BIOL 120 Exam 2
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
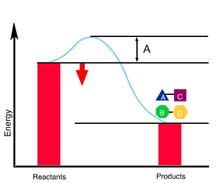
What is the correct label for A?
Energy of activation (EA)
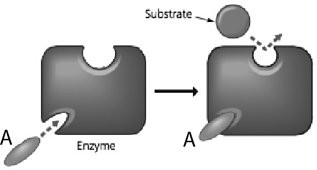
In the figure, how does the molecule labeled A affect enzyme function?
? It is an inhibitor that changes the enzyme’s active site ?
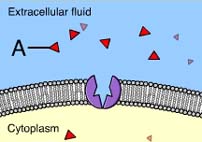
Structure A is a ____
Solute
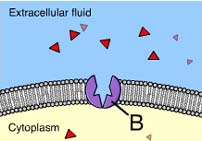
Structure B is a ____
Transport protein
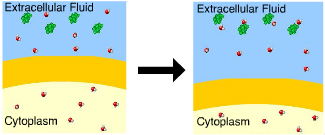
This cell is in a(n) ____ solution
Hypertonic
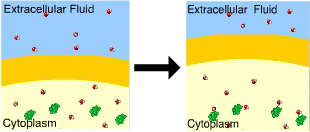
You know that this cell is in a(n) ____ solution because the cell ____
Hypotonic…swelled
You know that this cell is in a(n) ____ solution because it ____
Hypertonic…lost water
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by lowering the ____, which allows the reaction to proceed much more quickly.
Activation energy
Lactose takes years to break down on its own. But if exposed to the protein lactase, the reaction proceeds very quickly, while lactase itself remains unchanged. Lactase is an example of a(n) ____.
Enzyme
An enzyme is considered a(n) ____ because it speeds up a chemical reaction without being used up.
Catalyst
During an enzymatic reaction, a molecule of ____ binds to the enzyme and is broken down into one or more molecules of ____, which are released.
Substrate…product
A(n) ____ is a molecule that can bind to an enzyme and prevent the enzyme from working.
Inhibitor
High temperatures or changes in pH can ____ an enzyme, causing it to lose its shape and biological activity.
Denature
The specific location within an enzyme molecule where the substrate binds is called the ____.
Active site
The ____ between an active site and its substrate often strains bonds and helps the reaction proceed.
Induced fit
What major theme of biology is represented in the following: The region of an enzyme called the active site has the shape and chemistry that fits one specific substrate molecule
Relationship of structure to function
What major theme of biology is represented in the following: There is more oxygen gas in the air of our lungs than in the blood. Therefore, oxygen moves by passive transport from the air into the bloodstream
Interactions within biological systems
What major theme of biology is represented in the following: Because all cells have a plasma membrane, it is logical to infer that membranes first developed in the earliest forms of life on Earth
Evolution
What major theme of biology is represented in the following: ATP energizes other molecules in cells by transferring phosphate groups to those molecules
Pathways that transform energy and matter
What is the best definition of energy?
The capacity to cause change
What is true about energy?
It cannot be created nor destroyed
What is an example of potential energy?
A bowling ball placed on the top shelf of a closet
How are combustion and cellular respiration different?
Cellular respiration breaks down sugar and combustion breaks down octane
What is the function of ATP?
It provides energy for cellular work
A space station orbiting Earth is exhibiting what type of energy?
Kinetic
“Conservation of energy” refers to the fact that ____
Energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be converted from one form to another
Chemical energy is a form of ____ energy
Potential
In your body, what process converts the chemical energy found in glucose into the chemical energy found in ATP?
Cellular respiration
What molecule do cells use to store the chemical energy released by the breakdown of food molecules during cellular respiration?
ATP
What are the components of the molecule ATP?
An organic molecule called adenosine and three phosphate groups
ATP drives work in cells by ____
Transferring its phosphate group to other cell molecules
Most enzymes are ____
Proteins
Enzymes work by ____
Reducing activation energy in a reaction
An enzyme is a(n) ____
Organic catalyst
What name is given to the reactants in an enzymatically catalyzed reaction?
Substrate
As a result of its involvement in a reaction, an enzyme ____
Remains unchanged
An enzyme is a molecule that ____
Changes the rate of a metabolic reaction without being consumed by the reaction
Activation energy can be described as ____
Energy that must be invested to start a reaction
What best explains the observation that enzymes are selective in the reactions they catalyze?
There is a precise compatibility between an enzyme’s active site and the substrate molecule
When molecules move down their concentration gradient, they move from where they are ____ to where they are ____.
More concentration, less concentrated
Diffusion across a biological membrane is called ____.
Passive transport
Endocytosis moves materials ____ a cell via ____.
Into…membranous vesicles
You can recognize the process of pinocytosis when ____
The cell is engulfing extracellular fluid
A white blood cell engulfing a bacterium is an example of ____
Phagocytosis
Facilitated diffusion is a form of ____ transport
Passive
What name is given to the process by which water crosses a selectively permeable membrane?
Osmosis
Exocytosis involves the movement of molecules from ____ the cell to ____ the cell.
Inside…outside
Endocytosis involves the movement of molecules from ____ the cell to ____ the cell.
