✅️⭐️5 - Thoracic Limb Muscles & Joints 1
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
intrinsic
intrinsic
extrinsic
The ______ muscles join the forelimb to the trunk and consist of superficial and deep layers
2 multiple choice options
synsarcosis
The type of attachment of the thoracic limb to the trunk and neck is called _____ - arrangement of muscles without forming a conventional articulation between the scapula-humerus and the body
ball-and-socket/ spheroidal joint
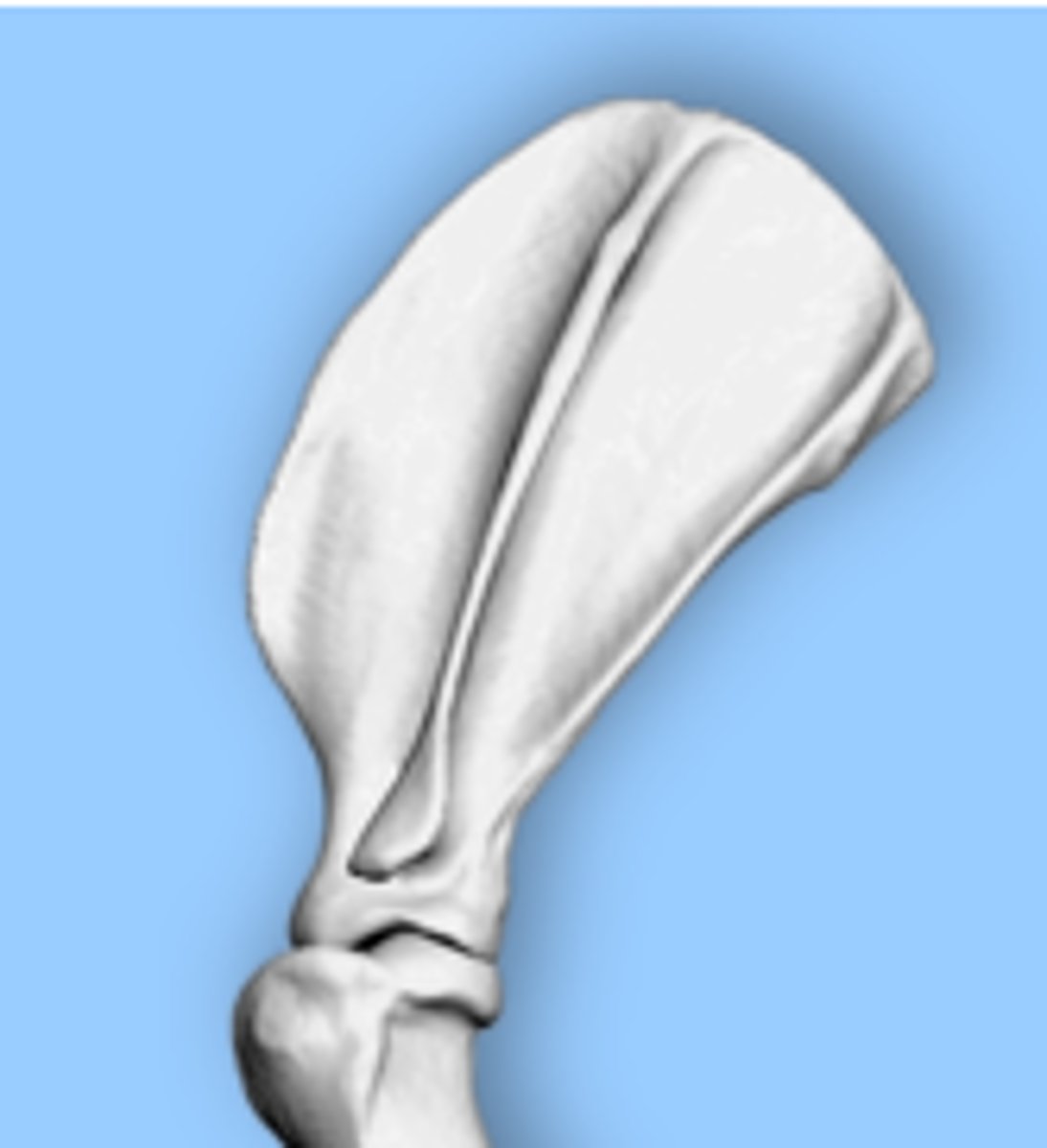
The shoulder consists of what type of joint?
reviewed
review
humeral
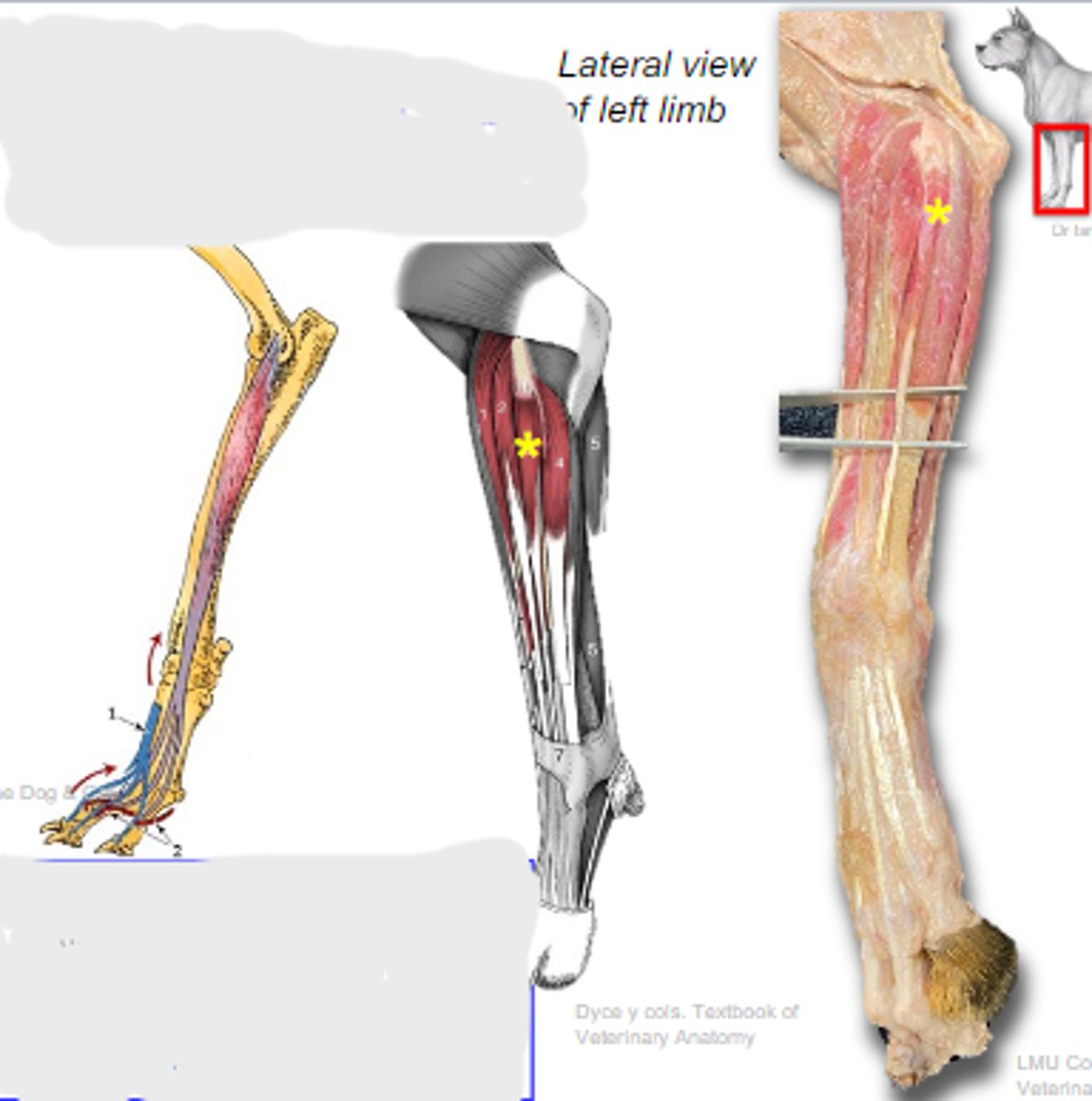
The lateral muscles of the shoulder act on what joint?
scapular and acromial
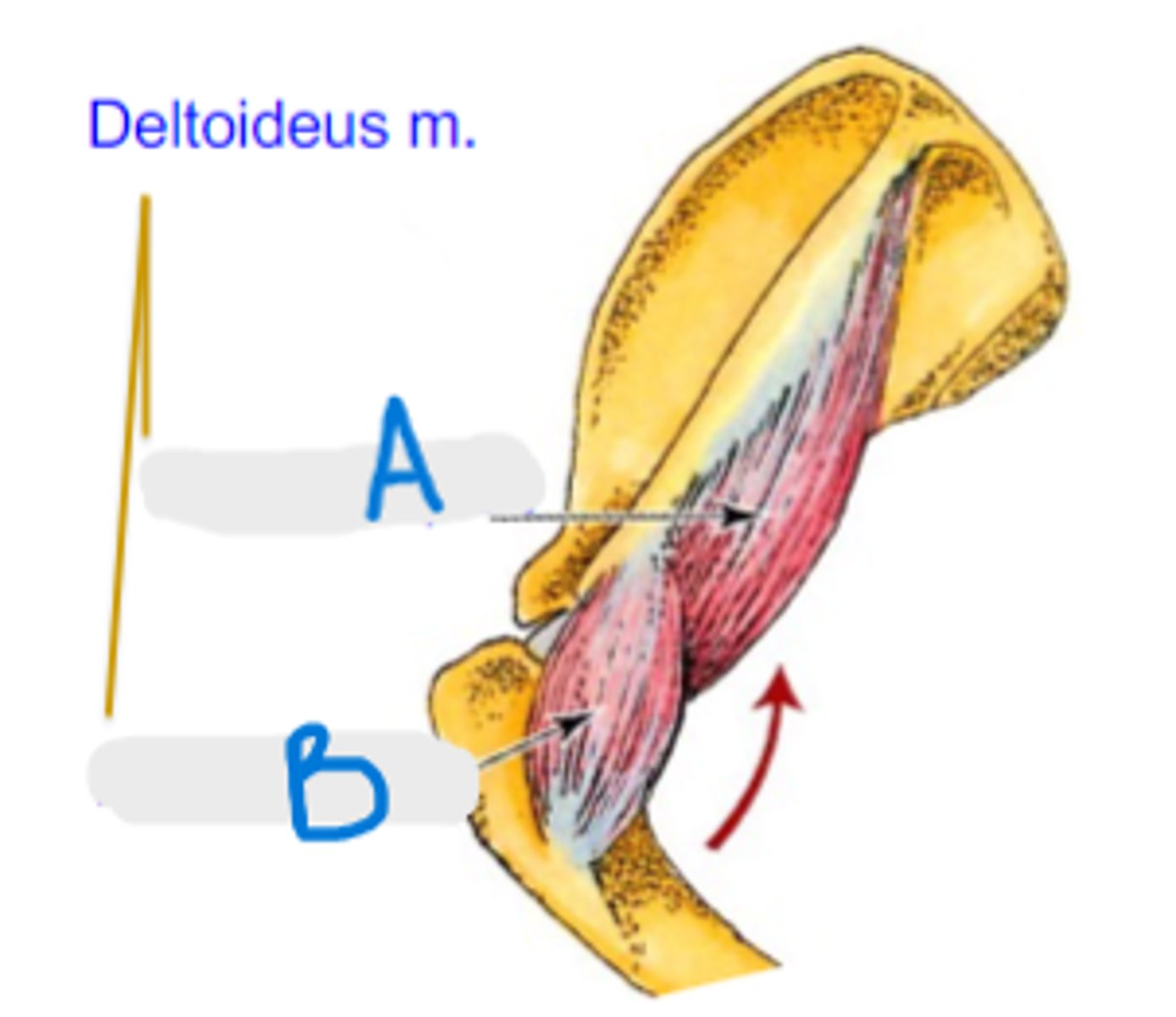
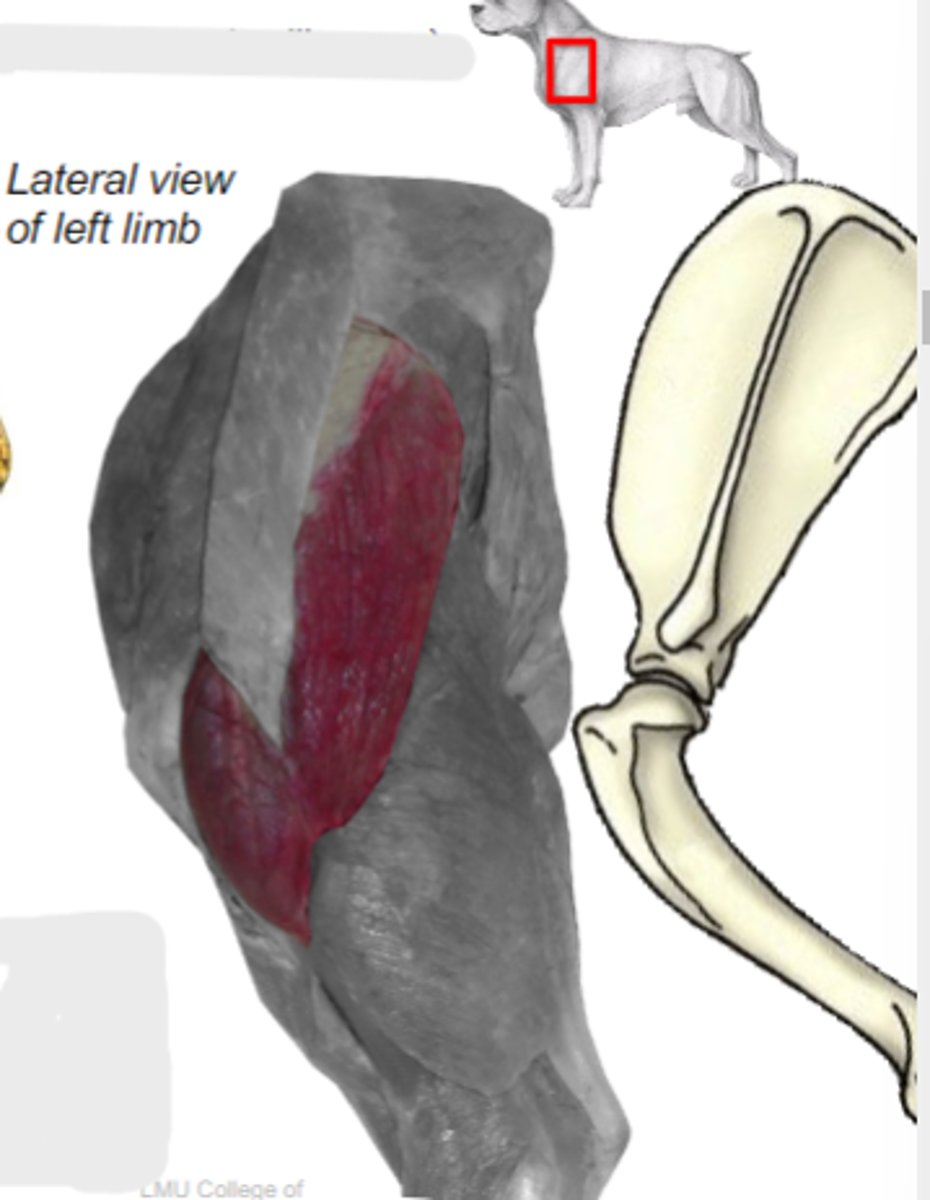
What are the 2 parts of the deltoideus muscle?
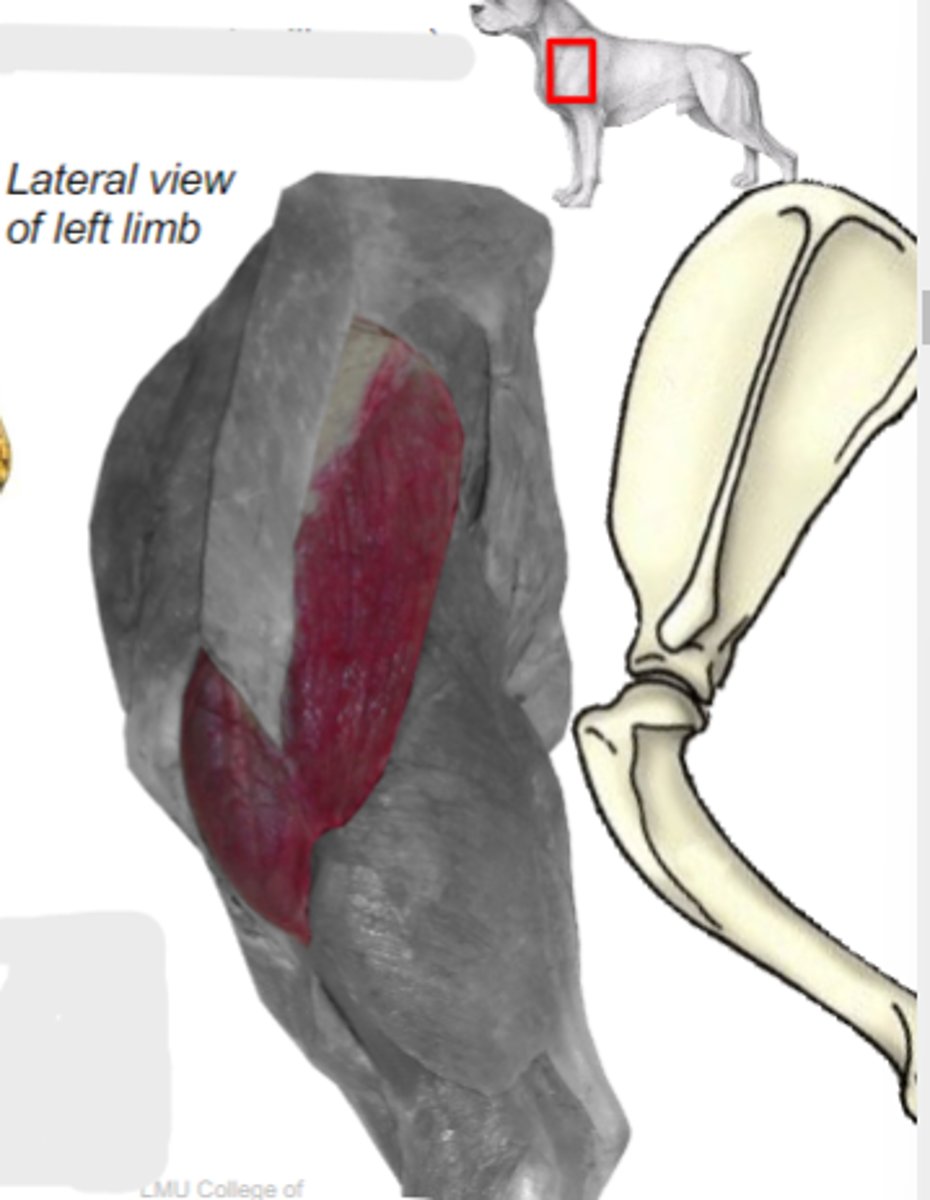
scapular part of deltoideus m.
What is A?
2 multiple choice options
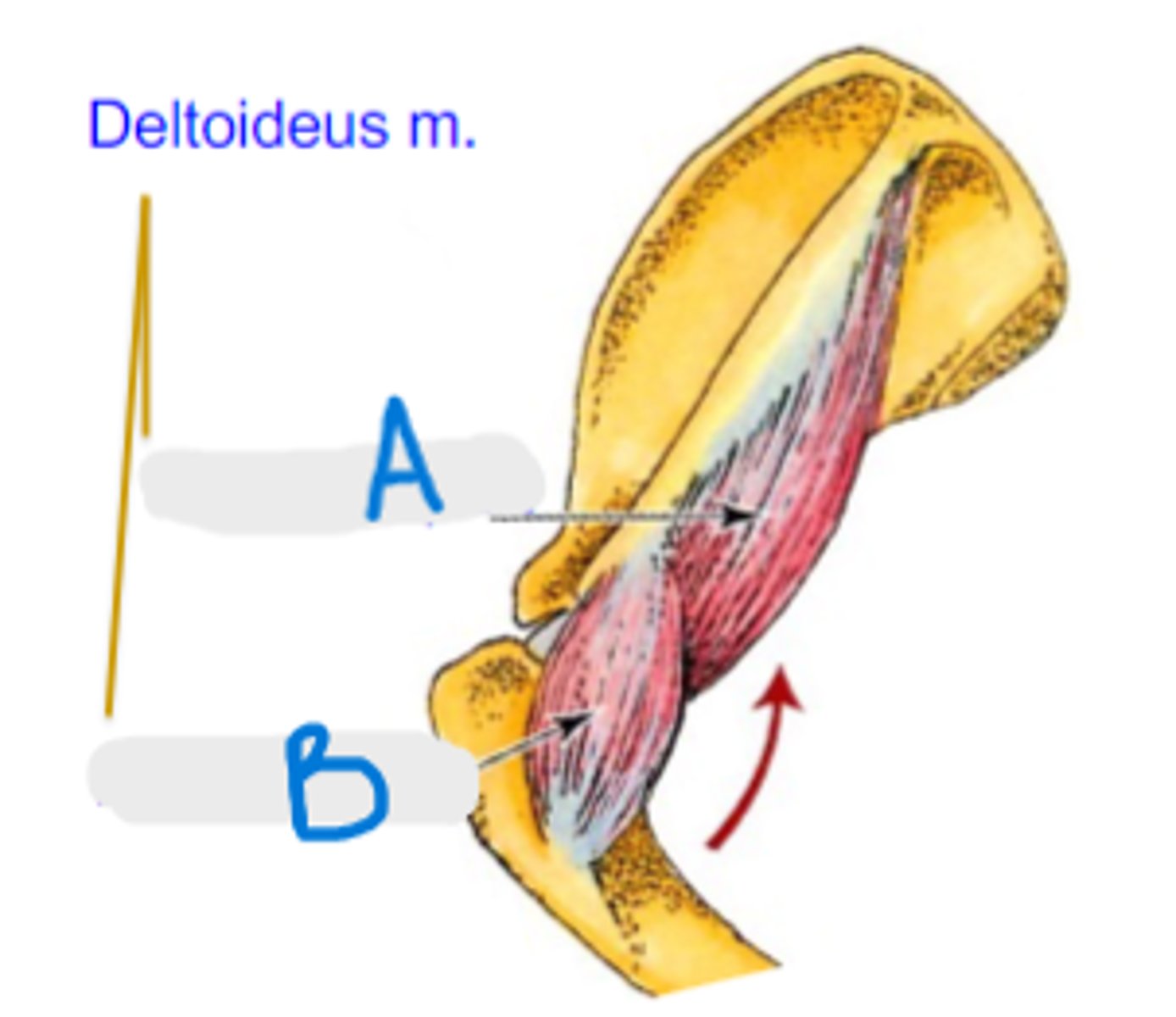
acromial part of deltoideus m.
What is B?
2 multiple choice options
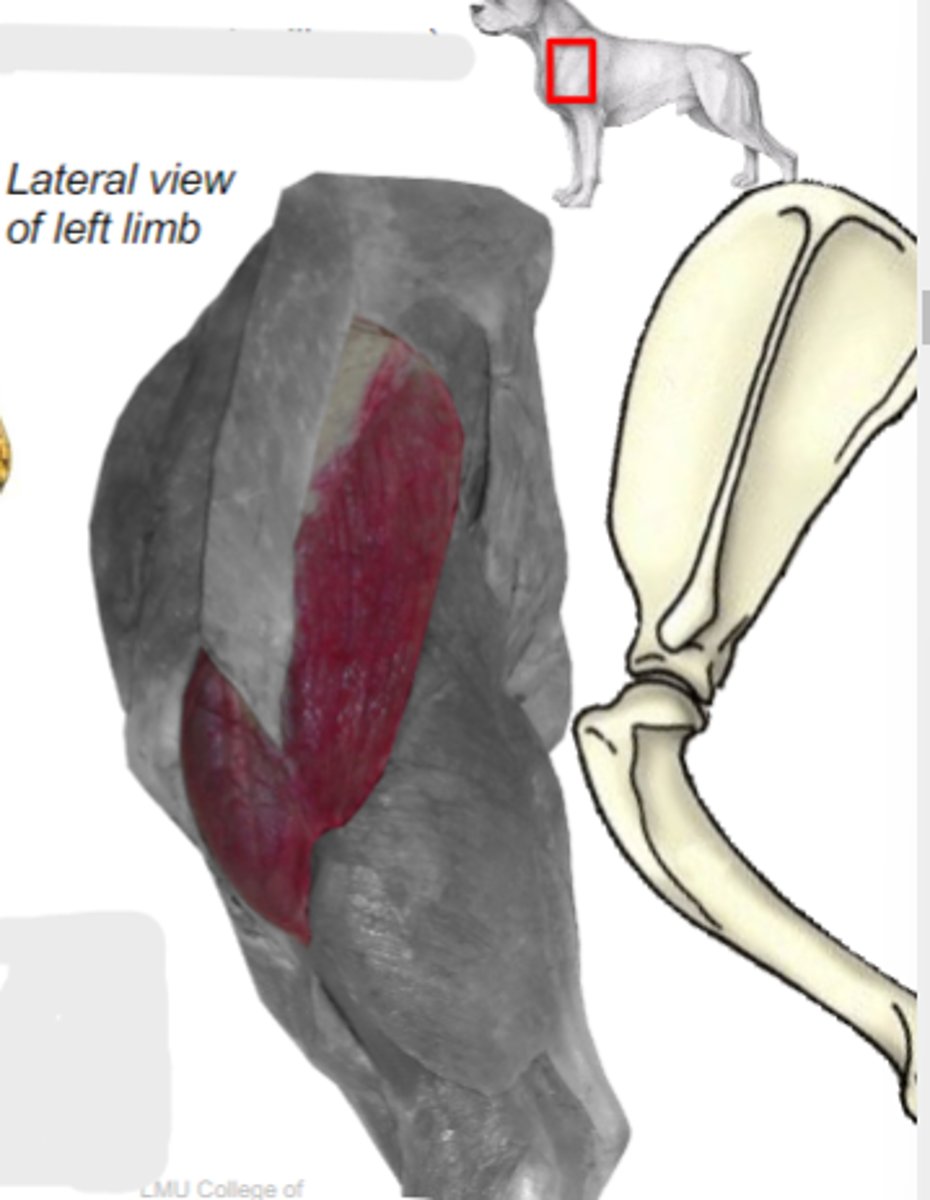
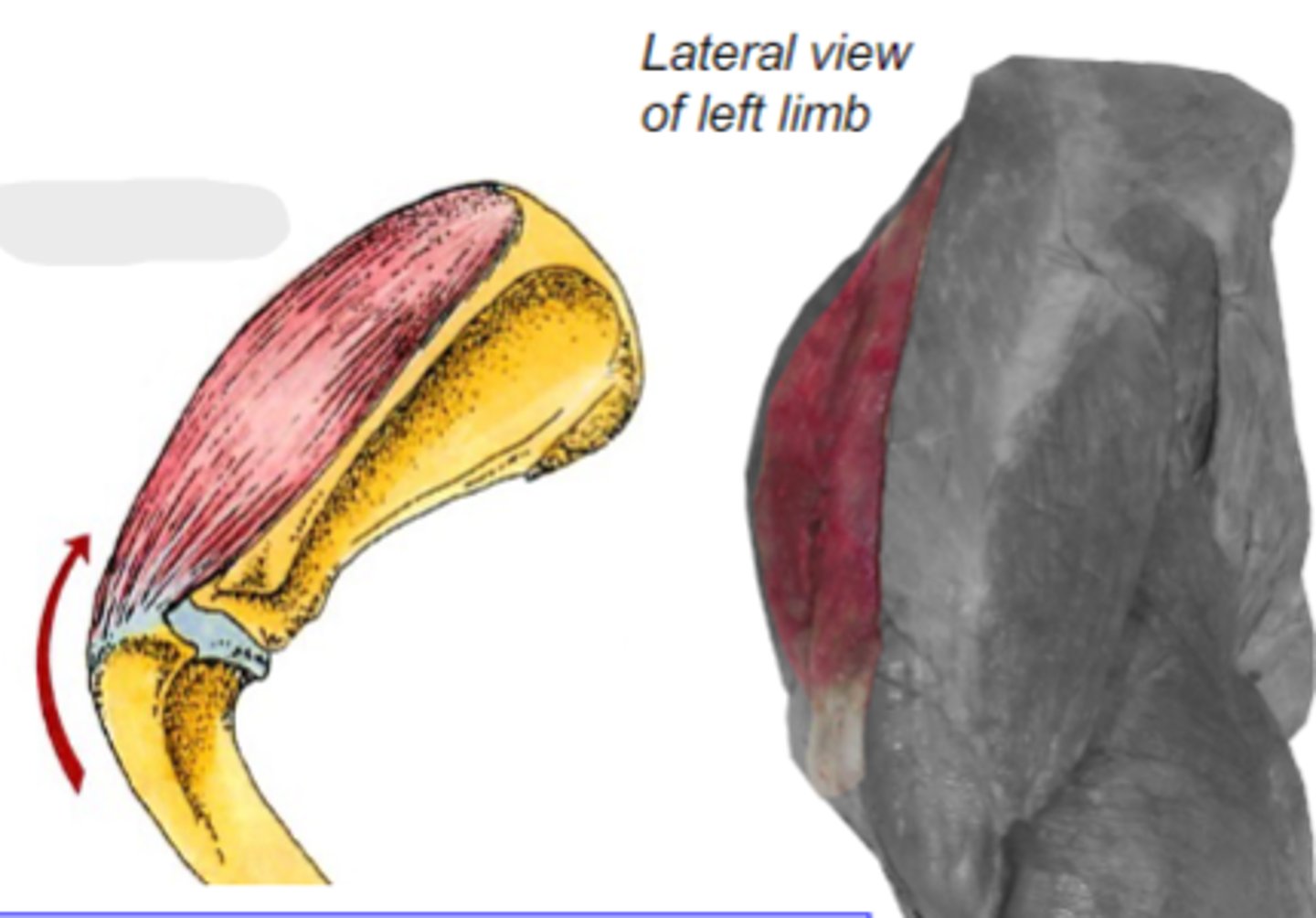
spine of scapula and acromion
Origin of deltoideus muscle:
deltoid tuberosity of humerus
Insertion of deltoideus muscle:
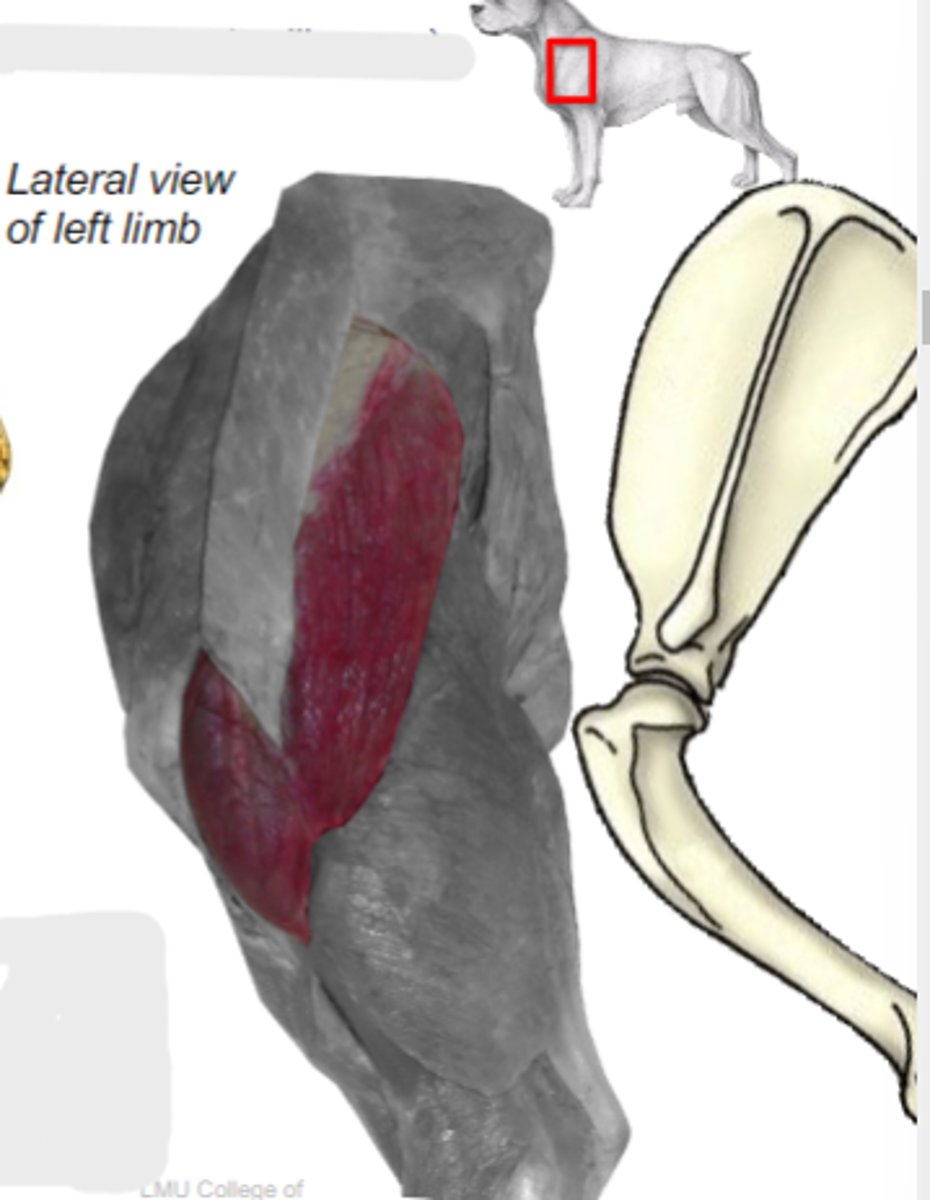
flex humeral joint
Action of deltoideus muscle:
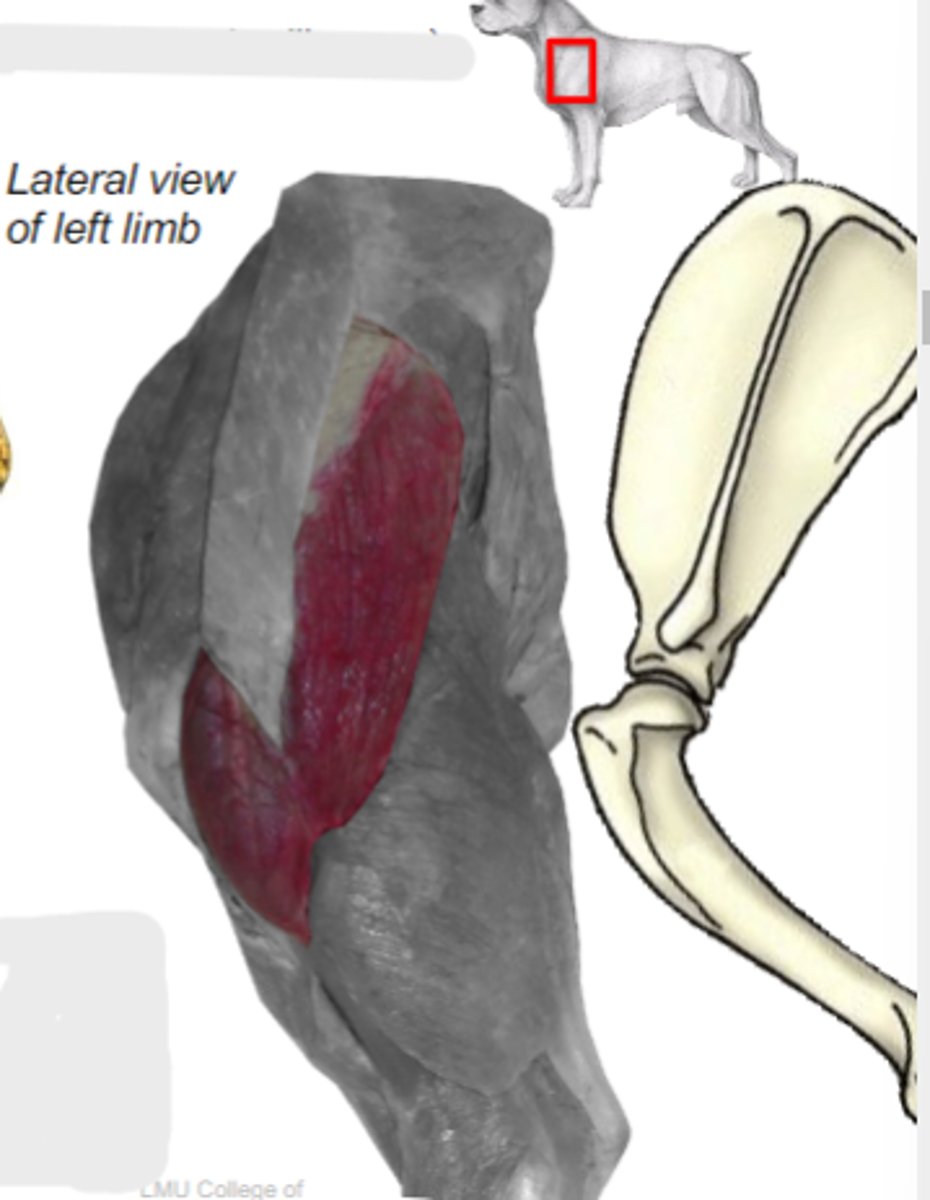
deltoideus
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: spine of scapula and acromion
Insertion: deltoid tuberosity of humerus
Action: flex the humeral joint
deltoideus
What muscle is shown?
