A-level Economics Theme 2
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Macroeconomics
The study of the economy as a whole, including inflation, growth and unemployment.
What is meant by GDP?
The output of an economy
Quantity/value of all goods/services produced in an economy in a 1 year period.
What is the difference between the expenditure and income approach when measuring GDP?
Expenditure: adds up value of all expenditure in economy
Income: adds up rewards for FOP used e.g wages from labour, rent from land etc
What is nominal GDP?
Actual value of all goods/services produced in an economy in a 1 year period NOT adjusted for inflation
What is real GDP?
Value of all goods/services produced in an economy in a 1 year period and it is adjusted for inflation.
What is the concept of Purchasing power parities?
Calculates relative purchasing power of different countries.
Shows number of units of a country’s currency needed to buy a product in the local economy
Makes a more accurate standard of living comparison
Aggregate demand
The total demand for all goods/services in an economy at any given average price level.
What are the 4 components of AD?
Consumption(C) + Investment(I) + Government spending(G) + Exports-Imports(X-M).
What are the % of each component that make up AD in the UK?
Consumption: 60%, Investment: 14%, Gov spending: 25%, Net exports: 1%.

Aggregate demand curve
Shows the relationship between average price level and the total output in an economy.
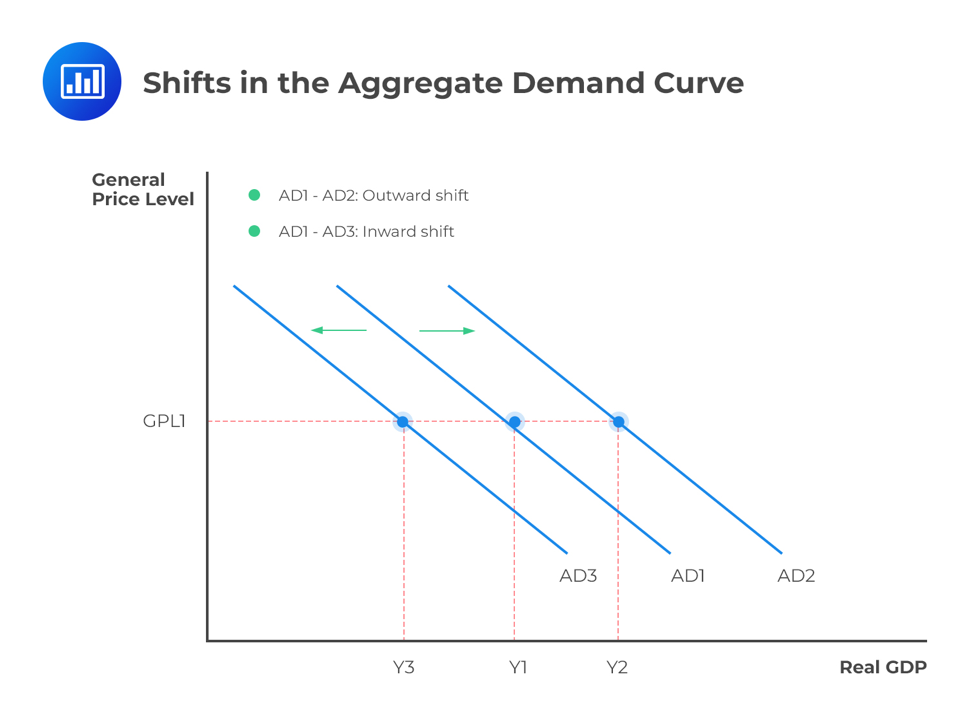
What causes shifts in the AD curve?
Any changes to the components of AD.
Basic concept of consumption?
Consumption increases as disposable income does and vice versa
e.g wages, transfer payments(benefits) increase = increase in disposable income
Formula for Marginal propensity to consume?
MPC = Change in consumption/Change in income
Formula for Average propensity to consume?
APC = Consumption/Income
What are the 5 determinants of consumption?
Interest rates
Changes to consumer confidence
Changes to wealth
Composition of households
Inflation & expectancy of inflation
What is investment?
The total spending on capital goods by firms.
What are the 7 determinants of investment?
Interest rates
Rate of economic growth
Business confidence
Demand for exports
Access to credit
Influence of government & regulations
Keynes & animal spirits
What is meant by net trade balance(X-M)
Difference between the value of exports and imports (X-M)
How does UK real income affect the net trade balance?
Increase = little effect on exports but effect on imports (Trade balance weakens)
How does increase in real income abroad affect net trade?
