Zoology Unit 5 (right from Study Guide)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is the amniotic egg?
A land adapted egg with a protective shell and specialized inside. It allows egg-laying mammals to reproduce away from water.
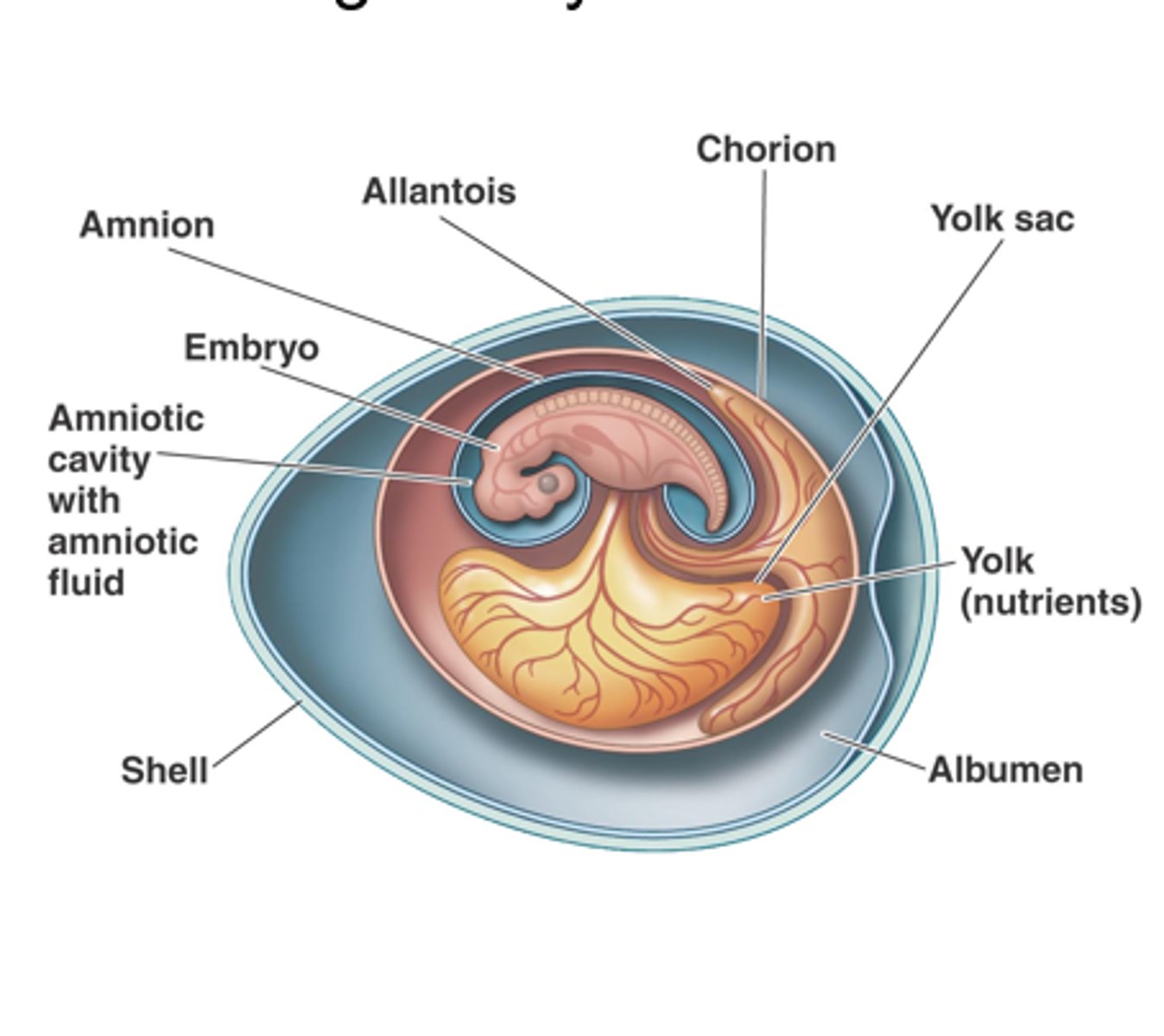
What are the different extramembranous layers in the amniotic egg?