suprascapular & axillary
What nerves are associated with the lateral muscles of the shoulder?
supraspinatus
What muscle is shown?
supraspinous fossa of the scapula
Origin of supraspinatus muscle:
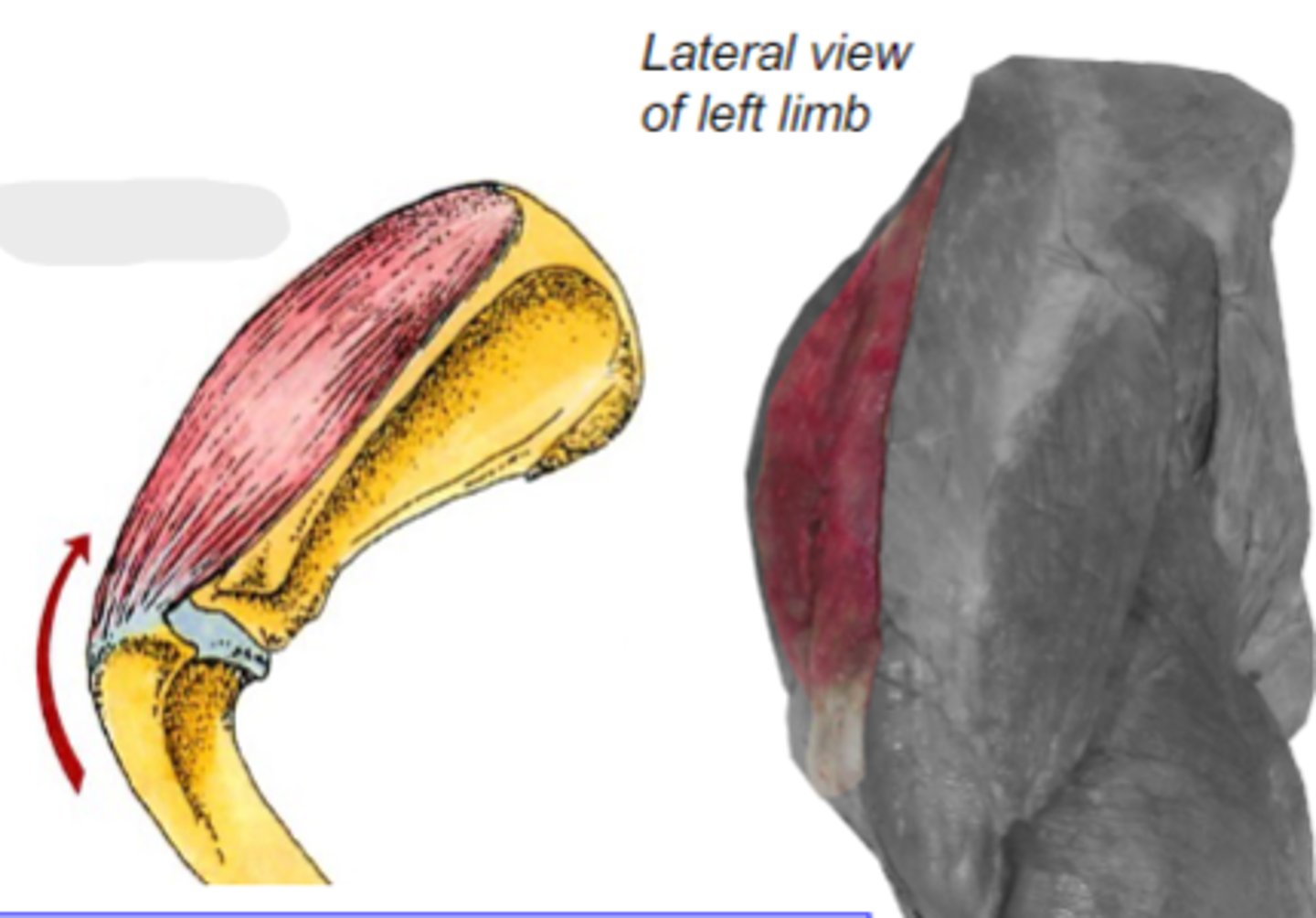
greater tubercle of humerus
Insertion of supraspinatus muscle:
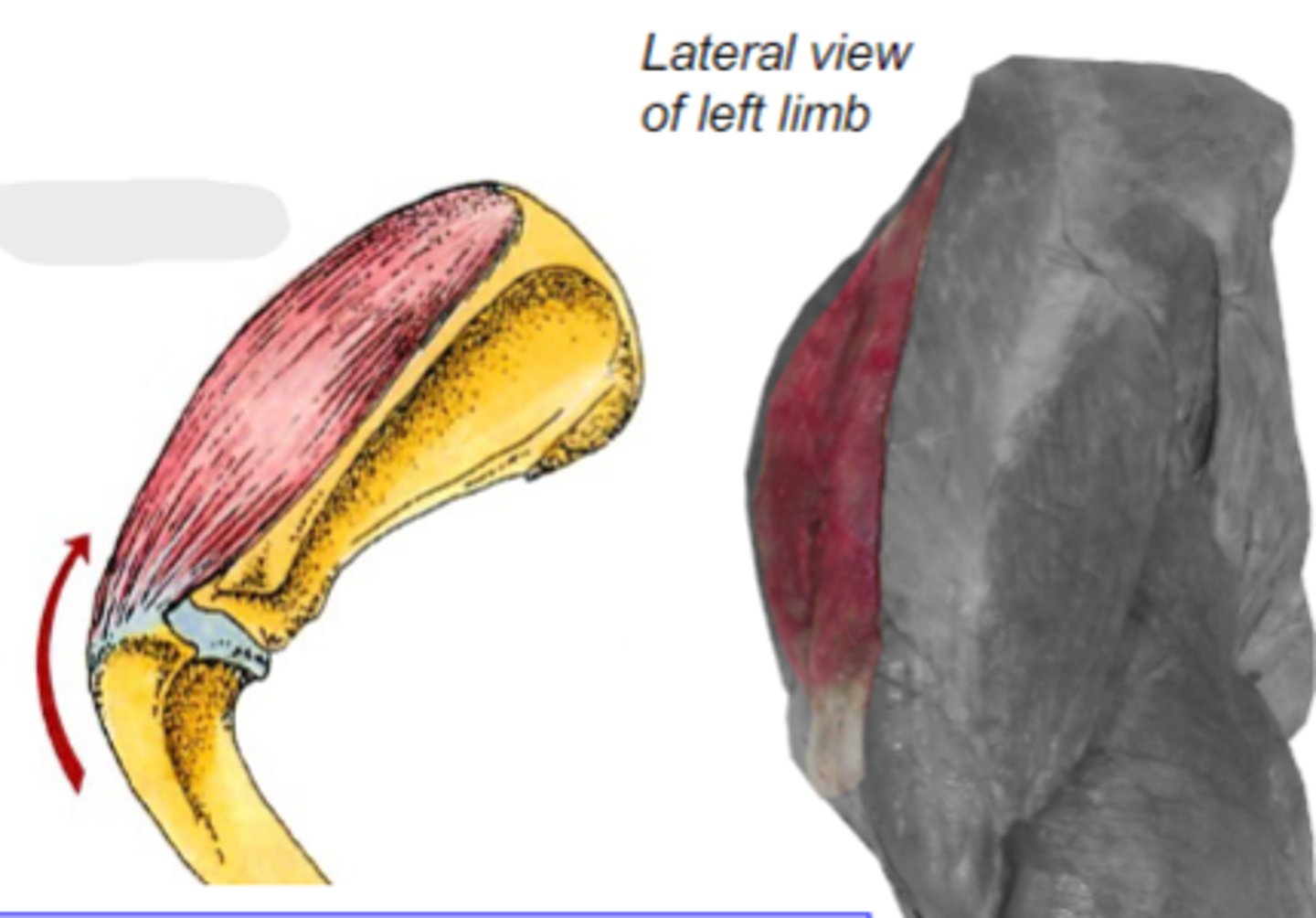
laterally stabilize humeral joint & extend the humeral joint
Action of supraspinatus muscle:
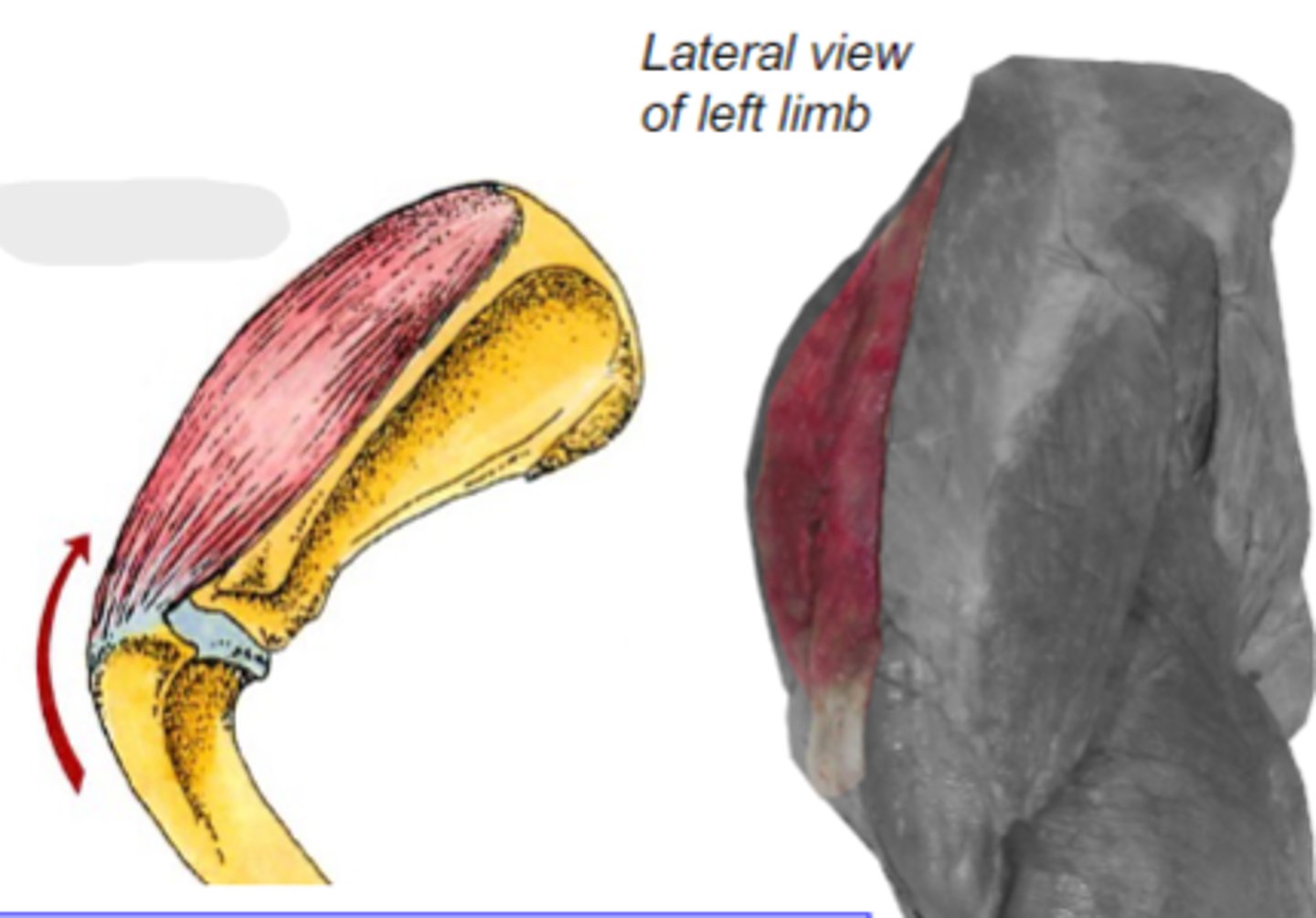
supraspinatus
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: supraspinous fossa of the scapula
Insertion: greater tubercle of the humerus
Action: laterally stabilize the humeral joint; extend the humeral joint
infraspinatus
What muscle is shown?
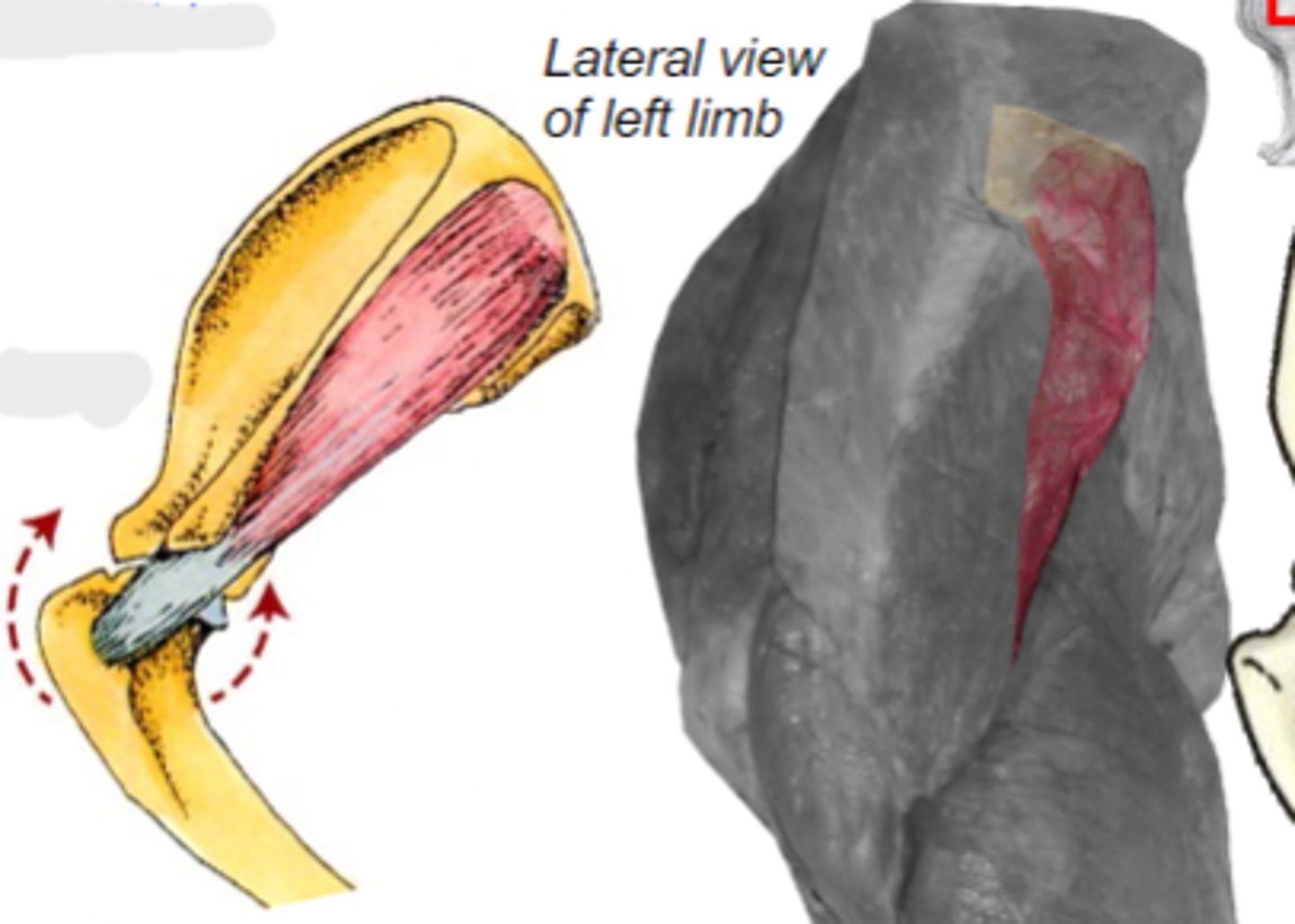
infraspinous fossa of scapula
Origin of infraspinatus muscle:
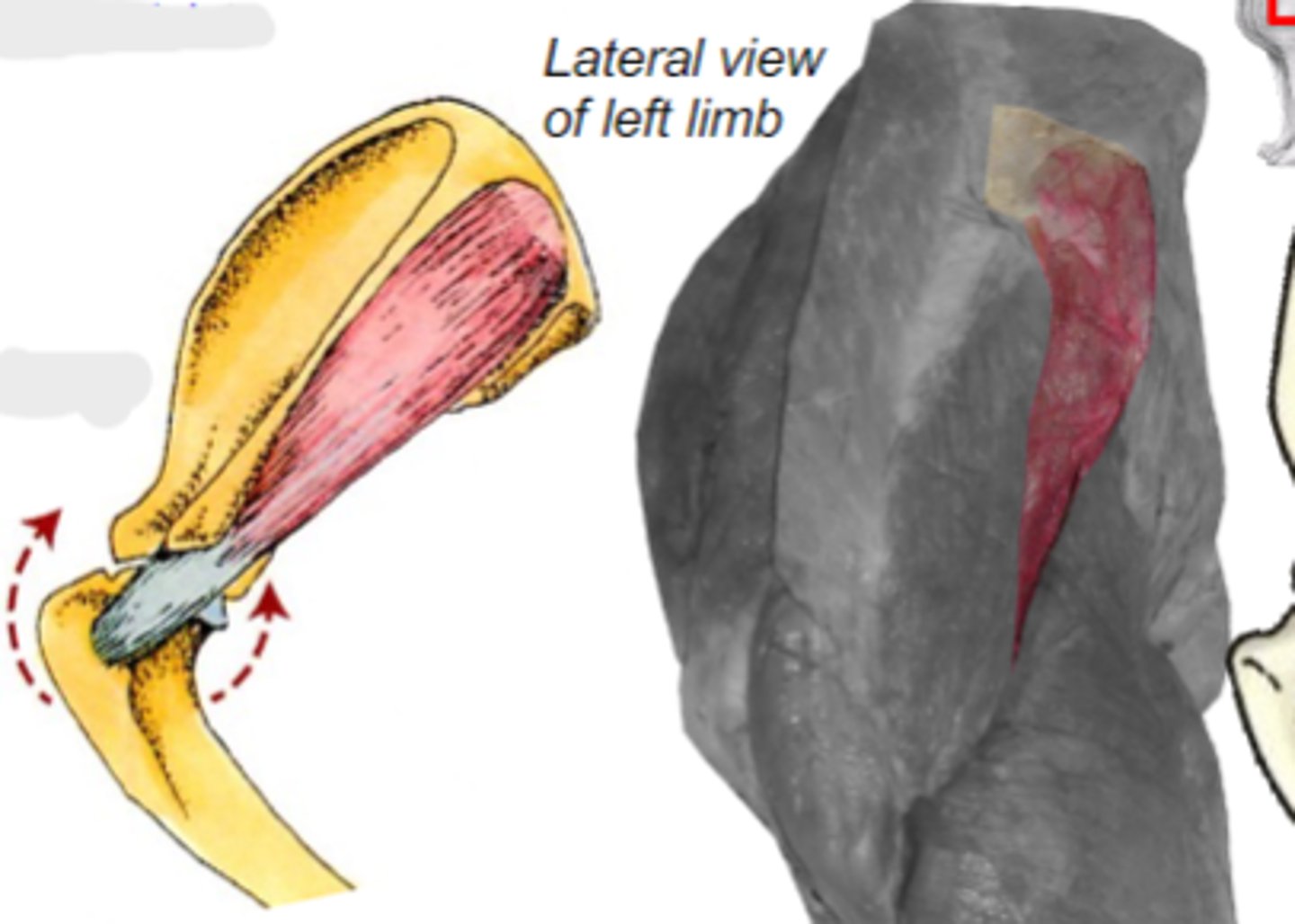
greater tubercle of humerus
Insertion of infraspinatus muscle:
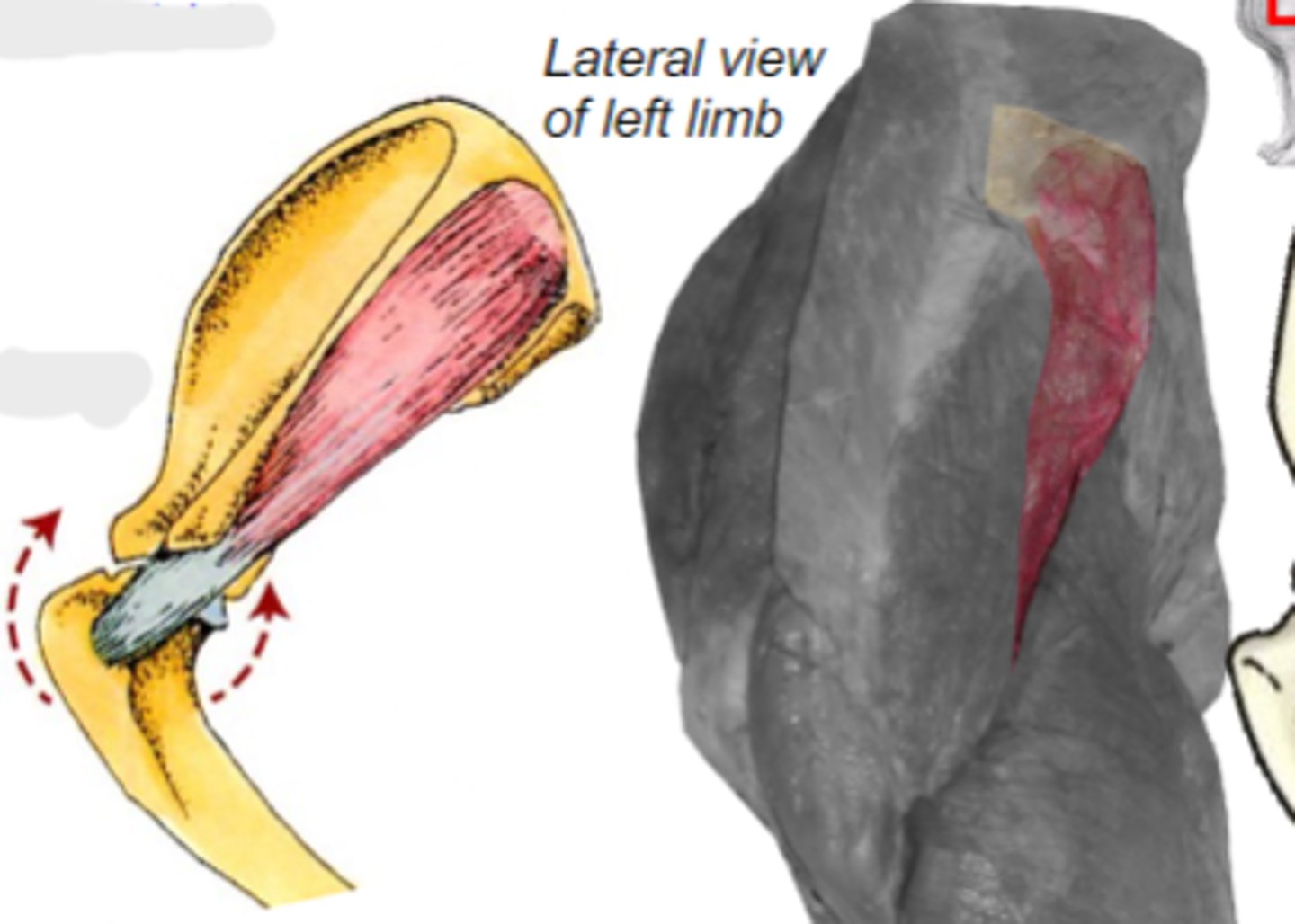
laterally stabilize humeral joint
Action of infraspinatus muscle:
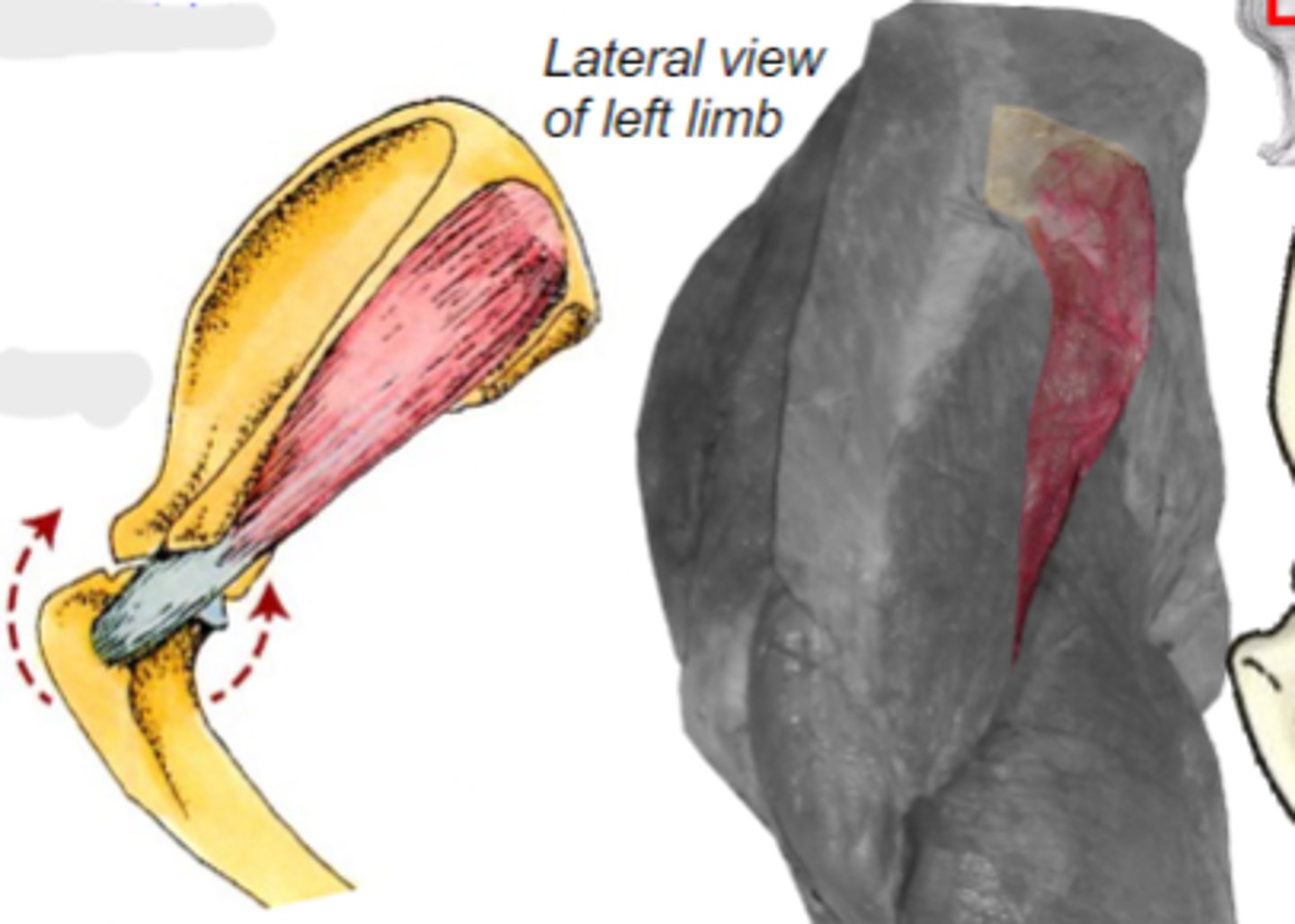
infraspinatus
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: infraspinous fossa of the scapula
Insertion: greater tubercle of the humerus
Action: laterally stabilize the humeral joint
spheroidal
The humeral joint is a _____ joint
teres minor
What muscle is shown?
