13 Alkenes
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
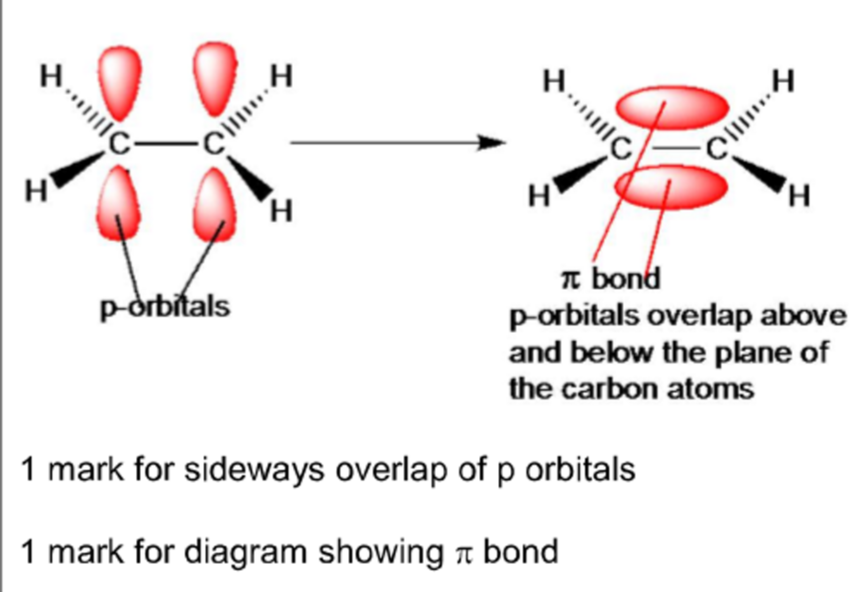
pi bond π
the sideways overlap of two p-orbitals, one from each carbon atom of the double bond
stereoisomers
molecules that have the same structural formula but a different arrangement of atoms in space
conditions for a molecule to have E/Z isomerism
a C=C double bond
each C in the double bond must be attached to two different groups
conditions for a molecule to have cis/trans isomerism
C=C double band
each C in the double bond must be attached to two different groups
one of the attached groups on each C atom must be a HYDROGEN
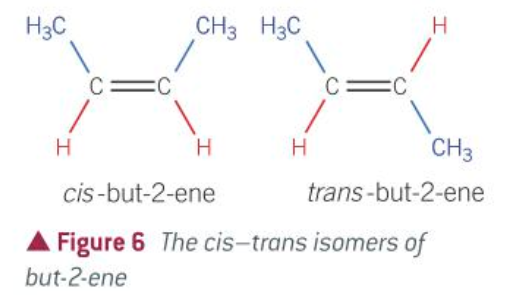
E and Z meaning
E = opposite sides
Z = zame zide
cis and trans meaning
trans = across (E)
cis = same side (Z)
skeletal formula for (Z) pent-2-ene
skeletal formula for (E) pent-2-ene

y r alkenes more reactive than alkanes
double bond: pi-bond readily breaks as it’s on the outside of the double bond
reactions of alkenes
hydrogenation of alkenes
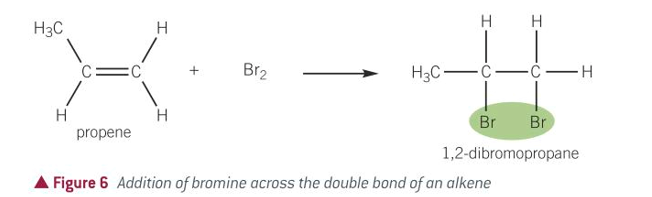
halogenation of alkenes
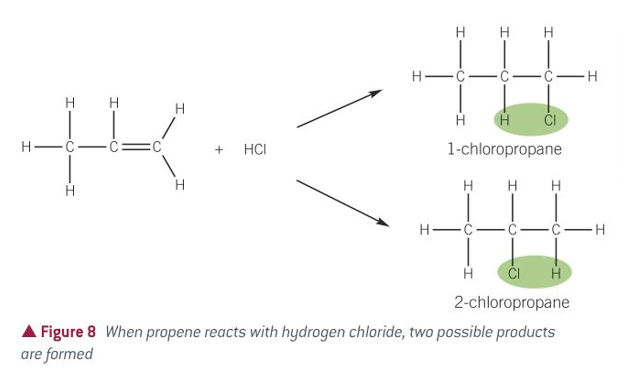
alkenes + hydrogen halides
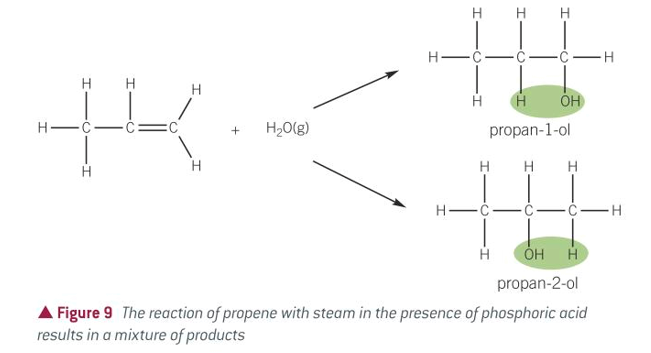
hydration of alkenes
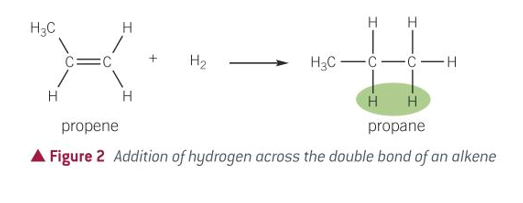
equation for hydrogenation of alkenes
equation for halogenation of alkenes
equation for alkenes + hydrogen halides
equation for hydration of alkenes
conditions for hydrogenation of alkenes
nickel catalyst
423K
what is hydrogenation of alkenes used for
solidification of vegetable oils
higher mpt as the chains are packed together more, greater SA in contact, greater LF
conditions for halogenation of alkenes
no conditions
describe a test for unsaturation
add orange bromine water
