AE2001 Fundamentals of ecology / 13 Mutualism
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Mutualism
Symbiotic relationship where both species benefit, crucial for biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Obligate mutualism
Relationship where both species depend entirely on each other for survival.
Example: yucca and yucca moths.

Facultative mutualism
Relationship that is beneficial but not necessary for survival. Example: nitrogen-fixing bacteria in legumes.
Pollination syndrome
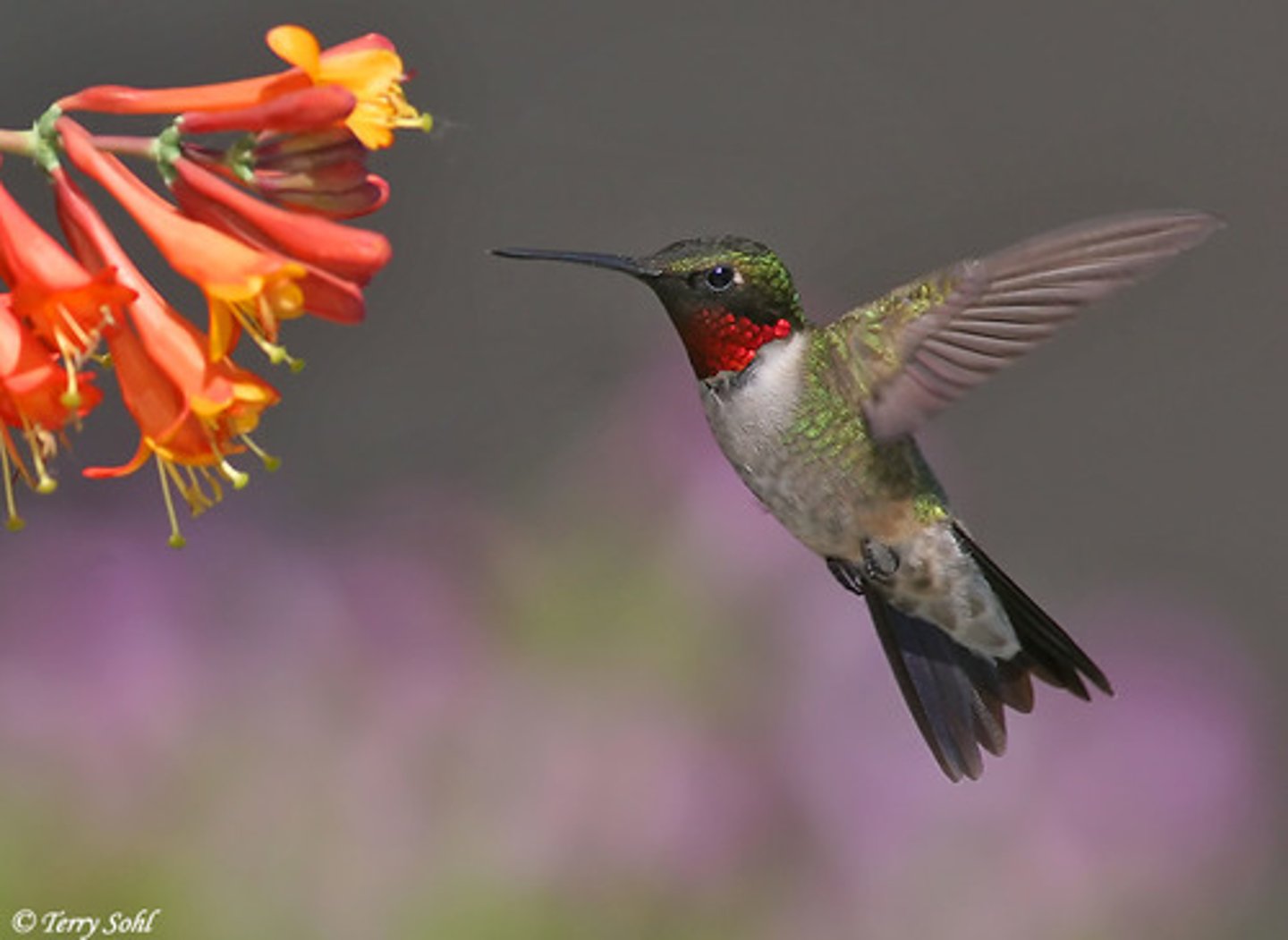
Specific traits in plants adapted to attract certain pollinators: scent, colour & flower shape.