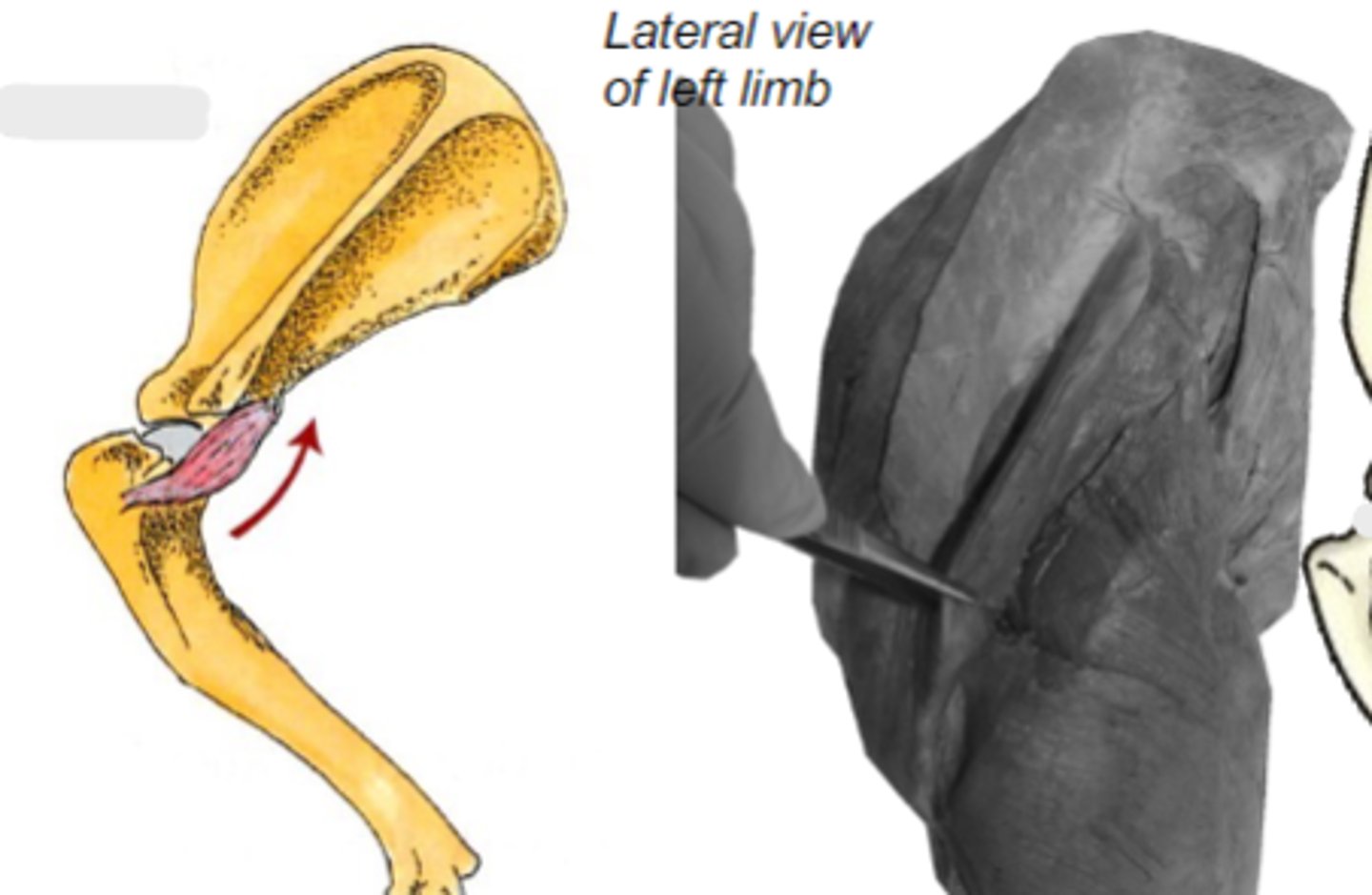
caudal border of scapula
Origin of teres minor:
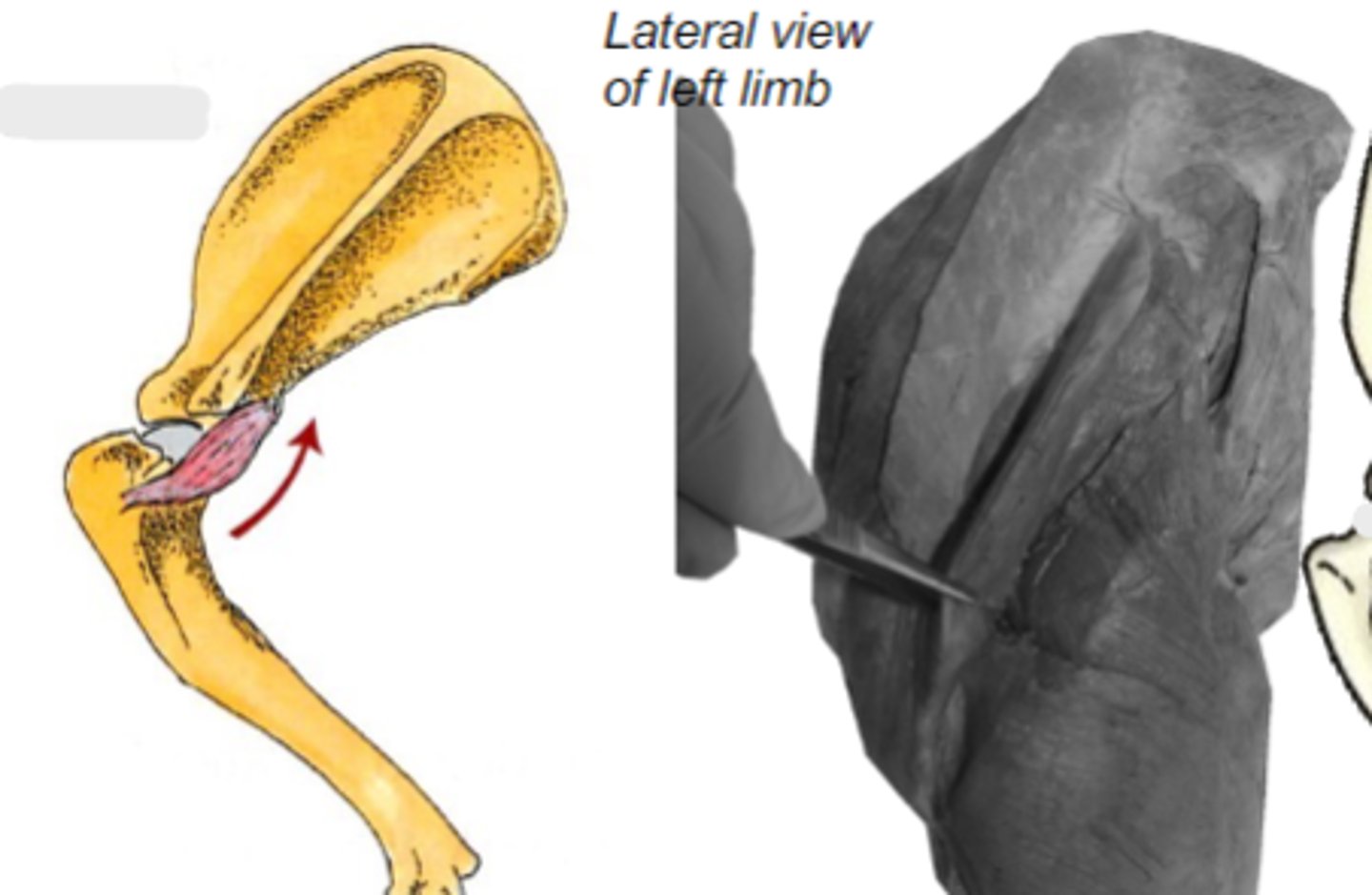
teres minor tuberosity of humerus
Insertion of teres minor:
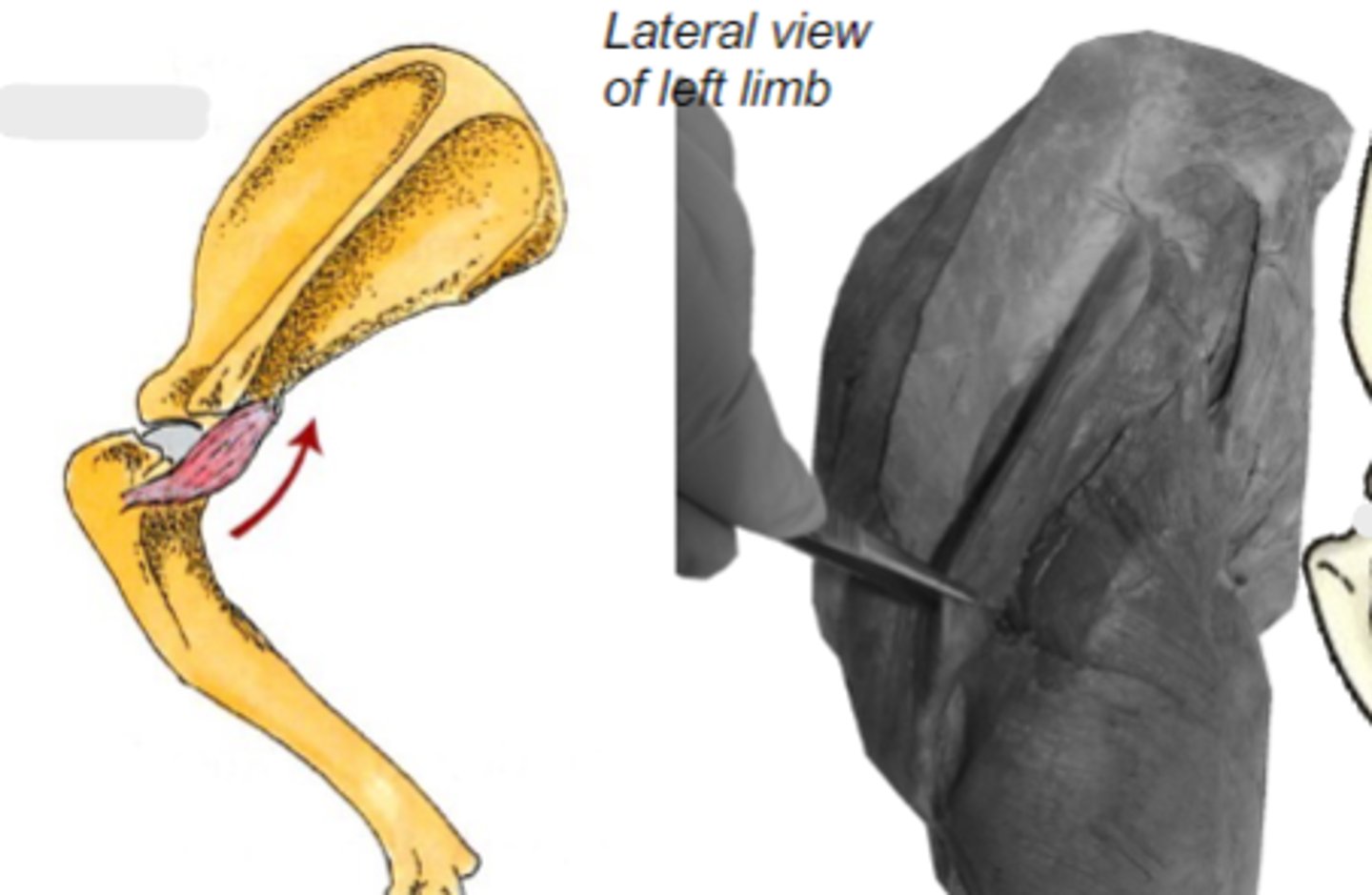
flex humeral joint
Action of teres minor:
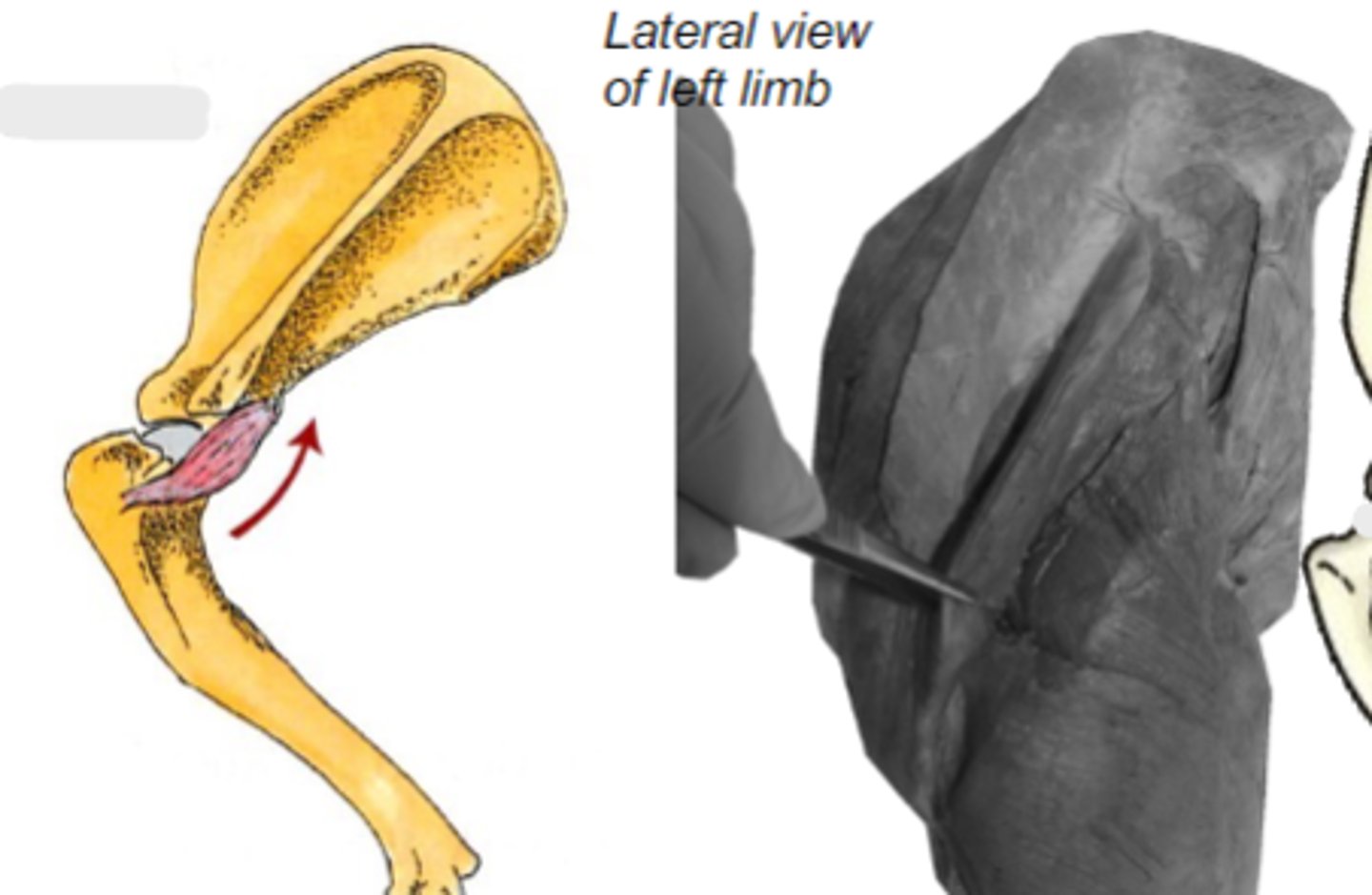
teres minor
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: caudal border of scapula
Insertion: teres minor tuberosity of the humerus
Action: flex the humeral joint
subscapularis
What muscle is shown?
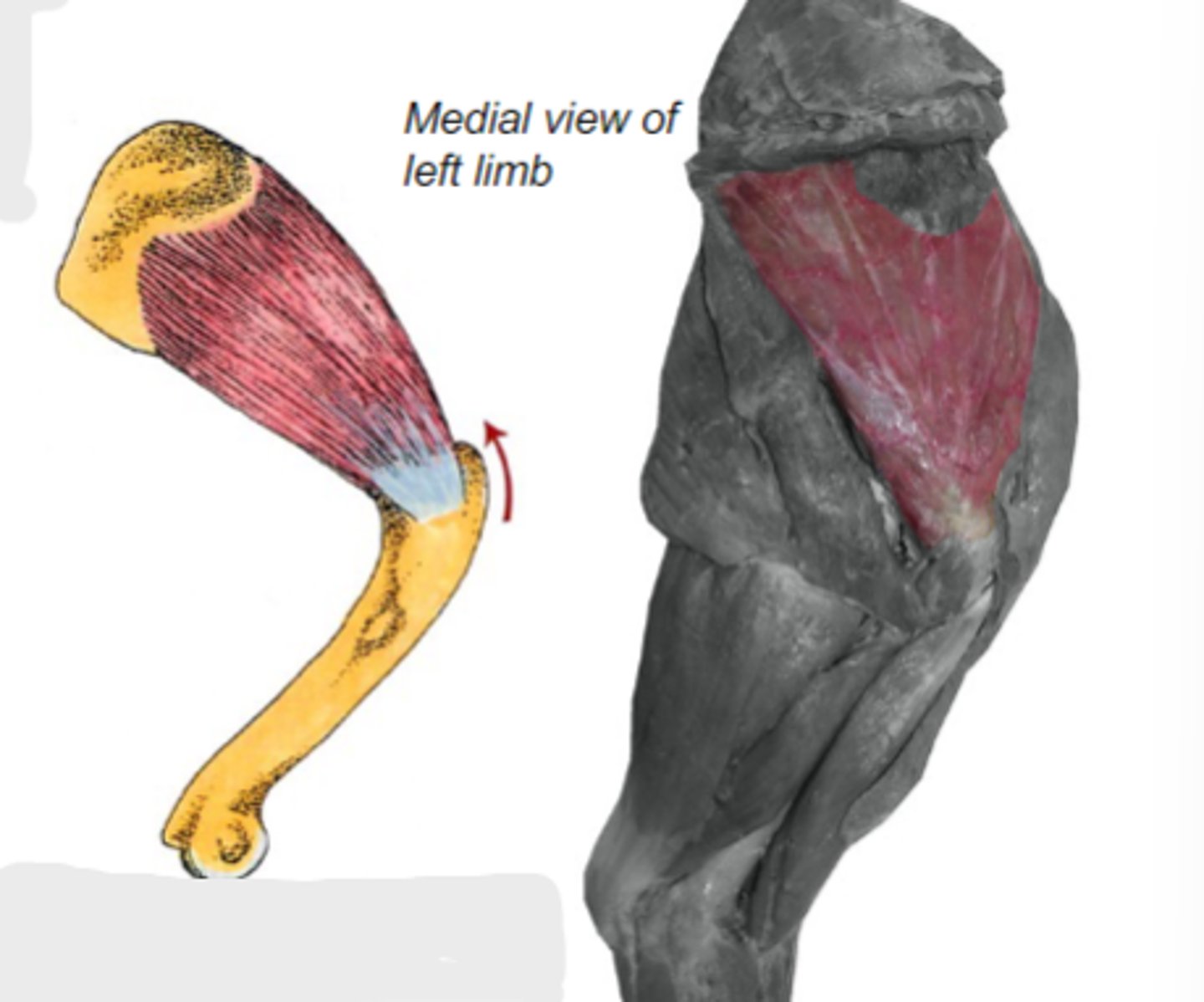
subscapular fossa of scapula
Origin of subscapularis:
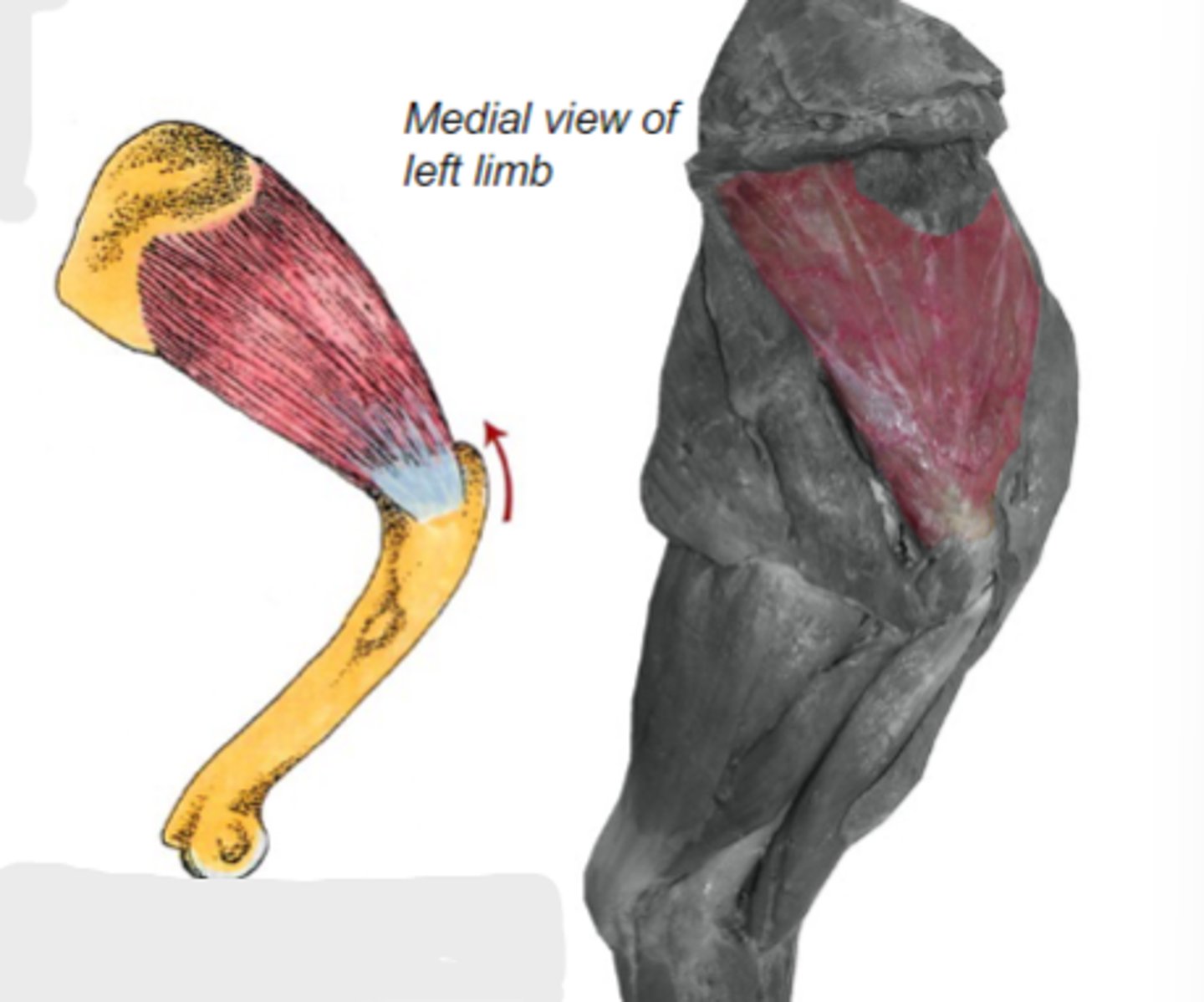
lesser tubercle of humerus
Insertion of subscapularis:
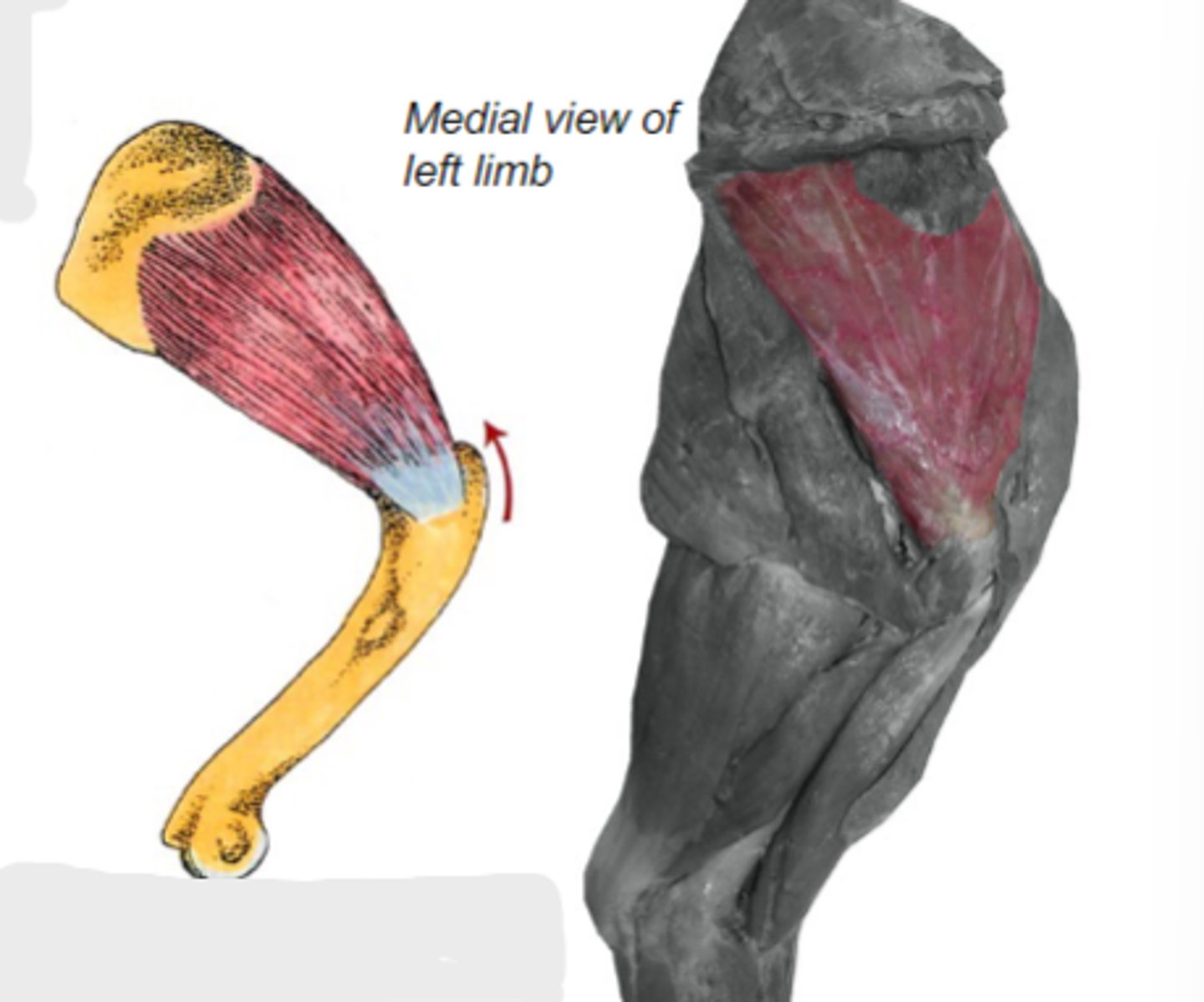
medially stabilize humeral joint
Action of subscapularis:
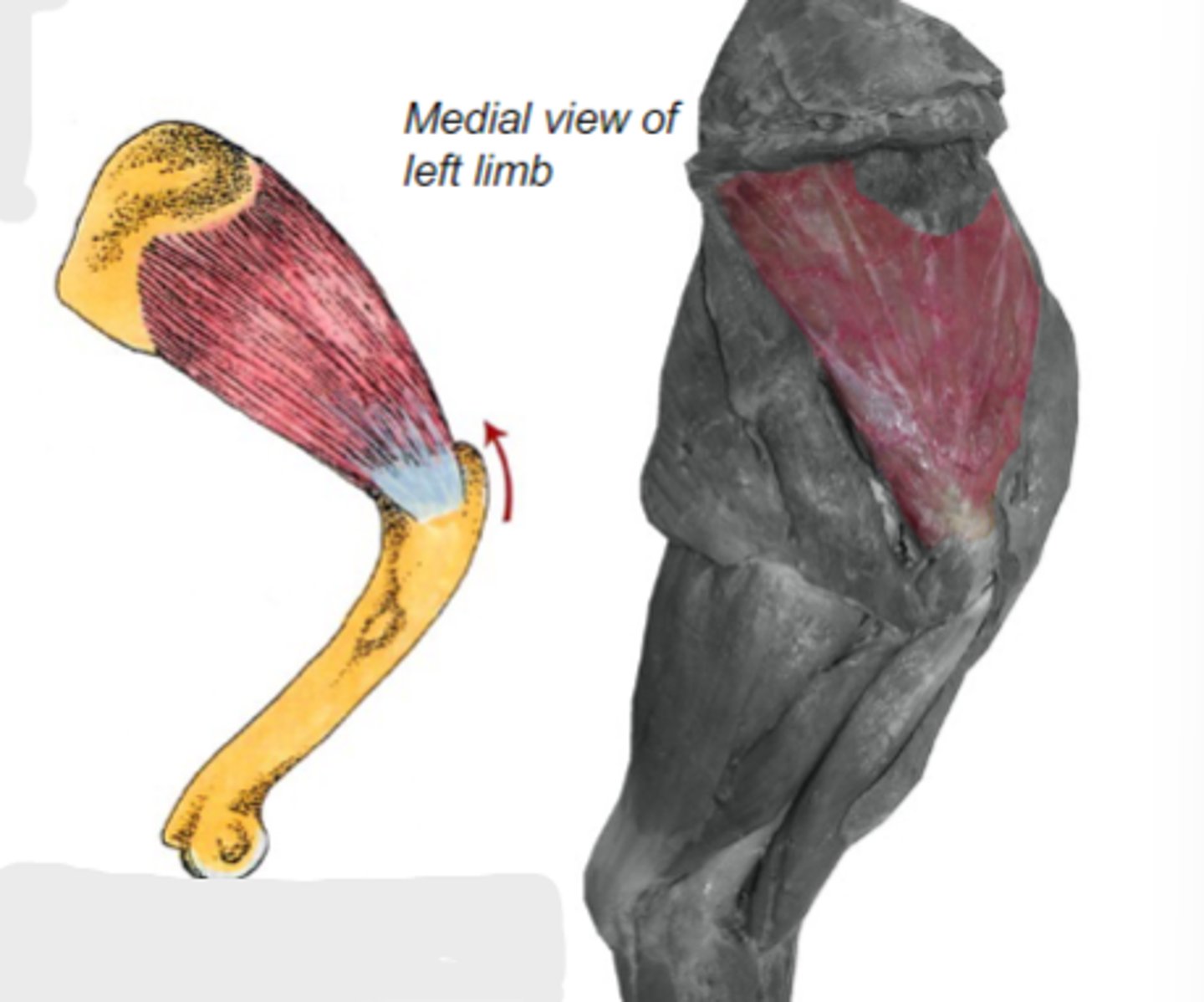
subscapularis
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: subscapular fossa of scapula
Insertion: lesser tubercle of humerus
Action: medially stabilize the humeral joint
teres major
What muscle is shown?
