25. Cardio Examination ECG
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Rapid Q: Practice Q 1
A clinician is auscultating a patient’s lungs. During auscultation, the clinician hears low pitched gurgling and snoring sounds. Which of the following sounds is the clinician MOST LIKELY hearing?
A. Vesicular
B. Wheezes
C. Bronchial
D. Rhonchi
D. Rhonchi

Rapid Q: Practice Q 2
A patient with dyspnea on exertion and has an FEV1 /FVC ratio of 65%. They report chest tightness and frequent coughing. Which lung volume would be decreased compared to a patient with a healthy pulmonary system?
A. Functional residual capacity
B. Residual volume
C. Total lung capacity
D. Expiratory reserve volume
D. Expiratory reserve volume

FEV1/FVC:
Normal = %
COPD = %
Restrictive Lung Disease = %
Normal = ≥ 70-80%
COPD = <70%
Restrictive Lung Disease = >80%
Rapid Q: Practice Q 3
When a physical therapist auscultates the patient’s heart, they hear an S4 heart sound. When can this heart sound be heard and what condition does it MOST LIKELY indicate?
A. Abnormal sound heard in early diastole; congestive heart failure
B. Abnormal sound heard in late diastole; congestive heart failure
C. Abnormal sound heard in early diastole; myocardial infarction
D. Abnormal sound heard in late diastole; hypertension
D. Abnormal sound heard in late diastole; hypertension

Heart Sounds:
S1:
S2:
S3:
S4:
S1: LUB
Closure of AV Valve
Bicuspid and Tricuspid Valve
Early Systole
S2: DUB
Closure of Semilunar Valves
Pulmonary and Aortic Valve
Late Systole
S3: Ventricular Gallop
Early Diastole
S4: Atrial Gallop
Late Diastole

Electrical Activity of the Heart:
Contraction of the Heart depends on what?
What is the Conduction System of the Heart?
Depolarization =
Repolarization =
Depends on the electrical stimulation of the myocardium
Conduction System:
Sinoatrial Node (SA Node) » Atrioventricular Node (AV Node) » Bundle Branches » Purkinje Fibers
Depolarization = Contraction
Repolarization = Relaxation
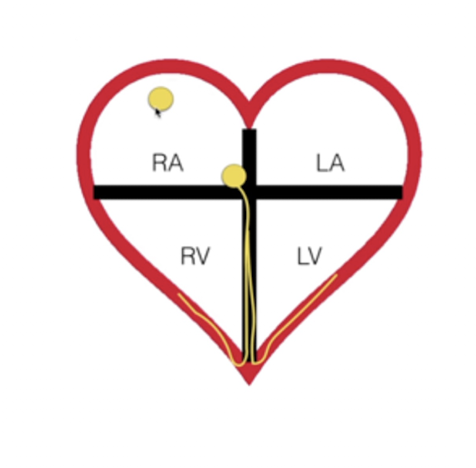
Electrical Activity of the Heart:
Describe:
Sinoatrial Node (SA Node):
Atrioventricular Node (AV Node):
Bundle Branches:
Purkinje Fibers:
Sinoatrial Node (SA Node):
Pacemaker
Initiates depolarization
Atrioventricular Node (AV Node):
Passes depolarization to Ventricles
Brief delay to allow for ventricular filling
Bundle Branches:
To L and R Ventricle
Purkinje Fibers:
Throughout Ventricles
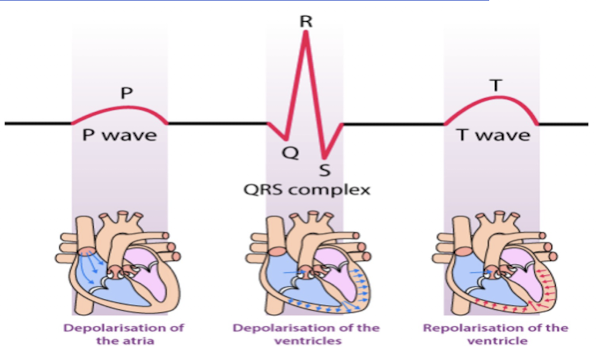
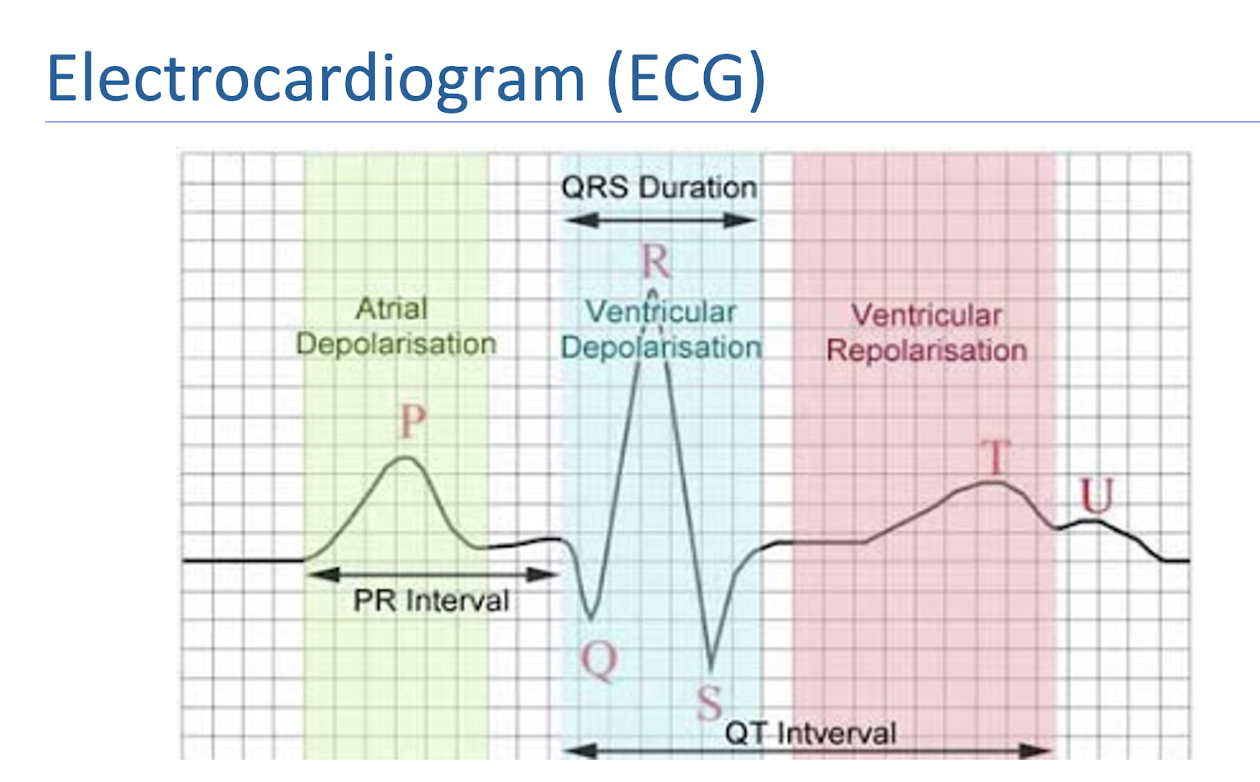
Electrocardiogram (ECG):
What is it?
P Wave:
QRS Complex:
T Wave:
What is it?
Records the electrical activity of the heart
P Wave:
Atrial Depolarization
QRS Complex:
Ventricular Depolarization and Atrial Repolarizarion
T Wave:
Ventricular Repolarization
Practice Q 4:
A physical therapist examines the output from a single lead ECG of a patient in an inpatient clinic. The six-second ECG strip is shown in picture below. What should the physical therapist determine the heart rate of the patient as?
A. 110 beats per minute
B. 70 beats per minute
C. 90 beats per minute
D. 60 beats per minute
C. 90 beats per minute
9 R Waves x 10 = 90bpm

