P3.1 General properties of waves
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
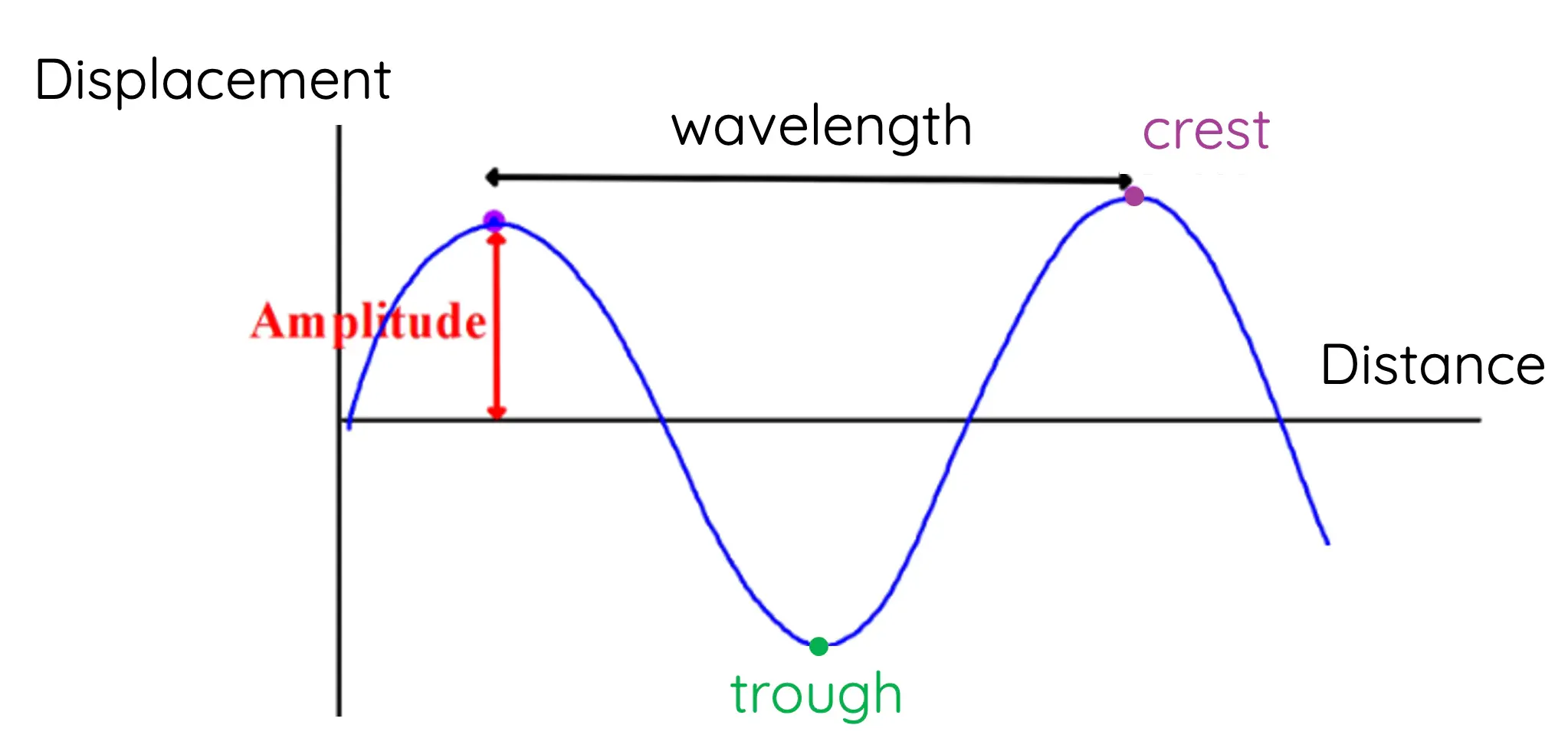
Label features of transverse wave
Amplitude: maximum disturbance caused by a wave (determines loudness)
Wavelength: distance between any point on a wave and the equivalent point on the next
Crest/peak: highest point of a wave
Troughs: lowest point of a wave
Frequency: the number of waves passing a fixed point per second (determines pitch)
Period: the time taken for one oscillation
What is the direction of oscillation in a transverse wave?