Example: Hummingbirds & flowers, plants evolve deep corollas, birds evolve longer beaks to minimize nectar loss.

Specialist vs. generalist pollinators
Specialists target specific plants for precise pollen transfer. (Agaonid fig wasps eggs inside fig flowers; larvae develop by consuming some seeds)
Generalists use multiple plant species, more resources but reduced pollination (honey bees)
Bee orchid mimicry
Ophrys apifera by mimicking female bees’ scent and appearance but pattracts male bees rovides no nectar reward.
Seed dispersal mutualisms
~30% of mutualisms involve animals dispersing seeds in exchange for food rewards. (Corvids cache seeds = plant dispersal when they forget where the seed was)
Bird- vs. bat-dispersed fruits
Bird-dispersed fruits = Small, brightly colored, no strong scent.
Bat-dispersed fruits = Larger, pale, strong smell, nocturnal attraction.
Leaf-cutting ants & fungus
Cultivation: Harvest leaves to grow mutualistic fungus Leucoagaricus gongylophorus, produces gongylidia as food.
Defense: Ants have Pseudonocardia bacteria in exoskeleton = antibiotics against parasitic Escovopsis fungus.
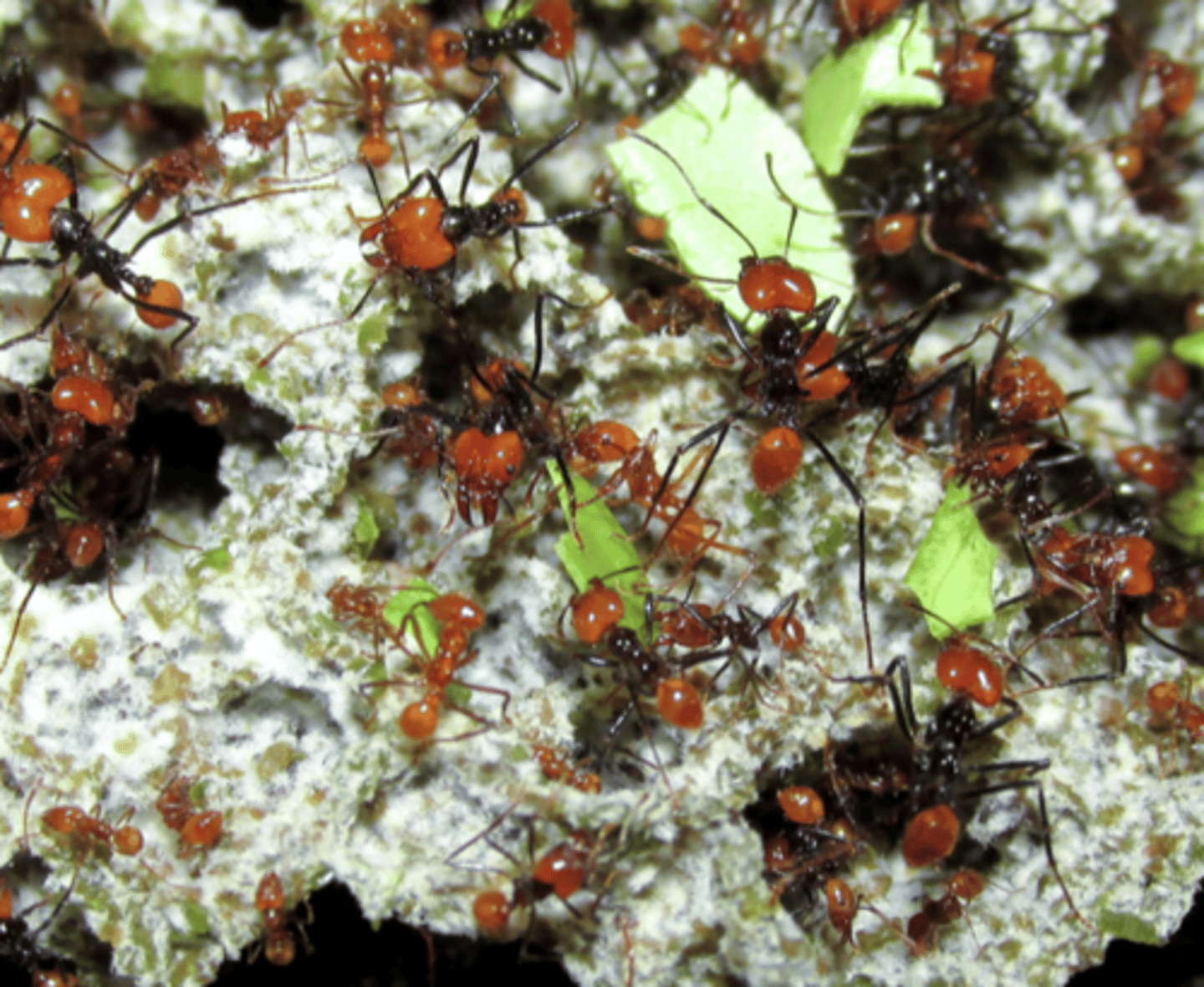

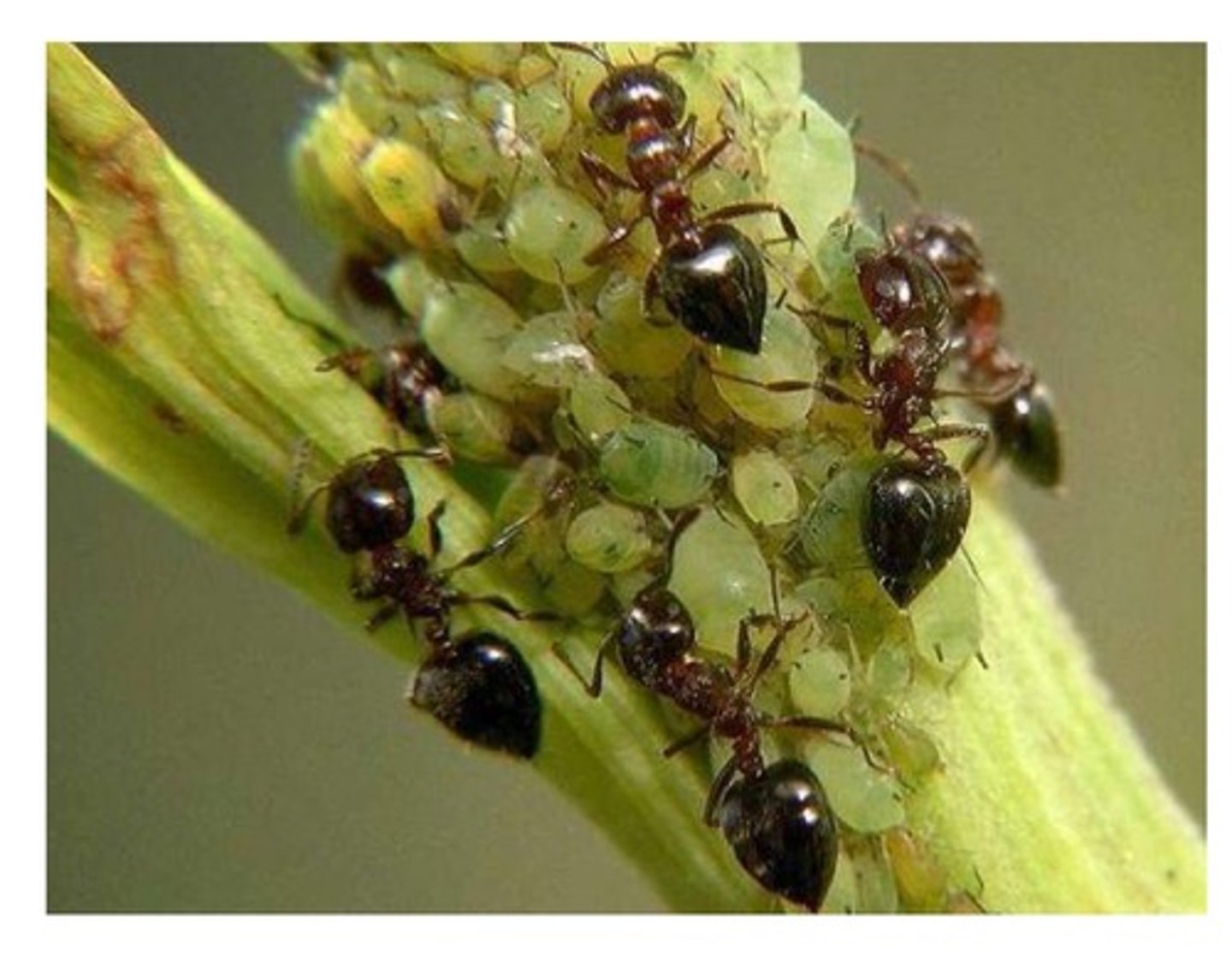
Ant-aphid mutualism
Ants protect aphids from predators in exchange for honeydew.

