AP Art History Content Area 2 (Etruscan & Ancient Rome)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
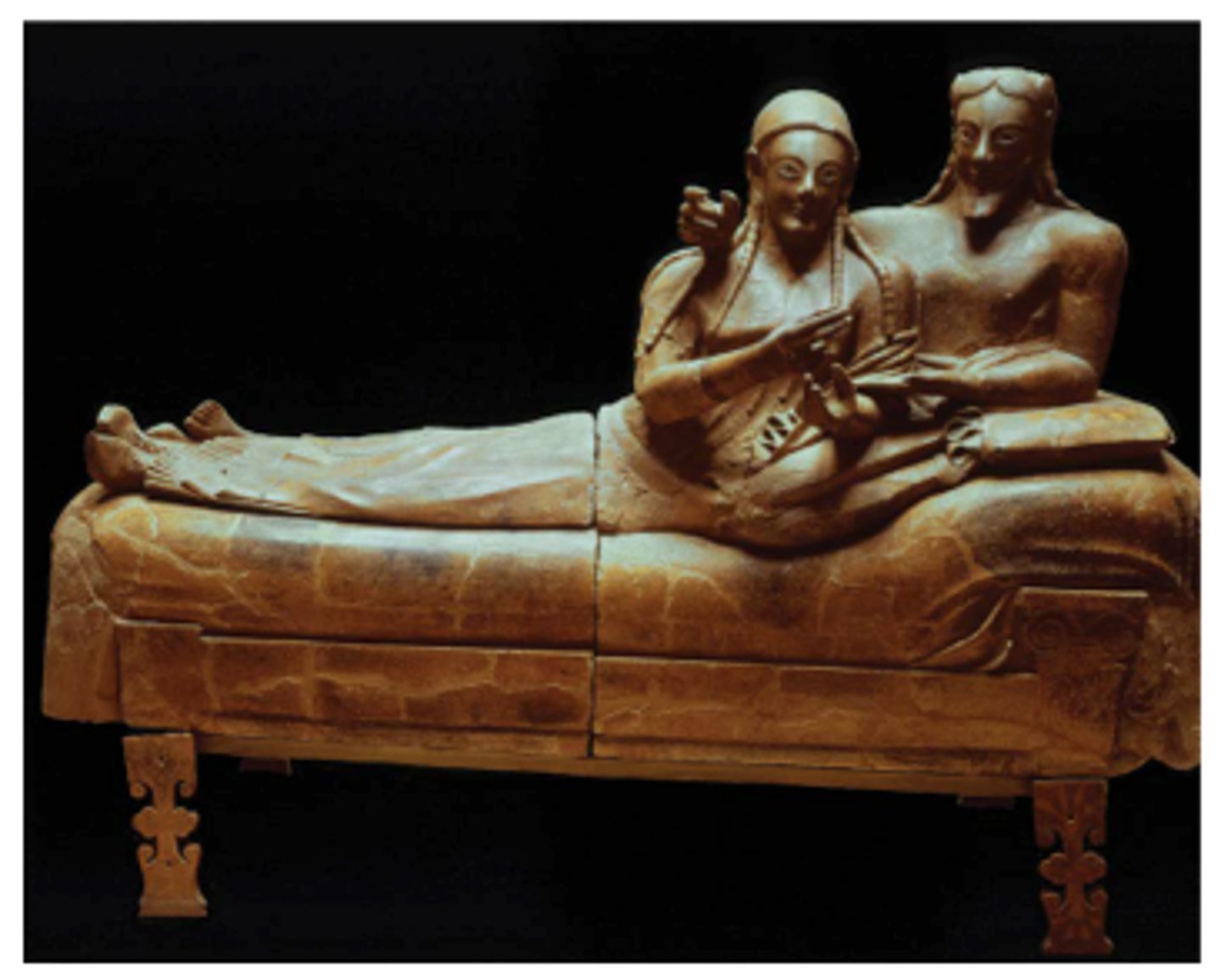
Sarcophagus of the Spouses
Date: 520 BCE
Period/Style: Etruscan
Original Location: Etruria (Tuscany)
Material/Technique: Terra cotta
Function: Discovered in a funerary complex at Cerveteri, Italy. Tombs and artworks depict daily Etruscan life.
Context: Depicts reclining couple pose were prominent among Etruscan art and influenced later Roman reclining art. Displays greater equality between men and women in Etruscan society.
Descriptive terms: terra cotta, reclining pose, tomb, necropolis

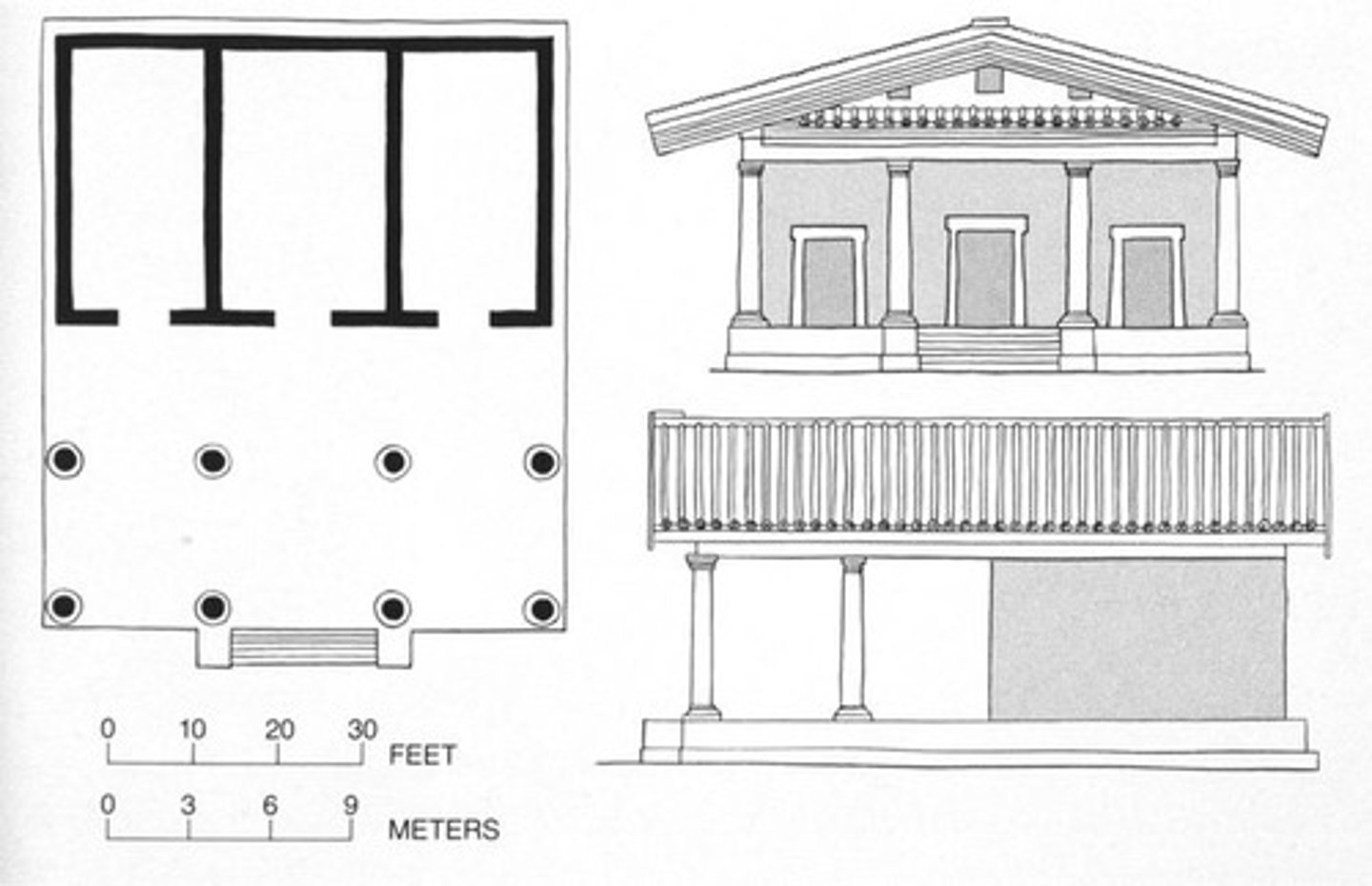
Temple of Minerva (plan)
Date: 510-500 BCE
Period/Style: Etruscan
Original Location: Portonaccio Temple, Veii, Italy
Material/Technique: Wood, mudbrick, tufa (volcanic rock)
Function: Rare surviving temple dedicated to Minerva/Athena.
Context: Only surviving records of the temple come from Vitruvius, influencing later Renaissance architects. Contains deep portico, non-fluted columns, and roofline sculpture were all popular in Etruscan architecture.
Descriptive terms: temple
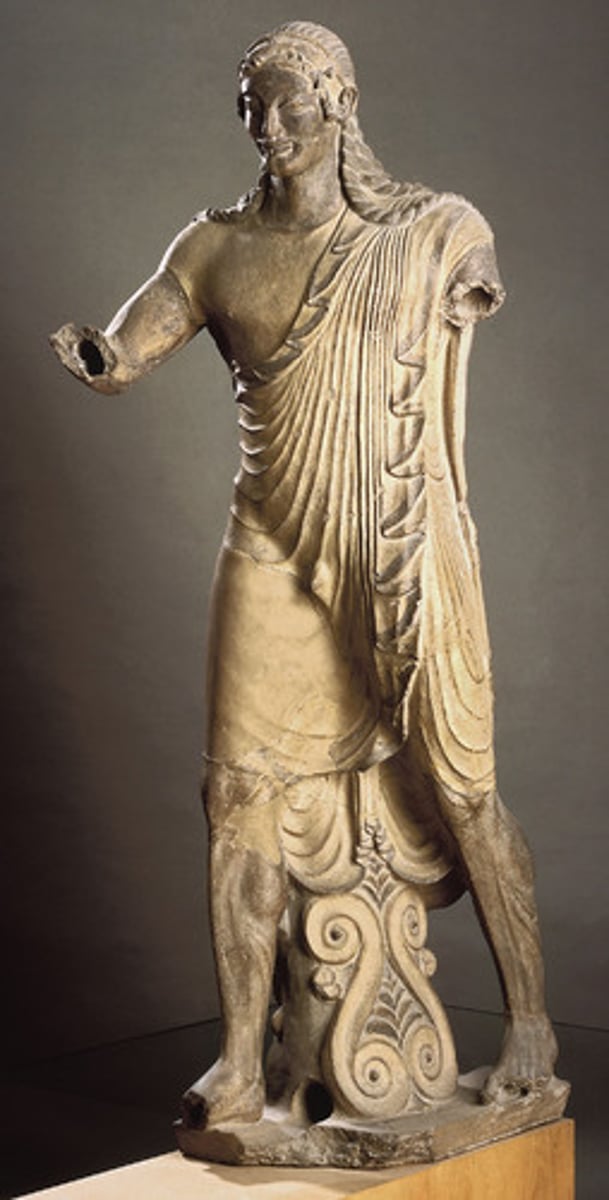
Sculpture of Apollo at Temple of Minerva
Date: 510-500 BCE
Period/Style: Etruscan
Original Location: Veii, italy
Artist: Master sculptor Vulca
Material/Technique: terra cotta
Function: Depicts god Apulu (Apollo) which adorns the roof of the temple.
Context: Statues often adorned Etruscan roofs. The Greek archaic smile influenced the facial features of Apollo (which were inspired by Egyptian statuary).
Descriptive terms: sculpture in the round, archaic smile, Etruscan

