Opiate analgesic MedChem
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What type of receptors are all opioid receptors?
GPCRs
What type of opioid receptor binds morphine most strongly?
Mu opioid receptor
What do all opioid receptors associate with?
Enkephalins
What does activation of the mu opioid receptor produce?
Analgesia but also side effects - respiratory depression, euphoria, addiction
What are mu and delta opioid receptors all sources of?
Pain stimuli
What are kappa opioid receptors associated with?
Non-thermal pain induced stimuli
What are enkephalins?
Series of small peptides that give rise to natural ligands/analgesics
What key functional groups do enkephalins have that enable them to bind to their receptors?
Ionic binding region, tyrosine binding site also that have hydroxyl groups that bind to the active site
What part of morphine binds to enkephalins?
Positively charged Nitrogen
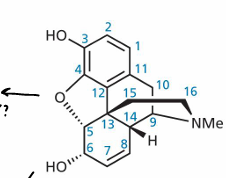
What are some key features of morphines structure?
3D structure, contains a phenol group, N and Methyl group allows binding to enkephalin
What further binding site does morphine not extend into?
P site of receptor
What are the 3 binding sites for opioid receptors?
T site/tyrosine, P site and ionic site
What are the characteristics of the P site?
Hydrophobic region
What key functional groups of morphine form interactions with opioid receptors?
Phenolic group on C3, bridging ether group carbons 4-5, hydroxyl group on C6, aromatic ring A, C=C double bond between C7-8, tertiary amine in ring E that can be protonated
What is the modification from morphine to make hydromorphone?
Removed alkene group - saturated ring made as double bond not essential for activity
Why does codeine have a lower activity compared to morphine?
Prodrug - methyl group altered to become morphine in vivo
What do the 2 acetate groups allow in 6-acetylmorphine?
Allows to cross BB and acetyl groups cleaved off - gives rise to activity but increases addictiveness
What are the 3 key bonds for interacting with opioid receptors?
Hydrogen Bond, Van der Waals, ionic
What is a pharmacophore?
Minimum required functional groups/structure needed for activity and links key functional groups together
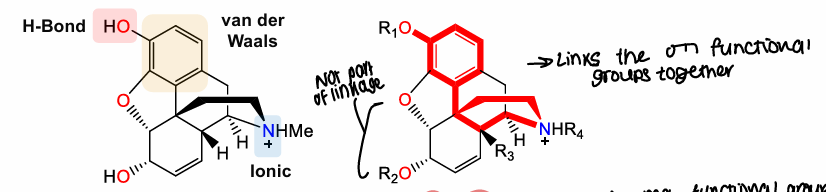
What does the pharmacophore work out?
Distances between each group and what each group should be
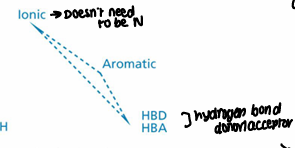
What is the opioid analgesic pharmacophore?
Ionic, aromatic, Hydrogen bond donor or acceptor
What are some examples of opioids with an addition of 14-hydroxyl group?
Oxymorphone, hydrocodone, oxycodone
What are the main changes for 14-hydroxyl group opioids?
No double bond, oxygen added to H group, methylated phenolic group
Why does hydrocodone have less activity compared to morphine?
Methylating hydroxyl group decreases the group activity - takes away a binding interaction
What happens when an additional C is added to the methyl group in morphine to make ethyl?
Decreases activity
What is the general trend adding more C’s (aside from ethyl and butyl) to morphine?
Increases antagonistic activity
What is an advantage of N-phenylethylmorphine?
14x more active agonist activity, exploits additional van der Waals interaction/TT-TT stacking
What is naloxone?
Inverse agonist at mu-opioid receptor
How does naloxone work?
Binds to the site but removes agonist potentials
What is a key functional group of naloxone?
Allyl group - CH2 to double bond
What is naltrexone?
Pure opioid antagonist
What is the use of naltrexone?
Used to remove morphines effects
What is the key functional group in naltrexone?
Cyclopropyl - large alkyl group with conformational restriction
What groups in naltrexone exploit new reactions in comparison to morphine?