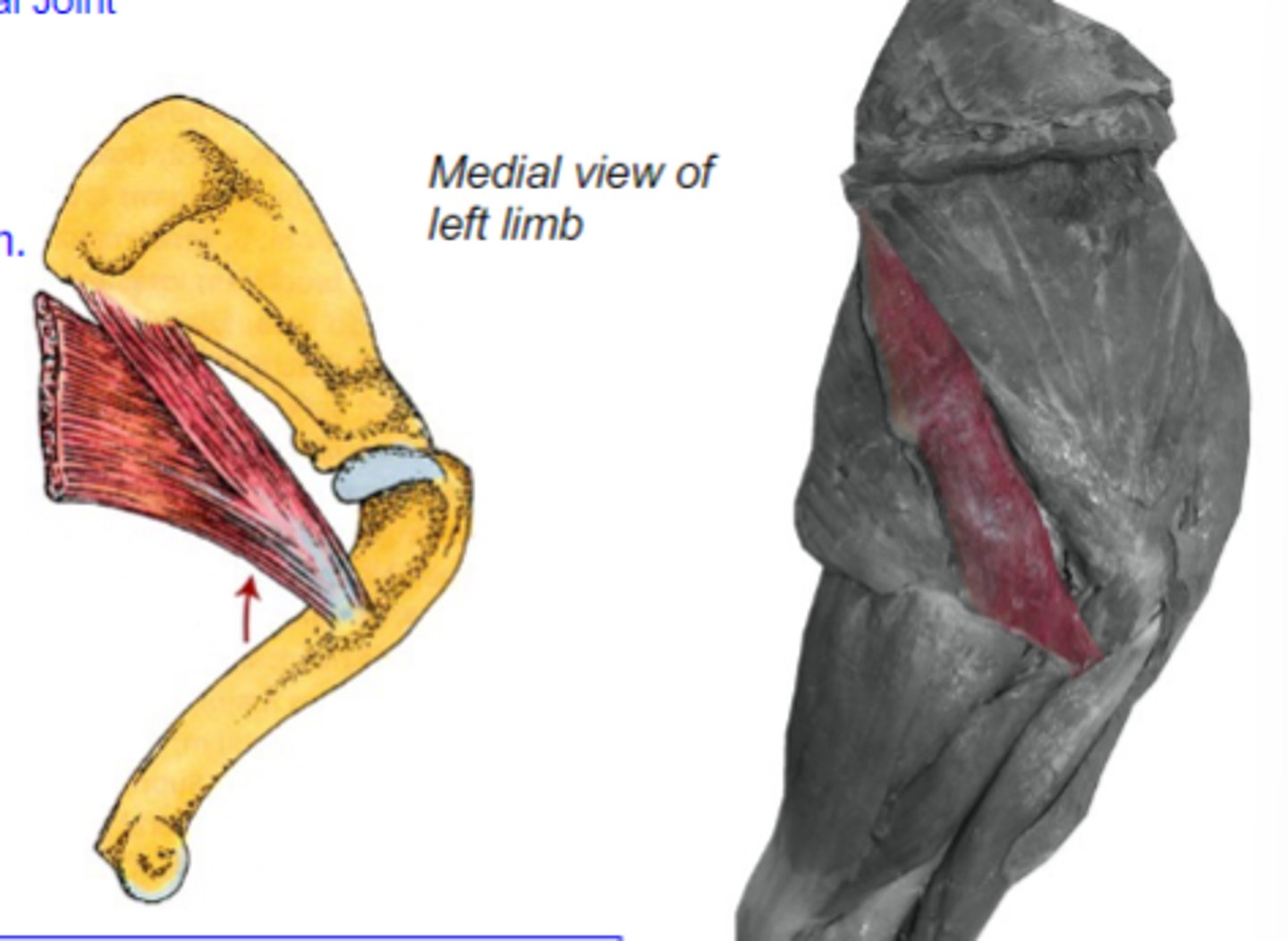
caudal border of scapula
Origin of teres major:
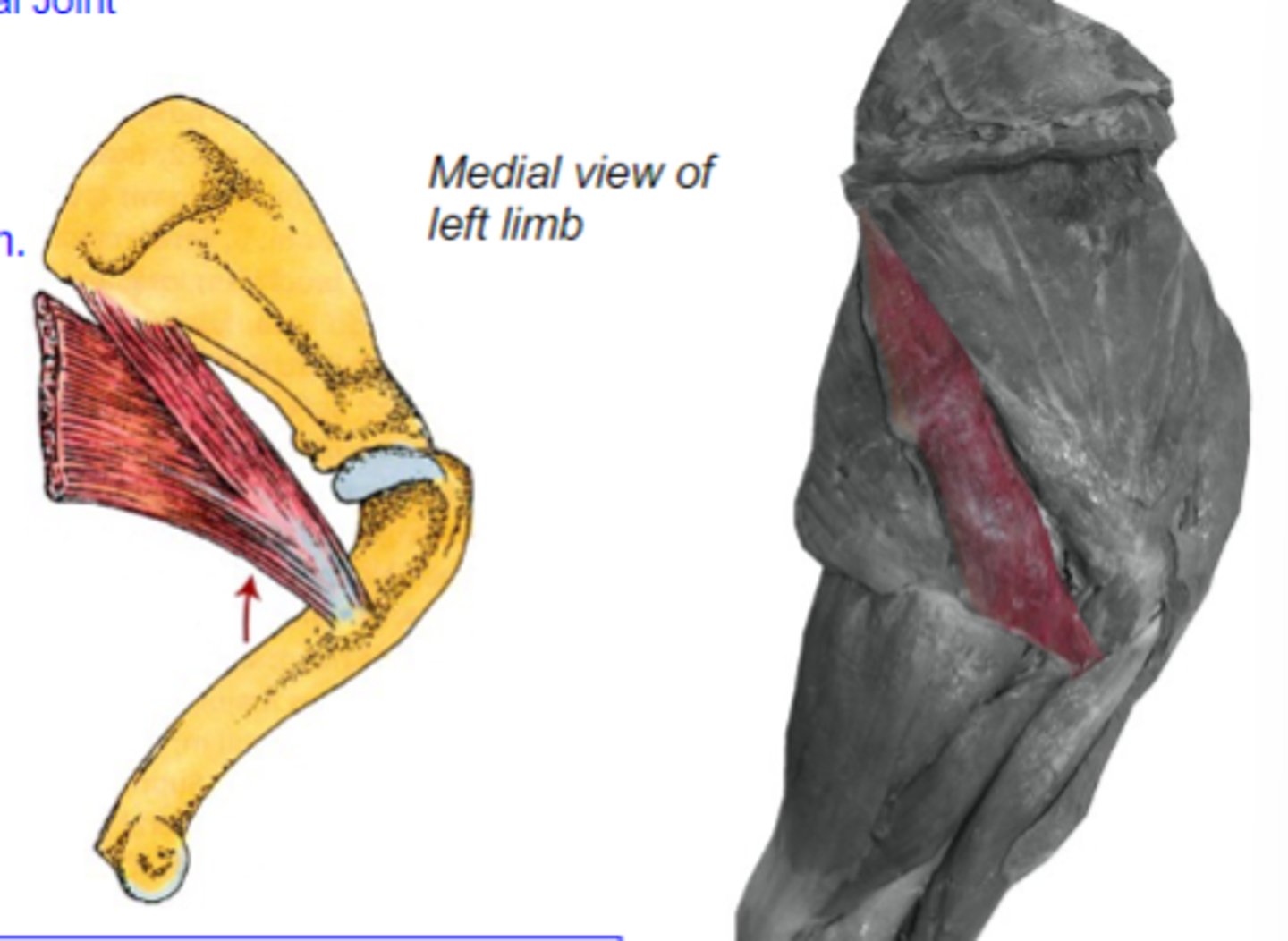
teres major tuberosity of humerus
Insertion of teres major:
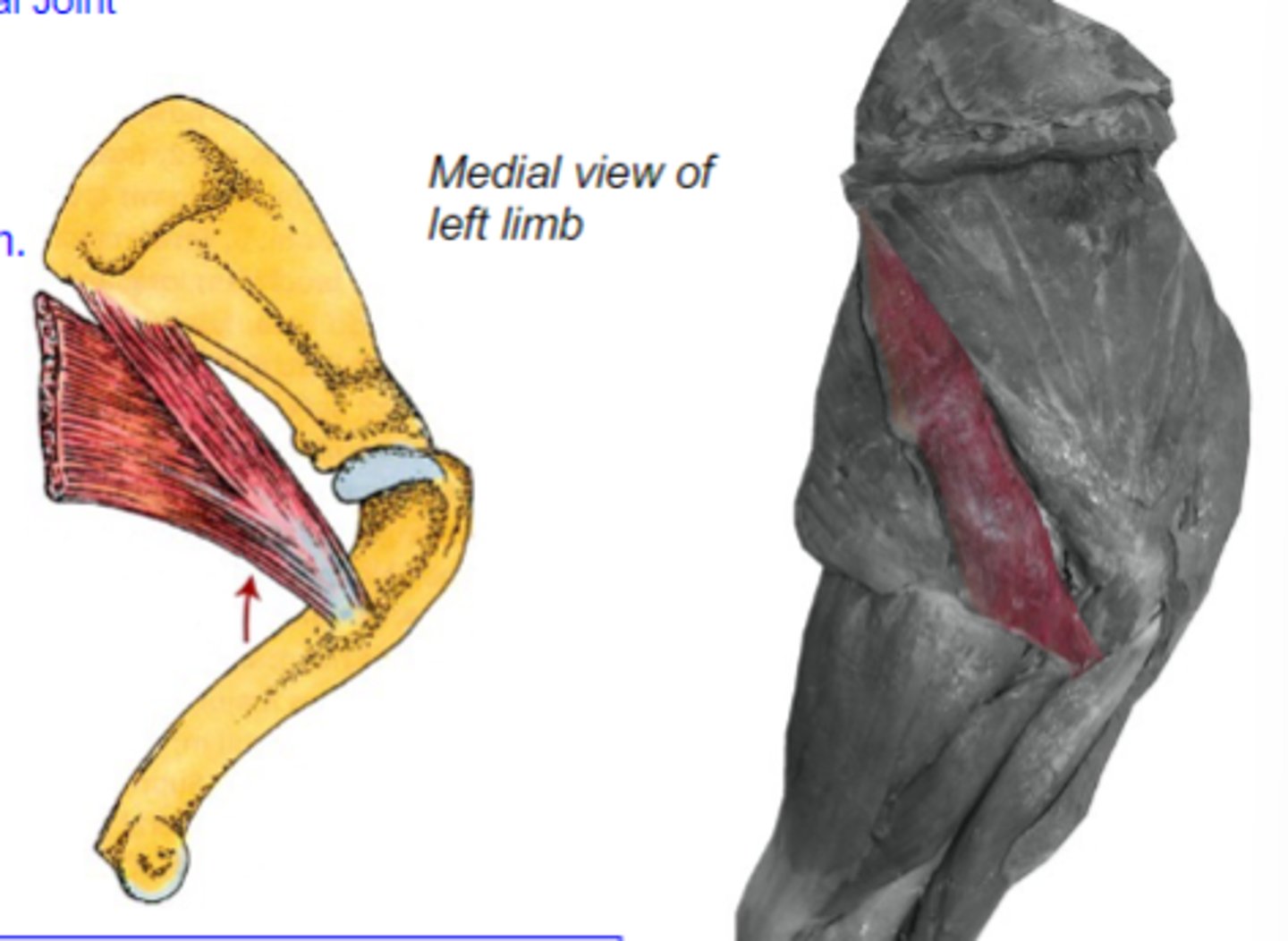
flex humeral joint
Action of teres major:
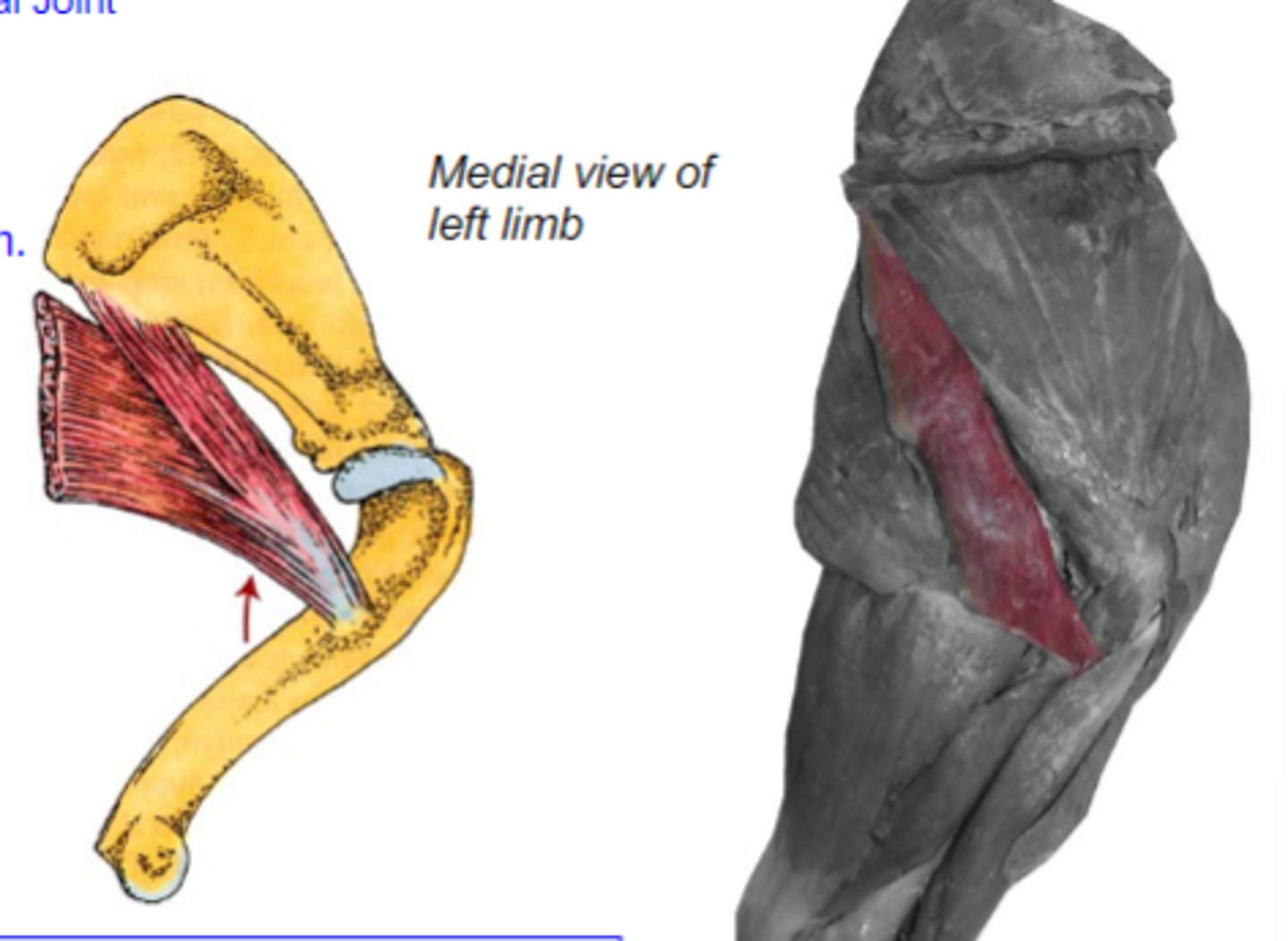
teres major
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: caudal border of scapula
Insertion: teres major tuberosity of humerus
Action: flex the humeral joint
coracobrachialis
What muscle is shown?
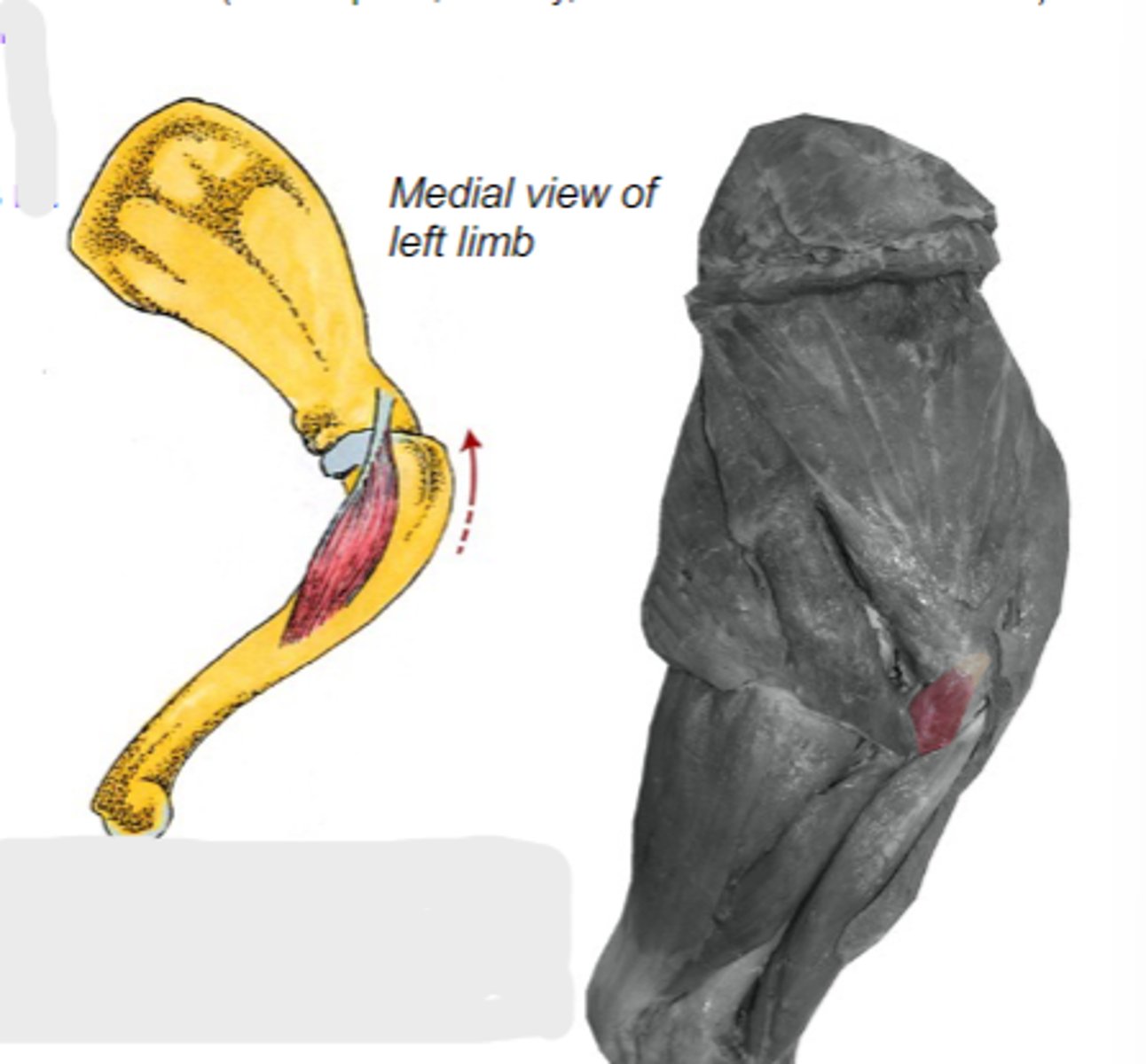
coracoid process of scapula
Origin of coracobrachialis:
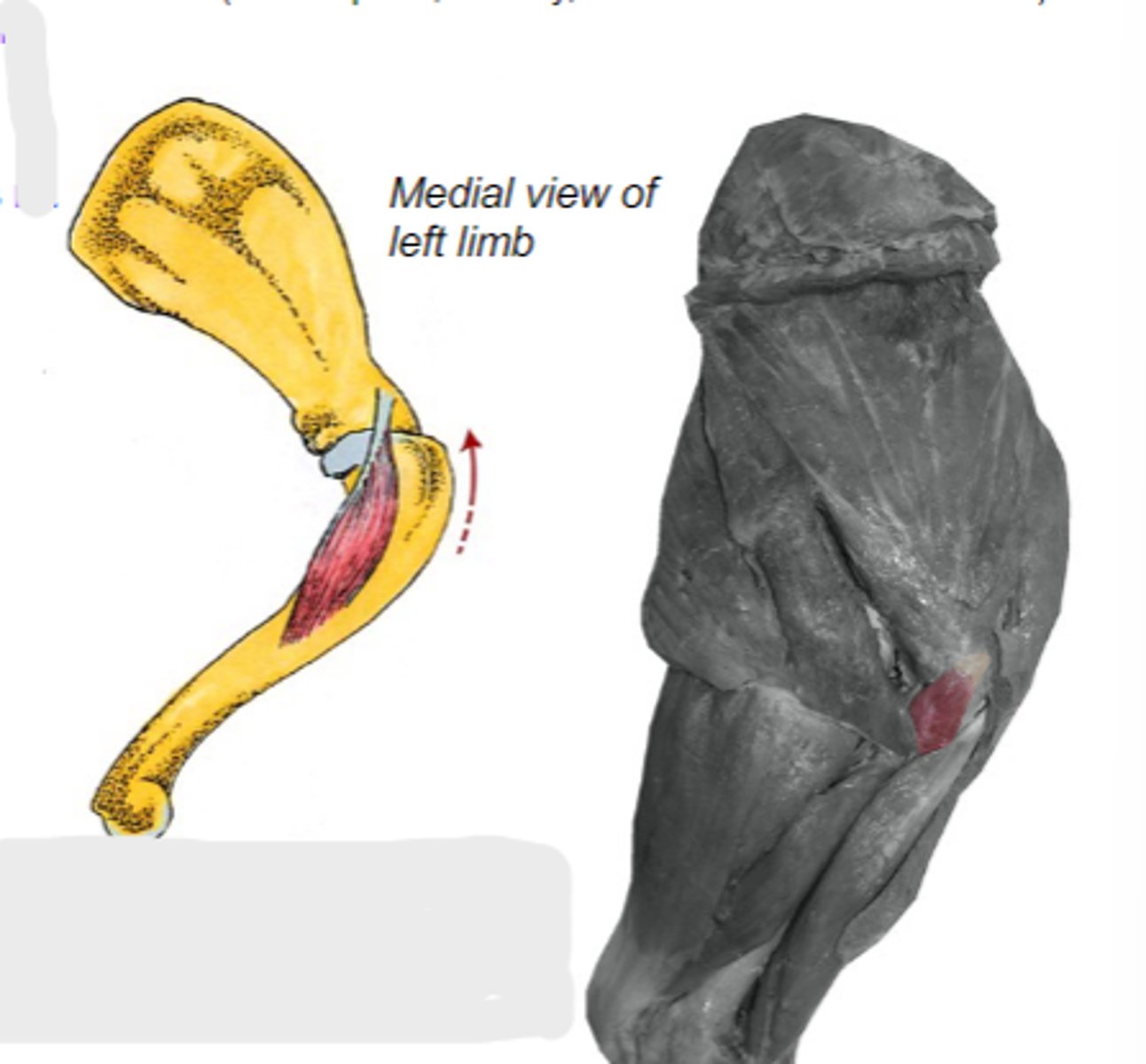
crest of the lesser tubercle of humerus
Insertion of coracobrachialis:
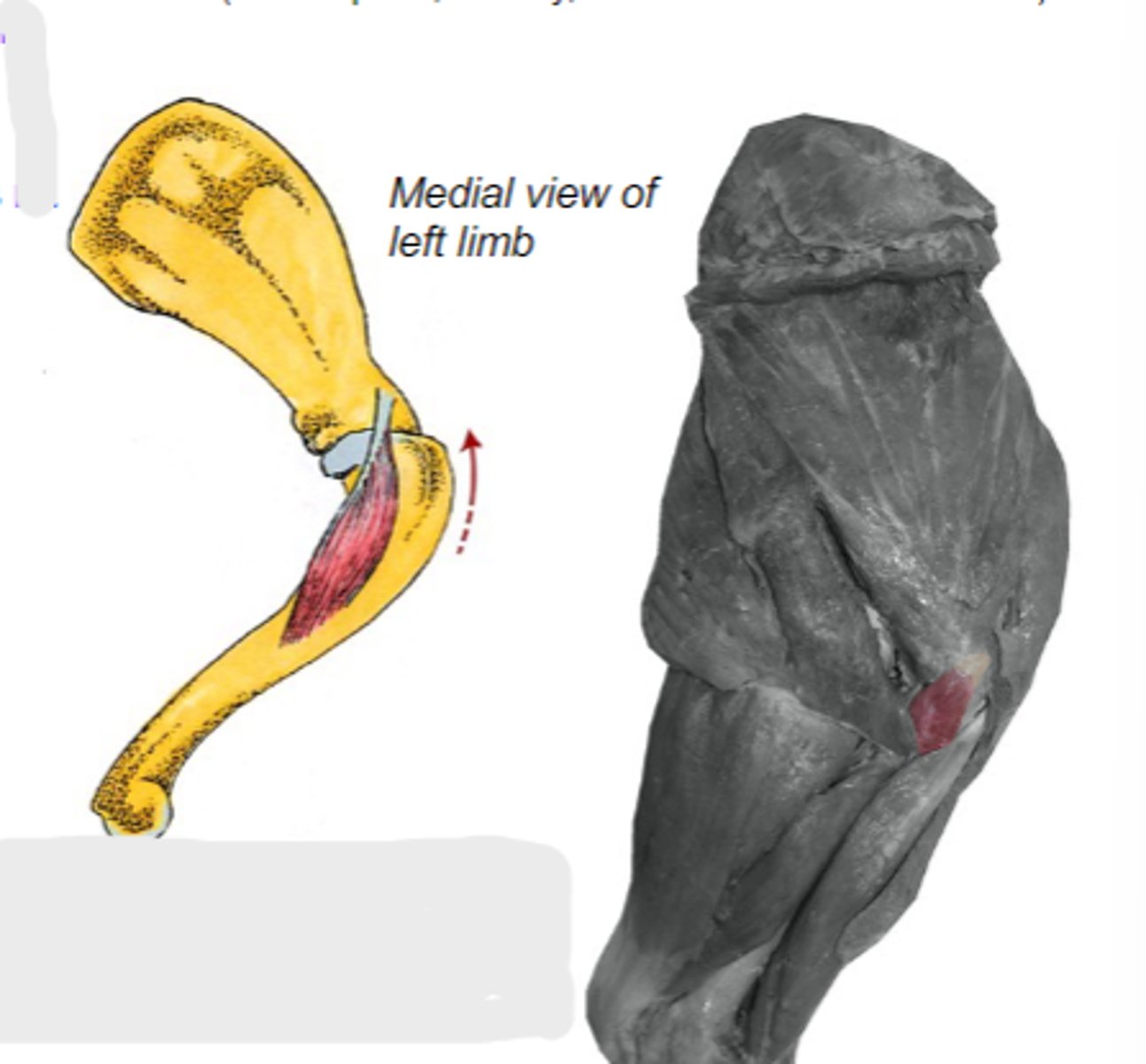
medially stabilize humeral joint
Action of coracobrachialis:
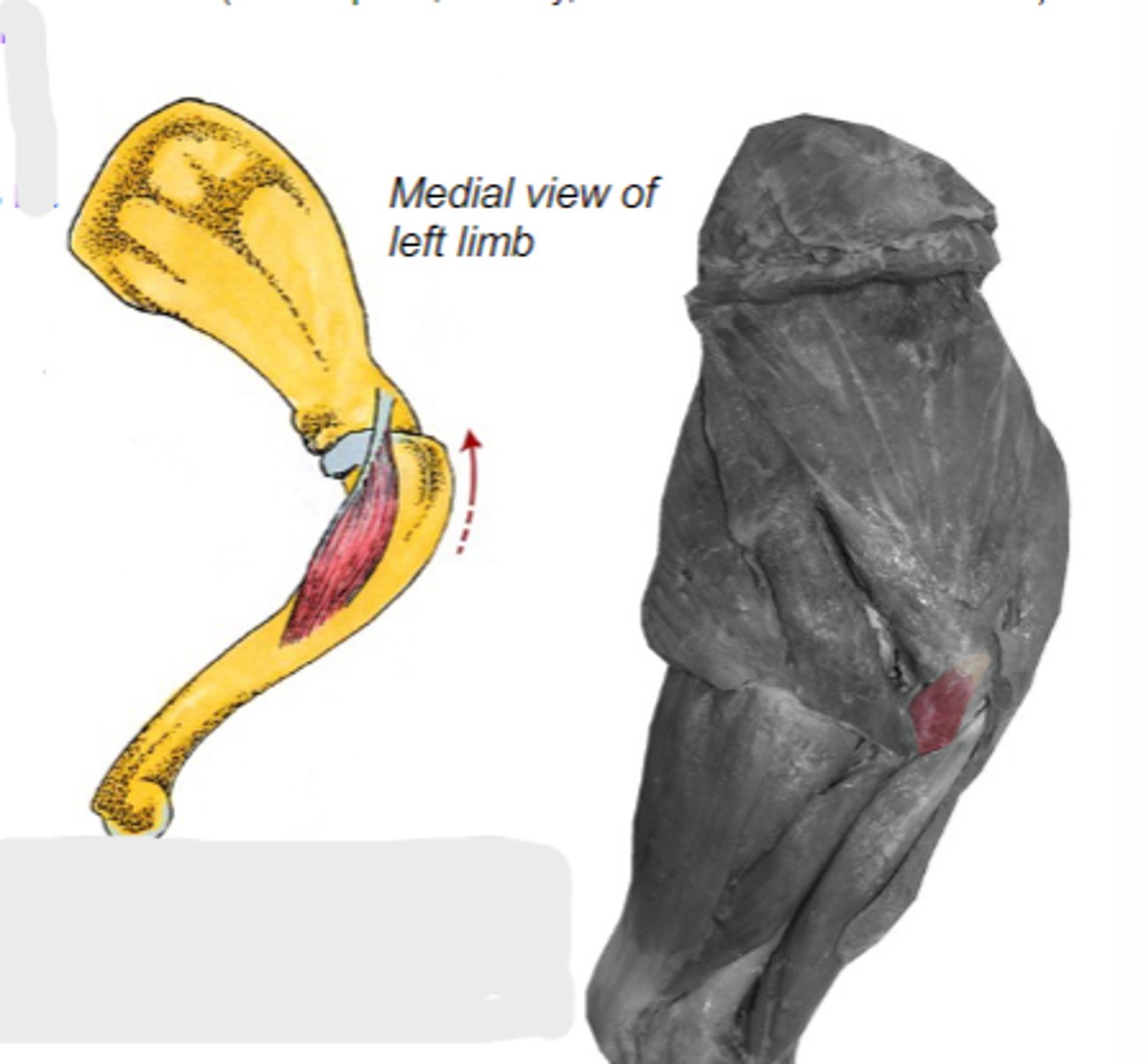
coracobrachialis
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: coracoid process of scapula
Insertion: crest of the lesser tubercle of the humerus
Action: medially stabilize the humeral joint
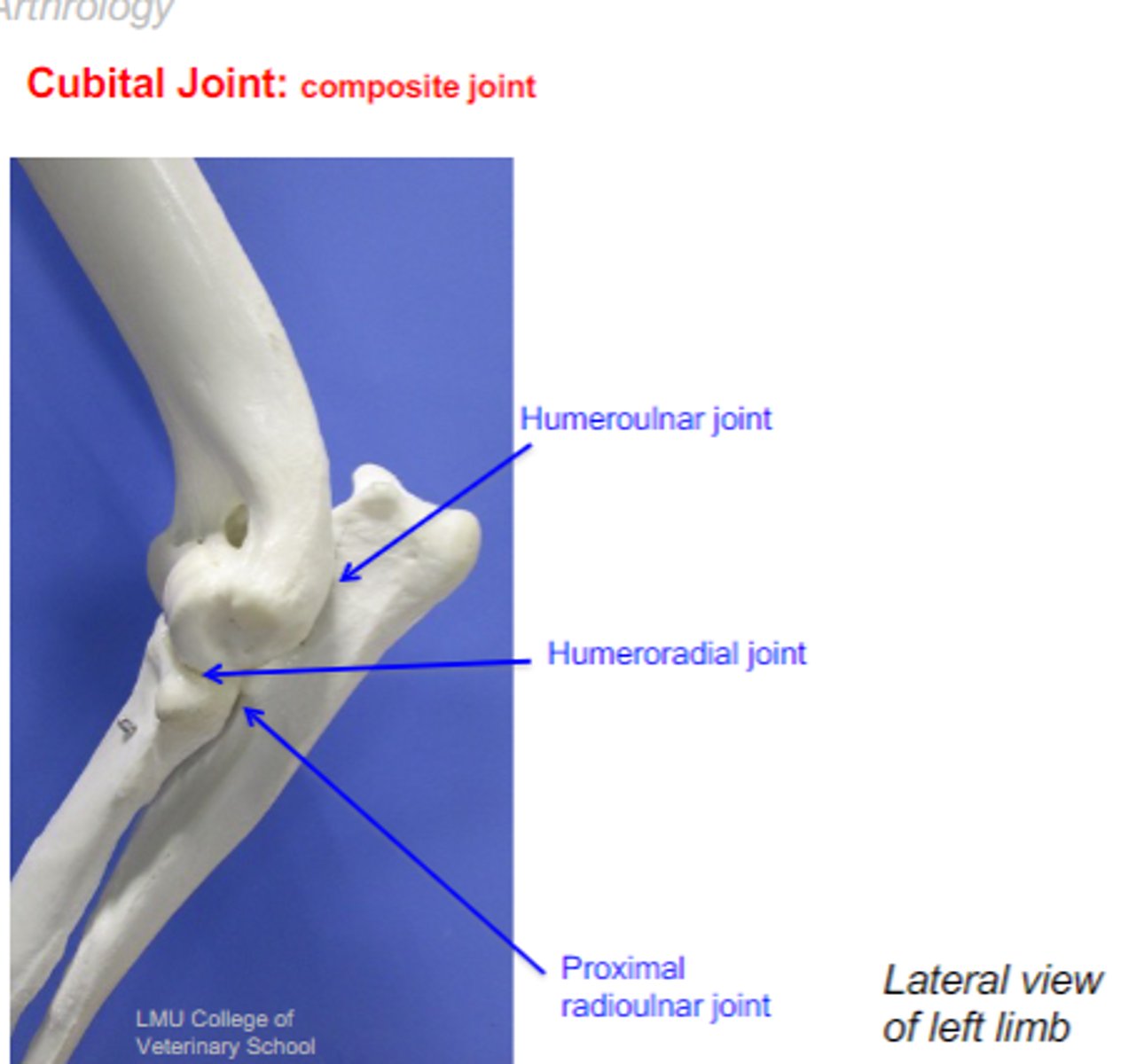
hinge
The humeroulnar joint is a _____ joint
pivot
The proximal radioulnar joint is a _____ joint
ellipsoidal
The humeroradial joint is a _____ joint
reviewed
review
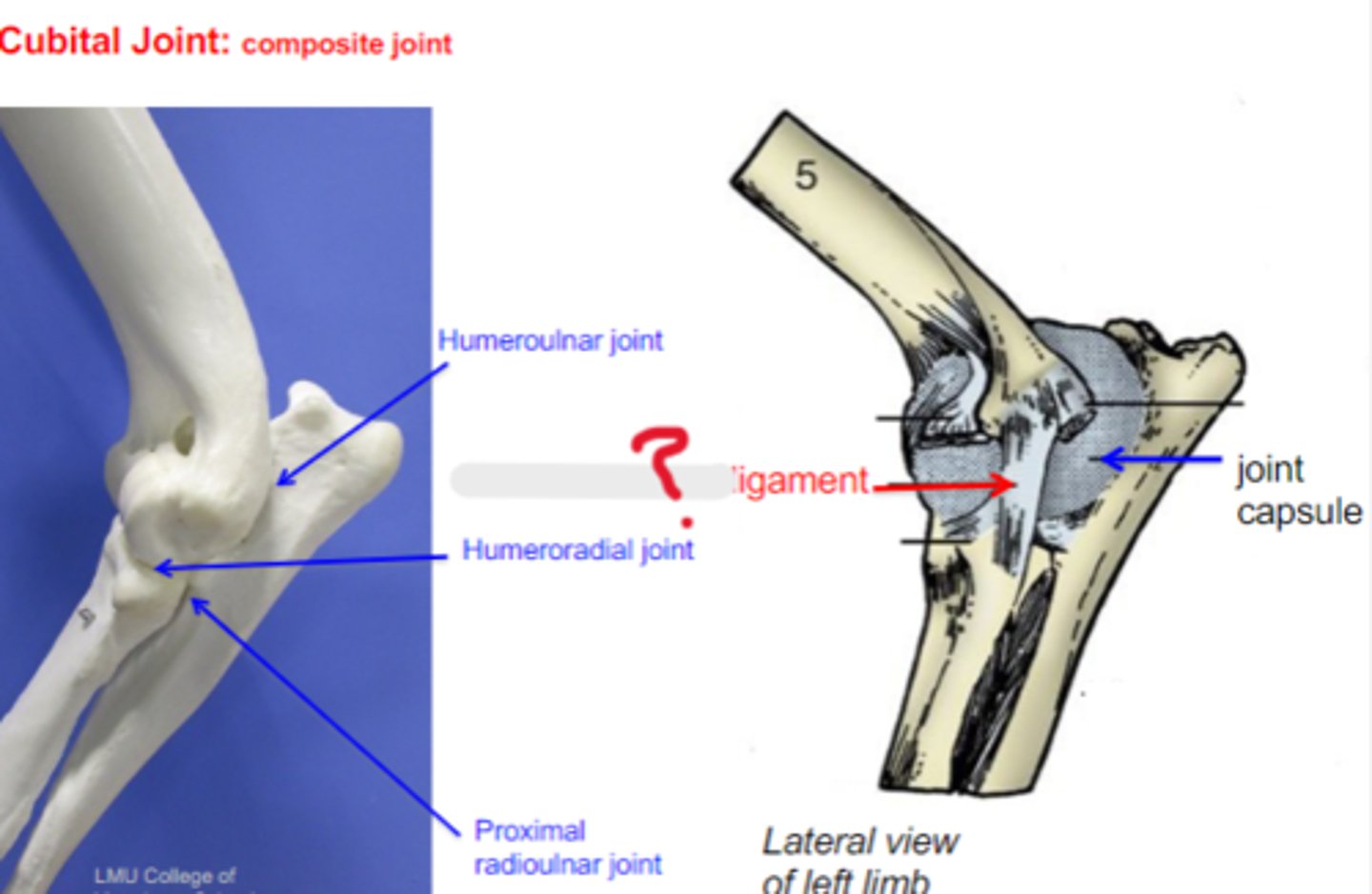
lateral collateral
What is the name of this ligament?
