Evolution
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ms. Stewart
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Sources of mutation
Foreign causes:
-radiation (eg. X-rays, UV)
-chemicals (eg. carcinogens, free radicals)
-viruses (eg. HPV)
Natural causes
-errors during DNA replication
only mutations in germ cells (makers of gametes) will get passed on to offspring
How Mutations Affect Proteins
changing one base can drastically, alter the function of the protein (and therefor function)
Variation vs. Adaptation (define)
Variation
-is the natural differences in traits within a species (color, size, speed)
Adaptation
-is a variation that becomes more common because it significantly increases survival and reproductive chances
an adaptation is a variation that works
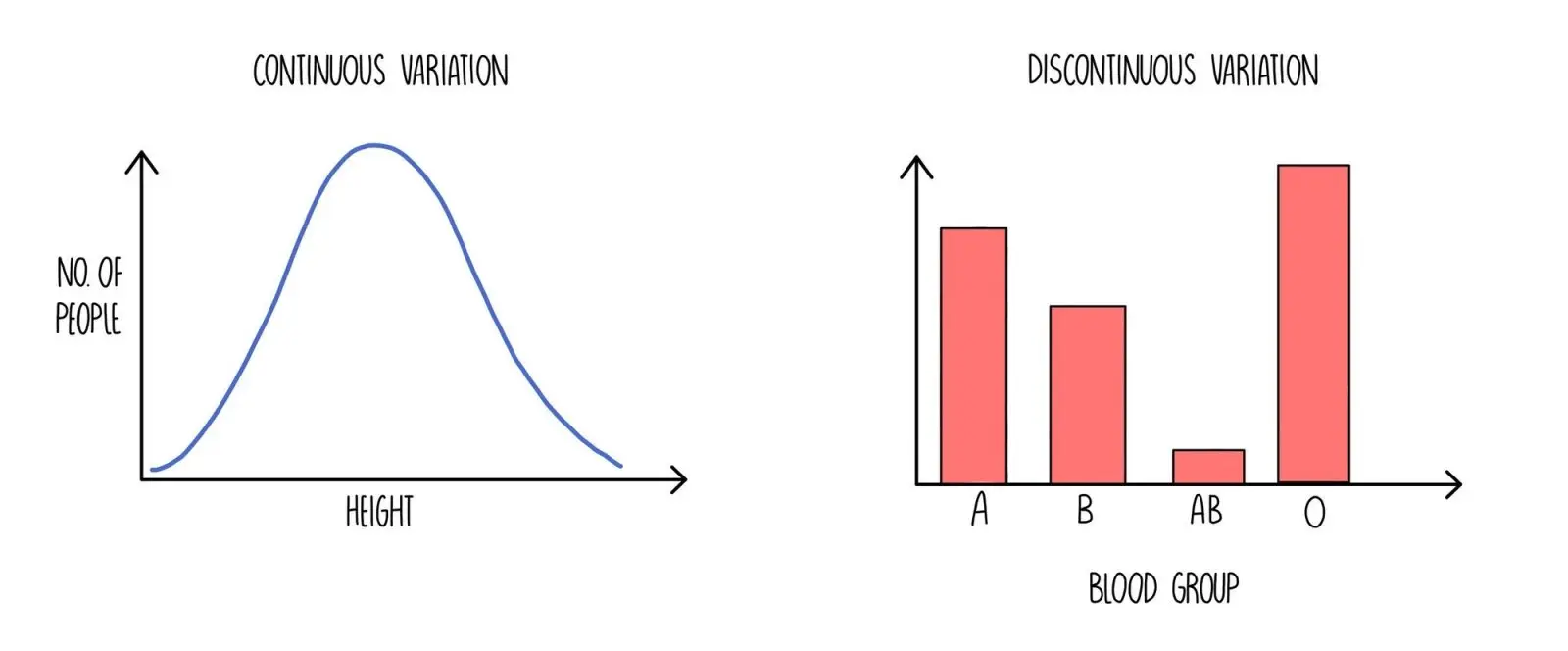
Continuous vs. Discontinuous Variation
Continuous
-a variation that gradually changes across a spectrum, with no distinct categories (Height, weight, arm span, leaf length, skin color) environment shapes the final trait
Discontinuous
-a variation that has distinct categories with no in between (Blood groups (A, B, AB, O), tongue rolling, flower color, seed shape)
think "range" for continuous and "categories" for discontinuous
Harmful, neutral and advantageous mutations
harmful
-negatively affect the organism (albinism in sunny climate)
neutral
-have no effect on the organism (eye color)
advantageous
-positively affect the organism (lactose tolerance)
Types of adaptations
Behavioral
-how the organism acts (i.e. aggressiveness…)
Structural
-physical changes (giraffe's neck or a bird's beak)
Physiological
-an internal bodily function (venom production or water conservation)
Selective pressures
environmental pressures that make a certain trait more favourable (predators, climate, food scarcity)
pressures drive evolution
Industrial revolution and its impact on adaptation
Introduced new environmental challenges
i.e. Black vs. White moth
The where initially many more white moths as they camouflaged in the trees better, but with the coal emissions from the indust. rev. the trees turned darker. Suddenly, the black moths had a huge advantage over the whites ones and made up (at peak) 98% of the moth pop. in Manchester.
