biopsychology 1
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
no evaluation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
what is the nervous system?
network of nerve cells that carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord
helps the body communicate
provides conciousness
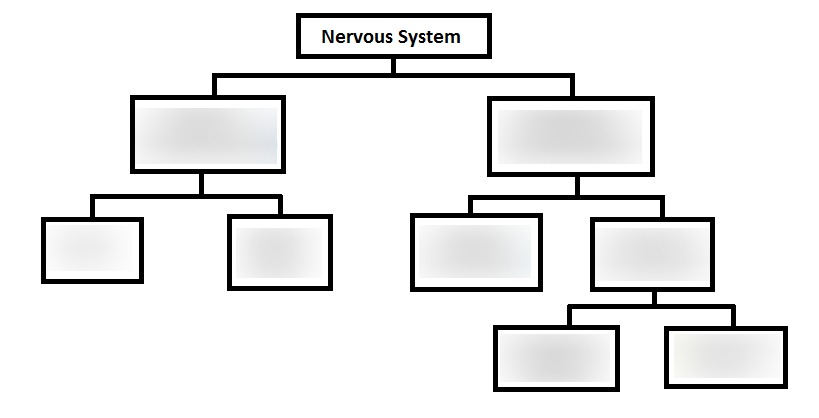
label this
what are the main functions of the central nervous system?
control behaviour
regulate body’s physical proceses
brain needs to be able to recieve information from sensory receptors and send messages to muscles and glands
the spinal cord attaches to the brain and nerve cells run the length of the spinal cord
explain the spinal cord in relation to the central nervous system
it relays information between the brain and body, allowing the brain to monitor and regulate bodily processes
spinal cord is connected to different parts of the body by pairs of spinal nerves which connect to specific glands or muscles
allows us to perform simple reflexes without direct involvement of the brain through circuits of nerve cells- e.g. pulling hand away from something hot
if it is damaged, areas below the damaged site will stop working
give a simple summary of functions of the spinal cord
relays info from brain and body
spinal cord connects to different parts of the body, specific glands and muscles
perform simple and quick reflexes
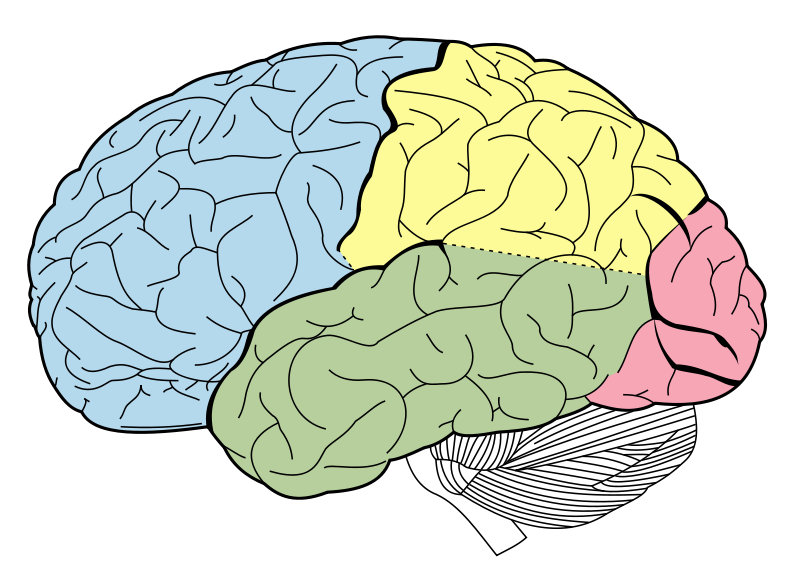
label this
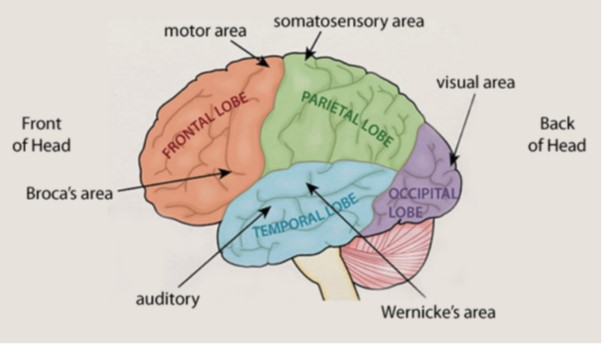
what is SPATVOMF
Somatosensory cortex
Parietal lobe
Auditory cortex
Temporal lobe
Visual cortex
Occipital lobe
Motor cortex
Frontal lobe
what is the outerlayer of the brain called? how thick is it?
cerebral cortex- 3 mm thick
where is the centre of concious awareness?
