Pediatric Hematology/Oncology: Tumors
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
solid, death, astrocytoma, posterior, location, headache, nausea, balance
Brain Tumors: Background
-Most common ______ tumor and second most common overall malignancy in children
-Leading cause of cancer _______ in children
-Etiology → unknown, genetic, environmental, and immune factors
-Most common types → medulloblastoma, ependymoma, ____________, brainstem glioma, craniopharyngioma, optic nerve glioma
2/3rds of all pediatric brain tumors are located in the __________ fossa
-Symptoms → depends on ________, cell type, and rate of growth
ICP symptoms → _________ (worse in AM), vomiting (worse in AM, without _______), lethargy, irritability
Cerebellum involvement → impaired coordination and _________ (ataxia, gait difficulties)
astrocytes, cerebellum, slow, unilateral, ataxia, vermis, CSF, fast, ependymal, lateral
Brain Tumors: Types
-Astrocytomas (20% cerebellar, 8% cerebral)
Arise from __________ in the __________ or cerebral hemispheres
_____ growing, often very large before diagnosed
Cerebellar astrocytomas often cause _______ symptoms such as head tilt, limb _______, and nystagmus
-Medulloblastoma (18%)
Arises in the _____ of the cerebellum and can extend into the 4th ventricle, subarachnoid space, and ____
_____ growing
-Ependyoma
Arises from ___________ cells that line the ventricular system
Most often 4th and _______ ventricles
pons, weakness, unilateral, contralateral, optic chiasm, slow, neurofibromatosis, visual, pituitary, slow, ICP, puberty
Brain Tumors: Types
-Brainstem Gliomas
Arise from the _____ or medulla
Can compress CN V-X
Can cause facial __________, limitation of horizontal eye movement, ataxia, and corticospinal tract dysfunction
Common presentation → _______ paralysis of CNS with _________ paralysis of the arm and leg, hyperreflexia, and extensor plantar responses
-Optic Nerve Gliomas
Arise from _____ _______ or optic nerve
Low grade astrocytoma
____ growing
Often associated with _____________ type I
Blindness or other ______ disturbances
-Craniopharyngioma
Arises near the _______ gland, optic chiasm, and hypothalamus
_____ growing
Can compress pituitary gland, hypothalamus, or optic chiasm and cause ___
HA, seizures, diabetes insipidus, early onset puberty, growth delay
MRI, vascularity, CSF, resection, chemotherapy
Brain Tumors: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis
Neurologic, developmental, and ophthalmic exams
____ is the imaging of choice
MRA to assess __________ of tumor and relationship to other major vessels
MRI of spine
LP to examine ____ for tumor cells
Histochemical and molecular genetic analysis
-Treatment
Surgical _________ unless contraindicated
Radiation and _____________
soft tissue, 10, rhabdomyoblasts, striated, anywhere, head, GU
Rhabdomyosarcoma: Background
-Most common _____ ________ sarcoma of childhood, accounting for > 50% of soft tissue tumors
-Overall rare
-Epidemiology
Most diagnosed by __ years old (peak 2-6 y/o and 15-19 y/o)
Male > Female
-Pathogenesis
Arises from embryonal _____________ that normally differentiate into _______ muscle
Can occur _______ there is striated muscle
Primary locations of _____ and neck, trunk, extremities, and __ tract
located, ptosis, urinary, mass, biopsy, blue cell
Rhabdomyosarcoma: Symptoms and Diagnosis
-Symptoms
Depends on where the tumor is _________
_____, dysphagia, facial nerve palsy, _______ obstruction, hematuria, abdominal pain
Painless, palpable or visible _____
-Diagnosis
________ of small, round mass is confirmatory
_____ _____ tumors
Serology
Imaging
resection, radiation, metastatic, widespread
Rhabdomyosarcoma: Treatment
-Surgical _________
-Chemotherapy
-_________
-20% have _________ disease at diagnosis
-Prognosis
Localized disease = 70% overall survival rate
________ disease = 20% survival rate
bone, 10-18, mesenchymal, metaphyses, long, femur, tibia, pain, redness, lung, fracture
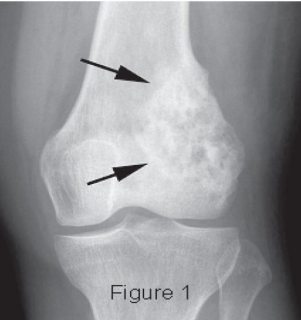
Osteosarcoma: Background
-Most common malignant _____ tumor in childhood
-Epidemiology → ___-___ years old
-Pathogenesis → Arises from bone producing ___________ cells
Occurs mainly in the __________ of ____ bones
Distal end of _____ or proximal end of _____ (MC)
Can extend beyond the bone into the soft tissues
-Symptoms → _____, swelling/warmth/_________ over the area, cough/SOB/chest pain if _____ mets, limp, pathologic __________
MRI, primary, CT, biopsy, osteoid, resection
Osteosarcoma: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis
___ to evaluate extent of the _________ tumor
Metastatic evaluation with bone scan and chest __
Tissue _______ (confirms), shows presence of _______
