Topic 4.6 - Vegetarian Diets
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
What does it mean to be a vegetarian?
* vegetarianism is the dietary practice of consuming foods of plant origin, including vegetables, fruit, grains, and nuts, and *excludes* the consumption of
* Meat
* Fowl (birds)
* Fish
* Meat
* Fowl (birds)
* Fish
2
New cards
Semivegetarian (or flexitarian)
food consumed: fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, legumes; *rarely* meat, seafood, poultry, eggs, dairy
* *typically exclude or limit red meat*; may also avoid other meats
* *typically exclude or limit red meat*; may also avoid other meats
3
New cards
Pescovegetarian (pescitarian)
foods consumed: similar to semivegetarian but *excludes*
*poultry*
* pesco means “fish,” the only animal source of protein in this diet
*poultry*
* pesco means “fish,” the only animal source of protein in this diet
4
New cards
Lacto-ovovegetarian
foods consumed: fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, legumes, dairy products (lacto), and eggs (ovo)
* *excludes animal flesh and seafood*
* *excludes animal flesh and seafood*
5
New cards
lacto-vegetarian
similar to lacto-ovovegetarian but excludes eggs
* relies on milk and cheese for animal sources of protein
* relies on milk and cheese for animal sources of protein
6
New cards
Ovovegetarian
foods consumed: fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, legumes, and eggs
* *excludes dairy, flesh, and seafood products*
* *excludes dairy, flesh, and seafood products*
7
New cards
vegan (also called strict vegetarian)
foods consumed: only plant-based foods (fruits,vegetables, grains, nuts, seeds, legumes)
* may not provide adequate vitamin B12, zinc, iron, calcium
* may not provide adequate vitamin B12, zinc, iron, calcium
8
New cards
macrobiotic diet
foods consumed: vegan-type diet; becomes more strict until almost all foods are eliminated; at the extreme, only brown rice and water or herbal tea
* taken to the extreme, can cause malnutrition and death
* taken to the extreme, can cause malnutrition and death
9
New cards
fruitarian
foods consumed: only raw or dried fruit, seeds, nuts, honey, and
vegetable oil
