(Baylor) Bio 1305 Chapter 6
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
T or F: Cells are related my descent from earlier cells.
True
Cellular structure determines what cellular attribute?
Cellular function
Describe the way in which a Light Microscope (LM) works.
Light is passed through the specimen and through the lenses with refract the light so that the image is magnified.
What does an electron microscope do?
It focuses a beam of electrons through or on the surface of a specimen and the microscope measures the wavelength to determine an image.
What is the difference between a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and a Transmission Electron Microscope(TEM)?
SEMs focus a beam of electrons ONTO THE SURFACE of specimen while TEMs focus a beam of electrons THROUGH a specimen to read internal structures.
What is the process and purpose of cell fractionation?
It takes cells apart and separates their major organelles to be able to study cell structure and function.
What are the two types of cells of living organisms?
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic cells
Where are Prokaryotic cells found?
Bacteria and Archaea.
Where are Eukaryotic cells found?
Animals, plants, fungi, and protists
The basic features of all cells are:____________________
plasma membrane, cytoplasm filled with cytosol, chromosomes, & ribosomes
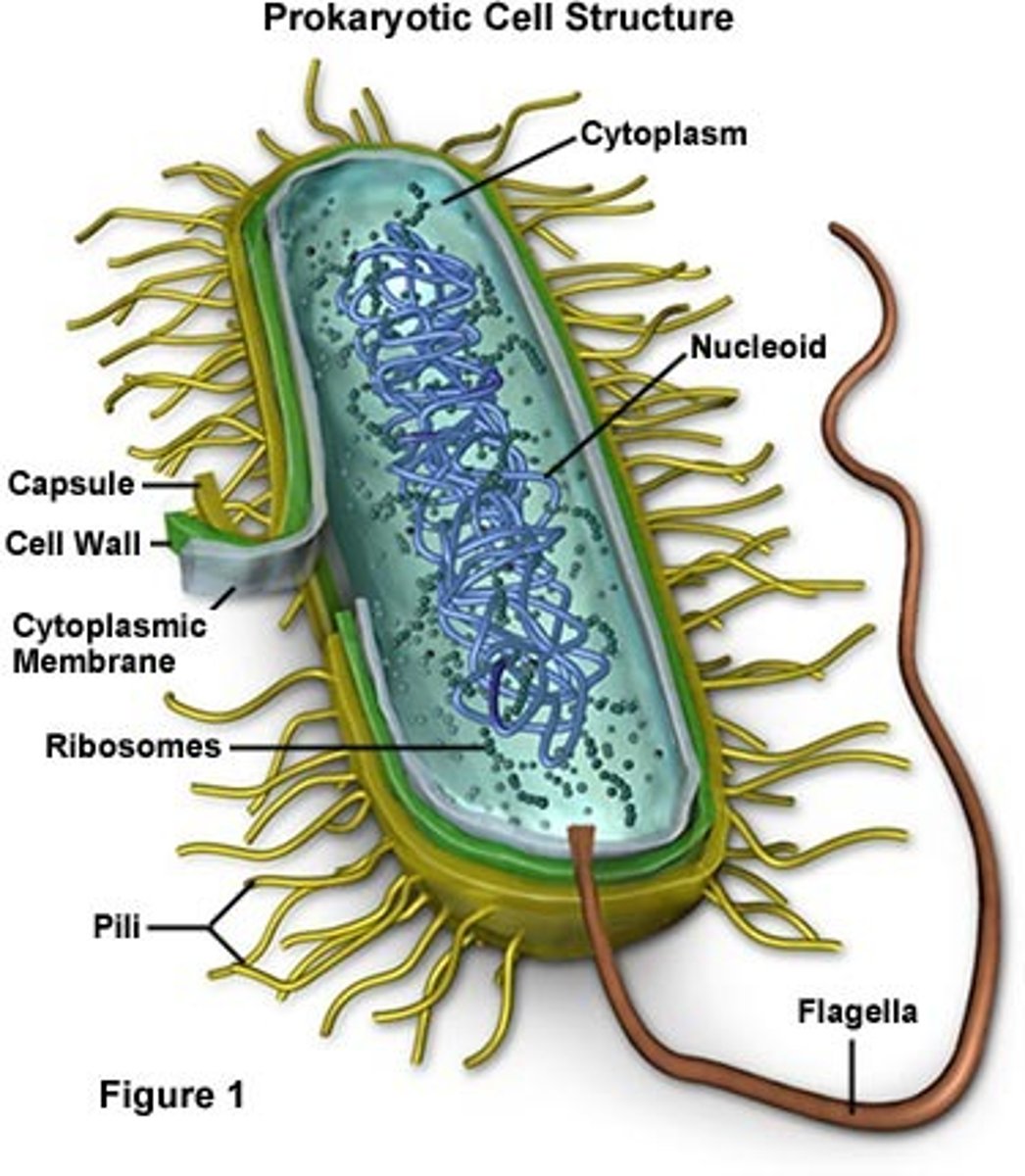
List the features of Prokaryotic cells.
-Has a nucleoid (DNA found there) & cell wall
-cytoplasm bound by plasma membrane
-no membrane-bound organelles
-has circular-shaped DNA
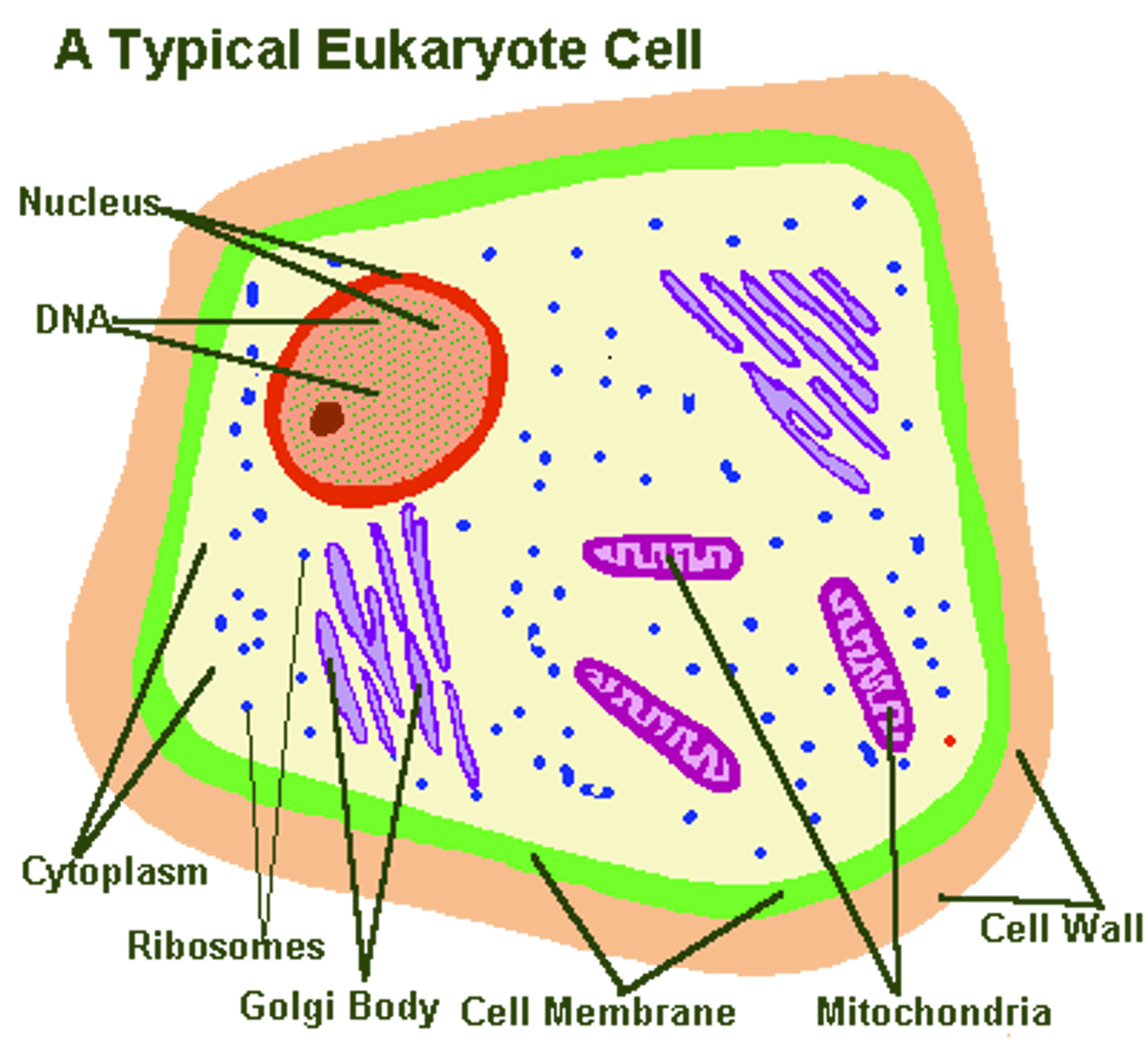
List the features of Eukaryotic cells.
-has nucleus (DNA found there)
-No cell wall
-membrane-bound organelles
-Cytoplasm & Cytosol between plasma membrane and nucleus
-has linear DNA
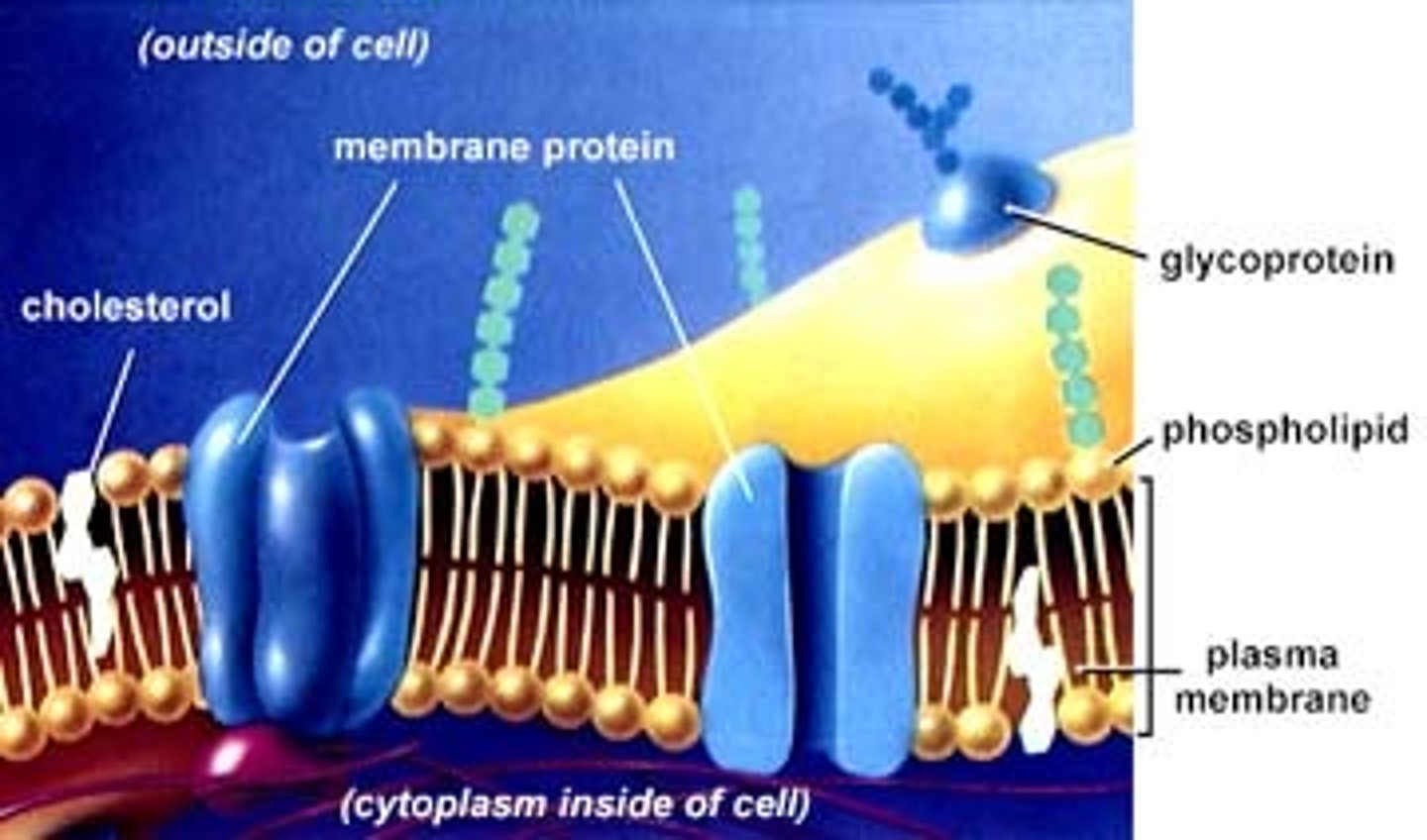
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
It acts as a selective barrier that allows passage of enough oxygen, nutrients, and waste to service the entire cell.
Do metabolic requirements determine how big a cell can get?
Yes
Surface area of cell increases by ____ and volume increases by ____.
n^2, n^3
The smaller the cell = _________ surface area relative to volume.
greater
What does the nucleus contain?
