ANEQ 102 Exam 3 CSU
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Horses are _____ eaters and _____ eaters
Continues and selective
What is a nutrient?
Any feed constituent that supports the body’s necessary functions.
What is a ruminant?
An animal with a stomach with 4 chambers
What is a non-Ruminant?
An animal with one stomach
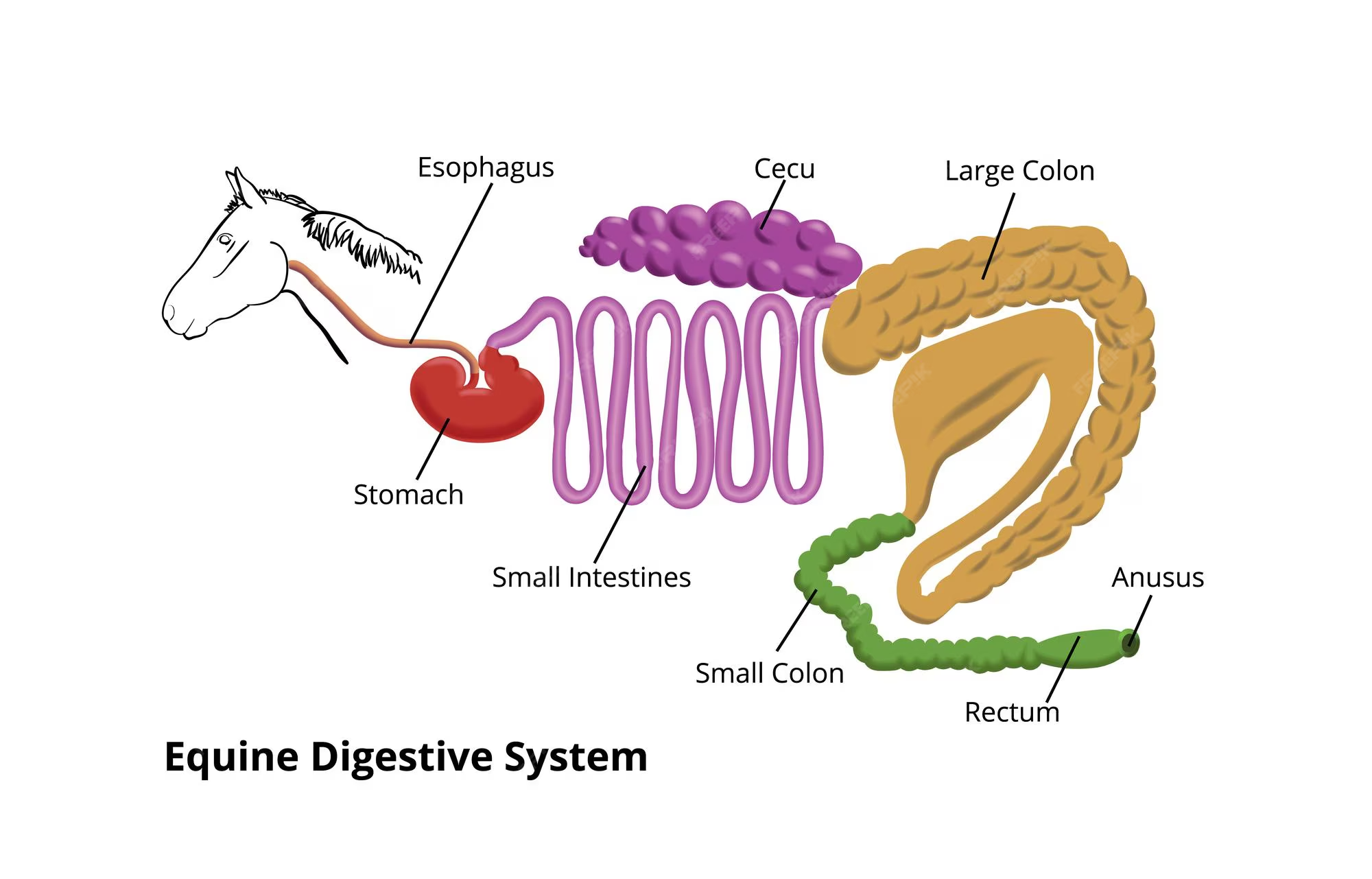
Parts of the horse’s digestion.
What is the purpose of the mouth?
Mastification and development of saliva.
What is the Stomach purpose?