* *very restrictive;* deficient in protein, calcium, zinc, iron, vitamin B12, riboflavin, other nutrients
vegetable oil
* *very restrictive;* deficient in protein, calcium, zinc, iron, vitamin B12, riboflavin, other nutrients
10
New cards
raw food diet
foods consumed: vegan-type diet with foods either sprouted or minimally heated
11
New cards
why do people choose vegetarian diets?
1. religious, ethical, food safety
* example: Many Hindus are vegetarian – the cow is a sacred animal
* ethical reasons related to practices in animal industry
* meat handling and illness
2. ecological benefits: impact of meat production on environment and greenhouse gas emissions
3. health benefits
12
New cards
vegetarianism in canada
* canada is home to approximately 466 000 vegans, and approximately 2 650 000 canadians have restricted dietary preferences due to food intolerances or allergies
13
New cards
positive health aspects of following a vegetarian dietary pattern
Health benefits of vegetarian diets:
* reduced intake of fat and total energy, reducing risk for obesity and type 2 diabetes
* lower blood pressure
* reduced risk for heart disease
* fewer digestive problems
* reduced risk for some cancers (colorectal)
* reduced risk for kidney stones and gallstones
* reduced intake of fat and total energy, reducing risk for obesity and type 2 diabetes
* lower blood pressure
* reduced risk for heart disease
* fewer digestive problems
* reduced risk for some cancers (colorectal)
* reduced risk for kidney stones and gallstones
14
New cards
positive health aspects of following a flexitarian dietary pattern
Health benefits of flexitarian diets:
* improved markers of metabolic health
* reduced risk for obesity and type 2 diabetes
* lower blood pressure
* improved markers of metabolic health
* reduced risk for obesity and type 2 diabetes
* lower blood pressure
15
New cards
life cycle
* well-planned meet nutrient needs and growth at all stages of life cycle
* more restrictive = likely to be unhealthy
* more restrictive = likely to be unhealthy
16
New cards
example #1: pregnancy
* pregnancy outcomes similar to omnivores
* special consideration for iron, zinc, B12, EPA, DHA