DNA, cell's genetic information
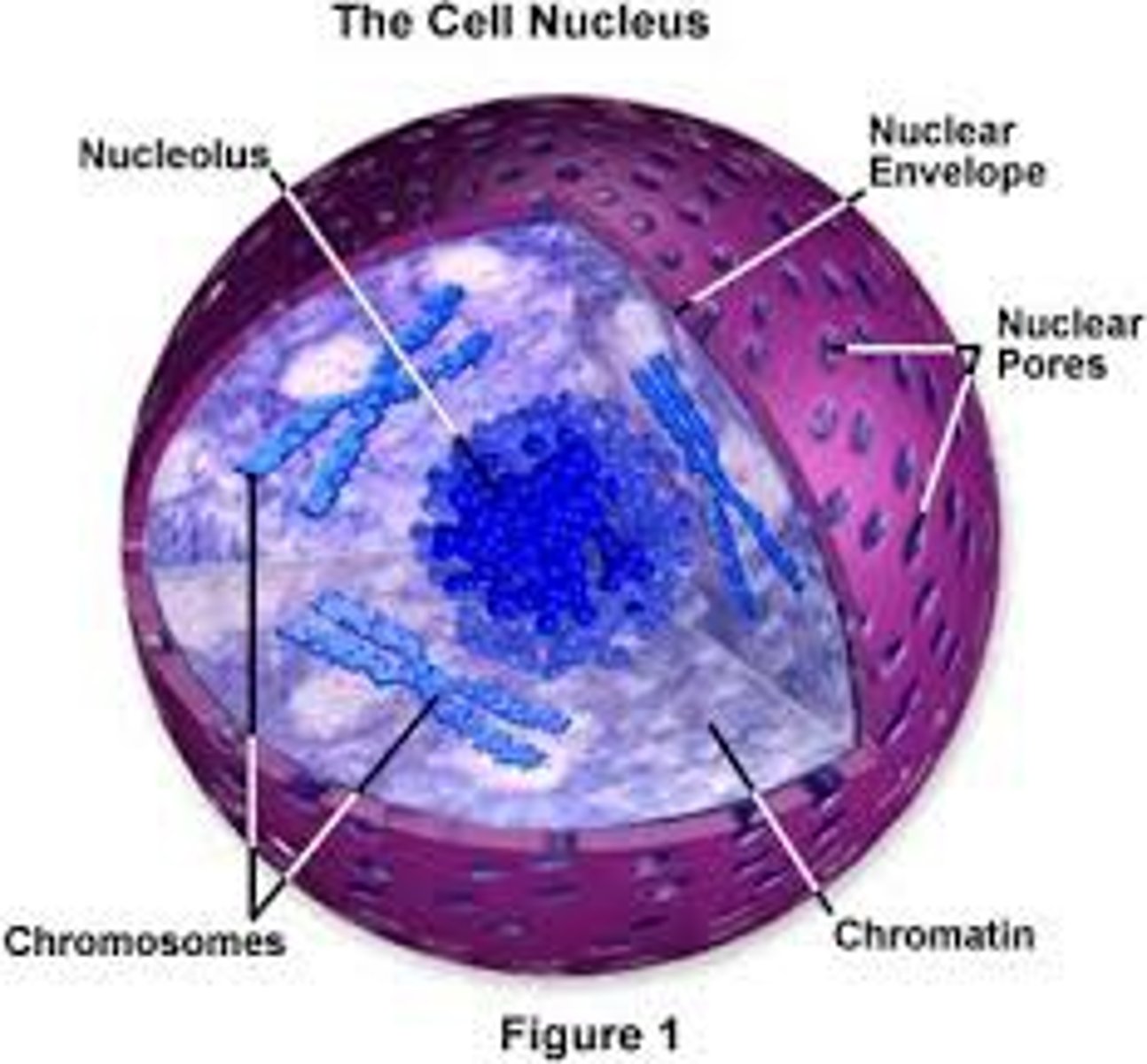
What does the nuclear envelope do?
It encloses the nucleus with a double membrane, separating it from cytoplasm.
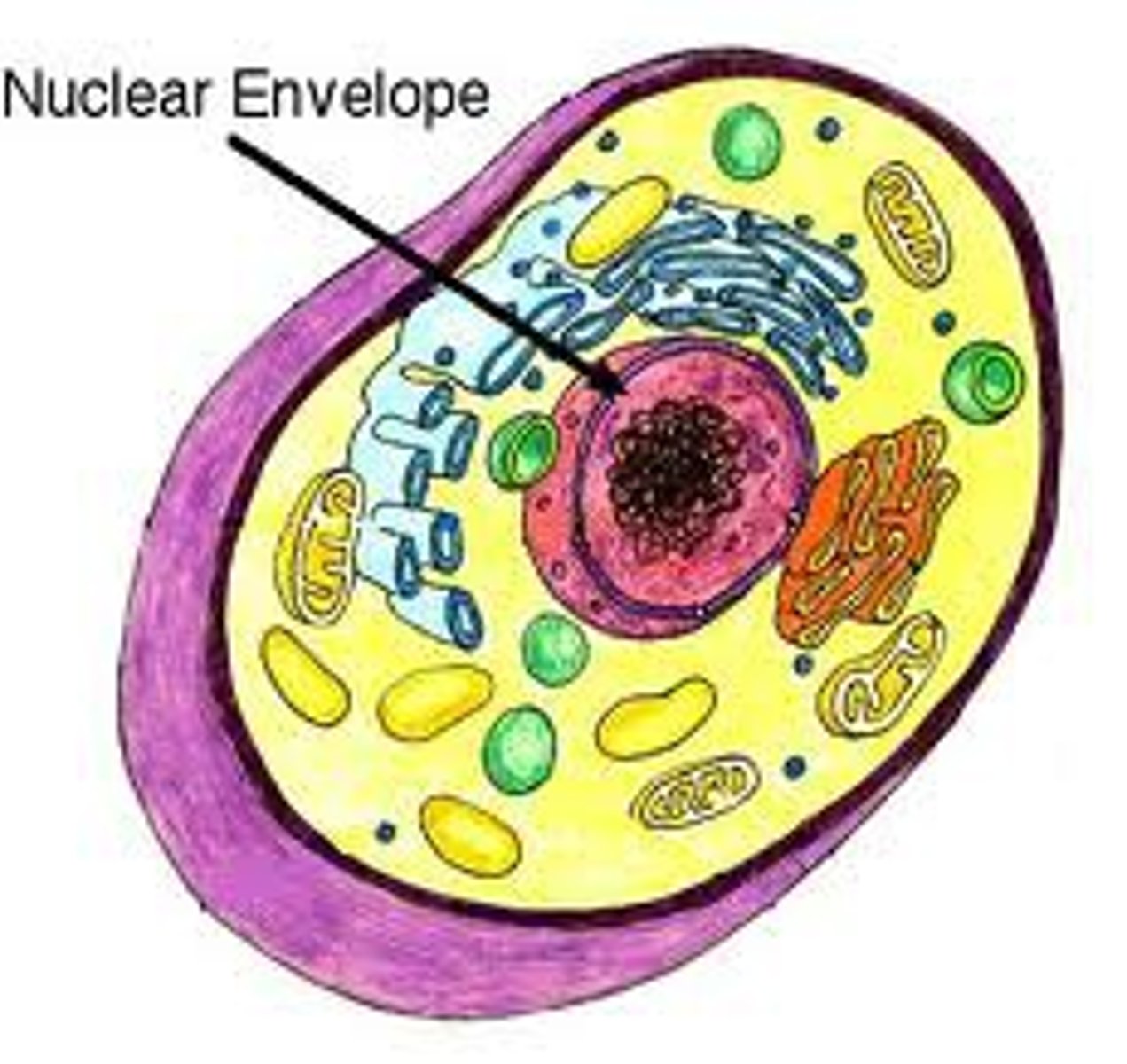
The inside of the nuclear envelope is lined by the _______________________, which maintains the shape of the nucleus by supporting it.
nuclear lamina
How is DNA organized inside the nucleus?
It is organized into chromosomes.
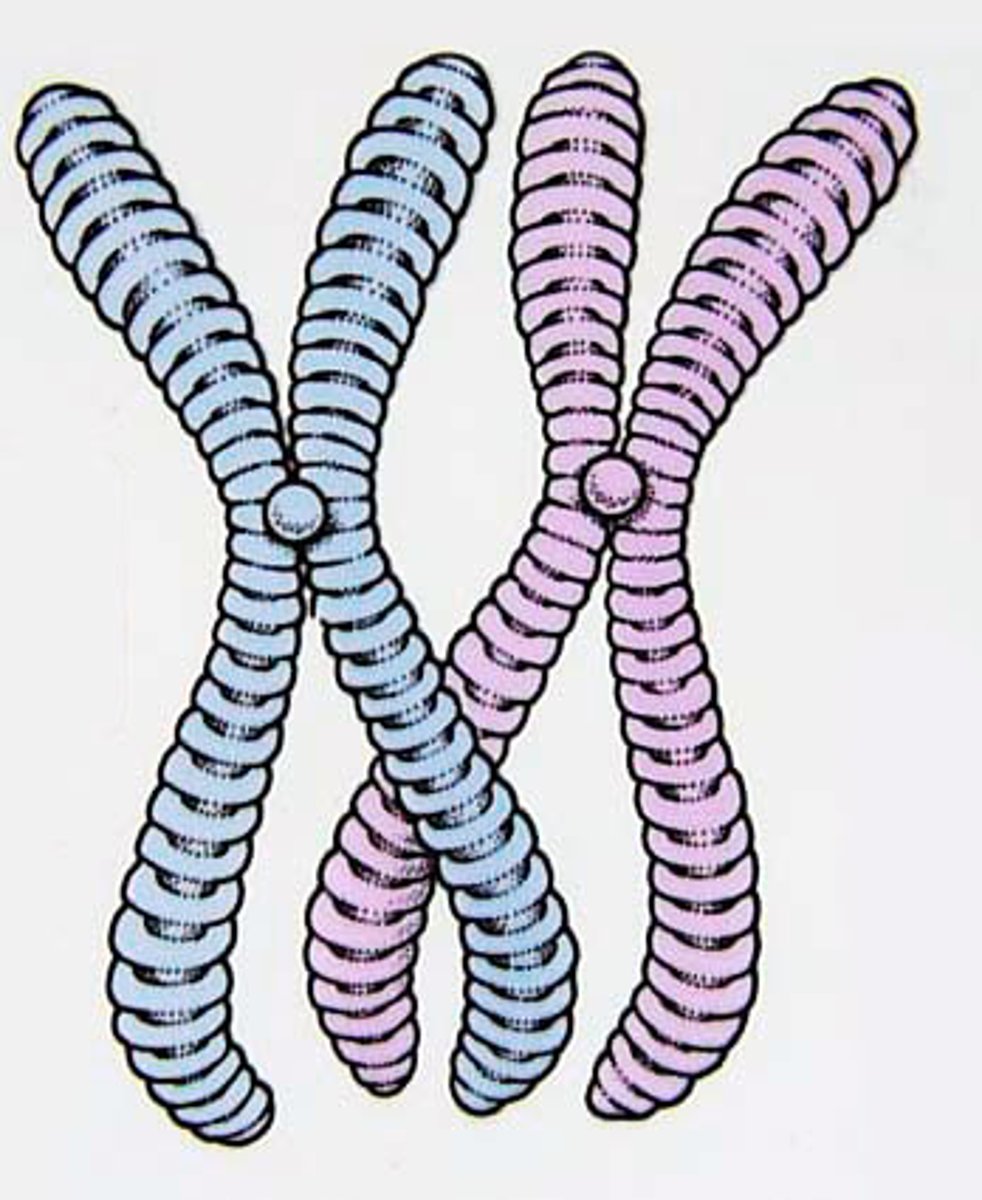
Chromosomes are made up of DNA and proteins, which is a complex called what?
Chromatin
Where is ribosomal RNA formed?
In the nucleolus found inside the nucleus.
What are Ribosomes made out of?
They are made of ribosomal RNA and proteins
What are the two places that ribosomes synthesize proteins?
In the cytosol (free ribosomes) & on the outside of the endoplasmic reticulum or nuclear envelope (bound ribosomes
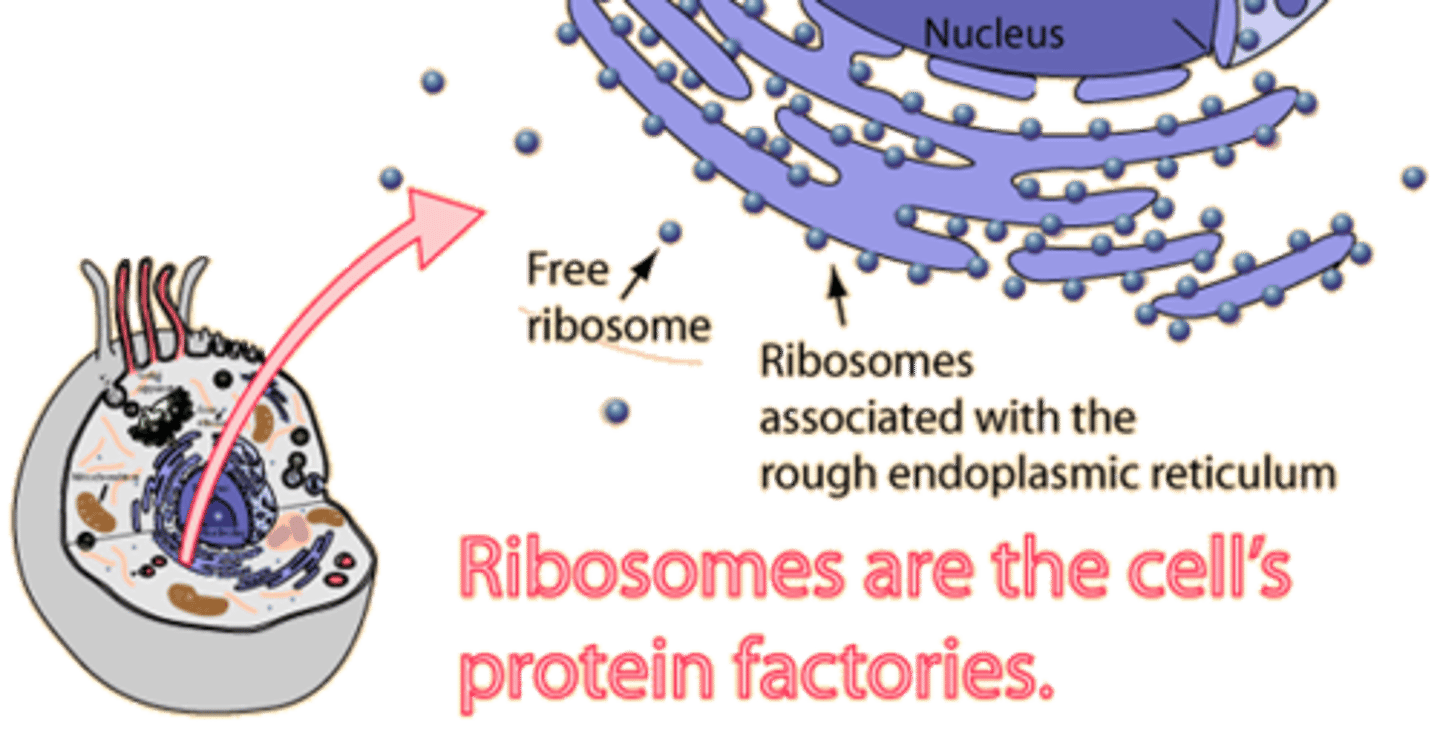
What is the function of free ribosomes?
