Week 3: Spoofing, flooding, and amplification
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
How are you identified on the Internet layer?
Identified by IP address
Who assigns IP addresses?
Users or software
What two types of IP systems are there?
- IPv4
- IPv6
How many bits is IPv4 made of?
32 bits
How many bits is IPv6 made of?
128 bits
How are you identified on the Link layer?
Identified by MAC address
Who assigns MAC addresses?
Device manufacturers on the NIC
What is the MAC address also known as?
Hardware/physical address
How many bits is the MAC address made of?
48 bits
What does ARP stand for?
Address Resolution Protocol
Why do we need to know how to link IP addresses to MAC addresses?
In order to transmit IP packets over a network, we need to package them in Link layer frames
Which protocol is used to translate from an IP to MAC address?
ARP
Which protocol is used to translate from a MAC to IP address?
RARP (Reverse ARP)
Where do ARP and RARP operate?
Between the Internet and Link layers
What does unicast mean?
Send to only one device
What happens when node A broadcasts an ARP request packet for node B's IP address?
Node B will unicast a packet to node A with its MAC address
What happens when a host broadcasts a RARP request with its MAC address to a RARP server?
The RARP server unicasts a reply telling the host its IP address
Who usually sends RARP requests?
- Diskless clients
- Jumpstart clients
Why do diskless clients send RARP requests?
Diskless clients only know their Ethernet address
Why do jumpstart clients send RARP requests?
Jumpstart clients contain local storage but use the Ethernet address to locate the jumpstart boot server
What is the type number for ARP frames?
0x0806
What is the type number for RARP frames?
0x8035
What happens when an ARP request message is generated?
1. ARP is called by hardware driver
2. Get IP address of the target
3. Translate the IP address to a MAC address*
4. Pass the message to the Link layer after it is packaged in a frame**
Where are IP-MAC address mappings stored?
In a translation table
What is the process of translating an IP address to a MAC address?
1. If the MAC address for the IP address is in the translation table, return the 48-bit MAC address to the hardware driver
2. Otherwise, prepare an ARP request message that is sent to retrieve the MAC address
What is the process of preparing an ARP request message?
1. Fill in the sender MAC address
2. Fill in the sender IP address
3. Fill in the target IP address
4. Fill in the field for the target MAC address with a 0
What is the process of preparing a Link layer frame?
1. Fill in the source address as the MAC address of the sender
2. Fill in the destination address as a broadcast message
3. Fill in the message type as 0x0806
What happens when an ARP request message is received?
1. Every host/router on the LAN receives the ARP frame
2. Target node replies with an ARP reply message containing its MAC address
What happens when every node on the LAN receives the ARP request frame?
ARP is invoked, and the translation table for
What happens when an ARP reply message is received?
Nodes update the translation table with the entry
What does ARP use to speed up translation table lookups?
They use an ARP cache
What type of cache is an ARP cache?
Least Recently Used (LRU) cache
Who maintains the ARP translation table?
The OS maintains the table
When is the ARP translation table updated?
Whenever any request or reply is received
What command can you use to access the ARP translation table in Ubuntu?
`arp -a`
What are 3 examples of attacks using ARP?
- ARP cache poisoning via spoofing
- MitM attack with ARP spoofing
- MAC flooding with ARP spoofing
What is ARP cache poisoning via spoofing?
When an attacker C learns the IP addresses of two victims A and B, and sends a spoofed ARP reply message pretending that the IP address of B maps to the MAC address of C
What is the consequence of ARP cache poisoning?
The spoofed victim's frames will now be received by the attacker
What are 4 methods to mitigating ARP cache poisioning?
