Huerta Exam 2: Sensory Screening and Evaluation
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
min 24
Audio
purposes of screening and evaluations
• Assess the extent of sensory loss
• Evaluate and document sensory recovery
• Assist in diagnosis
• Provide prognostic information
• Determine impairment and functional limitations
• Provide directions for OT treatment
tests that evaluate function:
1) functional hand tests
2) simulated activities
3) ADL and IADL performance
basics of sensory assessment: cognition
client must have adequate cognition
basics of sensory assessment: vision
must be occluded
*can first show how to do it with vision but then test without it
basics of sensory assessment: body parts
supported without providing stimuli
basics of sensory assessment: environment
reduce environmental stimuli
basics of sensory assessment: concentration
ensure clients ability to concentrate
basics of sensory assessment: assessment tools
we must determine the appropriate assessment tools
basics of sensory assessment: methods
use standardized methods of administration
Basics of Sensory Assessment
• Client must have adequate cognition
• Vision occluded
• Body part supported without providing stimuli
• Reduce environmental stimuli
• Ensure client's ability to concentrate
• Determine appropriate assessment tools
• Use standardized methods of administration
general sensory test procedures
1) make sure the client understands the procedure
2) perform trial with vision
3) occlude vision
4) test unaffected side first
5) test affected side second
what side will we test first
a) affected
b) unaffected
unaffected
timesaving method to determine if sensation is abnormal
screening
... sites can be used to reflect larger points of the hand innervated by the same peripheral nerve.
specific sites
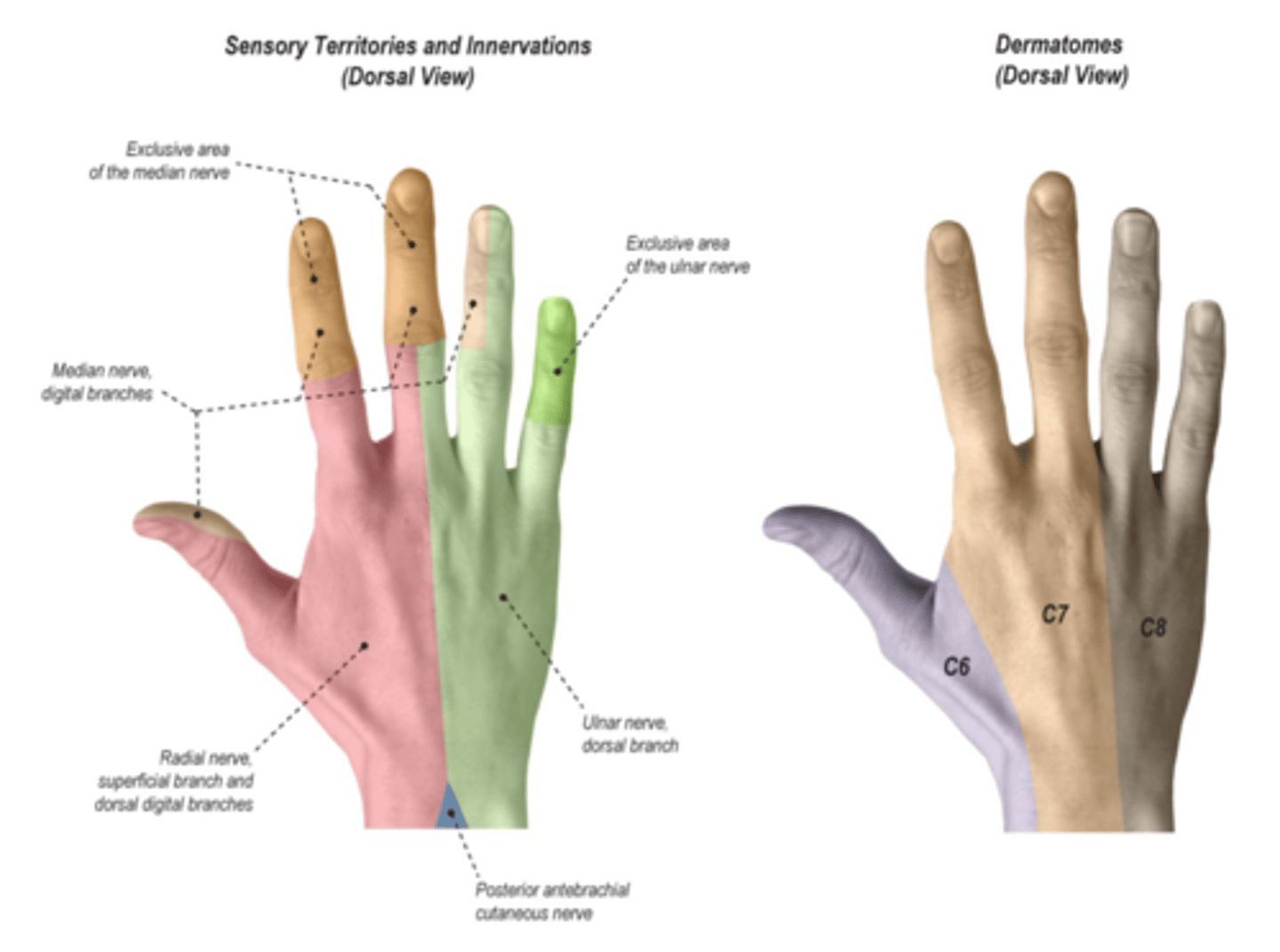
For screening median nerve function, what do we test?