* special consideration for iron, zinc, B12, EPA, DHA
17
New cards
example #2: vegan diets appropriate for young children
* lacto-ovo diet as nourishing as a diet that includes meat and fish
* zinc and heme iron would be low in a lacto-ovo diet
* need to enhance foods to provide these nutrients
* zinc and heme iron would be low in a lacto-ovo diet
* need to enhance foods to provide these nutrients
18
New cards
example #3: children and teens
* lower risk for overweight/obesity
* increased fruits/vegetables; fewer sweets, salty snacks, and saturated fats
* ample energy = normal growth
* special consideration for vit B12, vit D, calcium, iron and zinc
* increased fruits/vegetables; fewer sweets, salty snacks, and saturated fats
* ample energy = normal growth
* special consideration for vit B12, vit D, calcium, iron and zinc
19
New cards
example #4: older adults
* nutrient intakes are similar or better than average omnivore
* nutrient dense choices
* protein – need may increase;
* special consideration vit D, vit B6, vit B12
* nutrient dense choices
* protein – need may increase;
* special consideration vit D, vit B6, vit B12
20
New cards
bioavaliability
* the degree to which the human body can absorb and utilize any given nutrient
21
New cards
vitamins to consider in a vegetarian diet
* Vitamin B12
* Vitamin D
* Riboflavin
* Vitamin D
* Riboflavin
22
New cards
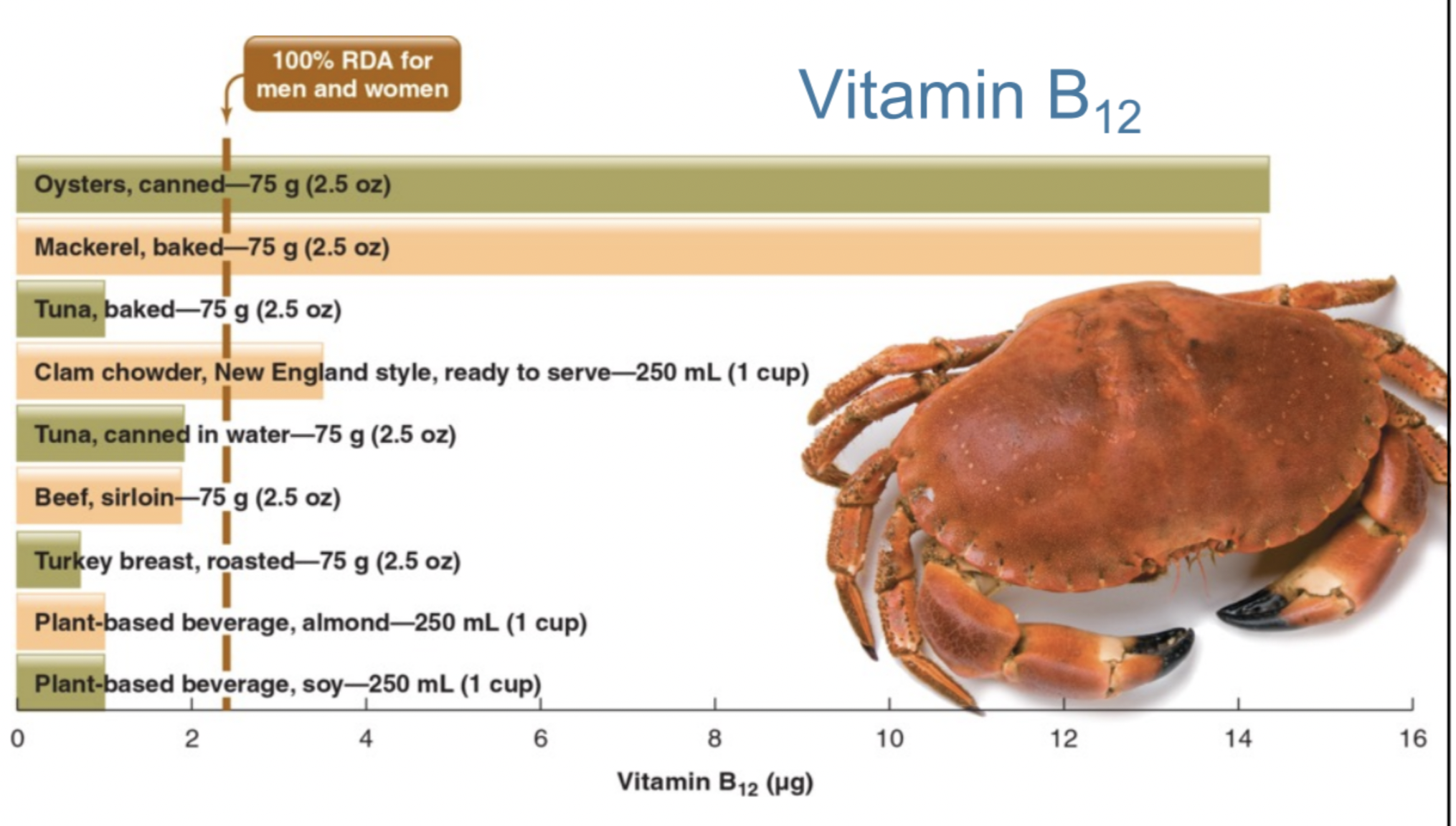
Vitamin B12
Function:
* assists with DNA synthesis
* protection and growth of nerve fibres
* fermented foods (tempeh, nori, nutritional yeast – not adequate sources)
* not reliable sources because they do not act the same way in the human body
* assists with DNA synthesis
* protection and growth of nerve fibres
* fermented foods (tempeh, nori, nutritional yeast – not adequate sources)
* not reliable sources because they do not act the same way in the human body
23
New cards
examples of foods with Vitamin B12 for vegetarian diet
* yogurt
* low-fat milk
* cheese
* eggs
* low-fat milk
* cheese
* eggs
24
New cards
examples of food with Vitamin B12 for vegan diet
* fortified plant-based beverages
* fortified foods (e.g. cereal)
* B12 supplements
* fortified foods (e.g. cereal)
* B12 supplements
