Floriculture-Plant ID, Disease, Pests, Prin. of Design
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
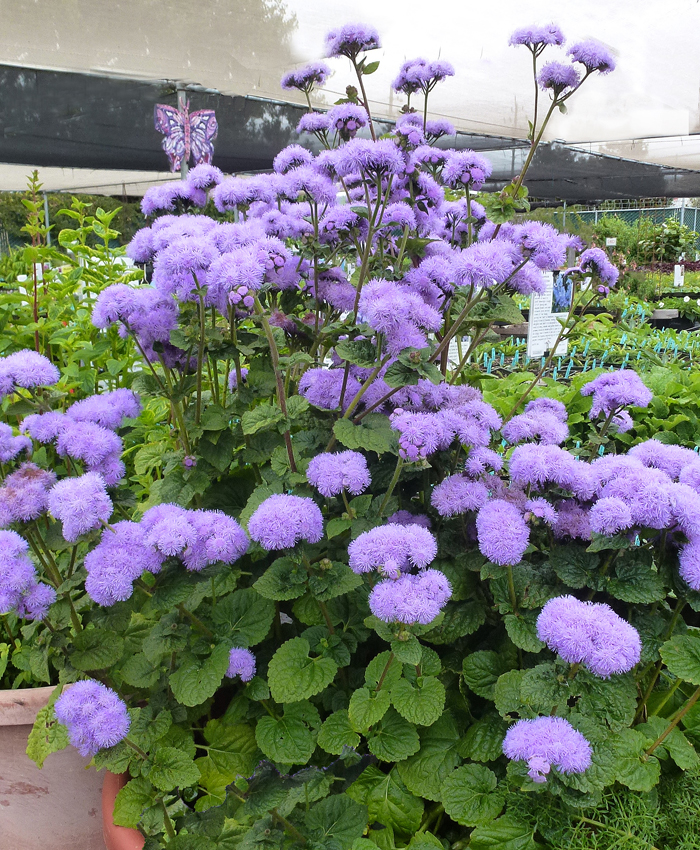
Ageratum/Ageratum houstonianum

Silver Vase Bromeliad/Aechmea faciata

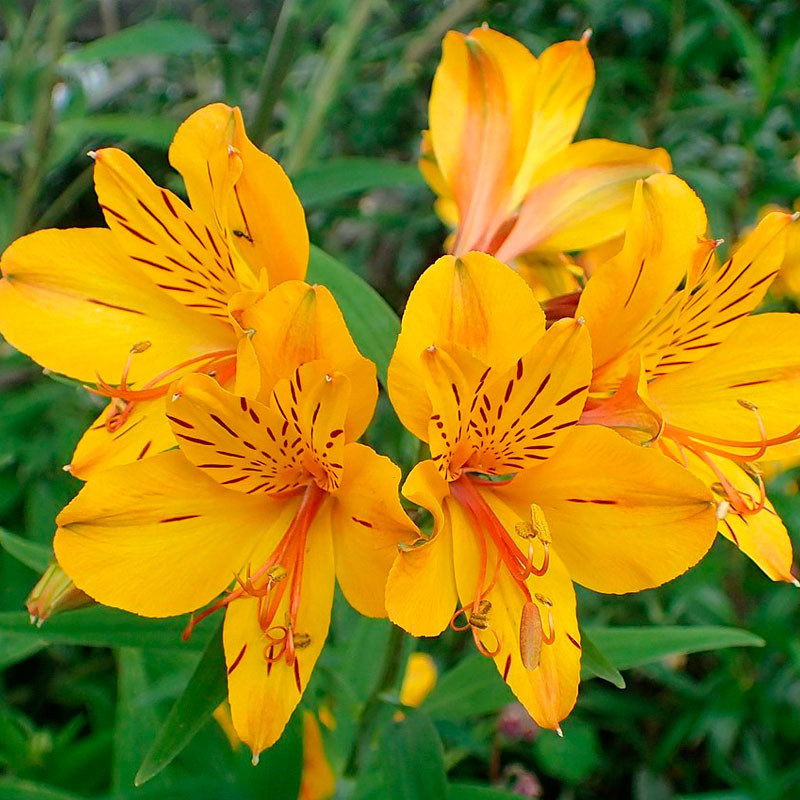
Peruvian lily/Alstroemeria aurantiaca

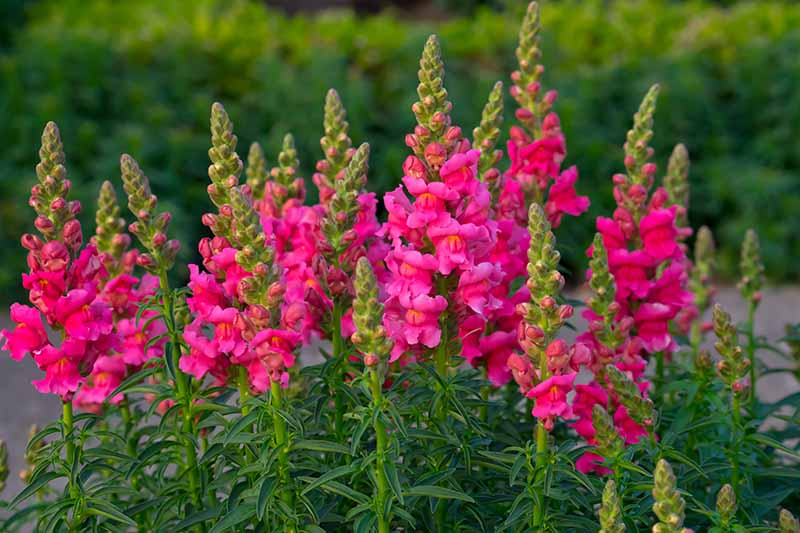
Snapdragon/Antirrhinum majus

Norfolk Island Pine/Araucarie heterophylla

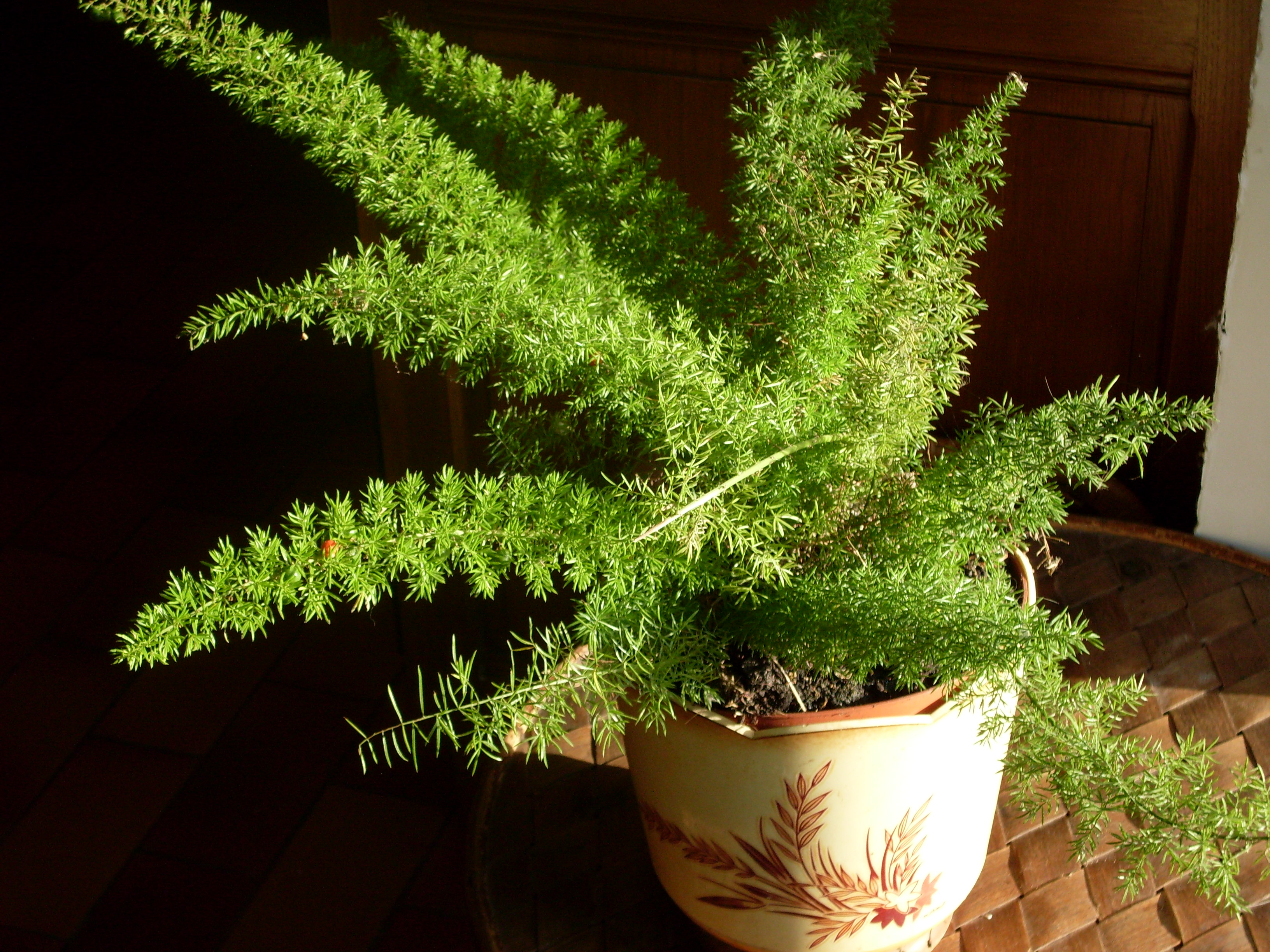
Sprenger’s Asparagus Fern/Asparagus densiflorus ‘Sprengeri’

