econ quiz market competition and law of demand
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What’s a market?
A place or system where buyers and sellers interact to exchange goods and services.
Demand demonstrates the behavior of
Consumers.
Supply demonstrates the behavior of
Producers.
Who is the buyer in the factor market?
Businesses.
Who is the buyer in the product market?
Consumers.
What’s a perfectly competitive market?
A market with many buyers and sellers offering identical products, where no single buyer or seller controls price.
Forms of imperfect competition
Monopoly, Monopsony, Oligopoly, Monopolistic competition.
Monopoly
A market with one seller controlling supply and price. Example: Local utility company.
Legal monopoly
A monopoly allowed by law, often regulated. Example: USPS.
Natural/virtual monopoly
A monopoly where one firm can provide goods/services more efficiently than multiple competitors. Example: Public water system.
Monopsony
A market with only one buyer. Example: Military buying jet fighters.
Oligopoly
A market with a few large firms dominating. Example: Airline industry.
Monopolistic competition
Many sellers offering differentiated products. Example: Restaurants.
What are heterogeneous goods?
Goods that are different in quality, features, or branding.
What are homogeneous goods?
Goods that are identical and interchangeable.
What does it mean if firms are price makers?
They can set the price because they have market power.
What does it mean if firms are price takers?
They must accept the market price; they have no control over pricing.
What is demand?
The desire and ability of consumers to purchase goods and services at different prices.
What is quantity demanded (QD)?
The specific amount of a good consumers are willing to buy at a certain price.
What changes quantity demanded?
A change in the price of the good.
What changes demand?
Changes in income, tastes, number of buyers, expectations, or prices of related goods.
Difference between changes in QD and demand
Change in QD = movement along the demand curve; Change in demand = shift of the entire demand curve.
What is the law of demand?
As price decreases, quantity demanded increases; as price increases, quantity demanded decreases (ceteris paribus).
What is equilibrium (E)?
The point where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
What does “ceteris paribus” mean?
“All other things held constant.”
How does income affect demand for normal goods?
Higher income increases demand.
How does income affect demand for inferior goods?
Higher income decreases demand.
What are “tastes and preferences” and how do they affect demand?
Changes in consumer likes/dislikes can increase or decrease demand.
How does the price of a complementary good affect its complement?
If the price of one rises, demand for the other falls (and vice versa).
How does the price of a substitute good affect its substitute?
If the price of one rises, demand for its substitute increases.
How do people behave if they believe the price of a good will increase in the future?
They buy more now.
How do people behave if they believe the price of a good will decrease in the future?
They wait and buy later.
How does the number of buyers in a market affect demand?
More buyers increase demand; fewer buyers decrease demand.
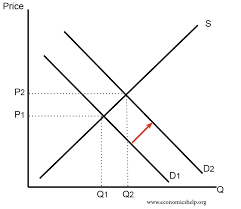
Draw an increase in demand and explain
Demand curve shifts right; equilibrium price and quantity both rise.
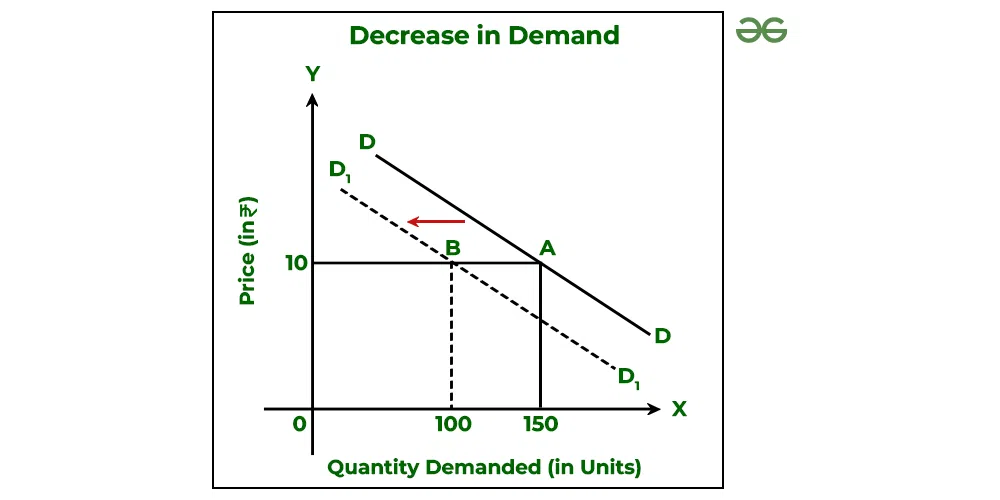
Draw a decrease in demand and explain
Demand curve shifts left; equilibrium price and quantity both fall.