25
New cards
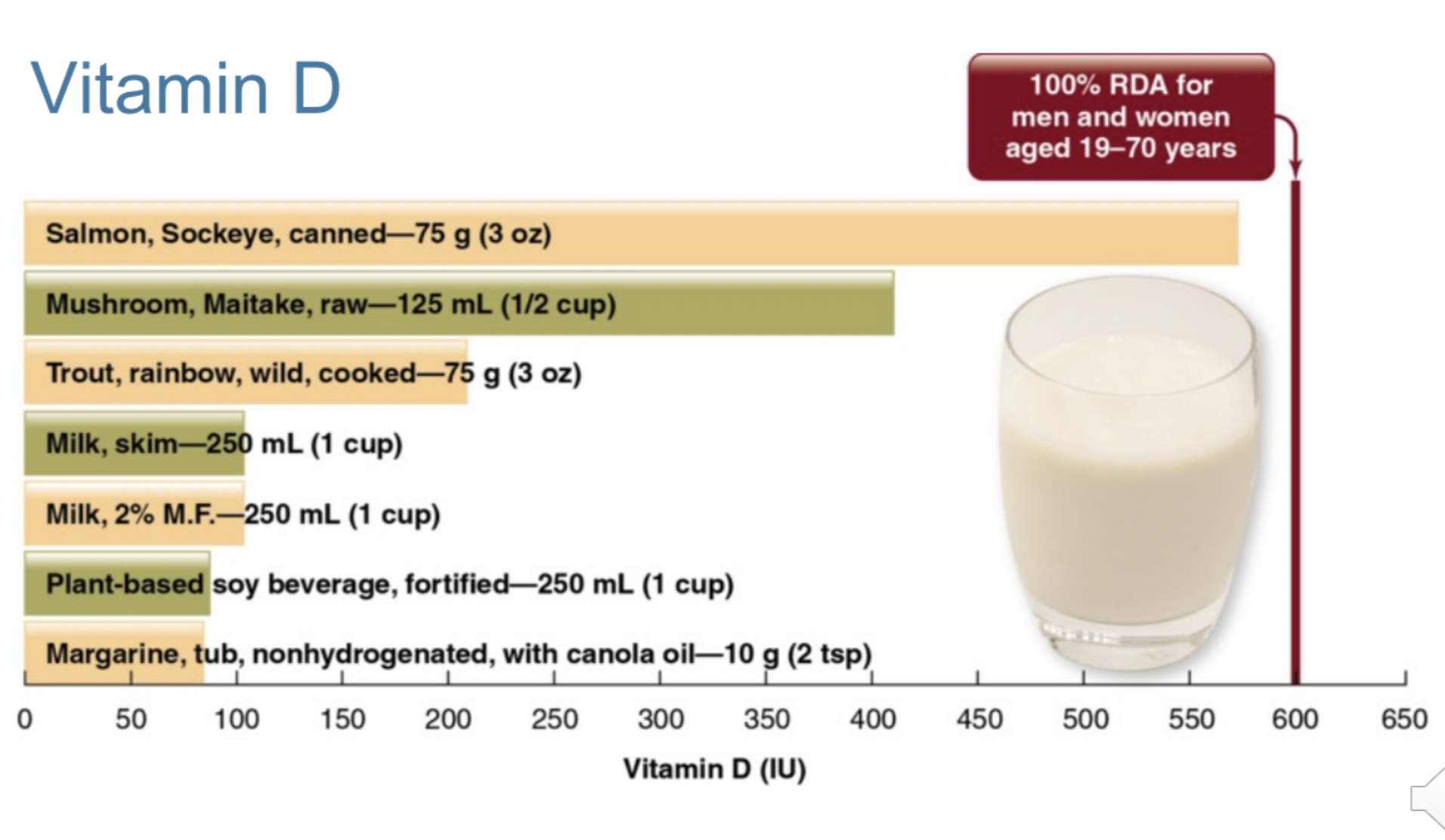
Vitamin D
Function:
* contributes to bone growth and regeneration
* facilitates calcium absorption
* sunlight activates vitamin D in skin (Canada May-Oct)
* supplement 1,000 IU , 10 mcg
* contributes to bone growth and regeneration
* facilitates calcium absorption
* sunlight activates vitamin D in skin (Canada May-Oct)
* supplement 1,000 IU , 10 mcg
26
New cards
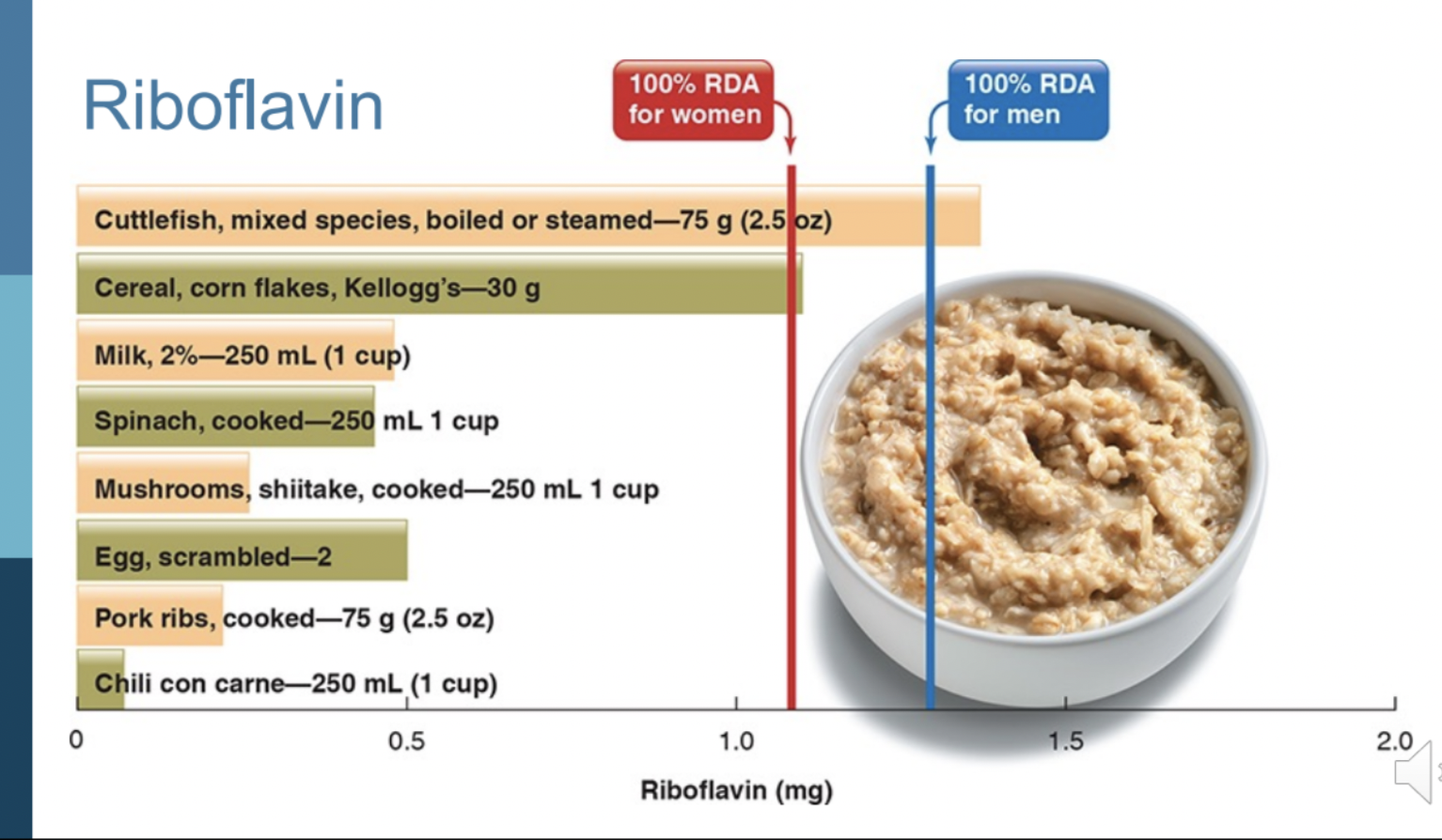
Riboflavin
Function:
* promotes release of energy
* component of coenzymes (FMN & FAD) for carbohydrate and fat metabolism
* part of antioxidant Glutathione Peroxidase
* supports normal vision and skin health
* promotes release of energy
* component of coenzymes (FMN & FAD) for carbohydrate and fat metabolism
* part of antioxidant Glutathione Peroxidase
* supports normal vision and skin health
27
New cards
Mineral Considerations for the Vegetarian Diet
* iron
* calcium
* zinc
* calcium
* zinc
28
New cards
Iron
Function:
* assists with oxygen transport
* involved in making amino acids and hormones
* vegetarians consume iron intakes equal to or greater than omnivores BUT body stores are lower
* assists with oxygen transport
* involved in making amino acids and hormones
* vegetarians consume iron intakes equal to or greater than omnivores BUT body stores are lower
29
New cards
Heme vs. Non-Heme Form
Food contains two types of iron
* heme iron: iron that is part of hemoglobin and myoglobin; found only in animal based foods such as meat, poultry, fish
* non-heme iron: iron not part of hemoglobin or myoglobin; found in animal and plant based foods
* Bioavailability of heme iron is greater than from non-heme
* heme iron: iron that is part of hemoglobin and myoglobin; found only in animal based foods such as meat, poultry, fish
* non-heme iron: iron not part of hemoglobin or myoglobin; found in animal and plant based foods
* Bioavailability of heme iron is greater than from non-heme
30
New cards
iron pt.2
* bioavailability of non-heme iron
* absorption varies depending on status and dietary enhancers and inhibitors
* DRI for vegetarians = 1.8 x
RDA
• Spinach and dark leafy greens
• Raisins
• Whole grains and