brain
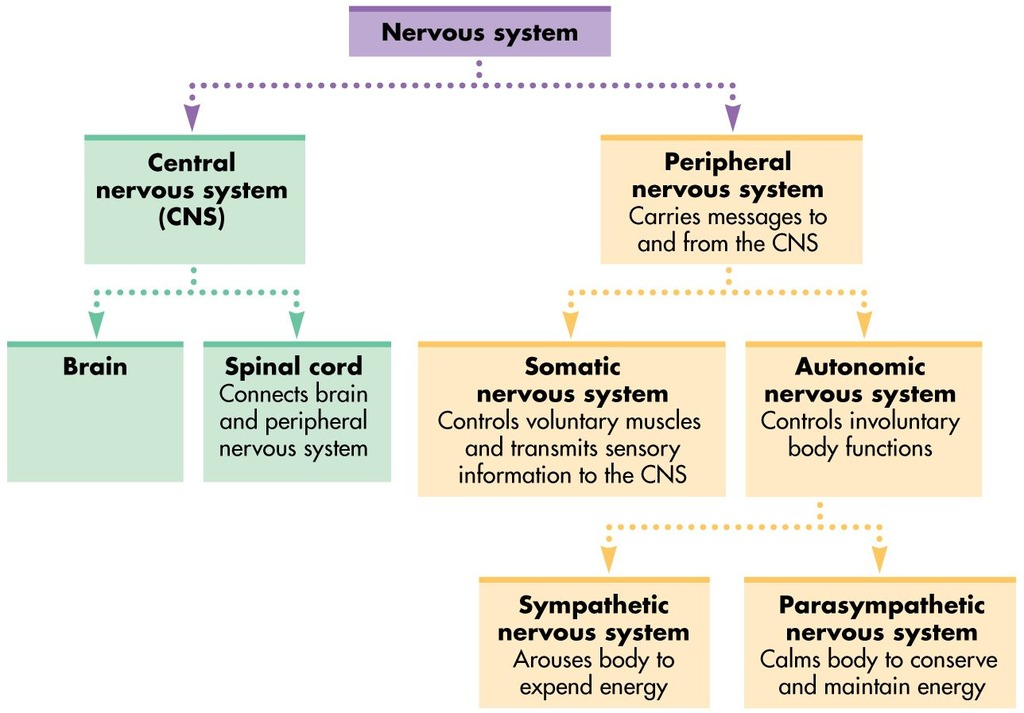
what are the two parts of the central nervous system called?
brain and spinal cord
what are the two parts of the peripheral nervous system called?
somatic and autonomic nervous system
what is the somatic nervous system?
voluntary actions
made up of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves
cranial nerves- come from under the brain
sensory neurons pick up from environment and the motor does the action for that
also involved in reflex actions
what is the autonomic nervous system?
involuntary actions
unconscious ones like breathing or digestion
this is needed so the body can work more efficiently
has 2 parts- sympathetic and parasympathetic
what is the sympathetic nervous system?
fight or flight
help us deal with emergencies- increase blood pressure and heart rate
neurons from SNS travel to almost every organ and gland
causes body to release stored energy
slows the less important bodily processes (e.g. digestion or urination) in emergencies so the energy can be used elsewhere like running
what is the parasympathetic nervous system?
rest and digest
slows heartbeat down and reduces blood pressure
bodily processes will start again, e.g. digestion
compare sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system for these:
pupils
heartbeat
digestion
pupils:
S- dilate / P- constricts
heartbeat:
S- increases / P- slows
digestive system:
S- decreases activity / P- increases activity
somatic nervous system: how many pairs of cranial nerves?
how many pairs of spinal nerves?
12 pairs of cranial nerves
31 pairs of spinal nerves
where are cranial nerves found?
from under the brain
what are neurons?