- Make cache entries expire
- Send unicast ARP messages rather than broadcasting
- Limit resending windows
- Create a static ARP table
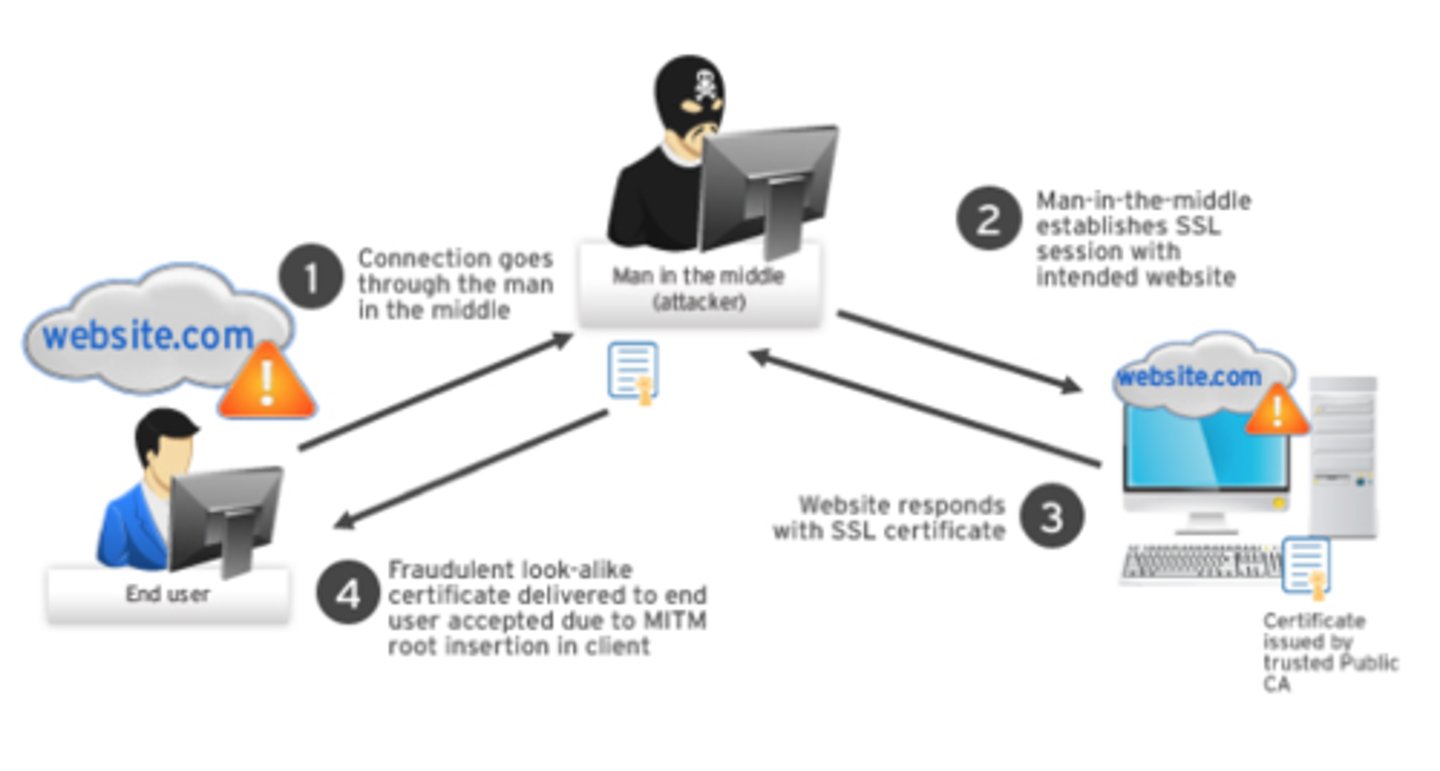
What is MitM attack with ARP spoofing?
Attackers can poisoning ARP caches for two victims A and B so that they receive all frames from communications between A and B
What is a CAM table?
A table in a switch that maps switch ports to MAC addresses
What does CAM stand for?
Content Addressable Memory
What happens every time a frame arrives at a switch?
The switch checks the CAM table to known which port to forward the frame to
What is MAC flooding with ARP spoofing?