Increase = effect on exports but little effect on imports (Trade balance strengthens)
How does appreciation/depreciation of UK £ affect net trade?
Appreciation = exports decrease but imports increase (Trade balance weakens)
Depreciation = exports increase but imports decrease (Trade balance strengthens)
How does protectionism affect the net trade balance?
Decrease = imports likely to rise and exports to increase (Trade balance weakens)
Increase = decreased demand for imports
What is inflation?
It is the sustained increase in the average price level of goods/services
APL measured checking prices of a basket of goods/services that an average household will pruchase each month(CPI)
The UK has an inflation target rate of 2% per annum
What is deflation?
Occurs when there is a fall in the average price level of goods/services in an econ
Only occurs when the % change in prices falls below 0%
What is disinflation?
Occurs when the average price level is still rising but at a lower rate than before e.g Y1 = 5%, Y2 = 4%
How is the inflation rate measured?
Calculated using an index with 100 as the base year
If the index is 100 in year 1 and 107 in year 2 then the inflation rate is 7%
Formula for CPI?
Cost of basket in year X/Cost of basket in base year x 100
The percentage diff in CPI between the 2 years is the inflation rate for that period. new-old/old x 100
What and how is the Retail price index calculated?
Same way as CPI but there are goods excluded from CPI that are in RPI e.g council tax, mortgage
What are the 4 causes of inflation?
Demand pull, cost push, increase in money supply and an increase in wages.
What is demand pull inflation?
Price rises caused by excess demand in the economy.
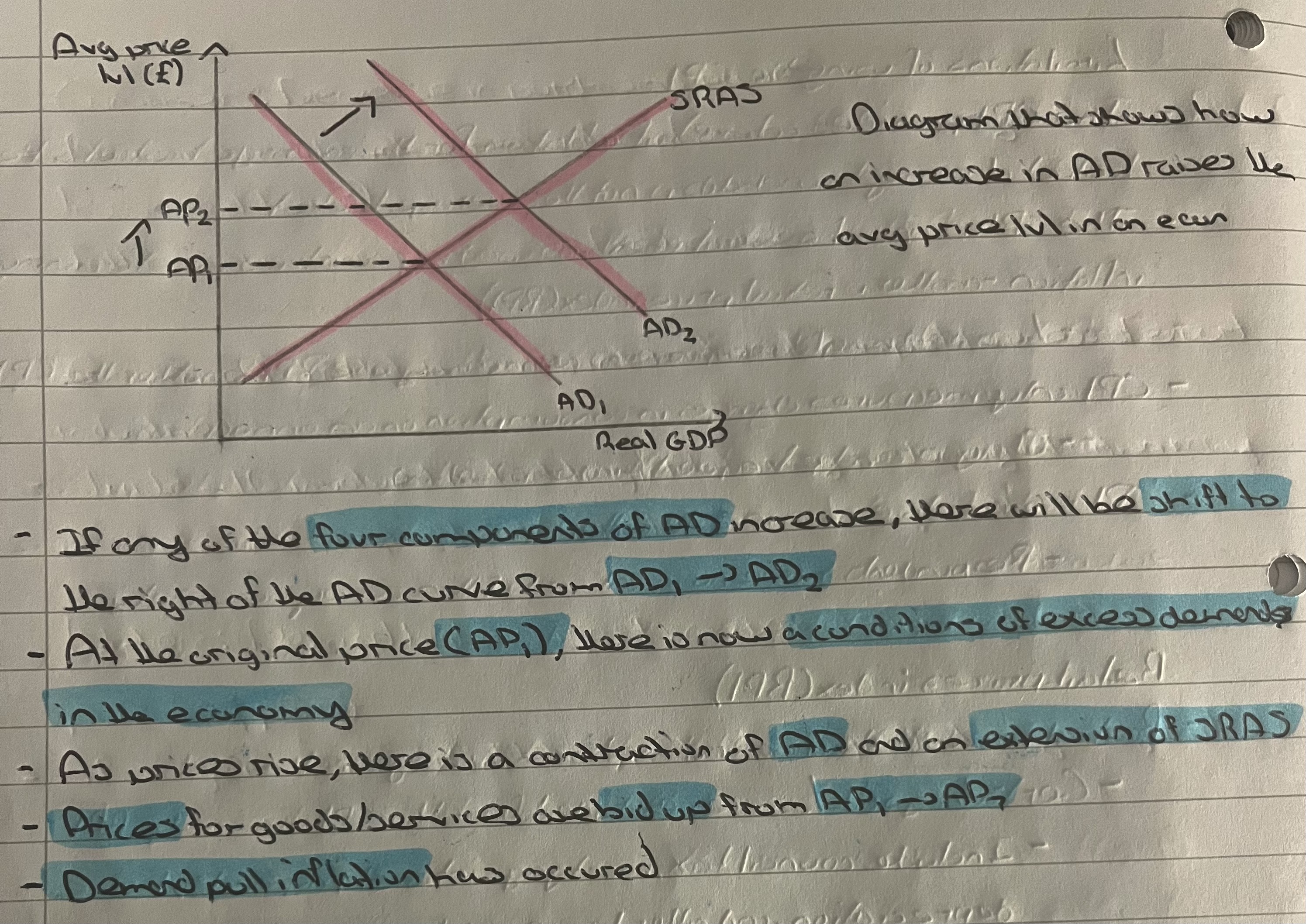
What is cost push inflation?
