biology topic 1
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Are branched or unbranched polysaccharides more easily broken down and why?
Branched, terminal ends easier to be hydrolysed
What polymer in starch has a helix spiral shape and why
Amylopectin as this makes it more compact making it more suitable for storage
What polysaccharide, amylopectin, amylose or glycogen have alpha glucose molecules?
All
Which one of the 3 has 1,6 glycosidic bonds as well as 1,4
Amylopectin and glycogen
What is more branched amylopectin or glycogen and why is it beneficial in animals
Glycogen as it has more terminal ends for QUICK hydrolysis and fast energy release, animals are very metabolically active so CAN SUIT THE DEMANDS of the cell
What are the 2 functions of polysaccharides?
Storage- energy, structural-cell wall
How is glycogen present in the liver/muscles
Visible granules, high respiration rate
Are lipids soluble or insoluble
Soluble in everything but organic solvents (alcohol)
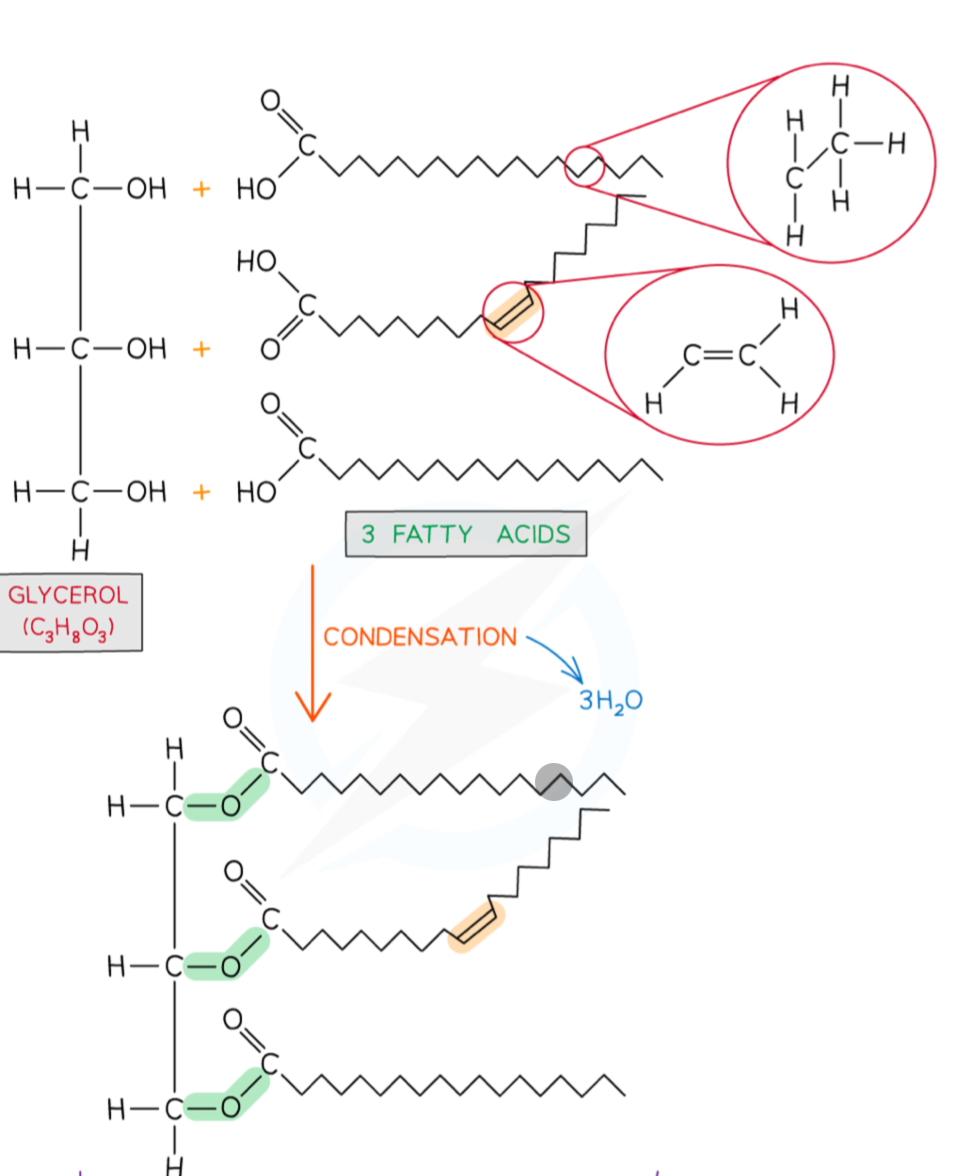
What are the monomers of a triglyceride?
Glycerol and 3 fatty acids
Functions of lipids
Fats and oils which can be used for energy storage, insulation and buoyancy, hormonal communication
Where are saturated and unsaturated fats from
Saturated- animal fat
Unsaturated- vegetable oil
Why are trans fatty acids bad
Can’t form ESC’s, can’t be metabolised,
Creates kink in hydrocarbon chain, can pack as compactly
weak intermolecular forces, liquid at RTP- low mp
How are triglycerides formed
By esterfication in a condensation reaction- 3 H20 molecules formed
Draw the formation of a triglyceride
What is a risk factor
Factor that increases the CHANCE of developing a particular disease
What’s is the incidence of a disease?
Increase presence of a risk factor increases incidence of a disease
Number of cases of a disease that occur within a particular group within a given time
Do HDL’s contain unsaturated or saturated fat?