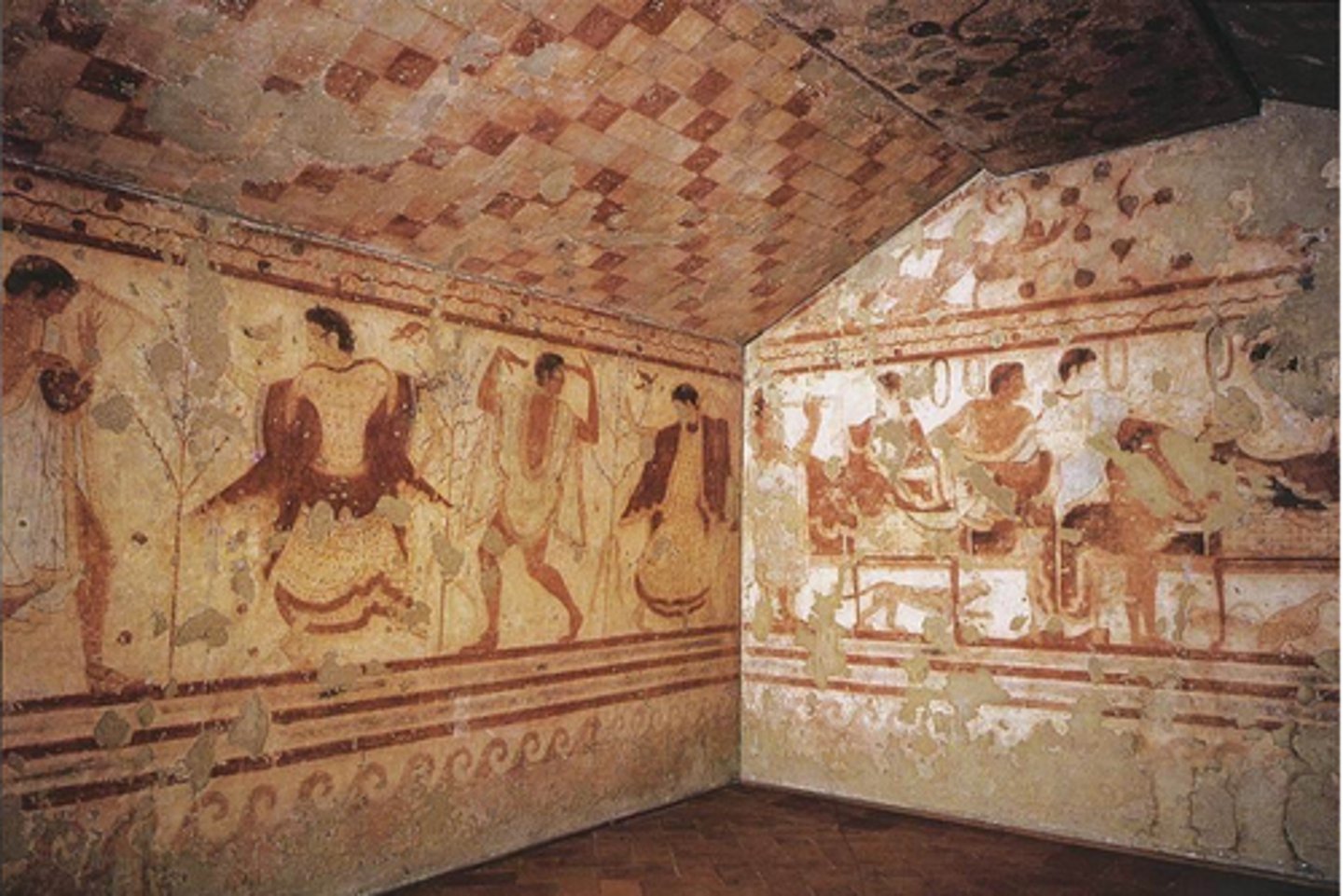
Tomb of the Triclinium
Date: 480-470 BCE
Period/Style: Etruscan
Original Location: Tarquinia, Italy
Material/Technique: Tufa and fresco
Function: Located within necropolis within Monterozzi, Italy.
Context: Frescoes depict banquet scene reminiscent of the style of Greek red figure technique. These frescoes serve as records for Etruscan afterlife beliefs.
Descriptive terms: tomb, necropolis, fresco