Price rises due to increases in COP in an economy.

What are changes to money supply?
If bank lowers interest rate = more borrowing by consumers and firms = increased consumption = demand pull inflation
What is meant by changes to wages?
Increased AD = demand pull inflation = workers now feel less well off as wages no longer have strong purchasing power = demand wage increases to compensate for higher prices = wage increases form of cost push inflation (rise in COP) = leads to even higher prices
What is unemployment?
Someone not working but actively seeking work
Who makes up the labour force?
Those actively working and the unemployed, usually between ages 16-65.
Who makes up the non labour force?
Those not actively seeking work e.g stay at home parents, pensioners, school children
What is meant when someone is “underemployed”?
They want to work more hours than they currently do.
Working in a job that requires lower skills than they have.
Often a result of cyclical/structural unemployment.
What is meant by economically inactive?
Those between 16-65 and not working/seeking work
Causes/types of unemployment
Structural unemployment
Cyclical/demand deficient unemployment
Seasonal unemployment
Frictional unemployment
Real wage unemployment
What is meant by structural unemployment?
Occurs when there is a mismatch between jobs & skills in an econ
What is meant by cyclical/demand deficient unemployment?
During e.g recession, fall in demand resukts in less need for labour and thus, less jobs
What is meant by balance of payments?
Countrys record of all financial transactions that occur between it and rest of world
What is a current account deficit?
Value of outflows greater than value of inflows
e.g imports > exports
What is the effect of a current account deficit?
A lack of exports harms AD as it is component but could raise tarrfis
Thus, firms who rely on imports = high cop = higher cost and passed onto consumer in form of higher price
comes at expense of inflation
Aggregate supply
Quantity of goods/services that producers in an economy are willing and able to supply at a given level of prices at a given time
Short-run aggregate supply curve
Influenced by changes in COP or productivity
Long-run aggregate supply curve
Influenced by a change in the productive capacity of the economy
Changed by changes to the quantity/quality of the FOP
Supply-side shocks
Factors such as changes in wage rates or commodity prices which cause the short run aggregate supply curve to shift.
What factors influence SRAS?
Change in cost of raw mats
Business taxes, subsidies, regulations
Supply shocks
Changes in exchange rates
Changes in tax rates
Explain changes in cost of raw mats
As price of input costs rise, fewer goods/services can be produced w same amount of money and vice versa
Explain changs in exchange rates
Appreciation: Firms who buy from abroad can import more at cheaper price = lower COP
Depreciation: Firms who buy from abroad face higher import costs = high COP = less output
What is the classical LRAS view?