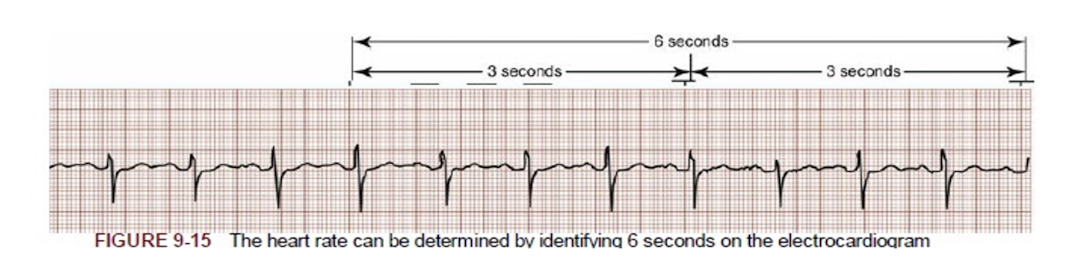
Calculate HR: 6 Second Method
Count off 30 large boxes =
1 Large Box =
So, 30 Large Boxes =
Then…
Count off 30 large boxes = 6 seconds
1 Large Box = 0.2 seconds
30 Large Boxes = 6 Seconds
Then…
Count the number of R waves in 6 seconds, and multiply by 10

Classification of AV Blocks:
1st Degree Heart Block =
2nd Degree Heart Block =
3rd Degree Heart Block =
1st Degree Heart Block =
Delay in Conduction
2nd Degree Heart Block =
Partially Blocked Conduction
3rd Degree Heart Block =
Fully Blocked Conduction