test the thumb tip, index tip, and index proximal phalanx.
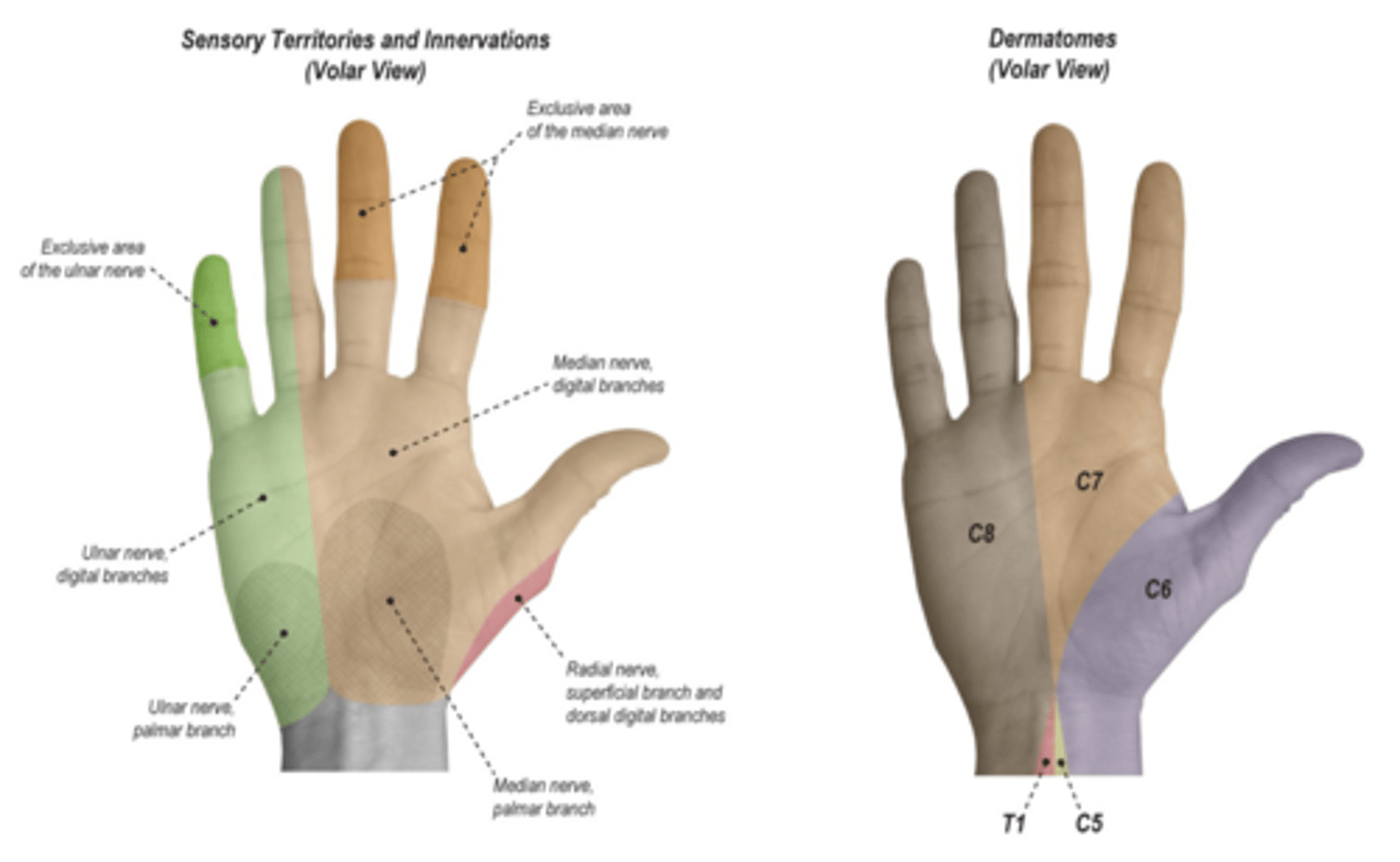
For screening ulnar nerve function, what do we test?
