Chemistry 4CH1 Flashcards (Paper 1 and 2)
1/220
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Paper 2 questions are indicated and are being added (search paper 2 to get questions from paper 2 only)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
221 Terms
Common salts of _________, ________ and _______ are soluble.
Sodium, potassium and ammonium. (In any order)
All nitrates are _________.
Soluble
Common chlorides are ______ except for ________ and ______________.
Common chlorides are soluble except for silver chloride and Lead (II) chloride.
Common sulfates are ________ except for ________, _______ and _______.
Soluble, except for Lead (II), Barium and calcium sulfate.
Common carbonates are _____ except for _______,_________ and ________.
Insoluble, except for sodium, potassium and ammonium.
Common hydroxides are _______ except for _______,________ and __________
insoluble except for sodium, potassium and calcium.
How to make lead sulfate? (5)
Add a spatula of lead nitrate to a test tube and add deionized water to dissolve it.
Shake thoroughly to dissolve all of the lead nitrate.
In a separate test tube, repeat this process but with one spatula of magnesium sulfate.
Tip both the solutions into a beaker, a precipitate of lead sulfate should form. Use filter paper, folded into a filter funnel, and stick it inside a conical flask.
Pour the contents of the beaker into the middle of the filter paper and the solution shouldn’t go above the filter paper because it can dribble down the sides.
Swill the beaker with more deionized water to get all the precipitate out.
Rinse filter paper with deionized water to make sure all magnesium nitrate is washed away.
Scrape the lead sulfate onto fresh filter paper and leave to dry in warm oven or desiccator.
Potassium Flame?
Lilac
Copper flame?
blue-green
Lithium flame?
red
sodium flame?
yellow
calcium flame?
orange-red
iron (III)
reddish brown
Copper (II) precipitate color?
blue
Iron (II)
green
Q: What acid is used to test for carbonates?
A: Dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl).
Q: What gas is released when carbonates react with HCl?
A: Carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Q: How can you confirm the presence of CO₂?
A: By using limewater, which turns cloudy
Q: What two solutions are used to test for sulfate ions?
A: Dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) and barium chloride (BaCl₂).
Q: What indicates a positive test for sulfates?
A: A white precipitate of barium sulfate (BaSO₄).
Q: Why is HCl added before barium chloride?
A: To remove any carbonate or sulfite ions that could interfere with the results.
Q: What two solutions are used to test for halide ions?
A: Dilute nitric acid (HNO₃) and silver nitrate (AgNO₃).
Q: What color precipitate is formed for each halide?
Chloride (Cl⁻):
Bromide (Br⁻):
Iodide (I⁻):
Chloride (Cl⁻): White (AgCl).
Bromide (Br⁻): Cream (AgBr).
Iodide (I⁻): Yellow (AgI).
Q: Why is nitric acid (HNO₃) used instead of hydrochloric acid (HCl)?
A: To remove any interfering carbonate or sulfite ions.
What gas is released when a carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid?
A) Oxygen
B) Hydrogen
C) Carbon dioxide
D) Sulfur dioxide
Answer: C) Carbon dioxide
Which test uses barium chloride solution?
A) Test for carbonates
B) Test for sulfates
C) Test for halides
D) Test for nitrates
Answer: B) Test for sulfates
Which of the following halides forms a yellow precipitate with silver nitrate?
A) Chloride
B) Bromide
C) Iodide
D) Fluoride
Answer: C) Iodide
What is the purpose of adding hydrochloric acid before testing for sulfates?
A) To dissolve the sample
B) To remove carbonate or sulfite ions
C) To create a reaction with silver nitrate
D) To produce carbon dioxide
Answer: B) To remove carbonate or sulfite ions
What acid must be used in the halide test instead of HCl?
A) Sulfuric acid
B) Hydrochloric acid
C) Nitric acid
D) Acetic acid
Answer: C) Nitric acid
Chlorine bleaches damp blue ______ paper, turning it white.
litmus
Oxygen ______ a glowing splint.
relights
Carbon dioxide turns ______ cloudy when bubbled through it.
limewater
Hydrogen produces a ______ sound when tested with a lighted splint.
squeaky pop
Ammonia turns damp ____ litmus paper _______.
red, blue
Chlorine gas initially turns damp blue litmus paper ______ before bleaching it white.