Wax Begonia/Begonia x semperflorens – cultorum cv.

Octopus Plant/Schefflera arboricola
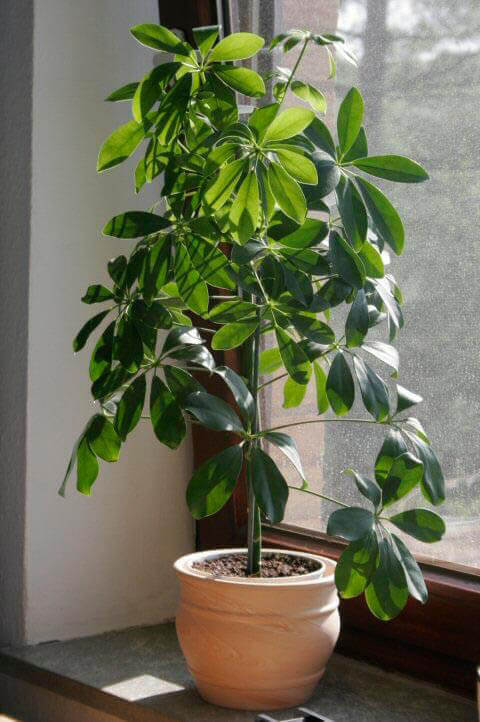

Fancy Leaved Caladium/Caladium x hortulanum

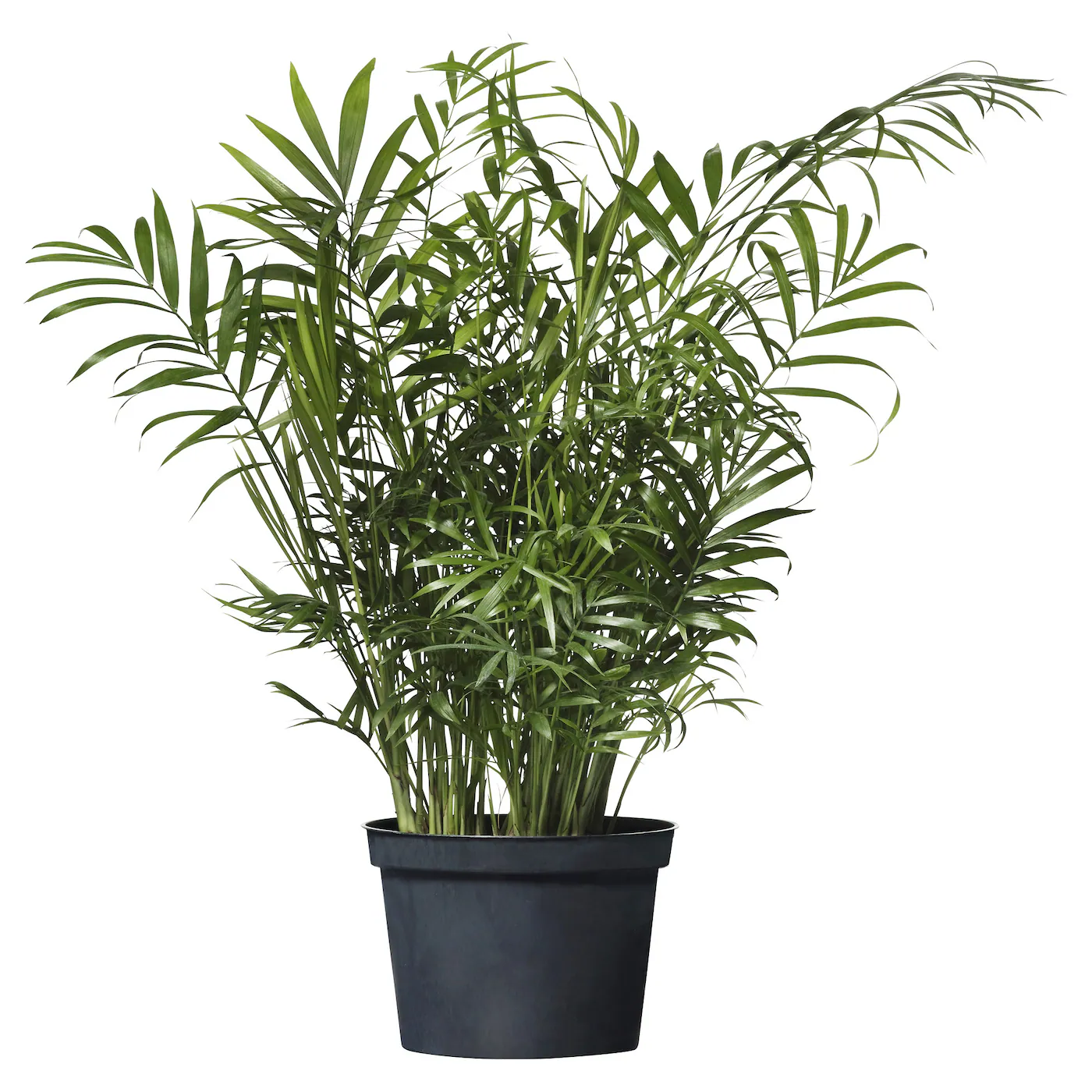
Parlor Palm/Chamaedorea elegans

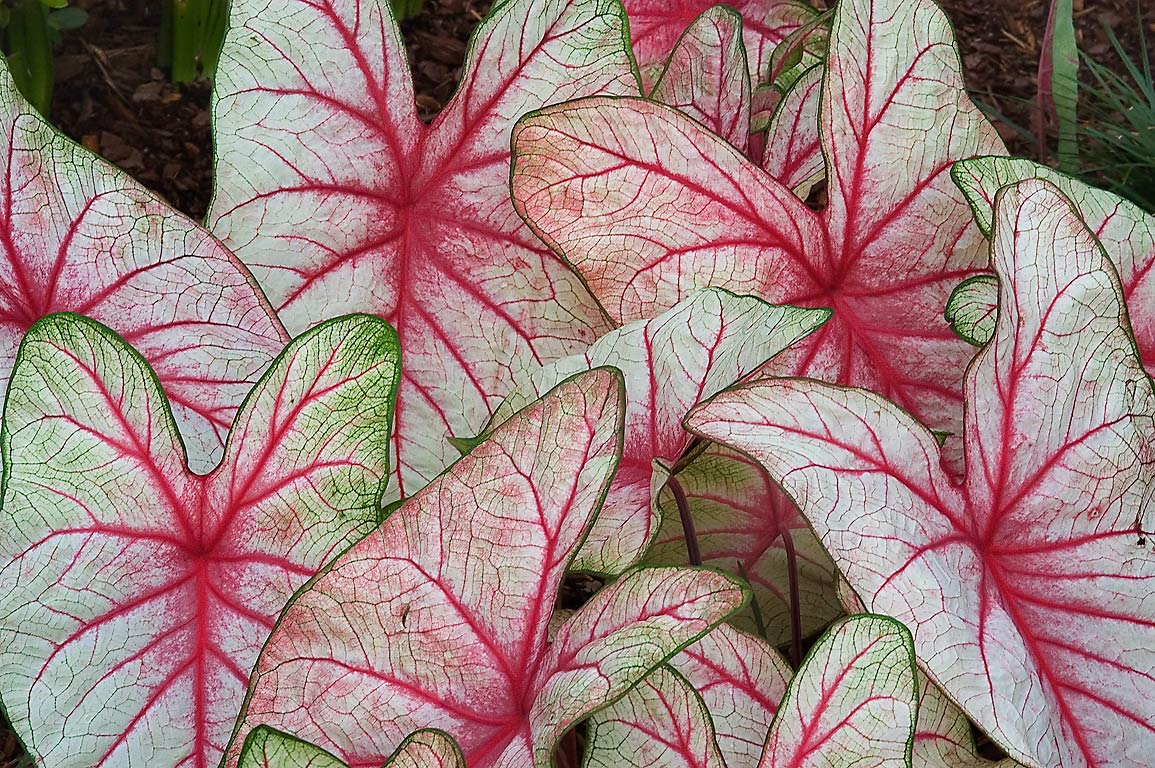
. Cockscomb/Celosia cristata
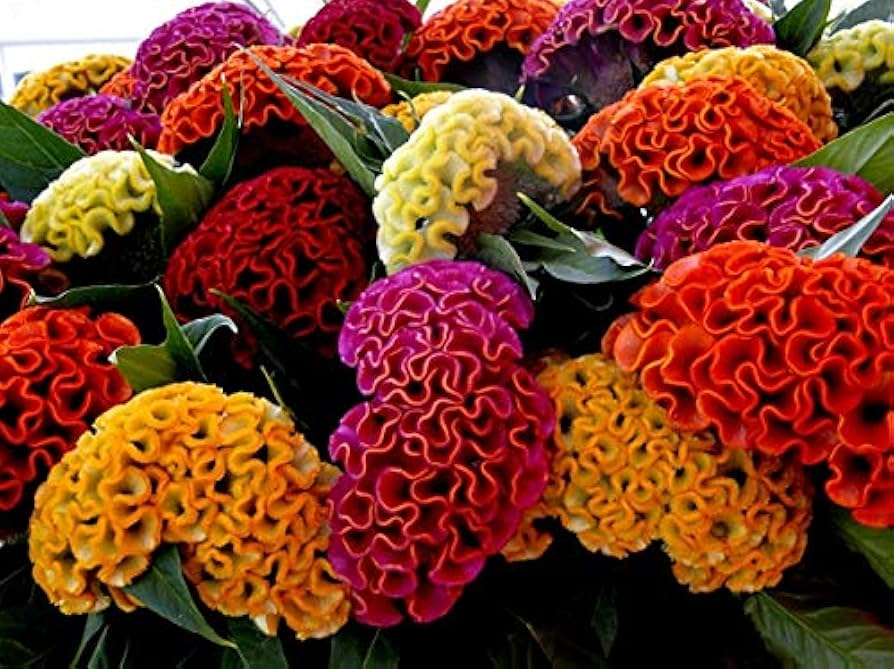

Spider Plant/Chlorophytum comosum

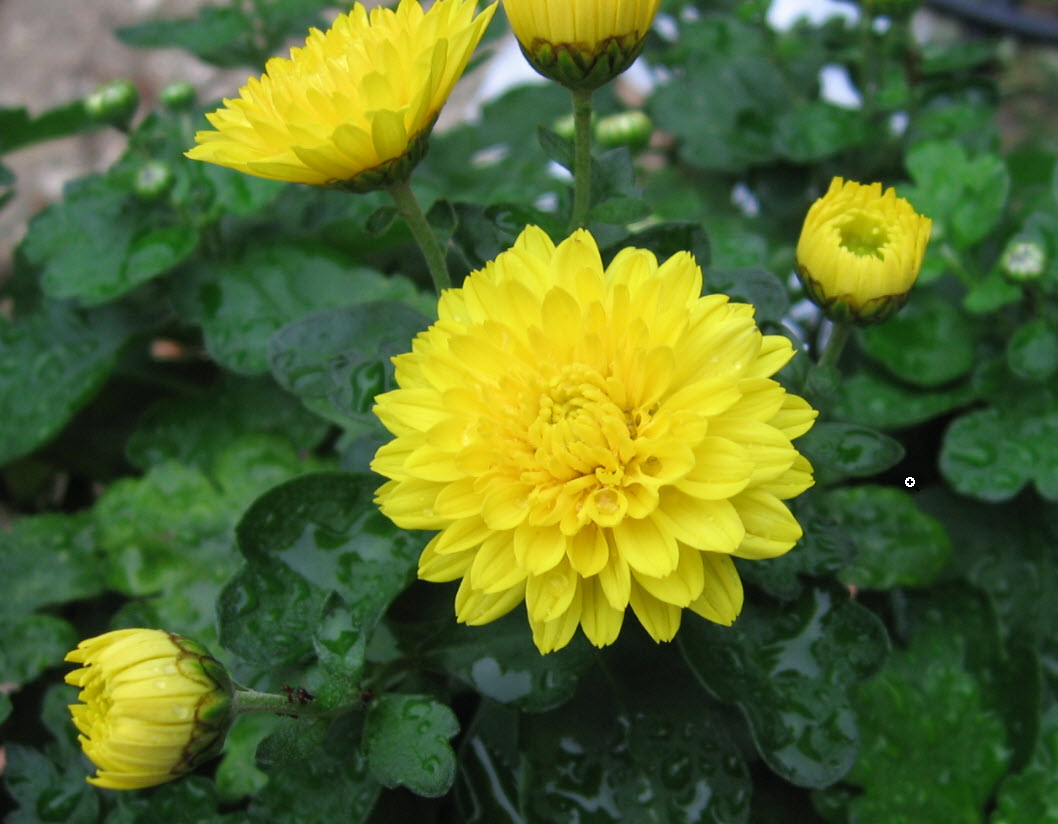
Florist’s Chrysanthemum/Chrysanthemum x morfolium