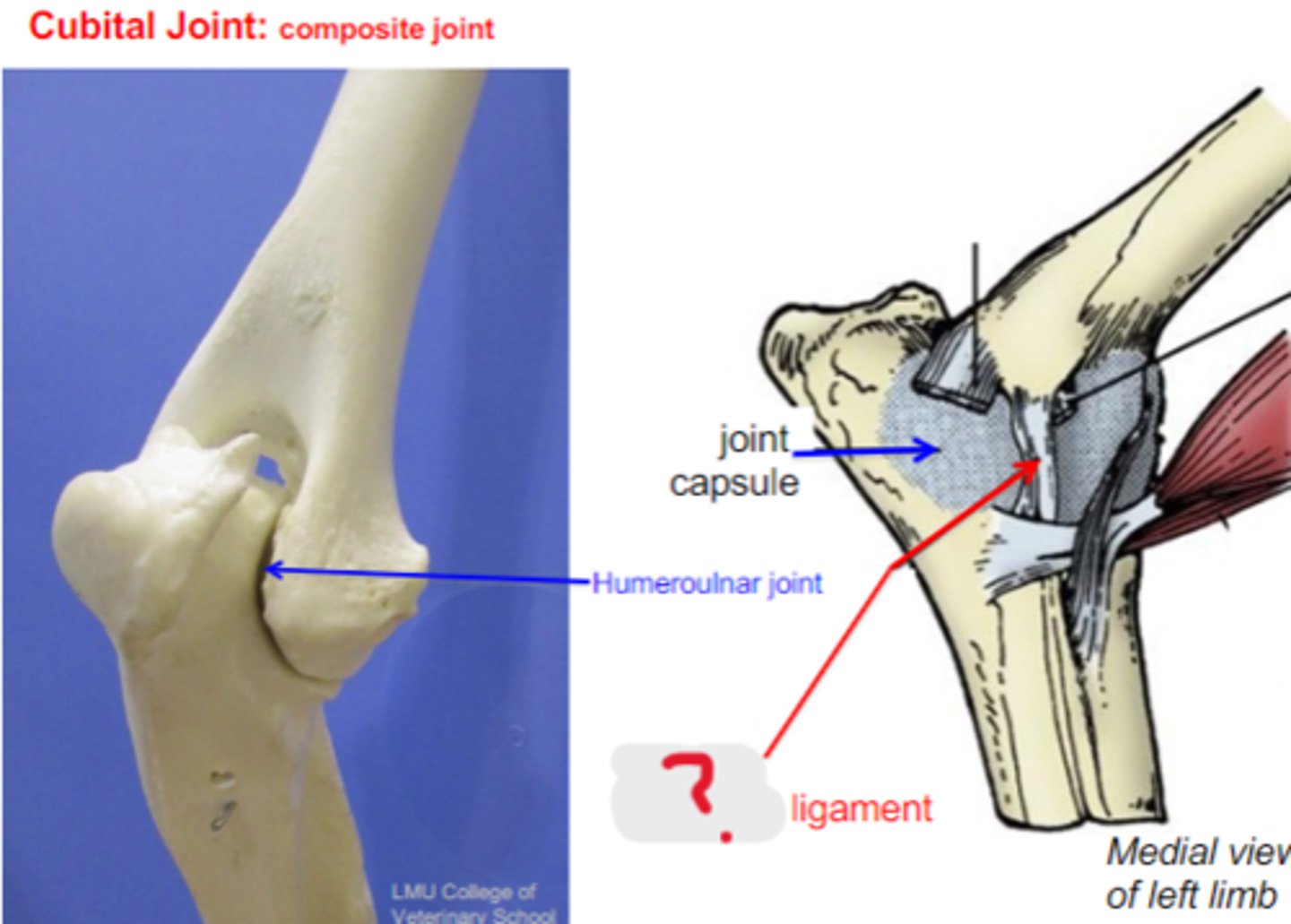
medial collateral
What is the name of this ligament?
cubital & humeral
The cranial muscles of the brachium act on what 2 joints?
musculocutaneous
The cranial muscles of the brachium are associated with what nerve(s)?
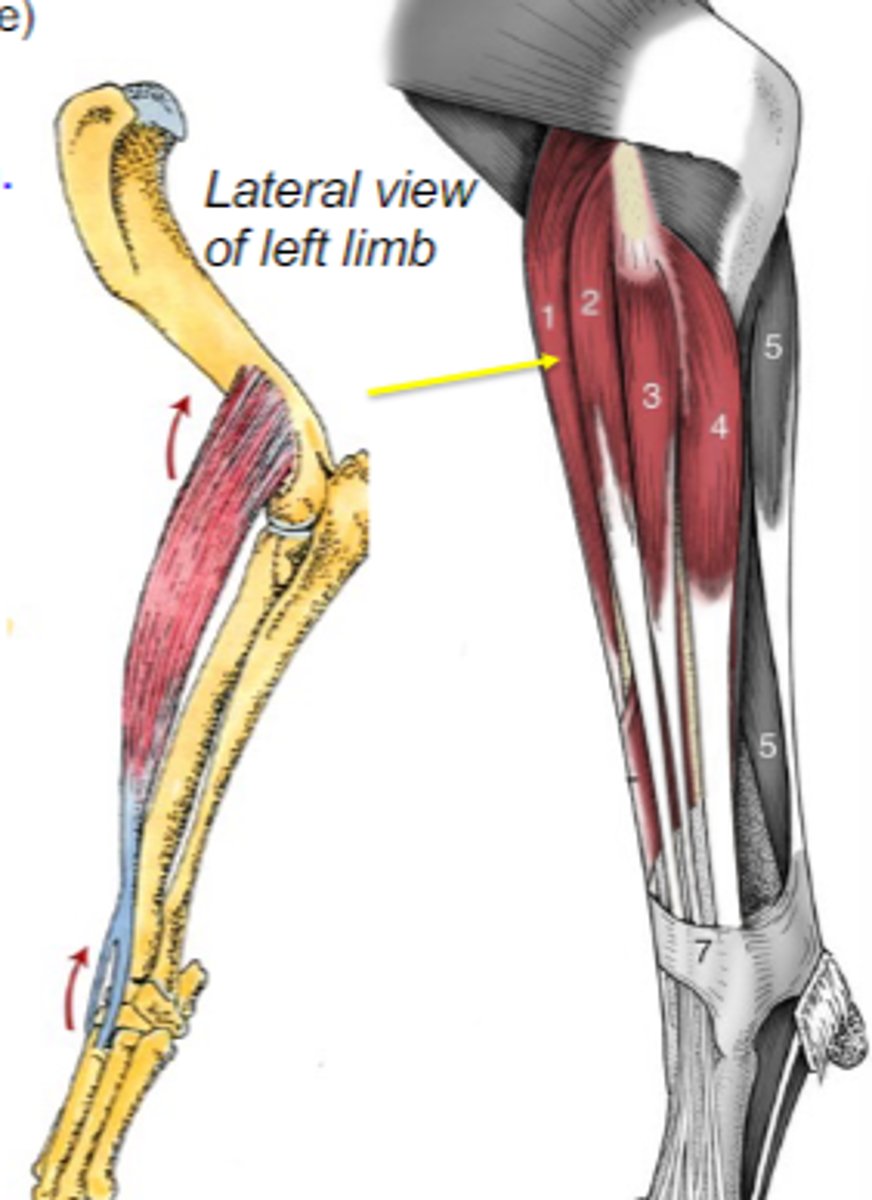
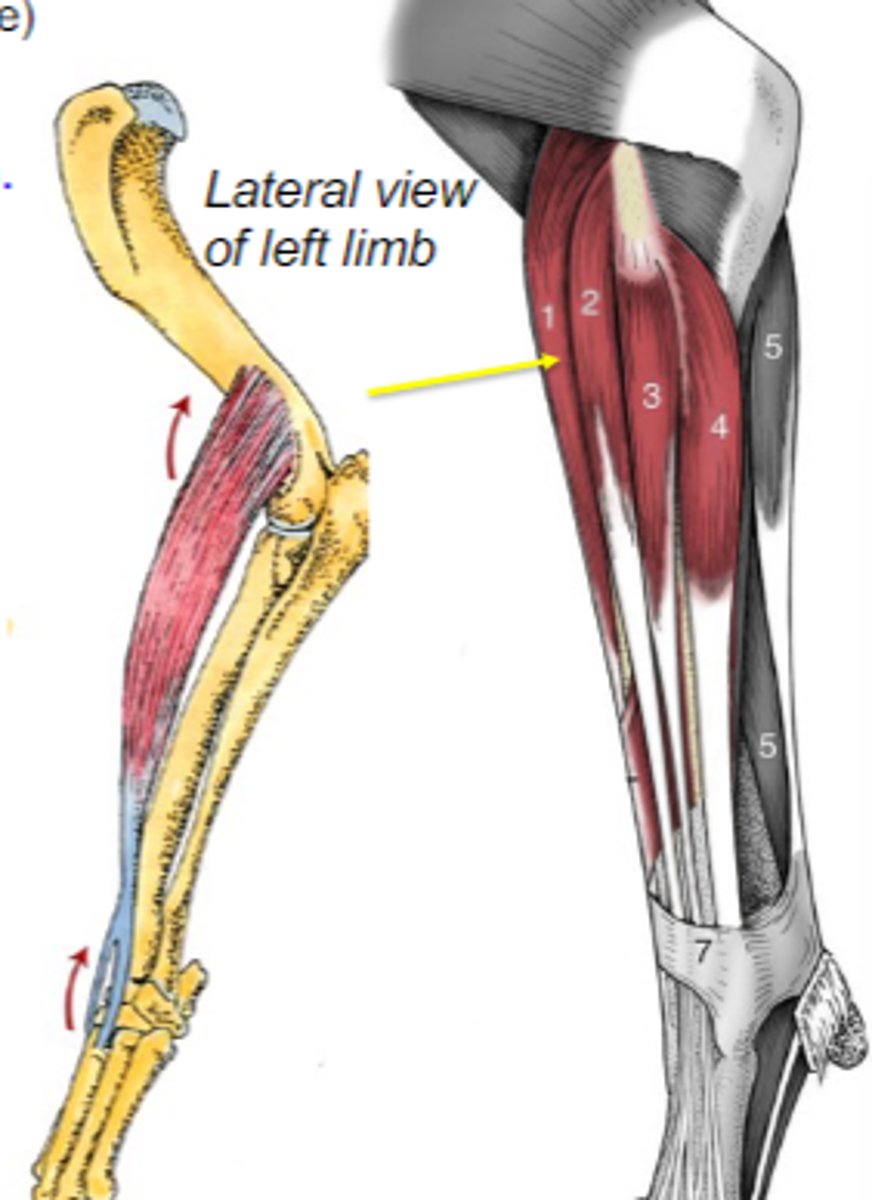
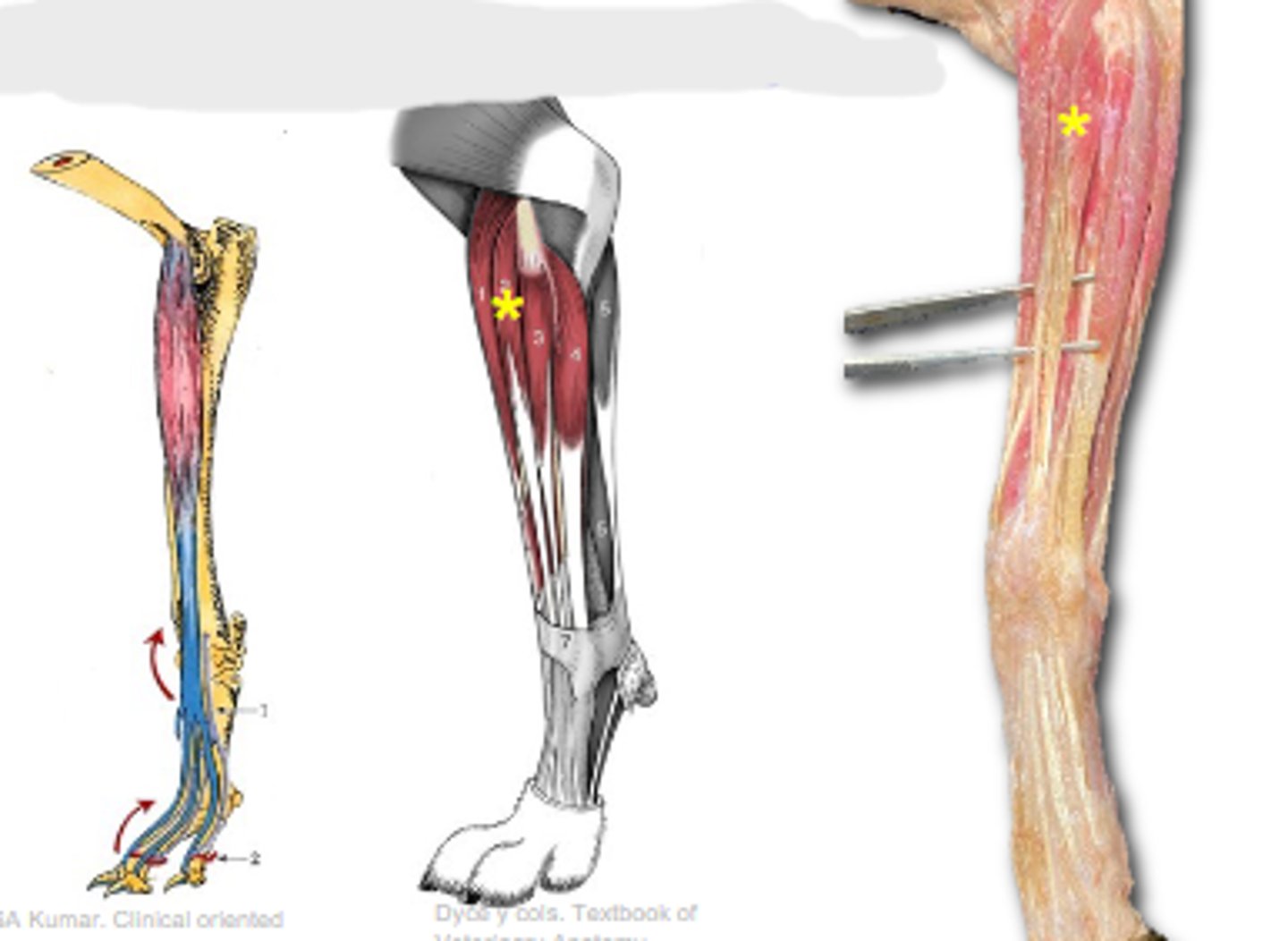
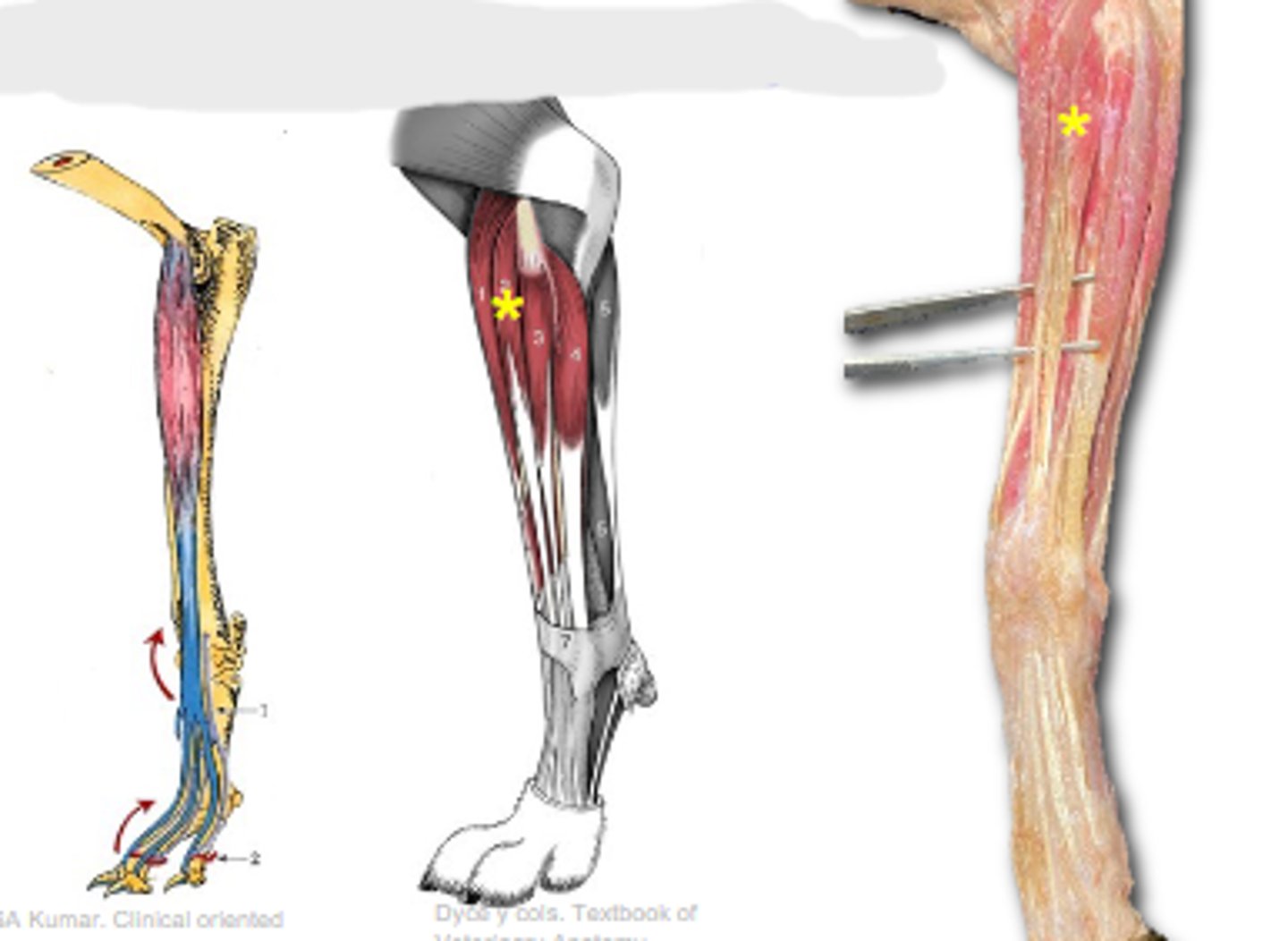
biceps brachii
What muscle is shown?
supraglenoid tubercle
Origin of biceps brachii:
radial tuberosity (and ulnar tuberosity in dog)
Insertion of biceps brachii:
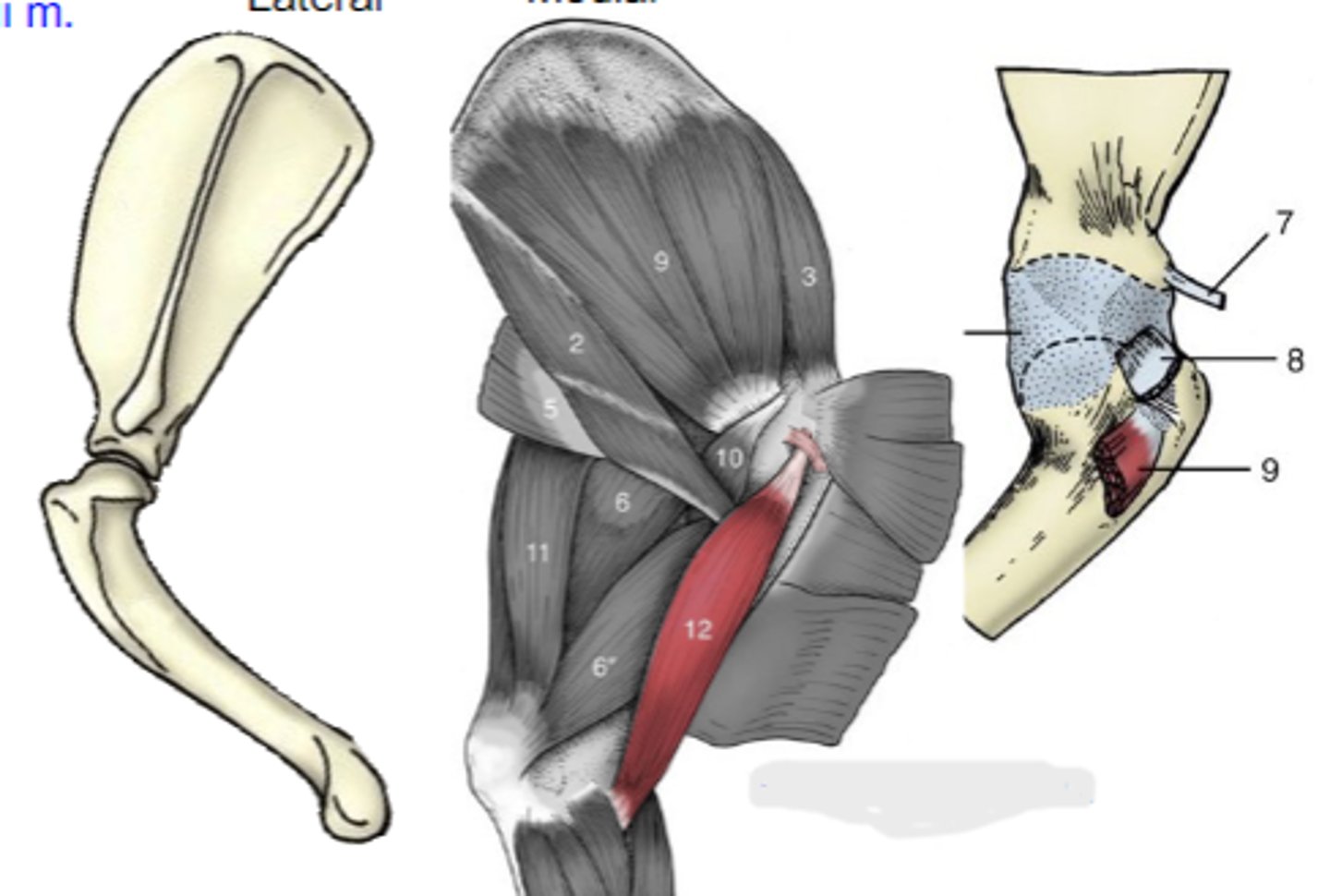
flex the cubital joint & extend the humeral joint
Action of biceps brachii:
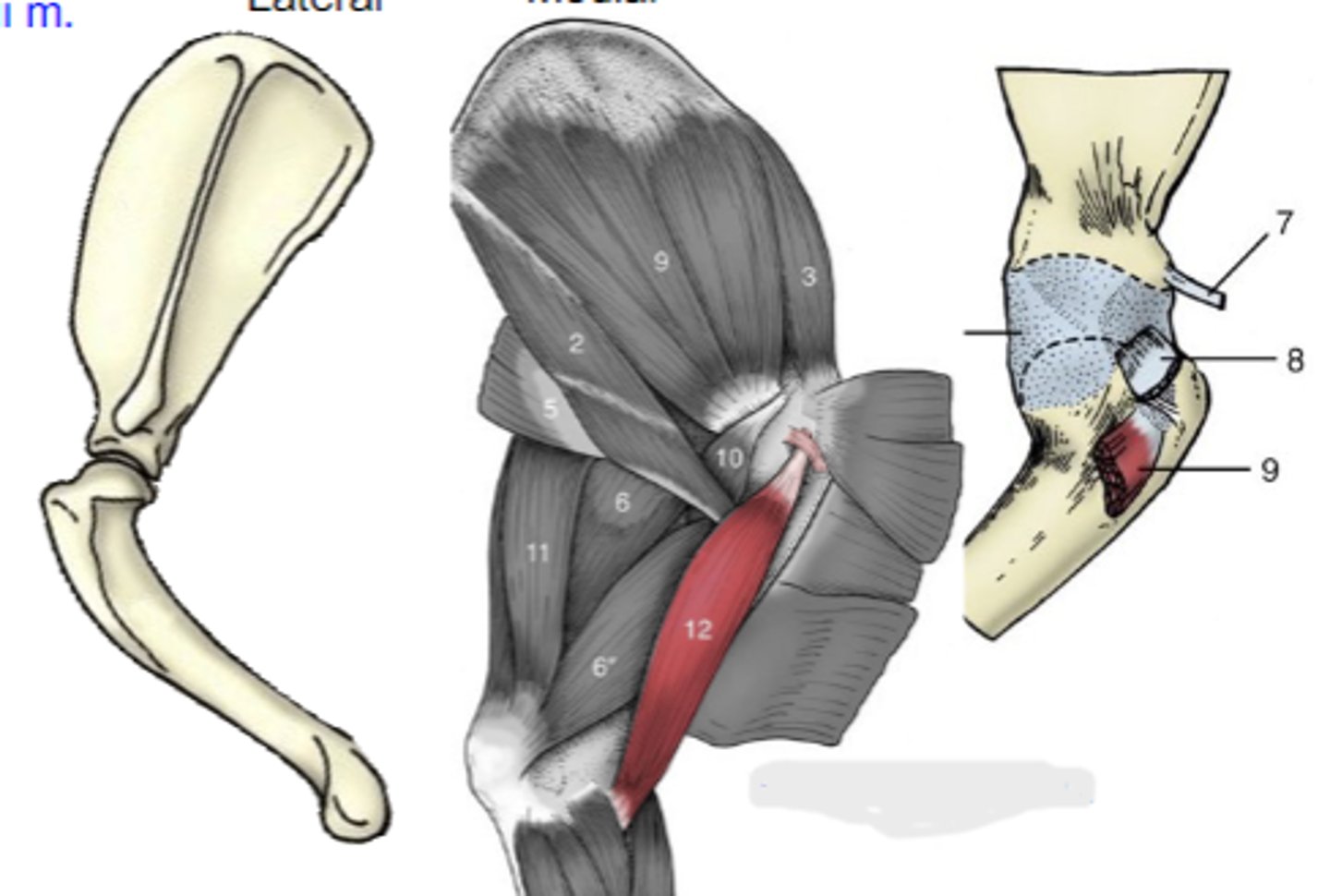
biceps brachii
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: supraglenoid tubercle
Insertion: radial tuberosity (and ulnar tuberosity in dog)
Action: flex the cubital joint; extend the humeral joint
brachialis
What muscle is shown?