-Treatment
Chemotherapy
Surgical ___________
bone, soft, lethal, 10-20, bone marrow, diaphysis, flat, pelvis, early
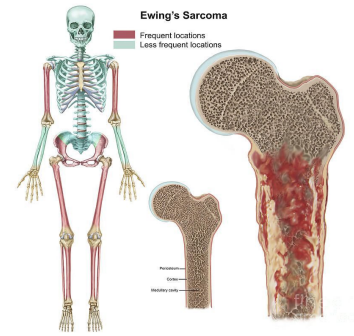
Ewing Sarcoma: Background
-Malignant tumor of _____ and _____ tissue
-Second most common but most _______ malignant bone tumor in childhood
-Epidemiology
Peaks between ___-___ years old
Male > female
Most common in Caucasians
-Pathogenesis
Neural crest cell origin
Arises from _____ ________ and can break through cortex to form soft tissue mass
Most often occurs in the _________ of long bones or ____ bones (femur, _____, tibia most common)
-Mets occur _______
pain, mass, MRI, biopsy, round, chemotherapy, resection
Ewing Sarcoma: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
-Symptoms
______ is most common
Soft tissue _____
Fever, malaise, anorexia
-Diagnosis
CT and ____ to evaluate extent of tumor
Met evaluation with bone scan, chest CT, bone marrow biopsy
_______ (confirms) → small, _______, blue cell tumors
-Treatment
_____________, radiation, surgical __________, or all of the above
Resection is a must

adrenal medulla, sympathetic, solid, 5, 17
Neuroblastoma: Background
-Derived from neural crest cells that form the _______ ________ and the _________ nervous system
-Epidemiology
Most common extra-cranial _____ tumor in infants <1 y/o
75% are found before age _ (median age __ months)
Rare after 10 y/o
-Etiology is unknown
mass, bowel, Horner, loss, sweating
Neuroblastoma: Symptoms
-Retroperitoneal region/adrenal medulla
Abdominal pain/_____, anorexia, _______ or bladder issues, spinal cord compression
-Mediastinum
Shortness of breath, infection, airway obstruction
-Cervical sympathetic ganglion
_______ syndrome
-Systemic symptoms
Weight _____, irritability, fatigue, fever
-Paraneoplastic syndromes
Secretory diarrhea, profuse ________, and opsomyoclonus
catecholamines, biopsy, resection, chemotherapy, radiation, metastatic, die
Neuroblastoma: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis
Urine ____________
CT
Bone scan
Bone marrow aspiration/biopsy
Tissue ________ (makes the diagnosis)
-Treatment
Low risk → surgical __________
Immediate risk → surgery then ____________
High risk → chemotherapy, resection, stem cell rescue, _________, sometimes immunotherapy
-70% have ___________ disease at diagnosis
-50% of children with high risk disease will ____ despite treatment
bilateral, 1st, 2-3, retinal, vitreous, CNS, choroid
Retinoblastoma: Background
-Etiology
Inherited → more likely to be ________
Acquired
-Epidemiology
Inherited → diagnosed within the ____ year of life
Acquired → diagnosed around __-__ years old
-Pathogenesis
Arise from ______ cells and extend into _________ humor
Can invade the optic nerve
Can gain access to subarachnoid space and ____
Metastasis possible if invade the ________
leukocoria, painful, CT, aspiration, MRI
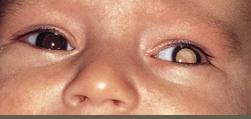
Retinoblastoma: Symptoms and Diagnosis
-Symptoms
Unilateral or bilateral
_________ (white reflex) → most common finding
Strabismus, ________ eye, limited vision
-Diagnosis
Full ophthalmologic exam
__ or orbits
Metastatic studies of bone marrow _________, LP, bone scan, ____
chemotherapy, glaucoma, inheritable
Retinoblastoma: Treatment
-External beam irradiation
-___________ (replacing irradiation), decreased need for enucleation
-Enucleation
Indicated if no vision, neovascular __________, inability to examine the treated eye, inability to control tumor growth with conservative therapy
-Monitor patients with _________ form for development of other tumors like osteosarcoma
1-5, 2-3, kidney, stem cells
Nephroblastoma/Wilms Tumor: Background
-Etiology
Mostly unknown
Sporadic vs inherited
-Epidemiology
Most diagnosed between __-__ years old with peak between __-__ years old
Female > male
AA > Caucasian > Asian
-Pathogenesis
Embryonal tumor of the _______ arising from abnormal proliferation of renal _____ _______ (metanephric blastema)
asymptomatic, mass, smooth, fever, CBC, CT, biopsy
Nephroblastoma/Wilms Tumor: Symptoms and Diagnosis
-Symptoms
_____________ abdominal _____ (MC) → firm, nontender, _______
Abdominal pain, ______, HTN, hematuria possible
-Diagnosis
____, UA, LFTs, BUN/creatinine
Abdominal US or __ shows solid intrarenal mass
CT of chest and abdomen/pelvis to assess for metastasis
Tumor ______ confirms diagnosis
resection, radiation, chemotherapy, nephrectomy
Nephroblastoma/Wilms Tumor: Treatment
-Surgical exploration and __________ followed by treatment based on histology
Chemotherapy with or without __________
-___________ followed by surgical resection
-Some low risk patients with unilateral disease can be cured with ___________ only