Y12 Psych - Brain and Behavior
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:54 AM on 10/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
3 principles of the bio approach
Behavior is largely determined by physiology, behavior can be genetically inherited, animal research can inform our understanding of human behavior
2
New cards
Phineus Gage theory
Human behavior is largely determined by physiology, specific regions of the brain have specific functions (brain localization)
3
New cards
Localization
Each different part of the brain
4
New cards
Function
Specific human behaviors and/or cognitive functions
5
New cards
Localization of brain function
The idea that different parts of the brain are responsible for specific behaviors, or that certain functions are localized in certain areas of the brain
6
New cards
Strict Localization
The idea that very particular parts of the brain perform particular functions, based on early research, over-simplified and reductionistic. Not a theory held by many anymore
7
New cards
Relative Localization
Localization exists for some functions under some conditions, some functions are weakly localized and often different parts of the brain work together to perform complex functions like memory, others are handled by larger areas, like hemispheres. More commonly held theory today
8
New cards
Hippocampus
A complex brain structure embedded deep into temporal lobe. It plays a major role in learning and memory.
9
New cards
Case study
Involves a variety of other research methods (interviews, observations, focus groups, etc.) in order to better understand the phenomenon under investigation, often uses purposive sampling. Generalizability often not as important due to studying small, often unique groups
10
New cards
Method Triangulation
The use of multiple methods to study a situation or phenomenon (ex. HM)
11
New cards
Neuroplasticity
The ability of the brain to change through the making and breaking of synaptic connections between neurons
12
New cards
Synaptic Plasticity
The ability of the neuron to form new synaptic connections and break up old ones (small scale)
13
New cards
Cortical Remapping
The phenomenon when brain area X assumes the functions of brain area Y, for example due to injury (large scale)
14
New cards
Neural Networks
Interconnected neural cells
15
New cards
Dendritic branching
Every time we learn something new, the neurons connect to create a new pathway in the brain
16
New cards
Neural pruning (synaptic pruning)
The process where unused neural connections fade away and are eliminated, increasing efficiency between pathways
17
New cards
Neurotransmitters
The brain chemicals that communicate information throughout our brain and body. They relay signals between nerve cells (neurons)
18
New cards
Neurotransmission
The chemical and electrical process by which signals (neurotransmitters) are passed from one neuron to another
19
New cards
Excitatory neurotransmitters
Have stimulating effects on the neuron. This means they increase the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential (stimulating effect)
20
New cards
Inhibitory transmitters
Prevents impulses from crossing the synapses, have repressing effects on the neuron. This means they decrease the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential (calming effect)
21
New cards
Excitatory vs. inhibitory neurotransmitters
In a state of balance. If they get off balance, mental disorders may occur
22
New cards
Agonists
Chemicals that enhance the action of a neurotransmitter
23
New cards
Antagonists
Chemicals that counteract a neurotransmitter and so prevent a signal from being passed further
24
New cards
Action potential
The local voltage change across the cell wall as a nerve impulse is transmitted
25
New cards
Serotonin
An inhibitory neurotransmitter that is involved in emotion and mood, balancing excessive excitatory neurotransmitter effects in your brain
26
New cards
Citalopram
Belongs to a class of antidepressant agents known as selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). It blocks the reuptake of serotonin at the synaptic cleft, resulting in more serotonin being present for longer.
27
New cards
Presynaptic neuron
A neuron (nerve cell) that fires the neurotransmitter as a result of an action potential entering its axon terminal
28
New cards
Postsynaptic neuron
A neuron (nerve cell) that receives the neurotransmitter after it has crossed the synapse and may experience an action potential if the neurotransmitter is strong enough
29
New cards
Synapse / Synaptic gap
The space in between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another
30
New cards
Reuptake
The reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by the cell that originally produced and secreted it. For example, serotonin.
31
New cards
Prosocial behavior
Helping / empathetic behavior
32
New cards
Utilitarianism
An ethical philosophy in which the benefit to the greatest number of people in the society is considered the greatest good, independent of the means to achieve it
33
New cards
Bidirectional ambiguity
This is the concept that in a correlational study, since no independent variable is manipulated, it is impossible to know if x causes y, y causes x, if they interact to cause behavior, or whether it is just coincidental and no relationship truly exists
34
New cards
Threshold of excitation
Received from the other neurons, and if the sum excitation exceeds the threshold, the neuron “fires” and generates an electrical pulse that travels along the body of the neuron (action potential)
35
New cards
Dopamine
An excitatory neurotransmitter involved in motivation, controlling brain’s reward and pleasure centres, and in regulating emotional responses.
Concentrated in a group of neurons called basal ganglia
Concentrated in a group of neurons called basal ganglia
36
New cards
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
37
New cards
How MRI works
- Participants lay very still in the machine
- Radio frequency pulses realign hydrogen atoms which give off energy
- The machine records the energy emitted from the hydrogen atoms
- Computer screen captures it in images, which allows researchers to see images of the size and structure of different parts of the brain.
- Radio frequency pulses realign hydrogen atoms which give off energy
- The machine records the energy emitted from the hydrogen atoms
- Computer screen captures it in images, which allows researchers to see images of the size and structure of different parts of the brain.
38
New cards
Why MRI is used
- Used in experiments and case studies where researchers want to study brain damage / the influence a variable may have on brain structure.
- Used to identify people with brain damage and can also be used to examine the influence of experience or the environment on the brain.
- To make conclusions about the relationships between brain structure (localization / neuroplasticity) and behaviors.
- Used to identify people with brain damage and can also be used to examine the influence of experience or the environment on the brain.
- To make conclusions about the relationships between brain structure (localization / neuroplasticity) and behaviors.
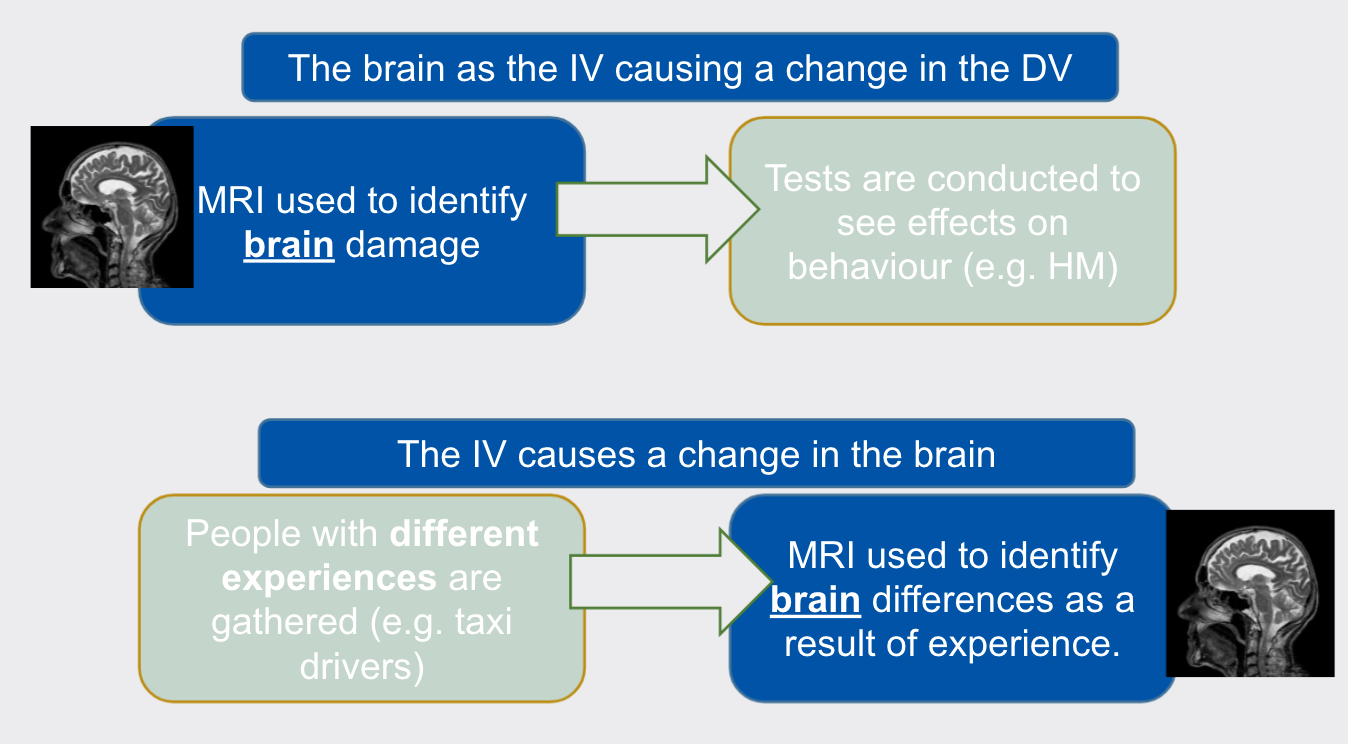
39
New cards
fMRI
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imagery
40
New cards
How fMRI works
Examines brain functioning / brain processes
Changes in the brain (neuroplasticity)
- Participants lay very still in the machine, given instructions on how to cognitively process the stimulus
- Records the change of blood flow in different areas of the brain as the task is being performed. This change in blood flow correlates with activity (more blood = more activity) and so the researchers can see which parts of the brain are active during particular tasks
Changes in the brain (neuroplasticity)
- Participants lay very still in the machine, given instructions on how to cognitively process the stimulus
- Records the change of blood flow in different areas of the brain as the task is being performed. This change in blood flow correlates with activity (more blood = more activity) and so the researchers can see which parts of the brain are active during particular tasks
41
New cards
Why fMRI is used
- Used in true experiments where researchers manipulate a variable that is hypothesized to affect behavior, such as a hormone or neurotransmitter
- Used to measure the effects of this variable on brain activity
- Allows researchers to gain a deeper understanding of just how the variable is affecting behavior because we can see how it might be affecting brain activity
- Used to measure the effects of this variable on brain activity
- Allows researchers to gain a deeper understanding of just how the variable is affecting behavior because we can see how it might be affecting brain activity
42
New cards
Aim, method, procedure, results, conclusion, evaluation
AMPRCE: How to Break Down a Study
43
New cards
Procedural memory
A part of the long-term memory that is responsible for knowing how to do things, also known as motor skills. Stores information on how to perform certain procedures, i.e. walking, talking and riding a bike.
44
New cards
Implicit memory
A form of long-term memory that doesn't require any conscious retrieval. Encompasses all unconscious memories, as well as certain abilities or skills (includes procedural memory)
45
New cards
Declarative (explicit) memory
Devoted to processing of names, dates, places, facts, events, and so forth, can be described with language, specialized for fast processing and learning.
46
New cards
Milner and Corkin / HM (1957 and 1997) - Hippocampus vs. Memory
!! LOCALIZATION STUDY !!
A - To explore the way the brain stores memories in the short and long-term
M - Case study: method triangulation
P - Psychometric (IQ test), direct obv., interviews, cognitive tests (memory recall), MRI
R - The hippocampus plays a critical role in converting short-term memories to long-term memories --- Short-term memory is not stored in the hippocampus
C - Implicit memory contains several stores in the brain: procedural memory, emotional memory and skills and habits
A - To explore the way the brain stores memories in the short and long-term
M - Case study: method triangulation
P - Psychometric (IQ test), direct obv., interviews, cognitive tests (memory recall), MRI
R - The hippocampus plays a critical role in converting short-term memories to long-term memories --- Short-term memory is not stored in the hippocampus
C - Implicit memory contains several stores in the brain: procedural memory, emotional memory and skills and habits
47
New cards
Voxel-based morphometry
VBM: provides a three dimensional measurement of volume of an area, typically used to measure the amount of gray matter in the brain
48
New cards
Maguire (2000) - Posterior hippocampus vs. spatial memory
!! LOCALIZATION / NEUROPLASTICITY STUDY !!
A - To investigate whether changes could be detected in the brains of London taxi drivers --- further investigate the functions of the hippocampus in spatial memory
M - Quasi-experiment: 16 male taxi drivers, 50 right-handed non-drivers, 32-62 yrs old, around 14 yrs as taxi drivers in London
P - Magnetic Resonance Imagery (MRI) for structure / anatomy --- Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) for the density of gray matter in the brain
R - The posterior hippocampi of taxi drivers were significantly larger relative to those of control subjects and that the anterior hippocampal region was larger in control subjects than in taxi drivers --- Hippocampal volume correlated with the amount of time spent as a taxi driver (positively in the right posterior and negatively in the right anterior hippocampus)
C - London taxi drivers’ volume of the posterior hippocampus expanded because of their dependence on navigation skills.
A - To investigate whether changes could be detected in the brains of London taxi drivers --- further investigate the functions of the hippocampus in spatial memory
M - Quasi-experiment: 16 male taxi drivers, 50 right-handed non-drivers, 32-62 yrs old, around 14 yrs as taxi drivers in London
P - Magnetic Resonance Imagery (MRI) for structure / anatomy --- Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) for the density of gray matter in the brain
R - The posterior hippocampi of taxi drivers were significantly larger relative to those of control subjects and that the anterior hippocampal region was larger in control subjects than in taxi drivers --- Hippocampal volume correlated with the amount of time spent as a taxi driver (positively in the right posterior and negatively in the right anterior hippocampus)
C - London taxi drivers’ volume of the posterior hippocampus expanded because of their dependence on navigation skills.
49
New cards
Draganski (2004) - Acquiring skills vs. Gray matter in mid-temporal lobe
!! NEUROPLASTICITY STUDY !!
A - To investigate the effects of learning a new skill, in this case juggling, on the brain
M - Lab (True) experiment: 20-24 yrs old, 21 females and 3 males. All non-jugglers at the start of the study --- Each participant had an MRI scan at the start of the study to serve as a base rate for gray matter (neural density) and brain structure
P - Randomly allocated to jugglers or non-jugglers --- jugglers were taught a three-ball cascade juggling routine. They mastered it and had a second MRI scan. After the scan, they were told not to juggle anymore. --- A third and final scan was carried out three months later. The non-juggling group served as a control group.
R - From the scans taken before the study began, they found no significant regional differences in gray matter between the two conditions --- After learning the skills, the jugglers showed a significantly larger amount of gray matter in the mid-temporal area in both hemispheres - an area associated with visual memory. Three months after the participants stopped juggling (many were no longer able to carry out the routine) the amount of gray matter in these parts of the brain had decreased
C - Learning a simple juggling routine increases the volume of gray matter in the mid-temporal area of both hemispheres (synaptic plasticity and dendritic branching). Lack of practice makes the area shrink but not back to its original size (neural pruning)
A - To investigate the effects of learning a new skill, in this case juggling, on the brain
M - Lab (True) experiment: 20-24 yrs old, 21 females and 3 males. All non-jugglers at the start of the study --- Each participant had an MRI scan at the start of the study to serve as a base rate for gray matter (neural density) and brain structure
P - Randomly allocated to jugglers or non-jugglers --- jugglers were taught a three-ball cascade juggling routine. They mastered it and had a second MRI scan. After the scan, they were told not to juggle anymore. --- A third and final scan was carried out three months later. The non-juggling group served as a control group.
R - From the scans taken before the study began, they found no significant regional differences in gray matter between the two conditions --- After learning the skills, the jugglers showed a significantly larger amount of gray matter in the mid-temporal area in both hemispheres - an area associated with visual memory. Three months after the participants stopped juggling (many were no longer able to carry out the routine) the amount of gray matter in these parts of the brain had decreased
C - Learning a simple juggling routine increases the volume of gray matter in the mid-temporal area of both hemispheres (synaptic plasticity and dendritic branching). Lack of practice makes the area shrink but not back to its original size (neural pruning)
50
New cards
Crockett (2010) - Serotonin vs. Prosocial behavior
!! NEUROTRANSMISSION STUDY !!
A - To investigate the effect of serotonin on prosocial behavior
M - True experiment; repeated measures design. The design was counterbalanced. The study was double-blind.
P - In condition 1, participants were given a dose of citalopram (an SSRI). In condition 2, they were given a placebo. Participants were given moral dilemmas based on the classic “trolley problem”.
R - In the impersonal (pulling the lever) scenario, participants’ responses were unaffected by citalopram. In the personal scenario, citalopram made participants less likely to interfere (less likely to push the man)
C - Citalopram reduces target acceptability of personal harm and in this sense promotes prosocial behavior. Increased levels of serotonin in the brain may cause people to be more opposed to the idea of inflicting harm on someone
A - To investigate the effect of serotonin on prosocial behavior
M - True experiment; repeated measures design. The design was counterbalanced. The study was double-blind.
P - In condition 1, participants were given a dose of citalopram (an SSRI). In condition 2, they were given a placebo. Participants were given moral dilemmas based on the classic “trolley problem”.
R - In the impersonal (pulling the lever) scenario, participants’ responses were unaffected by citalopram. In the personal scenario, citalopram made participants less likely to interfere (less likely to push the man)
C - Citalopram reduces target acceptability of personal harm and in this sense promotes prosocial behavior. Increased levels of serotonin in the brain may cause people to be more opposed to the idea of inflicting harm on someone
51
New cards
Fisher, Aron and Brown (2005) - Dopamine vs. Romantic love
!! NEUROTRANSMISSION STUDY !!
A - Test the hypothesis that there are specific neural mechanisms associated with romantic love.
M - Self-selected sample --- 10 women and 7 men who were intensely in love for an average of 7.4 months --- The researchers first conducted a semi-structured interview to establish the duration and intensity of the participants’ feelings of romantic love --- Each participant completed the Passionate Love Scale - a Likert scale questionnaire that measures traits commonly associated with romantic love --- Compare what participants reported on the questionnaires to their brain activity as seen through the fMRI.
P - The participants looked at the photograph of their beloved for 30 seconds while they were scanned --- They had a filler task to distract them before they looked at a neutral photograph for 30 seconds while being scanned --- Repeated six times
R - The brain’s reward system was particularly active when the lovers looked at pictures of the object of their love --- Increased activity in the areas of the brain with high levels of dopamine neurons --- The more passionate they were, the more active the brain’s reward circuitry was. --- The fMRI scans supported a correlation between the attitudes towards the lover and brain activity. According to Fisher, romantic love is not an emotion, but rather a motivation system, a need or a craving, designed to enable lovers to mate. Fisher claims that specific brain systems have evolved to motivate individuals to mate.
C - This could perhaps explain why attraction is normally linked to increased energy, focused attention, obsessive following, sleeplessness and loss of appetite. Dopamine is behind the intense motivation to win a specific mating partner in the early stages of human romantic love. In this way, humans are very much like other animals.
A - Test the hypothesis that there are specific neural mechanisms associated with romantic love.
M - Self-selected sample --- 10 women and 7 men who were intensely in love for an average of 7.4 months --- The researchers first conducted a semi-structured interview to establish the duration and intensity of the participants’ feelings of romantic love --- Each participant completed the Passionate Love Scale - a Likert scale questionnaire that measures traits commonly associated with romantic love --- Compare what participants reported on the questionnaires to their brain activity as seen through the fMRI.
P - The participants looked at the photograph of their beloved for 30 seconds while they were scanned --- They had a filler task to distract them before they looked at a neutral photograph for 30 seconds while being scanned --- Repeated six times
R - The brain’s reward system was particularly active when the lovers looked at pictures of the object of their love --- Increased activity in the areas of the brain with high levels of dopamine neurons --- The more passionate they were, the more active the brain’s reward circuitry was. --- The fMRI scans supported a correlation between the attitudes towards the lover and brain activity. According to Fisher, romantic love is not an emotion, but rather a motivation system, a need or a craving, designed to enable lovers to mate. Fisher claims that specific brain systems have evolved to motivate individuals to mate.
C - This could perhaps explain why attraction is normally linked to increased energy, focused attention, obsessive following, sleeplessness and loss of appetite. Dopamine is behind the intense motivation to win a specific mating partner in the early stages of human romantic love. In this way, humans are very much like other animals.