There are 4: Yolk Sac, Amnion, Chorion, Allantois
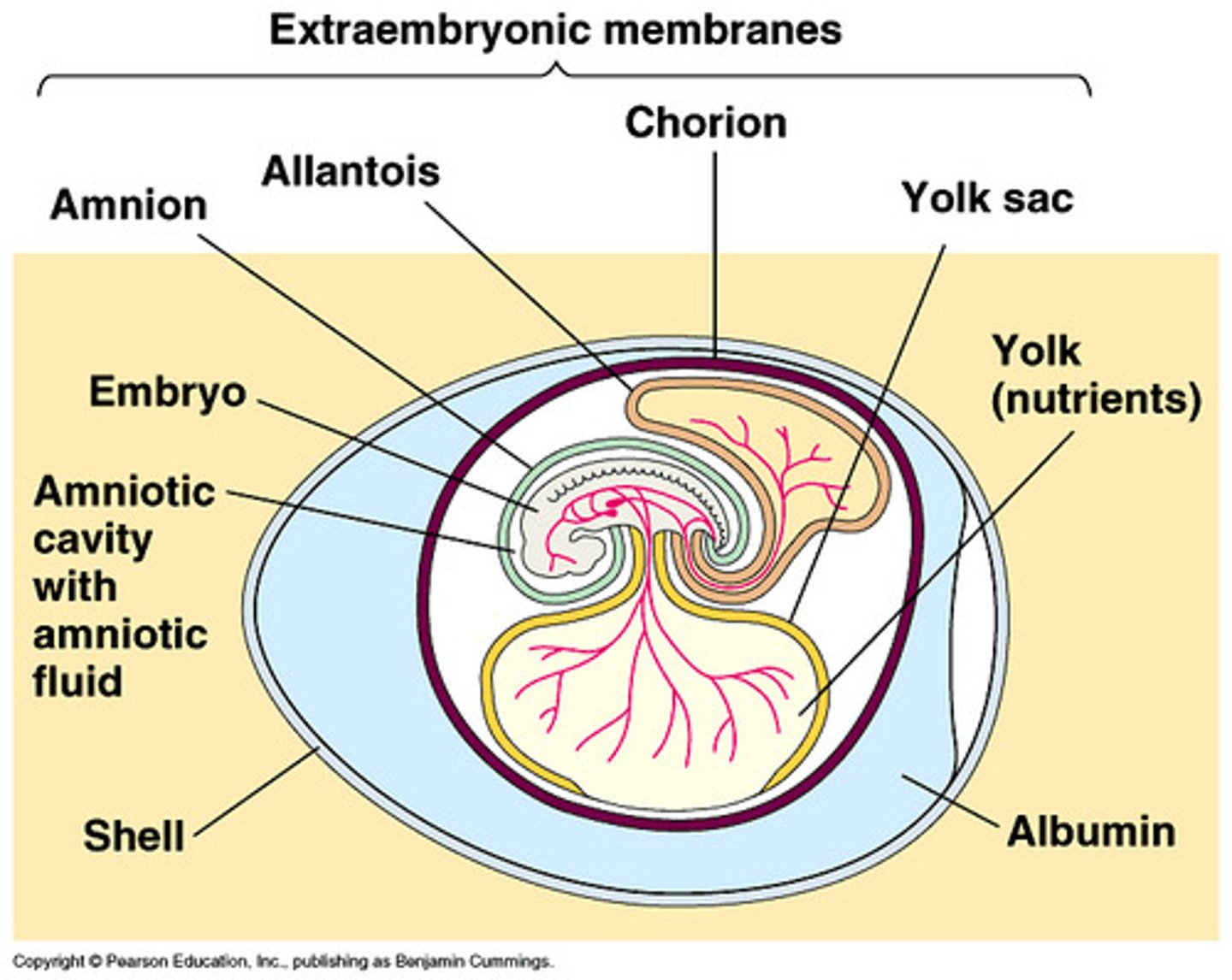
What does the Yolk Sac do?
It surrounds the yolk and provides nutrition in the form of lipids and proteins.
What does the Amnion do?
It is a fluid filled cavity surrounding the embryo that provides it with internal aquatic environment.
What does the Chorion do?
It is a flexible membrane surrounding the embryo and all other membranes. It helps facilitate gas exchange between the embryo and external environment.
What does the Allantois do?
This is an extension of the hindgut, it also helps with gas exchange by fusing with the Chorion. It stores nitrogenous waste also.
Why is the amniotic egg a novel adaption?
It is a novel adaption/extremely important because it allowed vertebrates to reproduce on land. It creates a contained aquatic environment for the embryo and frees the parent from needing to approach the water to lay eggs.
Why could it be dangerous for a vertebrate to approach water to lay eggs, and therefore the reason they need the amniotic egg?
There is high aquatic predation of eggs. There is also other hazards like drowning, desiccation, and aquatic predators on land mammals.