AV Blocks » 1st Degree
1st Degree
Characteristics: (3)
Seen also in athletes with…
T/F: Generally, WONT progress, BENIGN condition/not serious
Characteristics:
AV Nodal Disease
PR Interval > 0.2 seconds (1 large box)
Each P is followed by QRS
Athletes c Increased Vagal Tone (Activity)
TRUE
NOTE:
Look at the constant elongation of PR
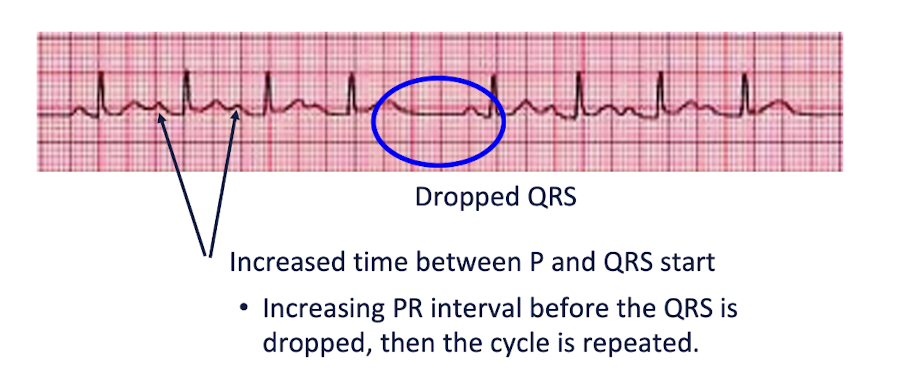
AV Blocks: 2nd Degree
Main Characteristics: (2)
What are the 2 Types?
Main Characteristics:
One or more - but not all - of the atrial impulses fail to conduct to the ventricles
Increased PR Intervals before QRS is dropped, then cycle is repeated
2 Types:
Type 1 // Winckebach // Mobitz Type I
Type 2 // Mobitz Type II
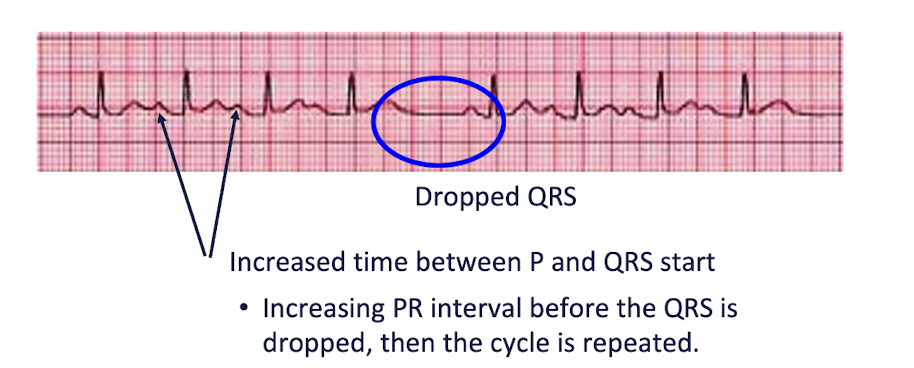

AV Blocks: 2nd Degree » Type I
AKA:
Characteristics: (3)
AKA:
Wenckebach
Mobitz Type I
Characteristics:
Disease of AV Node
PR Interval gets PROGRESSIVELY LONGER each beat until a QRS is “DROPPED”
PATTERN IS DESCERNED
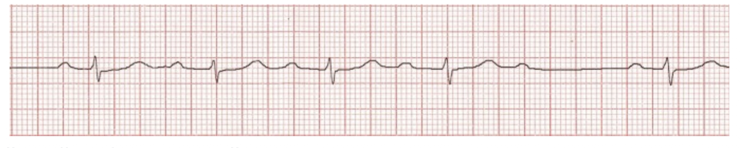

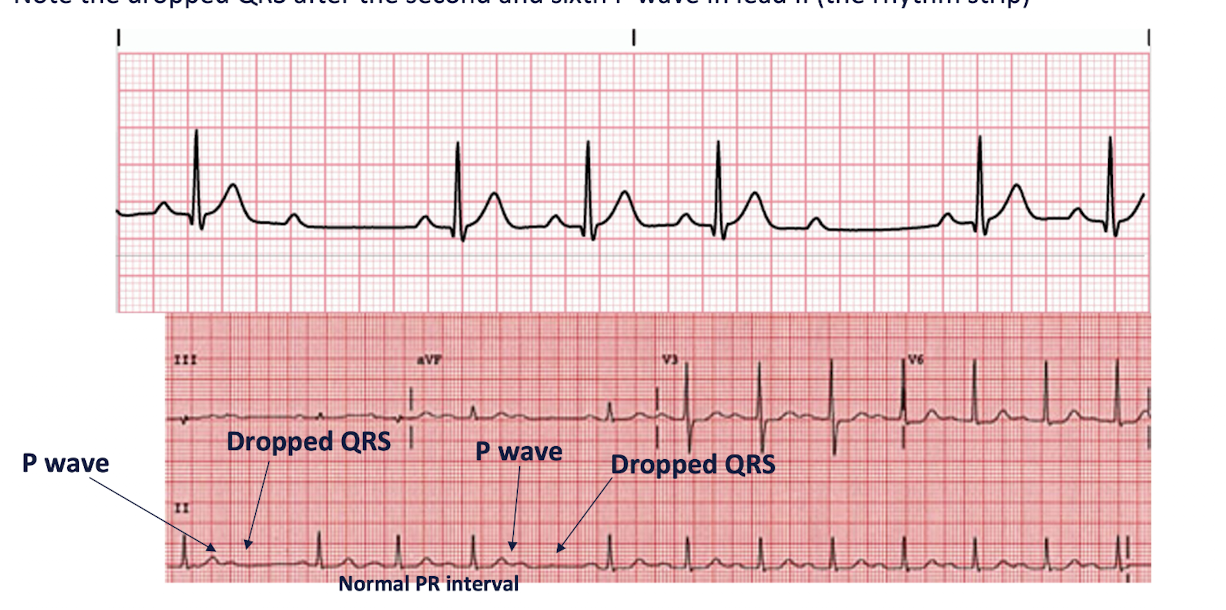
AV Blocks: 2nd Degree » Type II
AKA:
Characteristics: (3)
AKA:
Mobitz Type 2
Characteristics:
Disease of the Bundle of His and Purkinje FIbers
PR Intervals are CONSTANT and QRS is “DROPPED” INTERMITTENTLY
NO PATTERN CAN BE DISCERNED (unpredictable)
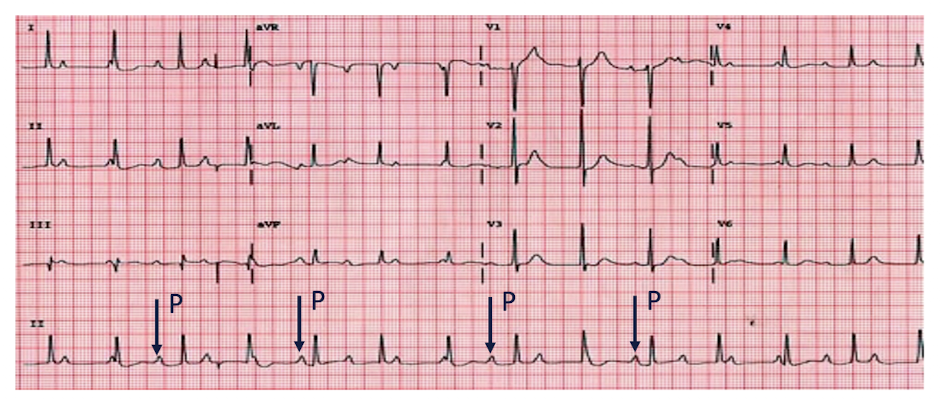
AV Blocks: 3rd Degree
Characteristics: (3)
The atrial rate is INDEPENDENT from ventricular rate
P wave and QRS march out separately
NO RELATIONSHIP AT ALL, of the PR Intervals
PR Interval is constantly changing and QRS is wide and bizarre because of ventricular origin