A) Blue
B) Green
C) Red
D) Yellow
Answer: C) Red
How do you test for chlorine gas?
Answer: It bleaches damp blue litmus paper, turning it white.
What gas relights a glowing splint?
Answer: Oxygen.
Describe the test for hydrogen gas.
Answer: A lighted splint produces a ‘squeaky pop’ when exposed to hydrogen.
What gas turns limewater cloudy?
Answer: Carbon dioxide
What gas turns damp red litmus paper blue?
Answer: Ammonia
What turns blue when it comes in contact with water?
Copper (II) sulfate
What is the original color of copper (II) sulfate?
White.
Explain how you test whether water is pure or not.
Pure was boils at 100 degrees and melts at 0 degrees. If the water doesn’t boil and melt at these temperatures, respectively, then it is not pure.
What is an isotope?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons (and electrons) but a different number of neutrons.
Name the following hydrocarbons:
1. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
2. CH3CH2CH2CH3
Pentane
Butane
What is an element? Give an example.
An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom.
An example of an element is Oxygen.
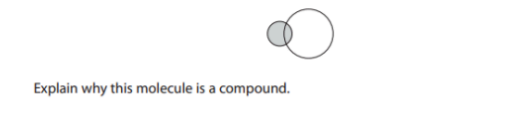
Explain why this molecule is a compound. (2)
It contains two different types of atoms/elements that are chemically bonded together.
Give an example of a compound? (2)
Methane ( CH4). It is made up of one carbon atom and 4 hydrogen atoms.
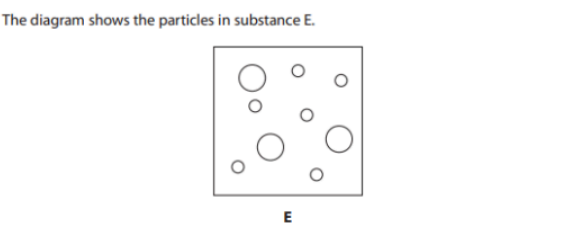
Give two reasons why substance E is a mixture (2)
Two different elements/atoms
They are not chemically bonded together

Each substance may be used once, more than once or not at all.
1) Compound:
2) Mixture:
1) Glucose / water
2) Air
The students has two solids, X and Y.
One solid is a pure substance and the other is a mixture.
Describe how the student could identify which solid is pure and which is a mixture by measuring a physical property of each solid. (3)
M1: Measure the melting point
M2: Fixed/sharp melting point means the substance is pure
M3: If solid melts over a range of temperatures, it is impure and a mixture
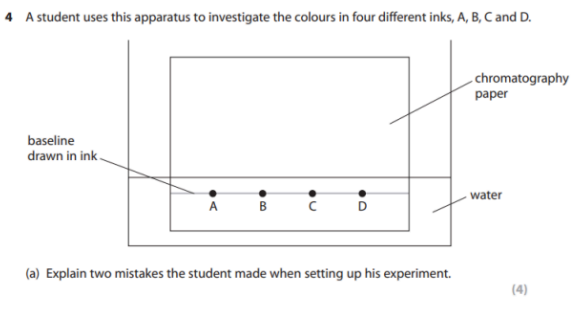
Explain two mistakes the student made while setting up the experiment. (4)
1) M1: The baseline has been drawn in ink
M2: and therefore will interfere with the results
2) M3: The water level is above the ink spots
M4: and hence the inks will mix with the water
How can we see which ink is insoluble in water?
The spot of the ink will not move up the chromatography paper.

Describe how the student should set up and carry out her experiment.
You may draw a diagram to help with your answer. (4)
M1: Put separate spots of ink on the pencil line.
M2: Pour some solvent into the bottom of the beaker
M3: Place the paper in the beaker so that the spots are just above the level of solvent.
M4: Leave until the solvent has risen up the paper to the top.