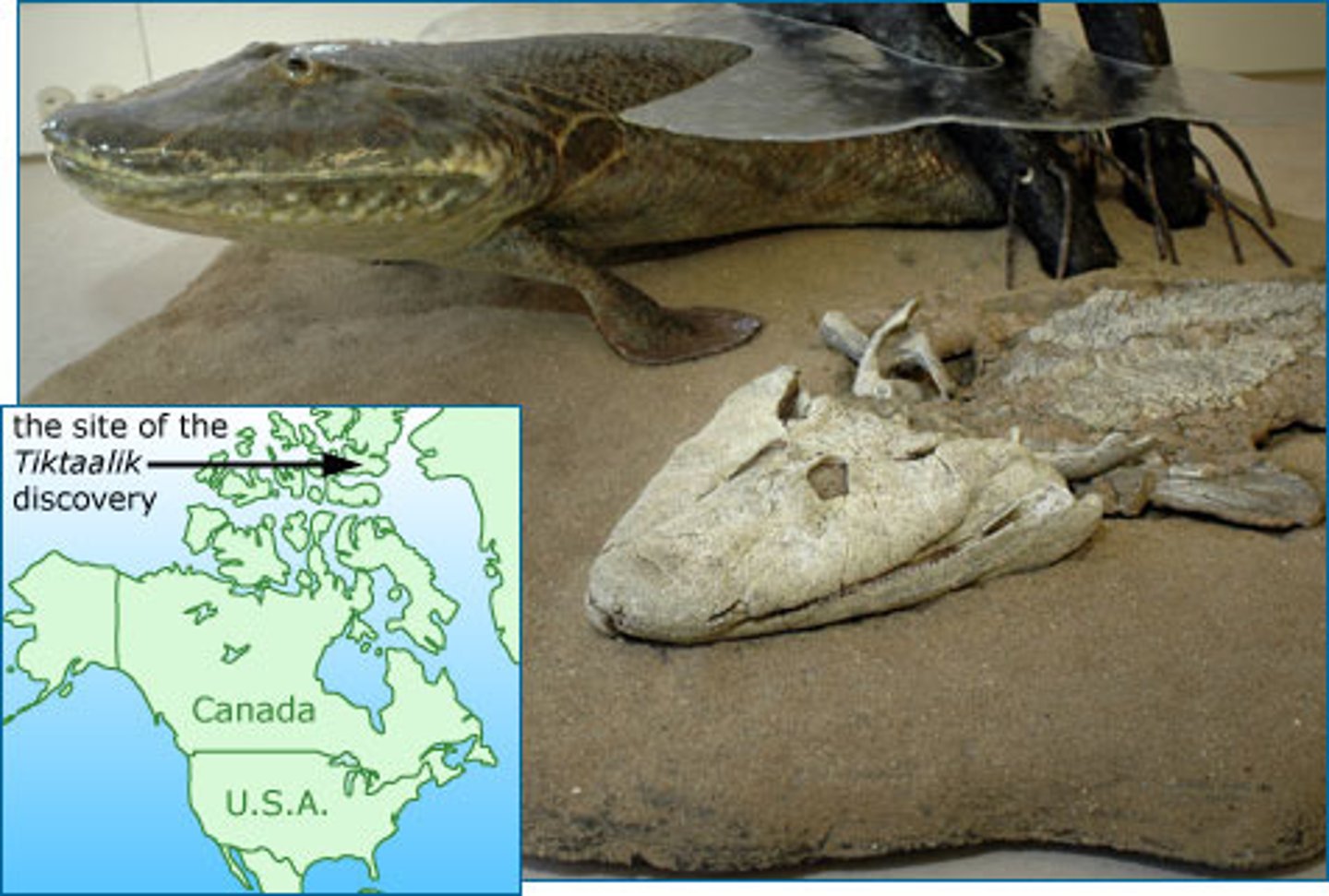
What is a Tiktaalik?
An extinct, 375-million-year-old fossil fish that shows characteristics of both fish and early four-legged land animals. Also sometimes called a "fishapod."
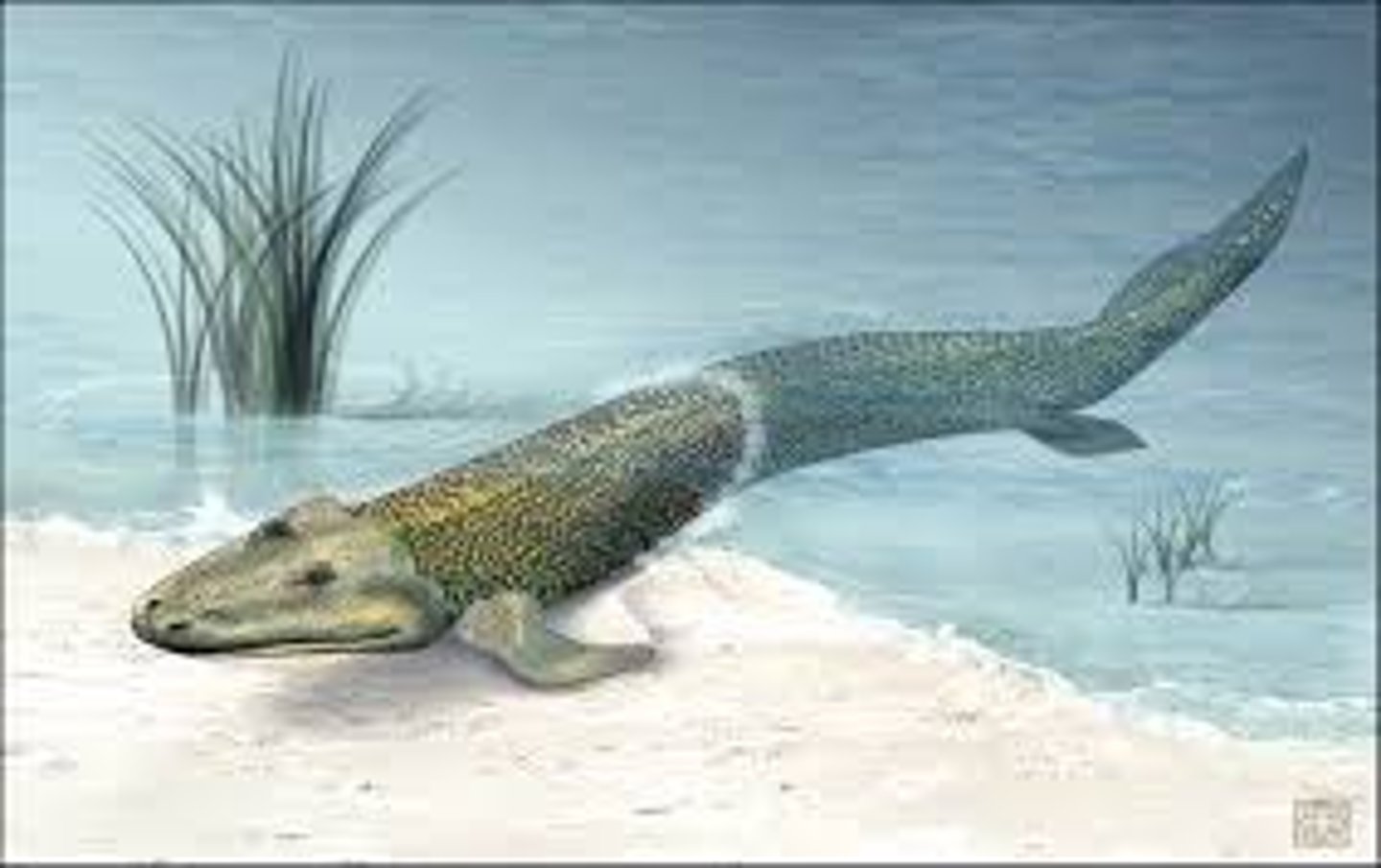

Why is Tiktaalik considered the ancestor of terrestrial animals?