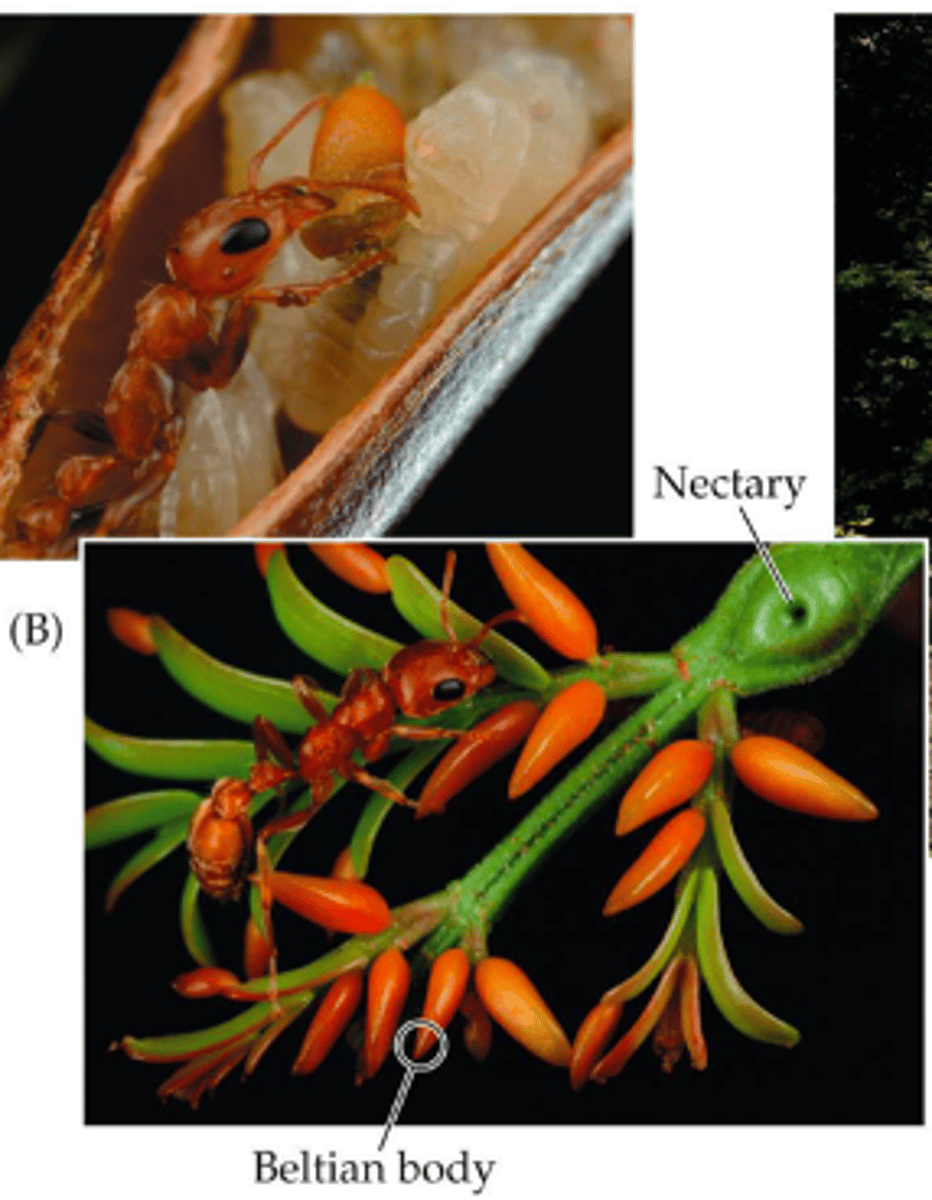
Ant-acacia mutualism
Acacia trees provide food (Beltian bodies) & shelter, ants protect against herbivores & competing plants.