Why is the line on the chromatography paper drawn in pencil rather than in ink? (2)
M1: Ink would dissolve in the solvent
M2: and will interfere and contaminate the results.
How can we check the solubility of a dye? (1)
Dyes that travel farthest up the paper/closest to the solvent front are the most soluble.
What is the formula for the Rf value?
Distance travelled by solute/Distance traveled by solvent
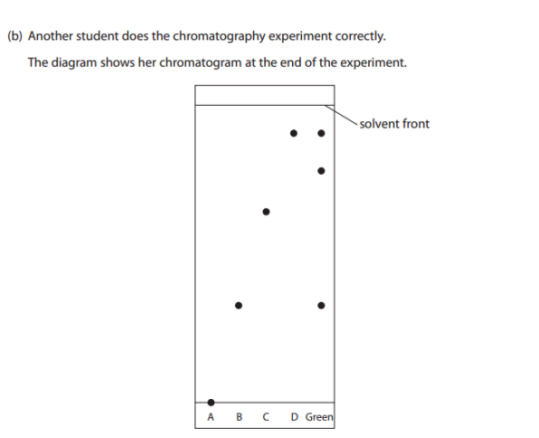
State what the chromatogram shows about the composition of the green food coloring? (3)
M1: Contains dye B and dye D
M2: Contains an unknown dye
M3: Doesn’t contain dye A or C
M4: Contains three dyes

Describe how compound D can be obtained from crude oil using the industrial process of fractional distillation. (4)
M1: Heat/Vaporize crude oil
M2: Pass into fractionating column
M3: Compounds/Molecules/Hydrocarbons separate because of the different boiling points
M4: compound D collected at the top of the column
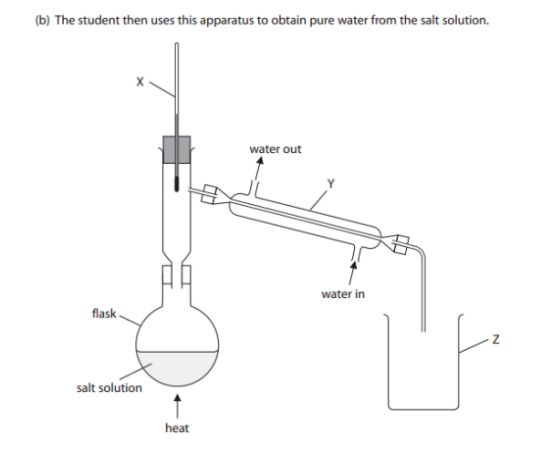
Name apparatus X, Y and Z. (3)
X: Thermometer
Y: (Liebig) Condenser
Z: Beaker
Explain what filtering, simple and fractional distillation are and give an example for each of them. (6)
Filtering:
Filtering is a method used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid by passing the mixture through a filter, which allows the liquid to pass through while trapping the solid.
Example: Separating sand from water using filter paper.
Simple Distillation:
Simple distillation is used to separate a liquid from a solution based on differences in boiling points (only works for substances with really big differences in boiling points, it does not work for similar boiling points).
Example: Separating pure water from saltwater.
Fractional Distillation:
Fractional distillation is used to separate a mixture of liquids with different boiling points (Can work with liquids with similar boiling points too).
Example: Separating ethanol from water or separating crude oil into different fractions like petrol and diesel.