test the distal and proximal ends of the small finger and the proximal ulnar aspect of the palm.
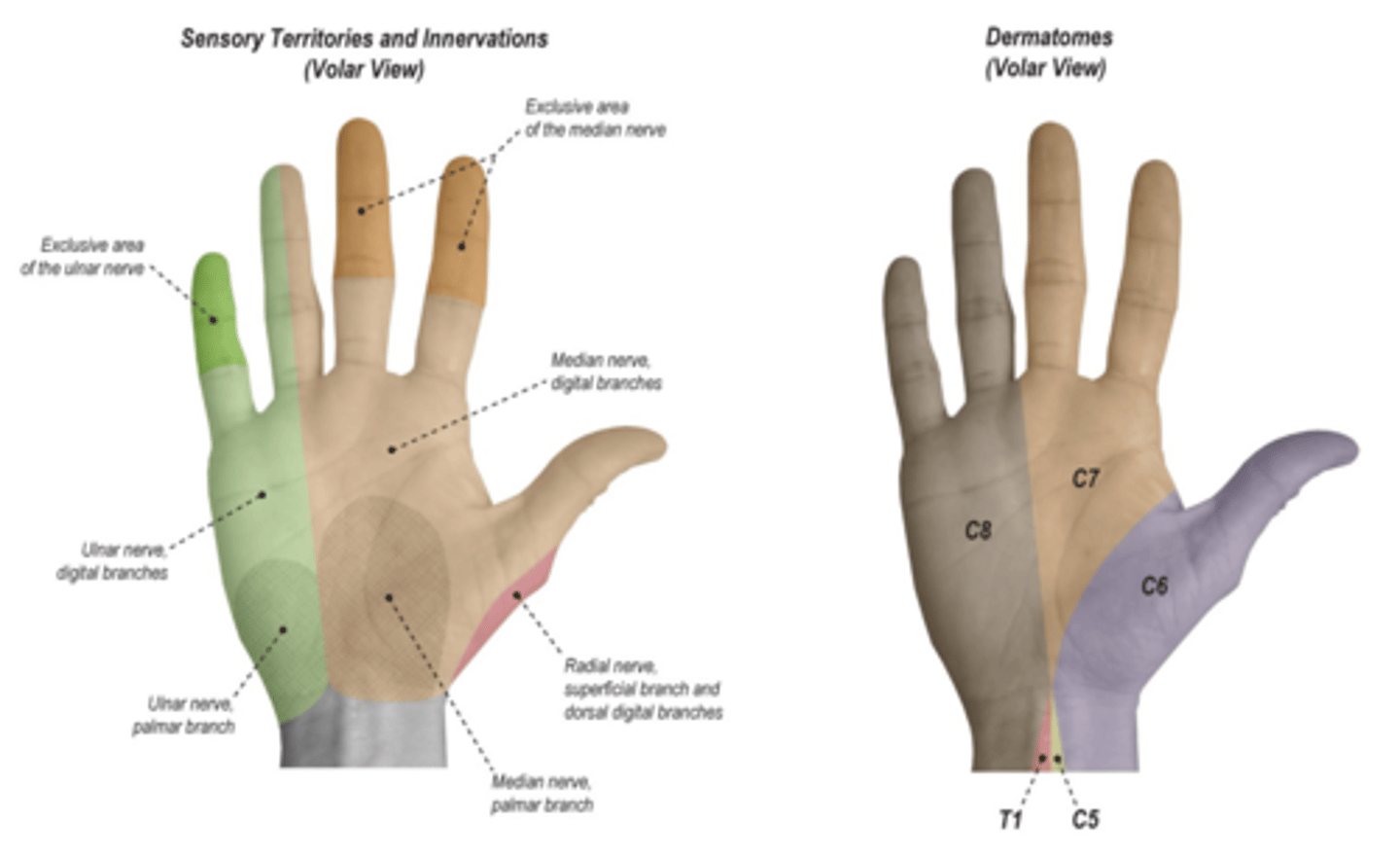
For screening the radial nerve, what do we test?