Mycorrhizae
Fungal-root mutualism where fungi enhance plant nutrient uptake in exchange for carbohydrates.

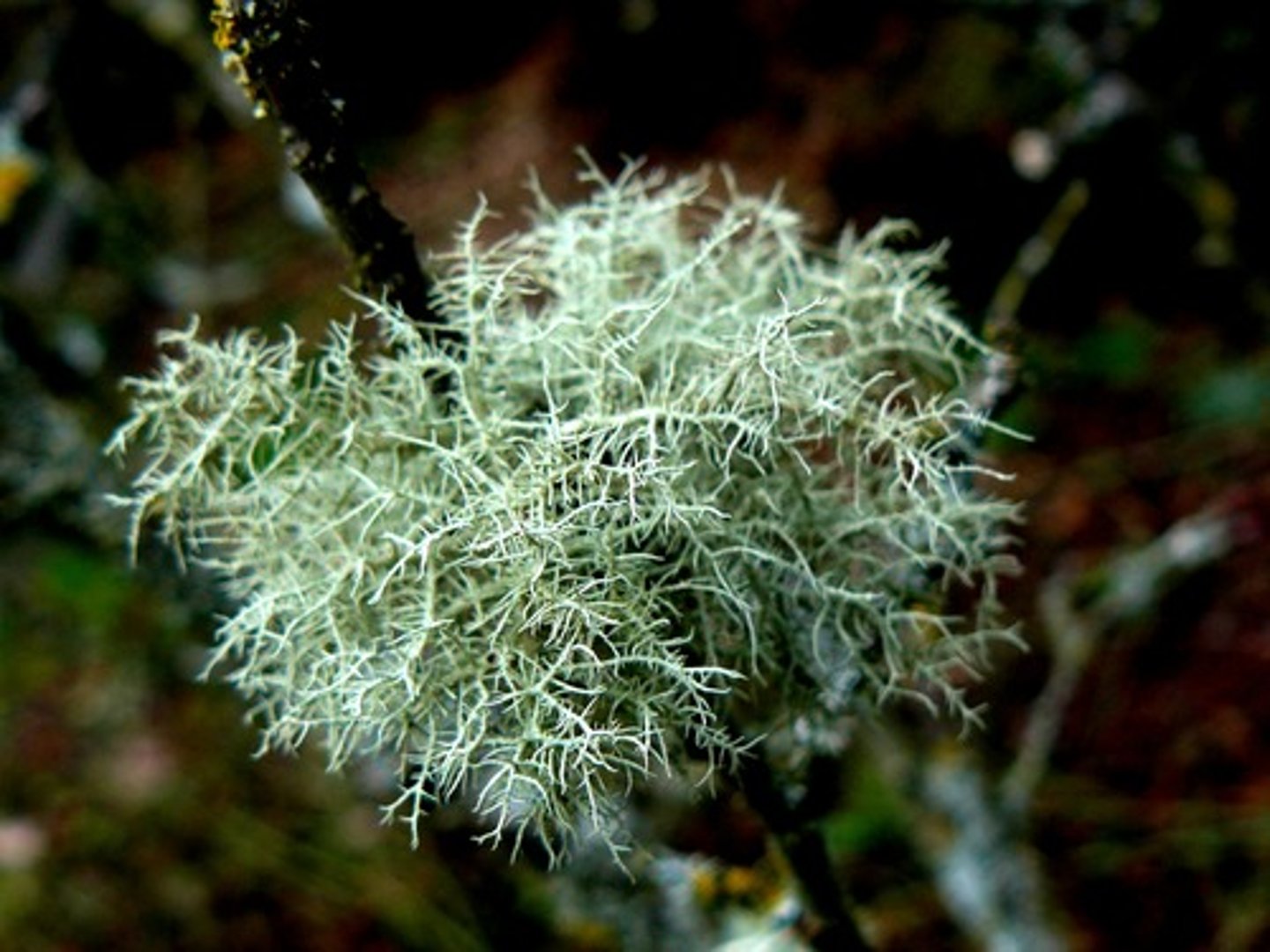
Lichens
Mutualism between fungi & algae. Algae provides food & fungi provides habitat.