specialised cells which transmit impulses to and from the CNS
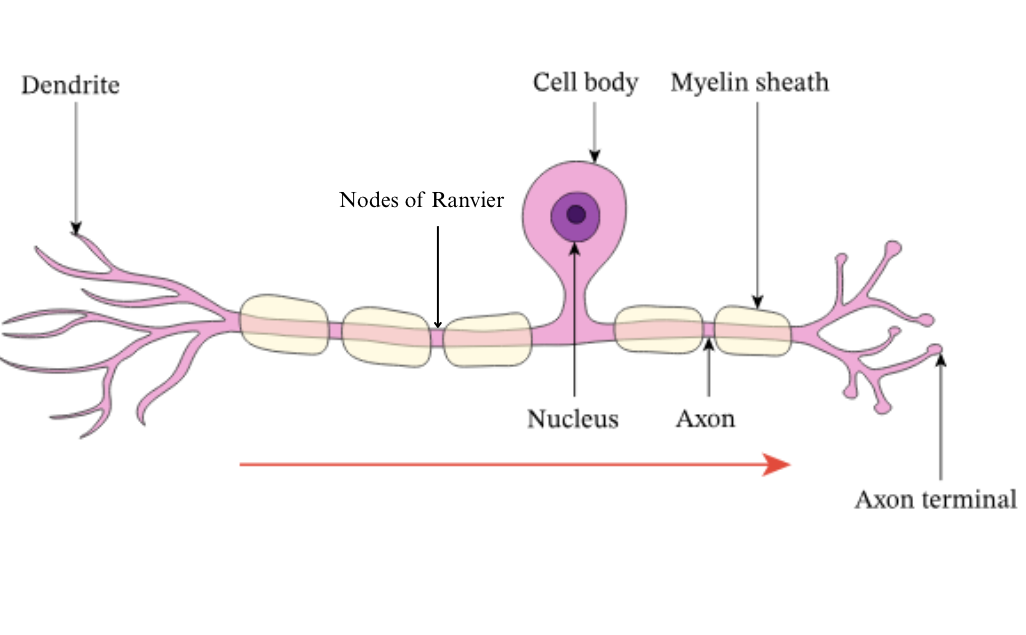
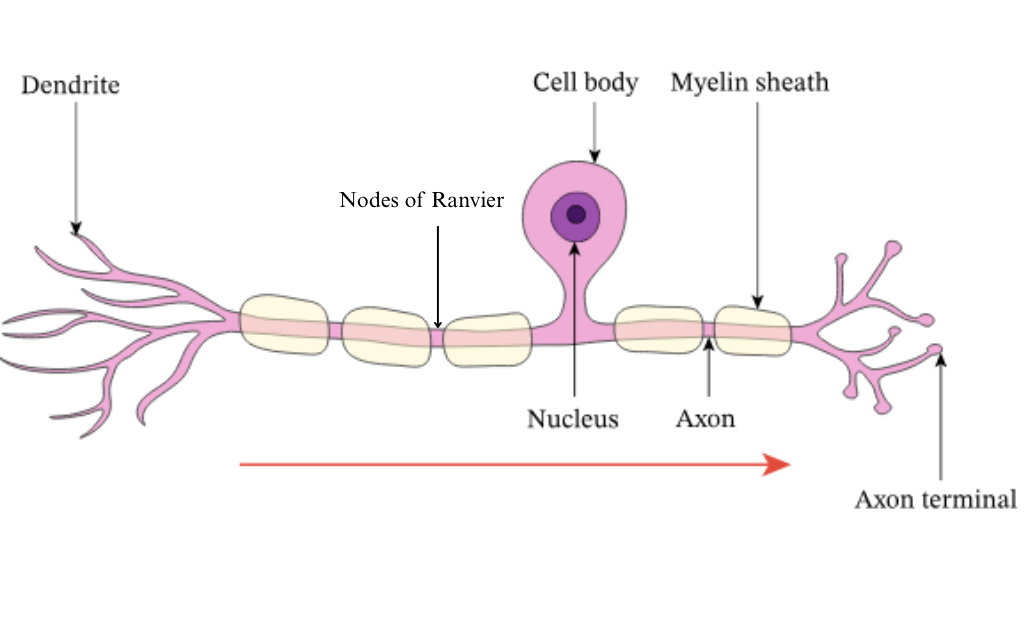
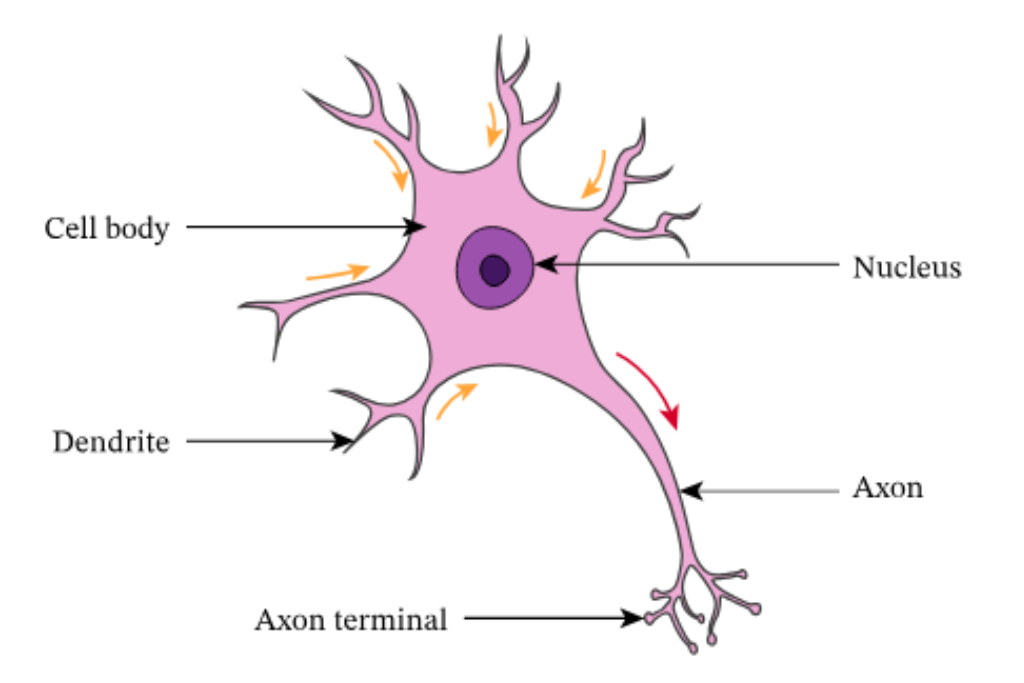
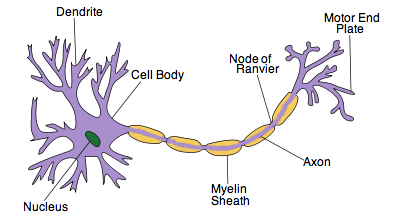
what is the axon terminal?
