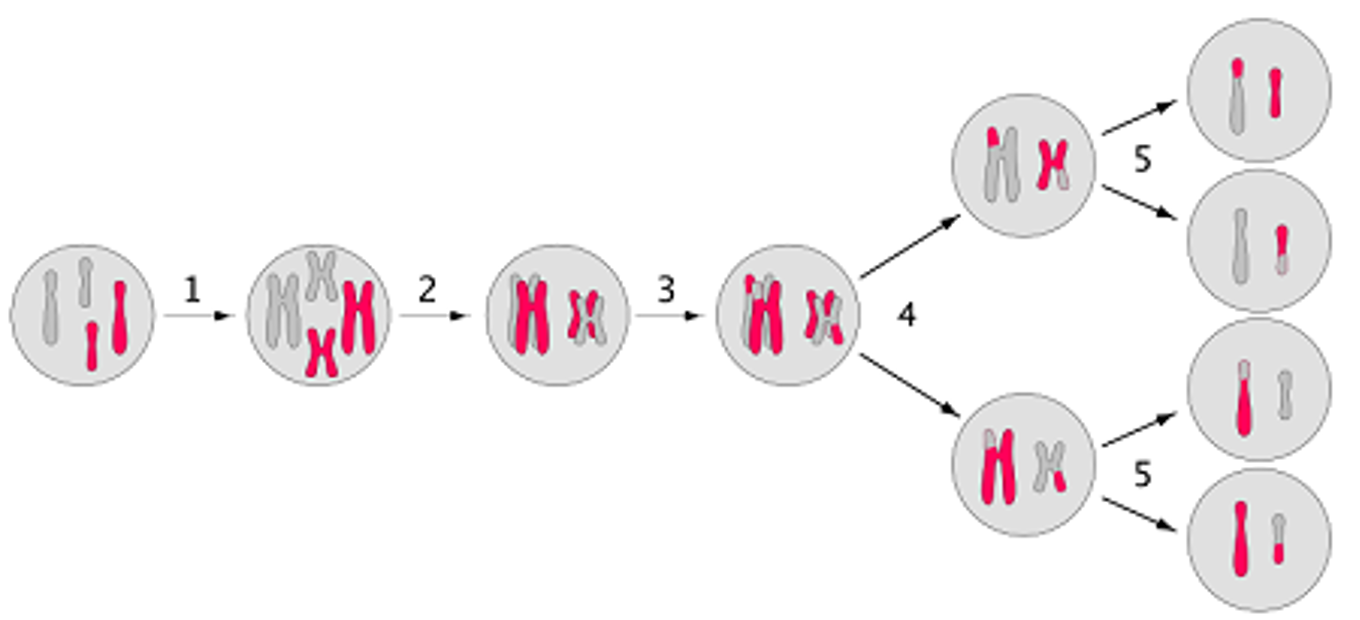
Importance of meiosis
•One characteristic of meiosis is that this process produces haploid daughter cells that vary in their genetic information.
•This is important as it means that the offspring will differ from one another and their parents.
•This generates genetic diversity, or variation, within a species.
Variation
Variations are the differences in traits, or phenotype, that occur between individuals of the same species.
How does variation occur
•A result of three reproductive processes that occur during meiosis:
⚬1.Crossing over & recombination
⚬2.Independent assortment
⚬3.Non-disjunction
Crossing over
•1.During prophase I in meiosis I, the chromatids of the homologous chromosomes tangle together. This is called crossing over.
•2.The point that the chromatids of homologous chromosomes cross over is called the chiasma.