will react w unsaturated if present - colour disappears
w alkane stays orange
what’s another name for a successful test for unsaturation
halogenation of alkenes
equation for alkenes + hydrogen halides
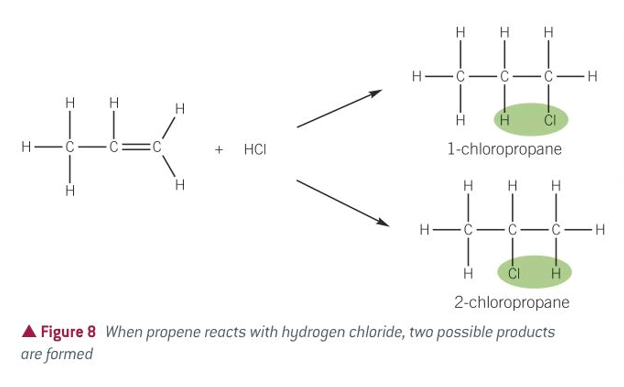
conditions for alkenes + hydrogen halide
GASEOUS hydrogen halide (bubble it through alkene if liquid)
how many products can be formed in alkenes + hydrogen halide
2, the H and X can go to either C atom when the C=C opens up
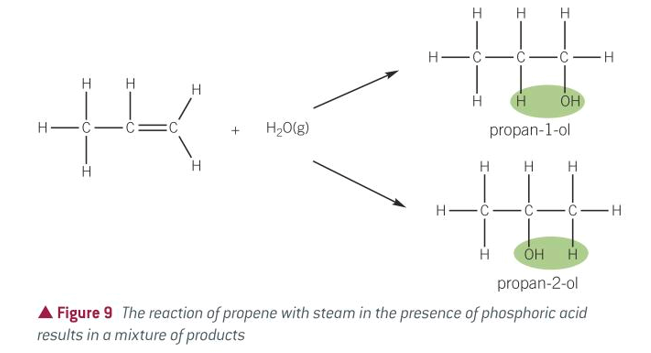
equation for hydration of alkenes
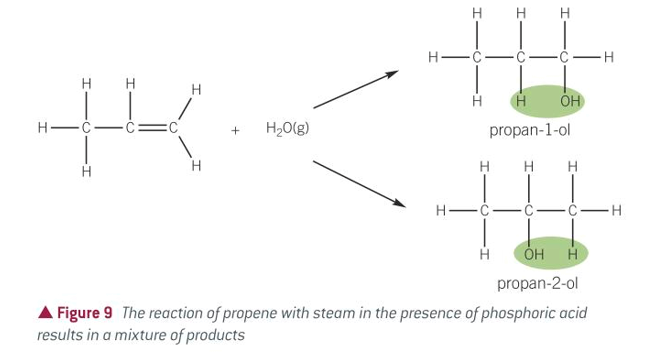
conditions for hydration of alkenes
STEAM
300C
Acid catalyst: PHOSPHORIC ACID H3PO4
60-70atm???idk
product of hydration of alkenes
alcohol
what is the shape and bond angle around a C=C
trigonal planar
120
what is the bond angle for cyclopropane and why
60 due to bond strain
what is the mechanism for addition reactions of alkenes and WHY
electrophilic addition
double bond, region of high electron density because of pi-electrons
attracts electrophiles
susceptible to electrophilic attack
electrophile def
electron pair acceptor
how can non-polar molecules act as an electrophile
the electron rich pi-bond repels electrons in non-polar molecules (like repels like)
induces a dipole
carbocation / carbonium ion
an ion containing a positively charged carbon atom
stabilities of carbocations
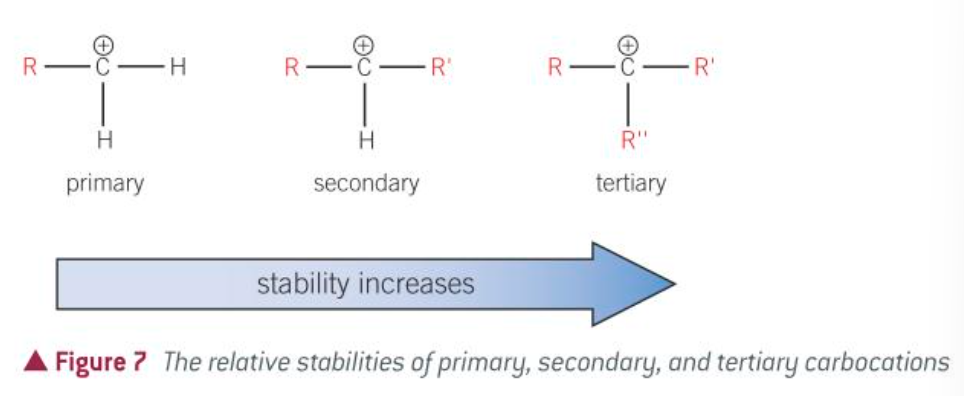
most stable carbocation
tertiary carbocation
how many Rs and Hs does a primary carbocation have
1xR
2xR
how many Rs and Hs does a tertiary carbocation have
3xR
no H
why is a secondary carbocation more stable than a primary carbocation
alkyl inducing effect
what is the major and minor in relation to stability
major: most stable
minor: least stable
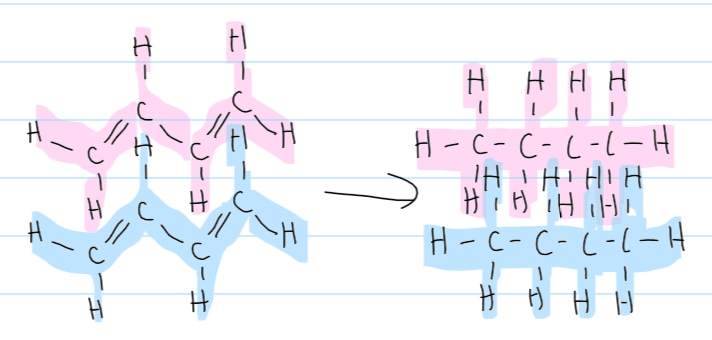