They are off-duty or making proteins for cytosol.

What is the function of bound ribosomes?
They make proteins for the cell to secrete.
List the 6 components of the Endomembrane System.
1. Nuclear Envelope
2. Endoplasmic Reticulum
3. Golgi Apparatus
4. Lysosomes
5. Vacuoles
6. Plasma Membrane
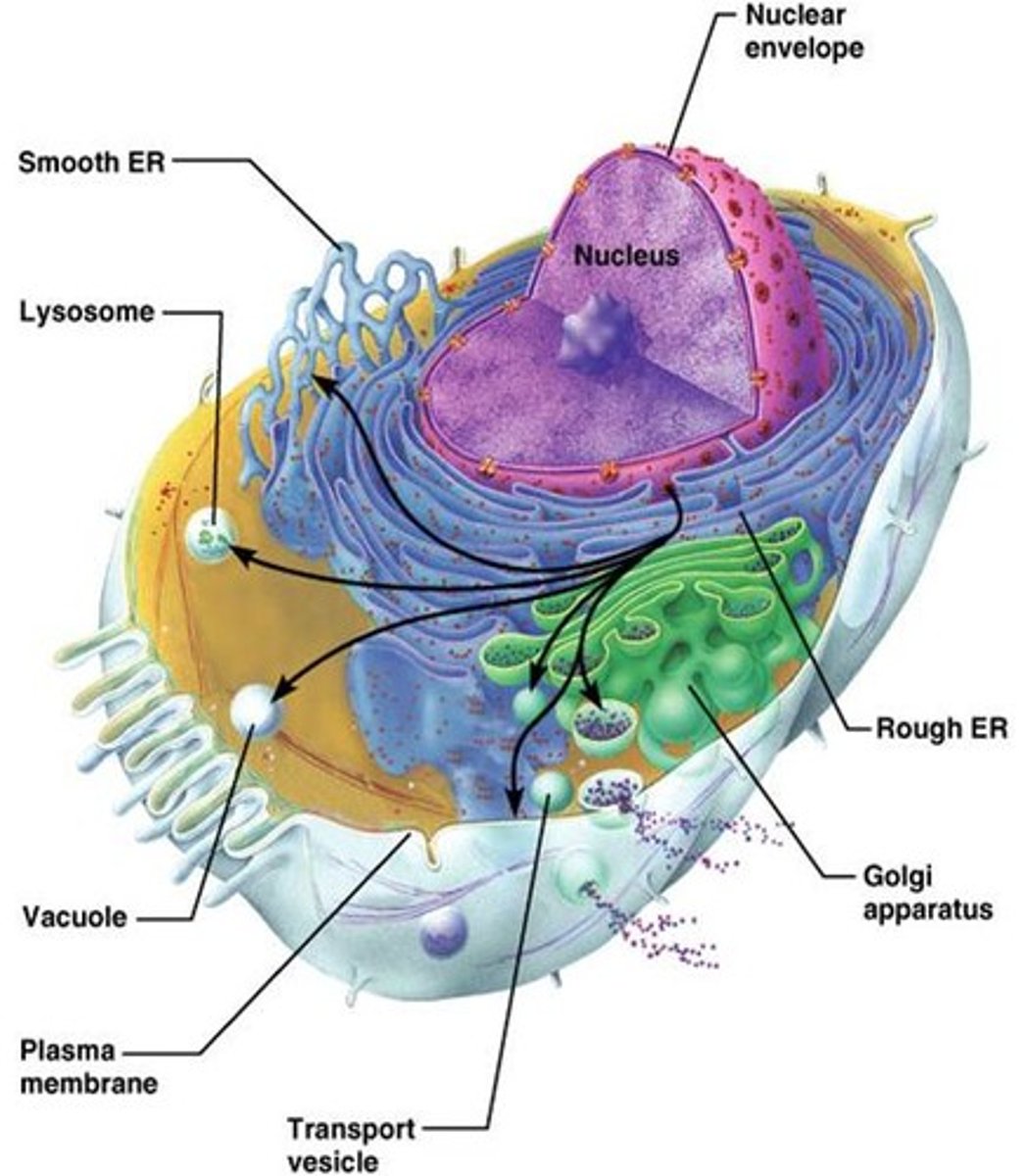
How are the components of the Endomembrane System connected?
They are connected via transfer by vesicles.
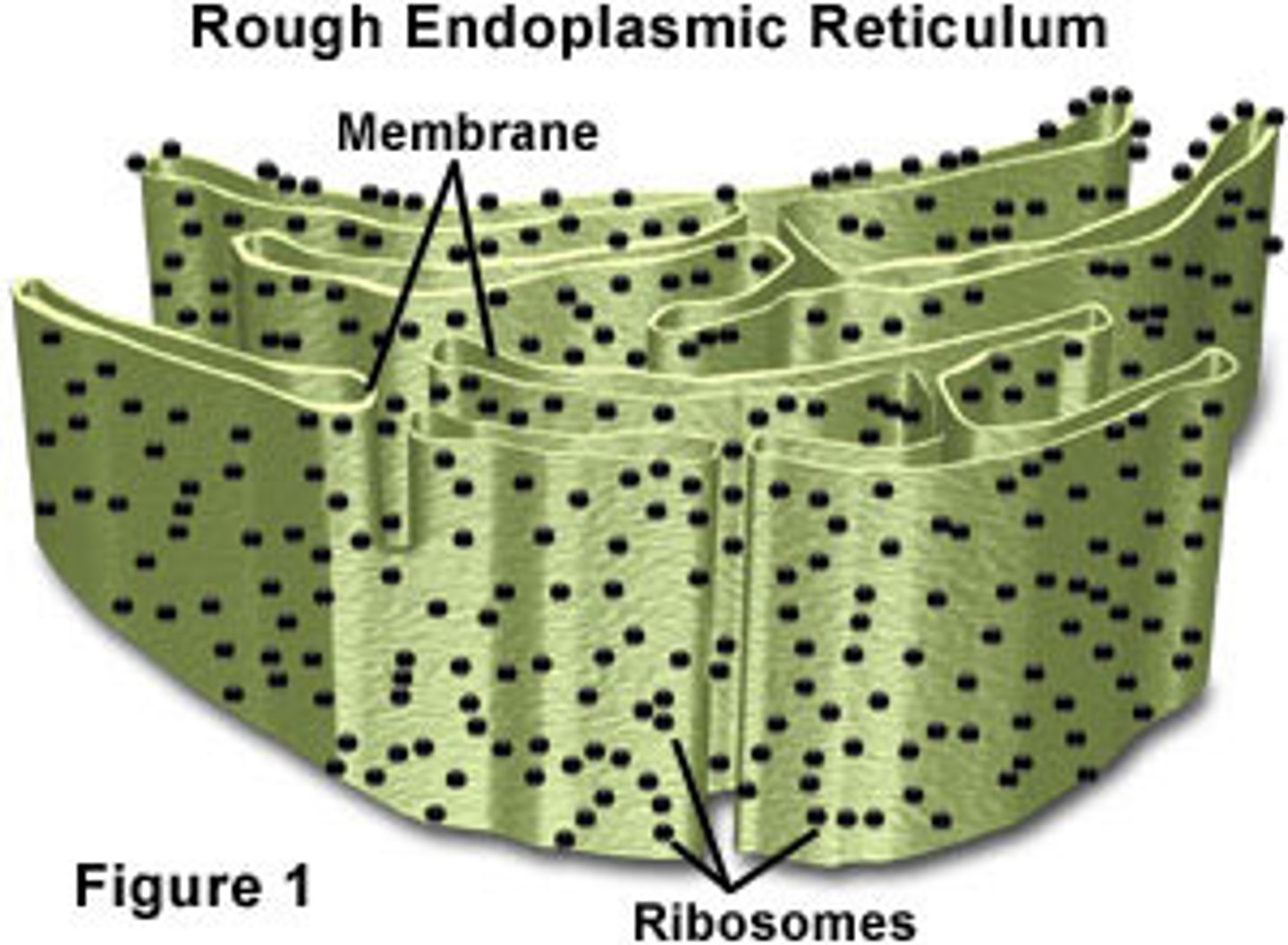
What are the two types of Endoplasmic Reticulum called?
Rough ER, which lacks ribosomes & Smooth ER, which surface is covered in ribosomes
What are the different functions of Smoot ER (SER)?
-Synthesizes Lipids
-Metabolizes carbohydrates
-Detoxifies drugs & poisons
-Stores Calcium Ions
What are the different functions of Rough ER (RER)?
-Secretes Glycoproteins (protein w/ bonded carbohydrates)
-Distributes transport vessels, proteins surrounded by membranes
-Is a Membrane Factory for the cell
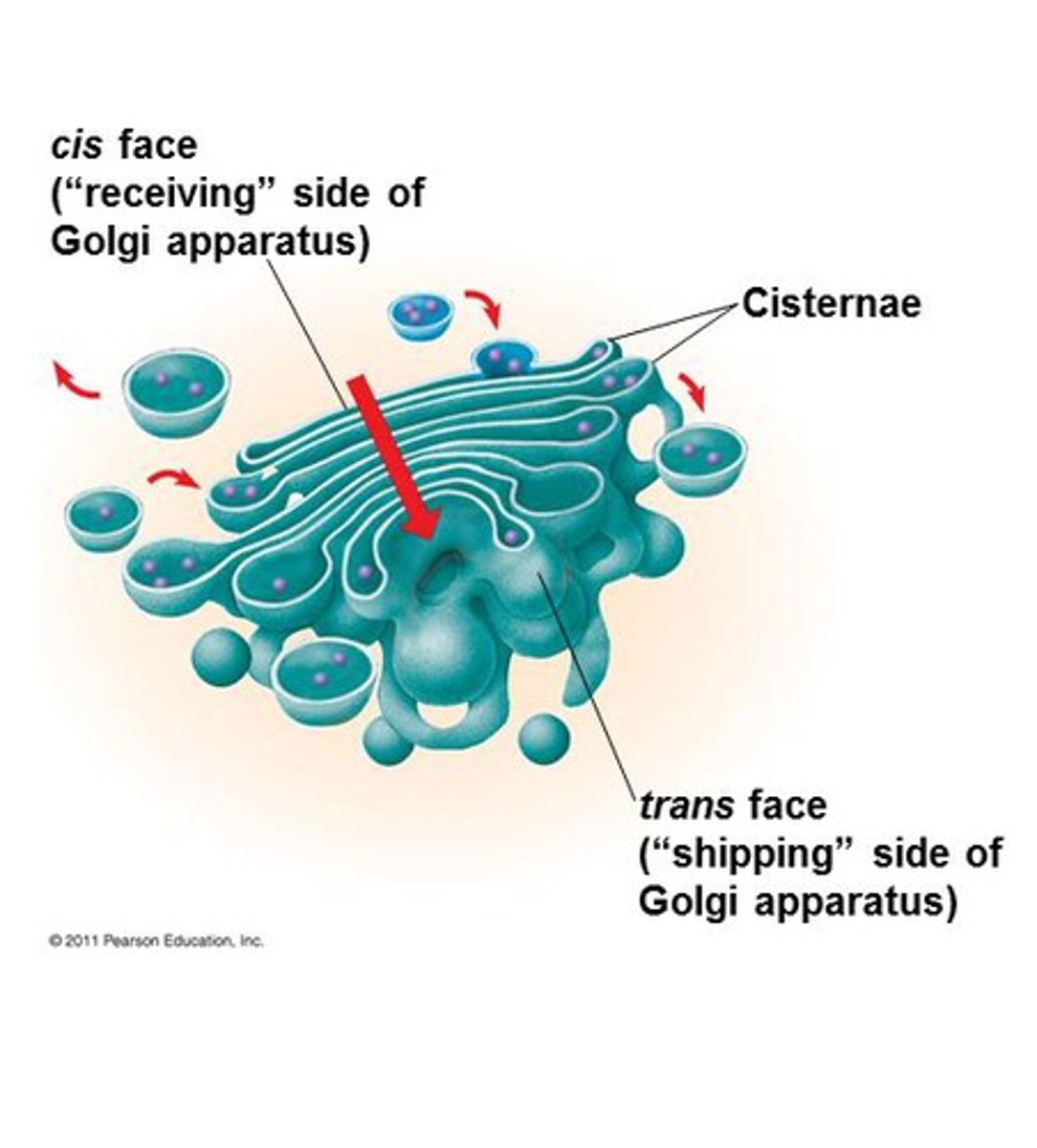
What does the Golgi Apparatus consist of?