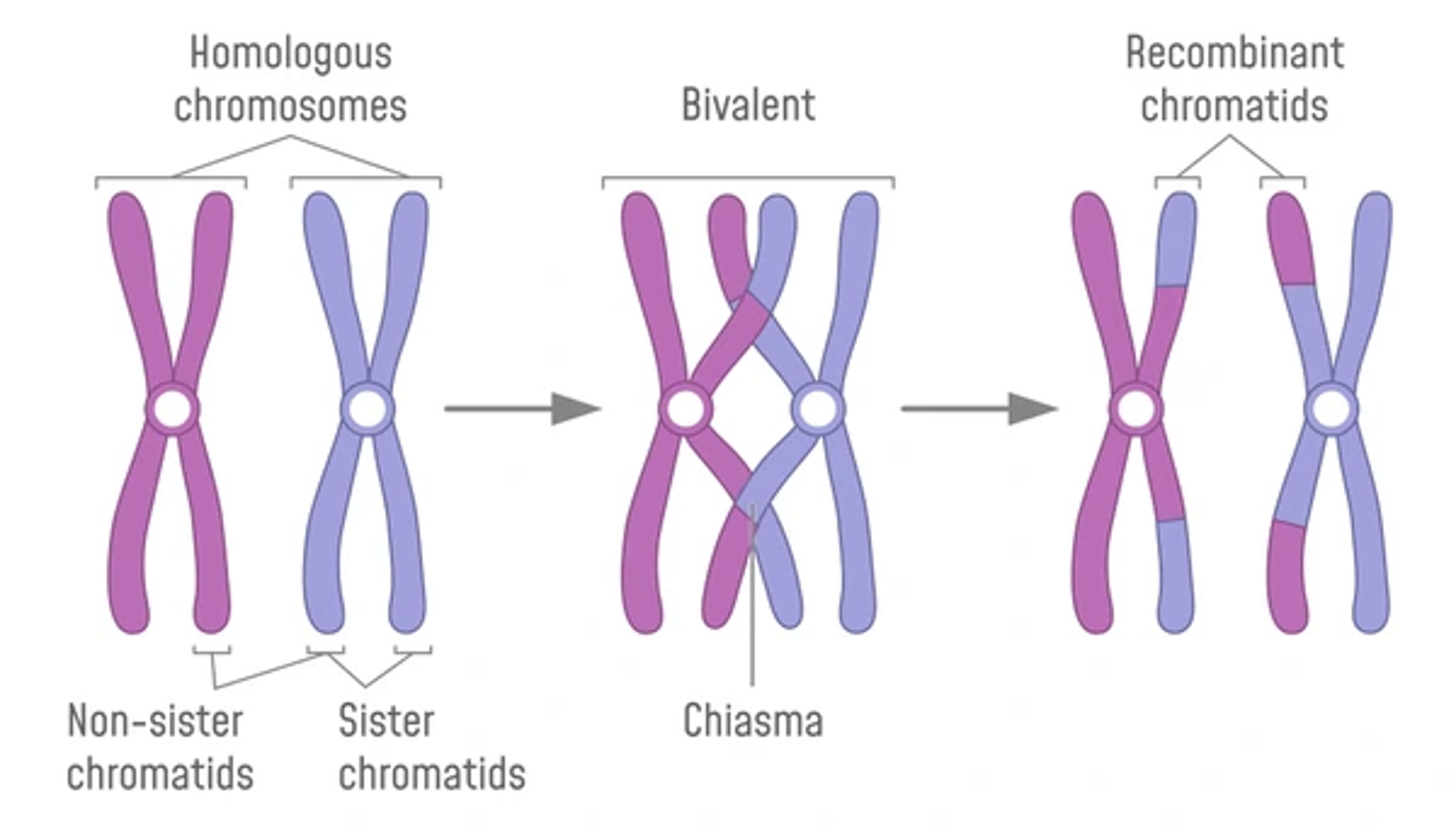
Recombination
•3.These overlapping chromatids may exchange segments of their DNA with each other. This process of exchange is called recombination.