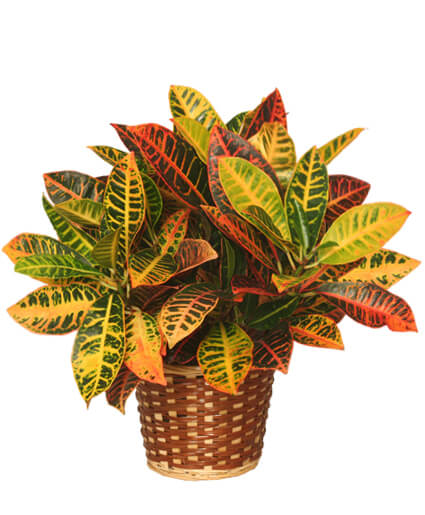
Croton/Codiaeum variegatum pictum

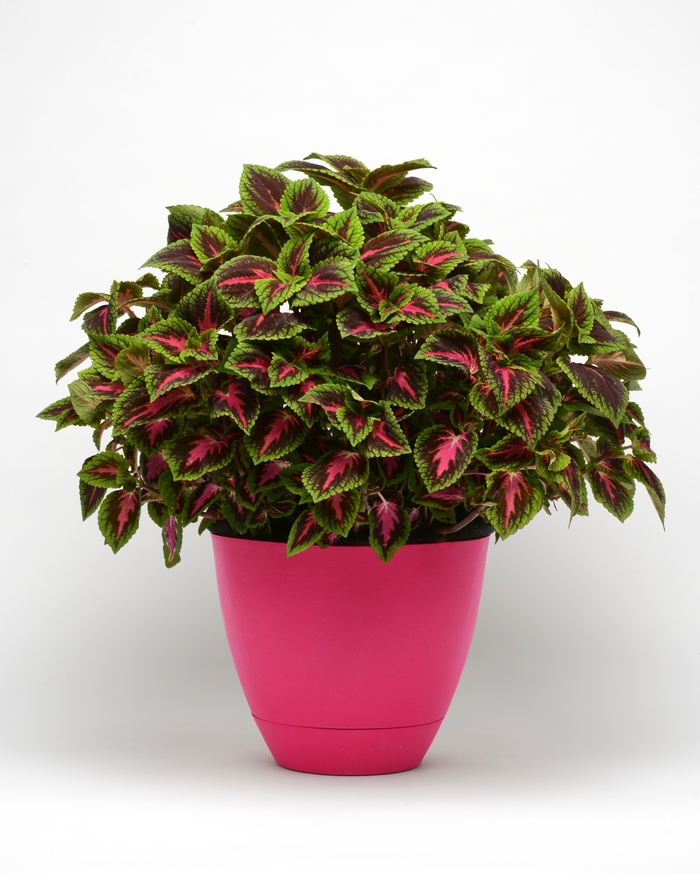
Coleus/Solenostemon scutellariodes

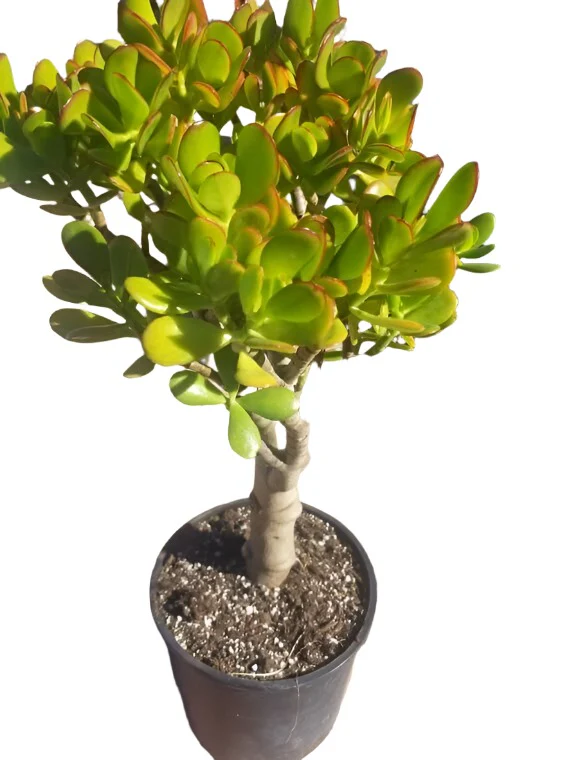
Jade Plant/Crassula argentea

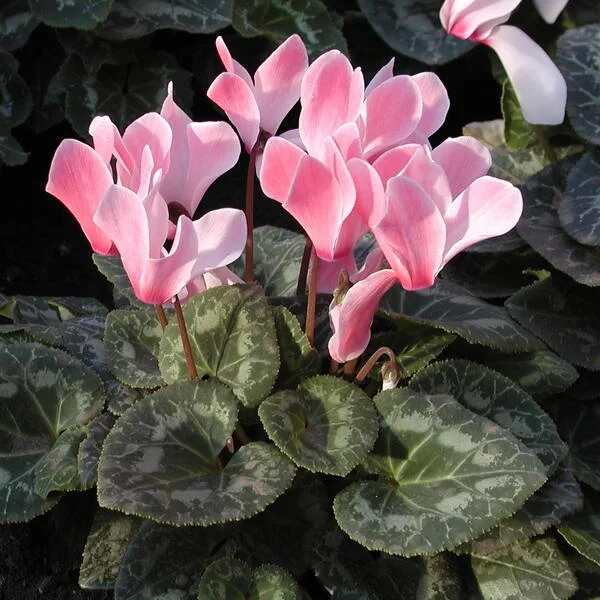
Florist’s Cyclamen/Cyclamen x persicum cv.