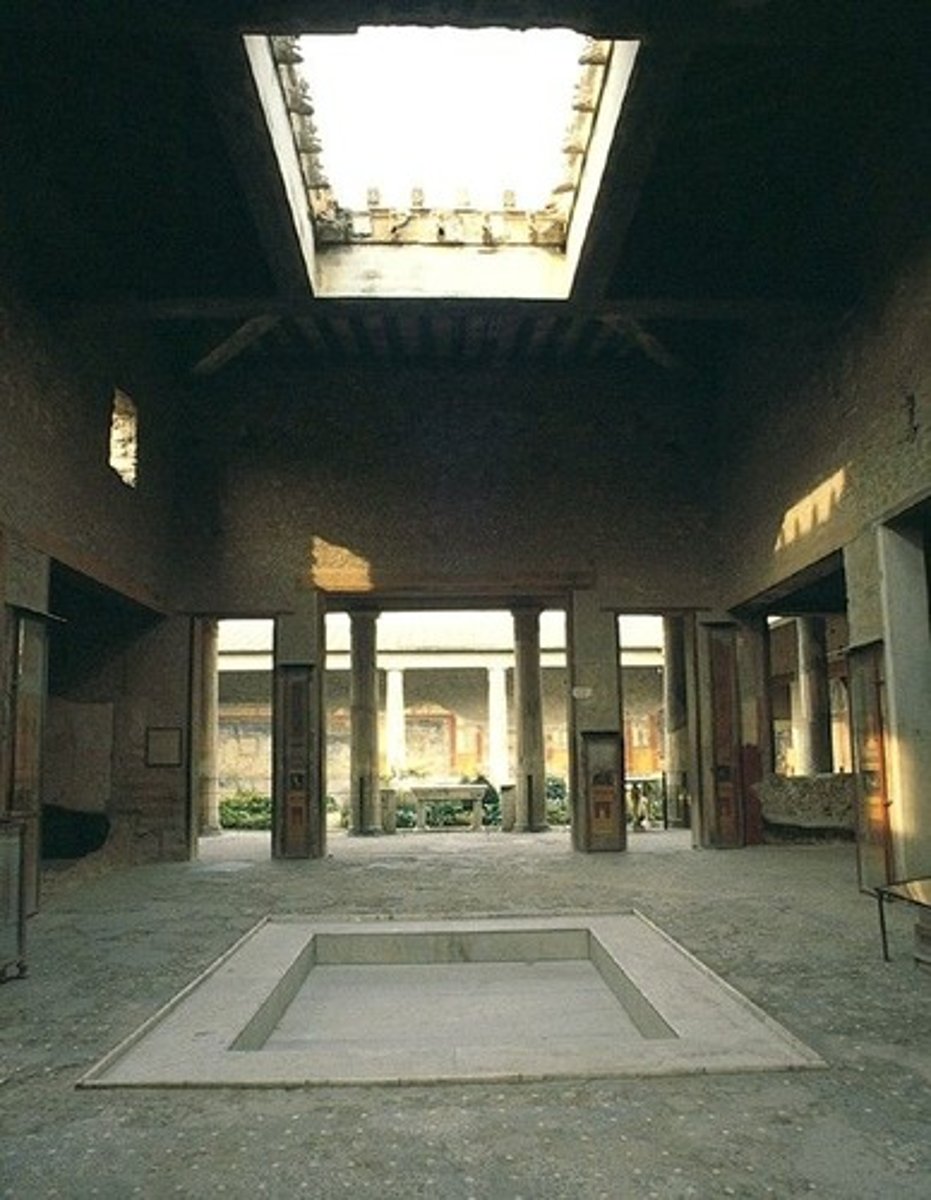
House of the Vettii (plan)
Date: 2nd century BCE; rebuilt 62-79 C.E.
Period/Style: Imperial Roman
Original Location: Pompeii, Italy.
Material/Technique: Cut stone and fresco.
Function: Elite Ancient Roman home
Context: Utilized courtyards and arias for natural light. Otherwise, exterior windows were nonexistent. Considered to be the transition from third to fourth style Roman painting. Lack of external views necessitated atmospheric perspective in frescoes.
Descriptive terms: frescoes, atmospheric perspective, nouveau-riche
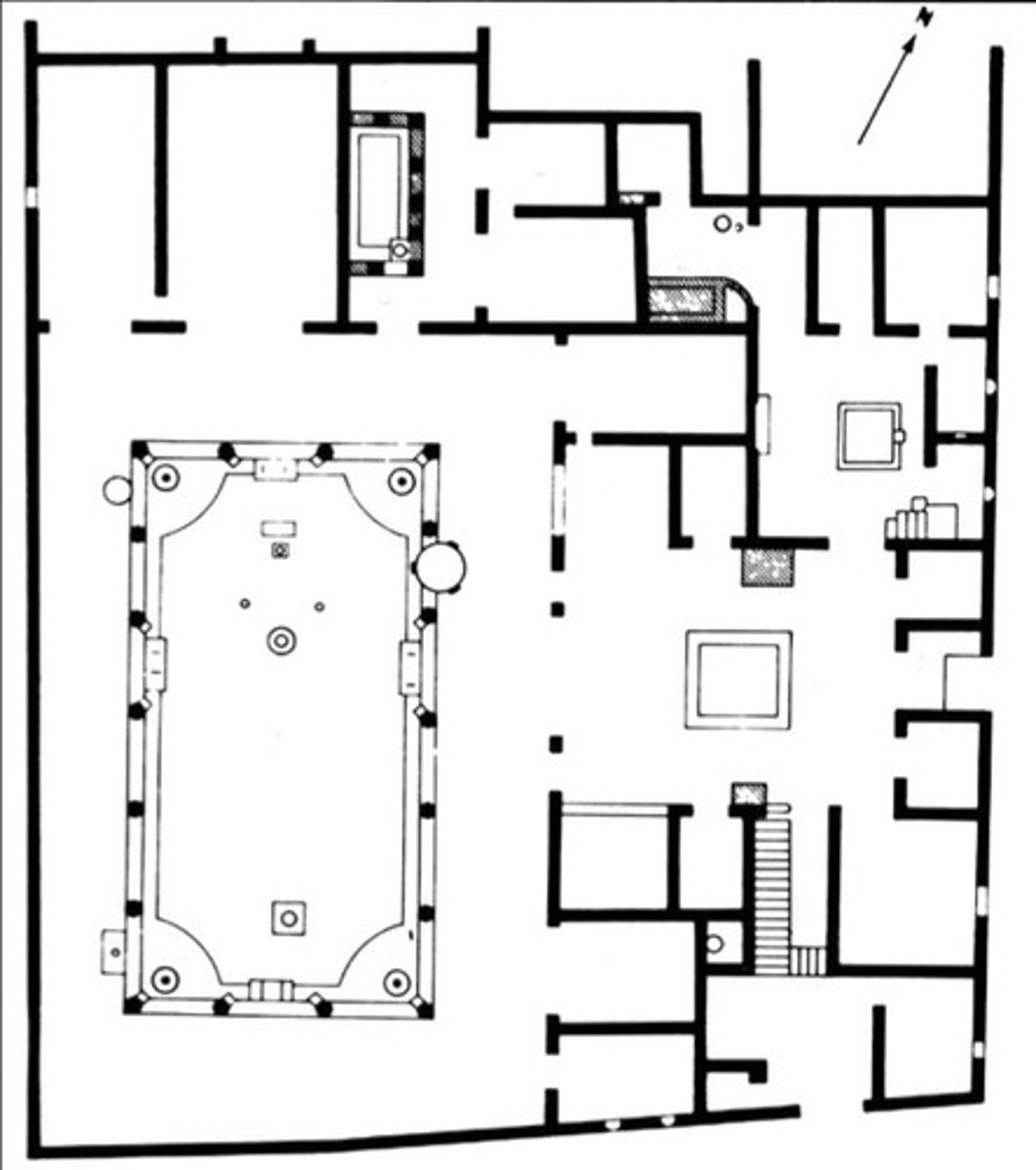
House of the Vettii (Atrium)
Served as one of two central areas open to the sky with rooms connected to allow light inside the home.

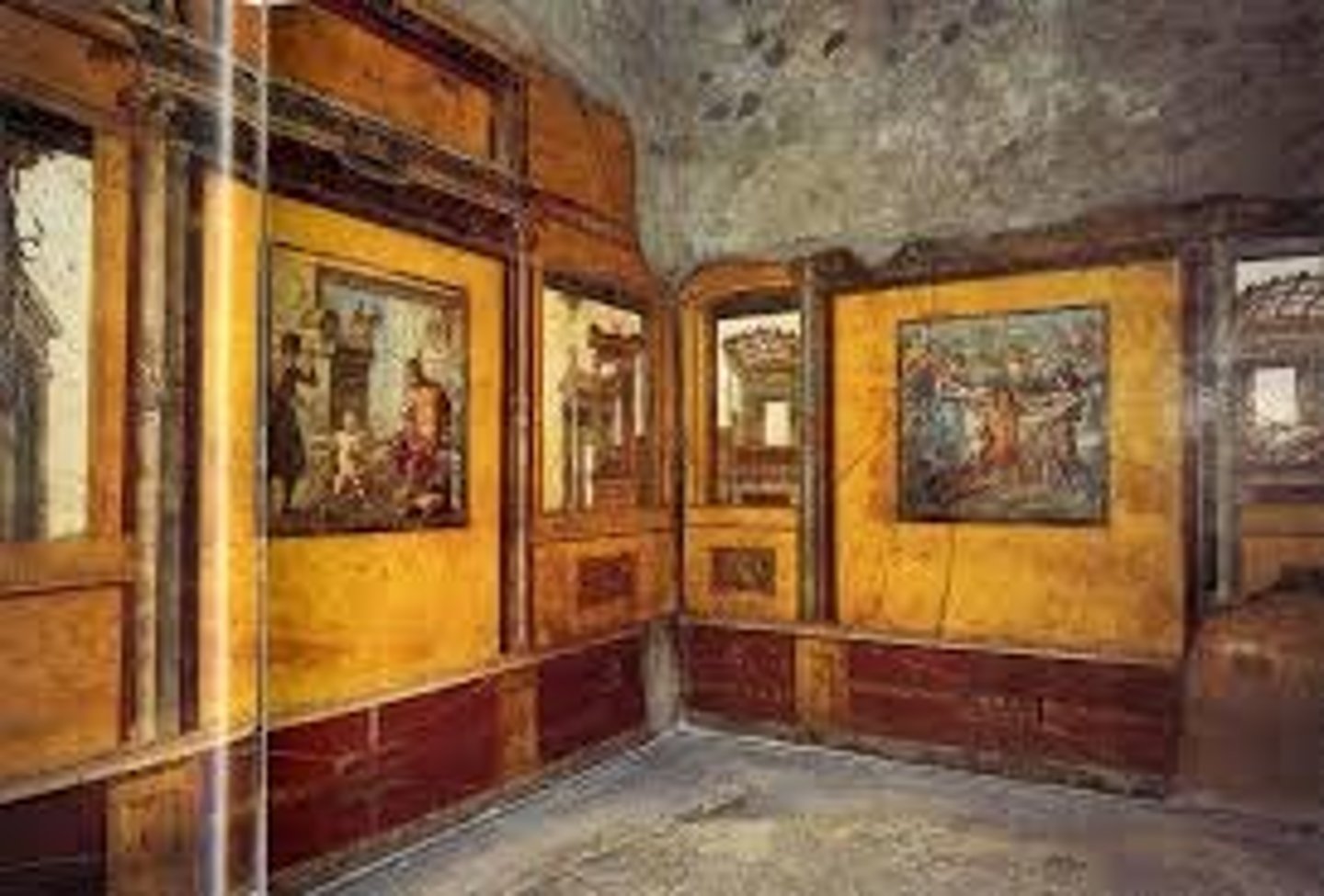
House of the Vettii (frescoes)
Frescoes were sexually graphic but their flamboyance was attributed to former slaves-turned-merchant owners.