LRAS is inelastic at a point of ful employment of all available resources
View believes that in long run, economy will always return to this full employment lvl of output
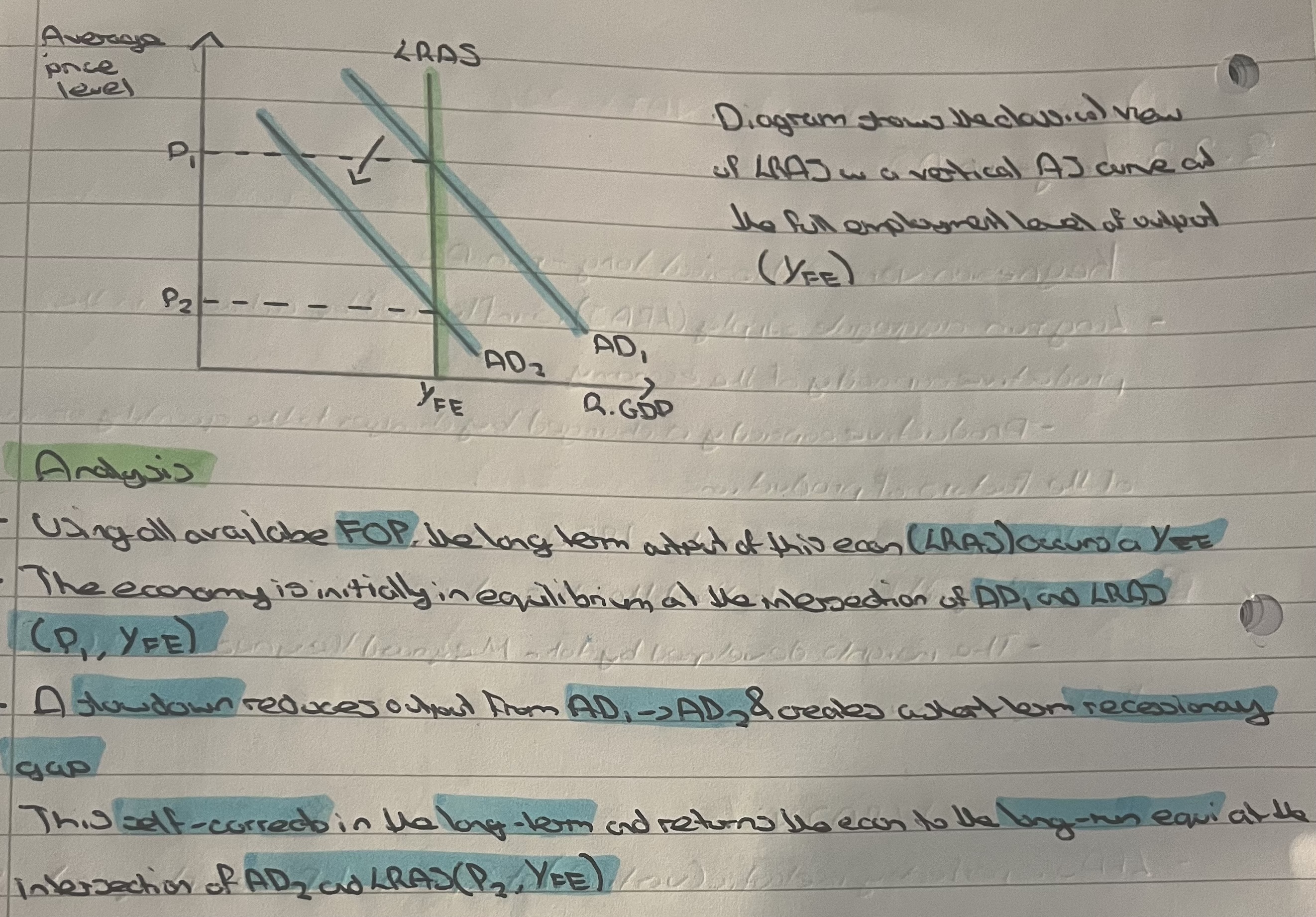
What is the keynesian LRAS view?
Curve is more L shaped
Supply is elastic at lower levels of output due to spare production capacity
Supply is inelastic at a point of full employment (Yfe) of all available resources.

What factors influence LRAS?
Technological advances
Changes in relative productivity
Changes in education & skills, increases quality of labour
Changes in government regulations
Demographic changes and migration
Competition policy
Circular flow of income
Economic model that illustrates money flows in an economy
Role of households
Households own the wealth in the economy (these are the FOP)
Households receive rent for land, wages for labour, interest for capital and profit for enterprise
With this income, they buy goods/services from firms
Role of firms
Firms purchase FOP from households
They use these resources to produce goods/services
They sell the goods/services to households & receive sales revenue
What is meant by national income
Value of the output of an economy over a period of time
Injections
Injections add money into the circular flow of income & increase its size.
Increased gov spending
Increased investment
Increased exports
Withdrawals or leakages
Money removed from the circular of income & reduce its size
Increased imports
Increased saving
Increased taxation by the gov
What is the impact of injections > withdrawals
Economic growth
What is the concept of the multiplier effect?
One individuals spending is another persons income.
Name an example of the multiplier process?