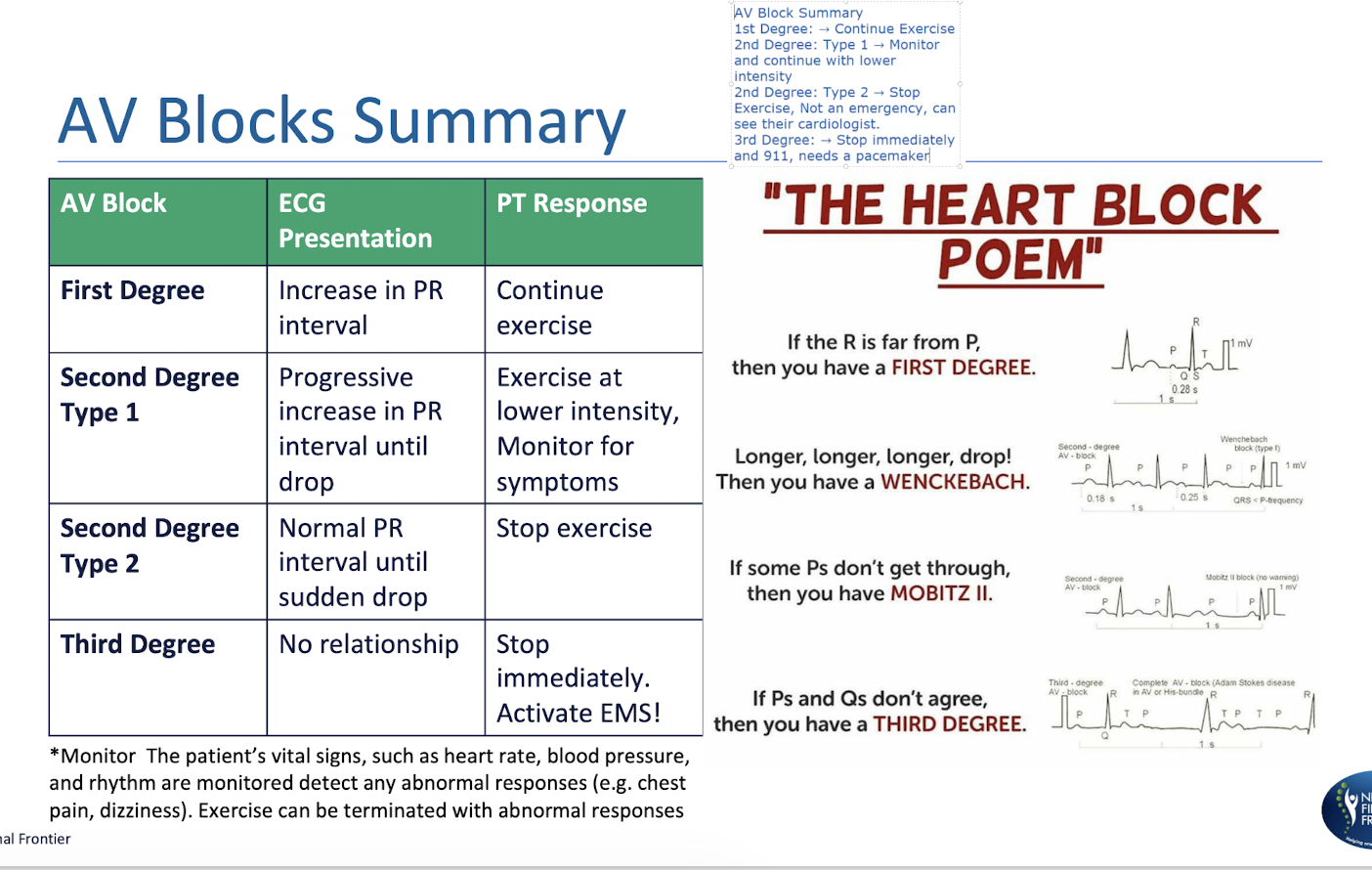
AV Block Summary:

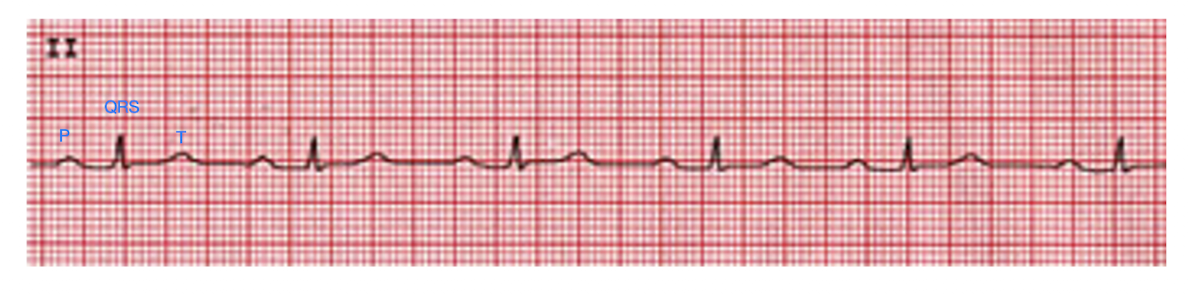
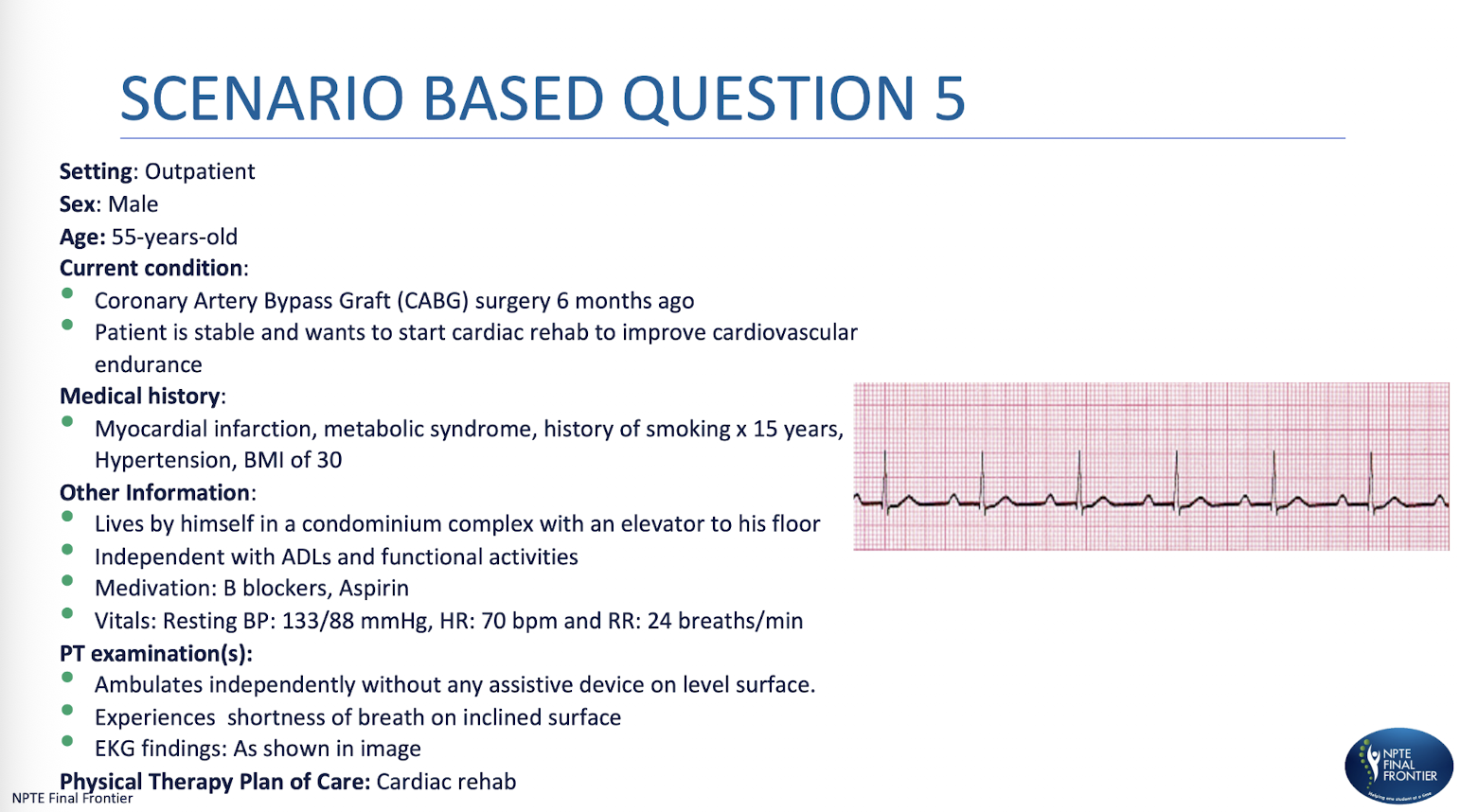
Scenario Based Q 1:
While walking on a treadmill, the physical therapist sees the ECG pattern, as shown. What is the MOST APPROPRIATE diagnosis?
A. First degree heart block
B. Mobitz type I heart block
C. Mobitz type II heart block
D. Third degree heart block
A. First degree heart block