test the radial back of hand, dorsal part of the thumb web space
if the distal aspect is intact, what does this mean?
everything else is intact
when conducting a sensory screening of the hand, we must note and document the appearance of:
- blisters
- altered sweat patterns
- calluses
- shiny or dry skin
- scar
- wounds
- atrophy of thenar and hypothenar eminences
sensory assessments: standardized tests
1) touch pressure
2) moving and static 2 pt discrimination
3) point localization
4) vibration threshold
sensory assessments: non standardized tests
1) awareness of touch, pain or pinprick
2) temperature
3) vibration
4) stereognosis
5) Moberg pick up
6) proprioception
7) kinesthesia
the least stimulus needs to elicit a response
stimulus threshold
stimulus threshold
the least stimulus needs to elicit a response
examples of stimulus thresholds
- light touch
- vibration
- cutaneous pressure
refers to the number of sensory receptors in one area
tactile discrimination
tactile discrimination
the number of sensory receptors in an area
distinguish different textures by touch
moving and static two point discrimination tests assess what?
tactile discrimination
proprioception evaluation
1) occlude vision
2) move the joint being tested into flexion or extension
3) ask the client to identify the position of the joint or ask them to replicate the position with their other limb
proprioception screening
test distally, move proximally if deficit is noted
uses both touch and proprioception to identify an object in-hand
stereognosis
stereognosis test
1) use familiar objects and place them in the client's hand
2) show the objects and tell them what they are
3) client manipulates object with vision occluded and is asked to identify objects or its characteristics
*client must have adequate motor function and communication skills
what assessment assesses pressure threshold?
semmes-weinstein monofilaments
where can the semmes-weinstein monofilaments be used?
on the entire body but mostly used for hands
Light touch is perceived by receptors in the
superficial skin
Light touch is important for ..., whereas deep pressure is important for...
light touch ->fine discriminatory hand use
deep pressure -> protective sensation.
Touch pressure testing examines the spectrum from
light touch to deep pressure.
.... is a good test to use for clients with nerve compression, such as carpal tunnel syndrome.
Touch pressure testing - semmes-weinstein monofilaments
Having intact ... is an indicator of better sensation than having only ....
a) light touch pressure awareness
b) deep touch pressure awareness
light touch pressure awareness
intact deep touch pressure awareness
what must be intact for two-point discrimination to be testable
Light touch pressure awareness
because the two-point discrimination test uses light touch.
semmes-weinstein monofilaments: green
normal
Semmes-Weinstein Monofilaments: blue
diminished touch
semmes-weinstein monofilaments: purple
diminished protective sensation (poses safety risk!!)
semmes-weinstein monofilaments: red
loss of protective sensation
semmes-weinstein monofilaments: untestable
no discrimination of levels of feeling (nothing)
normal
a) green
b) blue
c) purple
d) red
e) untestable
green
diminished light touch
a) green
b) blue
c) purple
d) red
e) untestable
blue
diminished protective sensation
a) green
b) blue
c) purple
d) red
e) untestable
purple
loss of protective sensation
a) green
b) blue
c) purple
d) red
e) untestable
red
no discrimination of levels of feeling
a) green
b) blue
c) purple
d) red
e) untestable
untestable
nerve function tests
1) ninhydrin test - sweat
2) wrinkle test - deinnervation
3) nerve conduction studies - invasive
ninhydrin test
decreased sweat secretion
assesses sympathetic function
test that assesses sympathetic function
ninhydrin test
test that identifies areas of deinnervation
wrinkle test
areas that do not wrinkle
invasive test fo nerve function that requires special training to administer/interpret
nerve conduction studies (outside of our scope)
What are provocative tests?