Flattened, mebranous sacks called CISTERNAE
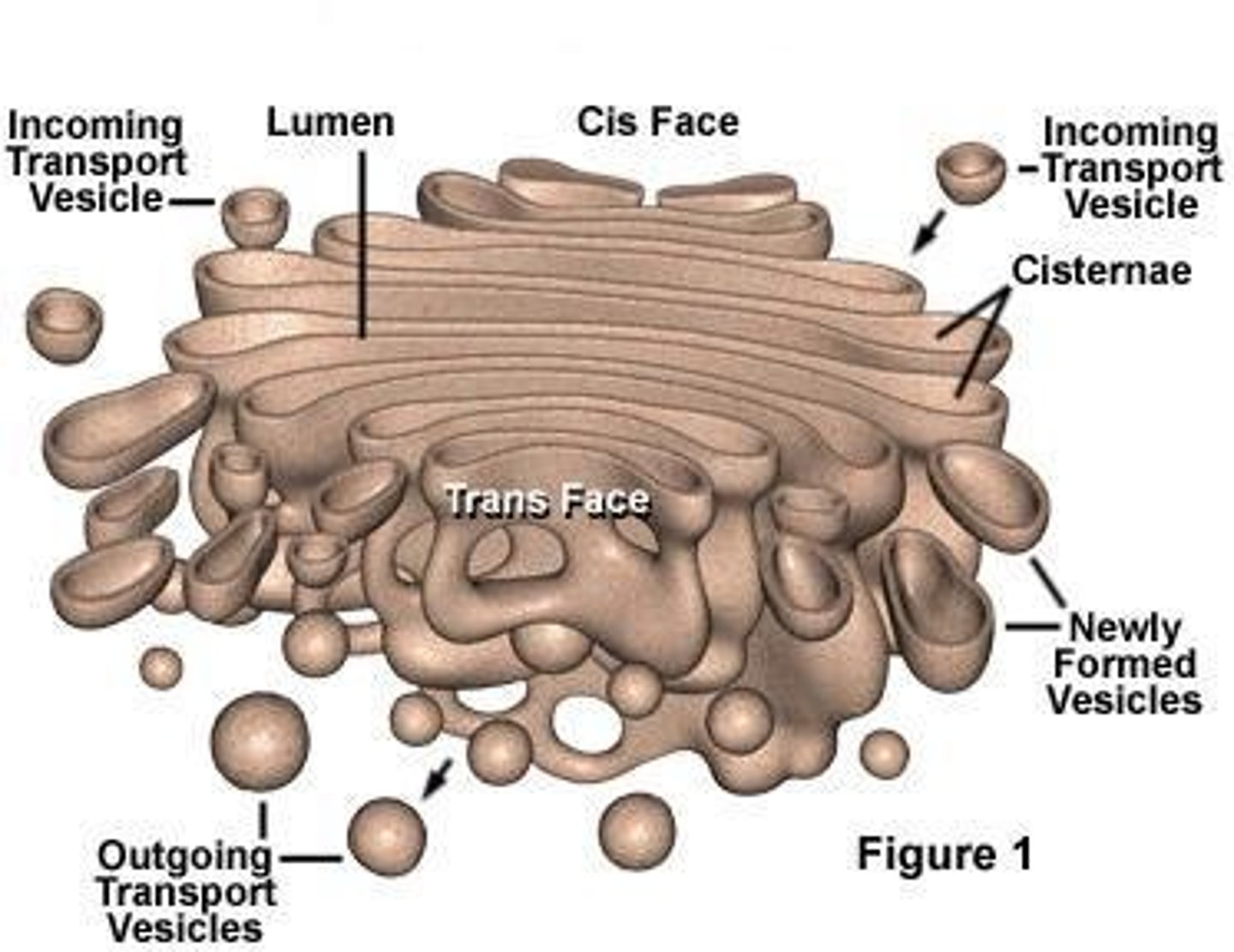
What does the Golgi Apparatus do?
It modifies products of ER, manufactures certain macromolecules, & sorts and packages materials into transport vesicles.
What is a lysosome?
It is a membranous sack of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest macromolecules.
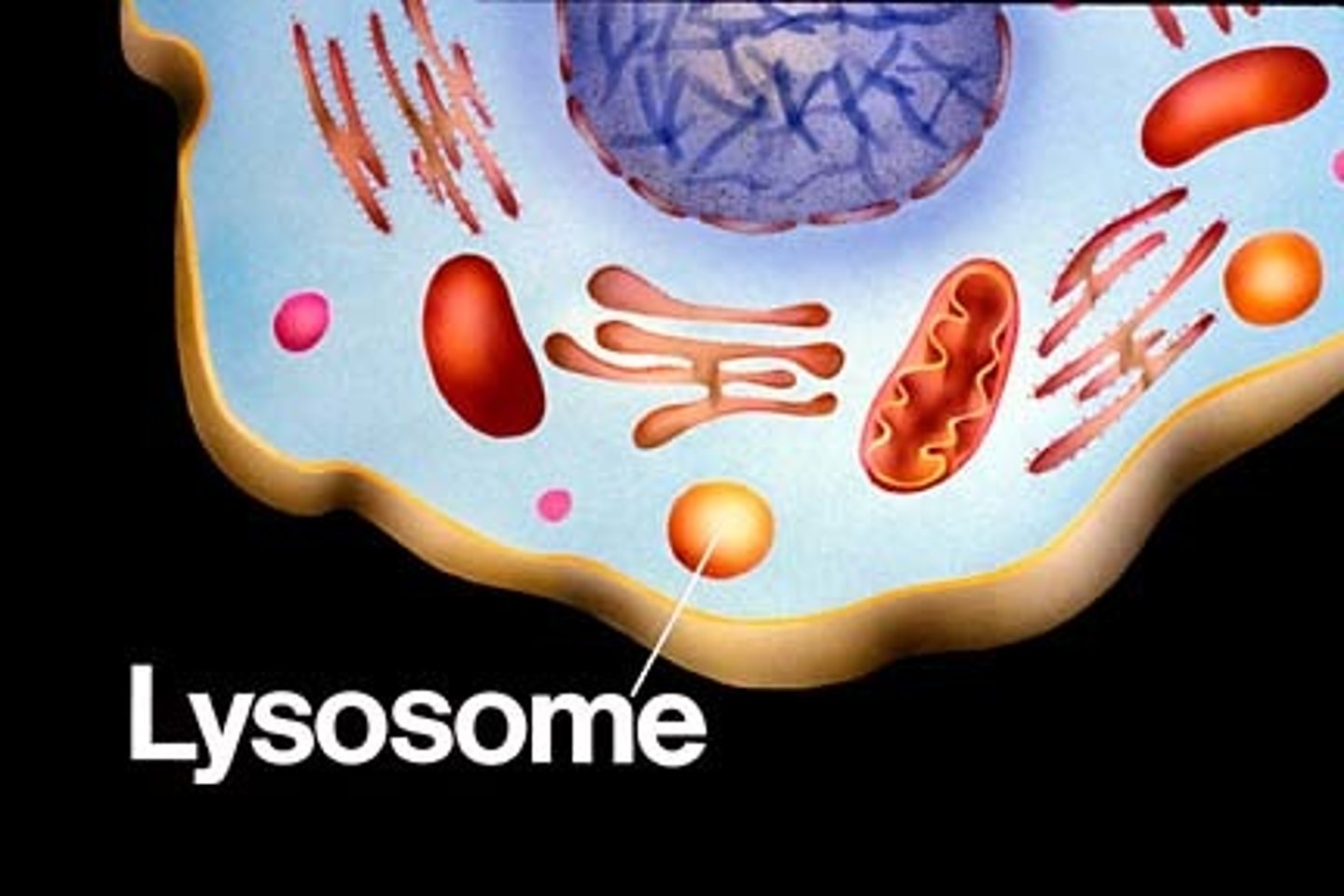
Describe the process of Phagocytosis.
A cell (usually amoebas & unicellular eukaryotes) digests another cell, creating a food vacuole. A lysosome then fuses with the food vacuole and its enzymes digest the food.
A food vacuole is formed by what process?
Phagocytosis
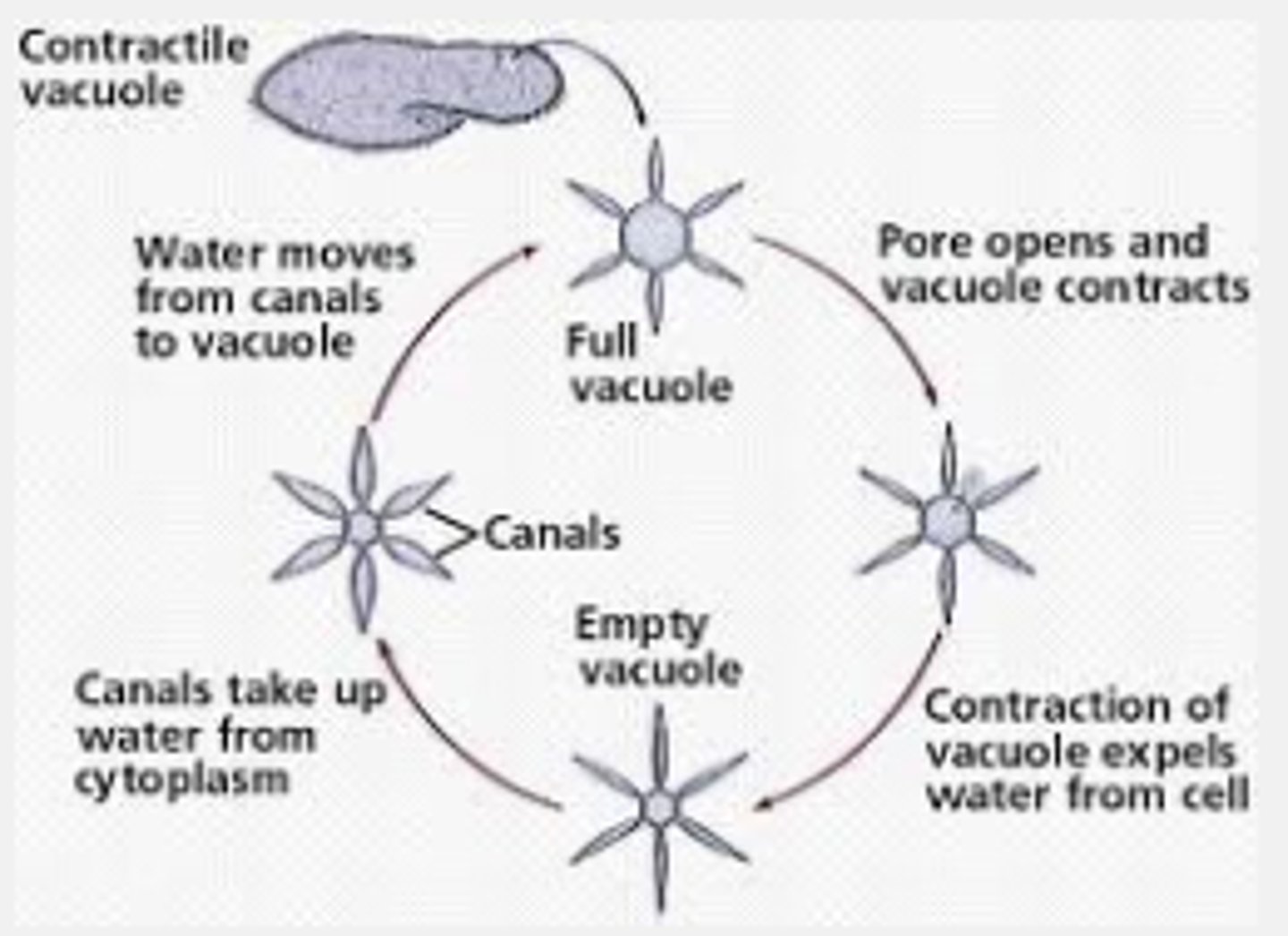
What does a Contractile Vacuole do?
It pumps excess water out of a cell, maintaining the right concentration of ions and molecules inside of the cell.
