AP Environmental Science: Unit 3 (Populations)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
K-Selected Species
“Quality”
Few offspring
Lots of prenatal care
Long lifespan
Produce few offspring at a time
Usually reproduce many times
More likely to be disrupted by environmental change
Examples of K-Selected Species
Most mammals
Birds
r-Selected Species
“Quantity”
Many offspring at once
Little to no prenatal care
Usually only reproduce once
Short reproduction time and lifespan
Most likely to be invasive
Better suited for rapidly changing environmental conditions
Examples of r-Selected Species
Insects
Fish
Plants
Survivorship Curve
Line that shows a cohort’s survival rate in a population from birth to death.
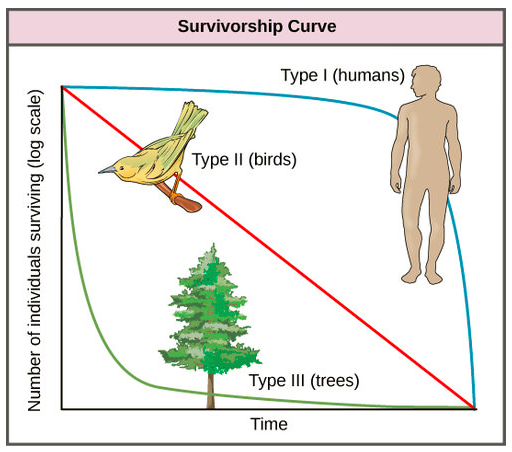
Characteristics of a Type I Species
Mostly K-selected species
High survivorship early in life because of prenatal care
High survivorship in mid-life because of big size and defensive behavior
Rapid decrease in survivorship in late life because of old age
Most mammals
Characteristics of a Type II Species
In between r and K-Selected Species
Steadily decreasing survivorship throughout life
Squirrels
Characteristics of Type III Species
Mostly r-Selected Species
Low survivorship in life because of little to no prenatal care
Few make it to mid-life
Slow, steady survivorship decline
Insects, Fish, Plants
Carrying Capacity (k)
The maximum number of individuals in a population that an ecosystem can support with its resources.
Population Overshoot
When a population briefly exceeds the Carrying Capacity.
Consequence: Resource depletion
Population Die-off
The sharp decrease in population size when resource depletion leads to many individuals dying.
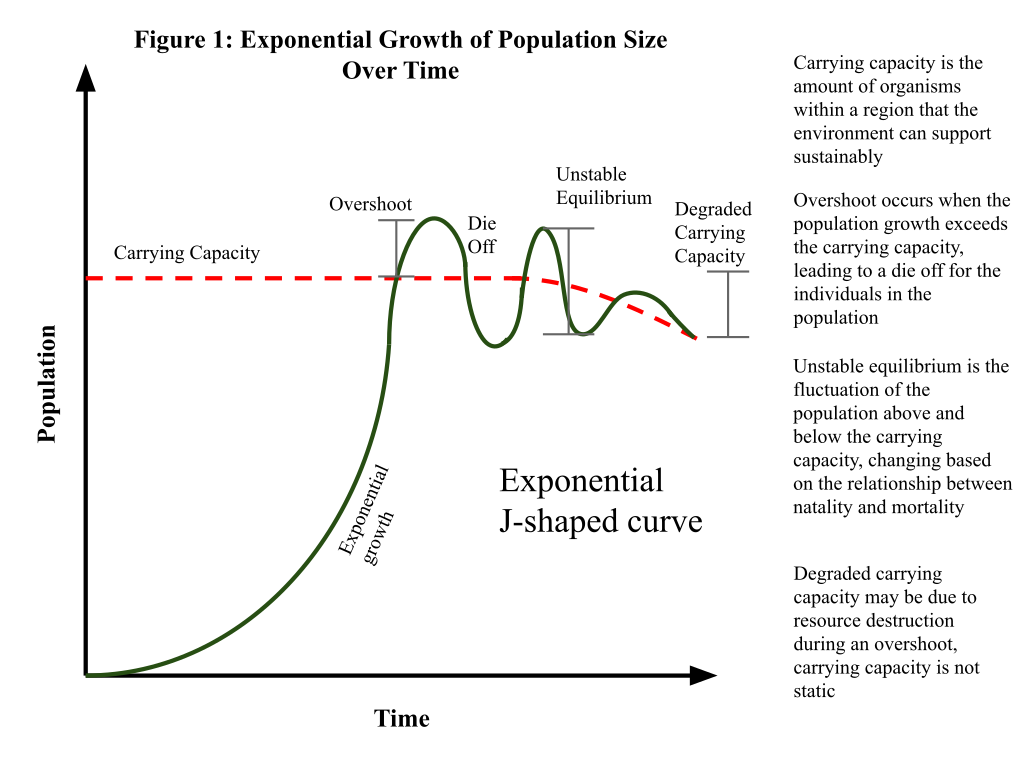
Characteristics of a Population
Size (N): Total number of individuals in a given area at a given time.
Density: Number of individuals per area.
Distribution: How individuals in a population are spaced out.
Types of Distribution
Random (e.g. trees)
Uniform (e.g. territorial animals)
Clumped (e.g. herd/group animals)
Density-Dependent Factors
Factors that influence population growth based on size