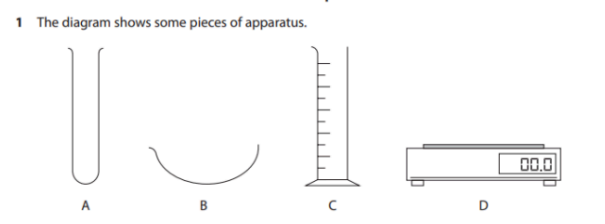
Give the name of each apparatus. (4)
A: Test tube / boiling tube
B: Evaporating dish
C: Measuring cylinder
D: Balance
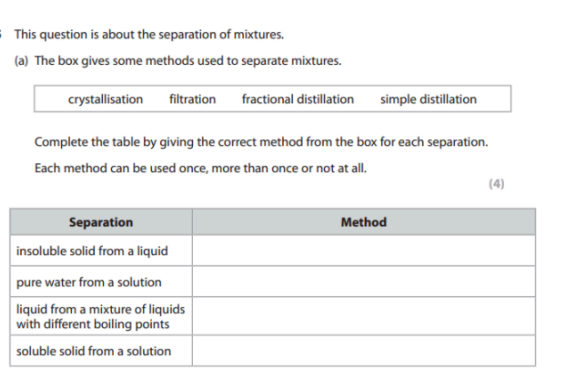
Filtration
Simple distillation
Fractional distillation
Crystallization
Which halogen has the palest color?
Fluorine
Which halogen is a solid at room temperature?
Astatine
An atom element X contains 14 protons, 14 electrons, and 15 neutrons.
Explain which group and period element X belongs to. (4)
It belongs in group 4 because it has the electronic configuration: 2.8.4. So, it has 4 electrons in the outer shell.
It belongs in period 3 because it has 3 electron shells.
State the relationship between the reactivity of group 7 elements and the size of atoms.
M1: As the atoms get bigger
M2: The reactivity decreases.
State the meaning of the term ionic bond. (2)
M1: Electrostatic forces of attraction
M2: between two oppositely charged ions
Explain why lithium chloride has a higher melting point than hydrogen chloride.
Refer to structure and bonding in your answer. (5)
Lithium chloride:
M1: giant ionic structure
M2: strong electrostatic forces of attraction
M3: between oppositely charged ions
Hydrogen chloride:
M4: simple molecular structure
M5: weak intermolecular forces of attraction
M6: more heat energy needed to overcome forces/break bonds in lithium chloride.
Why does potassium sulfate have a high melting point? (4)
M1:Potassium sulfate has a giant ionic structure
M2: Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
M3: these forces are strong
M4: a large amount of energy is needed to overcome the forces and break the bonds
Why does magnesium sulfide have a high melting point? (3)
M1: Strong electrostatic force of attraction
M2: between Mg2+ and S2- (oppositely charged ions)
M3: so a lot of energy is required to overcome forces of attraction and break bonds.
Diamond is a naturally occurring form of carbon that is a giant covalent structure.
Why does diamond have a high melting point? (3)
M1: covalent bonds are strong
M2: many covalent bonds need to be broken
M3: a large amount of energy is required to break the bonds
Explain why graphite is soft and conducts electricity.
Refer to bonding and structure in your answer. (5)
M1: The structure is in layer
M2: There are weak forces of attractions between the layers of atoms
M3: layers can slide over each other (therefore its soft)
M4: each carbon atom is covalently bonded to three other carbon atoms
M5: so one delocalized electron per carbon atom
M6: delocalized electrons flow throughout the structure (therefore graphite conducts electricity.)
Explain why diamond has a much higher melting point than C60 fullerene? Refer to structure and bonding in your answer. (4)
M1: Diamond is a giant covalent structure
M2: (melting diamond) covalent bonds are broken
M3: C60 is a simple molecular structure
M4: (when melting C60) intermolecular forces of attraction are overcome
M5: more energy is needed to break covalent bonds in diamond than intermolecular forces
Explain the different ways magnesium and magnesium chloride conduct electricity. (4)
M1: magnesium has delocalized electrons
M2: electrons can move
M3: magnesium chloride can only conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in solution
M4: ions are free to move in molten and dissolved state but not in solid state
Explain three properties of copper that make it a suitable metal to use in electrical wiring. (6)
M1: conducts electricity
M2: delocalized electrons can move
M3: malleable
M4: layers of cations
M5: slide over each other
M6: high melting point
M7: strong electrostatic forces of attraction between cations and delocalized electrons.
What is the difference between dilution and diffusion?
Dilution is the process of reducing the concentration of a solute in a solution by adding more solvent. The particles of solute move further apart, leading to reduced concentration.
Diffusion is the random movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until both area’s have the same concentration (particles spread out evenly).