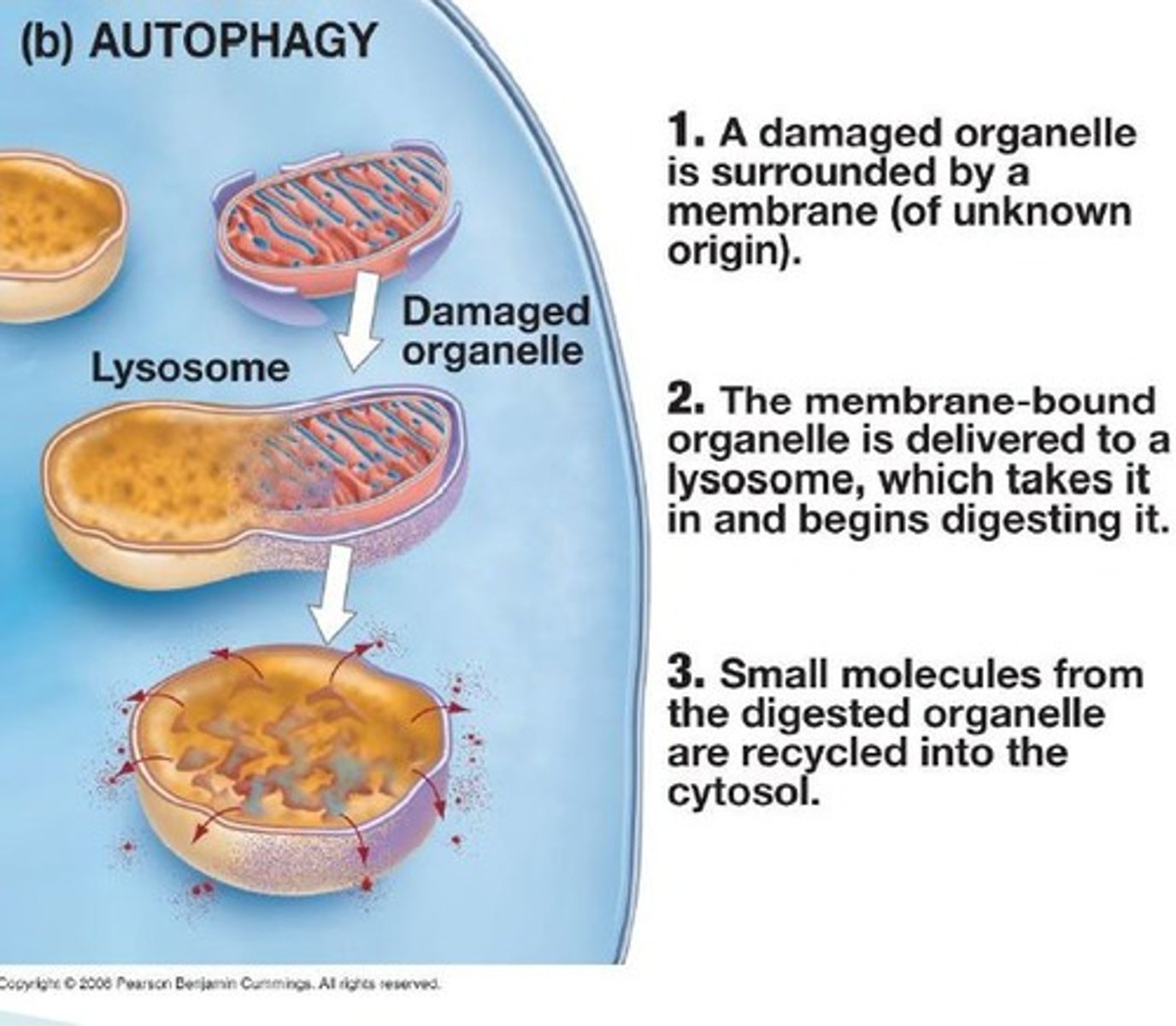
What happens in Autophagy?
Lysosomes use their hydrolytic enzymes to recycle dead organelles and macromolecules by fusing to them.
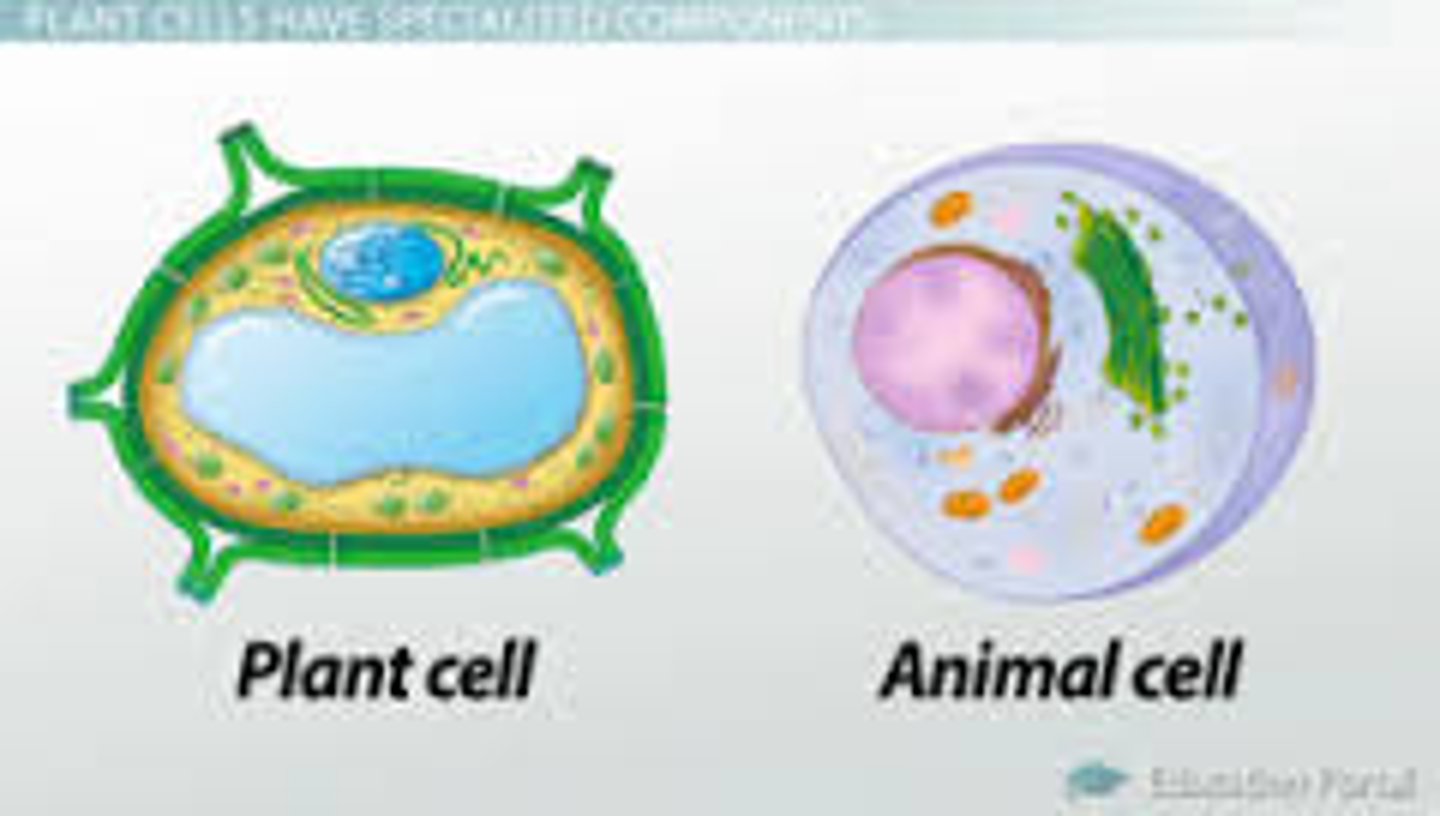
Plant cells generally contain a _________________________ which develops by coalescence of smaller vacuoles and enlarges at the vacuole absorbs ___________, enabling the cell to become larger with minimal investment in new cytoplasm.
Central vacuole, water
Where are mitochondria and chloroplasts found?
Mitochondria are found in eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria in ANIMALS and Chloroplasts in PLANTS & ALGAE.
What do mitochondria function as?
The are the sites of cellular respiration which uses oxygen to create ATP by extracting energy from sugars, fats, and other fuels.
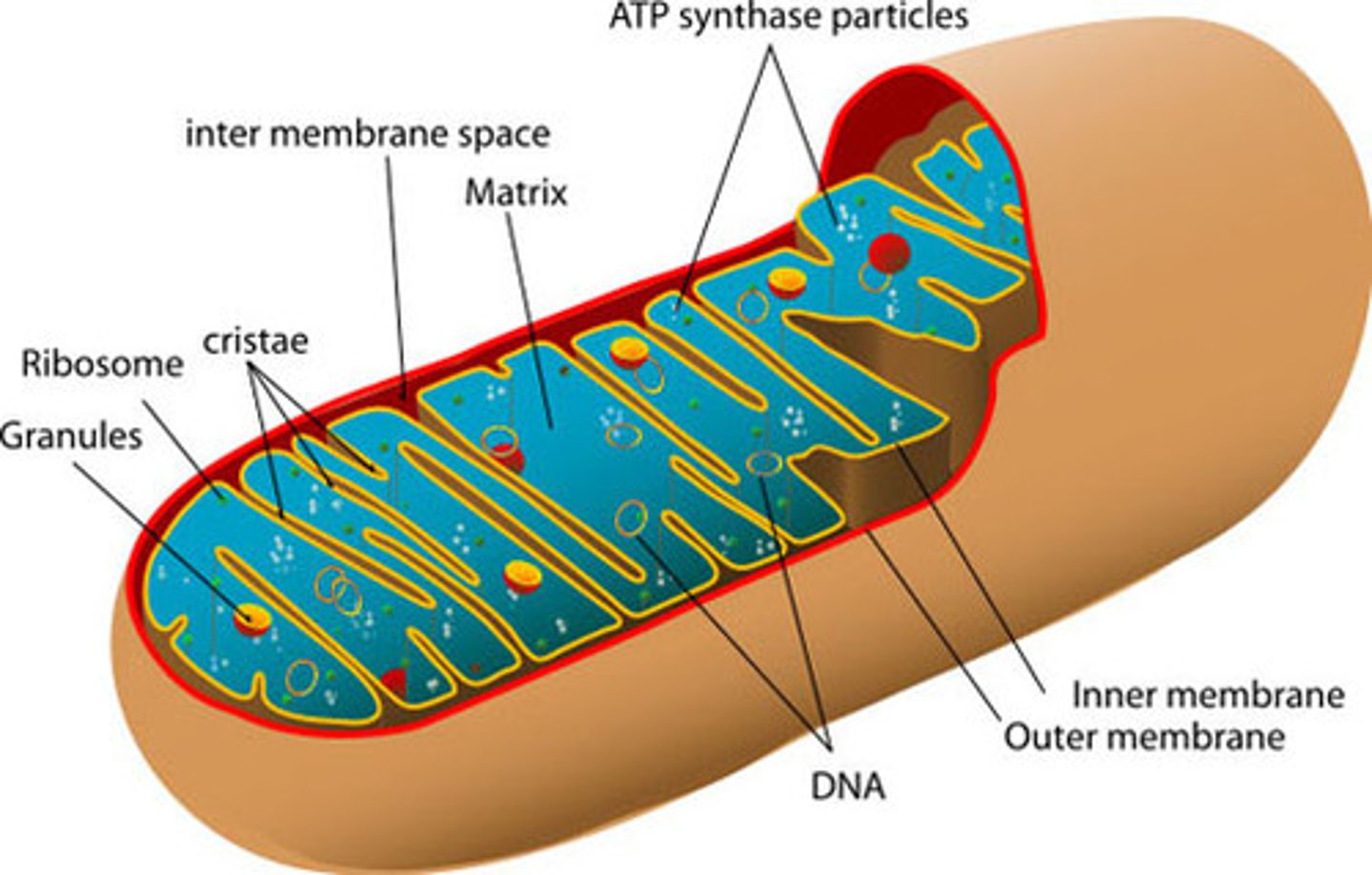
What do chloroplasts function as?
They are sites of photosynthesis where solar energy is converted to chemical energy by absorbing sunlight and using it to drive the synthesis of organic compounds (sugars from CO2 and H2O)
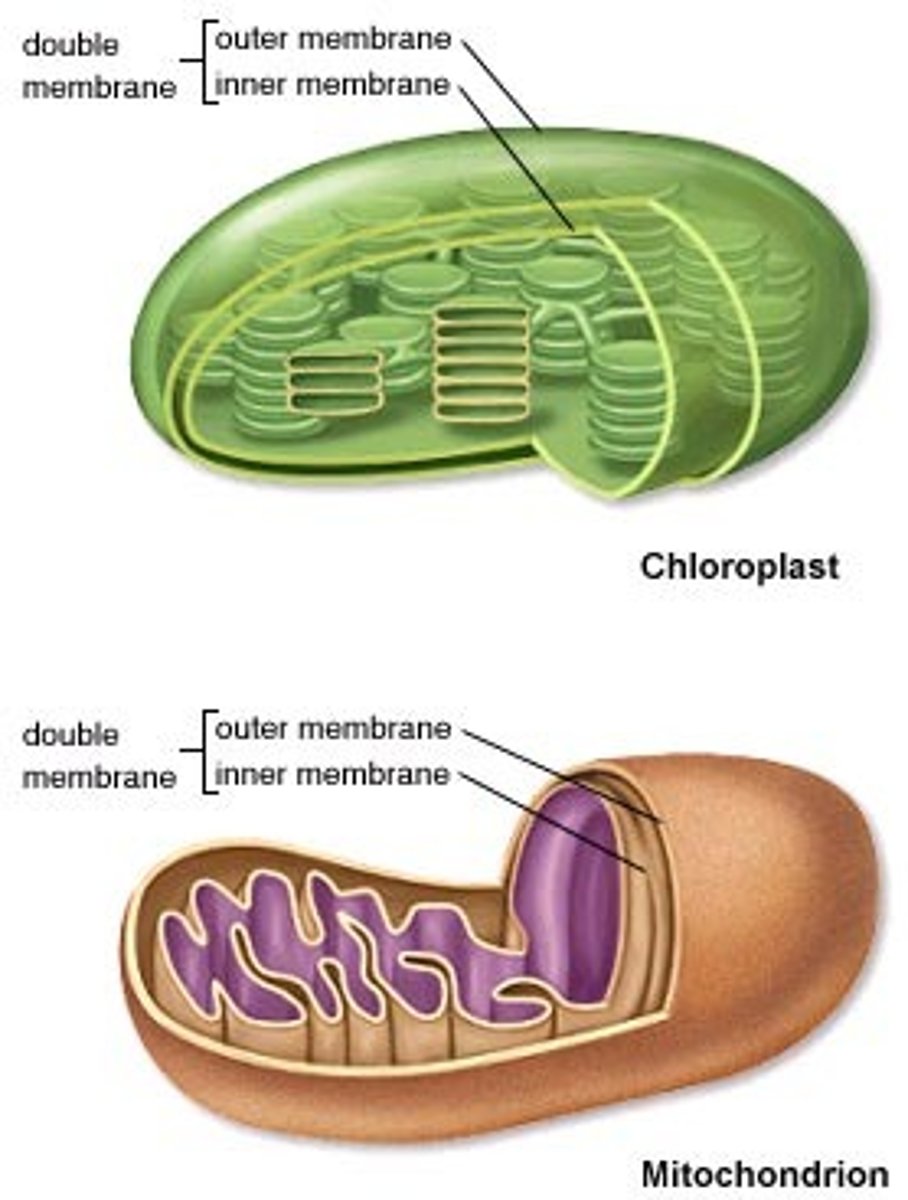
What are the characteristics of mitochondria & chloroplasts?