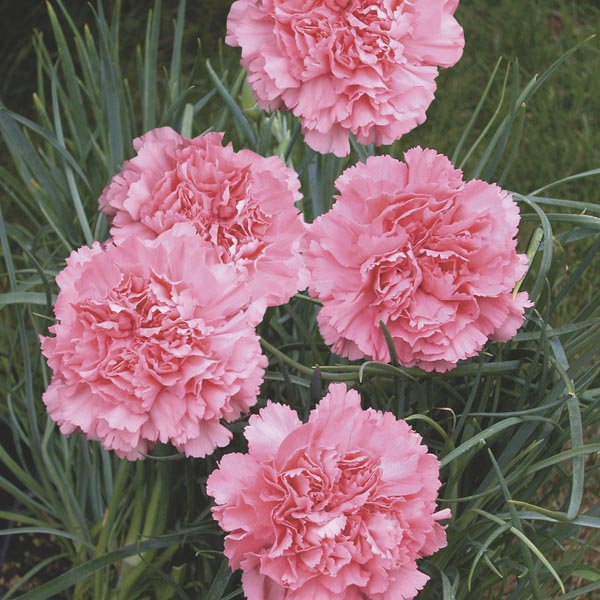
Carnation/Dianthus caryophyllus

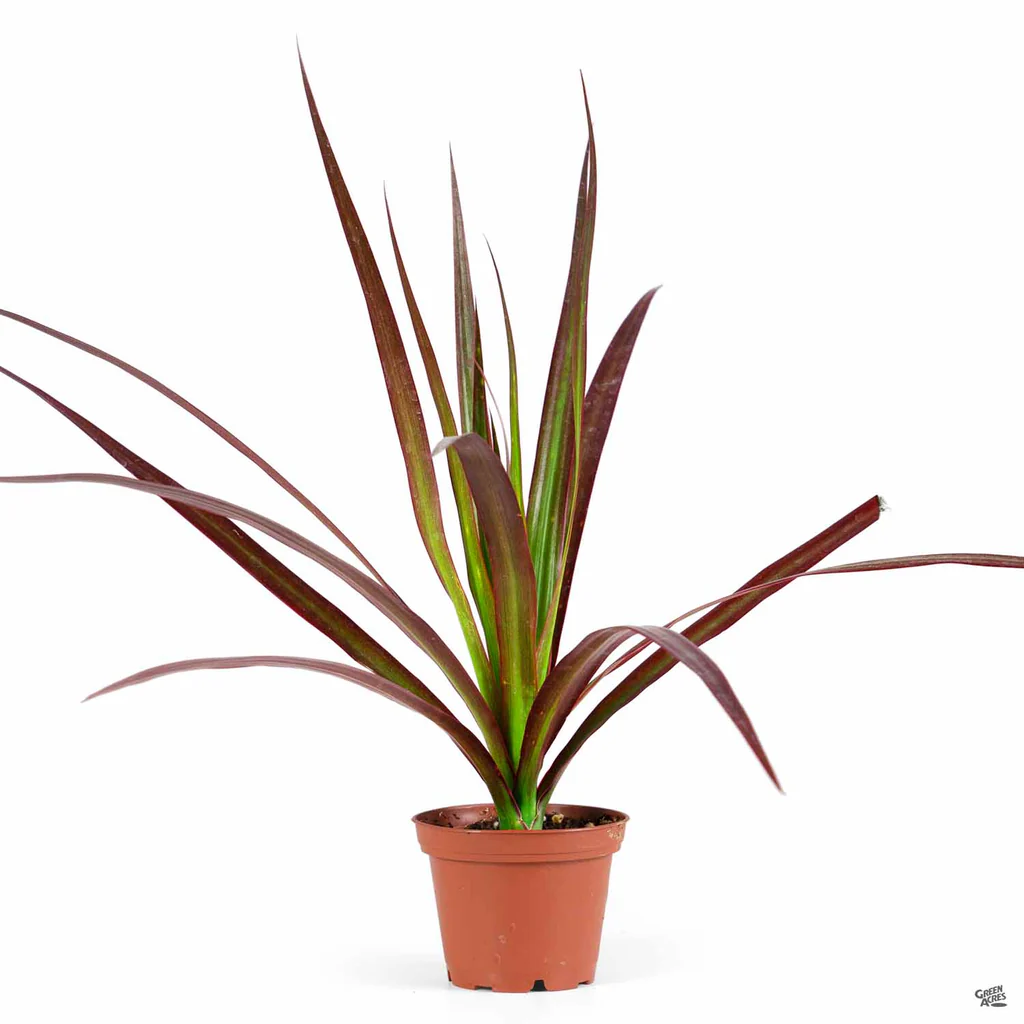
Red Edged Dracana/Dracena cincta

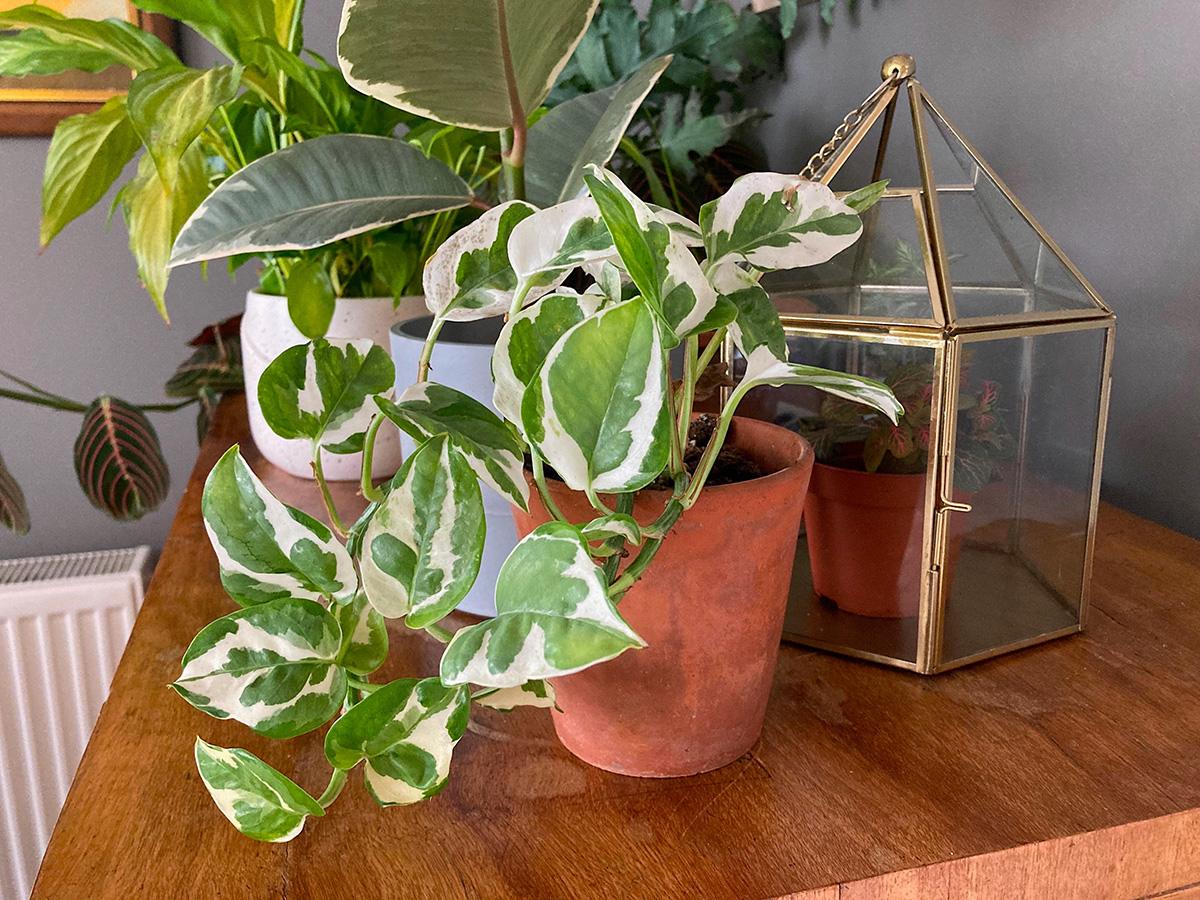
Golden Pothos, Devil’s Ivy/Epipremnum aureaum

Poinsettia/Euphorbia pulcherrima