Does the ring of ammonium chloride form exactly in the middle of the test tube, if not, why? (2)
The white ring of ammonium chloride forms closer to the hydrochloric acid. This is because ammonia particles are smaller and lighter so they diffuse through the area quicker, so they travel a greater distance therefore meeting closer to the cotton wool soaked in HCl.
Describe what the student would observe when placing a test tube with bromine and a test tube with air opposite to each other and removing the glass plate separating them? (3)
The brown bromine gas will start to gradually diffuse through the air due to the random motion of particles. In the end, both the test tubes will have a light brown color due to the bromine spreading evenly throughout both the test tubes.
Charge and symbol of a silver ion?
Ag +
Symbol and charge of Iron (2)
Fe 2+ and Fe 3+
Symbol and charge of copper
Cu2+
Symbol and charge of lead?
Pb 2+
Charge and symbol of zinc
Zn 2+
Charge and symbol of hydrogen
H +
Charge and symbol of hydroxide?
OH-
Charge and symbol of ammonium
NH 4+
Charge and symbol of carbonate?
CO3 2-
Charge and symbol of nitrate?
NO3 -
Charge and symbol of sulfate?
SO4 2-
Explain why sodium and sodium chloride have different melting points.
In you answer you should refer to
The type of particles
The type of forces between the particle of each substance (5)
positive ions / cations and delocalsed electrons (1)
electrostatic forces (1)
positive an negative ions / cations and anions (1)
electrosatic forces (1)
Forces in Na are weaker (1)
Give the symbol and charge for the following ions.
1. Silver
2. Copper
3. Iron (involves 2)
4. Lead 9. Carbonate
5. Zinc
6. Hydrogen
7. Hydroxide
8. Ammonium
9. Carbonate
10. Nitrate
11. Sulfate
Ag+
Cu2+
Fe2+ Fe3+
Pb2+
Zn2+
H+
OH-
NH4+
CO32-
NO3-
SO42-
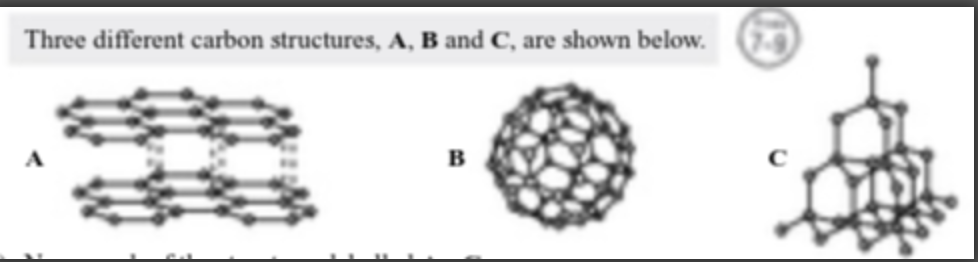
Explain how the bonding in structures A and C affect their conductivity and hardness. (4)
Graphite/structure a can conduct electricity because it contains delocalised electrons that can move around [1 mark].
diamond/structure c doesn't conduct electricity because it doesn't contain any charged particles that can move around [1 mark].
diamond/structure c is hard because the strong covalent bonds hold the atoms in a rigid lattice structure [1 mark].
graphite/structure a is soft, as the layers of graphite are held together by weak intermolecular forces [1 mark].
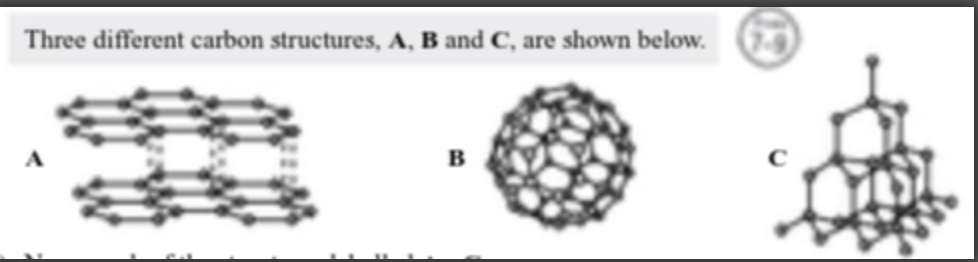
A and B both sublime, explain why B sublimes at a lower temperature than A.
structure B is a simple molecular substance [1 mark]
so only weak intermolecular forces need to be broken to separate the molecules [1 mark].
in order for a to sublime, strong covalent bonds need to be broken, which would require more energy [1 mark].
