FEMA NIMS/ICS
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Incident Command System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
ICS
Incident Command System
What is ICS?
A standardized approach to incident management. Is a part of the National Incident Management System (NIMS)
What are the features of ICS?
ICS features a manageable span of control.
Designated Incident Facilities
Resource Management
Dispatch/Deployment
Integrated Communications
Information and Intelligence Management
When is ICS used?
To manage any type of incident including planned events. It is applicable to all types of incidences regardless of of size or cause.
What are the 3 major components of NIMS (National Incident Mgmt. System)?
Resource Management
Command and Coordination including ICS
Communication and Info Mgmt.
Incident Action Plan (IAP)
Covers what is happening during the operational period of an incident.
It includes:
What must be done.
Who is responsible.
How info is communicated.
What should be done if someone is injured.

Span of Control
The number of individuals or resources that one supervisor can manage effectively during an incident. The optimal span of control ratio is 1:5 (1 supervisor for every 5 subordinates)
What support facilities can the ICS establish?
1) Incident Command Post (ICP)
2) Incident based staging areas and camps (think arrest teams, decon, etc.)
3) mass casualty triage areas/decon areas etc.
4) point of Distribution
5) Emergency Shelters
What are the 5 major ICS functional areas?
Command, Operations, Planning, Logistics and finance/admin
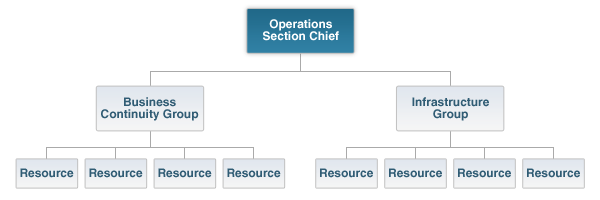
ICS Operations Section Responsibilities
Implement strategies to carry out incident objectives
Directs the management of all tactical activities on behalf of the Incident Commander
Supports development of IAP to ensure it reflects current operations
Organizes, assigns and supervises the tactical response resources
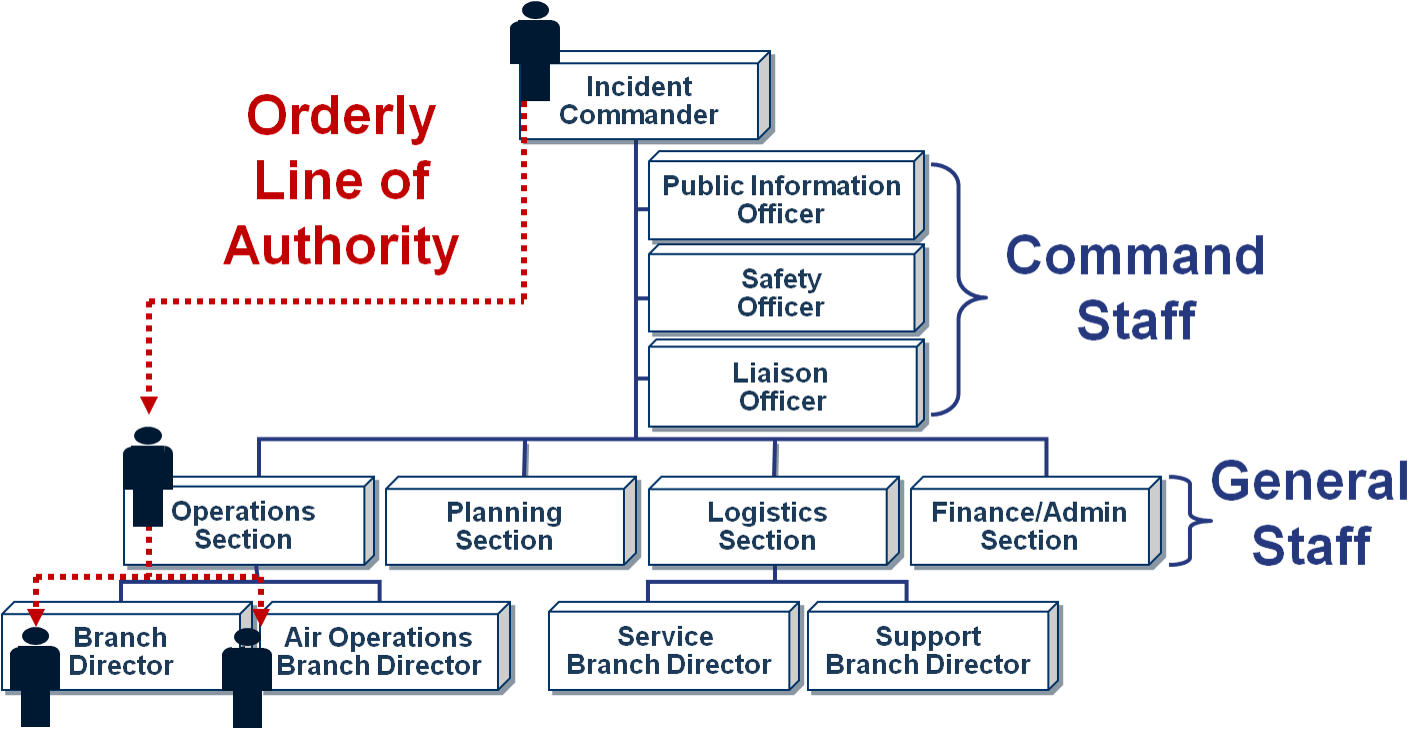
Chain of Command within the ICS
A system that clarifies the roles, responsibilities, and hierarchy within an organization during an incident, ensuring clear lines of authority and accountability.