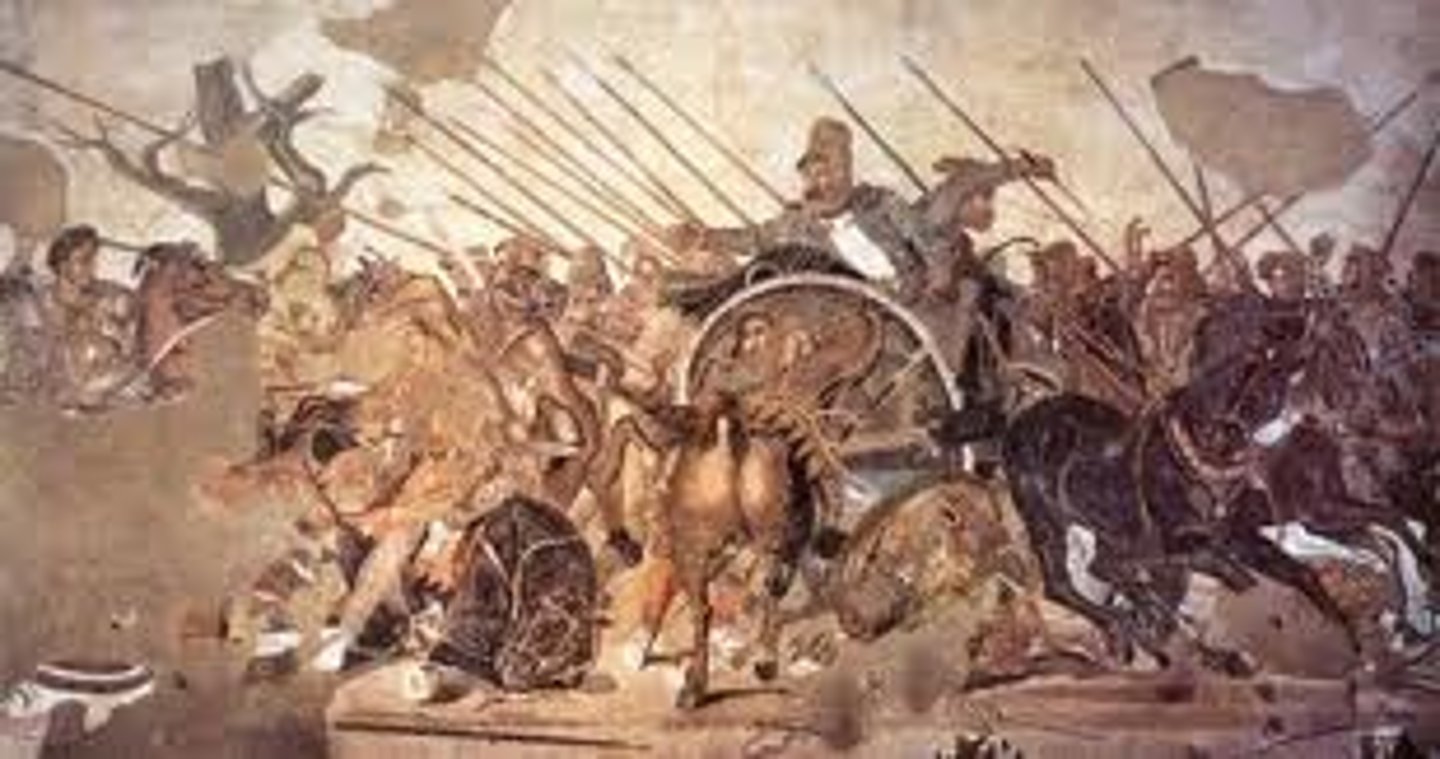
Alexander Mosaic from the House of Faun
Date: 100 BCE
Period/Style: Republican Rome
Original Location: Pompeii, Italy
Material/Technique: Tessarae mosaic
Function: Depicts battle between Alexander the Great and Darius III.
Context: Common style of floor decoration. Roman copy of a former Hellenistic Greek painting/mosaic. Spears point toward Alexander to indicate his victory.
Descriptive terms: mosaic, floor decoration

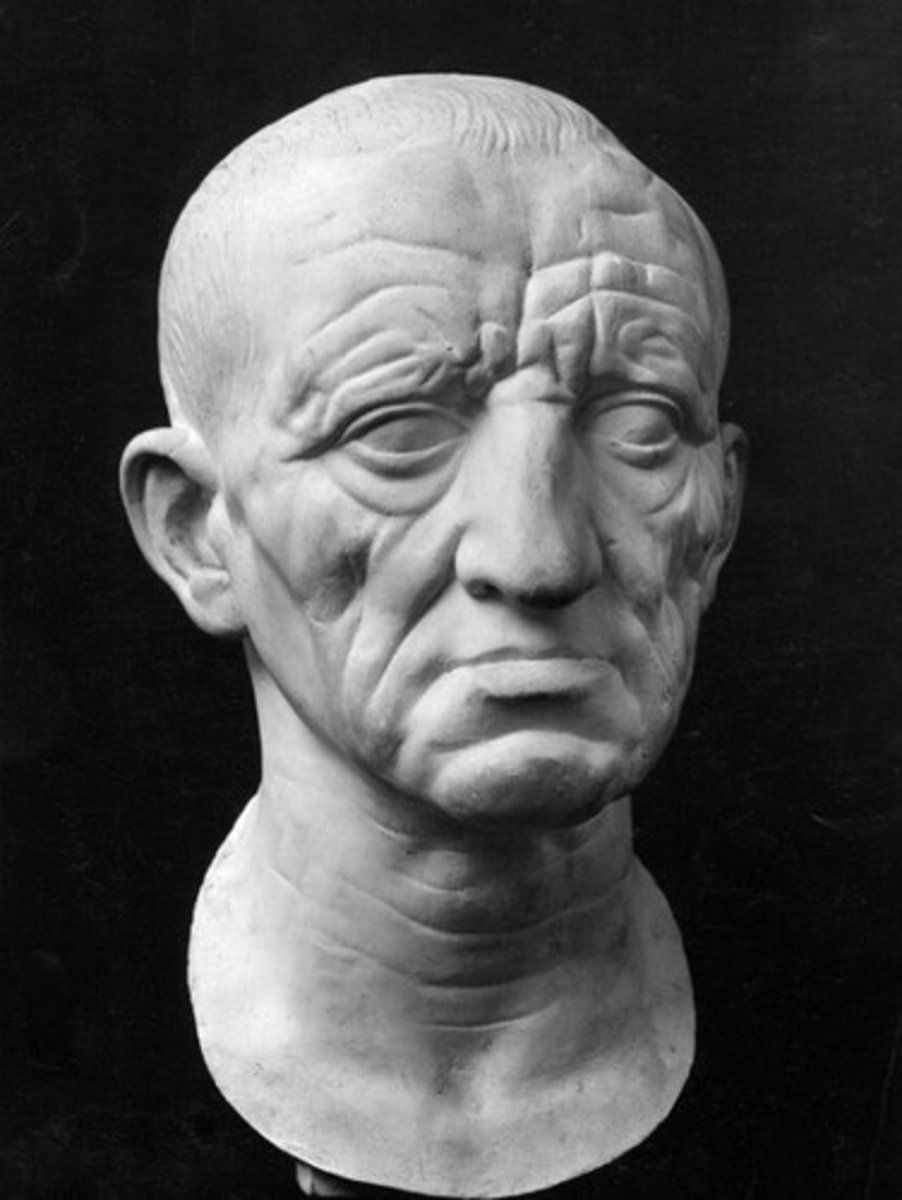
Head of a Roman Patrician
Date: 75-50 BCE
Period/Style: Republican Roman (Verism)
Original Location: Italy
Material/Technique: Marble
Function: Honors an elder Roman senator; displayed in elite homes.
Context: Uses verist (very realistic) portrayal borrowed from Hellenistic Greek style. Head busts were an Etruscan tradition.
Dterm-8escriptive terms: Verism, Republican Roman, portrait, sculpture in the round, bust

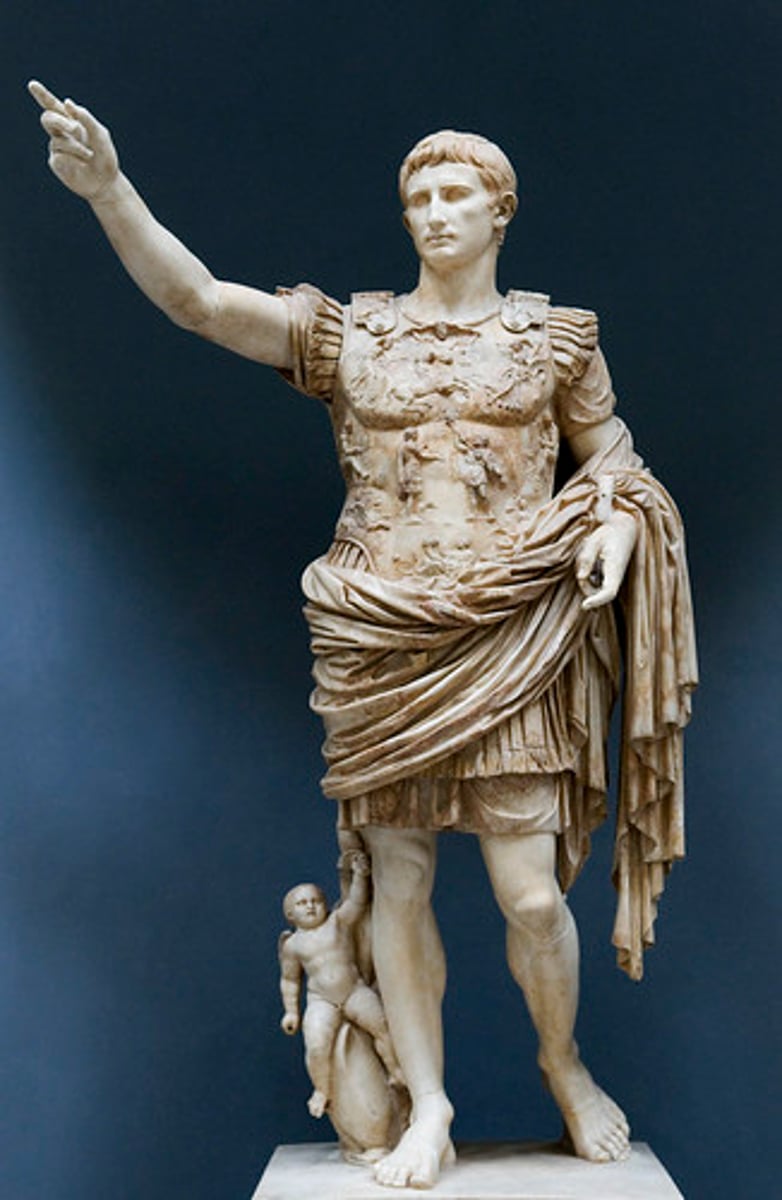
Augustus of Primaporta
Date: Early 1st century CE
Period/Style: Imperial Roman
Original Location: Rome, Italy
Material/Technique: Marble
Function: Commissioned by Augustus as a portrait for political propaganda
Context: Recalls the perfect, ideal Classical Greek portrayal. Verist portraits fell out of style in Imperial Rome. Cupid alludes to divine rule. Resembles the proportion of Doryphoros and composition of The Orator. He roleplays as a Roman general in military garb. He appears eternally youthful in his depictions.
Descriptive terms: sculpture in the round, political artistic propaganda, Imperial Roman, contrapposto