Tiktaalik possesses a unique combination of both land and fish. It was the first ever spotted to seemingly be "evolving" out of the water and gaining traits of land animals.
What are the fish-like structures in Tiktaalik?
Tiktaalik had scales, gills, and fins.
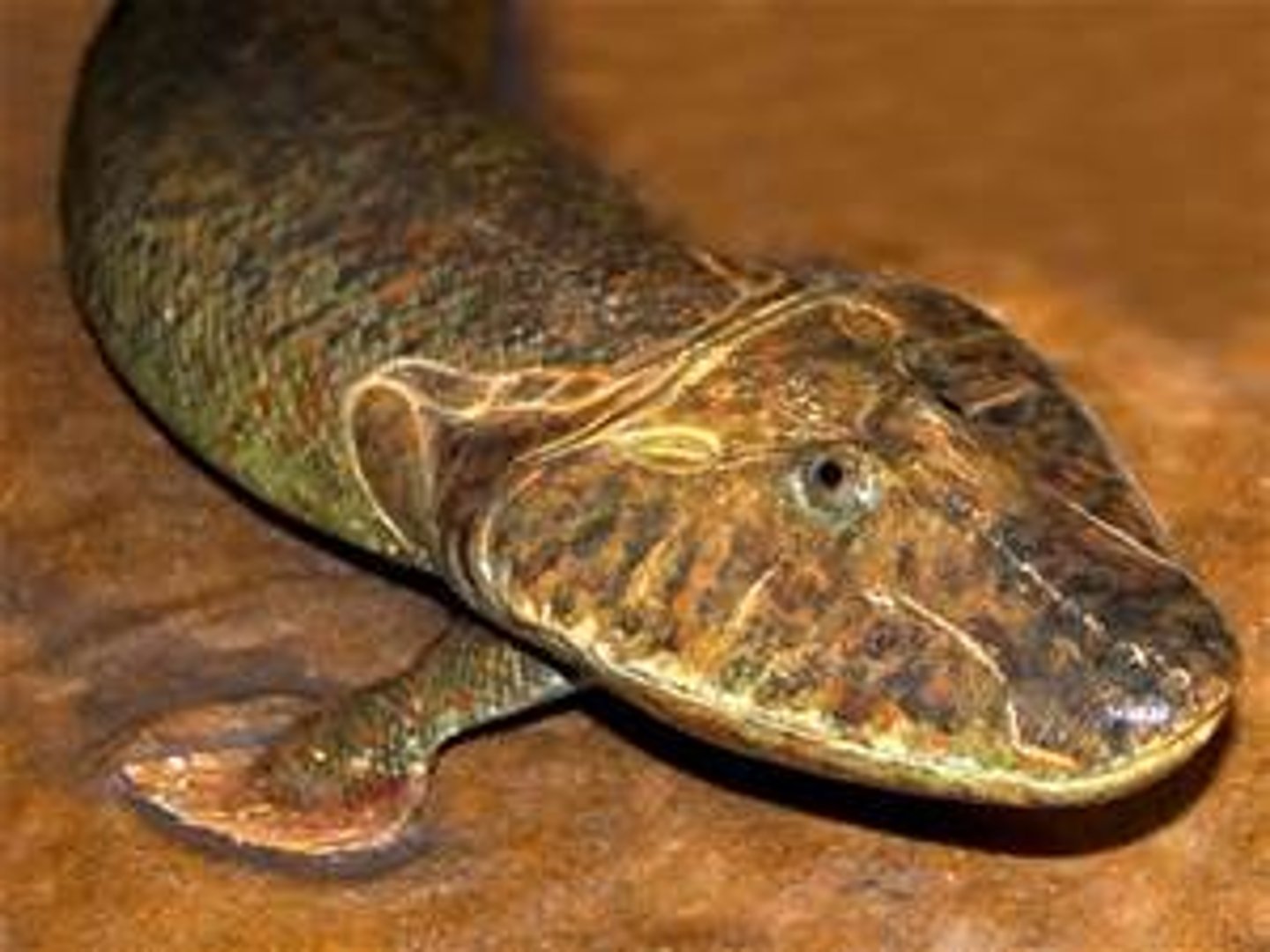

What are the terrestrial-like structures in Tiktaalik?