Benjamin Fig/Ficus benjamina

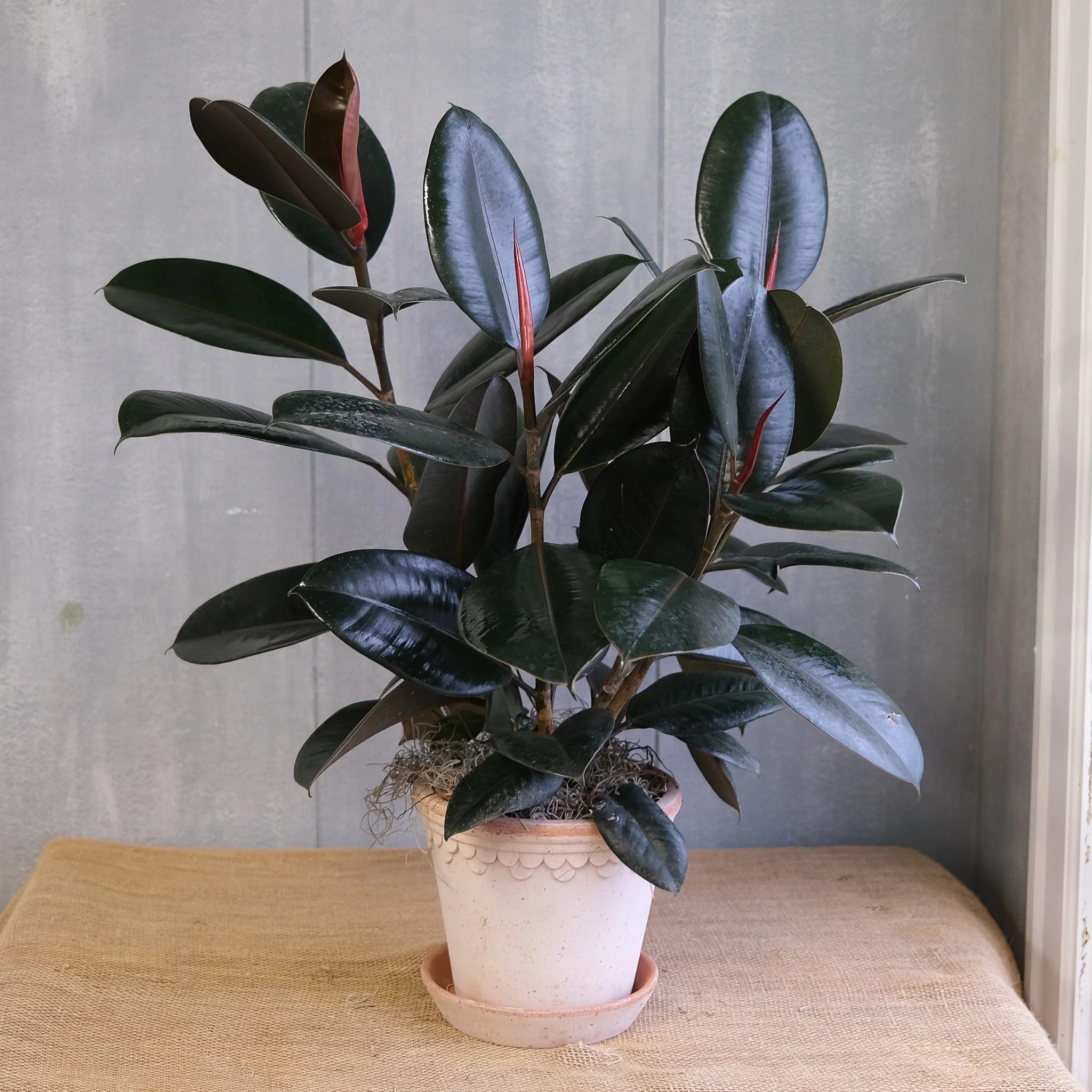
Rubber Plant/Ficus elastica

Peacelily/ Spathiphyllum sp.

Garden Gladiolus/Gladiolus x hortulanus
``

Gerbera Daisy/Gerbera jamesonii

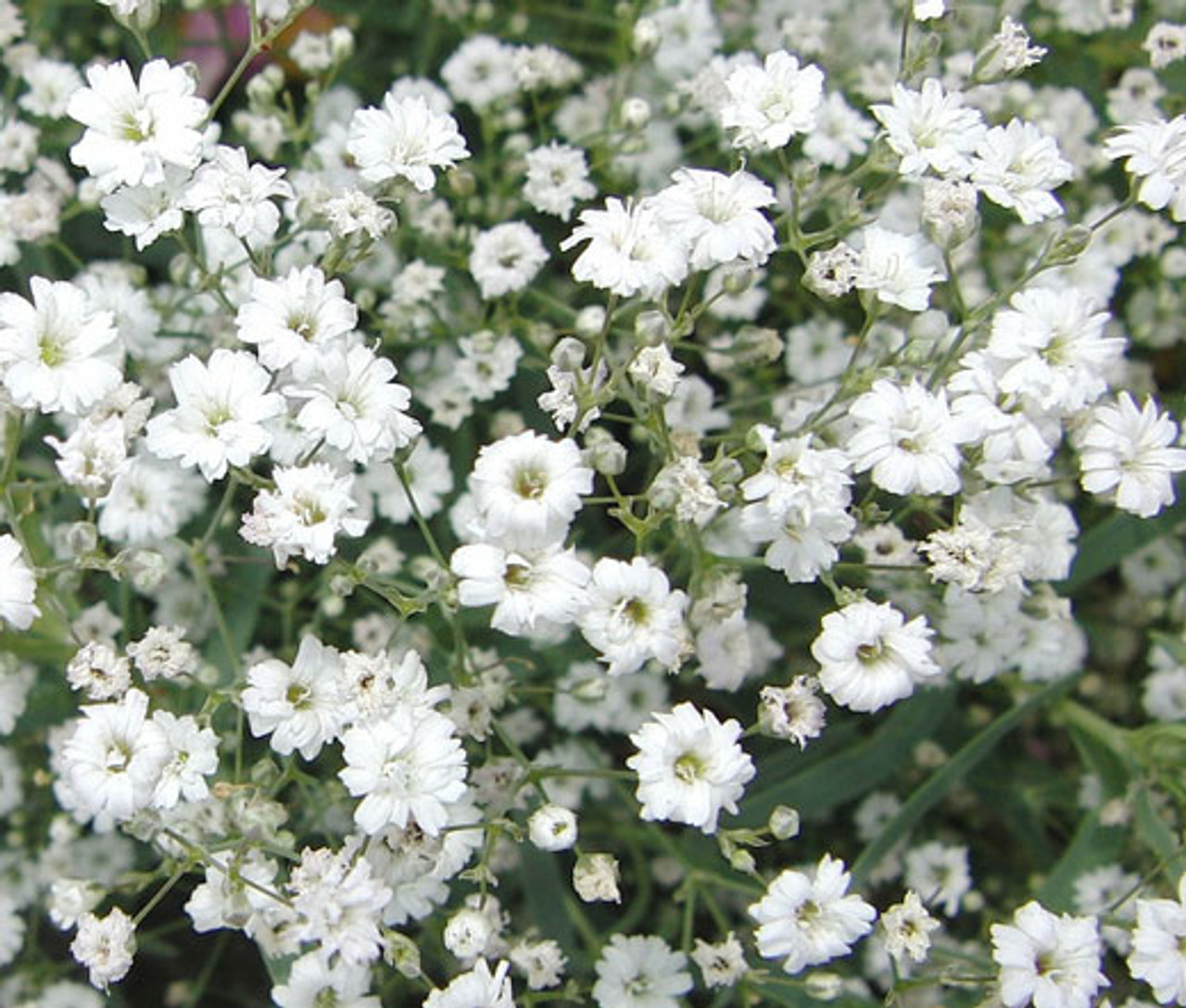
Baby’s Breath/Gypsophila elegans cv.