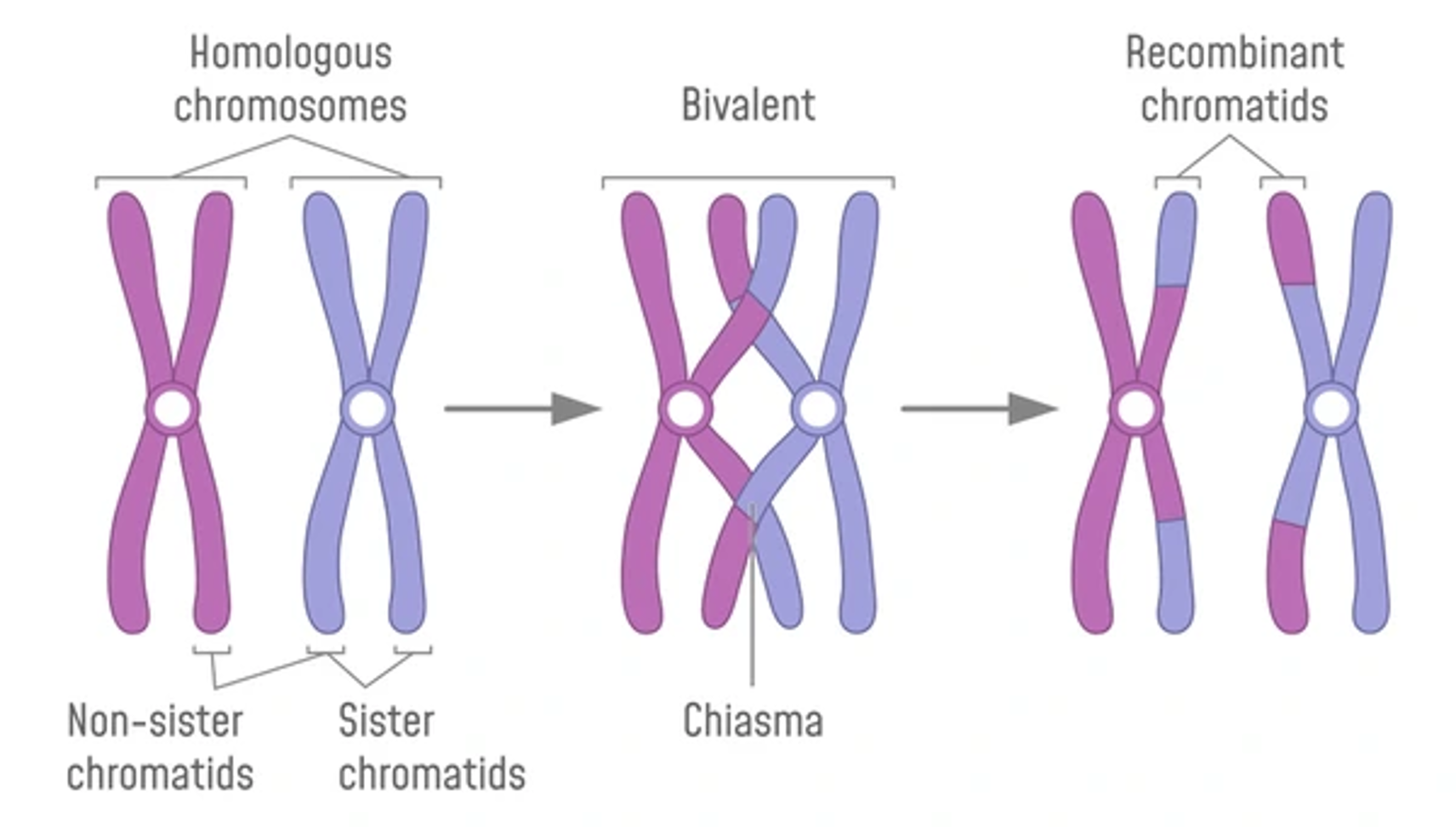
Crossing over + recombination (afterwards)
•4.The resultant chromatids now consist mainly of the DNA from the original chromatid but also partly that of the other chromatid. This results in new combinations of alleles.
•5.This means that a chromatid that has undergone crossing over has a unique DNA sequence that originates from the combined DNA of the maternal and paternal homologous chromosomes.