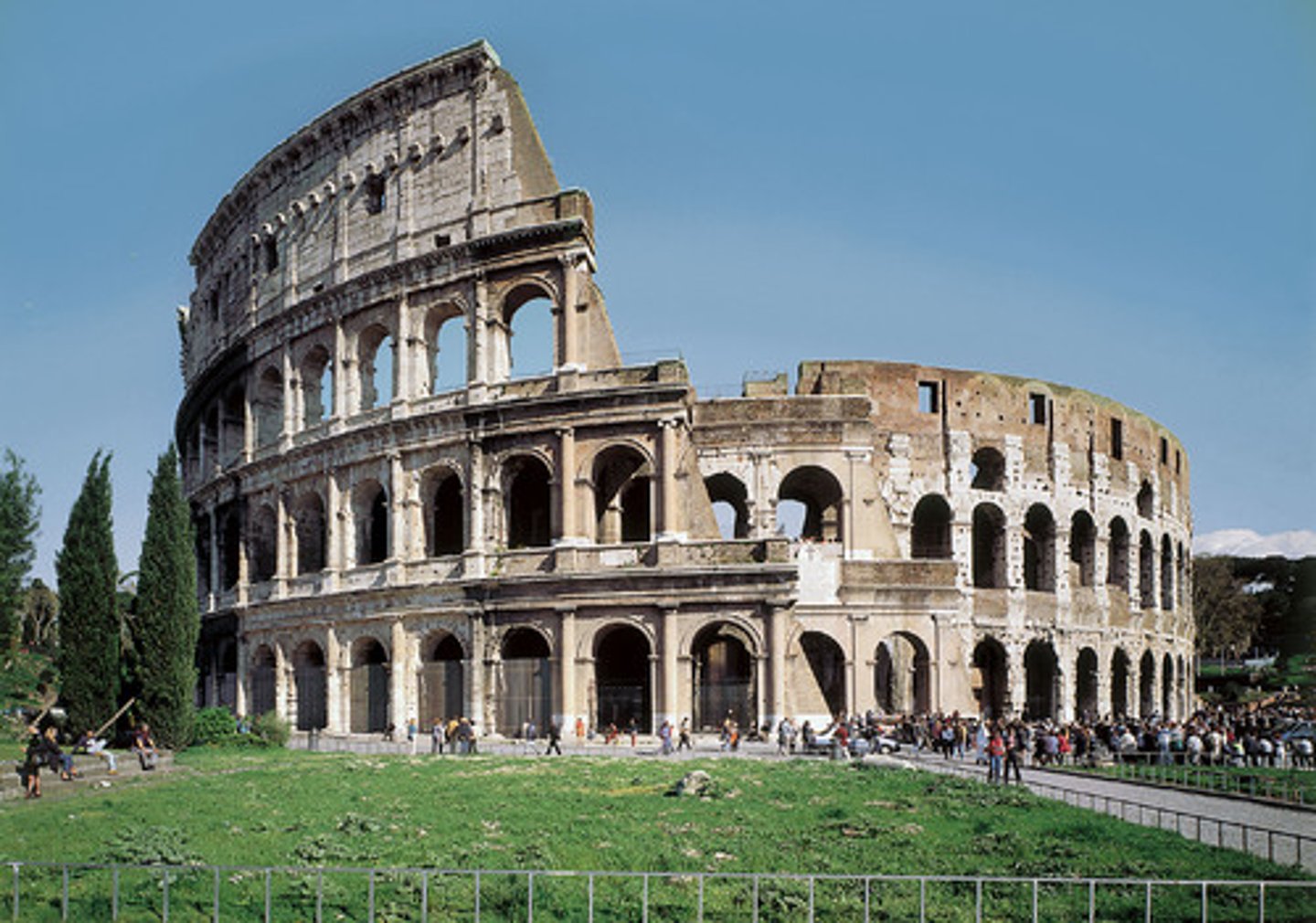
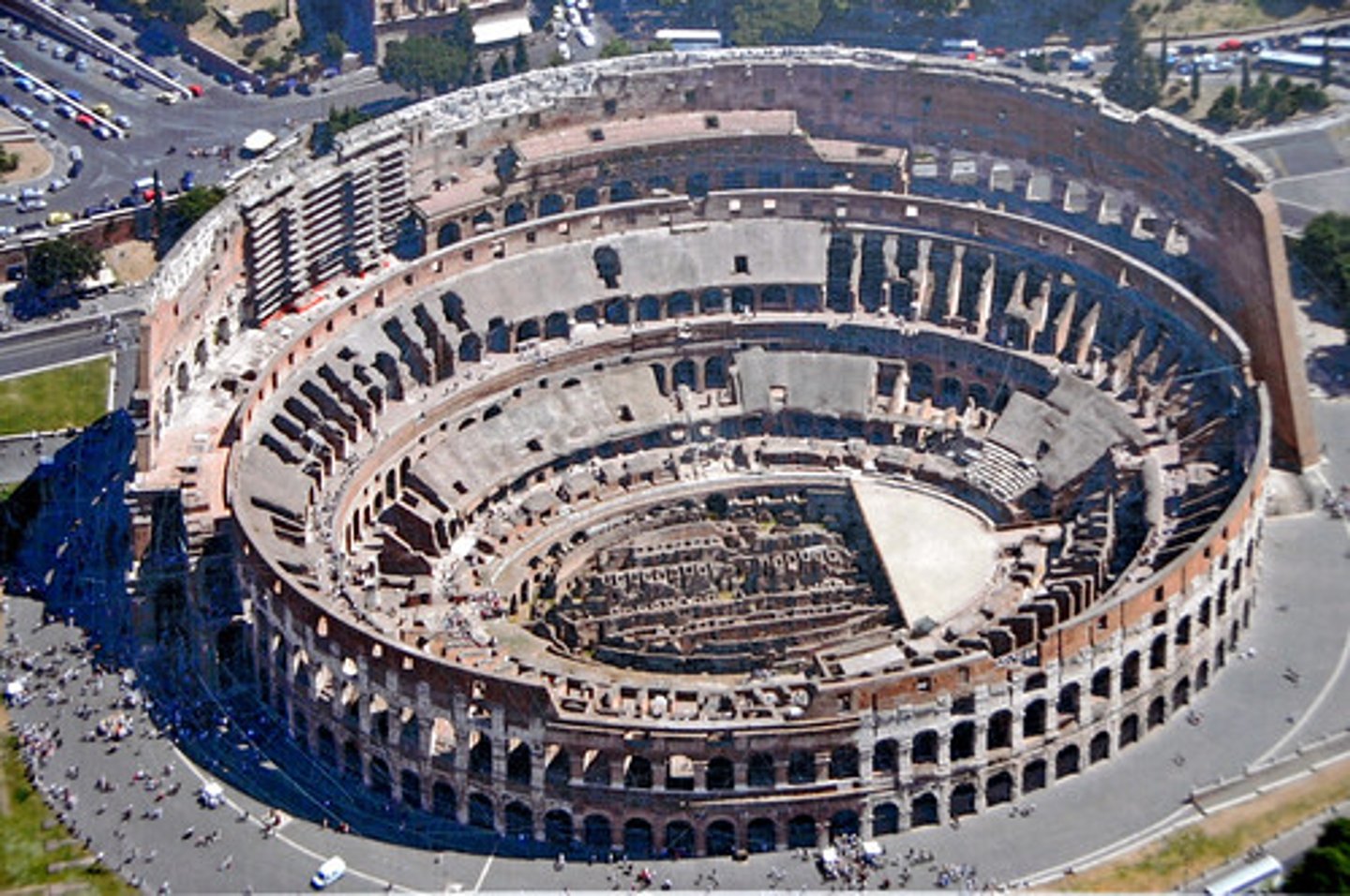
Colosseum (Flavian Amphitheater)
Date: 70-80 CE
Period/Style: Imperial Roman
Original Location: Rome, Italy
Material/Technique: Stone and concrete
Function: Built under Flavian rule to please the Roman citizens by showcasing gladiator battles.
Context: Begun construction under Vespasian and ended under Titus. Contains an intricate drainage system which allowed for flooding the arena for naval battles. Barrel-vaulted arches. Also displays all three Greek column orders, Doric followed by Ionic and Corinthian. The columns provide no structure and set a standard for Roman homes to follow. The velarium (retractable roof) shaded the elites in the topmost section.
Descriptive terms: amphitheater, architecture, Roman concrete