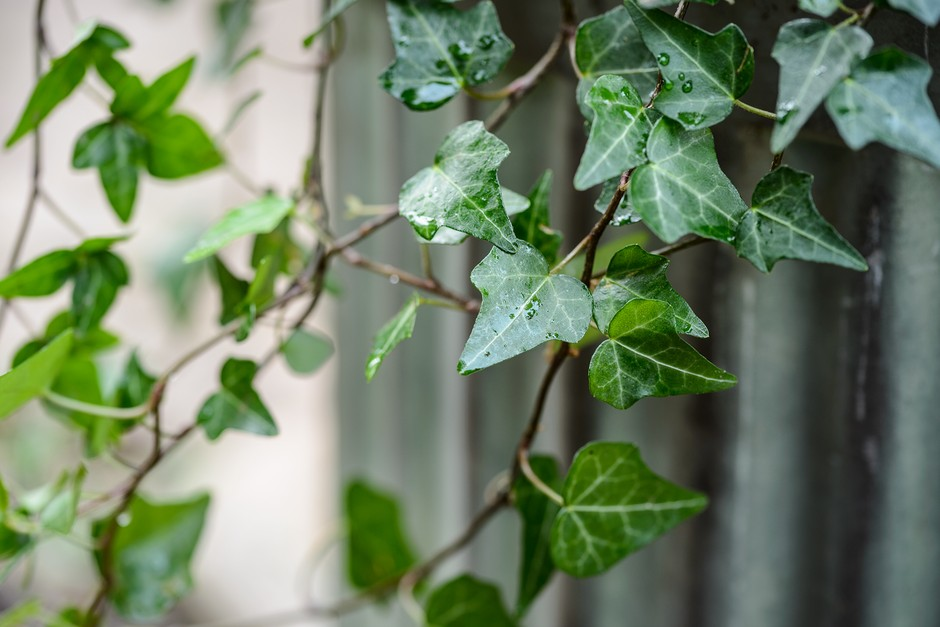
English ivy/Hedera helix

Sunflower/Helianthus annus

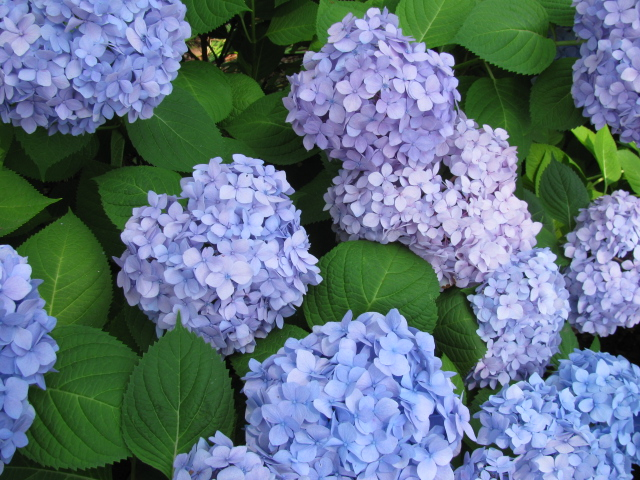
Florist Hydrangea/Hydrangea macrophylla cv.