Outside…inside
A vesicle inside the cell fuses with the plasma membrane and releases its contents outside the cell is ____
Exocytosis
____ is a form of passive transport in which molecules move across the plasma membrane using a transport protein.
Facilitated diffusion
The plasma membrane forms a pocket that pinches inward, forming a vesicle that contains material from outside the cell is ____
Endocytosis
____ is a form of passive transport in which molecules move across the plasma membrane by crossing a lipid bilayer.
(Simple) Diffusion
____ requires energy from the cell. Molecules move against their concentration gradient.
Active transport
The ideal osmotic environment for an animal cell is a(n) ____ environment.
Isotonic
An animal cell placed in a(n) hypotonic solution will ____.
Gain water, swell, and possibly burst
There is a net diffusion of water out of an animal cell when it is placed in a(n) ____ solution.
Hypertonic
The ideal osmotic environment for a plant cell is a(n) ____ environment.
Hypotonic
A plant cell placed in a(n) hypertonic solution will ____.
Lose water and plasmolyze
A plant cell surrounded by a(n) isotonic solution will be ____.
Flaccid (limp)
The passive movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration is called ____.
Diffusion
An animal cell placed in a hypertonic solution will ____ water by ____.
Lose…osmosis and shrivel
In osmosis, water moves across a selectively permeable membrane toward the ____ solution; that is, toward the solution with the ____ solute concentration.
Hypertonic…greater
The concentration of calcium in a cell is 0.3%. The concentration of calcium in the surrounding fluid is 0.1%. How could the cell obtain more calcium? Through ____ transport.
Active
“The use of energy to move molecules across a membrane” is the definition of ____.
Active transport
What is sometimes referred to as cell eating?
Phagocytosis
What is sometimes referred to as cell drinking?
Pinocytosis
Can an object at rest have energy?
Yes; it can have potential energy because of its location or structure
What major theme of biology is illustrated by the following: You turn the crank of a well, raising a bucket of water from below ground to the surface.
Pathways that transform energy and matter
How does ATP power cellular work?
ATP is hydrolyzed into ADP + Pi. The Pi is transferred to another molecule such as an ion channel or an enzyme, activating that molecule
What is the source of energy regenerating ATP from ADP?
Chemical energy harvested from sugars and other organic fuels via cellular respiration
How does an enzyme recognize its substrate?
The substrate and the enzyme’s active site are complementary in shape and chemistry
How does an enzyme affect the activation energy of a chemical reaction?
By lowering the activation energy
Which major theme of biology is illustrated by the following: Enzymes unravel and stop functioning if the environment gets too hot.
The relationship of structure to function
Which major theme of biology is illustrated by the following: Your ability to walk depends upon the coordination of many different enzymes and other cellular structures.
Interactions within biological systems
What does it mean to say that molecules move ‘down the concentration gradient’?
Molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Why is facilitated diffusion a form of passive transport?
It uses proteins to transport materials down a concentration gradient without expending energy
What two processes make up bulk transport?
Endocytosis and exocytosis
What are two examples of endocytosis?
Phagocytosis and pinocytosis
What are the four types of tissues?
Epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous
Place these levels of biological organization in order from largest to smallest: Cell, organ, atom, organ system, molecule, organism, tissue, macromolecules
Atoms, molecules, macromolecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism
Bird wings are hollow, which makes them lighter. How does this illustrate the structure-function principle?
The structure of the wing, with hollow bones, makes it lightweight, which correlates with the function of flight
Which major theme of biology is illustrated by the following: Your body is able to build new muscle when nutrients absorbed by the digestive system are transported by the circulatory system to tissues of the muscular system.
Interactions within biological systems
Which major theme of biology is illustrated by the following: Your body is able to build new muscle when nutrients absorbed by the digestive system are transported by the circulatory system to tissues of the muscular system.
Information flow
Which process helps maintain homeostasis?
Negative feedback
What is the difference between negative and positive feedback?
Positive - end results intensify the process; Negative - end result inhibits the process
When you flush a toilet, water begins to refill the tank. The rising water level lifts a float. When the float reaches a certain height, it stops more water from entering the tank. This is an example of what kind of homeostatic control? Why?
This is an example of negative feedback because the result of a process (water filling the tank) inhibits that same process
What are three features of the human body that helps release heat?
Sweating, dilation of blood vessels, panting
What are three features of the human body that help to retain body heat?
Shivering, constriction of blood vessels, increased metabolic rate
A patient receives fluid through an intravenous (IV) line that causes his interstitial fluid to have a very high solute concentration. What will happen to his cells?
They will shrink as water exits via osmosis
What is a nephron?
Basic functional unit of the kidney
What are the four processes of the nephron that occur as kidney tubules process blood and create urine?
Filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion
Which major theme of biology is illustrated by the following: Your kidneys contain highly branched tubes that allow for a large volume of fluid to be in contact with cells, aiding filtration.
Relationship of structure to function
A correct comparison between a benign and a malignant tumor is that ____
Benign tumors do not metastasize, malignant tumors do
A cell that neither gains nor loses a net amount of water at equilibrium when it is immersed in a solution is ____
Isotonic to its environment
A diver at the top of a diving board contains ____ energy
Potential
The sum total of all the chemical reactions that occur in organisms is called ____
Metabolism
Facilitated diffusion across a biological membrane requires ____ and moves a substance ____ its concentration gradient
Transport proteins; down
An object at rest has no ____ energy, but it may have ____ energy resulting from its location or structure
Kinetic; Potential
A boulder at the top of a hill is or is not an example of potential energy?
It is
Glucose molecules provide energy to power the swimming motion of sperm. In this example, the sperm are changing ____
Chemical energy into kinetic energy