Consumer confidence increase has led to more spending
Thus, higher consumption
This shifts AD1 outwards to form AD2
Businesses receive more revenue/profit from increased consumer spending
Thus, will REINVEST into business e.g. capital goods
Investment will cause SECONDARY shift outwards from AD2 TO AD3
Same applies to negative multiplier effect
Marginal propensity to import (MPM)
Proportion of additional income that is spent on imports
MPM = % change in imports/% change in income
Marginal propensity to save (MPS)
Proportion of additional income that is saved
MPS = % change in savings/% change in income
Marginal propensity to tax (MPT)
Proportion of additional income that goes towards tax
MPT = % change in tax/% change in income
Marginal propensity to consume (MPC)
Proportion of additional income that is spent
MPC = % change in consumption/% change in income
Marginal propensity to withdraw (MPW)
The increase in withdrawals from the circular flow (S + T + M) divided by the increase in income that caused them (i.e. change in W / change in Y); this is the same as the sum of the marginal propensity to save, tax and import (MPS + MPT + MPM).
Significance of the multiplier in shifting AD
Greater withdrawals = smaller value of the multiplier and vice versa
Any factor that affects disposable income will change MPC and thus, the multiplier
E.g. increase in taxes/interest rates, lower multiplier
E.g. consumer confidence increase = MPC increase and thus, greater multiplier
What is meant by short run economic growth?
Changes to any of the components of AD will cause short term econ growth
Shown by outward shift in AD
Shown by moving from a point inside PPF closer to curve
What is meant by long run economic growth?
Caused by any improvements to quality/quantity of the FOP
Factors include determinants of LRAS
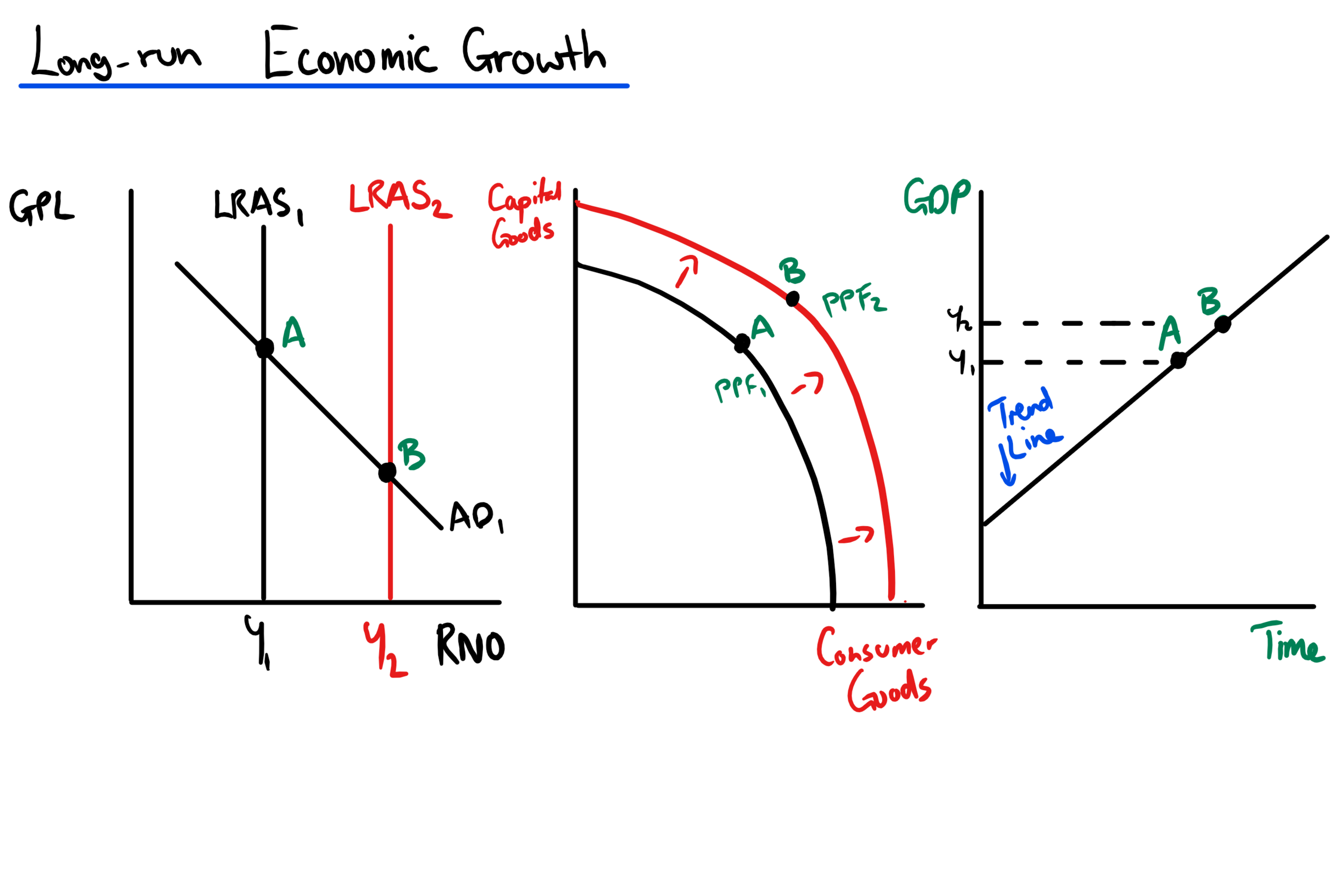
Actual growth?
