First Aid & CPR Final Exam
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
abdominal thrust
thrusts administered to the abdomen of a responsive, choking person to dislodge an object blocking a person’s airway
acute coronary syndrome (ACS)
often described as a heart attack; occurs when there is reduced blood flow to the tissues of the heart
airway
the passage between mouth and lungs that allows life-sustaining oxygen into the body
altered mental status
a significant change in a person’s personality, behavior, or consciousness, which may indicate a serious medical problem
amputation
a complete loss of a body part
anaphylaxis
a severe allergic reaction with an extreme response of the body’s immune system to something it is very sensitive to
arterial bleeding
a wound to an artery, which is characterized by bright red, oxygen-rich blood spurting from the wound
asthma
reactive airway disease, narrowing the small air passages in the lungs and causing difficulty breathing
automated external defibrillator (AED)
a small, portable, computerized device that allows a minimally trained bystander to provide defibrillation much faster than EMS
bloodborne pathogens
infectious microorganisms in human blood that can cause disease in humans. Includes Hep B (HBV), Hep C (HCV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
a combination of rescue breaths and chest compressions performed on a person experiencing cardiac arrest, intended to restore some oxygen to the brain
chain of survival
early access to EMS
early CPR
rapid defibrillation
effective advanced care
integrated post-cardiac care
a concept of 5 interdependent links that describe the most effective approach for treating sudden cardiac arrest.
chest compression
a basic CPR skill that creates increased pressure in the chest cavity and direct compression of the heart. This forces blood to move from the chest to the lungs, brain, and rest of the body
chest thrust
thrusts administered on the breastbone of a responsive, choking person to dislodge an object stuck in the person’s airway
compression-only CPR
a simple, but limited approach to treating sudden cardiac arrest that is being widely promoted to people who are not formally trained in CPR
CPR mask
a protective barrier device used to prevent exposure to potentially infectious body fluids while performing rescue breaths on a person. this mask fits over the mouth and nose of the person and includes a one-way value to blow through.
defibrillation
the delivery of an electrical shock through the heart intended to end chaotic electrical activity in the heart and allow the heart’s normal electrical activity to return
diabetes
a disease in which the body cannot effectively use sugar for energy, which can lead to life-threatening problems if not managed properly
diabetic emergency
often characterized by an altered mental status
direct pressure
pressure applied directly to a bleeding site until bleeding stops. it is the standard method for controlling external bleeding.
dislocation
the separation of bone ends at a joint
DOTS. (Deformities, Open injuries, Tenderness, Swelling)
mnemonic device used to help with physical assessment
emergency action plan (EAP)
used to help ensure safe and healthy conditions at work by providing step-by-step procedures on how to report and respond to emergencies
emergency medical services (EMS)
an emergency medical response system developed within a community, consisting of a specialized communications network and trained professional responders, all accessible through an emergency phone number (e.g. 911)
epinephrine auto-injector
a prescribed medication device with a spring-loaded needle, designed for easy use by a minimally trained person. intended for use in treating a life-threatening allergic reaction. it delivers a measured single dose of epinephrine
evisceration
the protrusion of abdominal organs through an open abdominal wound
FAST (Face droop, Arm drift, Speech difficulty, Time to activate EMS)
mneumonic device used to help with stroke assessment
fracture
a break in a bone
frostbite
the freezing of skin and underlying body tissue in extremely cold conditions
Good Samaritan Law
A law enacted to legally protect trained providers who voluntarily stop to help, act prudently, do not provide care beyond training, and are not completely careless in delivering emergency care
head tilt-chin lift
the recommended technique to open and maintain the airway of an unresponsive person. This pulls the tongue forward and lifts the tongue away from the back of the throat.
heart attack
also known as acute coronary syndrome
hypoglycemia
low blood sugar. a diabetic condition that can rapidly develop and become life threatening.
hypothermia
a generalized cooling of the body that is a life-threatening condition, occurring when the internal core body temperature has decreased to 95*F or less.
impaled object
an object that penetrates a body part and remains embedded
implied consent
a legal concept referring to the assumption that an unresponsive person would give permission to be helped if responsive
internal bleeding
a condition in which an injury causes bleeding inside the body, which can be difficult to detect. If it goes untreated, it can lead to shock and become a life-threatening problem
mechanism of injury
a concept used by first aid providers to quickly suspect injury due to evidence that significant force has impacted a person’s body
naloxone
a medication that can temporarily reverse the life-threatening effects of opioids. It is administered either through an auto-injector device or through an aerosol that is sprayed into the nose. This is becoming more readily available to lay providers.
overlay shield
a protective barrier device used to prevent exposure to potentially infectious body fluids while performing rescue breaths on a person. This lays over the face and includes a one-way valve or filter to blow through
primary assessment
an initial approach to quickly identify if a life-threatening condition is present
protective barrier
an item that helps reduce the risk of exposure to blood and other potentially infectious body fluids. (e.g. disposable gloves, CPR masks, and face shields)
recovery position
a side-lying position in which an unresponsive breathing person is placed to drain fluids from the mouth and keep the tongue from blocking the airway
rescue breaths
artificial breaths given to someone who is not breathing. administered by blowing air into the mouth to inflate the lungs
SAMPLE (Symptoms, Allergies, Medications, Past medical history, Last oral intake, and Events leading to problem)
mnemonic device used to help provides remember what to ask a person about
secondary assessment
used when there are no life-threatening conditions to gather additional information about the person’s chief complaint, physical signs, and additional information related to what is going on
seizure
jerking or convulsive activity of the body triggered by excessive electrical activity within the brain
shock
a life-threatening condition that develops when poor blood flow created a shortage of oxygen to body tissues
spinal motion restriction
the use of the hands to gently hold both sides of the head to restrict spinal movement. Done to prevent additional damage from a suspected spinal injury.
splint
a device used externally to immobilize a painful, swollen, or deformed limb in order to decrease pain and prevent further injury
sprains
tearing injuries to ligaments that hold joints together
standard precautions
a consistent set of protective practices used whether or not an infection is suspected. The approach is the same for everyone, regardless of relationship or age
strains
stretching or tearing injuries to muscles or tendons
stroke
sudden brain cell death caused by the loss of oxygen to brain tissue either by a blockage in a blood vessel or bleeding into the brain tissue when a weak blood vessel wall bursts open
sudden cardiac arrest (SCA)
the abrupt loss of the heart’s ability to contract and push blood forward through the circulatory system. Typically caused by a sudden disruption of the heart’s electrical system.
torniquet
a binding device used on a limb above a heavily bleeding wound to control bleeding
unresponsive
a condition in which a person does not respond to physical or verbal attempts to get a response
ventricular fibrillation
a chaotic, quivering heart rhythm that prevents the normal contraction of the heart and the ability to pump blood
SETUP (Stop, Environment, Traffic, Unknown hazards, Personal Safety)
mneumonic device that can help you remember the important points of making sure it is safe to provide care

