Honors Biology Final Exam
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Microscope
A tool that uses lenses to magnify small objects, making them appear larger and easier to study.
10x Lens
This is the low-power objective lens, offering a magnification of 10x. With a 10x eyepiece, the total magnification is 100x.
4x Lens
This is the scanning objective lens, providing the lowest magnification (4x). When combined with a 10x eyepiece, the total magnification is 40x.
40x Lens
This is the high-power objective lens, providing a magnification of 40x. When used with a 10x eyepiece, the total magnification is 400x.
Coarse Adjustment Knob
A big knob on a microscope that moves the stage up and down to help focus the image. You use the coarse adjustment knob only with the low-power objective lens to get the object roughly into focus.
Fine Adjustment Knob
A small knob on a microscope that makes tiny changes to focus the image clearly. You use the fine adjustment knob with medium and high-power objective lenses to sharpen the image after using the coarse knob.
What is Proper Handling for Microscope
Carrying it with both hands, one on the arm and the other under the base, to prevent damage.
Biomolecule
A molecule that is produced by a living organism.
Macromolecule
A molecule containing a very large number of atoms, such as a protein, nucleic acid, or synthetic polymer.
Carbohydrates
A type of molecule, mainly sugars and starches, that our bodies use for energy
Nucleic acids
Vital biomolecules that store and transmit genetic information in all living organisms. (DNA, RNA)
Proteins
Nutrients the body uses to build and maintain its cells and tissues.
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Cell theory
Fundamental concept of biology that states that all living things are composed of cells; the cell is the basic unit of life, and all cells come from pre-existing cells.
Eukaryotic cell
Cells that contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
Prokaryotic cell
A simple, single-celled organism lacking a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
Plant cell
eukaryotic cells that make their own food through photosynthesis.
Animal cell
the fundamental units of life for animals
Nucleus
Control center of the cell. The structure in a cell that contains the chromosomes. The nucleus has a membrane around it, and is where RNA is made from the DNA in the chromosomes.
Cell membrane
The semipermeable membrane surrounding the cytoplasm of a cell. Thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
Cytoplasm
the watery, jelly-like substance inside a cell, surrounding the nucleus and containing all the cell's organelles.
Vacuole
a membrane-bound sac within a cell that serves various functions, including storage, waste disposal, and maintaining cell structure.
Lysosome
Membrane-enclosed organelles that contain an array of enzymes capable of breaking down all types of biological polymers—proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Cytoskeleton
A network of protein fibers within a cell that provides structural support, enables cell movement, and organizes the cell's internal components.
Centriole
a small, tube-like structure found in animal cells that helps organize spindle fibers during cell division.
Ribosome
small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm in all cells, they make proteins.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
a internal membrane system of membranes inside a cell through which proteins and other molecules move; Eukaryotic cells contain this.
Golgi apparatus
organelle in eukaryotic cells that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials from the endoplasmic reticulum for storage in the cell or release outside the cell.
chloroplasts
Organelles that capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell.
mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production, usually found in large numbers.
cell wall
A strong supporting layer around the membrane produced by many cells including most prokaryotes.
phospholipid bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up cell membranes.
hydrophilic
water loving
hydrophobic
water hating
fluid mosaic
A model that describes the cell membrane as a flexible layer made of many small parts, like proteins and lipids, that move around.
selective permeability
A property of a plasma membrane that allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
membrane proteins
proteins that are either partially or completely embedded within, or attached to, the cell membrane or the membranes of organelles within a cell.
Cell Transport
the movement of molecules, ions, and other substances across the cell membrane.
Active transport
The movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration
Passive transport
A type of membrane transport that does not require energy to move substances across cell membranes.
Diffusion
The process by which particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
Simple diffusion
a passive transport mechanism where substances move across a membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, driven by the concentration gradient.
facilitated diffusion
This process, in which molecules that cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels.
Osmosis
The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane.
Aquaporin
Water channel proteins that facilitate the rapid transport of water across cell membranes.
isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution. The cell stays the same.
hypertonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is greater than that of the cell that resides in the solution, causing the cell to shrink.
hypotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is less than that of the cell that resides in the solution, causing the cell to swell and possibly burst.
protein pump
Transmembrane proteins that actively transport molecules across cell membranes against concentration or electrochemical gradients.