Unsaturated fat
What is the role of HDL
Reduce blood cholesterol levels when they’re too high
Carry cholesterol to liver to be broken down and excreted REDUCING blood cholesterol levels
What do you need to reduce the risk of CHD to do with lipids
A healthy ratio of LDL:HDL
3:1 max 5:1
What are things definitely needed when studying the risk factor of a disease
sample size- large, more representative
Individuals in the sample- can only draw conclusions about those included in the sample
Control group- to ensure no other factors are impacting the results
Statistical significance- large differences between groups to to ensure its not random chance
Influence of other variables
How to tell if groups are significantly differnet
If standard deviations overlap- not significantly different
If standard deviations do not overlap- significantly different
What is a causation
When 1 variable directly produces an effect in another variable
What’s a correlation
When 2 variables change in relation to each other but one doesn’t cause the other
How is diet a lifestyle factor associated with CVD
A diet high in saturated fats increase blood cholesterol levels, increasing chance of atheroma formation
High salt increases blood pressure
How High blood pressure associated w CVD risk
Increase risk of artery wall damage, increase atheroma formation, increasing thrombosis
Causes of high blood pressure
Stress, alcohol, poor diet
How is smoking associated w cvd risk
Carbon monoxide reduces haemoglobin oxygen carrying activity, decreased volume of oxygen going to cells, decreasing rate of respiration to cells
How are genetics associated with cvd risk
Inherited alleles more prone to high bp or high cholesterol
How is age associated with increased risk
As age increases blood vessels become more fragile increasing extent of damage and atheroma formation more likely
How is biological sex associated with CVD
Men more likely yto suffer due to lower oestrogen hormone levels, which increases levels of HDL in blood
How has education to public decreased risk factors of CBD with diet
Food labels with traffic light warnings, people can make more informed decisions about what they’re eating
How can healthcare professionals identify obesity in patients
Waist to hip ratio,
BMI
So obese individuals can make lifestyle choices to reduce their weight
How have they tried to decrease smoking as a risk factors
Advertising, health warnings existing on all packets free prescriptions to stop individuals from smoking
How have they tried to reduce lack of execrise as a risk factor
Increased hours of physical education in schools
Initiatives to encourage exercise
What is the type of drug used to lower blood cholesterol for CVD patients and how does it do this
Statins
Inhibits enzyme in liver that produces ldl
Reducing ratio of LDL:HDL in blood
Reducing atheroma formation
Red cutting risk of arteries narrowing and atherosclerosis development
What are the side effects of statins
Tiredness, nausea, diarrhoea, muscle weakness
People may start to neglect a healthy diet
How does ACE antihypertensives reduce BP
Blocks ACE production, reducing arterial constriction and lowering BP
How do anticoagulants help with CVD
Reduce risk of blood clot formation
What are side effects of ACE’s
Dizziness, abnormal heart rhythm, impaired kidney function
How do calcium Channel blockers help CVD
Disrupt ca2+ ion movement through calcium channels in the cell membrane, reduce muscle contraction, increases diameter of arteries, reduces force of heart beat and lowers blood pressure
How do diuretics work as a antihypertensive
Increase volume of urine, increasing volume of Na and water in body, decreasing blood volume, decreasing blood pressure
What are symptoms of diuretics
Occasional dizziness, nausea and muscle cramps
Symptoms of calcium channel blockers
Headaches, dizziness, swollen ankles, constipation
Risks of anticoagulants
Uncontrolled bleeding, possible internal bleeding
Differences between calcium blockers and ACE inhibitors
Similarities- both lower blood pressure
Differences- ACE block ace oriction reducing artery restriction increasing diameter fo arteries whereas CCB- prevent calcium from entering heart muscles, increasing diameter of arteries
How does aspirin reduce blood clot formation
Make platelets less sticky, and they’re unable to form a platelet plug
What are the side effects of aspirin
Irritates the stomach lining causing stomach bleeding
What is both aspirin and warfarin
An anticoagulant
Differentiate between warfarin and aspirin
Warfarin blocks the formation of clotting factors in the liver, aspirin make platelets less sticky reducing their their ability to stick together
What is the surgical method to treat CVD
Balloon and stent
How does the process of a stent being inserted work
A catheter is inserted into an artery, usually in the groin
Using a catheter the stent is guided to the artery
The balloon is inflated and the artery expands around it
This pushes on the atheroma and widens the artery restoring blood flow
The catheter is removed leaving behind the stent to keep the artery open
Do LDLS contain saturated or unsaturated fat
Saturated fat
What is the role of LDL’s and how
Increase blood cholesterol levels when its too low
Bind to receptors on cell surface membranes, allowing it to be taken up by the cell from blood
What are issues of high levels of LDL
can block ember and receptors increasing blood cholesterol
Can lead to formation of plague/ atheroma or action
Why are lipids better storage molecules than carbohydrates
Lower proportion of oxygen
Comparison of unsaturated sand saturated fats
They both have hydrocarbon tails
They both have a carboxyl grouP
Saturn’s has more h atoms
Unsaturated has more c=c bonds
Unsaturated can have kinked chains
How can alcohol control Ute to CVD
Alcohol can increase heart rate/bp
Can strain artery walls, increased risk of atheroma formation - thrombosis
Features of a glycosidic bond
Formed from 2 OH groups
Strong covalent bind
Links to ether c1,6, 1,4
Acts as a bridge via 1 oxygen atom