-Enveloped by a double membrane
-Contain free ribosomes & circular DNA molecules
-Grow & reproduce somewhat independently in cells
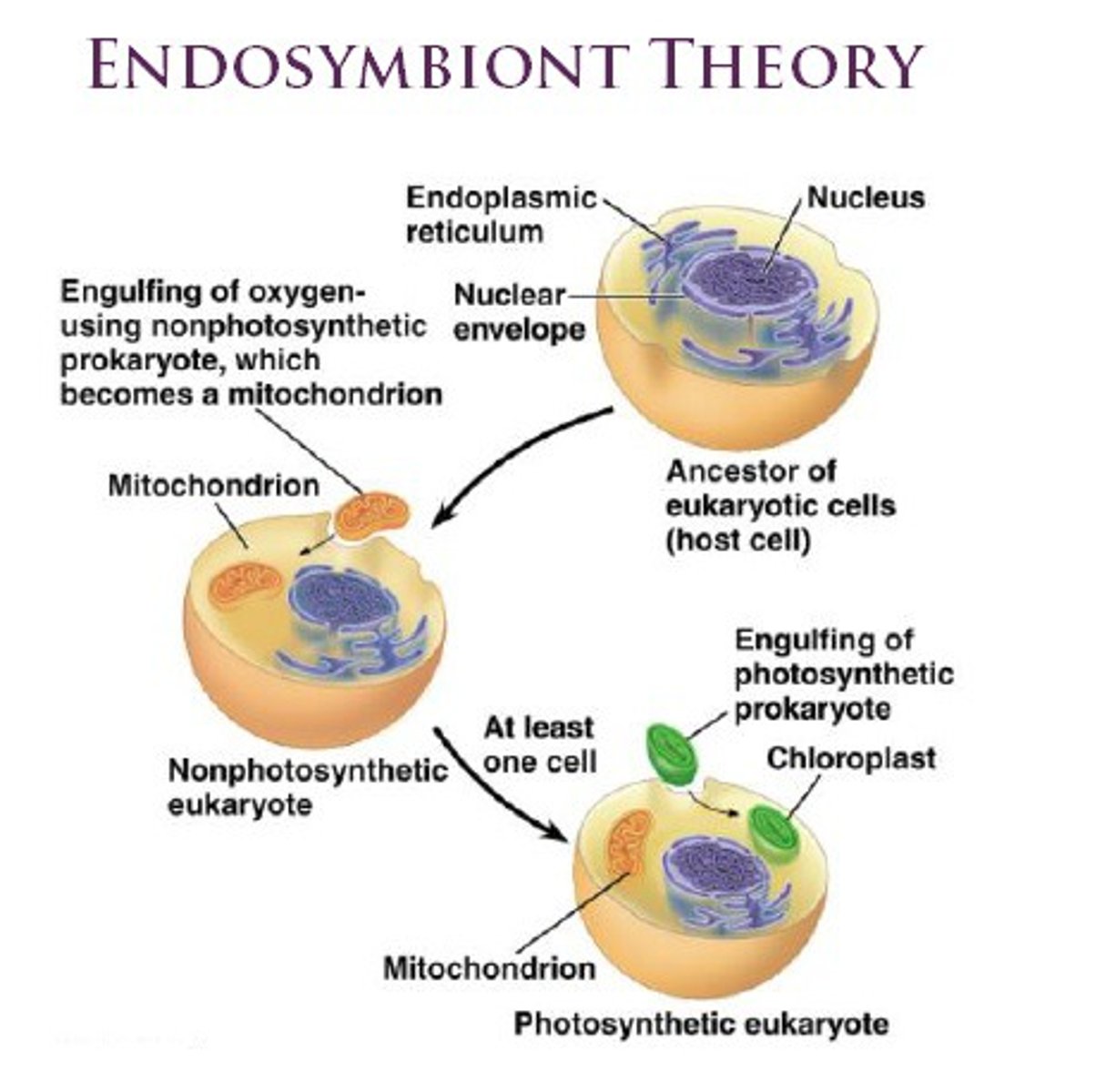
What is the story of the Endosymbiont Theory?
An ancestor of eukaryotic cells engulfed a non-photosynthetic prokaryote cell which formed an endosymbiont relationship with its host. The host cell and endosymbiont merged into a single, eukaryotic cell with a mitochondrion. At least one of these cells may have taken up a photosynthetic prokaryote, becoming the ancestors of the cells which contain chloroplasts.
Eukaryotes have a smooth outer & inner membrane which is folded into a ___________.
Cristae
How do cristae in Mitochondria help ATP production?
The folds in the cristae provide a larger amount of surface area for enzymes to synthesize ATP.
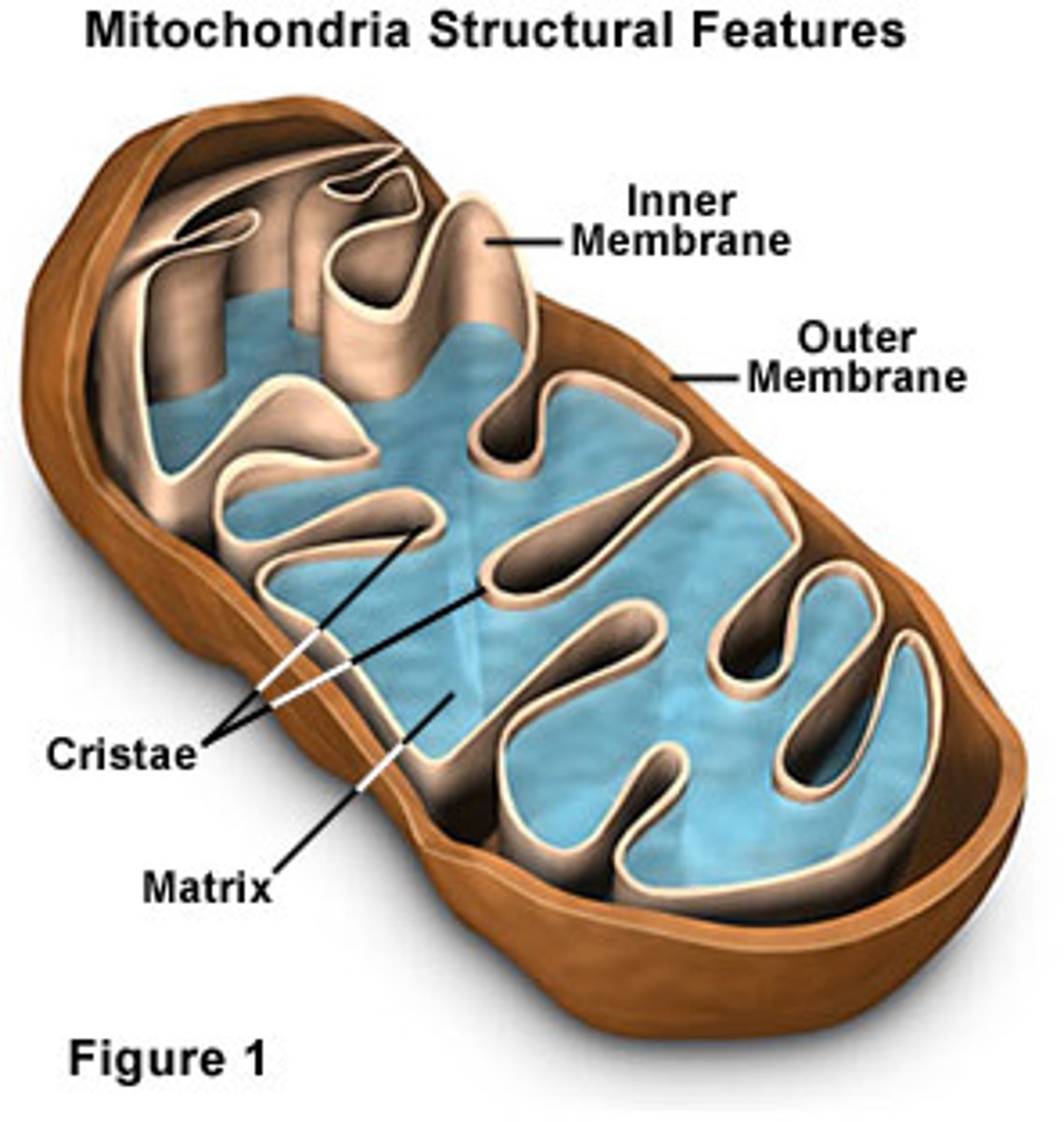
What 2 compartments within the mitochondria does the inner-membrane create?
-Intermembrane space (space between inner & outer membranes)
-Mitochondral matrix: where some steps for cellular respiration are catalyzed
How are chloroplasts stored within a plant cell?
They are separated from the cytosol by a double-membrane envelope.
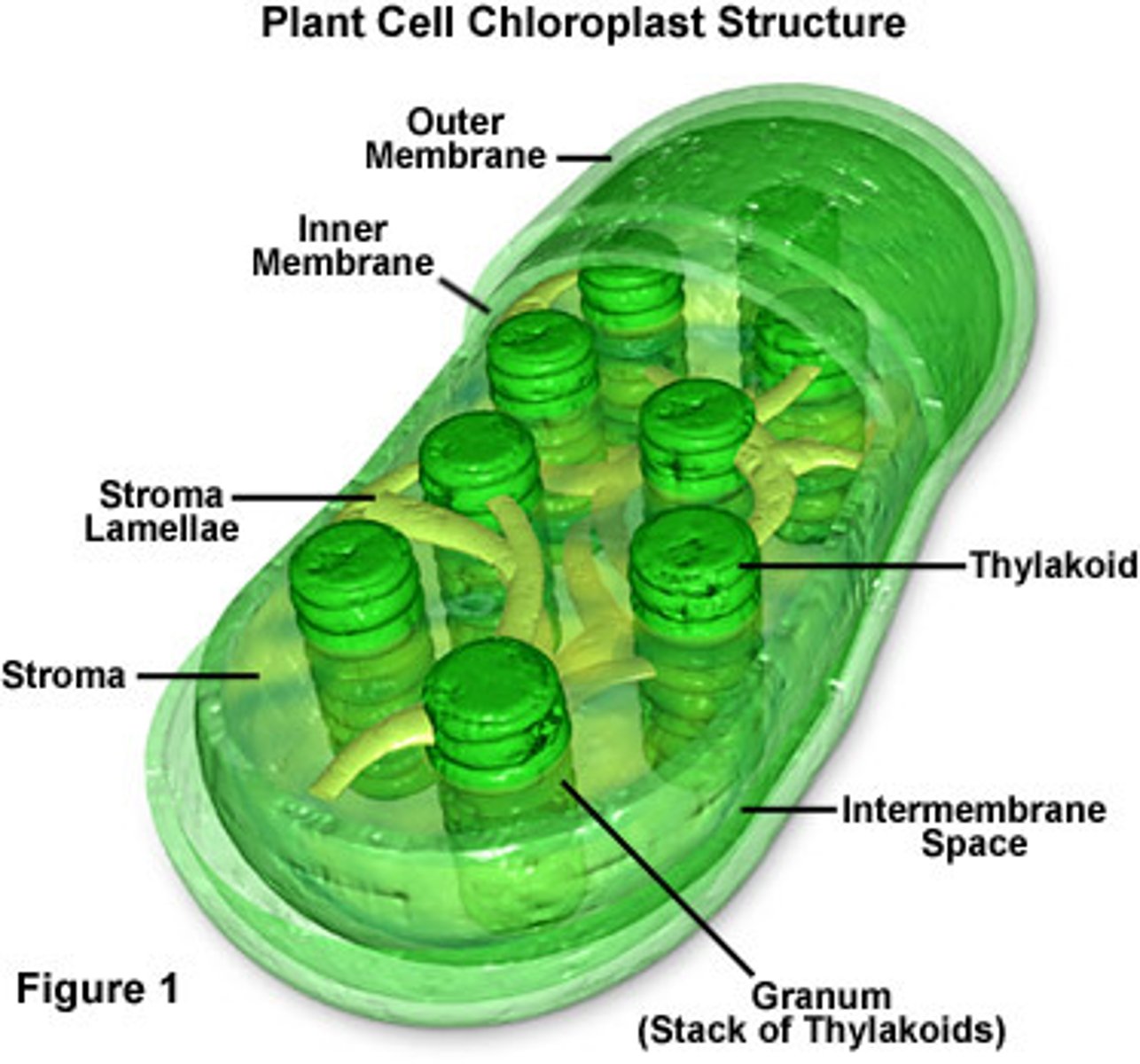
What are thylakoids within a chloroplast?
They are flattened, interconnected sacs, which are sometimes stacked like poker-chips into grana.