Sight of digestion
Protein digestion starts in the…..
Stomach
What is the purpose of the small intestine?
Sight of enzyme digestion and sight of absorption of nutrition.
What is the purpose of the cecum?
Where microbial fermentation occurs and where volatile fatty acids are.
The large intestine includes the ____ and ____.
Large Colon and Small Colon
What is the purpose of the large colon?
VFA synthesis and absorption, and B-vitamins synthesis.
What is the purpose of the small colon?
Sight of water “re-obsorption” and development of horse apples.
What are the 6 classes of nutrients?
Energy
Lipids
Protein
Minerals
vitamins
water
Carbohydrates are the _____
Primary source of energy
What types of minerals are there?
Macrominerals and microminerals.
There are ___ soluble vitamins and ___ soluble Vitamins
Water and fat
What are feedstuffs?
Roughages, concentrates, and supplements.
What is the feedstuff “rule of thumb”?
Energy
Protein
CAP
Vitamins
What should you consider when choosing roughages?
Quality
Nutrient value
Time of harvest
What horse may be getting it?
Textured concentrates are_____
Sweet feeds
Processed Concentrates are____
Pelleted/extruded feedstuff
Complete feeds are___
Concentrate and roughage together
What book do we use for horse nutrition info?
“Nutrient Requirements Horses”
What two things should you consider when feeding?
Feed intake and feed selection
Feed intake ranges from __________ of body weight.
1.5% to 3%
supplements should be feed when?
Only when needed
Body scoring ranges from _____
1-9
A body condition of 1 means what?
A horse is emanciated
A body condition score of 5 means what?
Horse is at a desired weight
Body condition score of a 9 means what?
Horse is obese
What are the levels of performance work?
Light- Western and English pleasure
Moderate- barrel racing
Heavy or intense- racing
When choosing feeds you must make choices based on the horses _____
needs
How munch feed should a horse get?
Min. 1.5% body weight Max 3% of body weight
How much forage/roughage should a horse get?
No less than 1% of BW
Horse should be mostly feed what?
Forages
What should you avoid when it comes to concentrate to forage ratios?
less than 50% forage
More than 50% grain
How much energy from fat is utilized?
90%
Fat decreases what?
Heat of fermentation
Build-up of lactic acid during intense work.
fatigue
A natural horse diet contains how much fat?
3-4% fat
what are supplements of fat?
vegetable oil
rice bran
animal tallow
Horses have no gall bladder, meaning they can digest a max of how much fat?
20% of fat in total diet
What is a geriatric horse?
Older horses who are declining both mentally and physically.
What decreases in a geriatric horse?
Fiber digestion
vitamin production and absorption
kidney function
liver function
immunes system
amount of teeth
What should you consider when choosing feeds for a geriatric horse?
highly palatable
easy to chew
clean and dust-free
pelleted pr extracted feeds
high quality hay
Soaked feeds are good for geriatric horses why?
Mashes are easy to eat.
What are the aims of training programs?
exercise capacity
time to onset of fatigue
performance
decreasing risk of injury
In equine exercise physiology, these body systems are important
Cardiovascular system
muscular system
thermoregulation
training and conditioning
What are the types of blood vessels?
arteries
veins
capillaries
Larger hearts allow for more intense exercise.
True or false
true
which horse has the largest heart?
Thorough Bread
Cardiac output equation
Cardiac output (Q)=stroke volume (SV) x HR
Where does the most oxygen go?
The muscles
Maximum O2 uptake
VO2max
Muscular systems functions are…
Oxygen uptake
lactate
Exercise and training
What are the muscular fiber classifications?
Type 1- slow, pasture
Type 2- Face/jumping, contraction speed
What is lactate?
energy-ATP production without oxygen
What are the effects of the condition in muscles?
Increased capillarization
increased transit time
increased oxidative capacity
increased capacity to use fat as fuel
increased myoglobin
Increased glycogen
Increased anaerobic muscle enzymes.
What are the pathways to get ATP?
Aerobic
Anaerobic
What are the important electrolytes?
NA and CI
How much chemical energy is converted to work?
25%
75% heat
How does exercising help bones?
remodeling
repair
Daily ingestion of potassium is what?
4000 mmol-150g
How much potassium is lost from sweat?
1.6g/l
What are some training Principles?
Objectives
Specificity
Intesnsity
Frequency
Length
Volume
What are exercises testing?
lactate threshold
heart rate