Perpendicular (at a right angle) to the direction of propagation
Examples of transverse waves
Electromagnetic radiation waves
Water waves
Seismic secondary waves
Waves in ropes
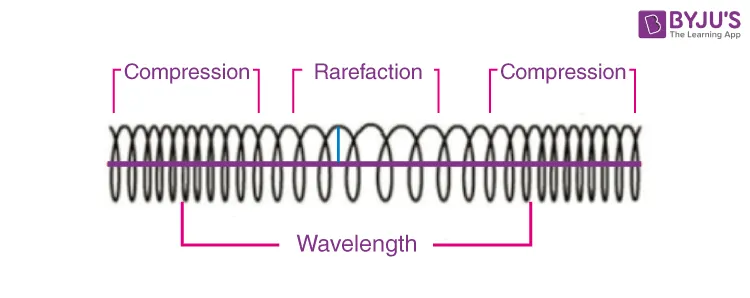
Label features of a longitudinal wave
Compression: regions where the particles of the wave are closest together
Have high pressure and high density
Rarefaction: regions where the particles of the wave are spread farther apart
Have low pressure and low density
What is the direction of oscillation in a longitudinal wave?
Parallel to the direction of propagation
Examples of longitudinal waves
Sound waves
Seismic primary waves
Compression waves in springs
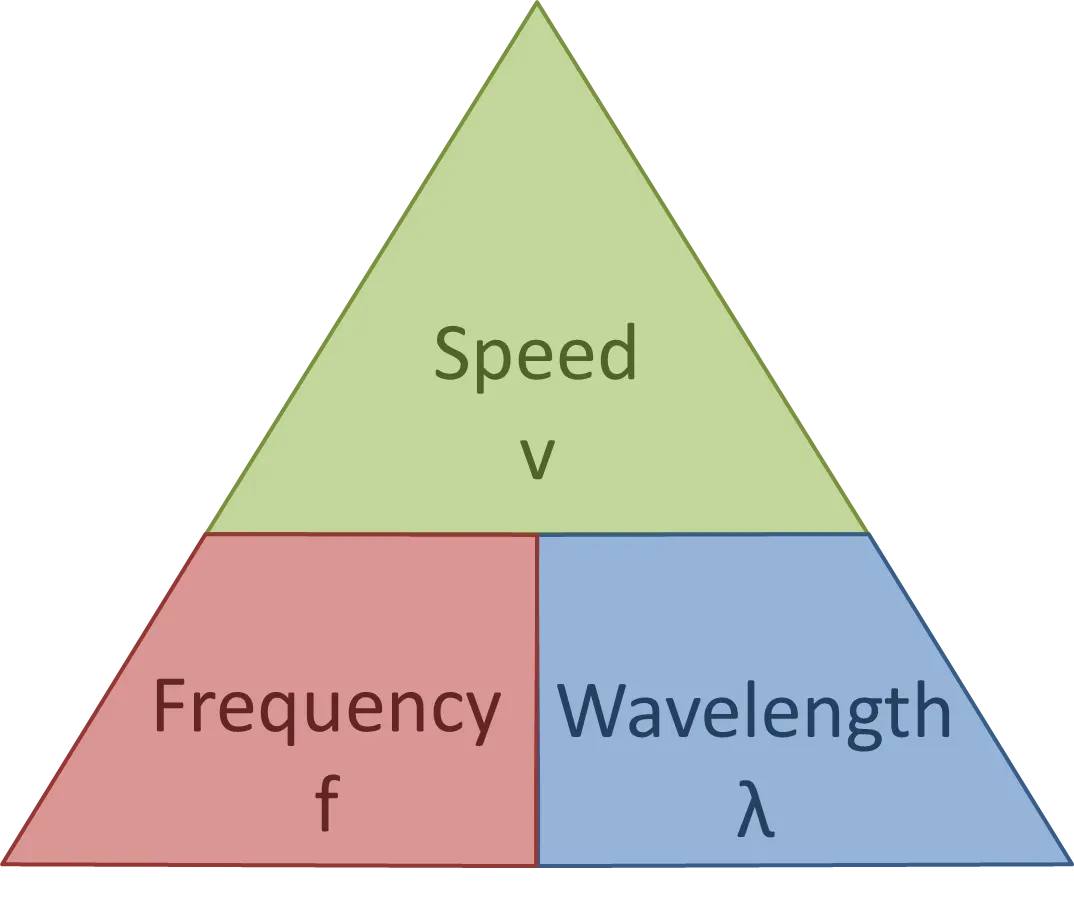
What is the equation for wave speed?
velocity (m/s) = frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m)
or v = fλ
Describe wave refraction
When waves hit a boundary with a different medium, it changes speed, wavelength and direction (depending on angle it hits medium at), but frequency stays the same