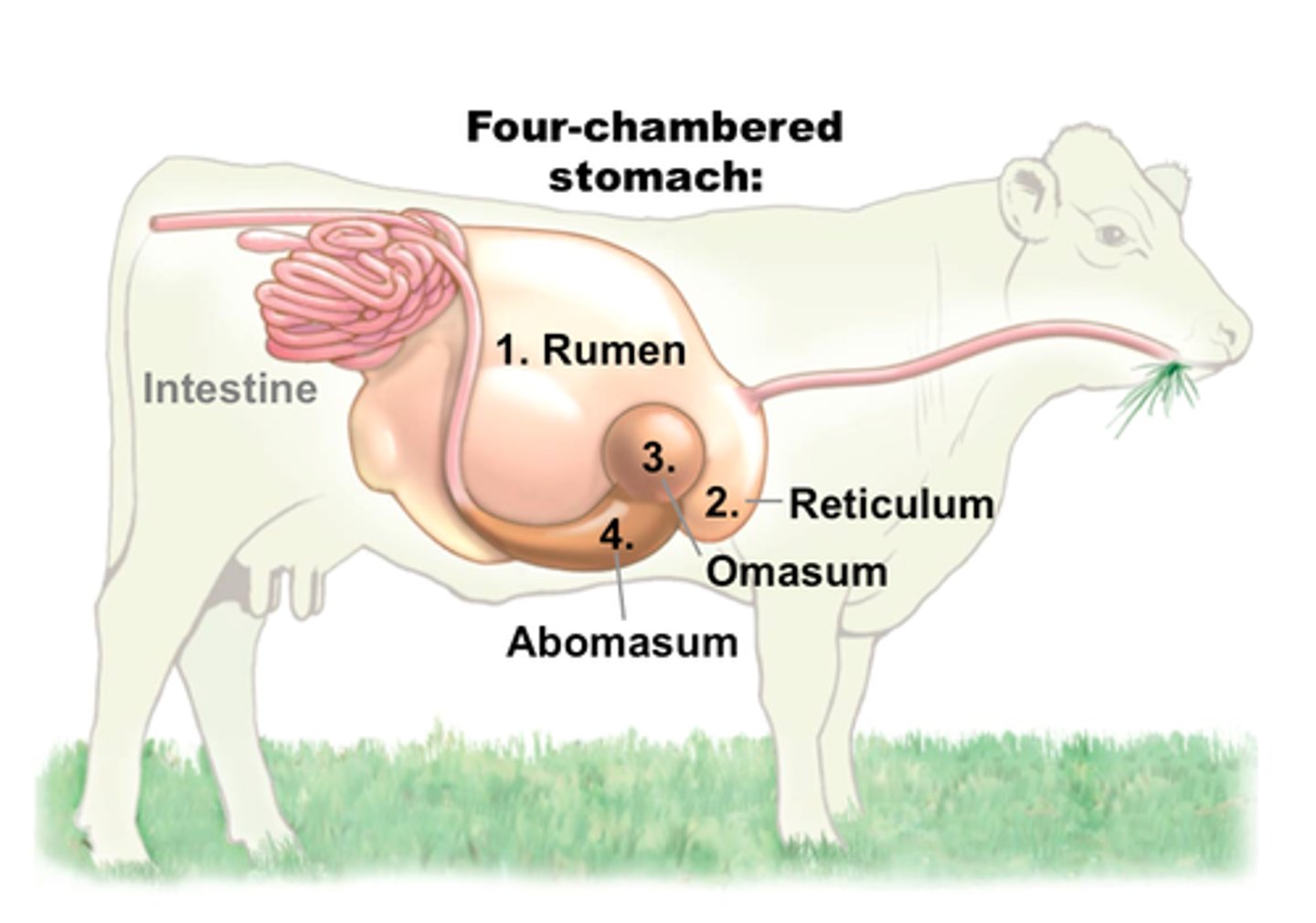
Ruminants & gut bacteria
Bacteria in herbivore guts break down cellulose = digestion of plant material.