polymers
large molecules formed from many thousands of repeat units of monomers
polymerisation
the joining of a very large number of monomer molecules to make a large polymer molecule w a higher molar mass
what happens when alkenes undergo addition polymerisation
the C=C double bond breaks open
what is required for industrial polymerisation
high temp
high pressure
catalysts
why are polymers unreactive
non polar
no pi-bond, only sigma bonds
many LF as v large
how can structures (and therefore properties) of polymers made of the same monomer be changed
altering the conditions in which the polymers are formed
HDPE
formed w use of catalysts and higher temps
harder
high SA contact w other molecules
greater LF
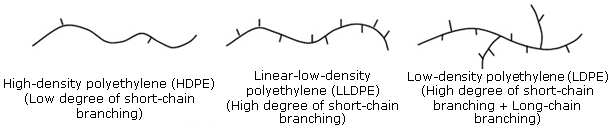
does HDPE have more or less branching than LDPE
HDPE has low degree of short chain branching
LDPE has high degree of short chain and long chain branching
y r plastics useful
readily available
cheap
convenient to throw away
can store food
pros and cons of recycling plastics
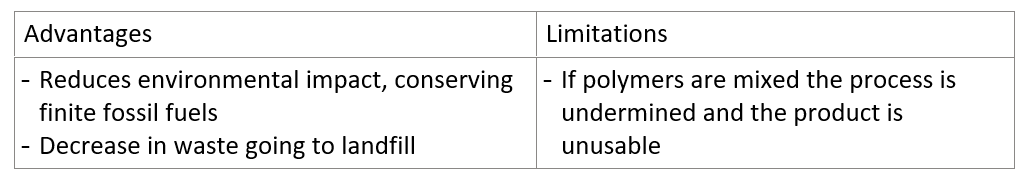
why is disposal of PVCs hazardous
high chlorine content and range of additives present
dumping in landfill not sustainable
released hydrogen chloride HCl (a corrosive gas) and other pollutants like toxic dioxins
what new technology is there to dispose/recycle PVC
solvents dissolve polymer
high grade PVC can be recovered by precipitation from solvent
solvent can be used again
why are waste polymers w a high stored energy value useful
can be incinerated to produce heat
generating steam
drives turbine
electricity produced
feedstock recycling
the chemical and thermal processes that can reclaim monomers, gases or oils from waste polymers
products resemble those produced in crude oil refineries