communicate with the next neuron in the chain
what is the mylon sheath?
layer that protects axon and speeds up electrical transmission
what is the axon?
carries action potential away from the cell body and down the length of the neuron
what is the cell body?
controls centre of the neuron
what is the nucleus?
contains genetic info of the cell
what are dendrites?
carry nerve impulses from neighbouring neurons/receptors to the cell body
what are nodes of ranvier?
gaps in the mylein sheath- speeds up action potential by forcing impulse to jump over the gaps in the axon
explain using neurons how someone can move hand to catch a ball
stimulus
sensory receptor
sensory neuron
relay neuron
motor neuron
muscle
response
what type of neuron is this?
sensory
label this sensory neuron
explain what the sensory neuron does
converts information from sensory receptor into neural responses
impulses are translated into sensations (e.g. pain or visual input) so we can respond appropriately
not all sensory info travels to the brain and stops at the spinal cord to allow reflex actions
what type of neuron is this
relay
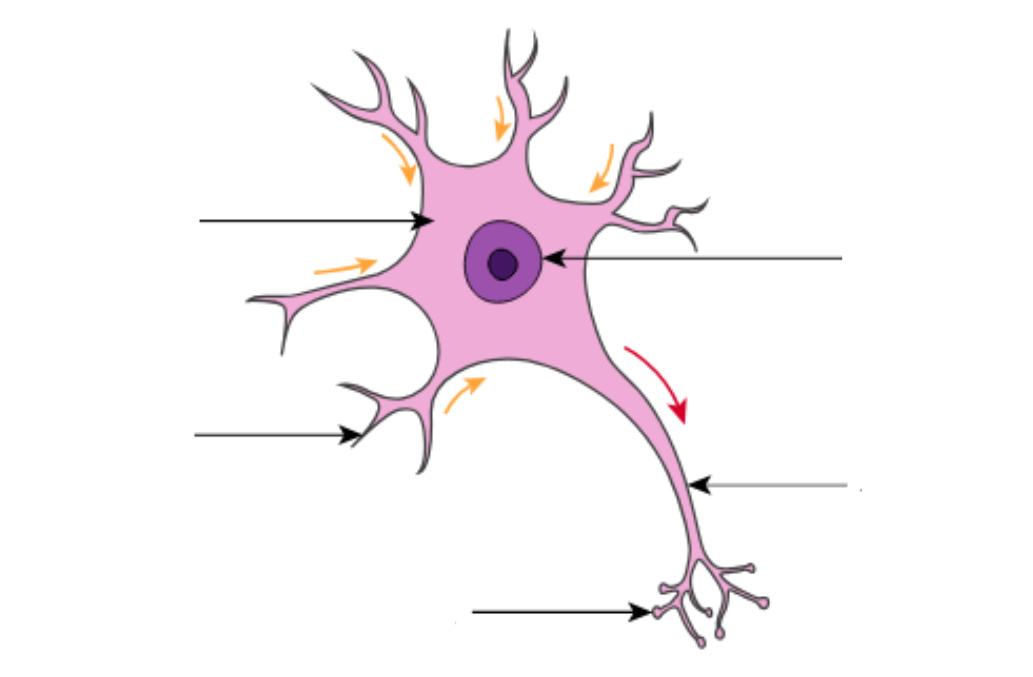
label this relay neuron
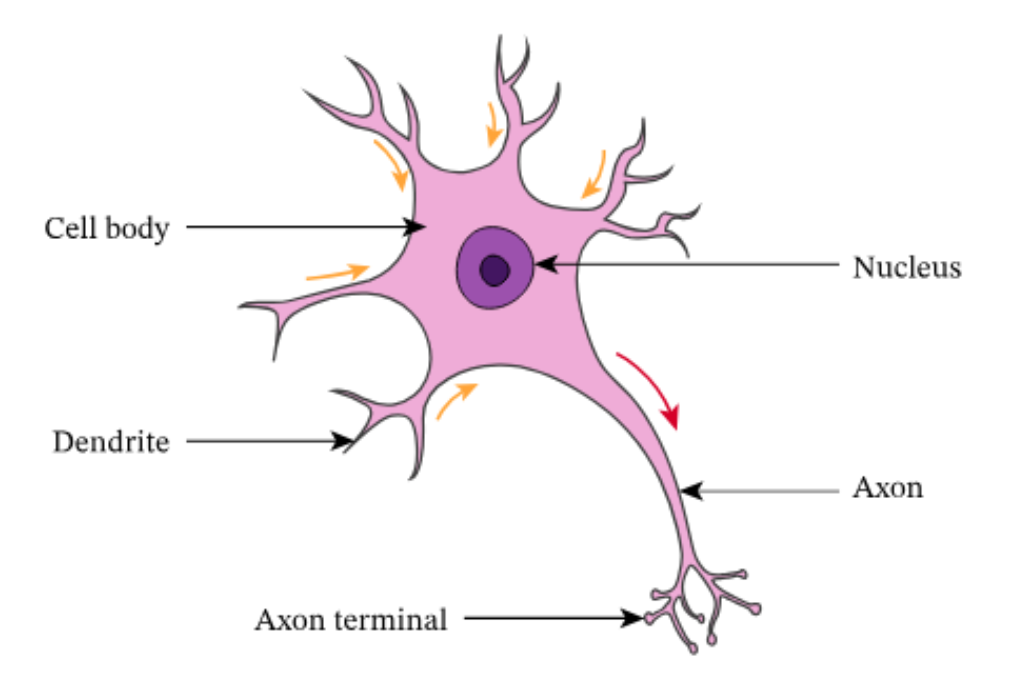
explain what relay neurons do
allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate with each other
lie between the brain and spinal cord
most neurons are relay neurons
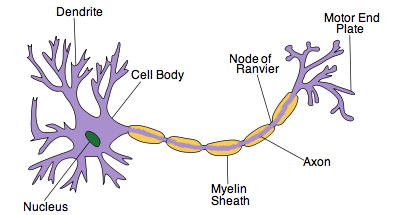
what type of neuron is this?
motor neuron
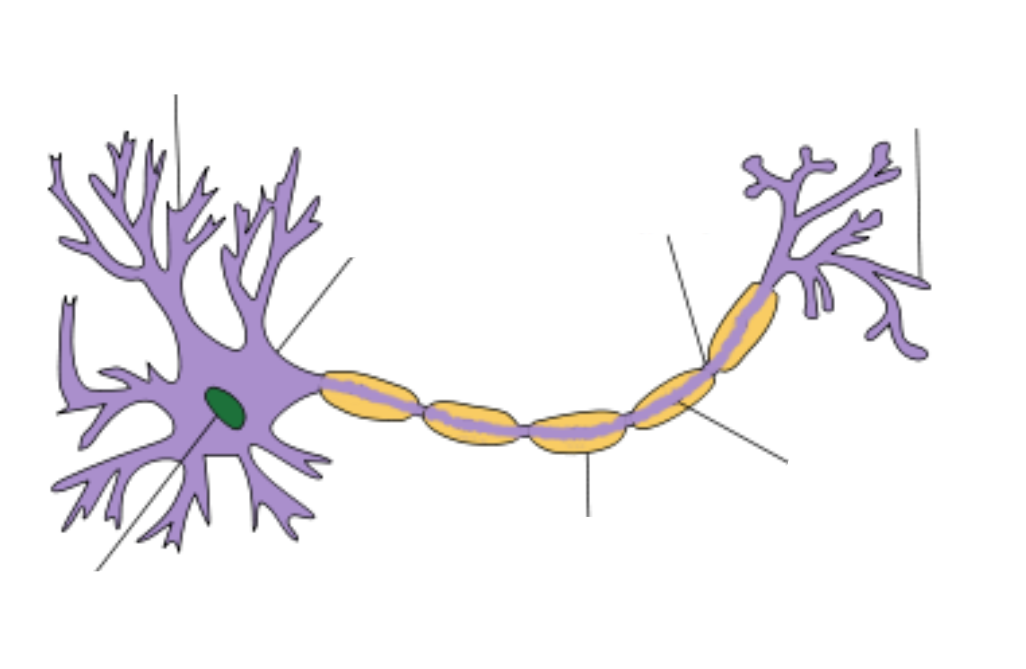
label this motor neuron
explain what motor neurons do
controls muscles and releases neurotransmitters that bind to receptors on muscles to trigger a response
axon fires = muscle contracts
muscle relaxation is caused by neuron not sending it signals
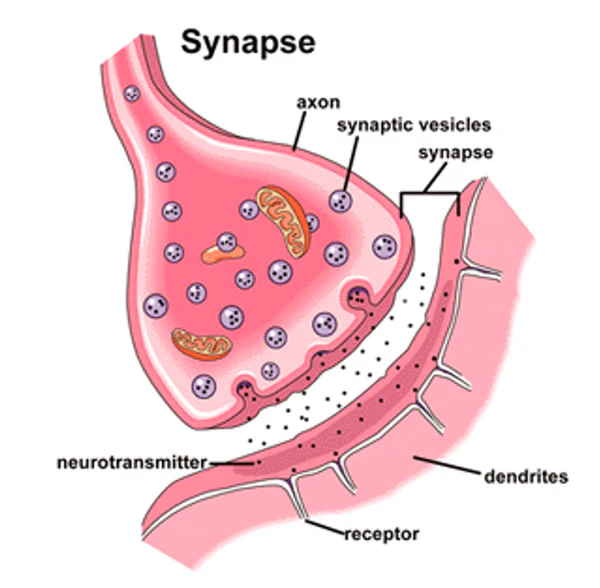
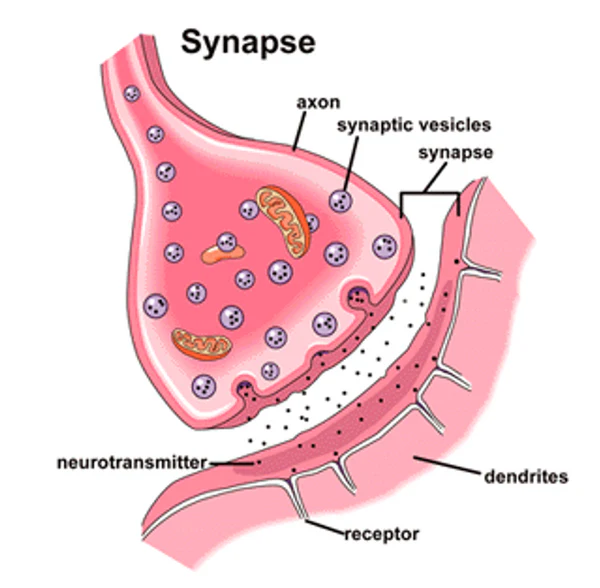
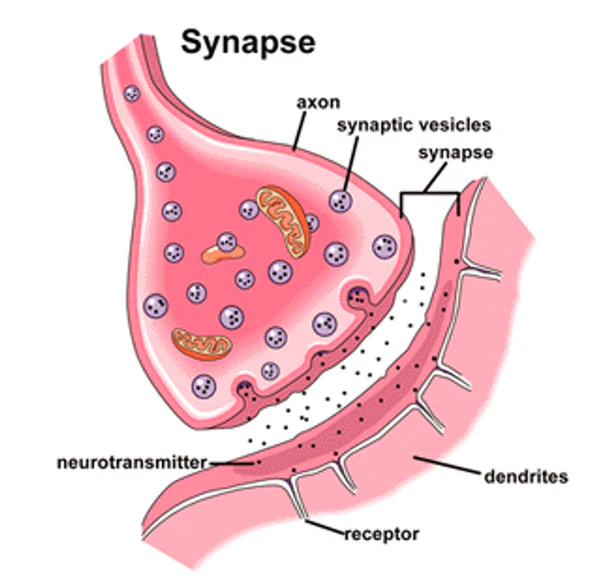
explain synaptic transmission stages
Axon: Action potential travels down the neuron and reaches the axon terminal
Tosses: This triggers the release of neurotransmitters from vesicles
Neurotransmitters: Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse
Between: Bind to receptor sites or are taken back to vesicles
Synapses: Summation. NTs are excitatory (positive charge- message more likely to fire) or inhibitory (negative charge- stops firing). Sum of Ex and In = whichever there is more of that’s what will happen (e.g. message will fire or message will stop) (only use if 6 marks)
explain summation in synaptic transmission
NTs are excitatory (positive charge- message more likely to fire) or inhibitory (negative charge- stops firing). Sum of Ex and In = whichever there is more of that’s what will happen (e.g. message will fire or message will stop) (only use if 6 marks)
what do excitatory neurotransmitters have and do?
positive charge- message more likely to fire
what do inhibitory neurotransmitters have and do?