Bulk transport
The movement of large molecules, particles, or fluids across the cell membrane.
endocytosis
A process that moves substances into a cell by engulfing them with the cell membrane.
phagocytosis
A process where cells engulf and digest solid particles like bacteria, dead cells, or foreign debris, acting as a crucial defense mechanism for the body.
Pinocytosis
A process by which the cell takes in the fluids along with dissolved small molecules.
exocytosis
A process for moving large molecules out of the cell to the cell exterior.
Homeostasis
mechanism that maintains a stable internal environment despite the changes present in the external environment.
cell specialization
the process in which cells develop in different ways to perform different tasks
Cell
Basic unit of life
Tissue
A group of similar cells that perform a particular function
Organ
Groups of tissue working together
Organ system
a group of organs that work together to perform a specific function in an organism's body.
Cellular Energy
the energy that cells utilize to perform their various functions, effectively powering all biological processes within an organism.
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants use sunlight to produce food (glucose) from carbon dioxide and water.
Respiration
the process by which cells break down food (usually glucose) to release energy.
Inputs for Photosynthesis
carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and sunlight.
Outputs for Photosynthesis
glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2).
Inputs for Respiration
glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2).
Outputs for Respiration
carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and energy in the form of ATP.
ATP
a molecule that stores and provides energy for cells to use.
Chlorophyll
the green pigment in plants that helps them absorb sunlight to make food through photosynthesis.
Thylakoids
flattened membrane sacs inside chloroplasts where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis happen
Stroma
the fluid-filled space inside a chloroplast that surrounds the thylakoids, where the light-independent (Calvin cycle) reactions of photosynthesis take place.
Light dependent reaction
the part of photosynthesis that uses sunlight to make energy-rich molecules like ATP and NADPH, and it also produces oxygen.
light independent reactions
the part of photosynthesis that use energy from ATP and NADPH to make glucose from carbon dioxide. These reactions don't need light to happen.
Glycolysis
the process where glucose is broken down into two smaller molecules called pyruvate, producing a small amount of energy (ATP) without needing oxygen.
Krebs cycle
a process in cellular respiration where pyruvate is broken down to produce energy carriers (like NADH and FADH2) that help make lots of ATP. It happens inside the mitochondria and needs oxygen.
Electron transport chain
a series of proteins in the mitochondria that use electrons from energy carriers to make a lot of ATP.
Aerobic
requires oxygen
anaerobic
does not require oxygen
Fermentation
a process cells use to make energy without oxygen, producing less energy and sometimes creating byproducts like lactic acid or alcohol.
lactic acid fermentation
a process where cells produce energy without oxygen and create lactic acid as a byproduct.
alcoholic fermentation
a process where cells make energy without oxygen and produce alcohol and carbon dioxide as byproducts.
Cell Cycle
the series of stages a cell goes through to grow and divide into two new cells.
Cell division
the process where one cell splits into two new cells.
Mitosis
the part of the cell cycle where the cell's nucleus divides, creating two identical nuclei for the new cells.
Asexual reproduction
when an organism creates offspring without needing a partner, producing genetically identical copies.
Sexual reproduction
when two parents combine their genetic material to create offspring that are genetically different from both parents.
Chromosomes
tightly coiled structures made of DNA that carry genetic information, especially visible during cell division.
chromatin
the loose, uncoiled form of DNA found in the nucleus when the cell is not dividing.