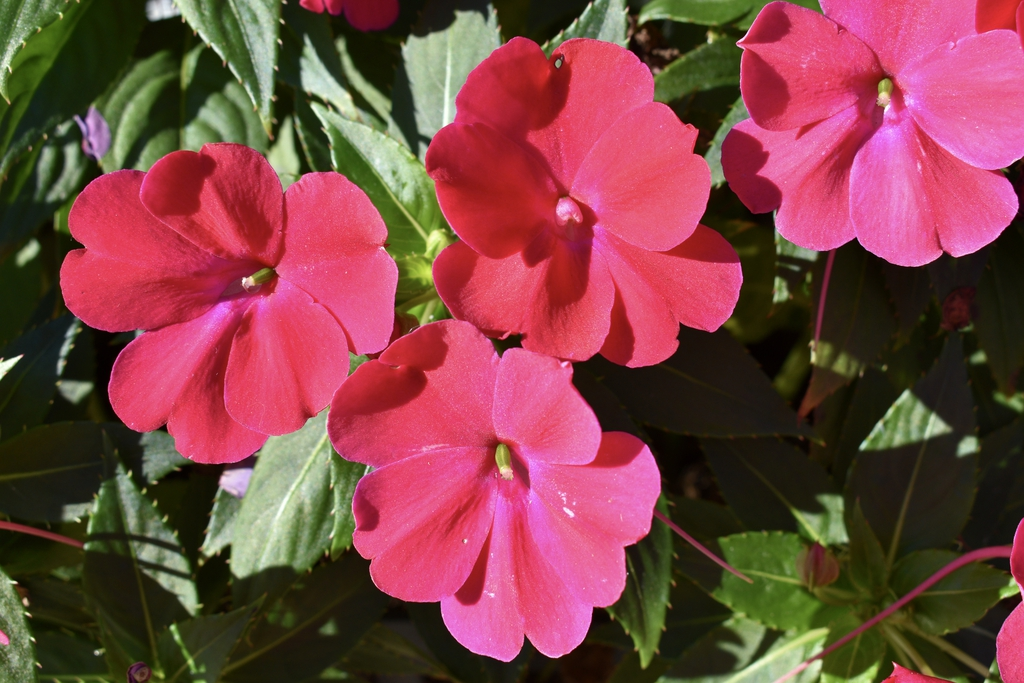
Impatiens/Impatiens hybrid cv

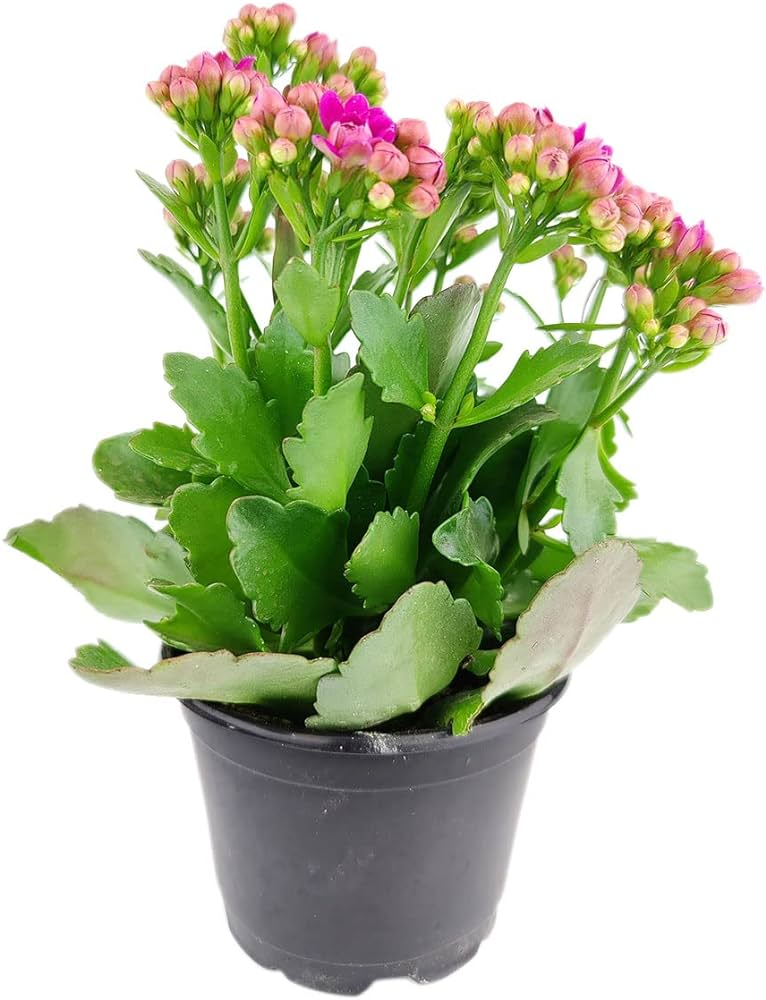
Kalanchoe/Kalanchoe blossfeldiana

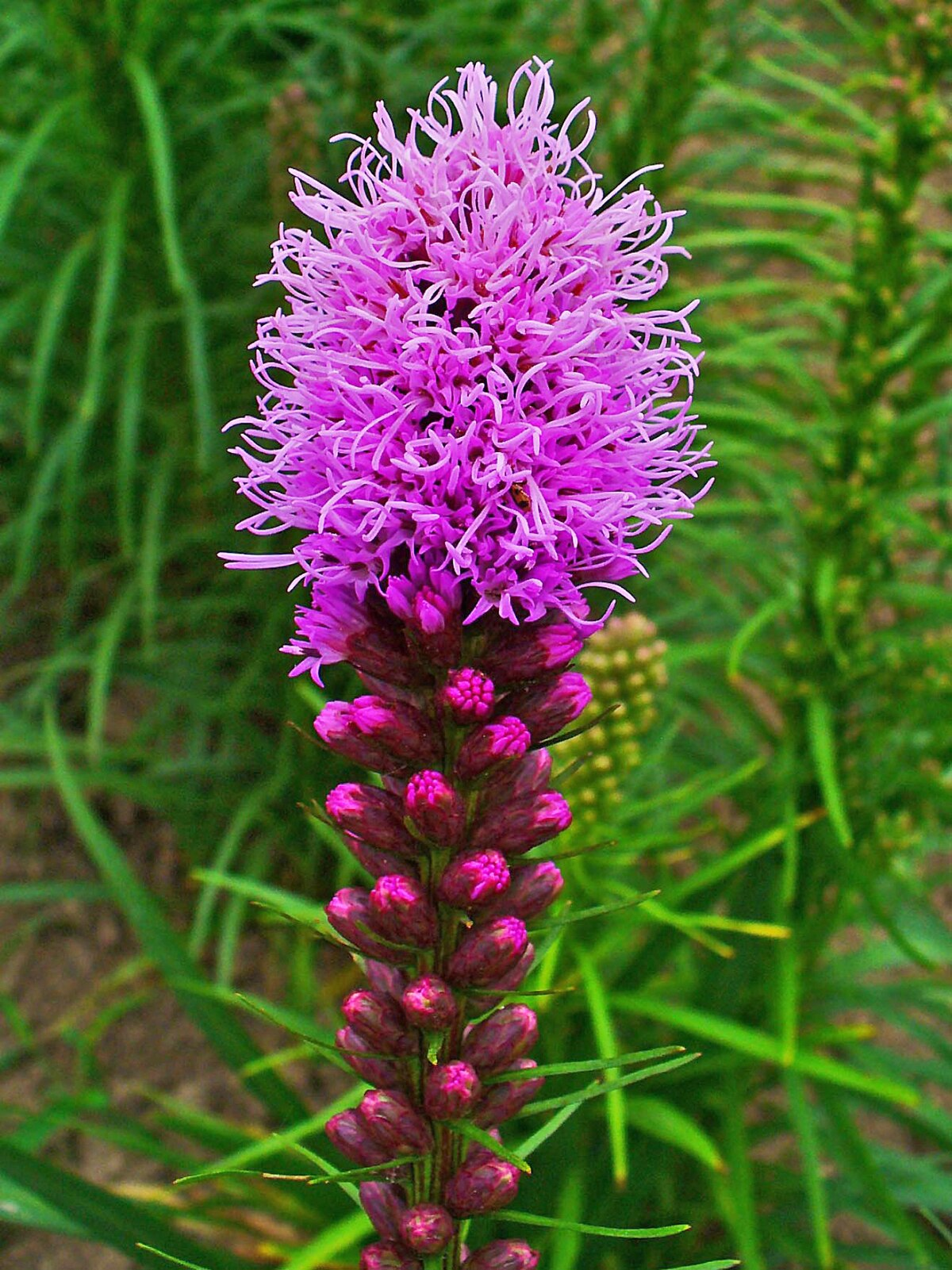
Liatris/Liatris spicata

Asiatic or Oriental Lily/Lilum hybridum cv.

Statice/Limonium sinatum

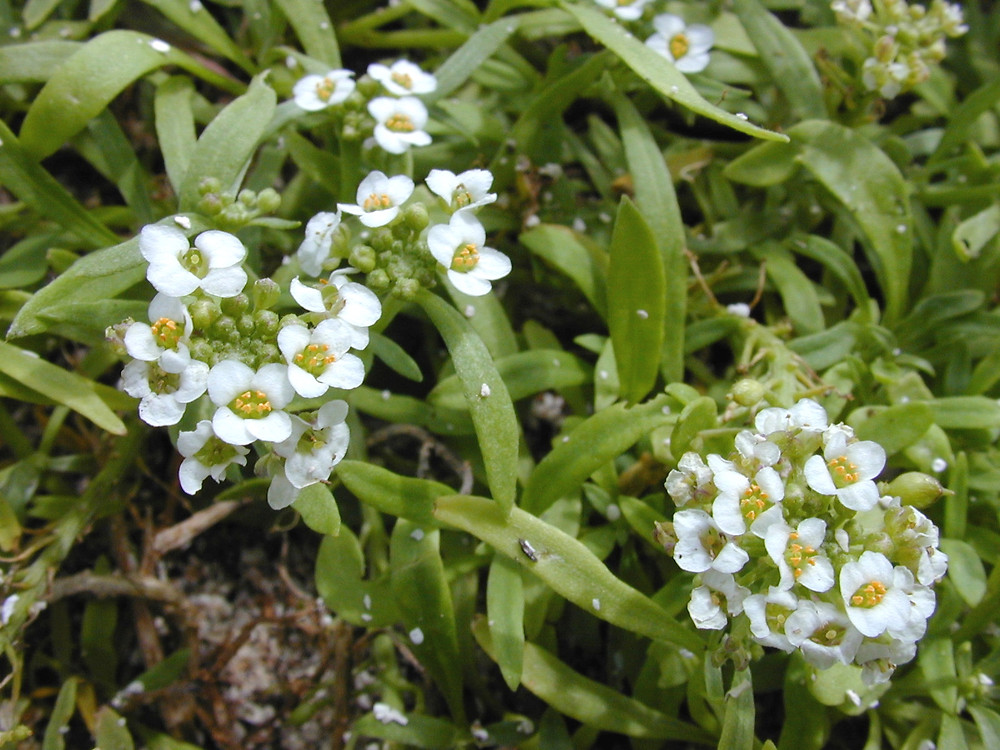
Sweet Alyssum/Lobularia maritima

Prayer Plant/Maranta leuconeura

Flowering Stock/Mitthiola incana cv.

50. Boston Fern/Nephrolepis exaltata

Zonal Geranium/Pelargonium x hortorum

Common Garden Petunia/Petunia x hybrida

Heartleaf Philodendrom/Philodendron scandens

54. Aluminum Plant/Pilea cadierei

Florist Azalea/Rhododendron simsii cv.