negative charge
stops firing of message
what is this?
synaptic transmission
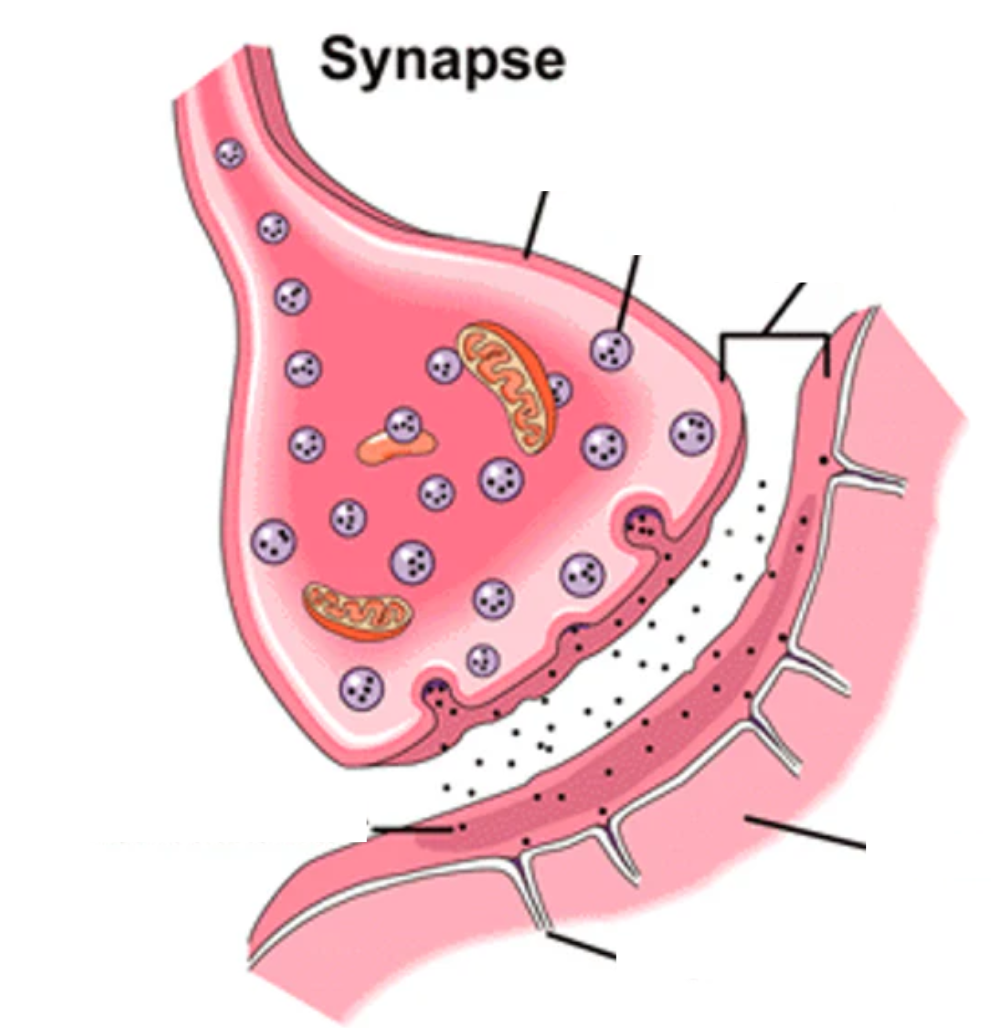
label synaptic transmission
what is the endocrine system?