Tiktaalik has a flat head, neck, robust rib cage, and fins that have limb bones that link to those of tetrapod. Some recent research also shows that its spine and ribs show relation to those of early land animals.

Give me some examples of an Amphibian.
Frogs, salamanders, toads, axolotls, caecilians, and newts.
What type of organs/systems do Amphibians have?
They have complex nervous systems, with digestive, excretory and reproductive systems. They have a cloaca, 3 chambered heart, as well as lungs (adults) and gills (larvae). Sense organs for sight, smell, taste, hearing, and touch are also present.
Describe amphibian blood flow through their circulatory system in depth.
Deoxygenated blood enters from the right atrium, then the ventricle, and then is pumped into the lungs/skin for oxygenation. This oxygenated blood from the lungs/skin returns to the left atrium and ventricle to be pumped throughout to test of the body.
Describe amphibian blood flow through their circulatory system with minimal details.
Amphibian blood flow involves a double circulation system with a three-chambered heart, featuring two atria and a single ventricle, that directs blood through two circuits to minimize mixing.
Defining characteristics of amphibians.
4 complex limbs, moist permeable skin, bony skeleton, most have water dependent reproduction.
What is the really big defining characteristic of amphibians that changed the course of animal evolutions?
They were the first vertebrate to live part of their life on land. More specifically, it was their special development of limbs with different amounts of digits.
How do amphibians reproduce?
A cool, wet habitat is a must for preoduction. MOST have water dependent reproduction/embryo development. They have sexual reproduction usually thru external (frogs) or internal (salamanders). Lay eggs.
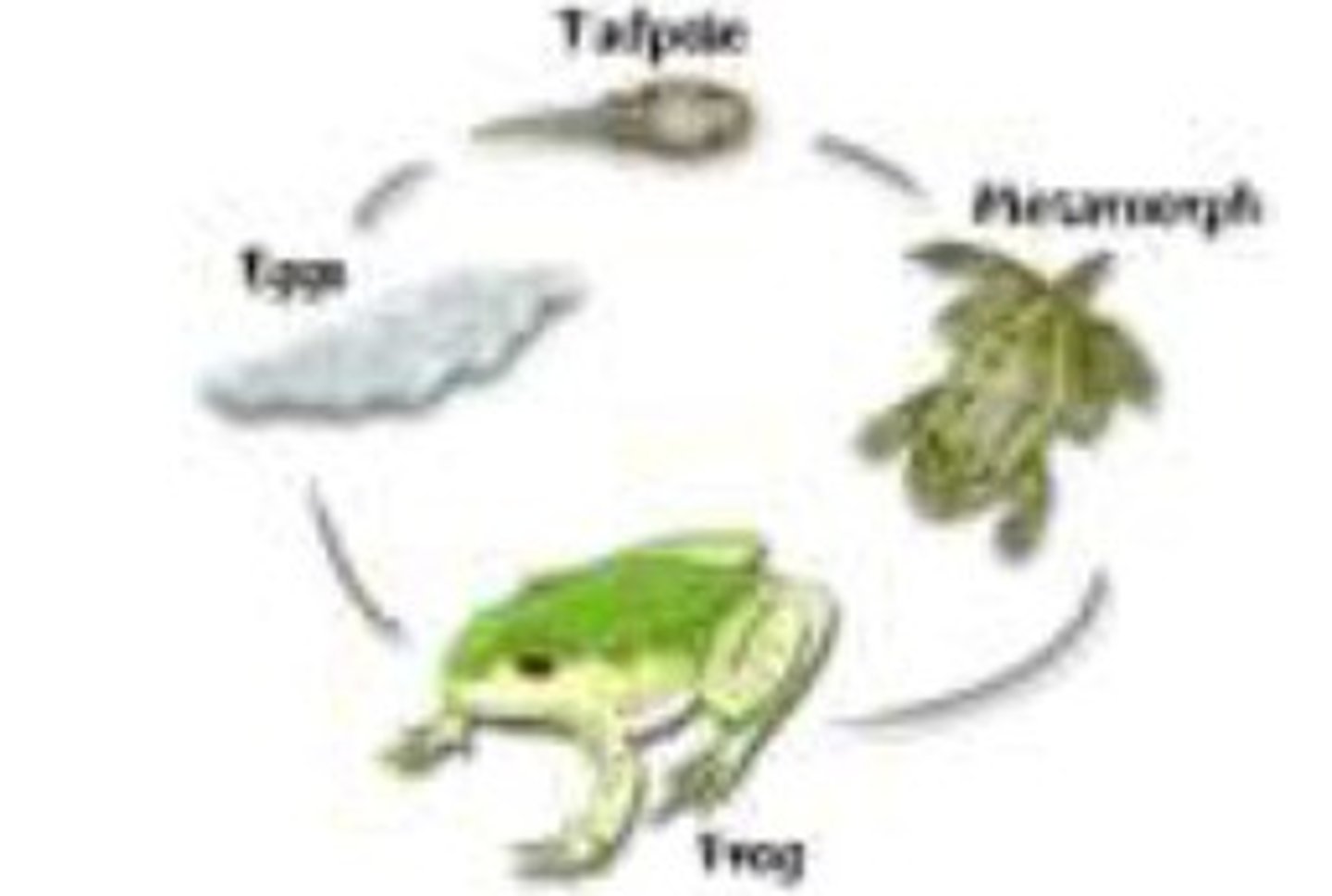
Describe the complete metamorphosis of larval amphibians.
This is the transition from aquatic larvae to terrestrial adult, controlled by hormones. The order goes egg, larvae, then adult. After egg, they gain gills and tail for swimming. As a larvae, or tadpole, they will develop limbs and get lungs. As adults, the tail will have been absorbed and can live completely on land. (This example is for frogs.)
What are the differences between the three Amphibian Orders (Urodela, Anura, Apoda)
Urodela (salamanders) - most ancestral, internal ears, paedomorphic, slender bodies