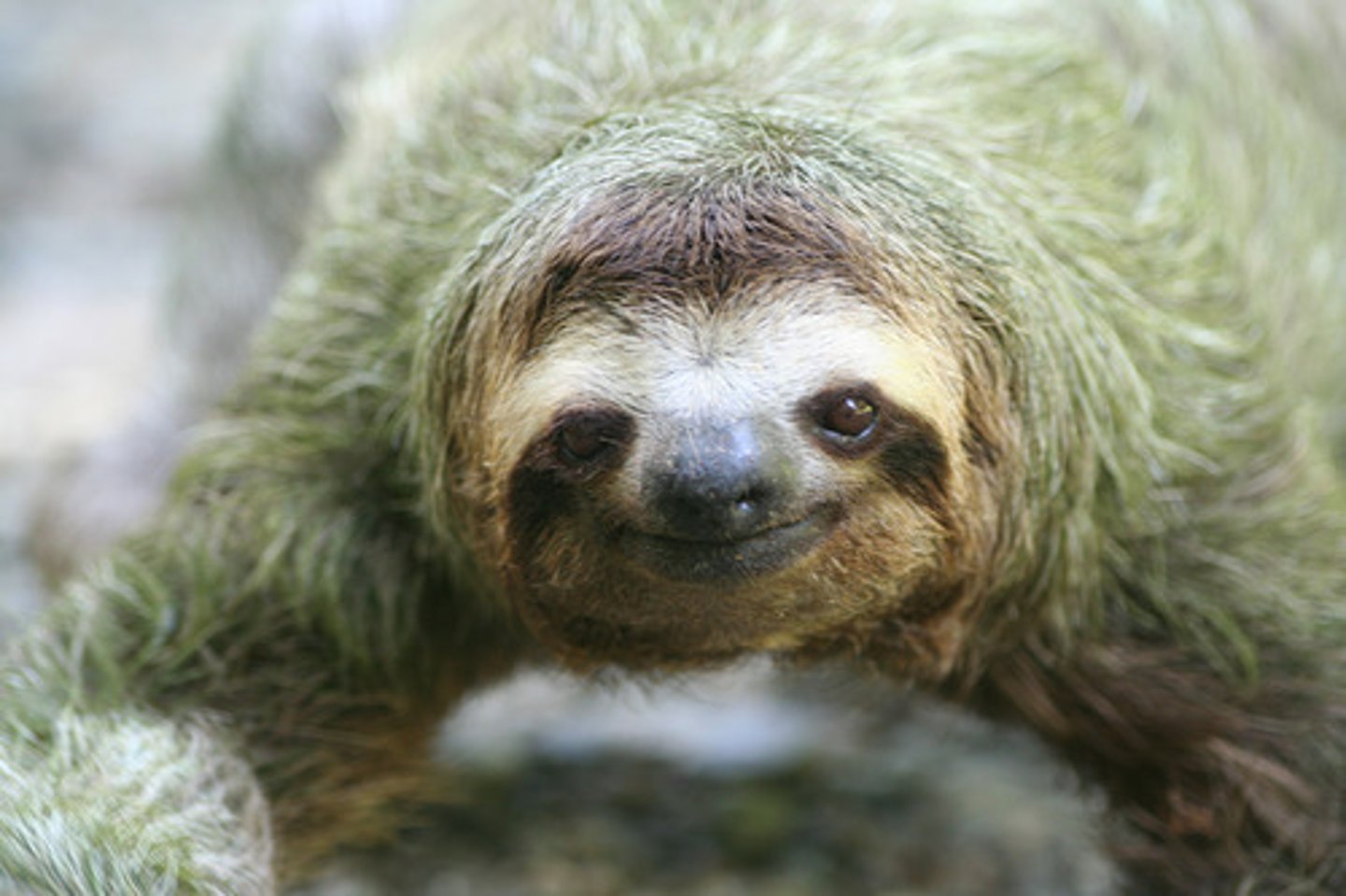
Sloth-algae-moth mutualism
Sloths fur = habitat for algae & moths.
Moths fertilise algae, increases growth.
Sloths consume algae for nutrients.

Sloth defecation cycle
Sloths descend to transport moths to oviposition sites = cycle of sloth fur algae growth.