Scenario Based Q 2:
Based on the diagnosed condition, what would be the MOST APPROPRIATE response by the physical therapist?
A. Stop the treadmill session immediately and contact the cardiologist.
B. Continue exercising at the current intensity without any modifications
C. Lower the exercise intensity and monitor the patient closely.
D. Have the patient rest, then reassess before resuming exercise.
B. Continue exercising at the current intensity without any modifications

Scenario Based Q 3:
The patient did not come for physical therapy for 3 consecutive visits. On following up with the patient’s caretaker, they mentioned that the patient was taken to the emergency room as they were experiencing increased shortness of breath at rest and cough with no evident peripheral edema. Which of the following is MOST LIKELY causing the patient’s symptom?
A. Biventricular heart failure
B. Right-sided heart failure
C. Cor pulmonale
D. Left-sided heart failure
D. Left-sided heart failure


ST Segment:
ST Segment Depression =
Depression Amount:
What should the PT do?
3 Characteristics:
ST Segment Depression = MYOCARIDAL ISCHEMIA
Depression Amount: > 2mm/2 small boxes
Call 911 + Stop Exercise
3 Characteristics:
Decreased Blood Supply
ST Segment Depression
T Wave Flattened or Inverted

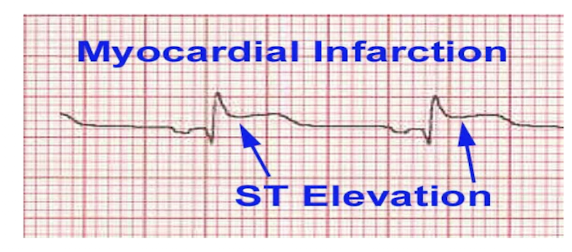
ST Segment:
ST Segment Elevation =
Elevation Amount:
What should the PT do?
2 Characteristics:
ST Segment Elevation = MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
Elevation Amount: > 1mm/1 small box
Call 911 + Stop Exercise
2 Characteristics:
Complete occlusion of blood supply and cell death
ST segment elevation
NOTE:
ElevaTION = InfarctION
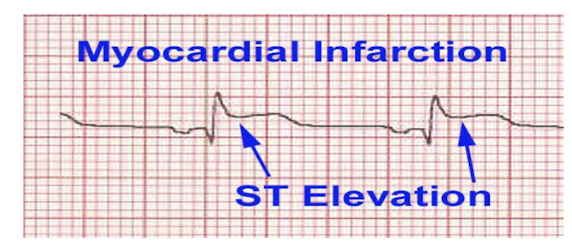

Practice Q 6:
A patient is walking on a treadmill with ECG leads attached. The physical therapist observes the ECG as shown in the image below. What is the MOST LIKELY diagnosis and intervention?
A. Myocardial ischemia that has an elevation of the ST segment greater than 1 mm and the PT should stop the protocol
B. Myocardial infarction that has an elevation of the ST segment less than 1 mm and the PT should stop the protocol and call 911
C. Myocardial ischemia that has an elevation of the ST segment less than 1 mm and the PT should stop the protocol
D. Myocardial infarction that has an elevation of the ST segment greater than 1 mm and the PT should stop the protocol and call 911
D. Myocardial infarction that has an elevation of the ST segment greater than 1 mm and the PT should stop the protocol and call 911

Supraventricular (“Atrial”) Arrhythmias:
What are the 4 Atrial Arrhythmias?
Atrial Rate:
Premature Atrial Contractions
Atrial Tachycardia
Atrial Rate: 100-250 bpm (fast)
Atrial Flutter
Atrial Rate: 250-350 bpm (very fast)
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Rate: 400-600 bpm (fastest)
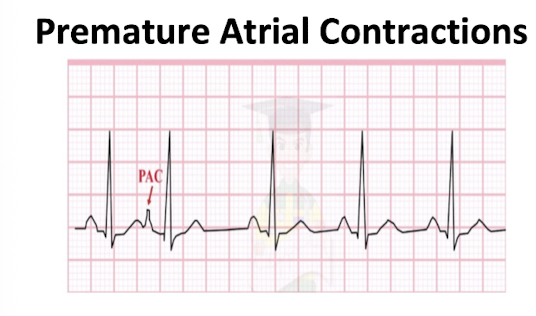
Premature Atrial Contraction:
NOTICE:
Look for:
Little bump AFTER T wave
P wave comes EARLY
QRS Normal
NO 911/NOT EMERGENCY
MONITOR AND CONTINUE AT LOWER INTENSITY
FLIP
Atrial Tachycardia:
NOTICE:
Look for:
T and P Overlap (appear only as 1)
NO 911/NOT EMERGENCY
MONITOR AND CONTINUE AT LOWER INTENSITY