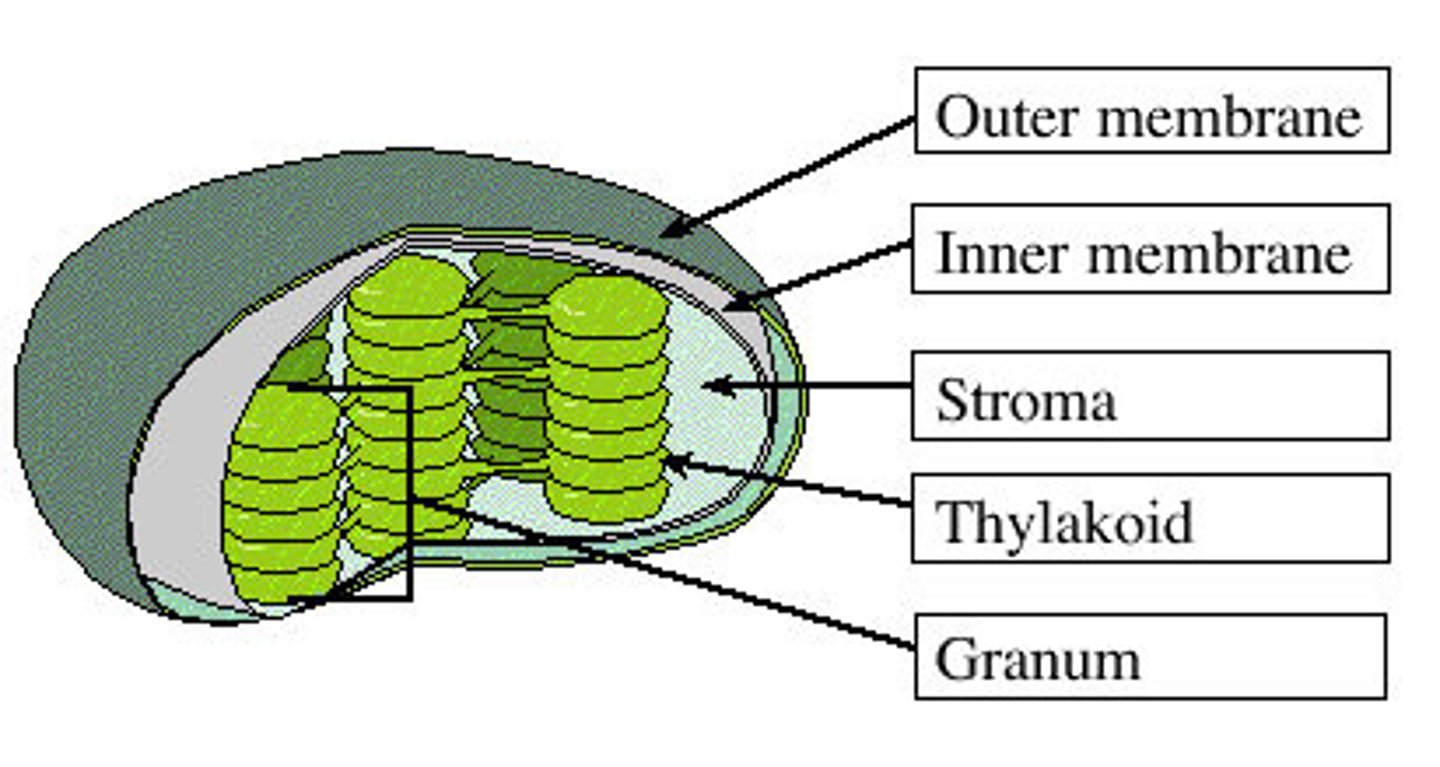
What is the fluid outside of thylakoids called?
Stroma
What family of plant organelles are chloroplasts part of?
Plastids
What are peroxisomes?
It is a membrane compartment that contain enzymes that remove hydrogens from certain substrates and transfer them to oxygens, creating H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide).
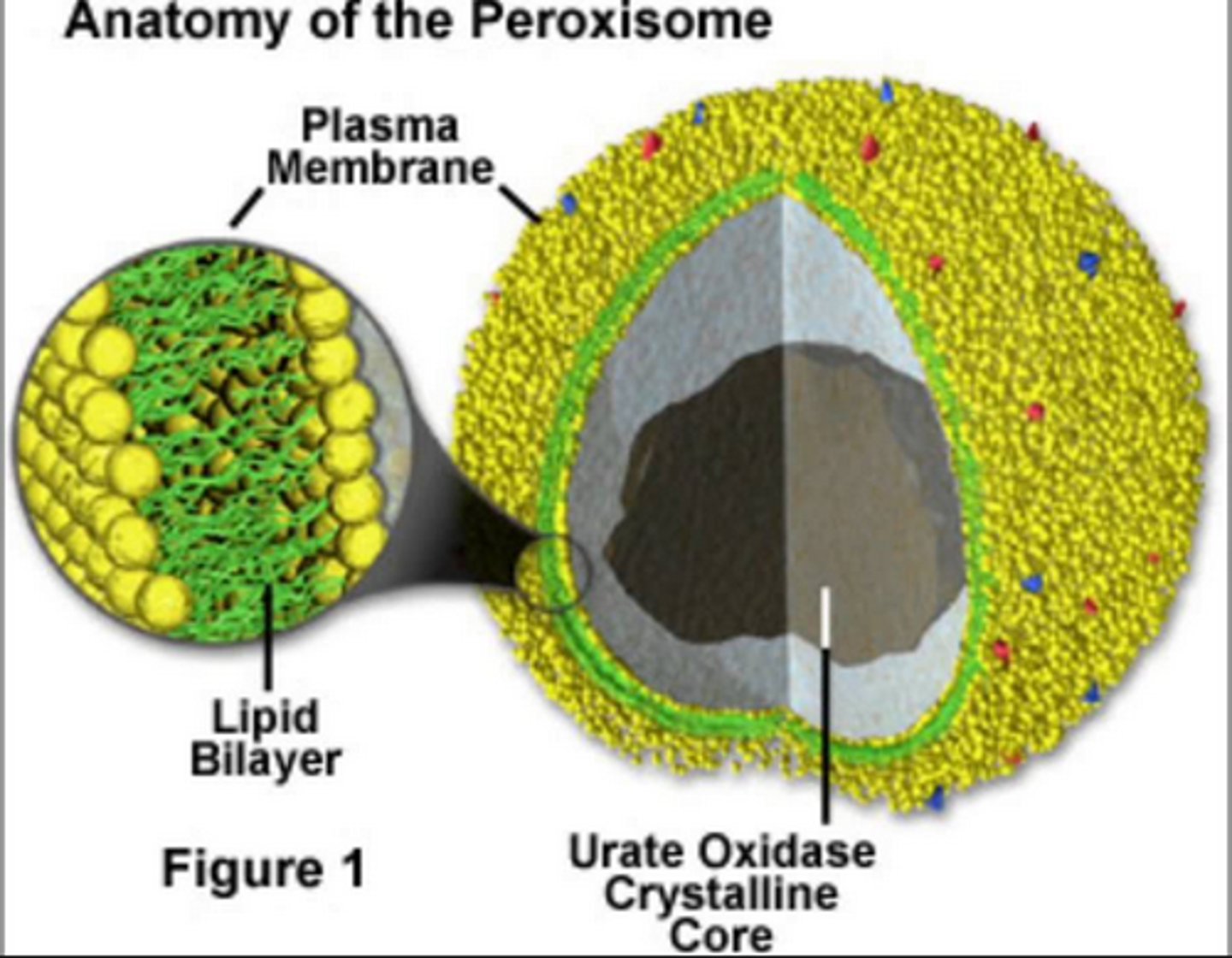
What do peroxisomes do?
-Break down fatty acids to smaller molecules
-Can detoxify alcohol & other harmful substances
What is the cytoskeleton of a cell?
It is a network of fibers extending through the cell.
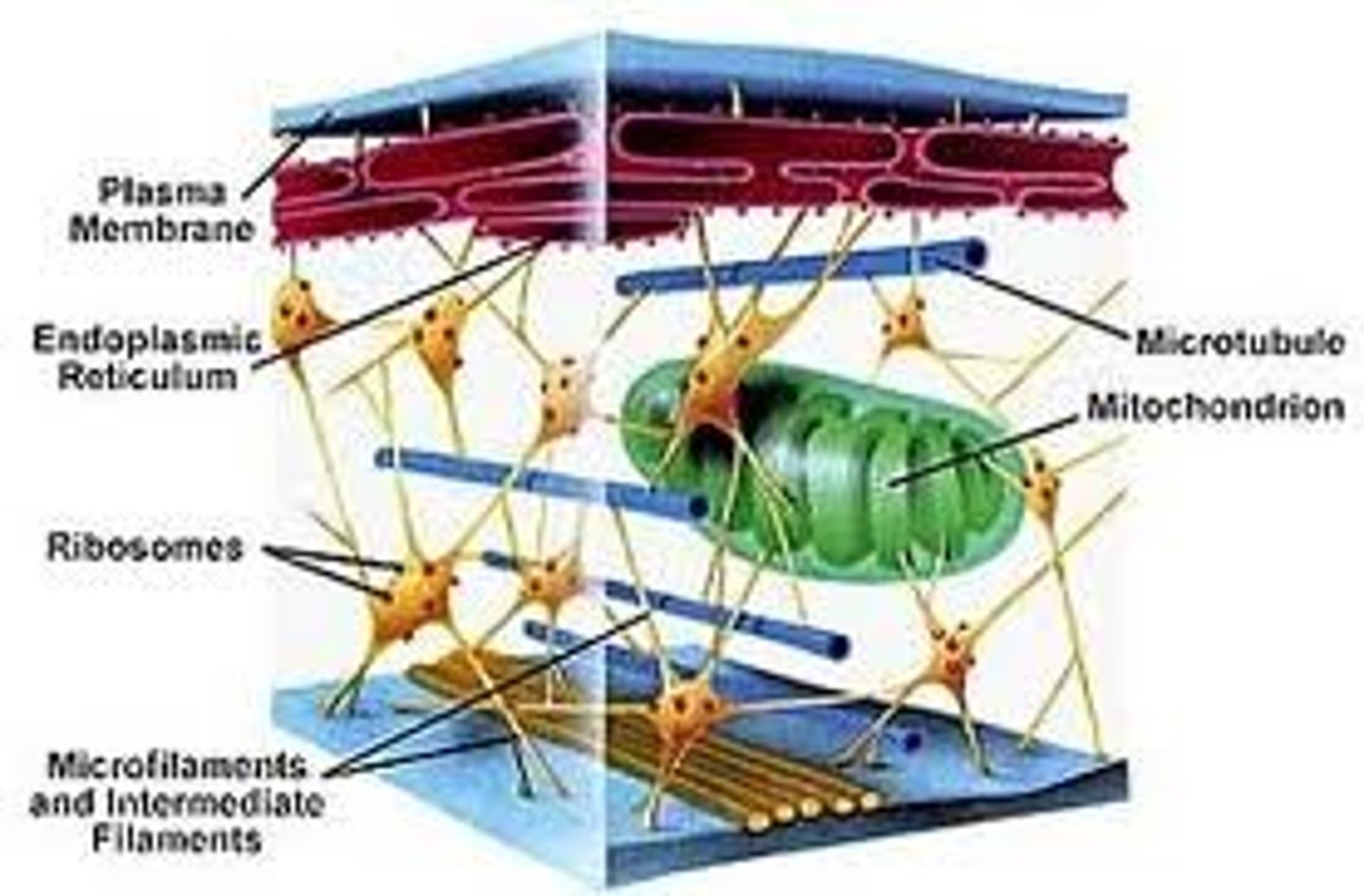
What are the 3 types of fibers used in the cytoskeleton?
-Microfilaments
-Intermediate Filaments
-Microtubules
What role does the cytoskeleton play in the function of a cell?
-Helps to support cell structure and anchor organelles
-Interacts with motor proteins to produce motility
-Provides "monorail" system for vesicles
-Microfilaments & Microtubules are polar & provide direction for cell.
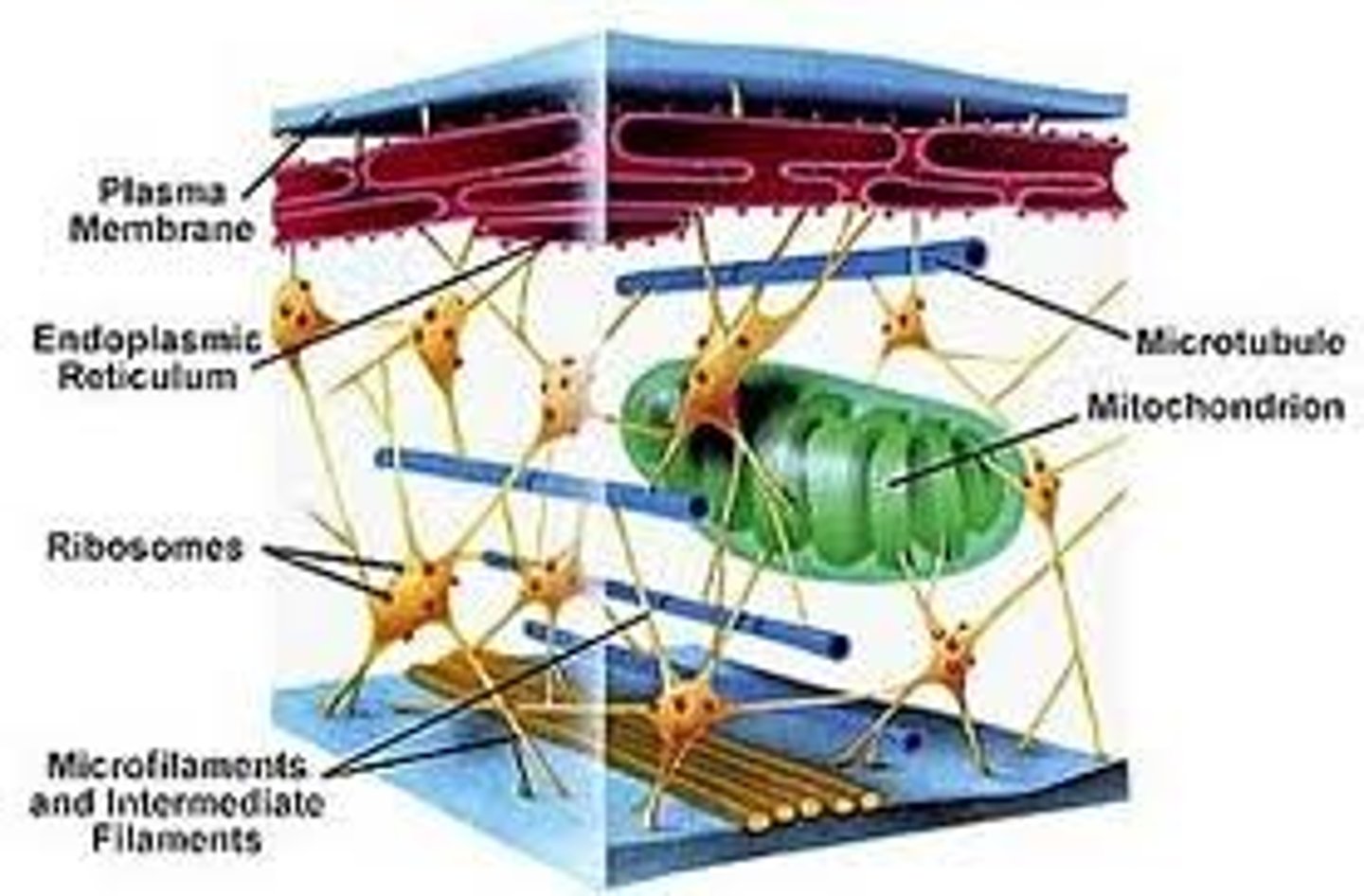
What is the order of thickest to thinnest components of the cytoskeleton?