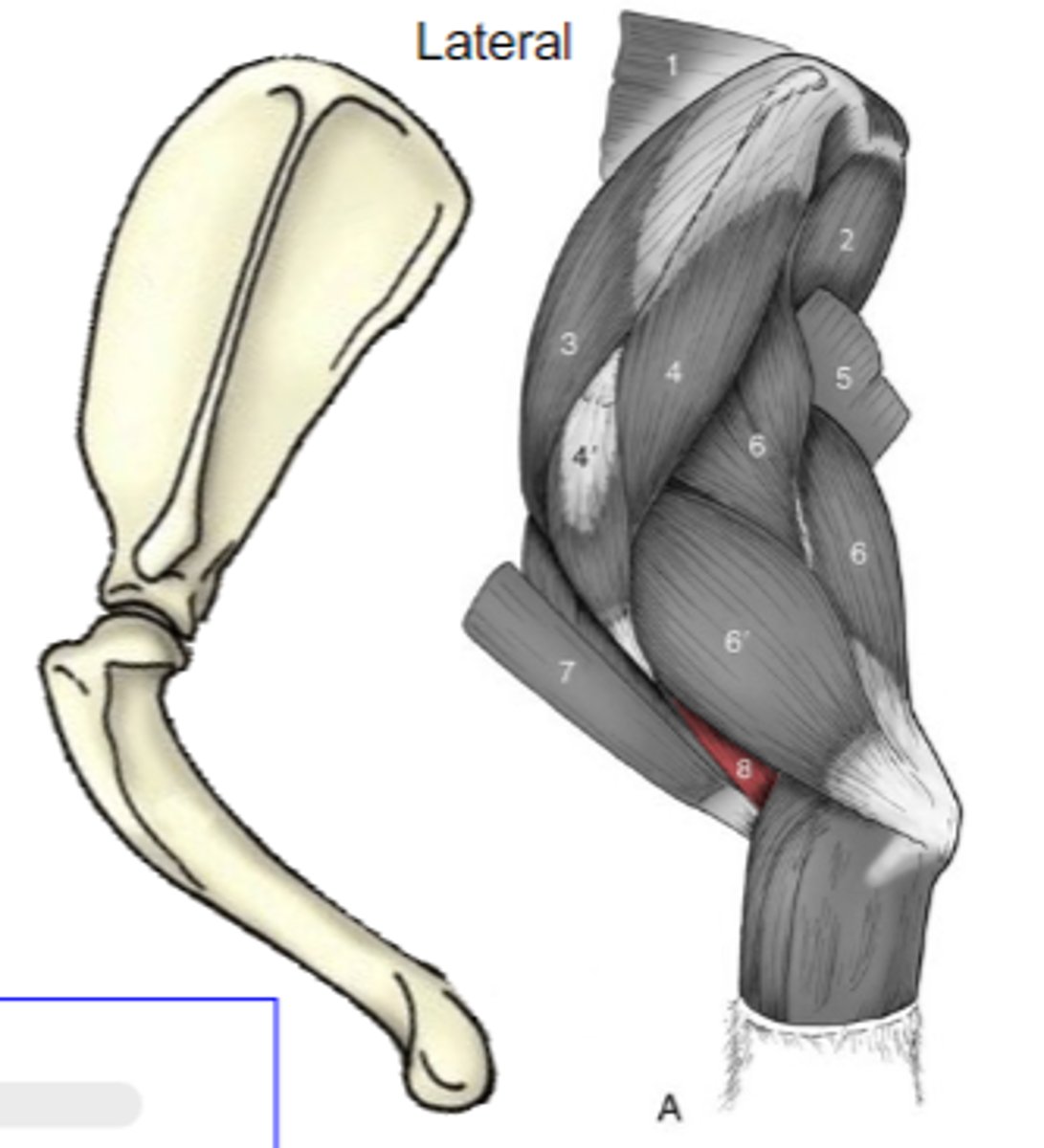
brachial groove of humerus
Origin of brachialis:
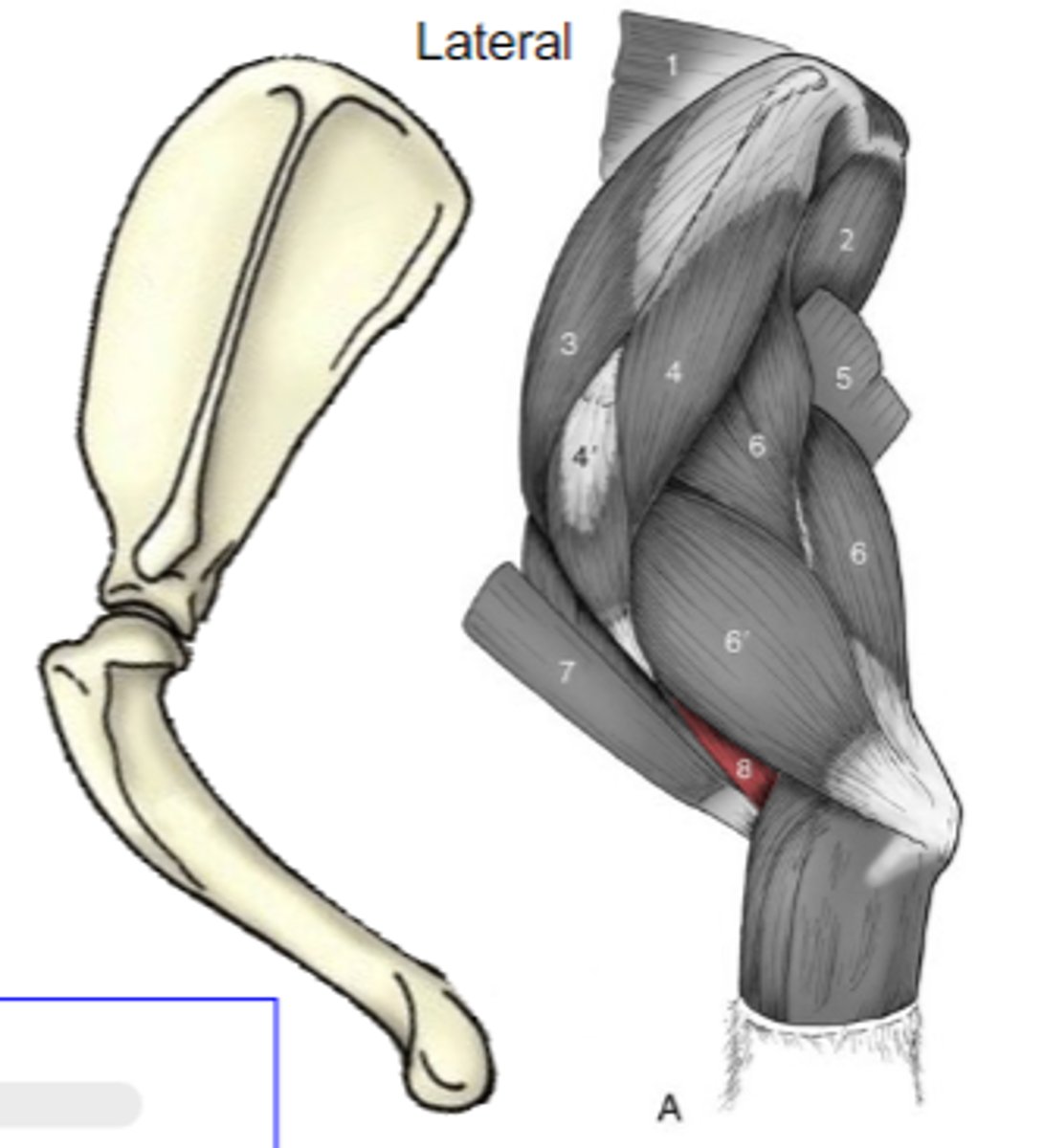
proximal radius and/or ulna
Insertion of brachialis:
flex cubital joint
Action of brachialis:
brachialis
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: brachial groove of humerus
Insertion: proximal radius and/or ulna
Action: flex the cubital join
cubital & humeral
The caudal muscles of the brachium act on what joints?
radial
The caudal muscles of the brachium are associated with what nerve(s)?
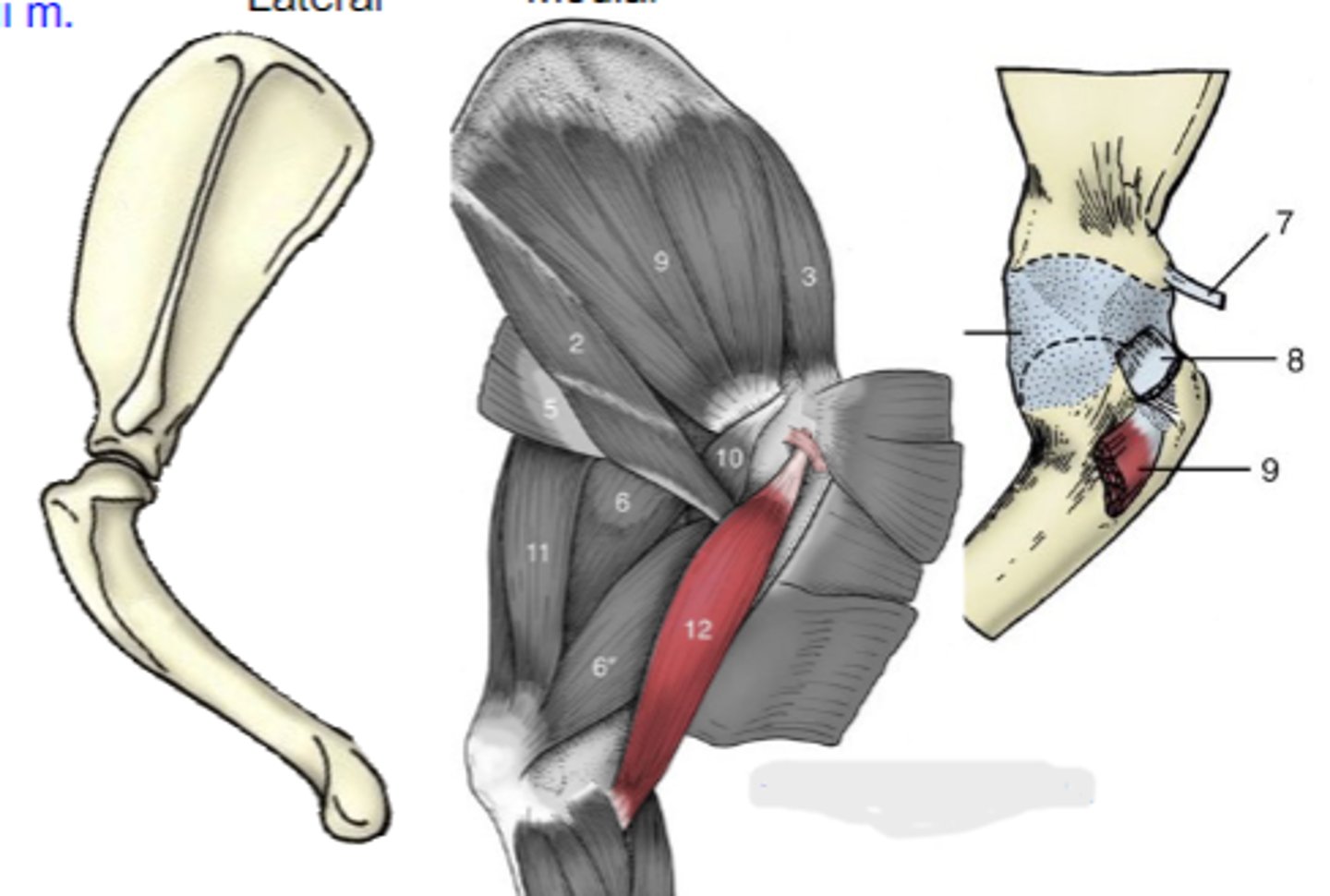
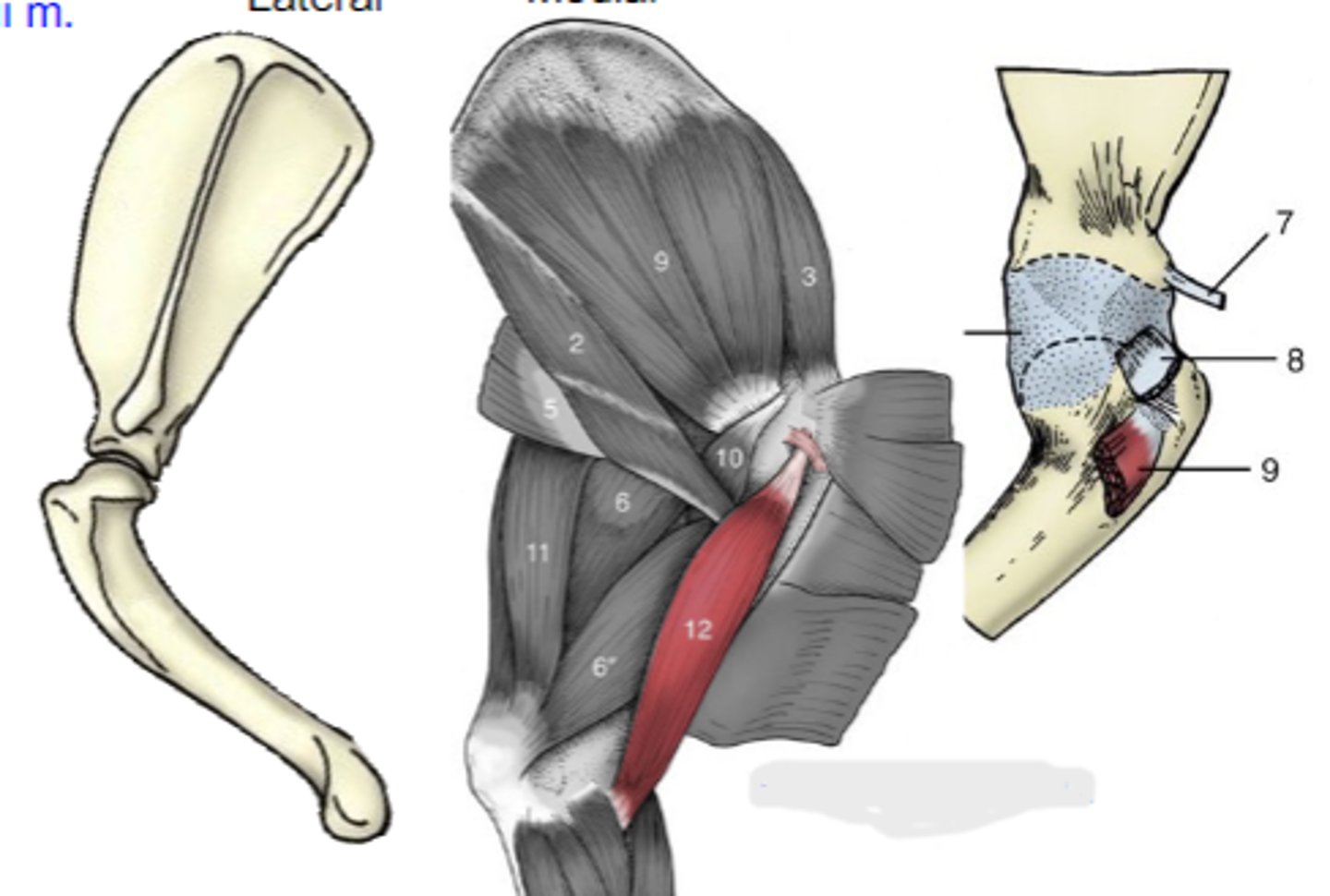
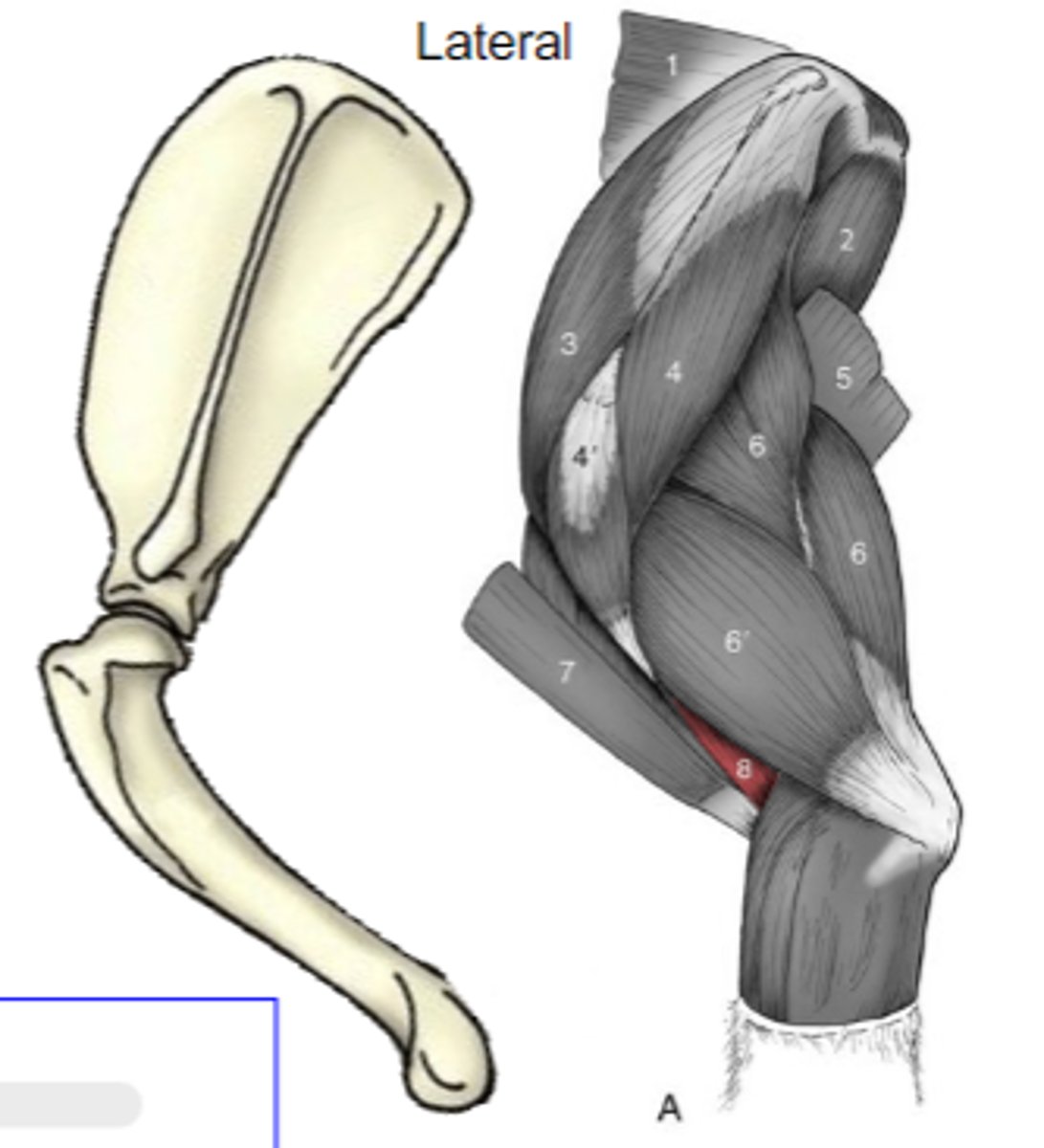
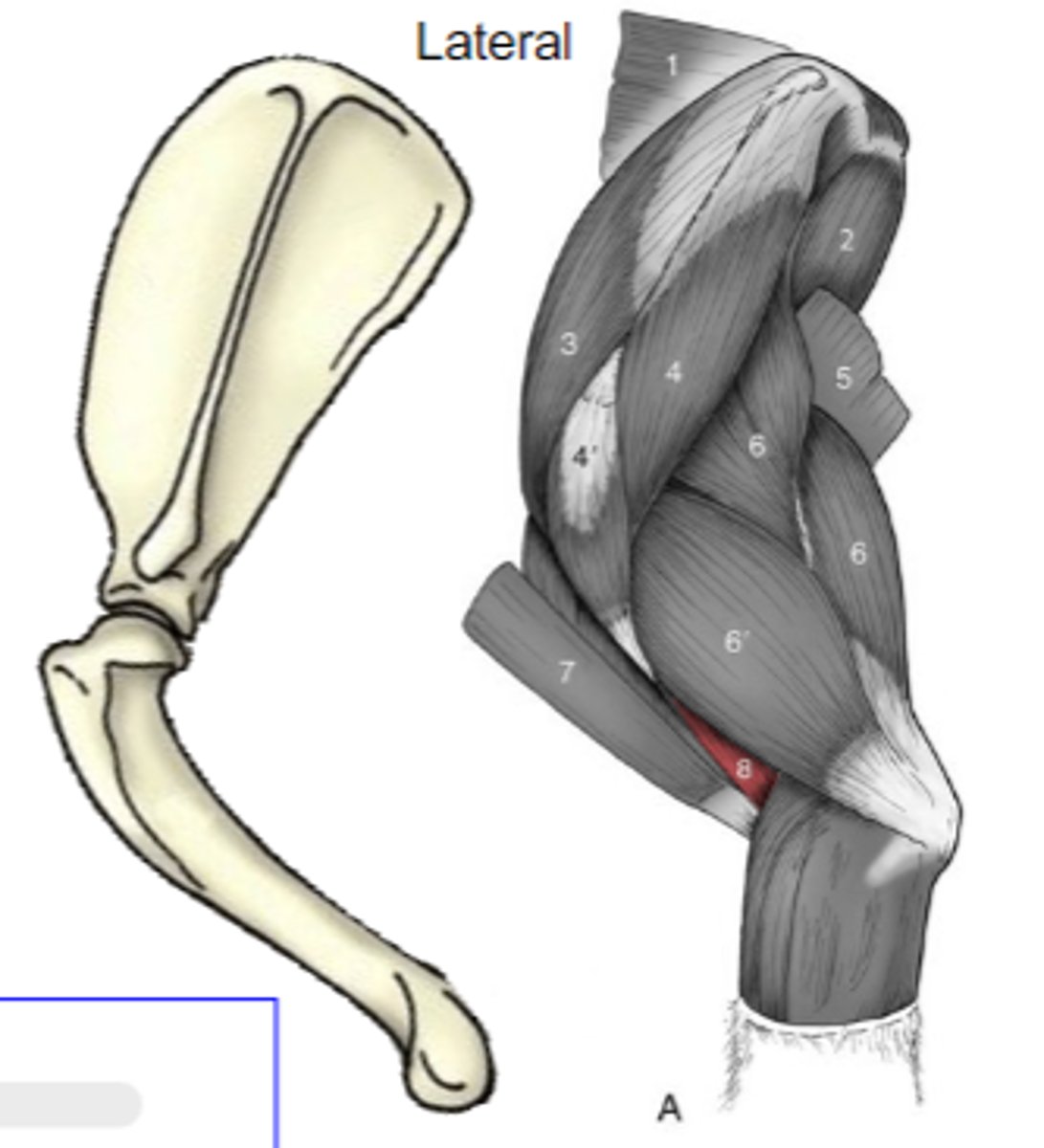
triceps brachii
What muscle is shown?
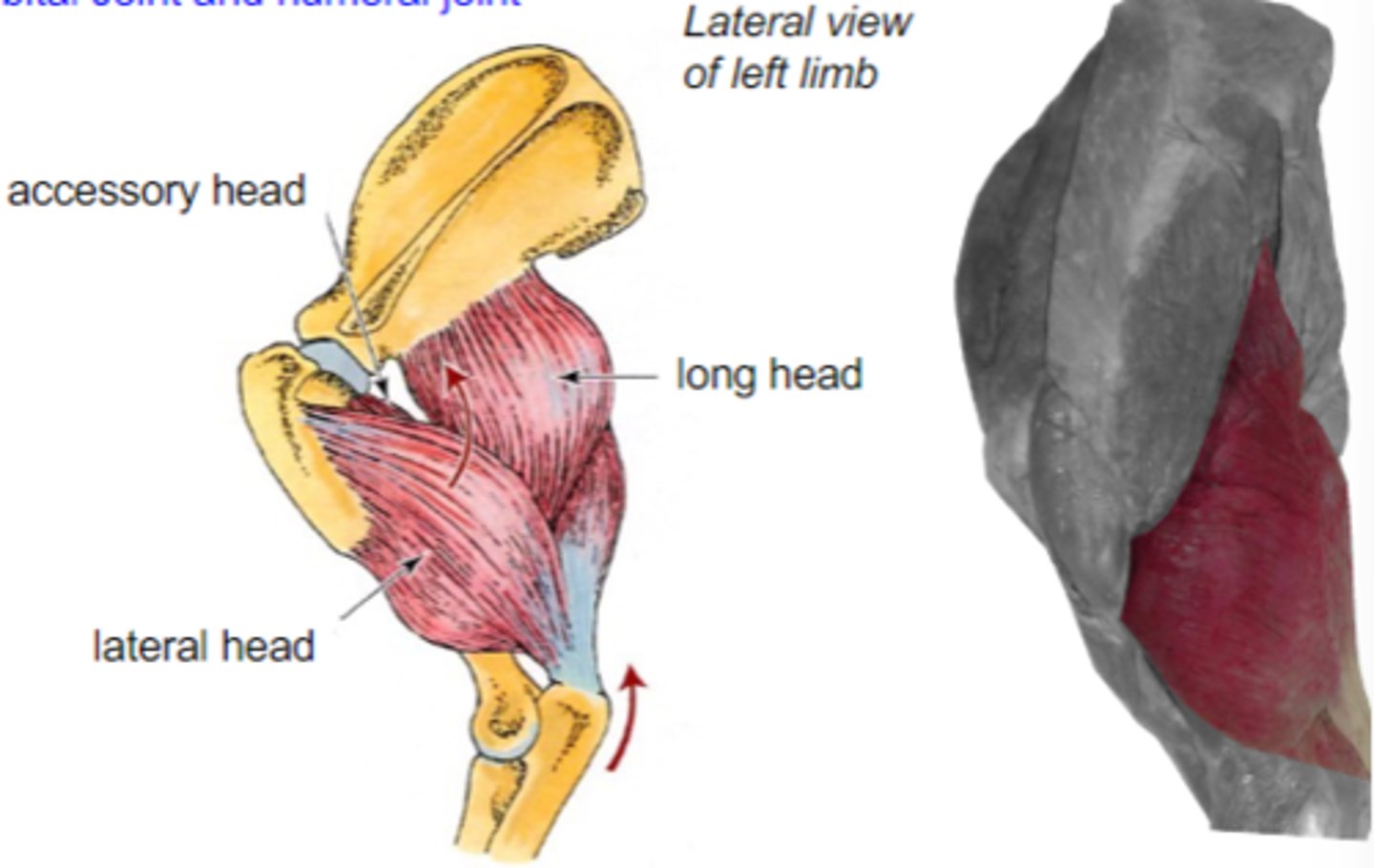
caudal border of scapula (long head)
proximal humerus (other heads)
Origin of triceps brachii:
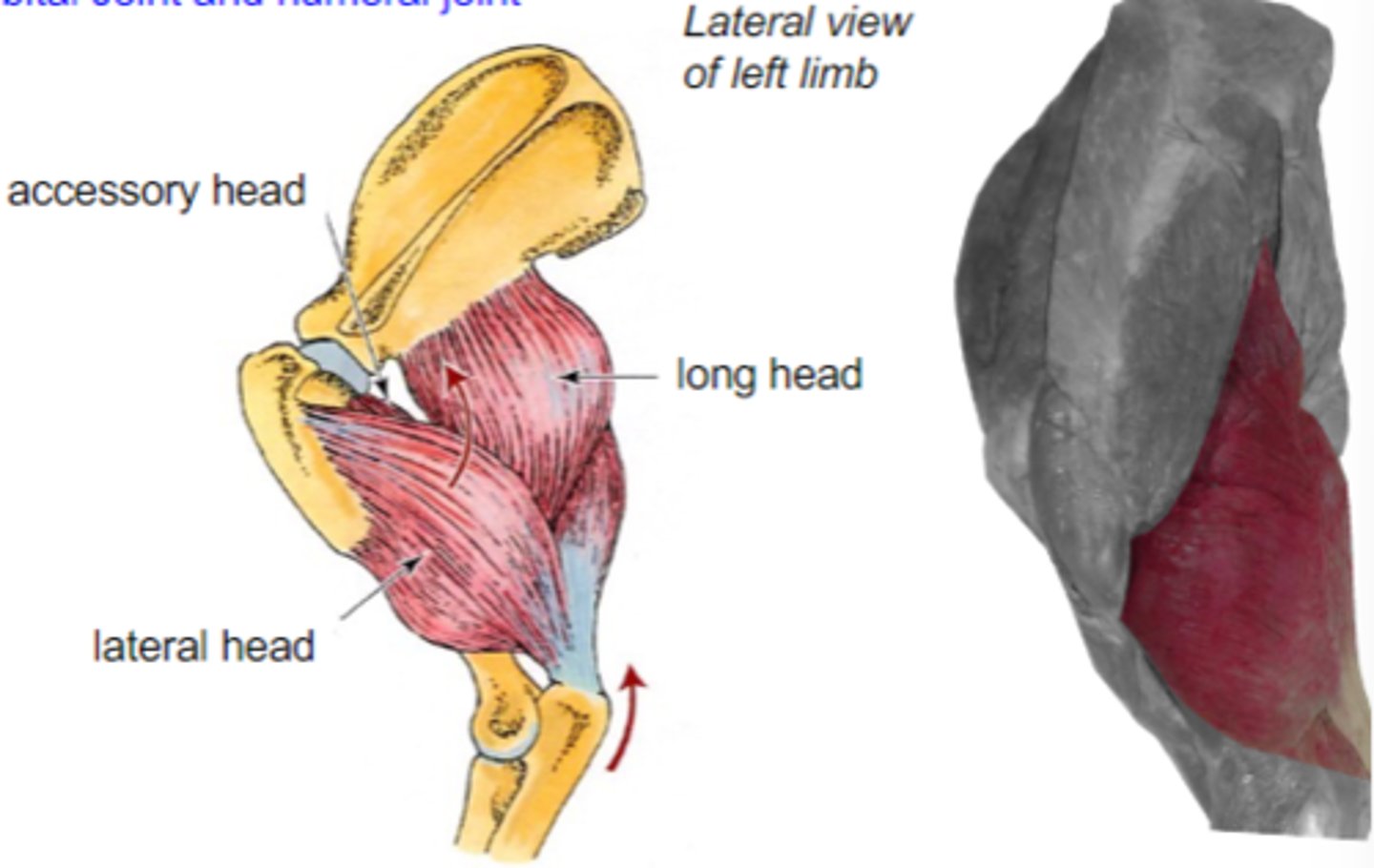
tuber olecrani
Insertion of triceps brachii:
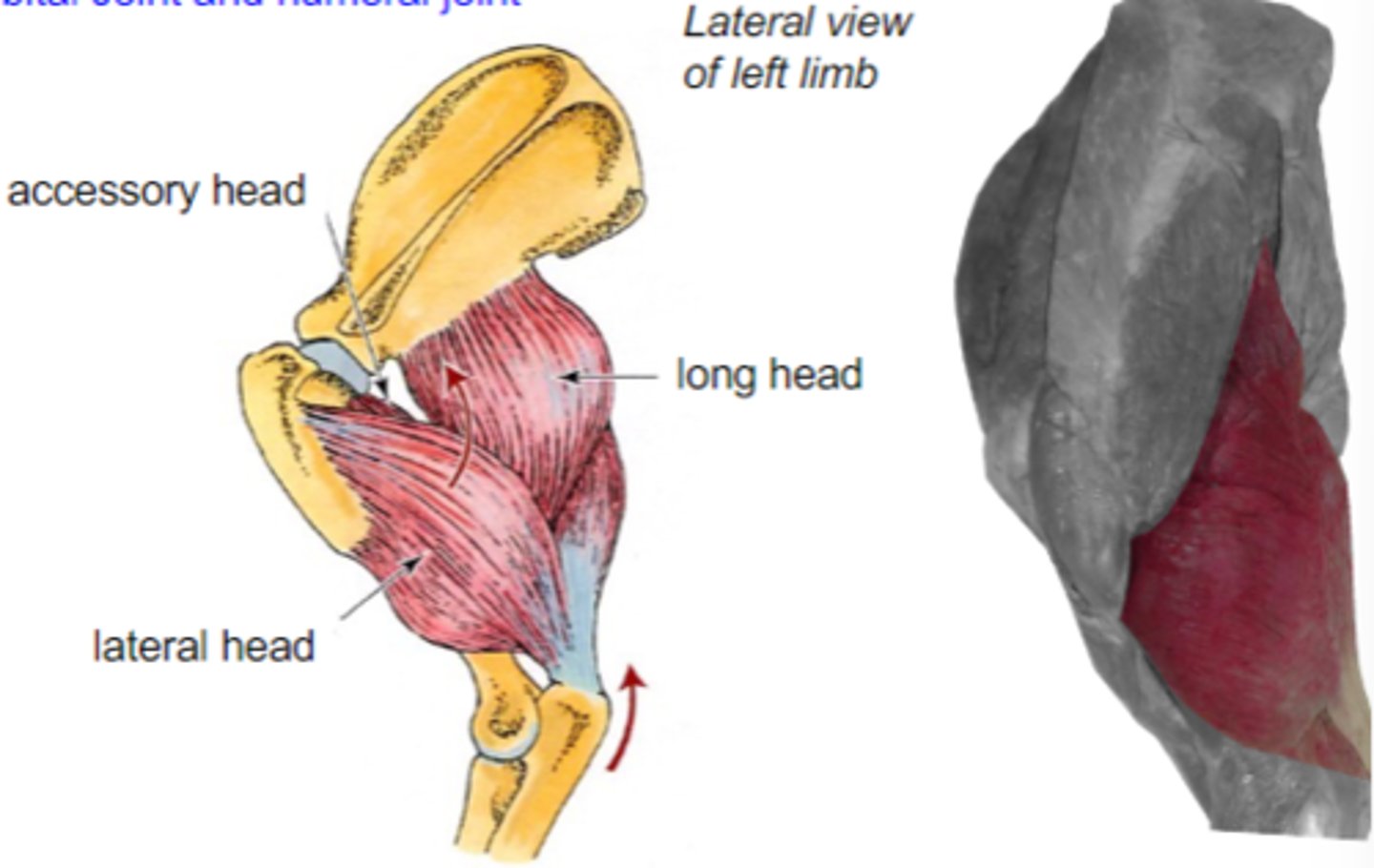
extend cubital joint (all heads)
flex humeral joint (long head only)
Action of triceps brachii:
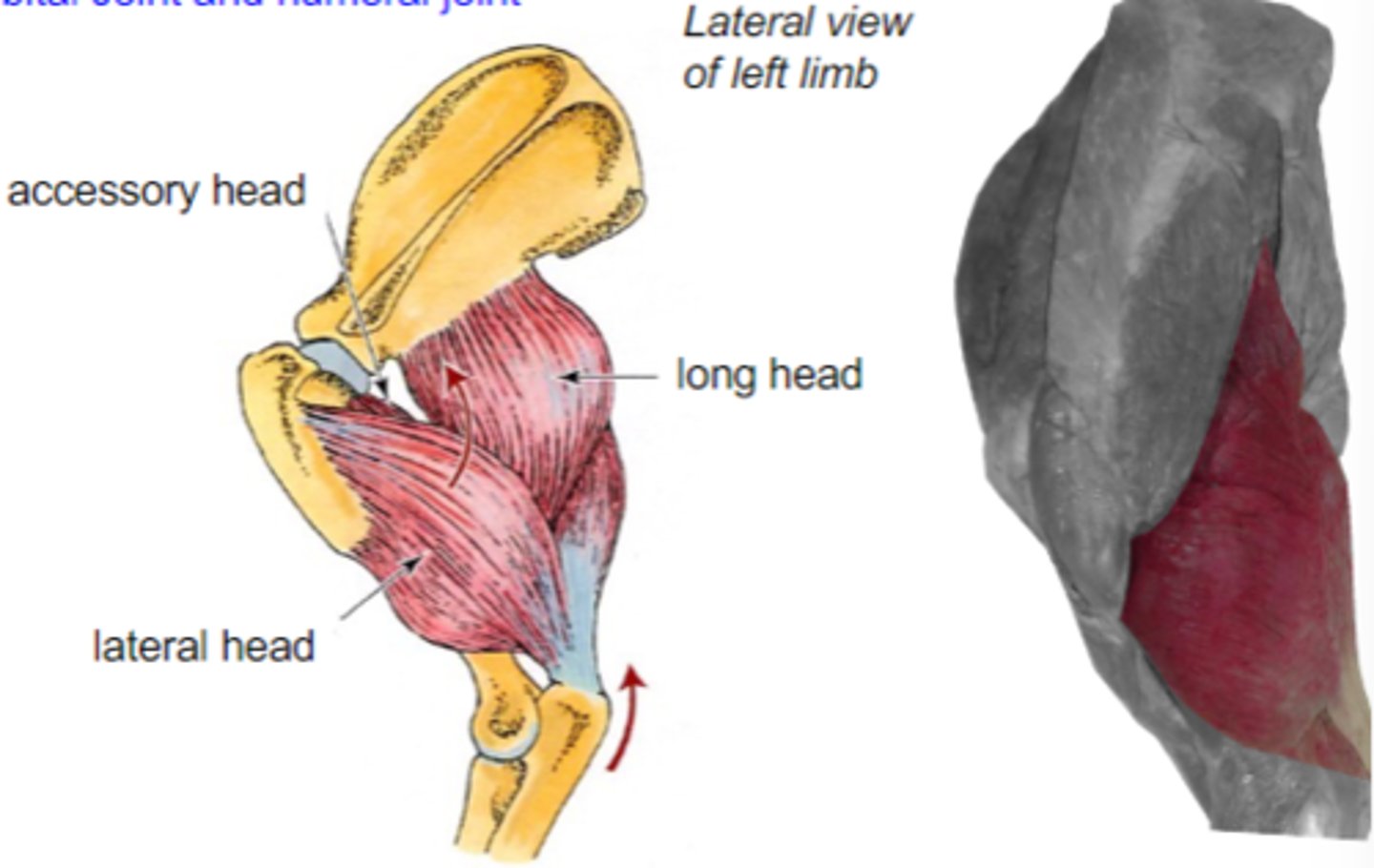
accessory, lateral, medial, and long heads
What are the 4 parts of the triceps brachii?
