Cell Diversity
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Explain cell diversity and its importance in multicellular organisms.
Cell diversity refers to the building blocks of life; varied and versatile. cells are the fundamental units of life. from simple bacteria to complex multicellular organisms.
E.g. Muscle cells adapted to allow movement through contractions.
Tissue (Roles in Animals and Plants)
Groups of similar cells working together that perform specific functions in organisms. Connective tissue supports, connects and separates other tissues. Plant tissue, vascular: transports water, nutrients and sugars.
Examples of tissues (3)
1.Bone tissue
2.Nervous tissue
3.Muscle tissue
Animal Tissue (Epithelial)
Covers surfaces, forms glands.
Animal Tissue (Connective)
Supports, connects, and separates other tissues.
Animal Tissue (Muscle)
Enables movement through contraction.
Animal Tissue (Nervous)
Transmits electrical signals for communication.
Plant Tissue (Diagram)
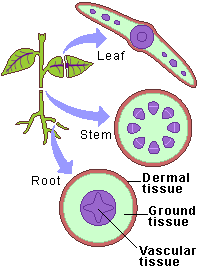
Plant Tissue (Meristematic)
Allows growth through cell division.
Animal Tissue (Ground)
Photosynthesis, storage and metabolic functions.
Plant Tissue (Vascular)
Transports water, nutrients, and sugars.
Plant Tissue (Dermal)
Provides protection and regulates gas exchange.
Functions of Tissues and Organs (Specialized roles in organisms)
Structural Support: Connective tissue provides framework and strength to organs in both plant and animals.
Energy Production: Chloroplasts in plants leaves perform photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy.
Waste Eliminations: Nephrons in animal kidneys filter blood and remove metabolic waste products.
Cell Specialization + Differentiation
Cell specialization or differentiation transforms unspecialized cells into specialized one, enabling them to perform distinct roles. It is crucial for the function of tissues and organs.
Differentiation is vital for…
Growth
Development
Maintenance of complex life
Cell Specialization (Examples)
Root hair cells: Absorb water and nutrients from soil.
Guard cells: Control opening and closing of stomata.
Muscle cells: Contract to enable movement.
Tissue Culture (Definition)
The growth of cells in a sterile nutrient medium outside an organism.
In vitro
Growth in glass
Sterile
No micro-organisms present.
Tissue Culture (Modern Application)
1.Production of pharmaceuticals.
2.Cancer research