Leatherleaf fern/Rumohra adiantiformis

African Violet/Saintpaulia ionantha

. Salvia/Salvia splendens

Snake Plant/Sansevieria trifasciata

Dusty Miller/Senecio cineraria

Nephthytis/Syngonium podophyllum

Marigold/Tagetes species

Poor Soil Drainage
Refers to soil that retains excessive moisture, hindering plant growth and root aeration.
Look for yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or plants struggling to thrive, especially after heavy rain.
To fix amend the soil with organic matter like compost, add perlite or sand, or consider raised beds or rain gardens.
It can lead to root rot and disease, negatively affecting plant health.

Overwatering
Depriving their roots of oxygen and leading to root rot, which then hinders the plant's ability to absorb water and nutrients.
This can result in yellowing leaves, stunted growth, wilting, and ultimately, plant death
Stop watering the plant immediately, allow the soil to dry out, and improve drainage

Insufficient water damage
Is when plants do not receive enough moisture, leading to stress and decline in health. Symptoms include wilting, discoloration, and premature leaf drop.
Wilting, discoloration, and premature leaf drop
To fix the issue, ensure regular watering, check soil moisture levels, and adjust irrigation practices to meet the plants' needs.

Inadequate lighting
Is when plants receive insufficient light intensity or duration needed for photosynthesis, resulting in weak growth. Symptoms include leggy stems, small leaves, and poor flowering.
Symptoms include stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and poor flowering. To remedy the issue, increase light exposure or replace artificial lights.
Can be fixed by increasing light exposure or using fluorescent grow lights.

Too much lighting
Is when plants receive excessive light exposure, which can lead to leaf scorch and hinder growth.
Symptoms include bleached or burnt leaves and wilting.
To fix the issue, reduce light intensity, provide shade, or move the plant to a less bright location.

Improper temperature
Is when plants are exposed to temperatures outside their optimal range, causing stress and potential damage.
Symptoms may include leaf curling, stunted growth, and increased susceptibility to disease.
To fix this, monitor the temperature, move plants indoors or adjust their environment to maintain the ideal temperature range.
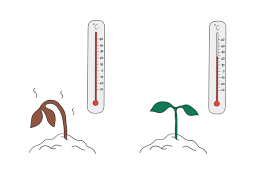
Iron deficiency
Occurs when plants lack sufficient iron, an essential micronutrient for chlorophyll production, leading to poor growth and yellowing of new leaves.
Symptoms may include interveinal chlorosis with green veins.
To fix this, iron chelates or foliar sprays can be applied to correct the deficiency.

Nitrogen deficiency
Occurs when plants do not receive enough nitrogen, a vital nutrient for growth and development, leading to poor leaf development and stunted growth.
Symptoms include yellowing of older leaves and overall reduced plant vigor.
To fix this, apply nitrogen-rich fertilizers or compost to improve nutrient availability.

Phosphorus deficiency
Occurs when plants have insufficient phosphorus, which is crucial for energy transfer and photosynthesis, leading to stunted growth and poor development.
Symptoms may include dark green or purplish leaves and delayed flowering. To fix this, apply phosphorus-rich fertilizers to enrich the soil.
To fix this,monitor soil pH and drainage to ensure phosphorus availability.

Salt Damage
A condition that arises when plants are exposed to excessive salt concentrations in the soil, which can lead to dehydration and nutrient deficiencies.
Symptoms may include leaf burn, wilting, and stunted growth.
To mitigate salt damage, leach the soil with fresh water and improve drainage.

Snails
Small mollusks with coiled shells that can be found in various habitats, including gardens and aquatic environments. They can be pests in gardens, feeding on leaves and flowers.
To Fix remove them by hand or use natural predators.

Slugs
Slimy creatures similar to snails but without a shell, commonly found in moist environments. They are also garden pests, consuming a variety of plants and causing damage.
To fix control their population by removing hiding places, using barriers, or employing natural predators.

Whiteflies
Small, white, winged insects that feed on the sap of plants, leading to yellowing leaves and potential plant stress. They can reproduce rapidly, causing significant infestations in gardens and greenhouses.
To fix apply insecticidal soap or introduce natural predators such as ladybugs.

Aphids
Small, soft-bodied insects that feed by sucking sap from plants, often causing stunted growth and distorted leaves. They reproduce quickly, leading to large populations that can damage a variety of plants in gardens and farms.
To fix control their numbers by introducing natural predators like ladybugs, removing infested plants, or using insecticidal soap.

Leaf miner
Insect larvae that burrow into leaves, creating visible tunnels and causing damage to foliage. They can affect a variety of plants, leading to reduced photosynthesis and overall plant health.
To fix implement cultural controls like removing affected leaves, using insecticides, or introducing natural enemies such as parasitic wasps.

Spider mites
Tiny arachnids that suck sap from plants, causing stippling and discoloration on leaves. They thrive in hot, dry conditions and can quickly lead to severe infestations.
To fix use miticides or introduce predatory mites.

Mealy bugs
Soft-bodied insects covered in a white, waxy substance that feed on plant sap. They can lead to yellowing leaves and poor plant health, often forming large colonies in warm environments.
To fix use insecticidal soap, introduce natural predators like ladybugs, or remove heavily infested plants.

Leafhopper
Small, jumping insects that suck plant sap, potentially transmitting plant pathogens. They can cause wilting and stunted growth in a variety of crops.
To fix use insecticides, promote natural predators, and implement crop rotation.

Spittlebug
Insects known for their distinctive frothy mass that they produce as a protective covering while feeding on sap from plants. They can cause damage by sucking the plant's nutrients, leading to wilting and reduced growth.
To fix use insecticides, introduce natural predators like birds, or promote plant health through proper watering and fertilization.

Scale
Small, immobile insects that attach themselves to plant stems and leaves, feeding on sap. They can cause wilting and discoloration, and may also secrete honeydew, attracting ants.
To fix use insecticidal soap, encourage natural predators such as wasps, or prune heavily infested areas.

Powdery Mildew
A fungal disease that appears as a white or gray powder on plant leaves and stems, typically thriving in warm, dry conditions. It can hinder photosynthesis and reduce plant vigor.
To fix use fungicides, improve air circulation, and ensure adequate watering to reduce leaf wetness.

Leaf Spot
A plant disease characterized by dark, discolored spots on leaves, often caused by fungal or bacterial pathogens. It can lead to leaf drop and reduced photosynthesis.
To fix use fungicides or bactericides, remove affected leaves, and ensure proper plant spacing for airflow.

Root Rot
A plant disease caused by overwatering or poor drainage, leading to the decay of roots and often resulting in plant wilting and yellowing leaves.
Proper watering practices and soil management can prevent this issue.

Damping Off
A fungal disease that affects seedlings, causing them to wilt and collapse, usually due to overly moist conditions and poor air circulation. It can lead to significant seedling loss before plants are established.
to fix improve drainage, reduce watering, and ensure adequate airflow.

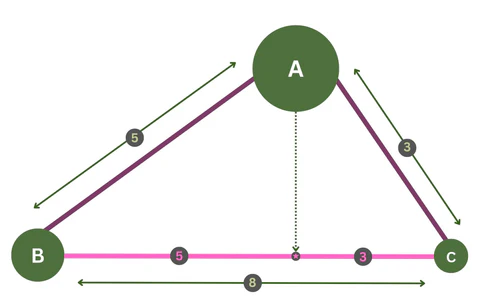
3-5-8 Rule
3: Represents the focal or main flowers, often the most eye-catching in the arrangement.
5: Includes the greenery, which provides the structure and backdrop for the flowers.
8: Consists of accent or filler flowers, adding texture and depth.
Prin. of Design-Harmony
Harmony ensures that all elements work together in a pleasing way. This means that the colors, textures, shapes, and sizes should complement each other and create a sense of unity.
Prin. of Design-Scale
Scale refers to the overall size of the arrangement in relation to its surroundings. A larger arrangement might be suitable for a larger space, while a smaller arrangement might be better for a smaller space.
Prin. of Design-Proportion
The size relationship between different elements should be harmonious. For example, the arrangement should be proportionate to the container and the space it's intended for.
Prin. of Design-Rhythm
Rhythm guides the eye through the arrangement, creating a sense of movement and flow. This can be achieved through repetition of elements like color, shape, or texture, or by varying heights and angles.
Prin. of Design-Contrast
Introducing contrast creates interest and visual appeal. This can be achieved by using different colors, textures, sizes, or shapes of flowers and foliage.
Prin. of Design-Dominance/Emphasis
A focal point or area of emphasis should draw the viewer's attention. This can be achieved by using larger flowers, contrasting colors, or placing specific elements in a more prominent position.
Prin. of Design- Balance
An arrangement should appear balanced, whether symmetrically or asymmetrically. Symmetry means equal weight and placement on both sides, while asymmetry uses different elements to achieve a sense of equilibrium.