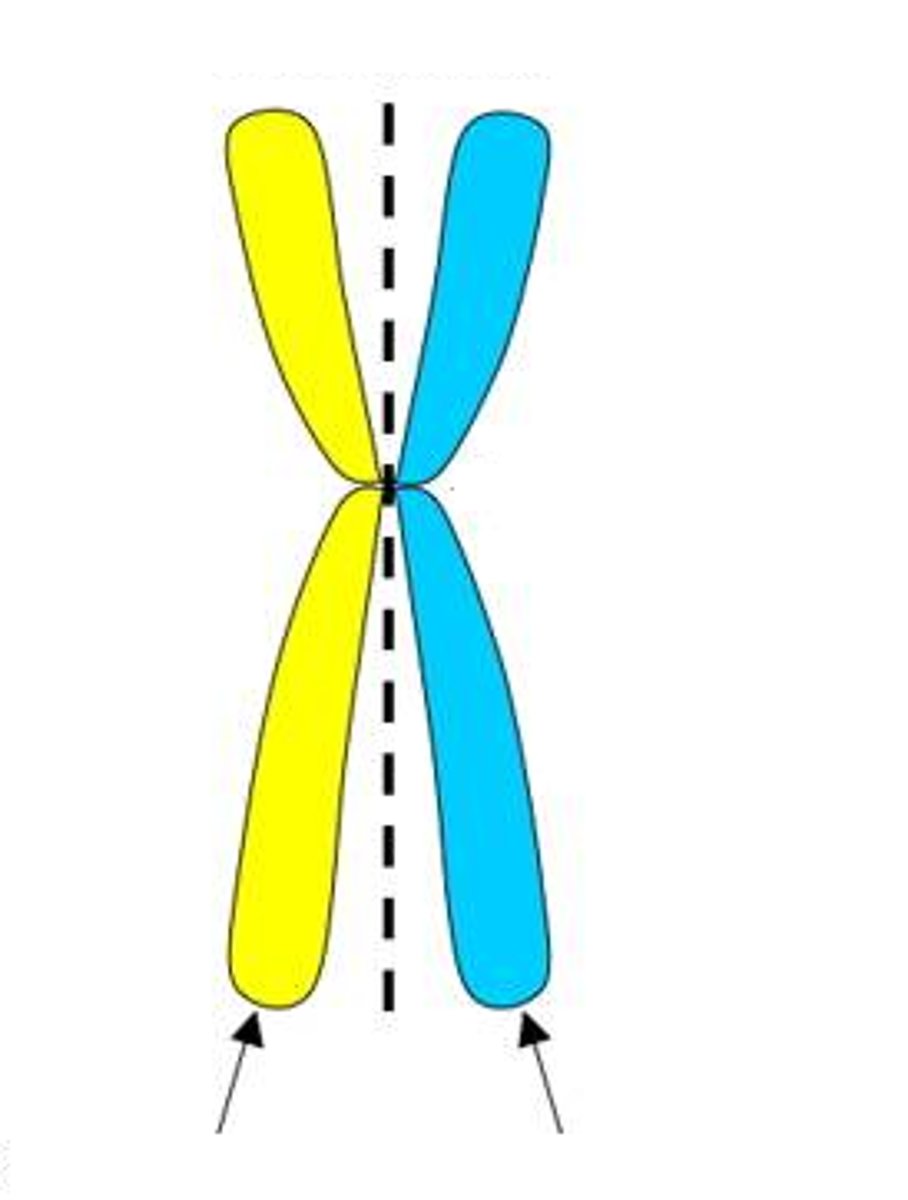
chromatid
one half of a duplicated chromosome, joined to its sister by a centromere.
Interphase
the phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows, copies its DNA, and prepares for division. It includes G1, S, and G2 phases.
Interphase G1 Phase
the first growth phase of the cell cycle, where the cell grows and carries out normal functions.
Interphase Synthesis Phase
the part of the cell cycle where the cell copies its DNA to prepare for division.
Interphase G2
the final part of interphase when the cell grows more, makes final preparations, and checks for any DNA errors before mitosis.
prophase
the first stage of mitosis when chromosomes condense, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and spindle fibers begin to form.
metaphase
the stage of mitosis when chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell, preparing to be separated.
anaphase
the stage of mitosis when the sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell.
telophase
the final stage of mitosis when the chromosomes uncoil, new nuclear membranes form, and the cell prepares to split.
cytokinesis
the final step of cell division where the cytoplasm splits, creating two separate cells.
Centromere
the part of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids are held together and where spindle fibers attach during cell division.
centrosome
the area in a cell where spindle fibers are organized, and it contains a pair of centrioles in animal cells.