Anura (frogs/toads) - very diverse, no neck, positive pressure breather, external ears, short bodies
Apoda (caecilians) - no limbs, slender bodies, internal ears, some can bear live young,
What are the three types of skulls present in amniotes?
Anapsid - no temporal fenestrae
Synapsid - single temporal fenestrae
Diapsid - two temporal fenestrae
Which groups have which type of skull?
Anapsid - turtles/tortoises
Synapsid - mammals and their familiar extinct ancestors
Diapsid - reptiles (not turtles) and birds.
What is the dilemma with testudines?
Appeared much before other reptilian orders. Their skulls appear to be anapsid but records show they were once diapsid. Created conflict and confusion in their family tree.
What type of organs/systems do Reptiles have?
Large cerebrum, 3 chambered heart, and respiratory (lungs), digestive, excretory, and nervous systems.
Describe reptile blood flow through their circulatory system in depth.
Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium, then to the ventricle, which pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation. Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium before entering the ventricle, where it mixes with deoxygenated blood before being pumped to the body via the aorta. (Crocodilians have 4 chambered heart so this is slightly different)
Describe reptile blood flow through their circulatory system with minimal details.
Reptile blood flow involves two circuits: a pulmonary circuit (heart to lungs and back) and a systemic circuit (heart to body and back), but most have a three-chambered.
Defining characteristics of reptiles.
Amniotic egg, thick skin with scales, keratinized epidermal structures like scales, claws, horns. Respiration occurs in lungs only.
Reptile reproduction:
Typically sexual with internal fertilization. Males use penis to transfer sperm into females cloaca. Most reptiles lay amniotic egg that develop on land (some, such as garter snakes and skinks give live birth!)
What about temperature dependent reproduction? What are generalized temperatures that determine male versus female in Crocodilia, Sphenodontia, and Testudine?
This just means the the temperature of the environment determines the sex of the eggs.
Crocodilia - Girls are cool, dudes are hot (~91+)
Sphenodontia - Girls are cool, dudes are hot (~72+)
Testudines - Guys are cool, chicks are hot (~89+)
What are the differences between the four Orders (Crocodilia, Sphenodontia, Squamata, Testudines)?