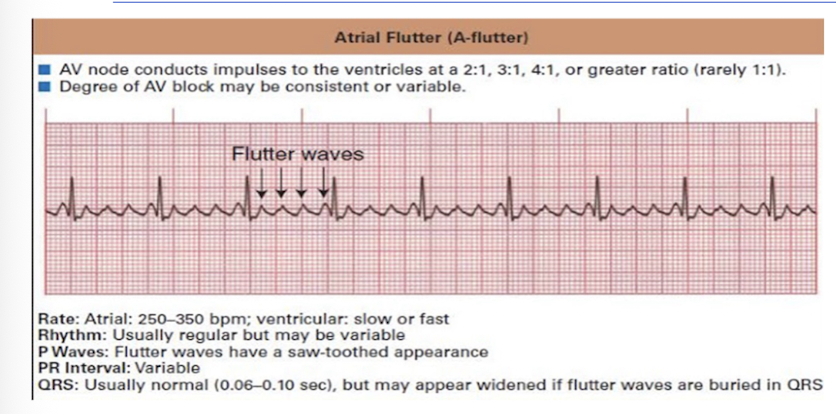
Atrial Flutter:
NOTICE:
Look for:
Sawtooth Pattern in P Wave
QRS Normal
NO 911/NOT EMERGENCY
MONITOR AND CONTINUE AT LOWER INTENSITY
FLIP
Atrial Fibrillation:
NOTICE:
Look for:
Quivering P wave
QRS Normal
NO 911/NOT EMERGENCY
Stop Exercise and report to Physician

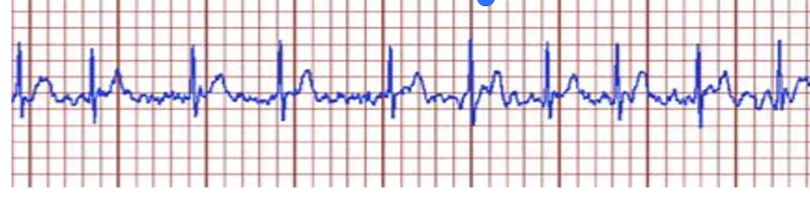
Practice Q 7:
A physical therapist is ambulating a patient, and they report palpitations, shortness of breath and fatigue. What should be the interpretation and immediate action according on the ECG strip shown below?
A. Ventricular fibrillation; Call for a defibrillator
B. Premature ventricular contractions; Take them to their bed and monitor for changes in ECG
C. Atrial Fibrillation; Stop exercise and report to the physician
D. 3rd degree heart block; activate emergency
C. Atrial Fibrillation; Stop exercise and report to the physician

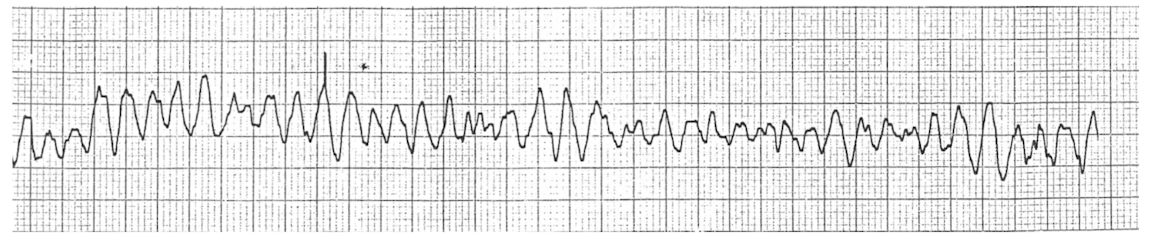
Practice Q 8:
While exercising a patient on the treadmill, the physical therapist notices the electrocardiogram as shown in the image. What should their INITIAL response be?
A. Continue walking at same intensity
B. Continue walking at lower intensity
C. Stop the treatment and monitor ECG for 10 minutes
D. Activate the emergency system or call 911
What is dx?
D. Activate the emergency system or call 911
Dx: Ventricular Fibrillation