Colosseum (Flavian Amphitheater) (aerial)

Forum of Trajan (reconstruction drawing)
Date: Forum, libraries, and marketplaces: 106-112 C.E.; column completed 113 C.E.
Period/Style: Imperial Roman
Original Location: Rome, Italy
Architect: Apollodorus of Damascus
Material/Technique: Brick and concrete (architecture); marble (column)
Function: It functioned as the largest Imperial Roman forum, used for emperors to display their greatness.
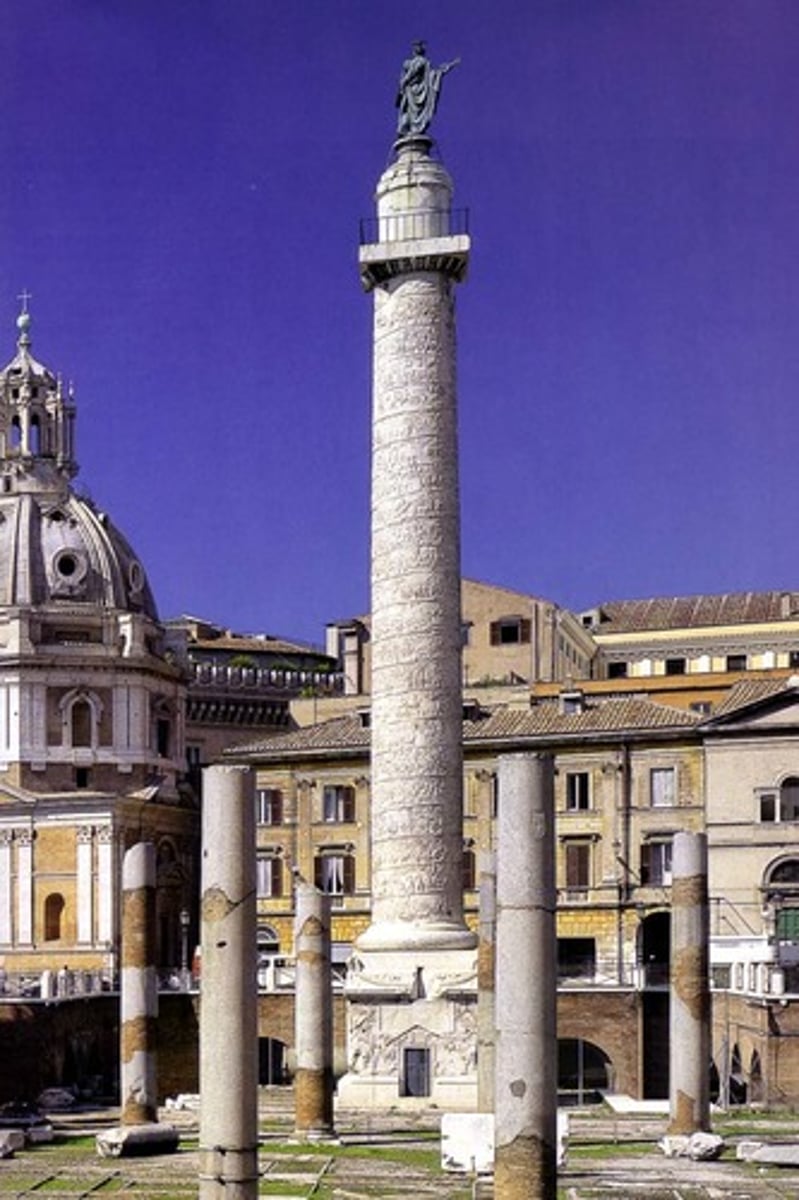
Context: The basilica became a governmental center for Rome (later adopted by Christians for worship). The Column of Trajan was built in a small courtyard decorated with bas-relief frieze commemorating Trajan's war victory. The Market of Trajan resembles a modern day mall. Basilica Ulpia contained five colonnaded naves and a coffered ceiling.
Descriptive terms: basilica, Imperial Roman, architecture, bas-relief, frieze
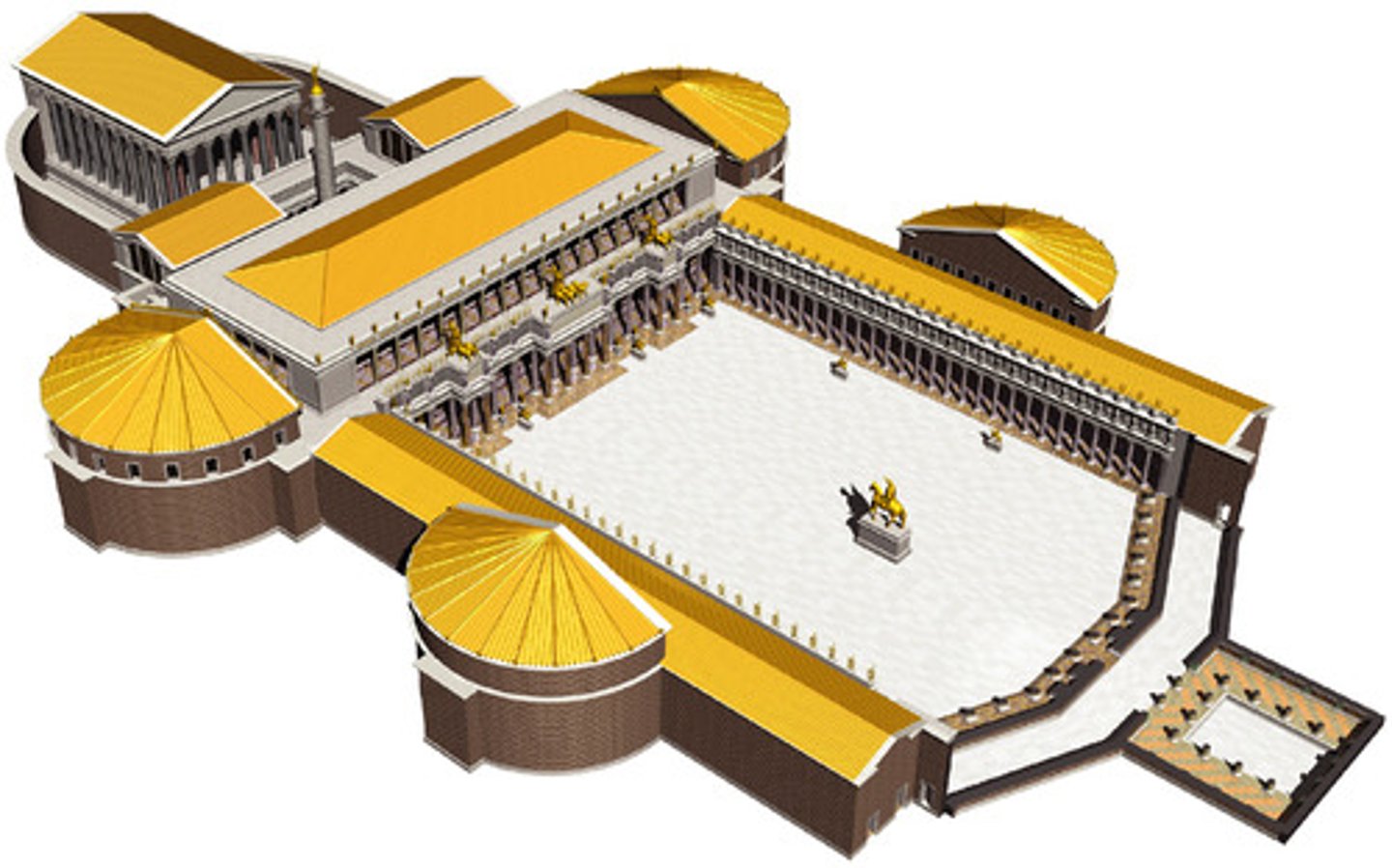
Forum of Trajan (Basilica Ulpia reconsctruction drawing)
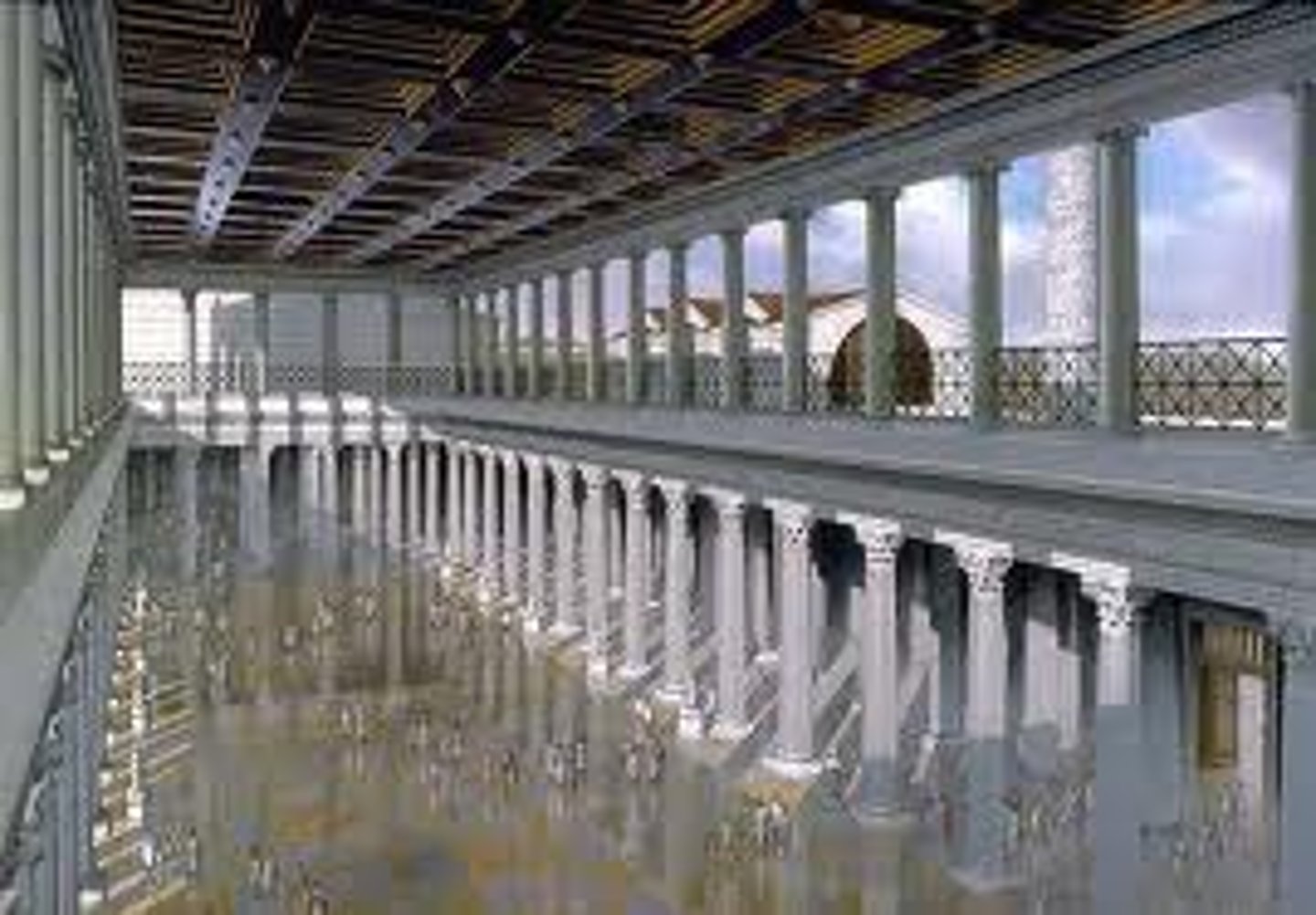