Page 3


Page 4


Page 7


Page 8

Page 9


Page 12

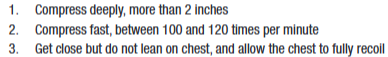
Page 13


Page 17


Page 22


Page 26

roll person on quickly to drain fluids. roll without twisting, like a log. remove any material still in mouth with a gloved finger
handle cold people gently to prevent cardiac arrest. if body is solid, do not start CPR
as quickly and safely as possible, get person onto solid ground, expect vomiting, do not attempt to expel water using abdominal thrusts
someone in cardiac arrest due to injury is unlikely to survive. If it is clear injury has caused arrest, do not start CPR
approach only if it is safe. electric shock can cause ventricular fibrillation. when safe, perform CPR and use an AED.
provide rescue breaths through surgical opening, or stoma, in neck using CPR mask or shield
How should you deal with the special CPR situations:
Fluids in airway
cold environments
drowning
serious injury
electric shock/lightning
neck breather

Page 30


Page 34


Page 38


Page 43


Page 46


Page 49


Page 56


Page 57


Page 58-1


Page 58-2


Page 59


Page 61


Page 64


Page 68


Page 70


Page 73

Page 75


Page 77

Page 79


Page 80


Page 82


Page 84

Page 85


Page 87-1


Page 87-2


Page 88


Page 89


Page 90


Page 92