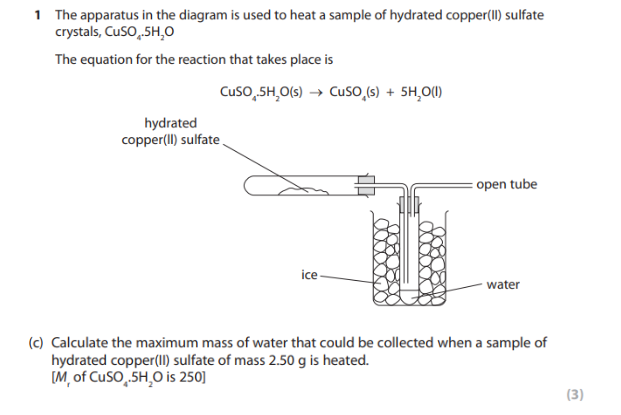
Answer: 0.9g
A student carried out an experiment to calculate the empirical formula of an oxide of iron. She burnt 3.808 g of iron until it had all reacted. She found that the mass of the product was 5.440 g. Ar of Fe = 56, O = 16. What is the empirical formula?
Answer: Fe2O3
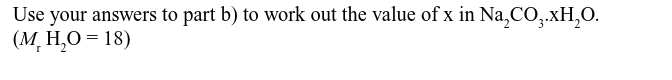
Mass of Na2CO3.xH2O is 7.724 and mass of Na2CO3 is 2.862 g, find the value of x.
x = 10
Sodium reacts violently with fluorine, at room temperature, to form sodium fluoride. Predict how astatine might react with sodium at room temperature. Explain your answer.(4)
Both astatine and fluorine have 7 outer shell electrons so they should react in a similar way [1 mark].
So astatine should react with sodium to form sodium astatide [1 mark].
But astatine would react more slowly than fluorine, as it would be less reactive [1 mark].
This is because it would be more difficult for astatine to attract extra electrons/form ions, as the extra electron would be added to a shell further away from the nucleus [1 mark].
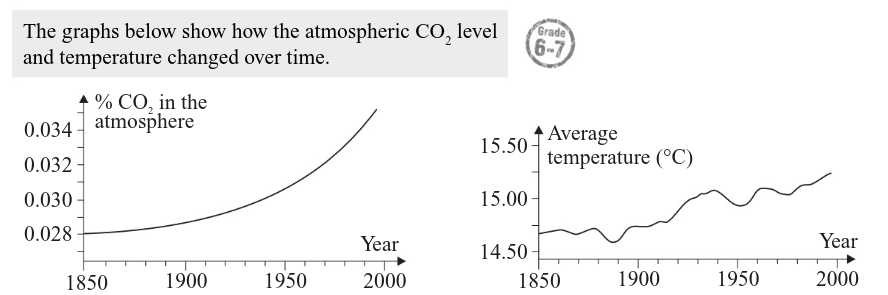
Describe the trends in the data and suggests reasons for them (4)
There was an increase in CO2 in the atmosphere between 1850 and 2000 [1 mark].
This is probably largely due to human activity (e.g. burning fossil fuels/deforestation) [1 mark].
The increase in CO₂ correlates with an increase in temperature over the same time period [1 mark].
The temperature increase is likely due to the increase in CO2 as CO2 is a greenhouse gas/ insulates the Earth
[1 mark].
Explain why it would be difficult to decide the order of reactivity of magnesium and zinc using these experiments. Suggest an experiment that could be used to decide which is more reactive (2)
It is not possible to tell the difference between magnesium and zinc since both have the same reaction with dilute acid (1 mark)
To find which is more reactive we could add zinc to water (1 mark)