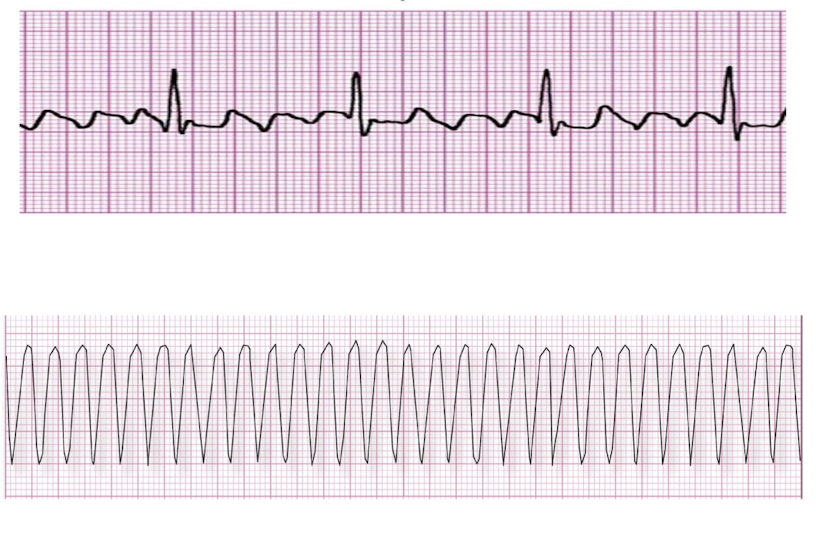
Guess the Strips
Atrial Flutter
V Tach
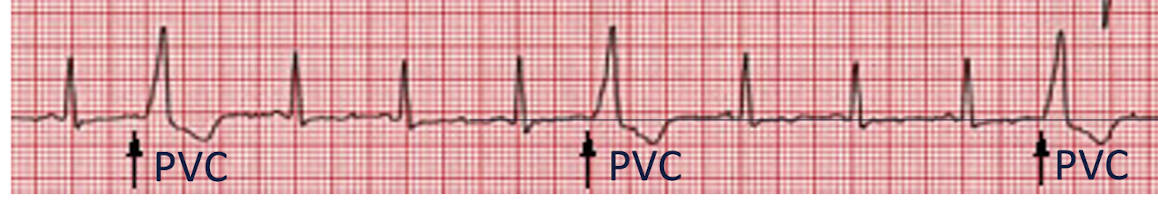
Premature Ventricular Contracture (PVC):
Heart beat initiated by:
Presentation: (2)
PVC that occur 3 or more in a row =
Heart beat initiated by Purkinje Fibers
Skipped beat or palpitations
Characteristics:
Ventricle contracts BEFORE the atria: cannot be filled optimally
No P, wide bizarre QRS
V Tach
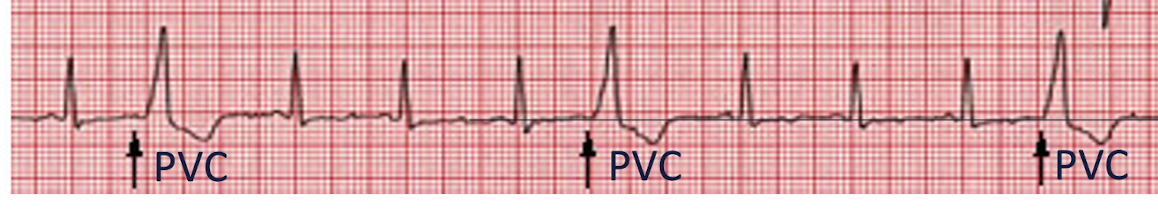
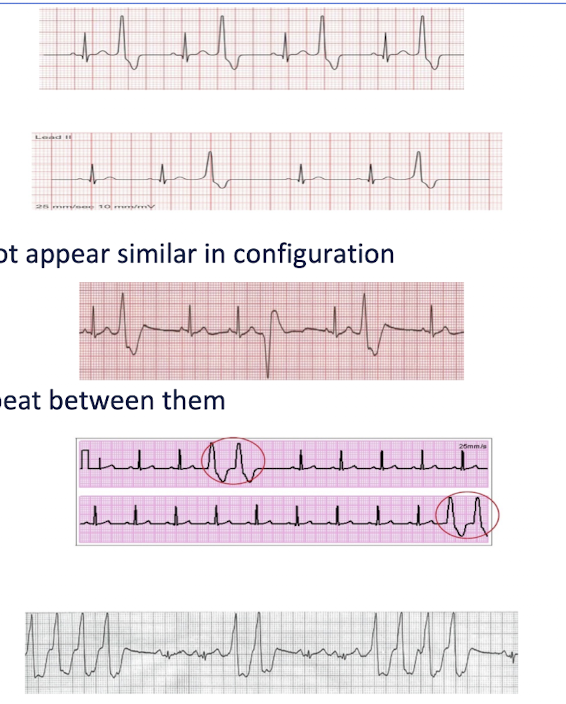
PVC Variations:
Bigeminy =
Trigeminy =
Multifocal PVC =
What should PT do?
Couplet =
What should PT do?
If 2 or more couplets =
3 or more PVC in a row =
What should PT do?
Bigeminy =
1 normal beat followed by 1 PBC
Trigeminy =
2 normal beats followed by 1 PVC
Multifocal PVC =
More than 1 PVC is present and 2 do not appear in similar configuration
STOP exercise and immediately refer (call 911)
Couplet =
2 consecutive PVCs together with not normal beat between them
STOP Exercise
If 2 or more couplets = Immediately refer (call 911)
3 or more PVC in a row = V Tach
STOP and call 911
Practice Q 9:
The physical therapist is working with a patient, who is 4 months post myocardial infarction, in a cardiac rehab facility. Upon increasing the workload, the physical therapist observes a unifocal PVC on the patient’s ECG. Which of the following is the MOST APPROPRIATE action by the physical therapist?
A. Continue to exercise and increase the intensity
B. Stop exercise because patient is undergoing ischemia
C. Keep exercising at a lower intensity; consultation with physician is not required here
D. Stop exercise and consult with physician before starting any exercise
C. Keep exercising at a lower intensity; consultation with physician is not required here