network of glands throughout the body that create and secrete hormones
instructs the glands to release hormones directly into the blood stream and be carried towards target organs
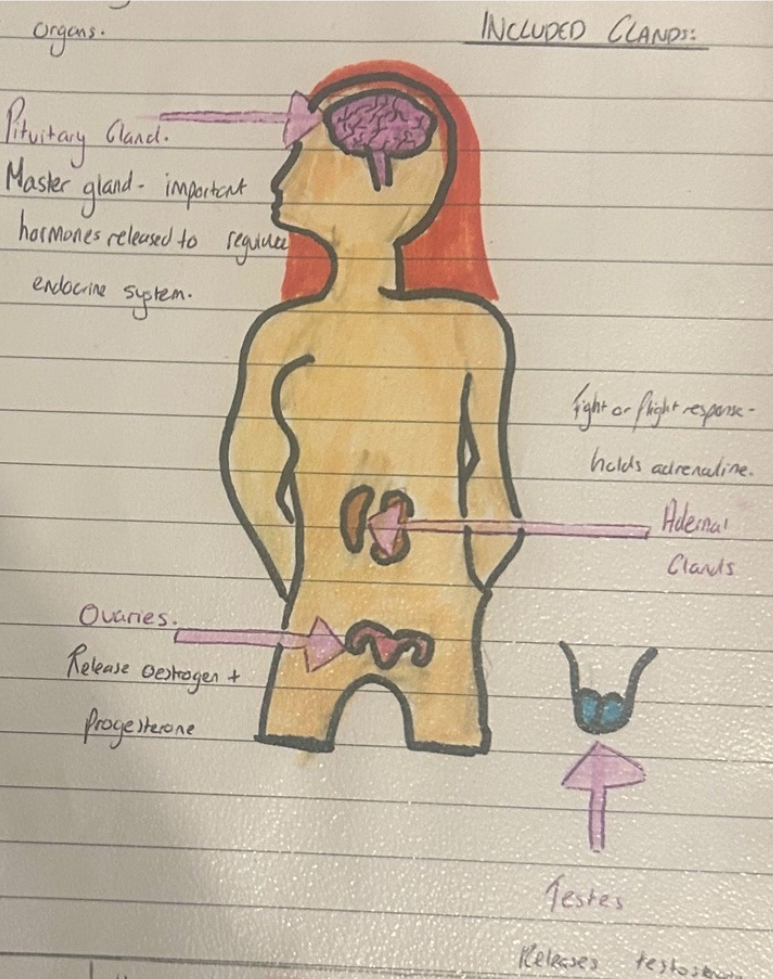
label the endocrine system
what does there have to be for cells for a hormone to influence it?
particular receptors for particular hormones
if cell doesn’t have that receptor, the hormone can’t influence it
why is timing of hormone release for the endocrine system critical?
there could be dysfunctions of the systems otherwise if levels are wrong or if timing is off
where is the pituitary gland and what does it do?
controlled by hypothalamus
known as the master gland- produces hormones that travel in the bloodstream to their target
the hormones either directly cause changes in body processes or stimulate glands to produce other hormones
high levels of hormones in other glands can stop the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland from release hormones to stop levels rising too high
explain the hormones released by the pituitary glands
PG has 2 parts- anterior (front) and posterior (back)
they release different hormones that target different parts of the body
anterior produces ACTH as a response to stress as well as LH and FSH to produce oestrogen, progesterone and testosterone
posterior produces oxytocin- this stimulates contractions during birth and helps mother infant relationships
what hormones does the anterior of the PG create?
ACTH- help with stress
LH and FSH (both help producing progesterone, oestrogen and testosterone)
what hormone does the posterior of the PG create?
oxytocin- stimulates contractions during birth and helps mother/infant bonding
explain the adrenal glands
2 glands that sit on top of the kidney
each has 2 parts- adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla
adrenal cortex:
on the outer part
produces cortisol (a stress hormone)
releases hormones that are necessary for life
has cardiovascular and anti-inflamatory functions
if cortisol levels are low, person has low blood pressure, poor immune system and can’t deal with stress
adrenal medulla:
on the inner part
releases adrenaline and noradrenaline
releases hormones that aren’t necessary for life
prepares fight or flight which helps body respond to stressful situations (adrenaline)
noradrenaline constricts blood vessels to increase blood pressure
what hormone does the adrenal cortex release? what does it do?
cortisol
if levels of cortisol are low the person has:
low blood pressure, poor immune function and inability to deal with stress
what hormones does the adrenal cortex release? what does it do?
adrenaline- prepares fight or flight which helps the body respond in stressful situations
noradrenaline- constricts blood vessels to increase blood pressure
what do the ovaries do?
2 ovaries- responsible for the production of eggs
produces oestrogen and progesterone
progesterone is more important post-ovulation
what do the testes do?
produce testosterone
causes facial hair growth, deepening of voice and growth spurts
plays a role in sex drive and strength
women also have this but in small volumes
explain the process of getting a hormone to the target area
hypothalamus → sends signal → pituitary gland → secretes hormones → blood stream → target gland
how does the endorcrine system balance concentration of hormones?
as levels of hormones rise, hypothalamus and PG shut down the secretion which allows stable concentration
what is fight or flight?
when a person experiences stressful/threatening situations their body has adapted to react quickly
link to sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
for acute stress (immediate like murder)
also activated when its unhelpful- e.g. before an exam
how does fight or flight happen biologically? (stages)
A- Amygdala- amygdala associates sensory signals with emotions like fear and sends the distress signal to the hypothalamus
H- Hypothalamus- hypothalamus releases CRH into the bloodstream
P- Pituitary gland- releases ACTH into the blood stream and then it goes to the target site
A- Adrenal medulla- releases adrenaline into the blood stream causing rapid changes
what hormone does the hypothalamus release in fight or flight?
CRH
what hormone does the pituitary gland release in fight or flight?
ACTH
what hormone does the adrenal medulla release in fight or flight?
adrenaline