What is mimicry and how is it an adaptation?
Mimicry is when an organism adapts to copy another organism’s, object’s or enviorment’s trait.
Works as it manipulates the perceptions of a third organism.
Main principles of evolution
-all species are related
-natural processes drive evolution
Charles Darwin: centers on natural selection
Evidence for evolution
Comparative anatomy
Embryology & development
Fossil records
DNA/biochemical comparisons
Biogeography
Observational evidence
define vestigial structures
Evolutionary remnants -things that had a use for our ancestors but no longer useful i.e. tailbone, appendix
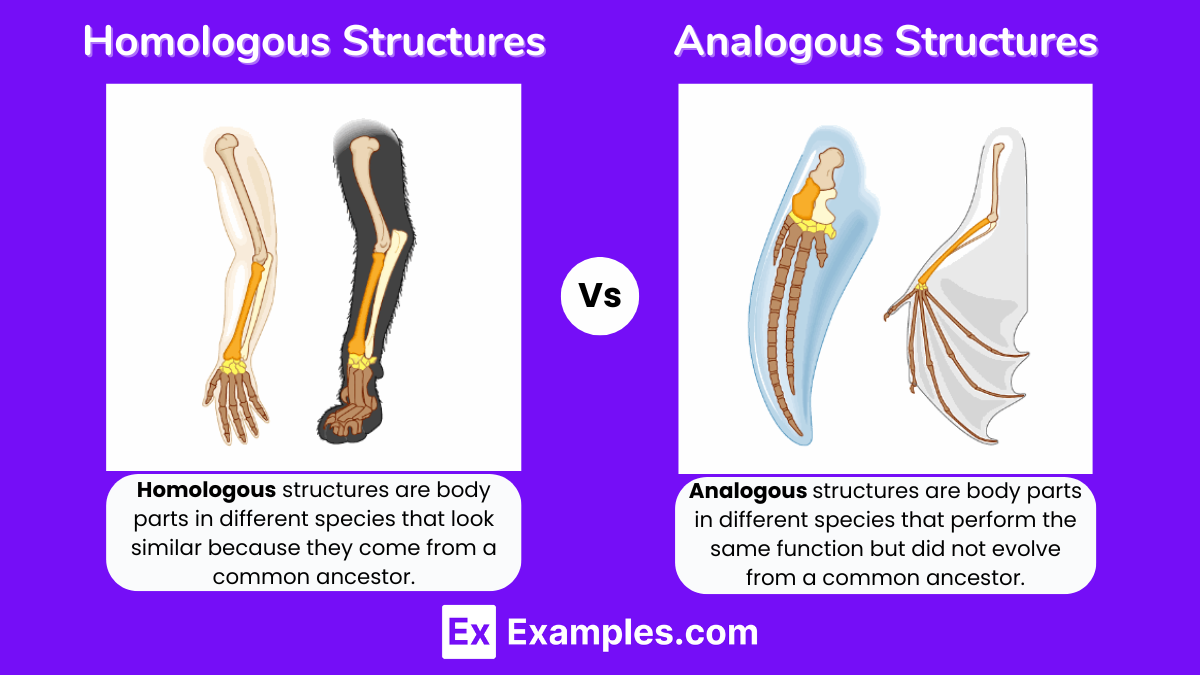
Homologous vs. analogous structures
Homologous
-Structures that come from the same origin point but have a different function i.e. human arm/whale flipper
Analogous
-Structures that come from different origin point but have the same function i.e. bird wing/insect wing
Transitional forms and examples
-an organism that connects 2 distant relatives
-Ambulocetus (land-whale)
-Tiktaalik (land-fish)
Darwin’s finches
While on the Galápagos Islands, Darwin discovered the finch, a bird that on each island have adapted differently depending on it’s food source. They were key to his theory of evolution.
i.e. big beaks for seeds/small beaks for insects
The danger of viruses being able to change quickly
-Allows them to evade the host’s immune system as well as vaccines.
define natural selection
The organism that are better adapted to their environment have better chances of reproducing and surviving.
Natural selection; fitness
The organism that can save the most energy gathering food is able to spend the most on reproduction.