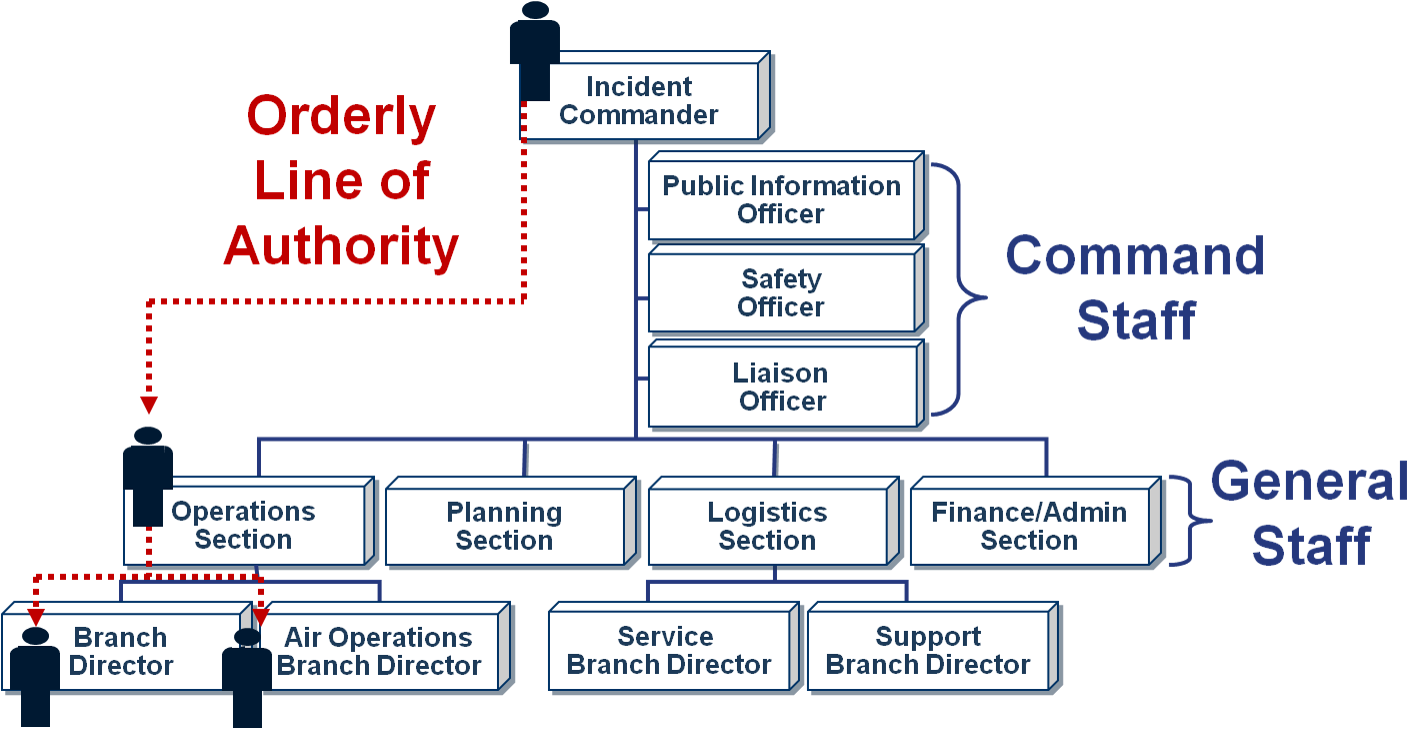
Chain of Command
Incident managers at all levels must be able to control the actions of all personnel under their supervision. The chain of command refers to each section and how they lead their section from information that flows down from the Incident Command Post/Commander.