Forum of Trajan (Trajan markets)
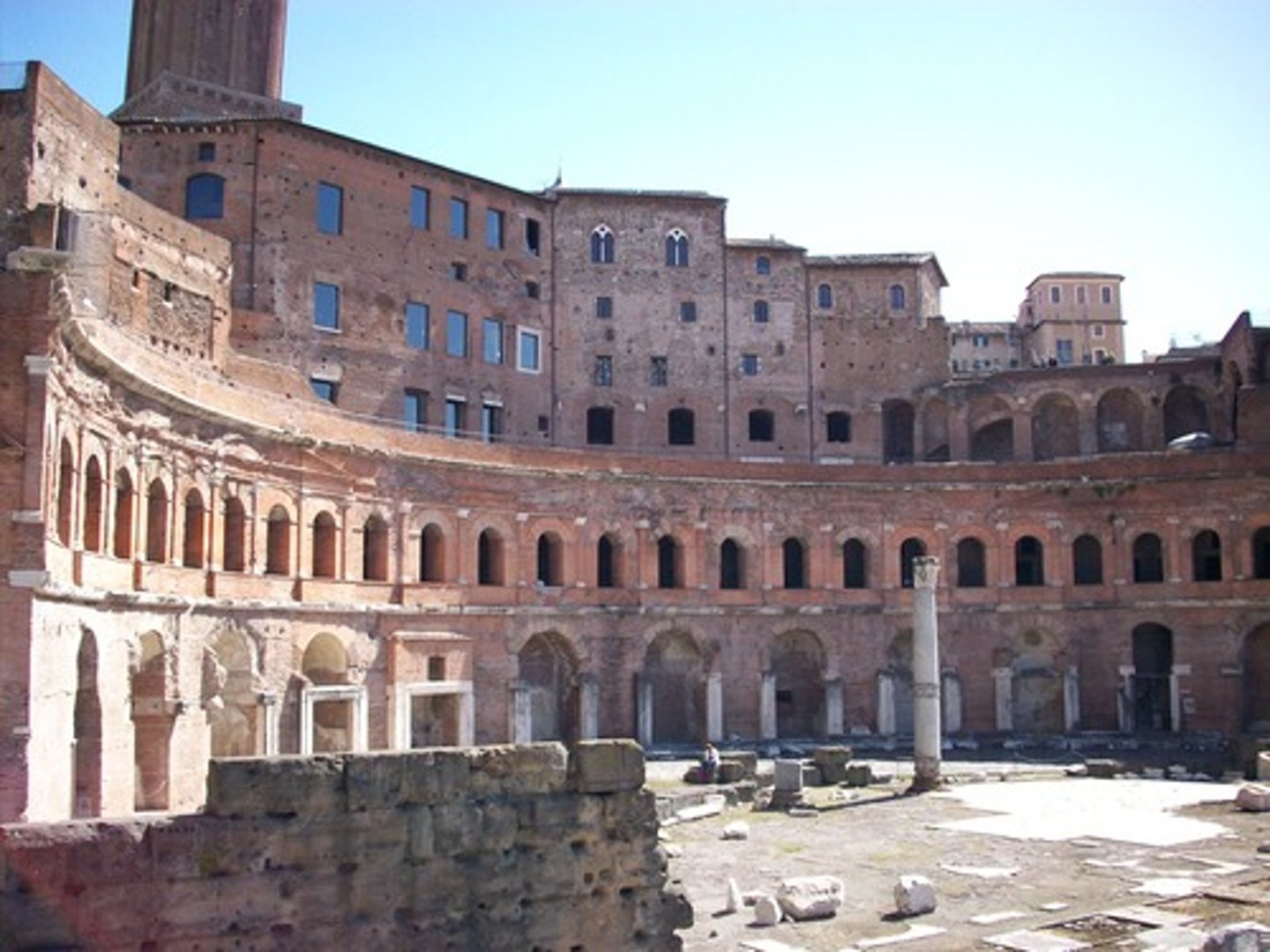

Forum of Trajan (Column of Trajan)