Natural selection; artificial reproduction
When humans make the reproductive decisions
Natural selection; sexual selection
Organisms select their mating partner depending on certain “desirable” traits
Gene pool (why is it good that it’s large)
Define.
-the collection of all the gene in a certain species
.
-If the gene pool is large it means that if a disease comes along, it won’t wipe out the whole pop.
types of selection
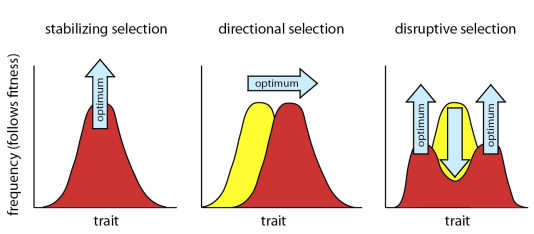
genetic drift
-change in allele freq. over generations due to random chance
genetic bottleneck
-one cataclysmic event drastically reduces the pop.
genetic flow
-the transfer of alleles from one pop. to another i.e. migration
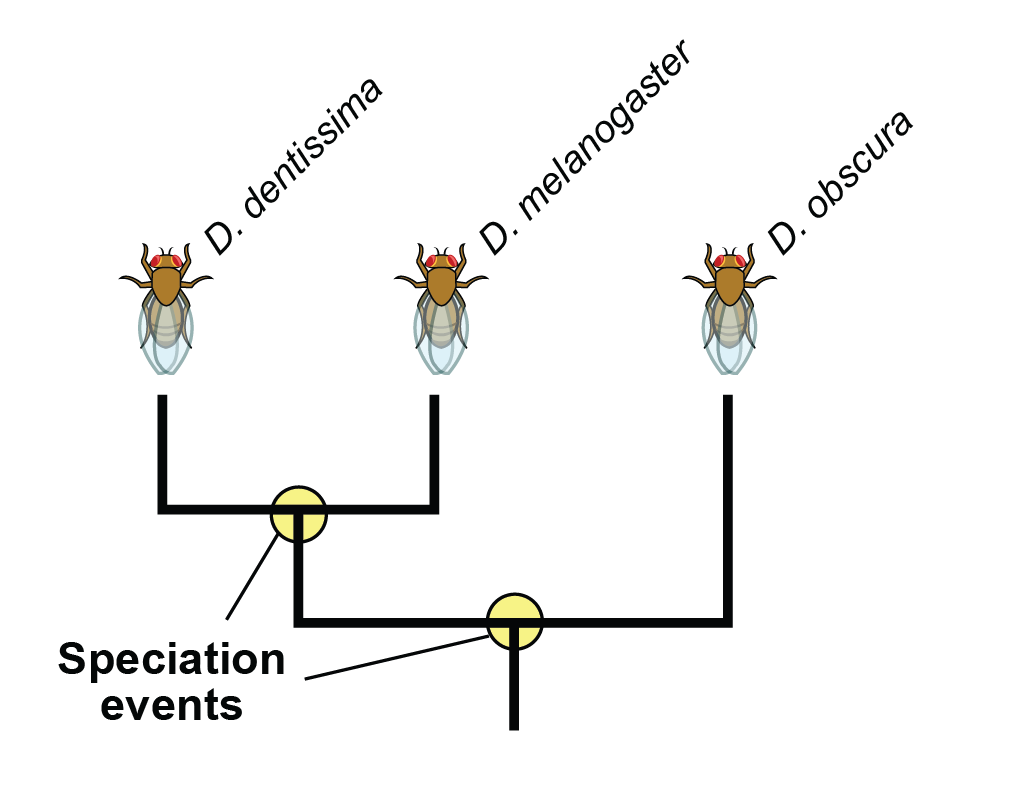
Speciation & Causes
-evolutionary process where pop. diverge created a new species
-allpactric
when a pop. is physically reproductively isolated from the rest of it’s species
-sympatric
when a species is reproductively isolated, not to do with geography, they still live together
i.e. (behavioral/temporal changes)
Abrupt speciation (a.s.)
-usually speciation takes place over many generations, but in plants this change can happen over just one generation
(bc they can still function with polyploid)
autopolyploids vs allopolyploids & connection to a.s.
Autopolyploids
-offspring that contain multiple allele sets from the same species
Allopolyploids
-offspring that contain multiple allele set from 2 different species
-Common in plants, connects to abrupt speciation bc polyploids are unable to mate with their parents generation making them reproductively isolated
major milestones in human evolution
-bipedalism
(freeing hands for tool use/improving efficiency)
-brain growth
(brain size tripled)
-tool use
-language
(spoken lang. enabled knowledge sharing)
modern evolution of humans
-Adult lactose tolerance evolved with dairy farming
-High-altitude adaptations in Tibetan/Andean populations
-Resistance to diseases like malaria and possibly the plague