Carbonyl forms new, stronger binding than morphine and blocks it from entering, cyclopropyl group sticks out to hydrophobic binding site
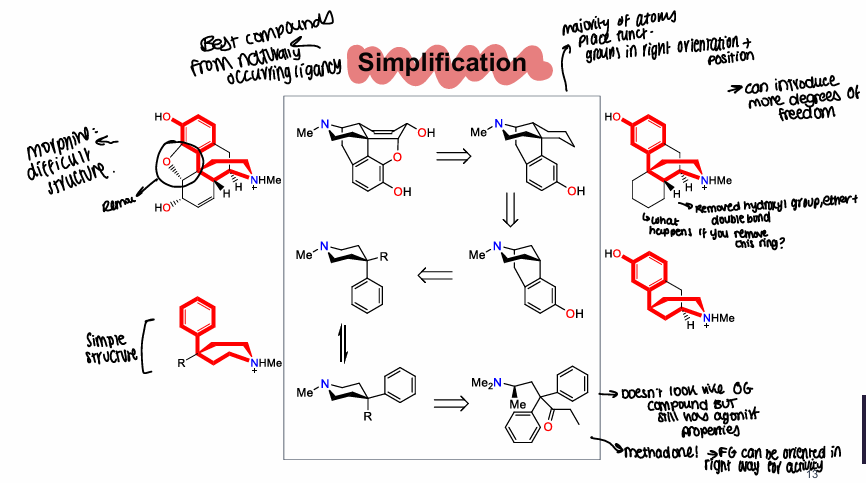
What is a diagram showing potential simplifcation of opioids?
Best compounds come from naturally occurring ligands, end result may not look like original compound but still has agonist properties
What are examples of morphinans?
Levorphanol, levallophan, N-phenylethyllevorphanol
What is an advantage of levorphanol?
Higher activity than morphine, still rigid and has lost non-essential functional groups
How does levallorphan work?
Antagonist due to allyl group
What are examples of 6,7-benzomorphans?
Phenazocine, pentazocine
What activity do 6,7-benzomorphans have?
Mixed agonist/antagonist
Where does pentazocine act?
Agonist at kappa and delta, weak antagonist at mu
What group is needed to lock phenazocine into conformation?
Methyl
What is a benefit of pentazocine despite it having lower activity compared to morphine?
Less sedative effective and less addictive potential
What is pethidine?
Very good short-acting analgesic that has a rapid onset but short lvied - good for minor injuries or in childbirth
What group has pethidine lost compared to other opioids?
Phenolic group
What is an analogue of pethidine?
N-cinnamoyl - 30x more potent
What are some key functional groups in N-Cinnamoyl pethidine?
Cinnamic acid residue that can extend and make more active, phenyl ring, rigid side chain
What is a downside of N-Cinnamoyl analogue of pethidine?
Morphine analogue is inactive
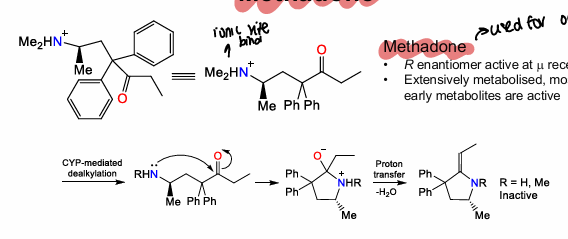
What is methadone used for?
Opioid addiction
What are some properties of methadone?
R enantiomer active at Mu receptor, methyl and N group is site of ionic binding, extensively metabolised,
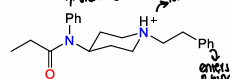
What is loperamide used for?
Diarrhoea to decrease gut motility
What is the structure of loperamide?
Similar to methadone, binds strongly to opioid receptor
What are examples of 4-anilinopiperidines?
Fentanyl, sulfentanil, alfentanil, remifentanil
What type of analgesic is fentanyl?
Non-opioid analgesic but can still cause addiction and death - synthetic analogue
What are some properties of fentanyl?
Phenol group attached to a N group binds strongly to TT-TT stacking, NH+ is ionic site of binding, end phenol group enters P binding site
What can be side effects of fentanyl due to its strong binding?
Respiratory depression and increases addictiveness
What problems does rigidification cause?
Decreased degree of freedom but molecule is more difficult to make
What can be an effect of oripavines - a more rigidified opioid?
More hydrophobic so more likely to cross into CNS
What activity does buprenorphine have?
Partial agonist - has some antagonistic properties