Attackers feed switches many frames with spoofed source MAC addresses to consume memory, which causes frames to be broadcasted on all switch ports
What does MAC flooding with ARP spoofing allows?
It allows attackers to sniff previously unseen traffic
What is a bot?
A software application programmed to do certain tasks automatically
What is a botnet?
Logical collection of internet-connected devices that have been infected + are controlled by a third party (essentially zombie devices)
How do attackers control botnets?
Using a command and control (C&C) software
How can we build a botnet?
1. Hackers use an exploit kit to infect computers with malicious app called a "bot"
2. Bot instructs infected PC to connect to their C&C server
3. Bots can then be rented out to use in DDoS attacks or to collect data that is sold
What is a botmaster?
The attacker controlling the botnet
Why are IoT devices targeted for botnets?
IoT devices are not that secure
Briefly, what is the TCP 3-way handshake?
1. Client sends a SYN packet to initiate a connection with a server
2. Server receives the SYN packet and sends a SYN-ACK packet to acknowledge the client and establish the connection
3. Client receives the SYN-ACK packet and sends an ACK packet to establish the connection
What is a TCP SYN flooding attack?
- Attacker floods a server with SYN packets without replying to the server with an ACK packet to establish a connection
- Server is left hanging, exceeding resource limits whilst waiting, causing DoS for genuine connection requests
What does DHCP stand for?
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
What is DHCP?
A protocol that automatically provides clients with IP addresses and other related configuration details
How do we define the stages of a DHCP communication?
DORA
What does DORA stand for?
- Discovery
- Offer
- Request
- Acknowledgement
Briefly, what are the DORA communication stages?
- DHCP client will offer itself to DHCP servers by sending messages with its MAC address
- A DHCP server responds with its IP address to offer itself
- DHCP client accepts the DHCP server's response and tells other servers it is off the market!
- DHCP server establishes the connection by acknowledging the client
What is an example of a spoofing attack associated with DHCP?
DHCP starvation
What is DHCP starvation?
- Attacker takes up all capacity on a DHCP server by spoofing a bunch of messages
- DHCP clients can't connect to anyone because no server has space to accept
- Attacker sets up a rogue DHCP server to trick the clients into connecting
What is an ICMP smurfing attack?
Attackers broadcast pings to a LAN to use all of its bandwidth, causing DoS
How may ICMP smurfing cause DoS on a victim?
Spoofing the source IP address on a ping causes all ping responses to be sent to the victim, inundating the victim
What is amplification?
Transformation of small amounts of traffic to larger amounts
What is NTP?
A UDP-based protocol that synchronises time keeping among computers
What does NTP stand for?
Network Time Protocol
How does an NTP client synchronise with an NTP server?
1. NTP client sends the server an NTP message with its local time on the timestamp (T1)
2. NTP server receives the message, and timestamps it with the server's local time (T2)
3. NTP server sends the message back to client with another timestamp (T3)
4. NTP client timestamps the message again with its arrival time (T4)
How do we calculate roundtrip delay of an NTP message?
T4 - T1
How do we calculate processing time at the NTP server on an NTP message?
T3 - T2
How do we calculate roundtrip delay of an NTP message on the network?
(T4 - T1) - (T3 - T2)
How do we calculate clock offset between an NTP client and NTP server?
( (T2 - T1) + (T3 - T4) ) / 2
What is an NTP amplification attack?
Use publicly accessible NTP servers to overwhelm a victim with UDP traffic
What is `monlist`?
A command provided by NTP monitoring services such as Ntpd that returns the list of recent hosts connected to the service
Briefly, how is an NTP amplification attack performed?
- Use a spoofed IP address in an NTP request message, and ask the NTP server to run the `monlist` command
- NTP server then sends an NTP response to the victim with all of the IP addresses, causing DoS
How large could the amplification factor be for an NTP amplification attack?
Up to 206x the size of the initial NTP request