Unified Command
When no one jurisdiction, agency, or organization has primary authority and/or the resources to manage an incident on its own. This approach brings together representatives from various organizations to effectively manage the incident collaboratively. The Unified Command can allocate resources regardless of ownership or location.
Unity of Command
Means that each individual involved in incident operations will be assigned – and will report – to only one supervisor.
NIMS
National Incident Management System provides the Nation's first responders and authorities with the same foundation for incident management.
NIMS Management Characteristics
Common Terminology
Modular Organization
Management by Objectives
Incident Action Planning
Manageable Span of Control
Incident Facilities and Locations
Comprehensive Resource Management
Integrated Communications
Establishment and Transfer of Command
Unified Command
Chain of Command and Unity of Command
Accountability
Dispatch/Deployment
Information and Intelligence Management
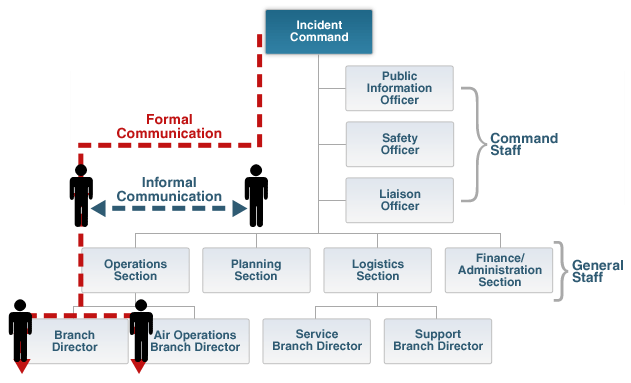
Integrated Communication
Formal communication must be used when:
Receiving and giving work assignments
Requesting support or additional resources
Reporting progress of assigned tasks
Other information concerning the incident or event can be passed horizontally or vertically within the organization without restriction. This is known as informal communication.
Informal Communication with the ICS is used…
to exchange incident or event information only.
Common Leadership Responsibilities
Communicates by giving specific instructions and asking for feedback.
Supervises the scene of action.
Evaluates the effectiveness of the plan.
Understands and accepts the need to modify plans or instructions.
Ensures safe work practices.
Takes command of assigned resources.
Motivates with a "can do safely" attitude.
Demonstrates initiative by taking action.
What should you do every day to ensure you are an effective leader?
Take charge within your scope of authority.
Be prepared to step out of a tactical role to assume a leadership role.
Be proficient in your job.
Make sound and timely decisions.
Ensure tasks are understood.
Develop your subordinates for the future.
Communication Responsibilities
Brief others as needed
Debrief their actions
Communicate hazards to others
Acknowledge messages
Ask if you do not know
Elements of a Briefing
Task- What needs to be done
Purpose- Why it should be done
End State- What it should look like when it is done
Incident Management Assessment
Corrective action report/After-Action Review (AAR)
Debriefing
Post-incident critique
Mitigation plans
Assessment of incident response effectiveness and areas for improvement.
Which Section is responsible for all support requirements needed to facilitate effective and efficient incident management, including ordering resources from off-incident locations?
Logistics

Typical Organizational Structure
Command: Incident Commander and other Command Staff
Single Resource: An individual, a piece of equipment and its personnel complement, or an established crew or team of individuals with an identified work supervisor that can be used on an incident

What are the overall priorities in an incident?
1) Life Safety
2) Incident Stabilization
3) Property Preservation
What do you have to consider during your initial response to an incident?
1) Nature and magnitude of the incident.
2) Hazard and Safety Concerns
hazards facing personnel and public
Evacuation and warnings
Injuries and casualties
Need to secure and isolate area
3) initial priorities and immediate resource requirements
4) location of ICP and staging area
5) entrance and exits routes for responders.
What do you need in order to have a successful incident response?
1) Objective- what u want to accomplish
2) Strategy- how you will accomplish the task.
3) Tactic- how you will execute the strategy.