triceps brachii
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: caudal border of scapula (long head); proximal humerus (other heads)
Insertion: tuber olecrani
Action: extend the cubital joint (all heads); flex the humeral joint (long head only)
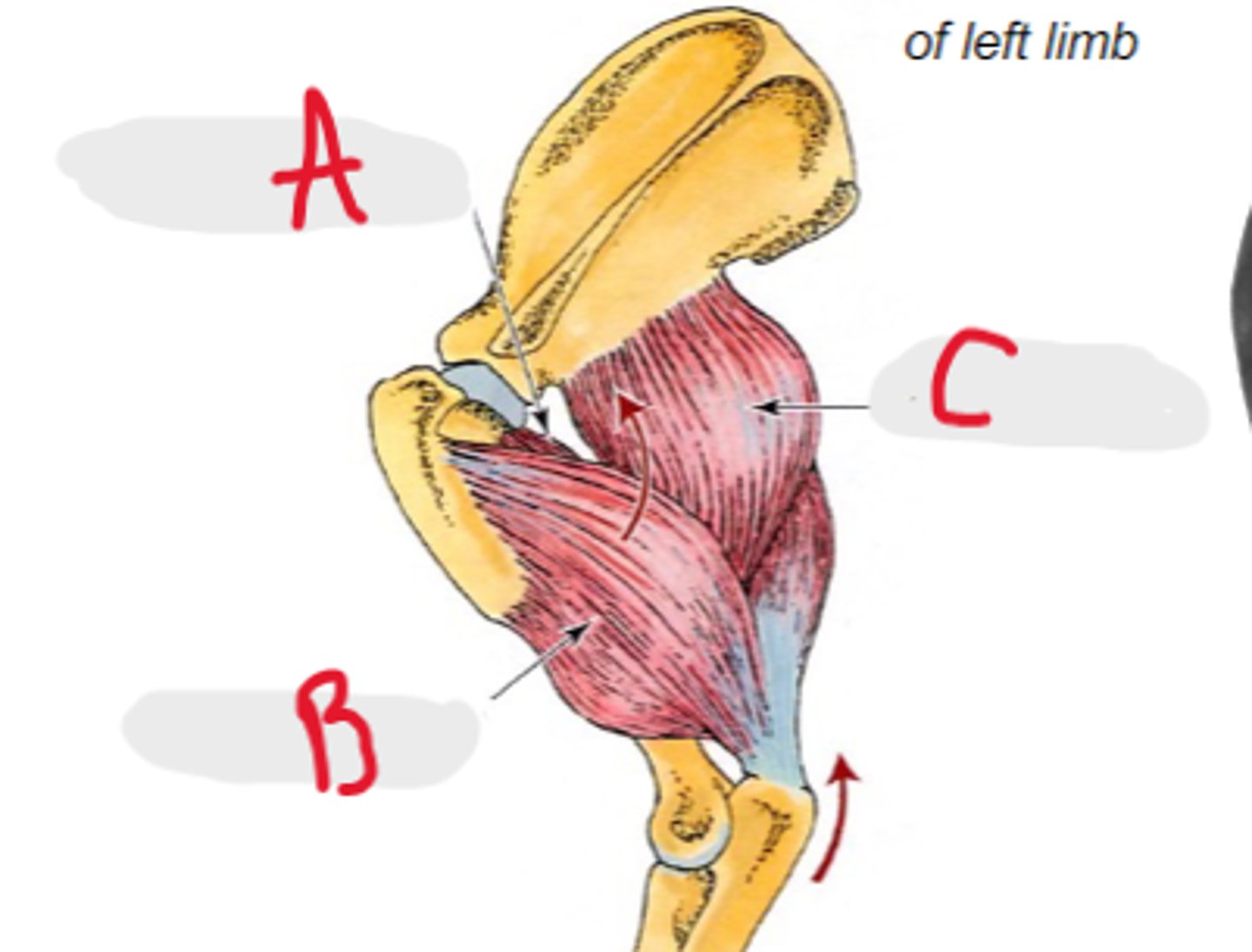
accessory head
What is A?
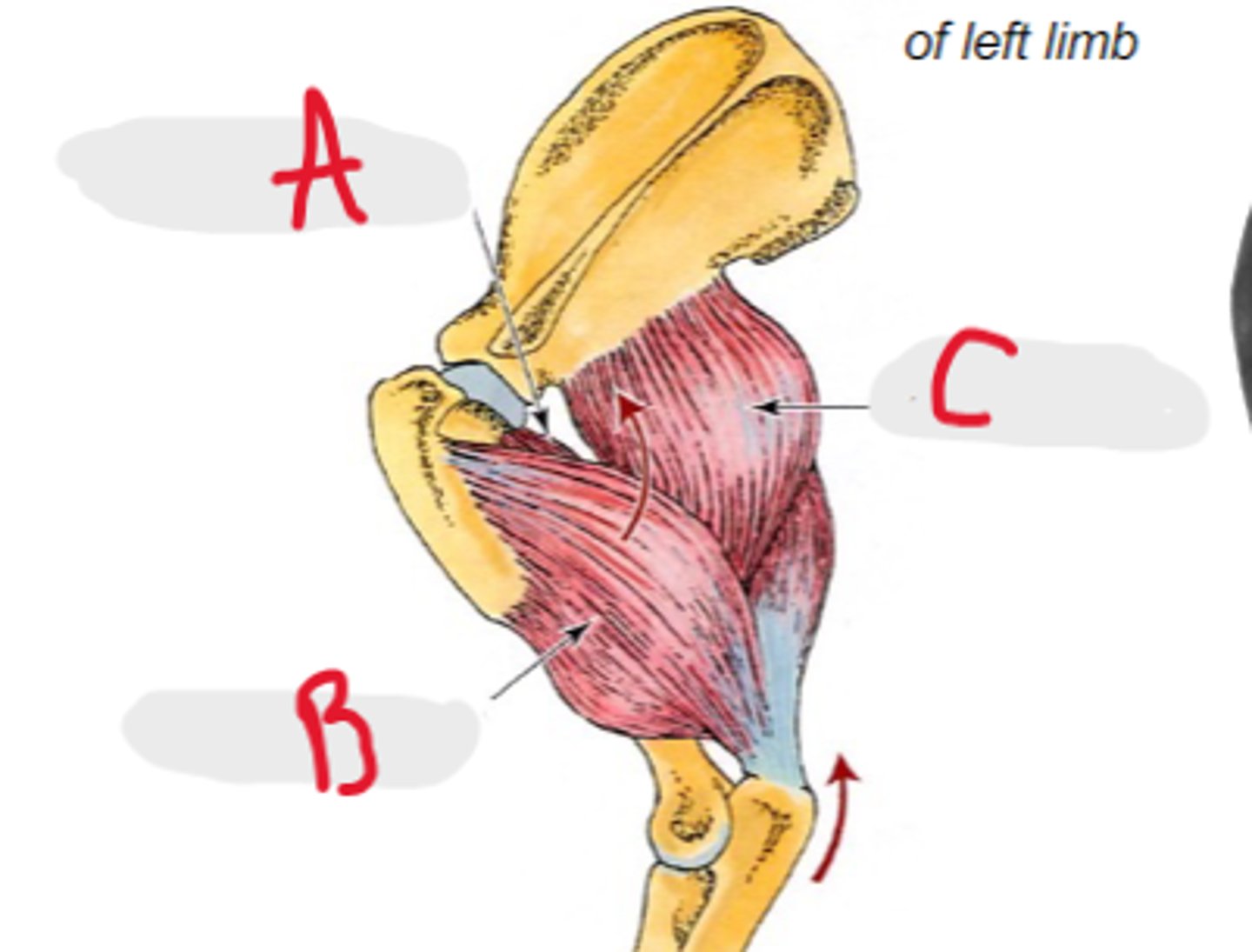
lateral head
What is B?
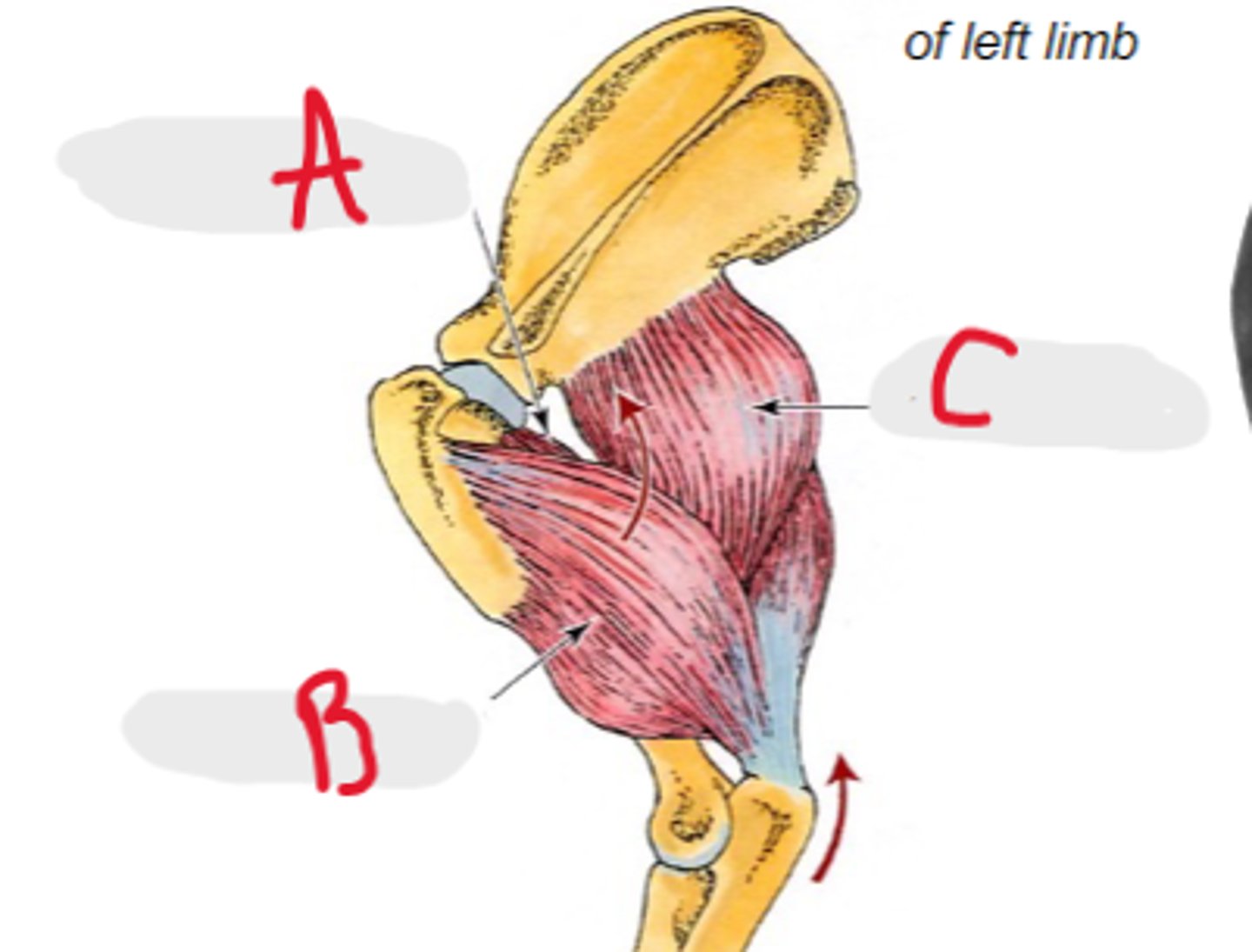
long head
What is C?
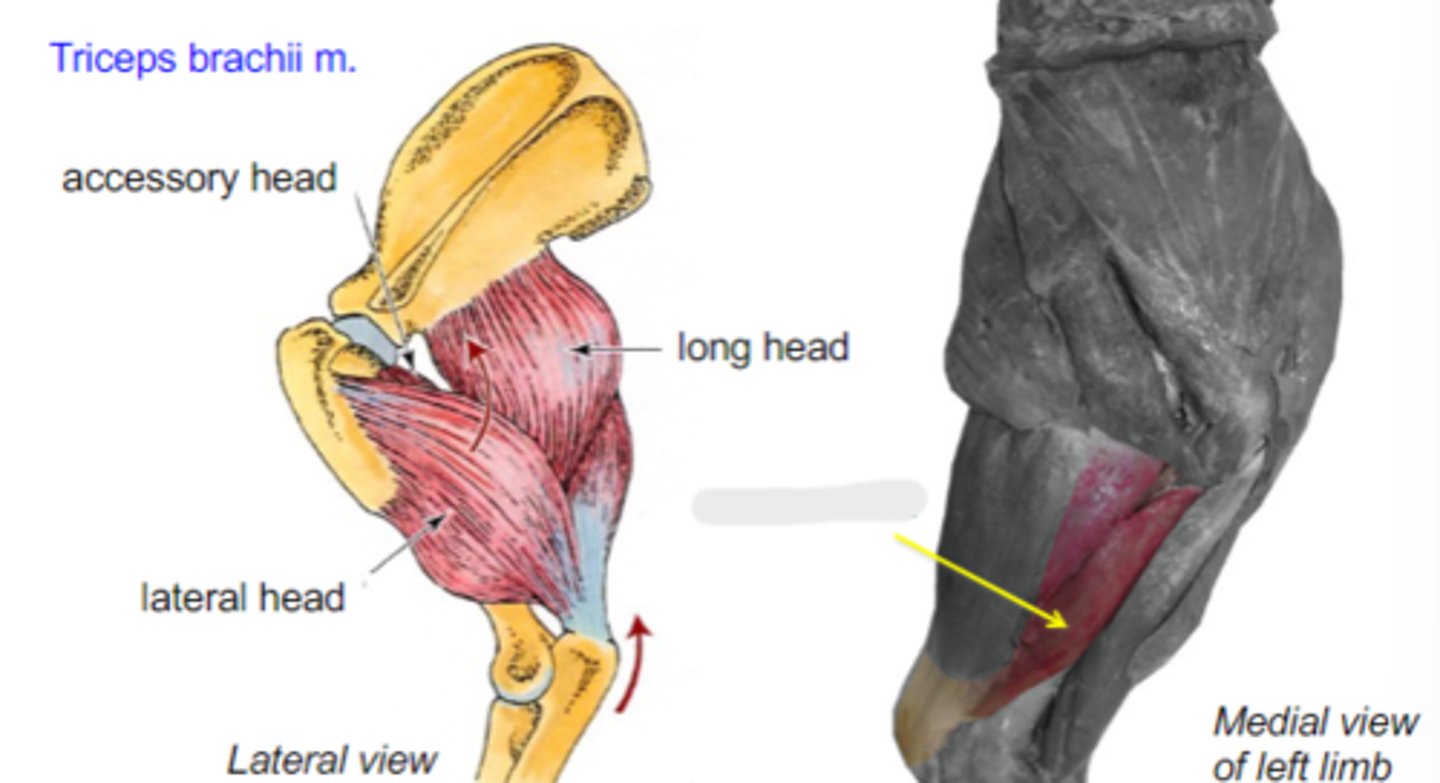
medial head
What is the yellow arrow pointing to?
tensor fasciae antebrachii
What muscle is shown?
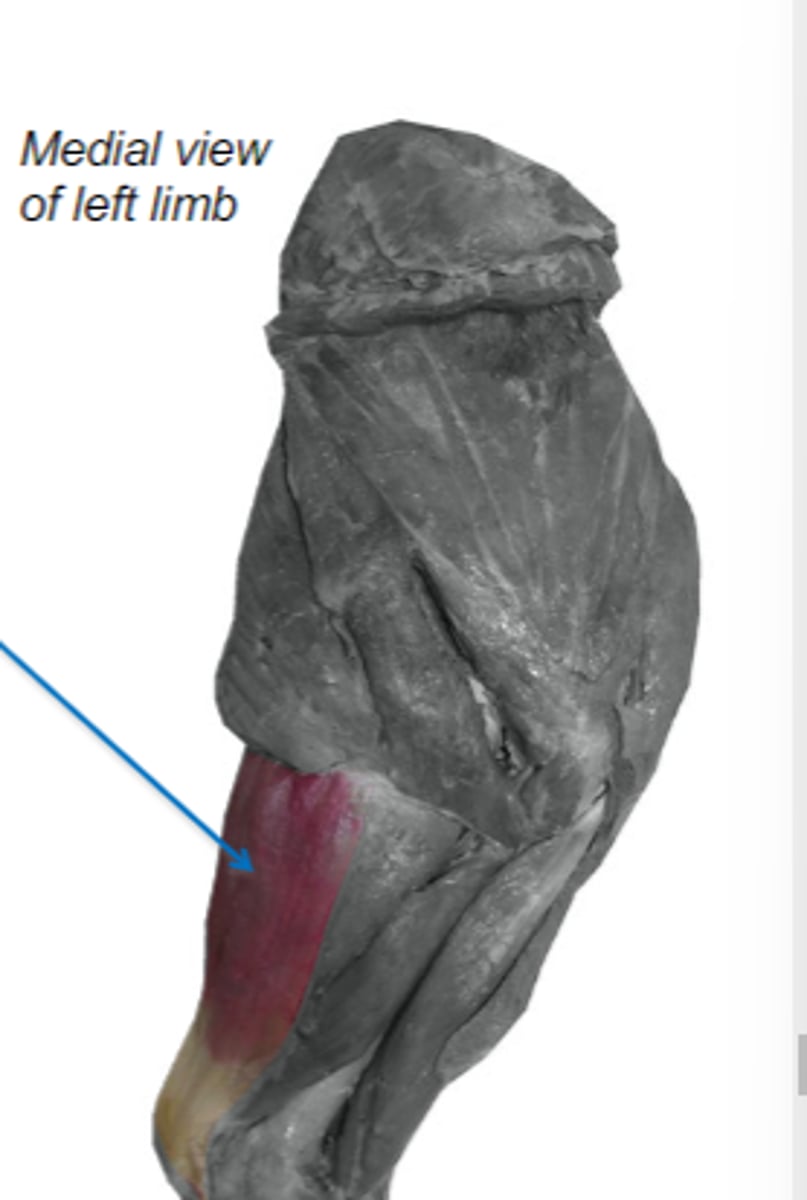
latissimus dorsi & associated fascia
Origin of tensor fasciae antebrachii:
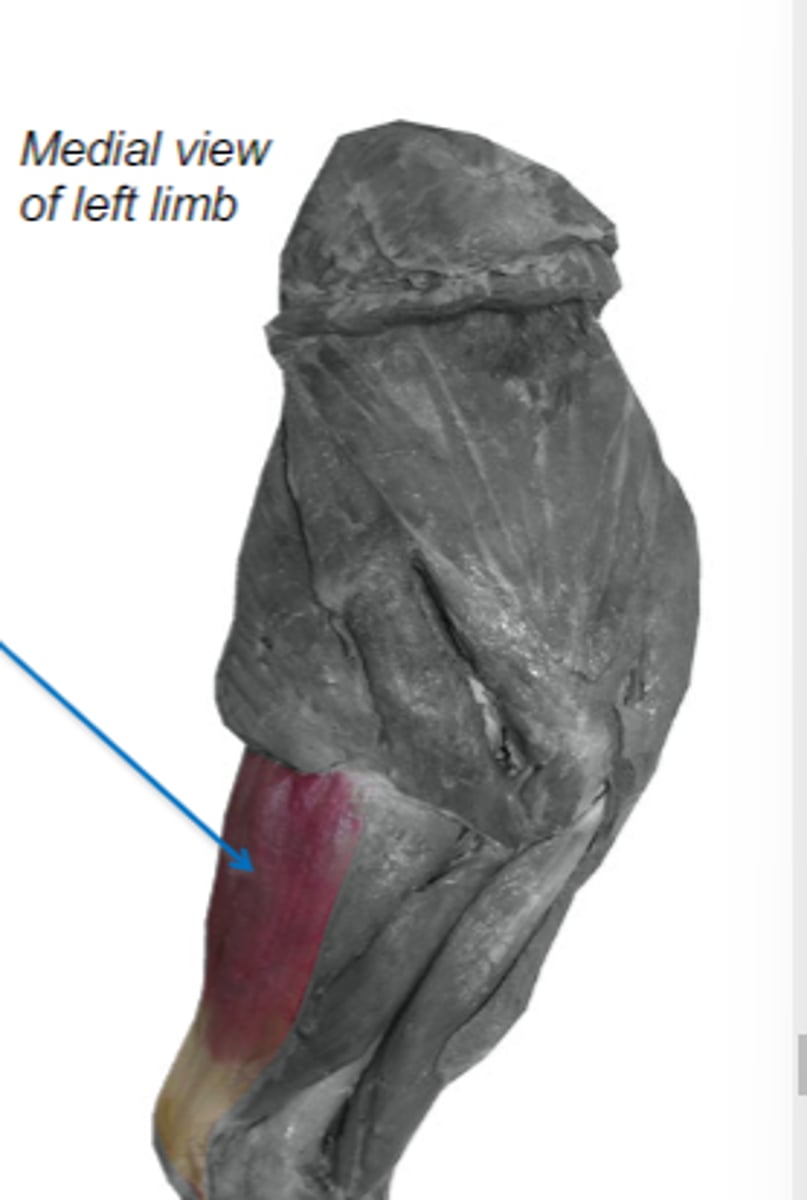
tuber olecrani
Insertion of tensor fasciae antebrachii:
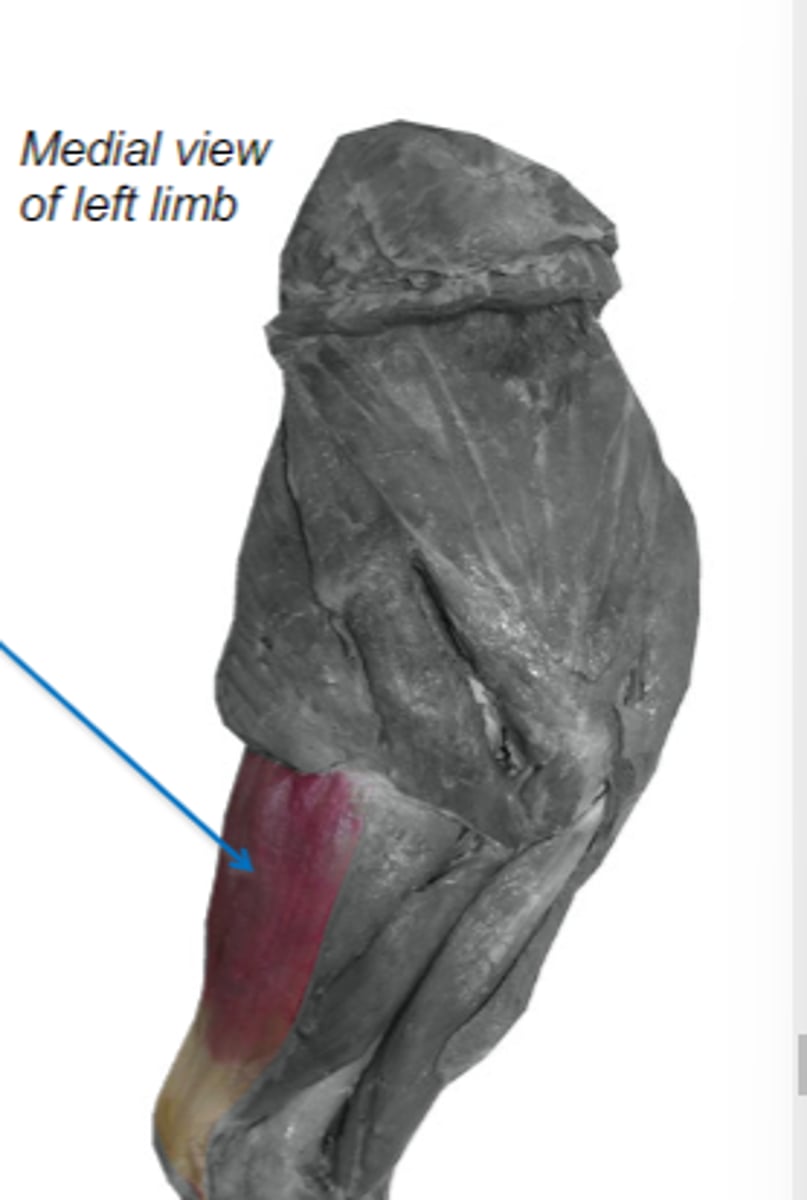
extend cubital joint & tense deep antebrachial fascia
Action of tensor fasciae antebrachii
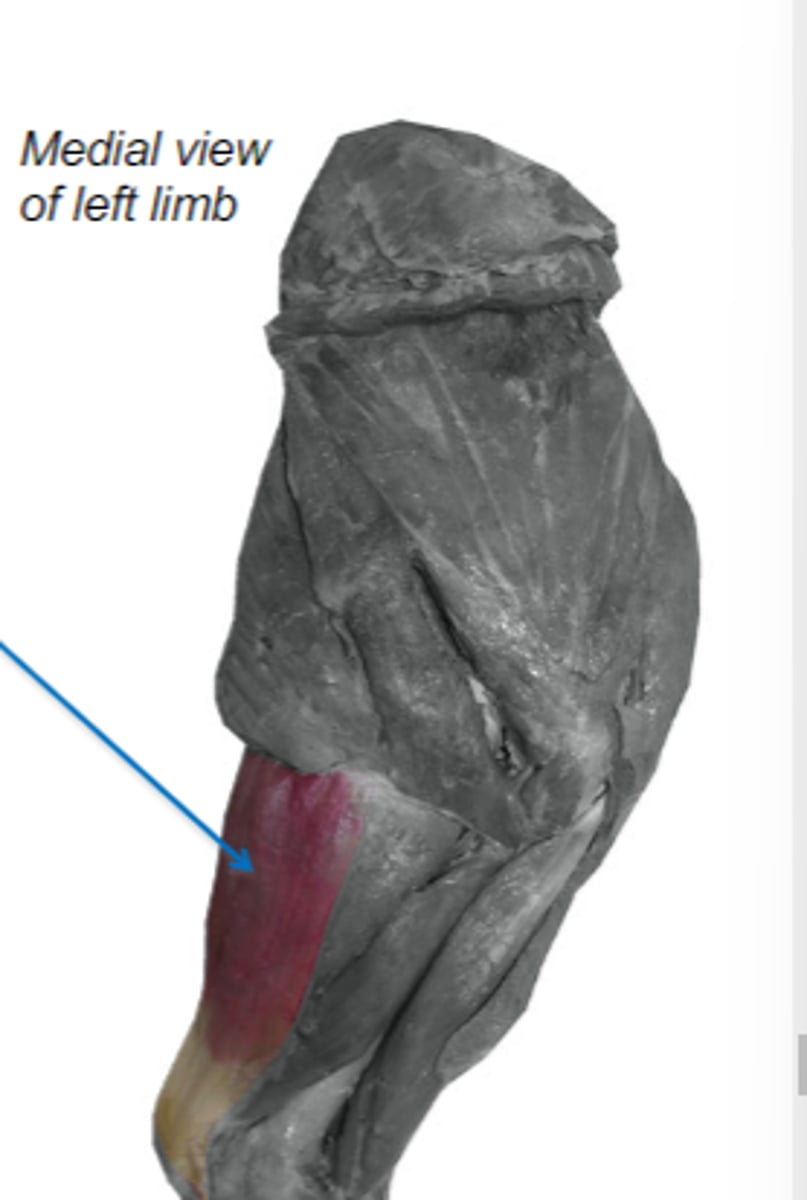
tensor fasciae antebrachii
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: latissimus dorsi and associated fascia
Insertion: tuber olecrani
Action: extend the cubital joint (and tense the deep antebrachial fascia)
anconeus
What muscle is shown?