i.e. raw materials for production of new polymers
able to handle unsorted and unwasted polymers
what are bioplastics produced from
plant starch, cellulose, plant oils and proteins
benefits of bioplastics
renewable and sustainable alternatives to oil based products
protects environment and conserves oil reserves
what are biodegradable polymers often made from
starch or cellulose
how are biodegradable polymers broken down
microorganisms
what is the chemistryey name for expanded polystyrene
poly(phenylethene)
what are expanded polystyrene plates/cups/food trays being replaced by
sugar cane fibre plates/cups/food trays
what are photodegradable polymers made of
oil based polymers
how do photodegradable polymers degrade
they contain bonds weakened by absorbing light to start the degradation
what is LDPE used for
plastic bags/films (plastic w little strength)
properties of LDPE
flexible, moisture-resistant material w elasticity
what is HDPE used for
children’s toys, water pipes (plastic w strength)
properties of HDPE
sturdy, durable, good chemical resistance
what is polypropene used for
food containers, kitchen equipment
what are PVCs used for
water pipes, waterproof clothing
films and sheeting, insulation and cable sheathing
the other name for PVC
polychloroethene
structure for polystyrene
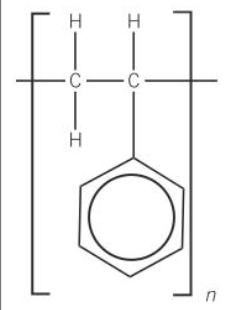
other name for polystyrene
polyphenylethene
what is polystrene used for
packaging material, food trays and cups
properties of polystyrene
insulating
what does PTFE stand for
poly(tetrafluoroethene)
structure for PTFE
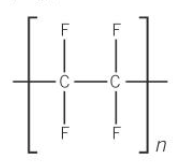
another name for PTFE
teflon
what is teflon used for
coating of non stick pans, permeable membrane for clothing and shoes
properties of PTFE/teflon
slippery