Microtubules, Intermediate filaments, Microfilaments
What do centrosomes do and in what types of cells are they located?
They are located near the nucleus in animal cells and are where Microtubules grow out from. Each centrosome contains a pair of centrioles.
What are centrioles composed of?
Composed of 9 sets of triplet microtubules arranged in a ring.
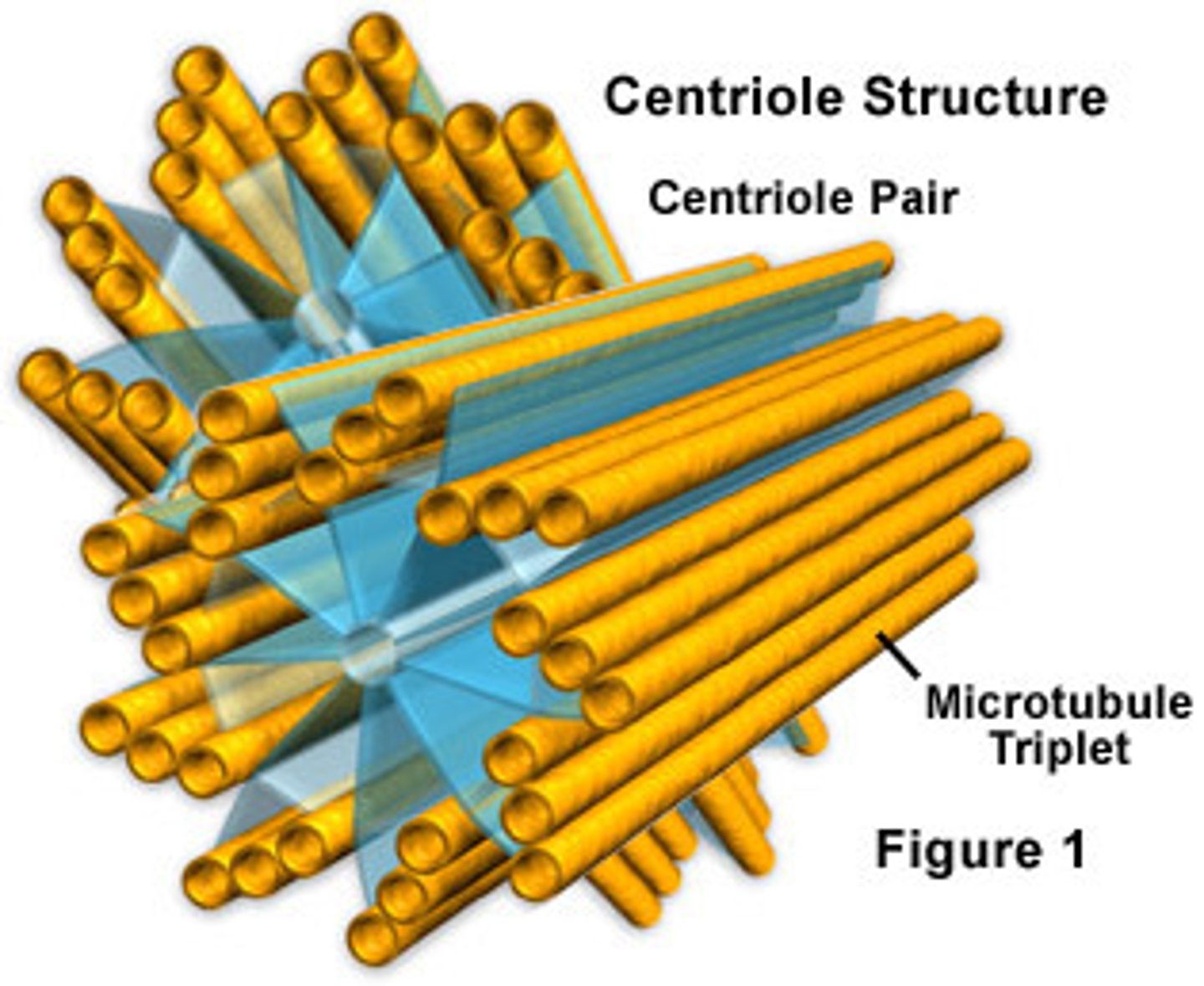
In eukaryotes, a specialized arrangement of microtubules is responsible for the beating of _______ and ____________, microtubule-containing extensions that project from some cells.
Cilia (cilium) & Flagella (flagellum)
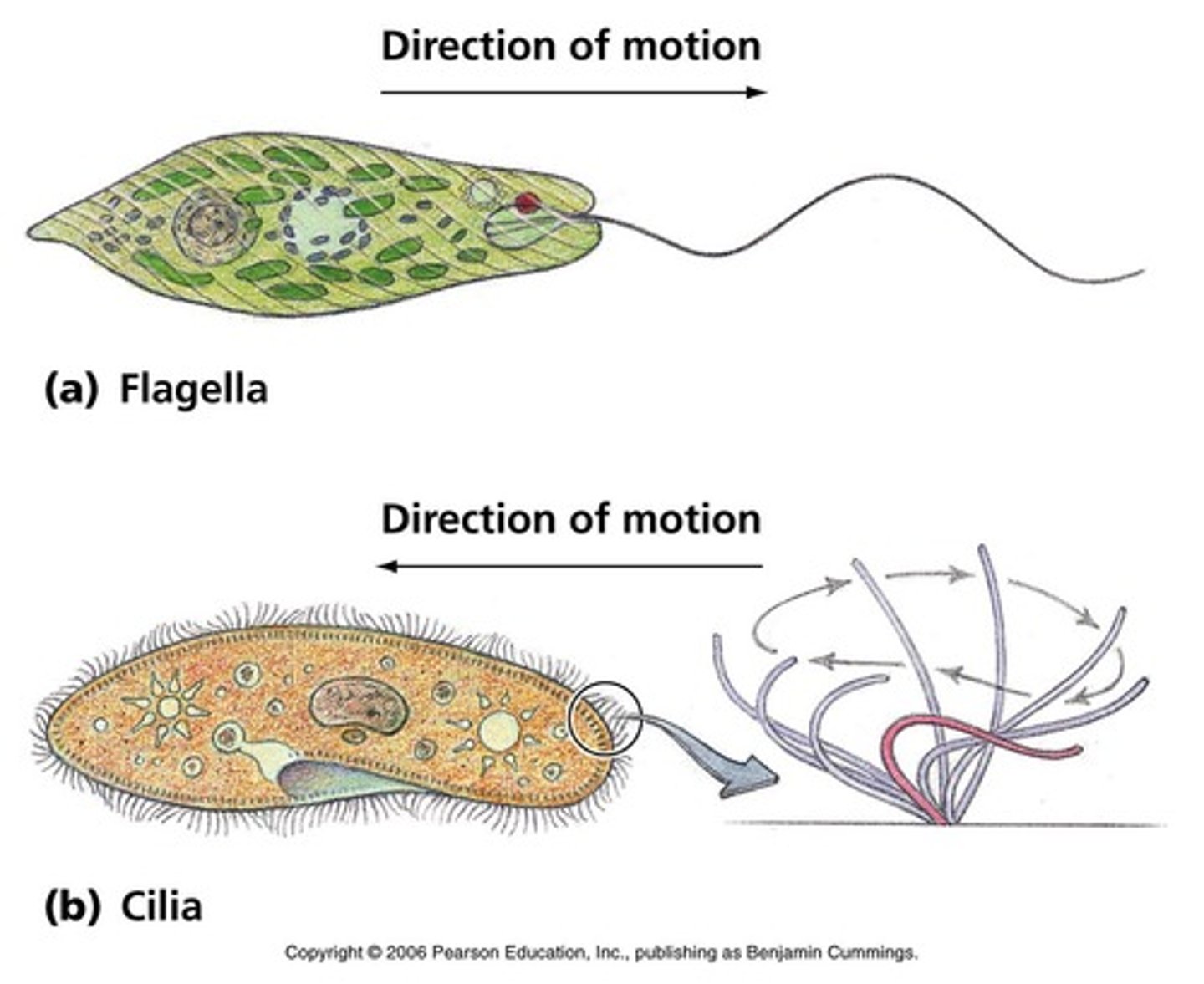
What are two types of motor proteins?
Myosin & Kinesin
What is another name for microfilaments?
Actin filaments
How are microfilaments arranged?
They are built as a twisted double-chain of Actin proteins
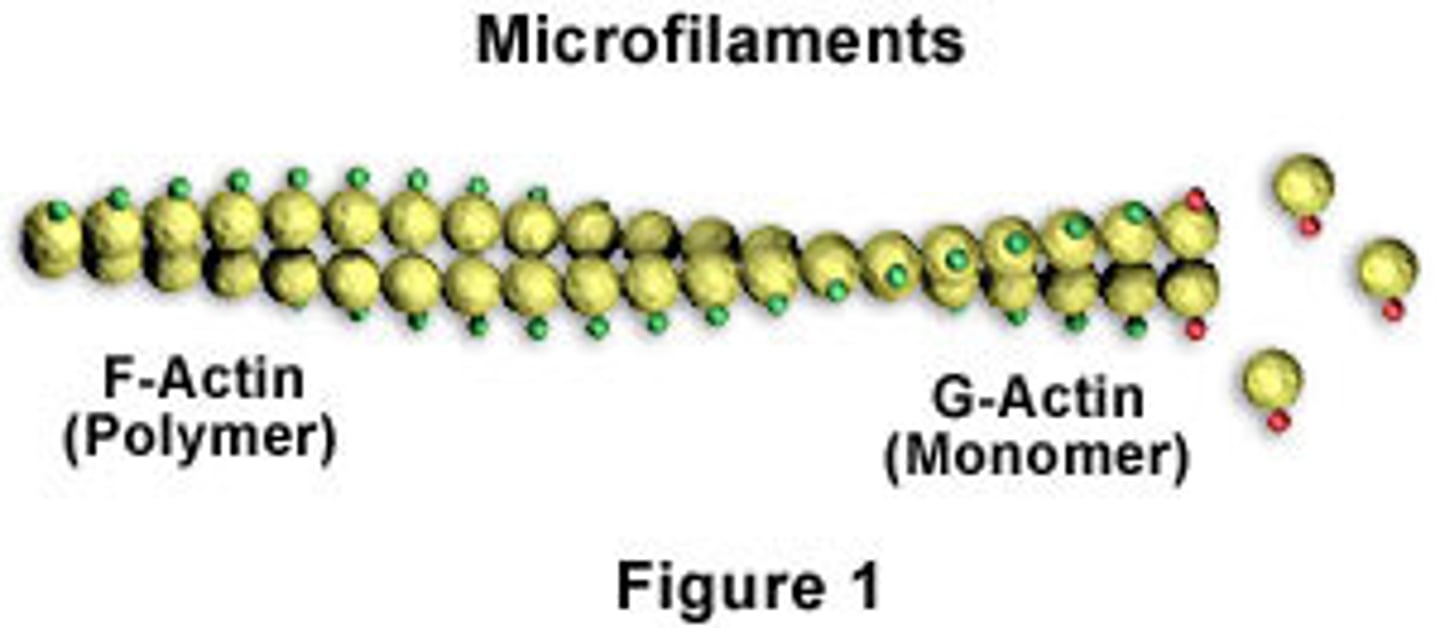
What are the purposes of microfilaments?
They bear tension (pulling forces) within the cell and help support cell shape by forming a cortex just inside the plasma membrane
T or F: Microvilli, composed of microfilaments, which are found in animal intestinal cells, have long thick projections which increase surface area & volume of cell.
True
Fill in the blank: Thousands of actin filaments and other thicker filaments made of a protein called ________ interact to cause contraction of muscle cells.
Myosin
Fill in the blank: In muscle, actin filaments arranged in a ____________ orientation.
Parallel
What takes place in Pseudopodia?
Extension and contraction through reversible assembly & contraction of actin units into microfilaments
How does cytoplasmic streaming affect cytosol within the cytoplasm?
It is the circular flow of cytosol within the cytoplasm of cells which speeds up distribution of materials within the cell.
What are the characteristics of Intermediate filaments?
-They are the medium sized cytoskeleton component
-They support shape and hold organelles into place
-More permanent than other two cytoskeleton components