Crocodilia - large, armoured, 4 chambered heart,
Sphenodontia - literally only one surviving species, primitive hearing, have 3rd eye when young,
Squamata - very diverse, almost exclusively tetrapods, unique scales
Testudines - appeared first, lost the temporal fenestrae, bony shell, no teeth, cannot expand ribs,
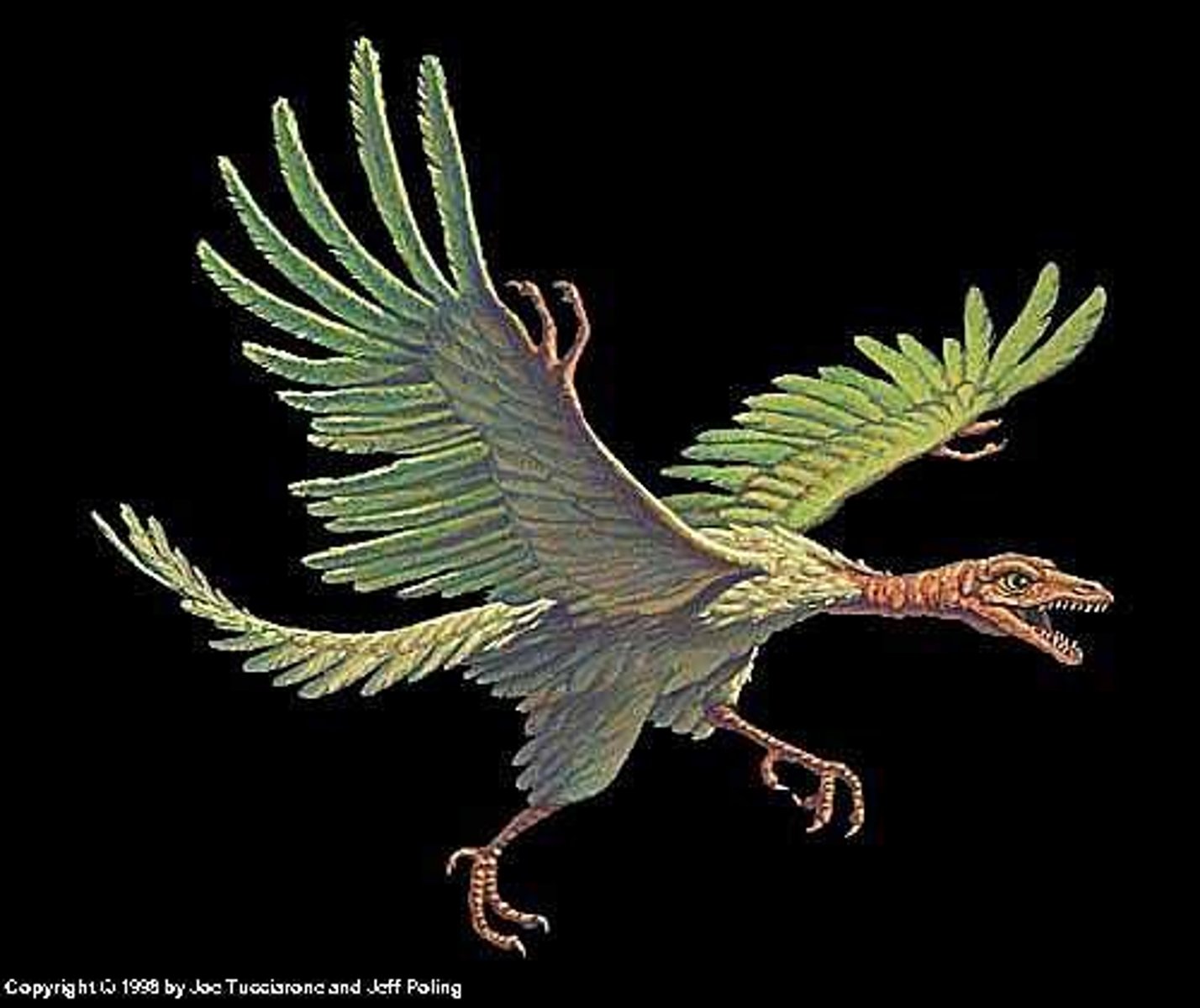
True or False: They evolved from therapod dinosaurs.
True. Only extant clade that evolved from therapod dinosaurs.

What type of organ/systems do Birds have?
Flat or Keeled sternum, warm blooded, highly adapted respiratory system, no urinary bladder but has extretory system, reproductive system, nervous/sensory system, acute color vision, 4 chambered heart
Describe bird blood flow through their circulatory system in depth.
Deoxygenated blood from the body enters the right atrium, moves to the right ventricle, and is pumped to the lungs to get oxygen. Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium, is pumped by the left ventricle throughout the body, and then returns to the heart to begin the cycle again
Describe bird blood flow through their circulatory system with minimum details.
Bird blood flow is a double-circuit system with a four-chambered heart that completely separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, similar to mammals
What are several advantages of having a four chambered heart for birds?
It gives birds complete separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, which supports the high metabolic rates used during flight. Basically, its extremely efficient and gives them greater endurance.
Bird defining characterisitcs:
Either have flat sternum or keeled sternum, feathers made of keratin, unique feather arrangement, light yet stable skeleton, have keratinized beak, big thigh muscles, voracious eaters, 9 air sacs, no urinary bladder, enlarged cerebrum and optic lobe, complex vocalizations, parental care is given, 4 chambered heart.
What are some of the many adaptations for flight in birds?
Literally every feature of a bird helps them fly.
Here's some anyways: feathers made of keratin, feather arrangement of wings into airfoils, light yet stable skeleton to reduce weight, vertebrae of fused to provide flight support, big thigh muscles to help their center of gravity, complex respiratory system to ensure they have fresh oxygenated air always, large optic lobe to help with flight and finding food, acute color vision
What are the advantages of flight?