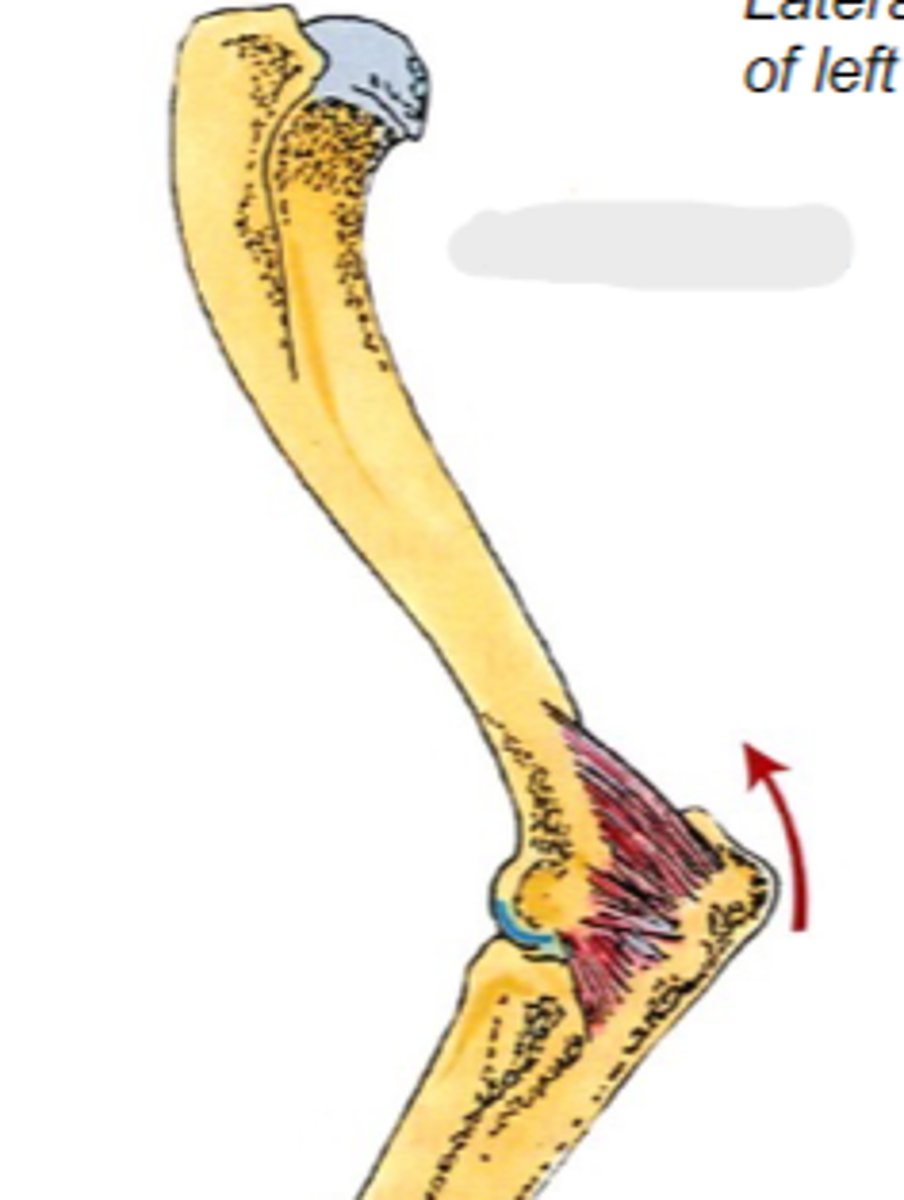
caudal aspect of distal humerus
Origin of anconeus:
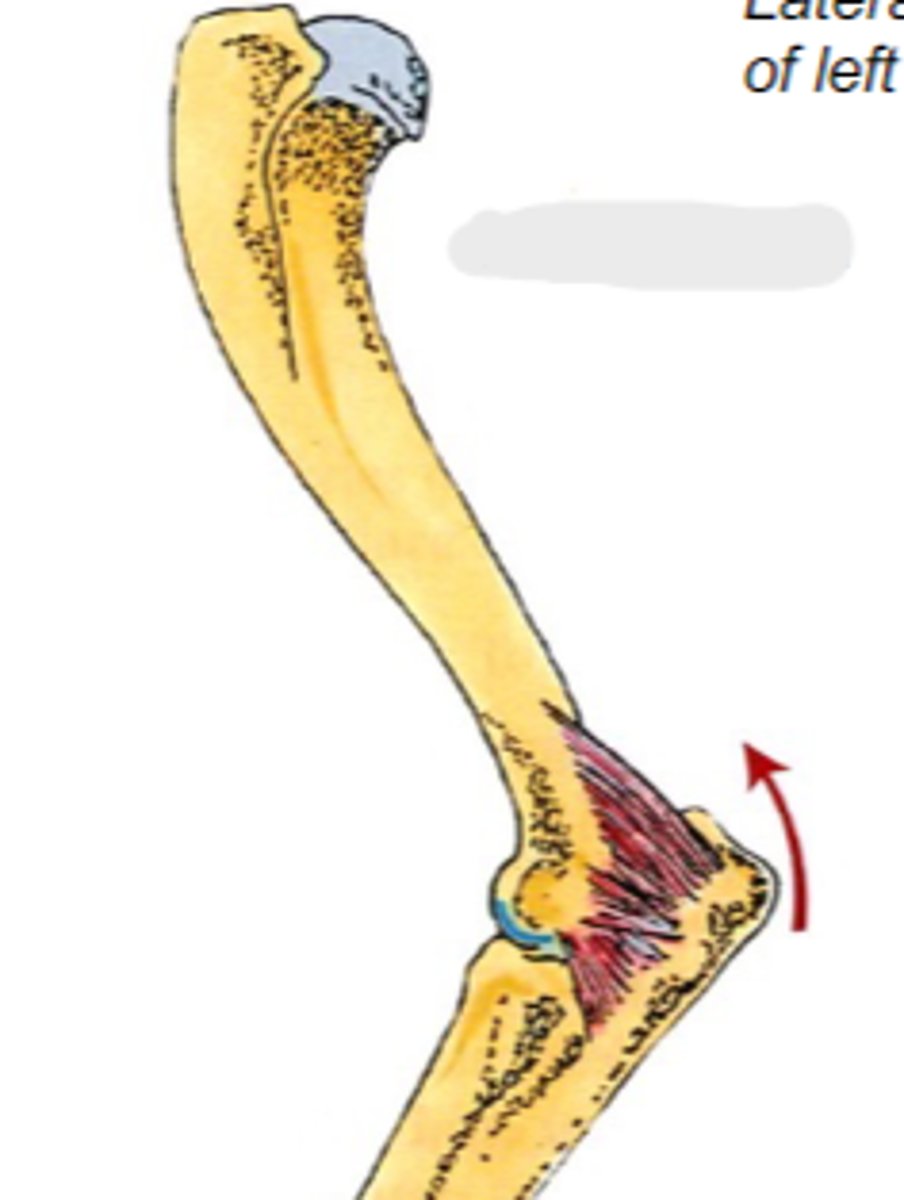
tuber olecrani
Insertion of anconeus:
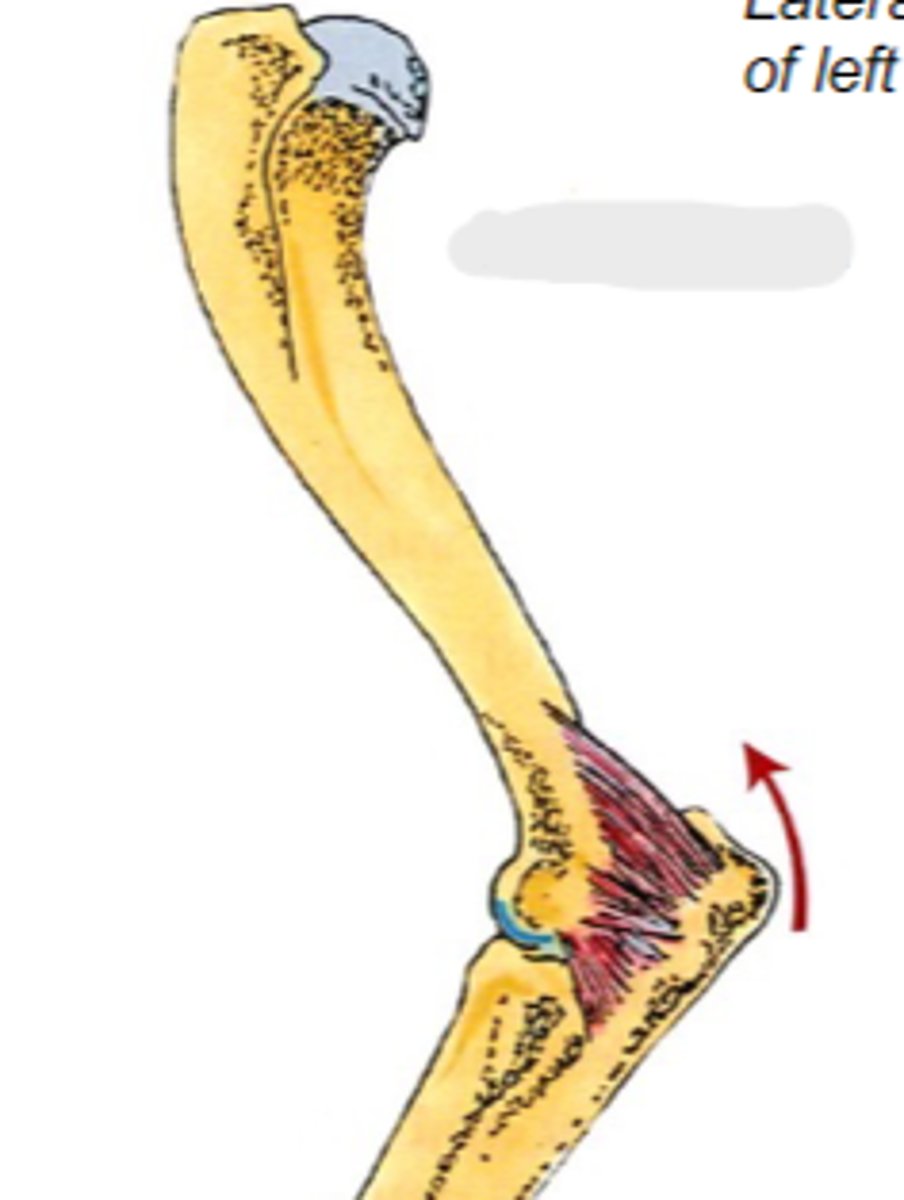
extend cubital joint
Action of anconeus:
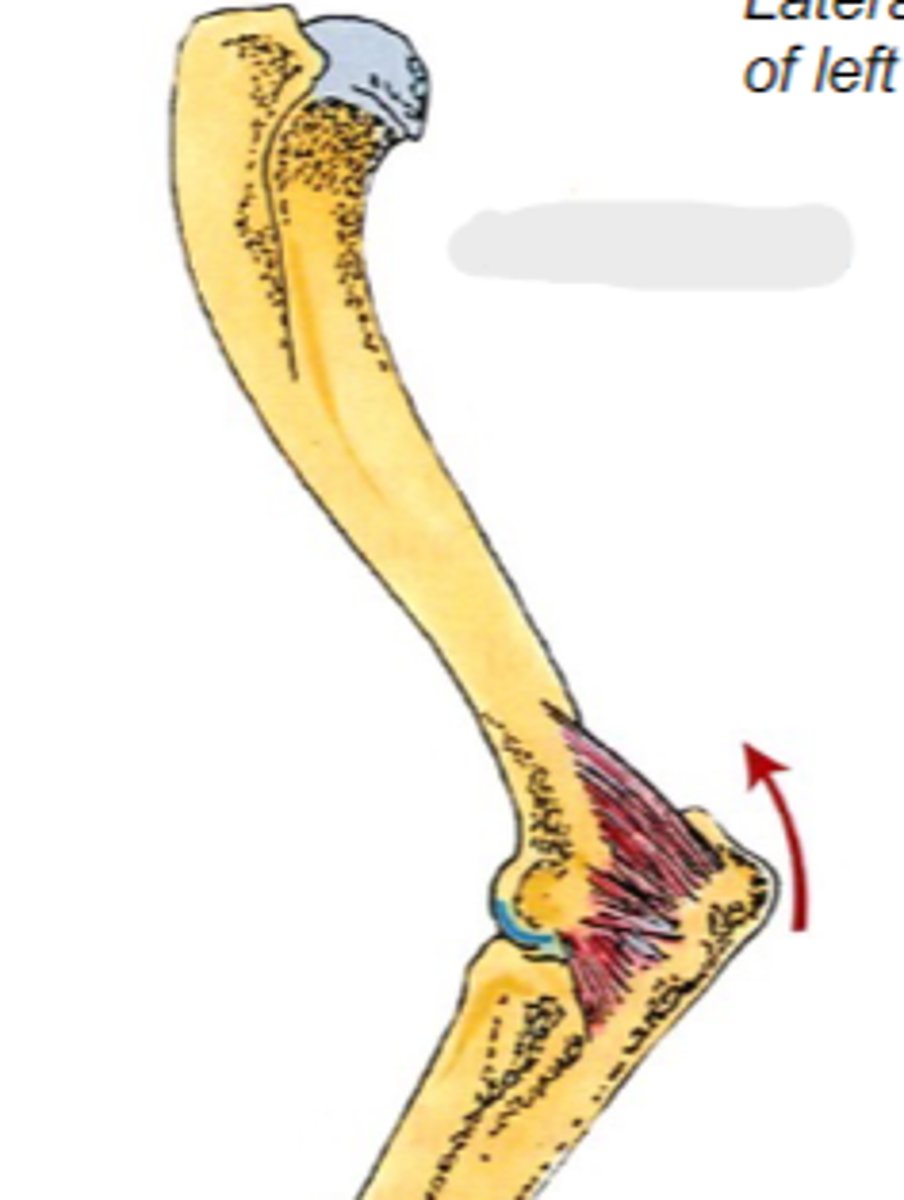
anconeus
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: caudal aspect of distal humerus
Insertion: tuber olecrani
Action: extend the cubital join
extensor
The following muscles are part of the [extensor/flexor] group:
-extensor carpi radialis m.
-extensor carpi ulnaris m. (ulnaris lateralis)
-abductor digit I longus m.
-common digital extensor m.
-lateral digital extensor
2 multiple choice options
![<p>The following muscles are part of the [extensor/flexor] group:</p><p>-extensor carpi radialis m.</p><p>-extensor carpi ulnaris m. (ulnaris lateralis)</p><p>-abductor digit I longus m.</p><p>-common digital extensor m.</p><p>-lateral digital extensor</p><p>2 multiple choice options</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ca0dda0e-904f-4a5b-aae1-9967dd818b62.jpg)
flexor
The following muscles are part of the [extensor/flexor] group:
-flexor carpi radialis m
-superficial digital flexor m
-flexor carpi ulnaris m
-deep digital flexor m
2 multiple choice options
![<p>The following muscles are part of the [extensor/flexor] group:</p><p>-flexor carpi radialis m</p><p>-superficial digital flexor m</p><p>-flexor carpi ulnaris m</p><p>-deep digital flexor m</p><p>2 multiple choice options</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dd5794f6-72a4-4438-bd0d-ee44c42e88a5.jpg)
extensor carpi radialis
What muscle is shown?
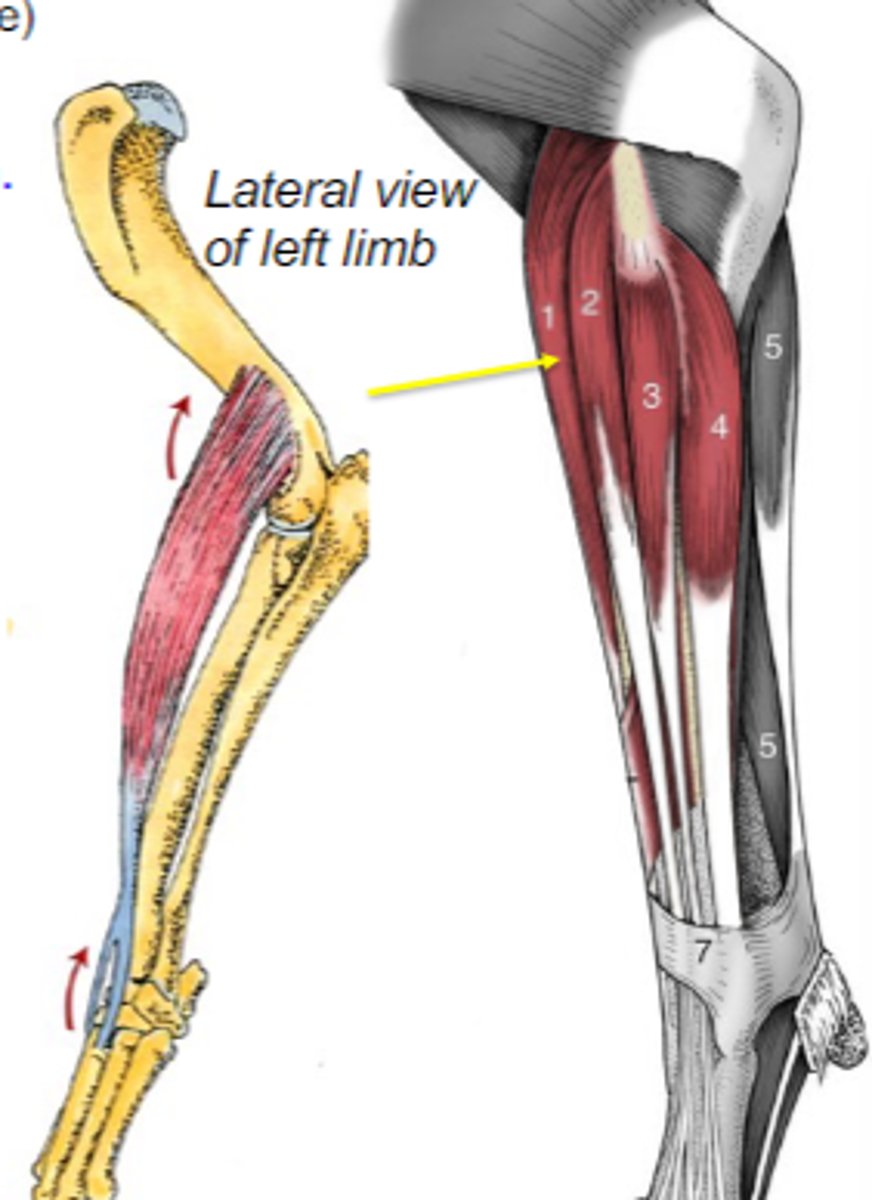
lateral epicondyle of the humerus (and its crest)
Origin of extensor carpi radialis:
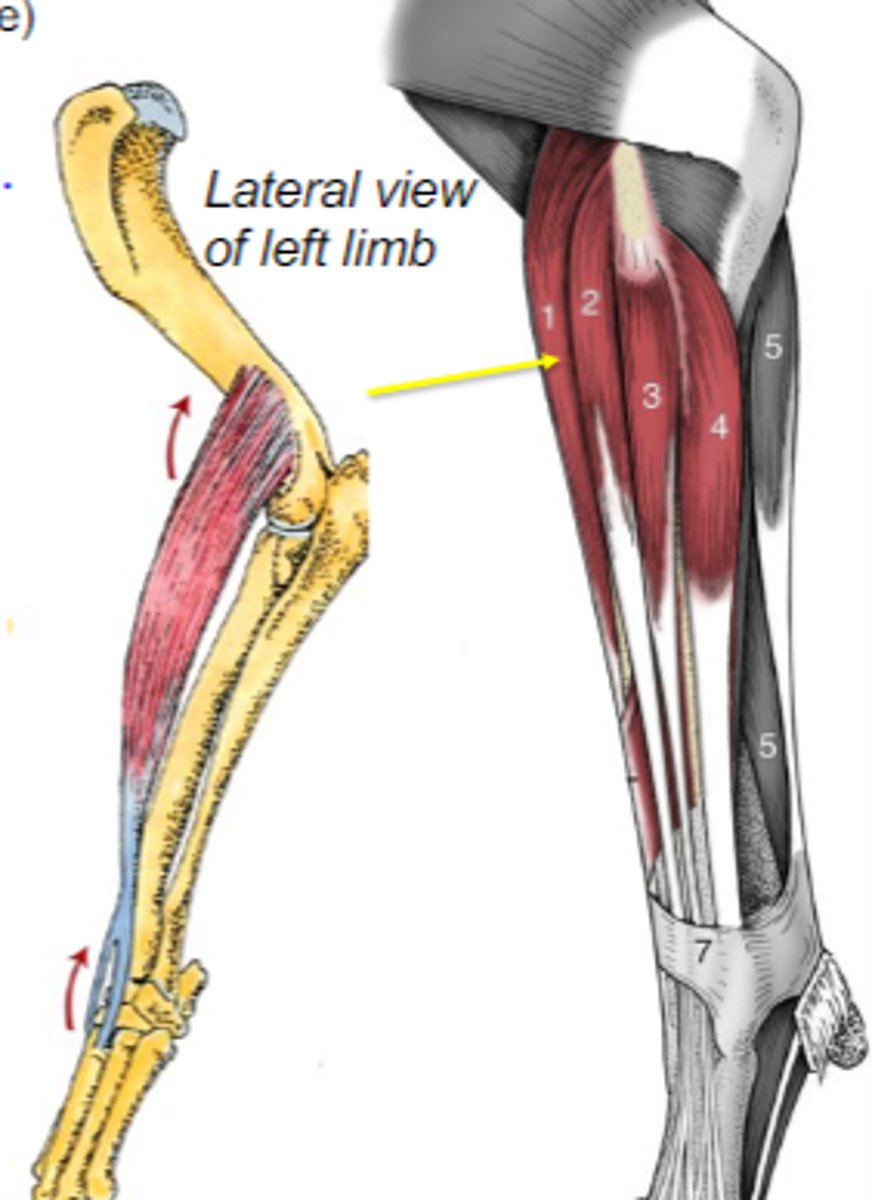
dorsal base of 2nd and 3rd metacarpal bone
Insertion of extensor carpi radialis:
extend carpal joints
Action of extensor carpi radialis:
extensor carpi radialis
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: lateral epicondyle of the humerus (and its crest)
Insertion: dorsal base of 2nd and 3rd metacarpal bones
Action: extend the carpal joints
common digital extensor
What muscle is shown?
lateral epicondyle of humerus
Origin of common digital extensor:
extend carpal and digital joints
Action of common digital extensor:
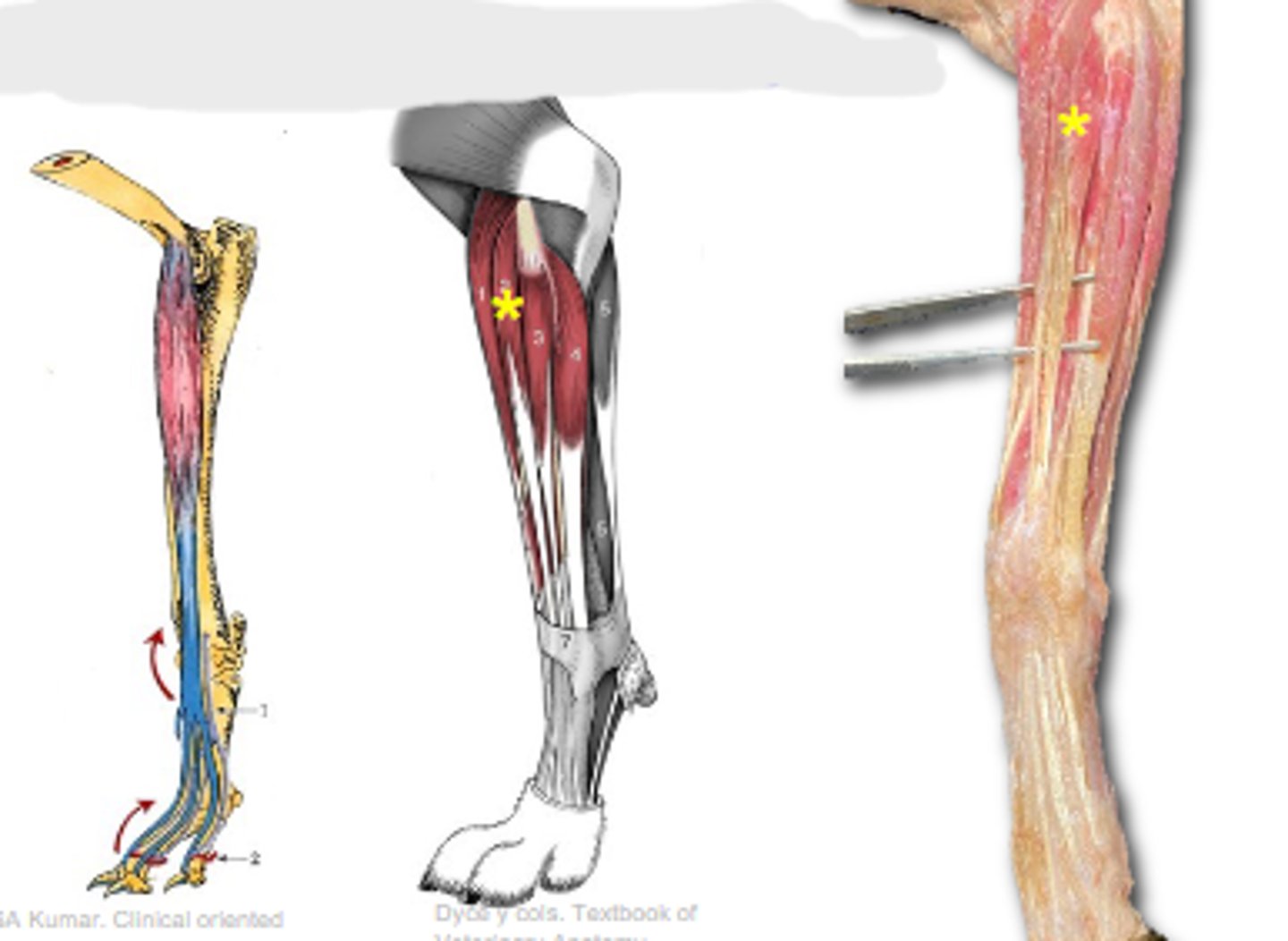
common digital extensor
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: lateral epicondyle of the humerus
Insertion: extensor processes of distal phalanges
Action: extend the carpal joints; extend the digital joints
extensor processes of distal phalanges
Insertion of common digital extensor:
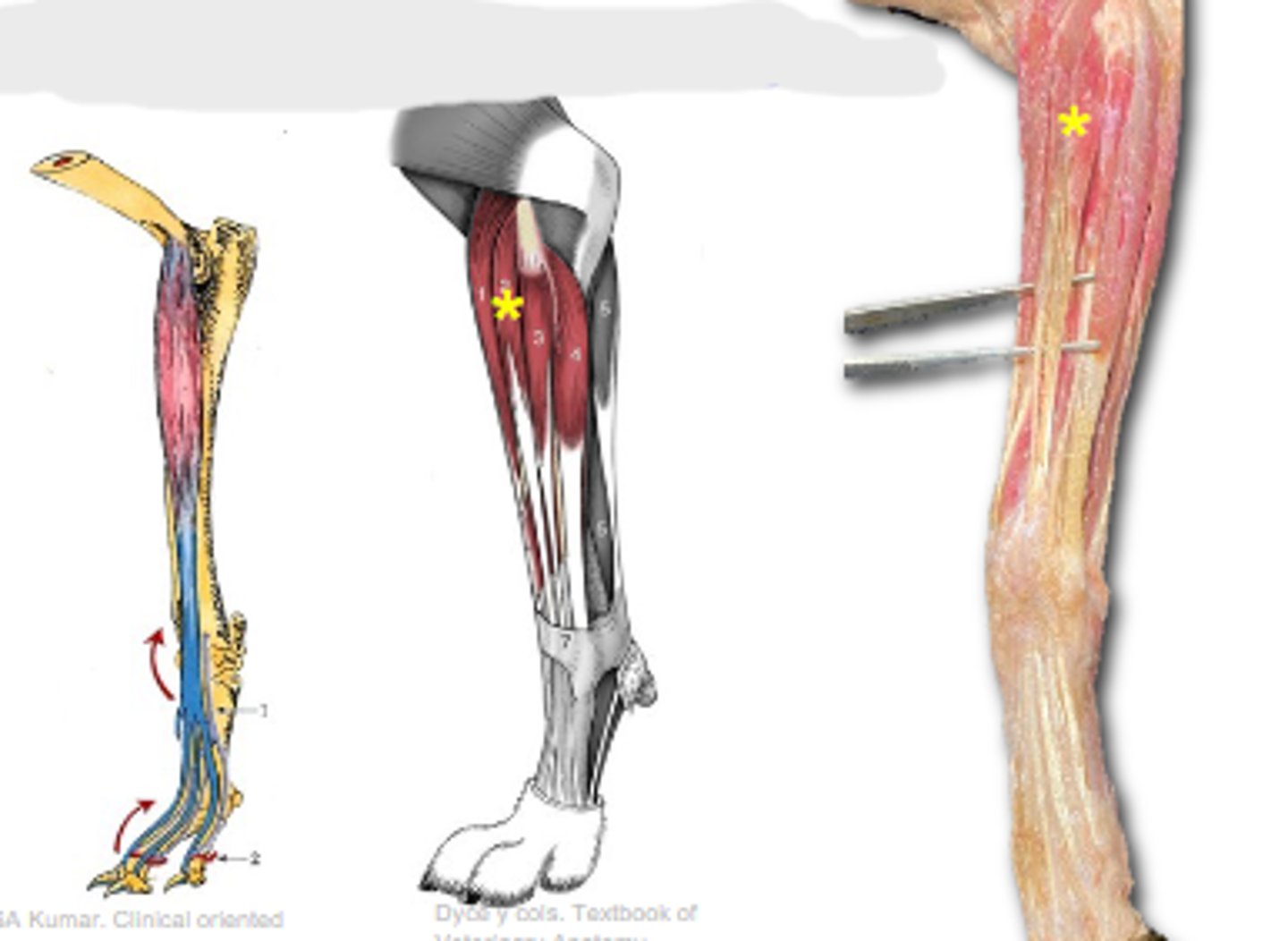
lateral digital extensor
What muscle is shown?
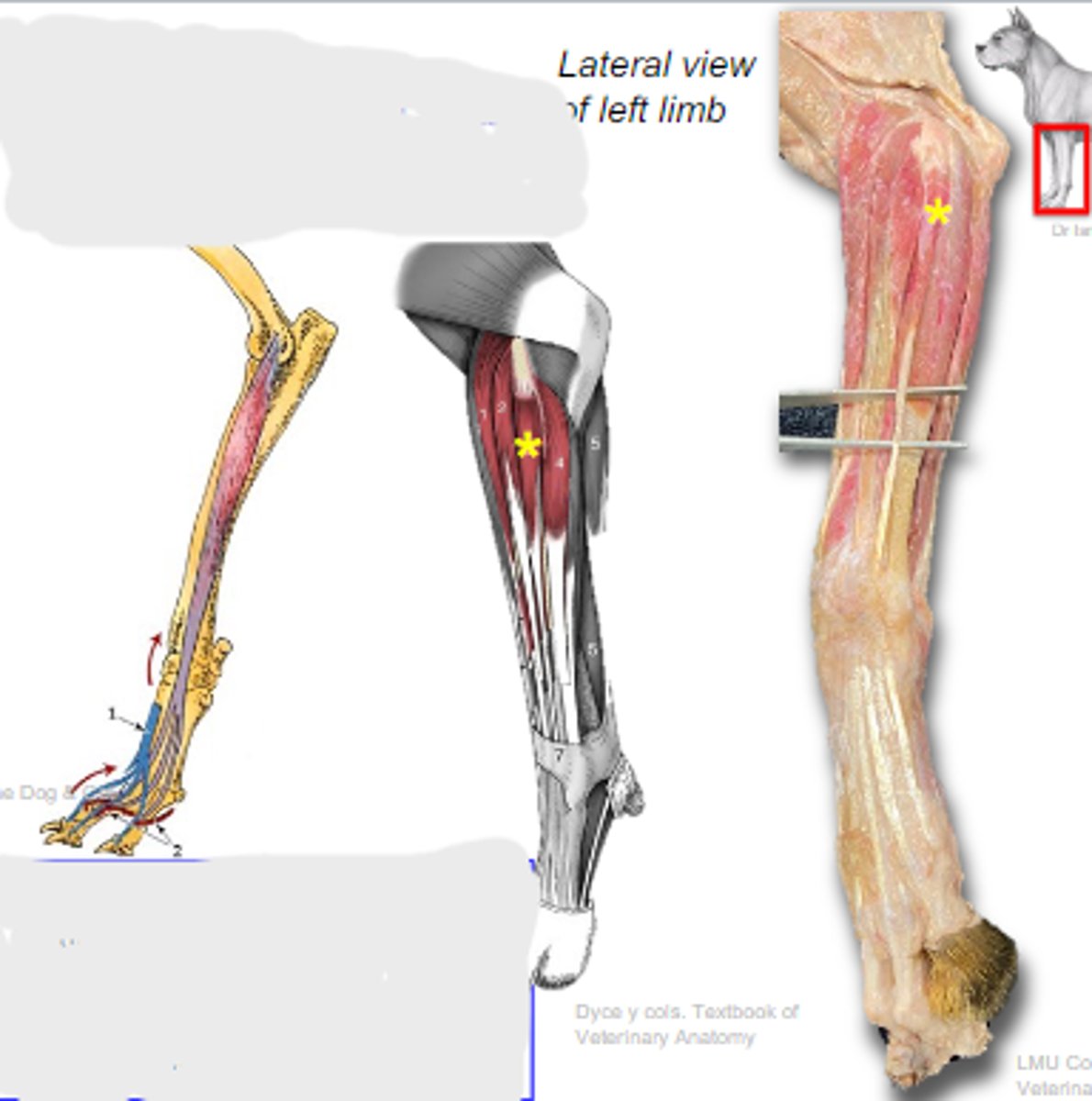
lateral epicondyle of humerus
Origin of lateral digital extensor: