Native americans rights and the impact of red power
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
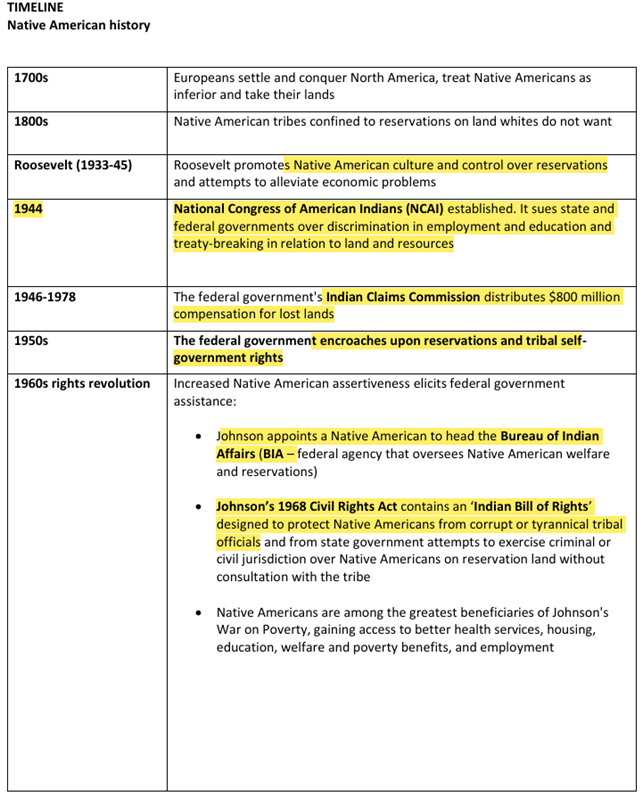
native american history
Native Americans in 1973
Population stood at 700k-800k, rising to 1.4 million in 1980.
Lived short hard lives on reservations.
Unemployment t ranged from 20% to 80%.
44-year life expectancy and high rates of suicide and alcoholism
Historic land treaty rights were frequently ignored.
Wanted the right to travel self -government to preserve their culture and identity.
1968 – American Indian movement (AIM) was formed and was inspired by Black power and red power
Organisations
Aims and methods included.
Stressing positive imagery
Monitoring police racism
Establishing survival schools
Occupations
1969 a group of AIM activists occupied the former federal prison of Alcatraz.
Major confrontation with law enforcement at Wounded knee in south Dakota, two people killed and12 wounded.
February 1973 – 50% unemployment, exceptionally high suicide, and alcoholism rates
Demanded free election of tribal leaders.
The review of all treaties that concerned the land rights.
When hostages were held at gunpoint, heavily armed deferral forces quickly besieged wounded knee, and two native Americans were killed.
Litigation
Gained some success is the law courts.
of Montana won a federal court victory enabling them to renegotiate mineral contracts. After 50 years of protest, controversy and litigation, coal mining on Navajo and Hopi reservation lands ceased in 2005.
The federal government and native Americans
red power paid off with the Indian self determination act passed by congress in 1974.
responded further with the Indian self determination and education assistance act 1975 which five tribes’ control over their federal aid programmes and reservation education.
Indian health care improvement act 1976 in which congress granted $1.6 billion to help improve the availability and delivery of healthcare for native Americans.
Native American litigants had similar mixed feelings about Supreme Court decisions:
In US v. Wheeler (1978), the Supreme Court affirmed the right of a federal court to try a Native American who had already been tried by his tribe. While the Court recognised the 'unique’ sovereignty (in the Native American context, the right to self-government on reservations) of Native American tribes, it said it was ‘limited.’
In Oliphant (1978), the Supreme Court limited tribal authority over non-Indians and Indians of other tribes on reservations.
While the American Indian Religious Freedom Act (1978) recognised rights to practise Native American cultural traditions, such as the use of the hallucinatory drug peyote, an increasingly conservative Supreme Court weakened the Act in 1990.
Native American rights in 1980
Greater rights to self-determination
were still frequently ignored.
The economic status of native Americans remained inferior to that of white people.