Lowest metabolic rate of any non-hibernating mammal; digestion takes 157 hours to 50 days.
Asymmetric mutualisms
Mutualisms can favour one species more = mutual benefit to parasitism.
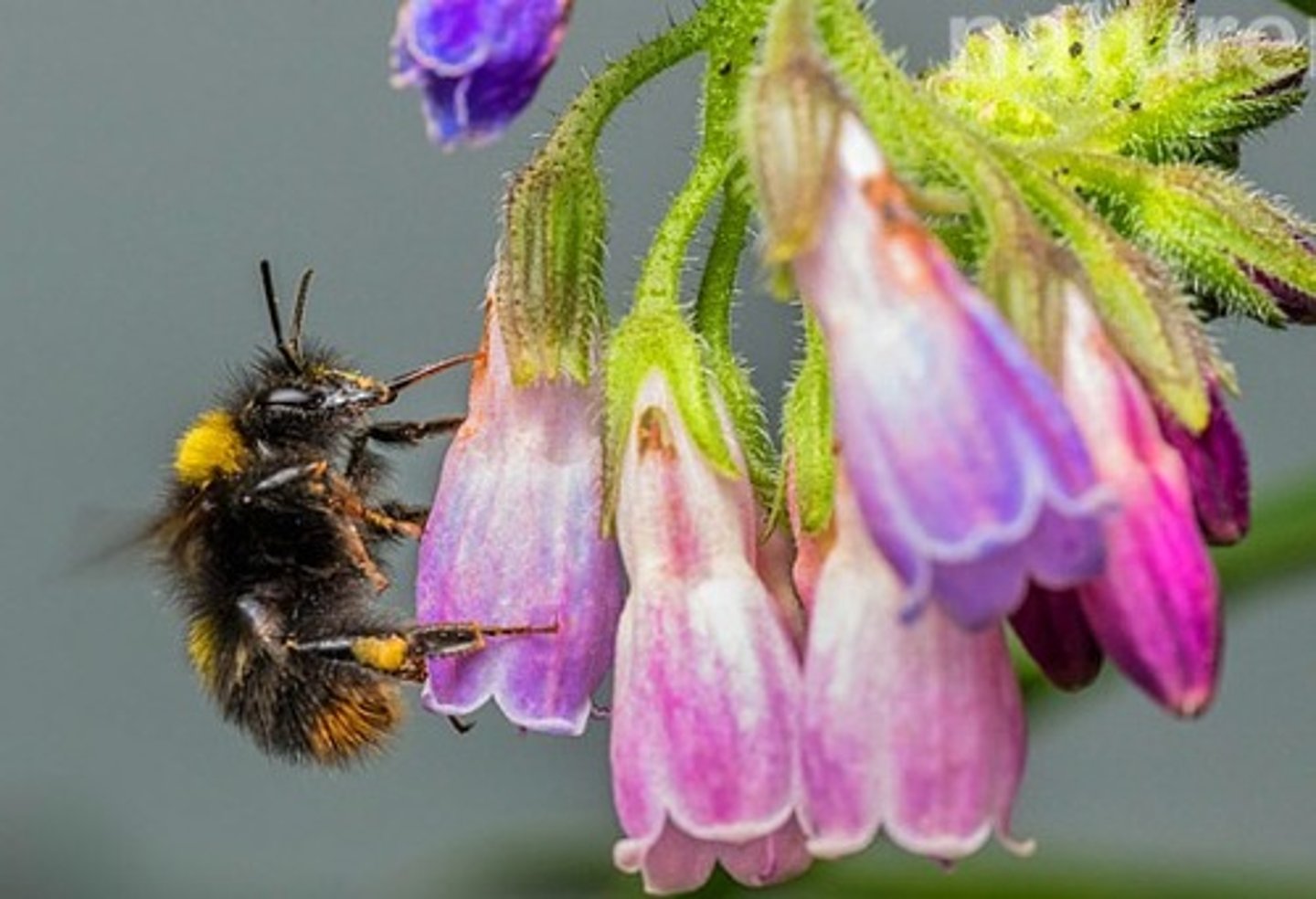
Nectar robbery
Bumblebees & other insects steal nectar by piercing flowers without pollinating them.
Example: Comfrey