Occurs when there is an increase in the quantity of goods/services produced in an economy in a given time period
Potential growth?
Is the increase in the productive potential of an economy shown by outward shift of PPF or LRAS
What are the 4 recognisable points in a trade cycle
Peak/Boom
Slowdown/downturn
Recession
Recovery
Characteristics of a recession
Defined as two consecutive quarters or more of negative econ growth
High unemployment
Spare production capacity
Low confidence for firms/households
Low inflation
Increased government expenditure
Characteristics of a boom
Decreasing unemployment and increasing job vacancies
Spare capacity reduced
High confidence in firms/households
Demand pull inflation
Improvement in gov budget as tax rev rises and expenditure falls
Benefits of econ growth
Increased incomes = better standard of living
Higher sales revenue
Increased investment increases potential output
Reduced expenditure by gov and higher tax rev due to income and business tax
Increased employment
Cons of economic growth
Rising AD = demand pull inflation = less purchasing power
Lack of equity e.g. rich get richer and poor get poorer
Increased inflation can harm export sales
Increased income = consumption of demerit goods
Increased price level = higher wages demanded = COP
What are the 7 macroeconomic objectives?
Economic growth
Low & stable rate of inflation
Low unemployment
Balanced government budget
Environmental sustainability
Balance of payments equilibrium on current account
Greater income equality
Economic growth
UK/nations have an annual rate of 2-3%
Low unemployment
Target rate for the UK is 4-5%
Low & stable rate of inflation
UK has target inflation rate of 2% using CPI
Demand side policies ease demand pull inflation
Supply side policies ease cost push inflation
Balance of payments
Aim to run at a small current account deficit
Balanced gov budget
UK aims to run at a balanced budget
If expenditure > revenue there is budget deficit
Has to be financed through public sector borrowing which adds to public sector debt
May have to raise taxes in long run
Reducing deficit can be bad
Cutting public sector pay, raising taxes, reduced spending on public & merit goods, reducing unemployment benefits
Environmental protection
Aim to reduce emissions by 72% by 2035
Reduce negative externalities of production
Causes of fiscal budget deficit
Recession causing unemployment
Decrease consumer spending & profits meaning less tax
Increase in welfare benefits
Increase in interest rate affecting public sector debt
Justification for budget deficit
Rise in borrowing to fund extra gov spending can boost AD
Demand side policy
Shift AD
What is fiscal policy?
Use of gov spending and taxation to influence AD
What is monetary policy?
Use of interest rates & money supply to influence AD - Bank of England sets
Adjustments to interest(not more than 0.25%)
Quantitative easing(increase supply of money in econ)
Exchange rates
Budget deficit
Expenditure > revenue
Budget surplus
Revenue > expenditure
What are direct taxes
Taxes imposed on income and profit
e.g. income tax, corporation tax, national insurance
What are indirect taxes
Imposed on spending
What is meant by expansionary demand side policies
Demand side policies that aim to shift AD outwards
e.g. expansionary fiscal/monetary policy
Examples of expansionary demand side policies?
Reducing taxes, increasing gov spending, decreasing interest rates
What is meant by contractionary demand side policies
Demand side policies that aim to shift AD inwards
e.g. Contractionary fiscal/monetary policies
Examples of contractionary demand side policies?
Increasing taxation, Reducing gov spending, Increasing interest rates
Strength and weakness of fiscal policy
S: Short time lag, increased consumption of merit/public good
W: Increased gov spending = budget deficit = debt for future = austerity, Conflicts between objectives e.g. cutting taxes = inflation
Strength and weakness of monetary policy
S: Considers long term, Targets inflation
W: Time lags of up to 2 years, conflicting objectives