enriched/fortified grains
• Legumes (beans)
* absorption varies depending on status and dietary enhancers and inhibitors
* DRI for vegetarians = 1.8 x
RDA
• Spinach and dark leafy greens
• Raisins
• Whole grains and
enriched/fortified grains
• Legumes (beans)

31
New cards
Iron bioavaliability (enhancers and inhibitors)
enhancers:
* low body stores
* vitamin C
* citric acid
* other organic acids
inhibitors:
* phytates
* polyphenolics
* low body stores
* vitamin C
* citric acid
* other organic acids
inhibitors:
* phytates
* polyphenolics
32
New cards
Calcium
Function:
* bone health maintenance
* assists with muscle contraction, blood pressure, and nerve transmission
* bone health maintenance
* assists with muscle contraction, blood pressure, and nerve transmission
33
New cards
Calcium pt.2
1. lacto-ovo vegetarians typically adequate calcium intake
* vegans
* Kale
* Broccoli
* Bok choy
* Beans
* Nuts and seeds
* Tofu
2. Calcium-fortified products
* soy beverages
* breakfast cereals
* orange juice

34
New cards
calcium bioavaliability
enhancers:
Low oxalate vegetables
* kale
* turnip greens
* bok choy
* Chinese cabbage
* vitamin D
inhibitors:
* oxalate
* phytate
* fibre
Low oxalate vegetables
* kale
* turnip greens
* bok choy
* Chinese cabbage
* vitamin D
inhibitors:
* oxalate
* phytate
* fibre
35
New cards
Zinc
Function:
* assists with DNA and RNA synthesis
* assists with immune function
* assists with growth
* many plants are good sources of zinc; poorly extracted compared to animal sources
* non-meat sources:
1. whole grains
2. beans
3. nuts and seeds
4. zinc-fortified breakfast cereals
5. soy products
* assists with DNA and RNA synthesis
* assists with immune function
* assists with growth
* many plants are good sources of zinc; poorly extracted compared to animal sources
* non-meat sources:
1. whole grains
2. beans
3. nuts and seeds
4. zinc-fortified breakfast cereals
5. soy products
36
New cards
zinc bioavaliability
enhancers:
soaking and sprouting
* beans
* grains
* nuts
* seeds
* leavening bread
* organic acids (citrus)
inhibitors:
* phytates
soaking and sprouting
* beans
* grains
* nuts
* seeds
* leavening bread
* organic acids (citrus)
inhibitors:
* phytates