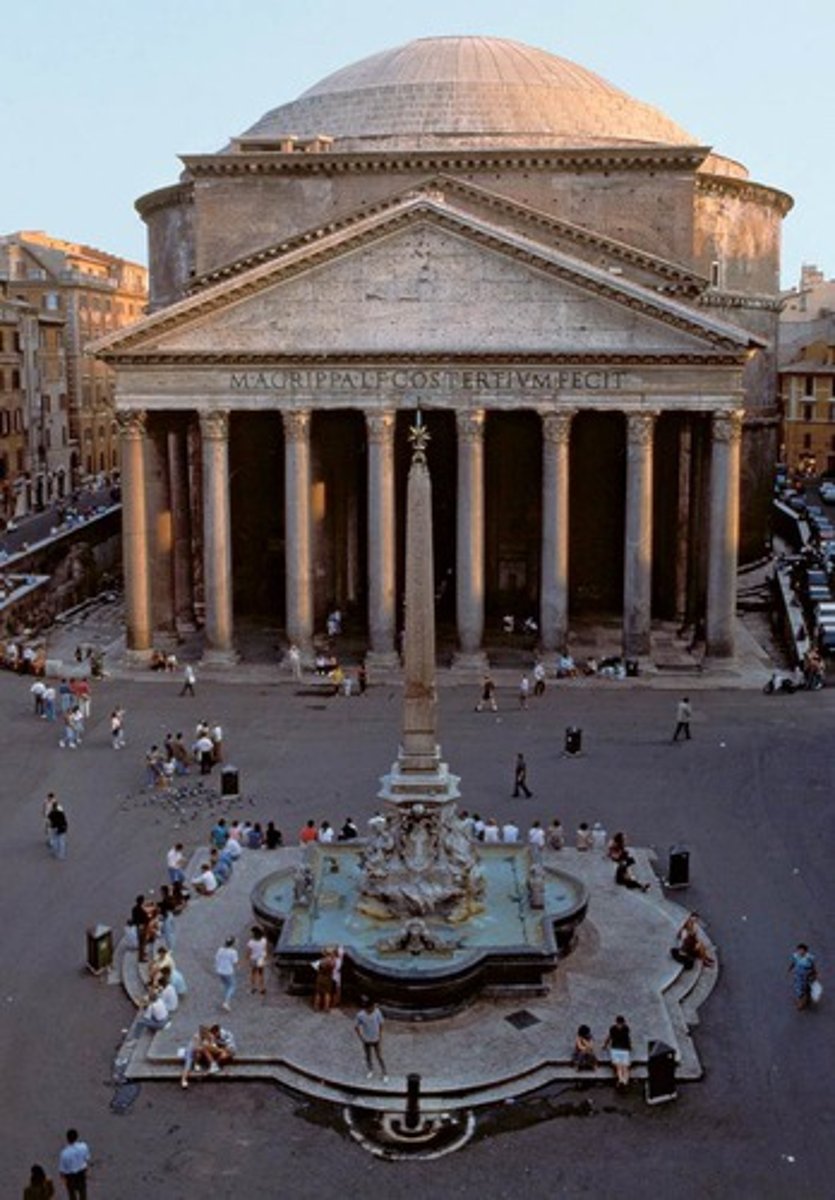
Pantheon
Date: 118-125 CE
Period/Style: Republican and Imperial Roman
Original Location:
Material/Technique: Concrete, Egyptian granite, and stone facing
Function: First built under Marcus Agrippa to commemorate Roman victory over Cleopatra and Marc Antony. The Pantheon was rebuilt by Emperor Hadrian who dedicated it to the gods after it was destroyed in a fire.
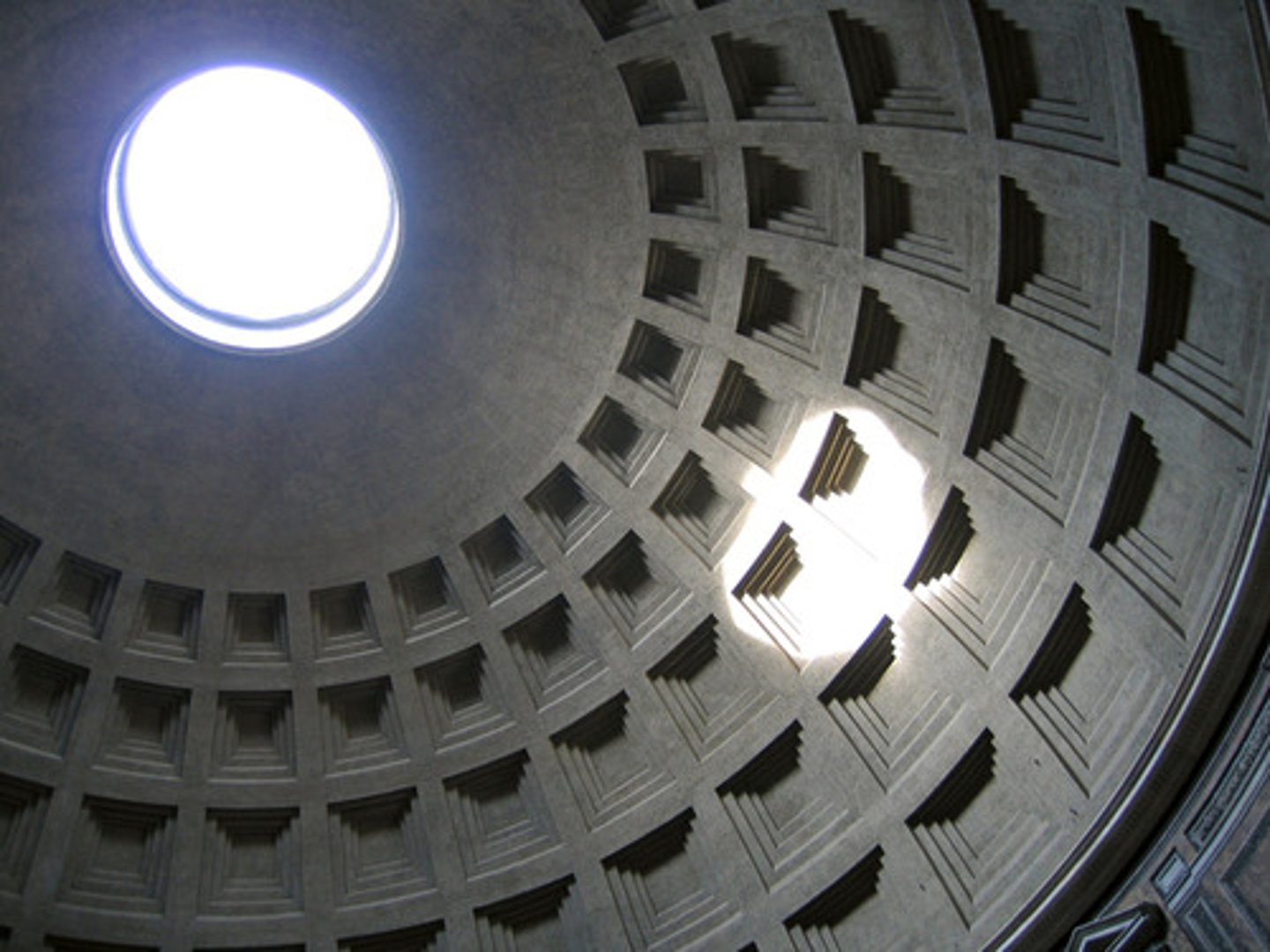
Context: Greek-influenced portico entrance and Corinthian columns. Pinnacle of concrete construction. Oculus located on the roof allowed smoke to leave and light to enter. Coffers reduced weight of the heavy dome. The front facade resembles Greek temple entrances, as Hadrian had a thing for Greek culture. Largest concrete dome in the world. The circle and square exterior and interior mirror represent harmony and perfection. Its exact purpose is still unknown. Roman statues are displayed inside the dome. Saved from Medieval destruction by consecrating as a church.
Descriptive terms: temple, architecture, sculptures, oculus, coffers, dome

Coffers
A recessed decorative panel that is used to reduce the weight of the dome and to decorate ceilings or vaults with gold adornments.

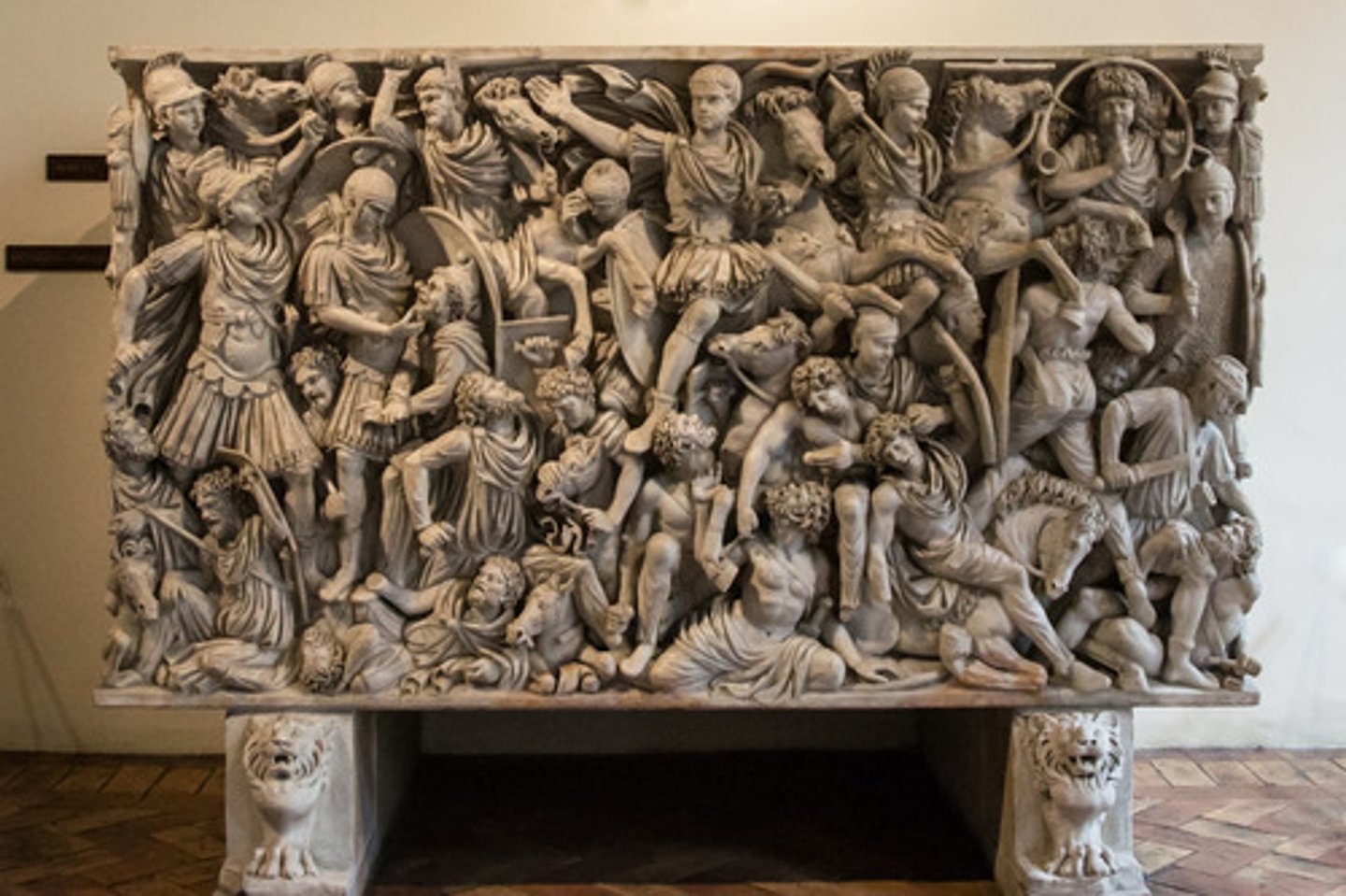
Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus
Date: 250 CE
Period/Style: Late Imperial Roman
Original Location:
Material/Technique: Marble
Function: Evokes chaos of a Roman-Barbarian battle and centers on the Roman commander whose tomb the relief adorns.
Context: Utilizes horrorvacui (fear of blank spaces). The composition is.reminiscent of Hellenistic/Pergamene Greek. Drill work characterized Late Imperial Roman art. Lacks realistic space and portrayal.
Descriptive terms: deep relief, frieze, tomb, Imperial Roman