Animals that fly have better advantages such as ability to escape predators, easy ability to migrate, high ground for hunting, nest off the ground to keep safe, less predators live in the air,
How do birds reproduce?
Sexual reproduction via internal fertilization. Usually, males have no penis. Sperm is transferred through cloacal kiss, female is oviparous. Eggs are laid in a built or dug nest.
What type of parental care do birds offer?
Baby birds are completely dependent on their parents, so parental care is offered, In most species, both mom and dad provide parental care. Both help nest, incubate, feed, protect, and teach to hunt/fly if applicable.
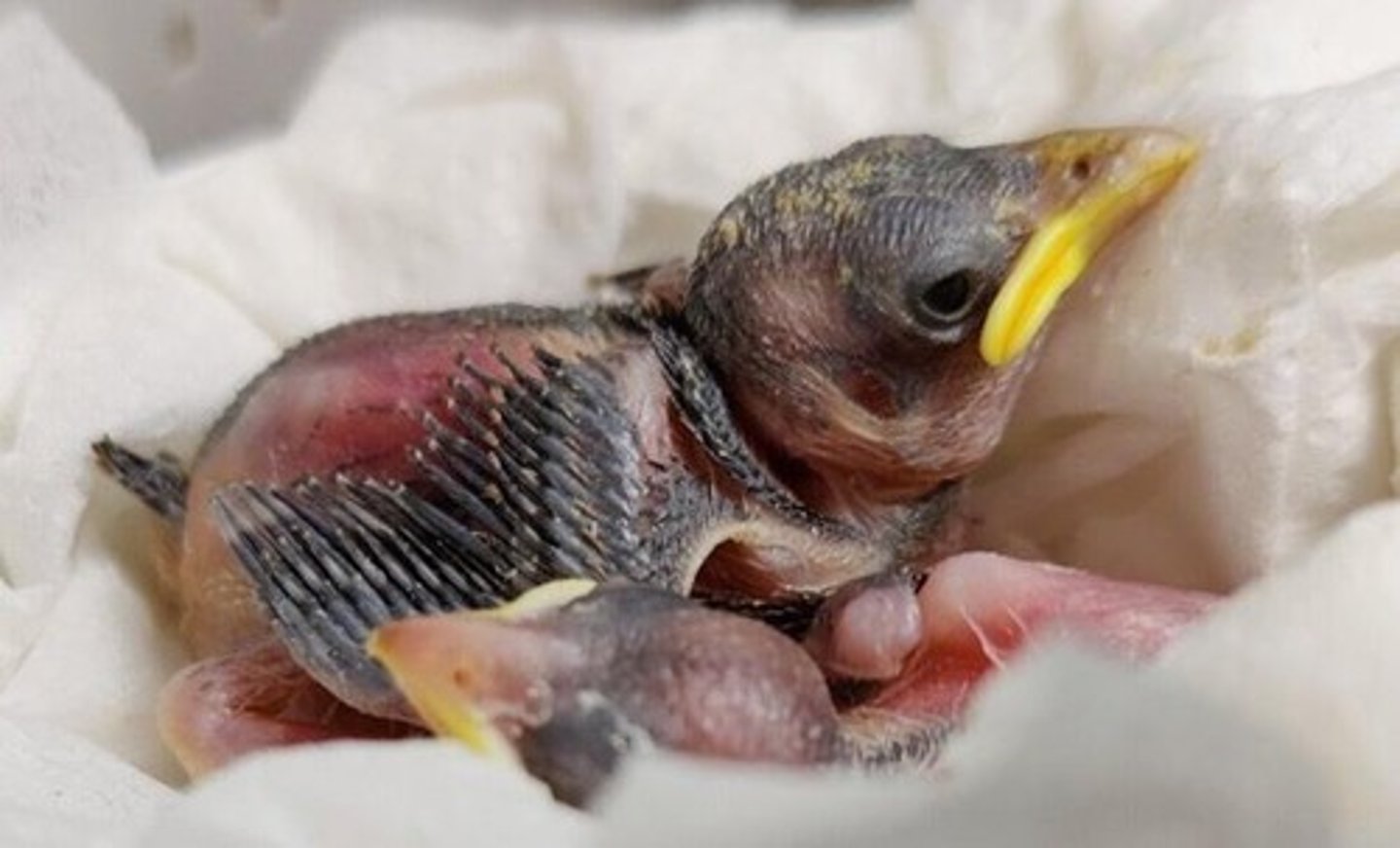
What is an altricial chick?
When they hatch, they are blind, with minimal feathers and are unable to move. They require extended and significant parental care. IE: Songbirds, woodpeckers, parrots, owls, etc.

What is a precocial chick?
When they hatch, their eyes are open, they have feathers and are able to move around. They can do most things themselves but parents stick around until they are able to fly. IE: Chickens, ducks, geese, sandhill cranes, etc.