tests that provoke symptoms
have a (+) result
types of provocative tests
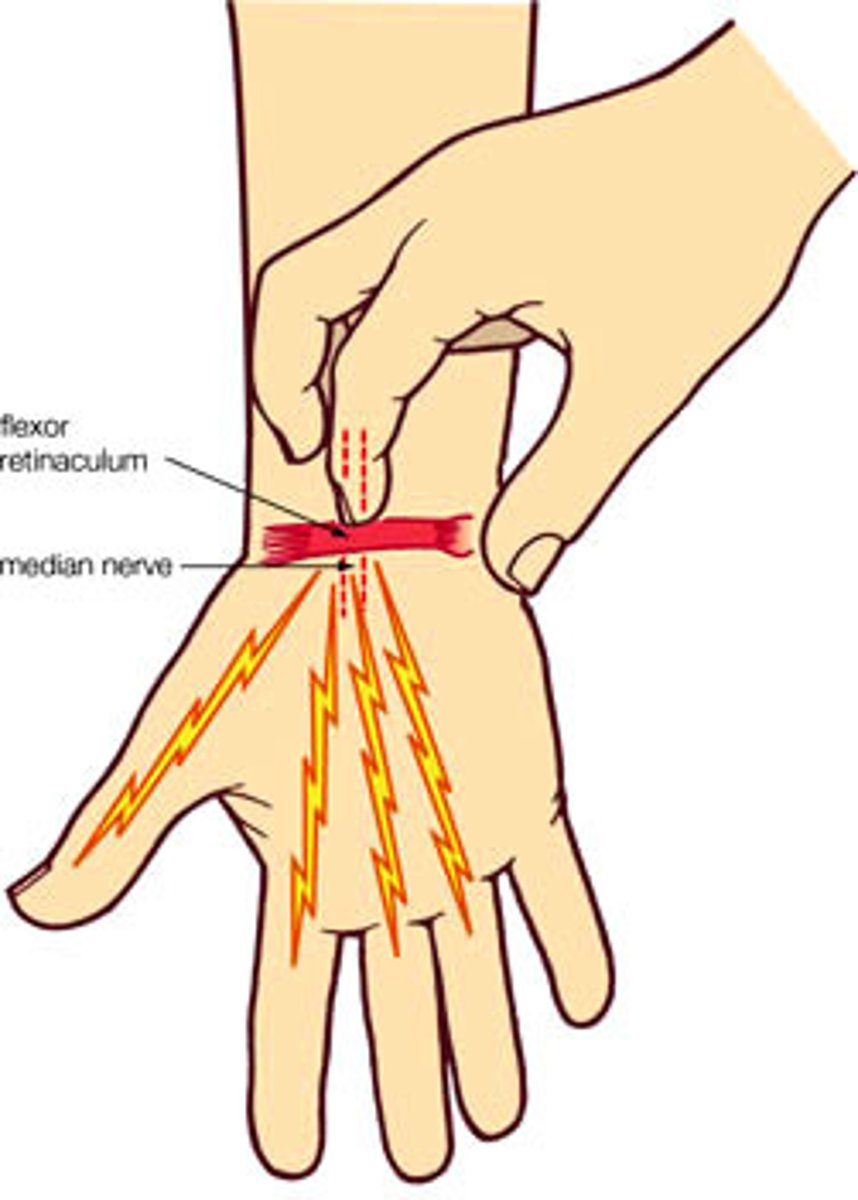
1) Tinel's sign
2) Phalen's test
test: tapping skin over damaged peripheral nerve
tinel's sign
Tinel's sign
a way to detect irritated nerves.
It is performed by lightly tapping (percussing) over the nerve to elicit a sensation of tingling or "pins and needles" in the distribution of the nerve.
Phalen's test is an essential test to detect
carpel tunnel syndrome
- compressed median nerve
Phalen's test
wrist flexion/extension provokes tingling in median nerve distribution
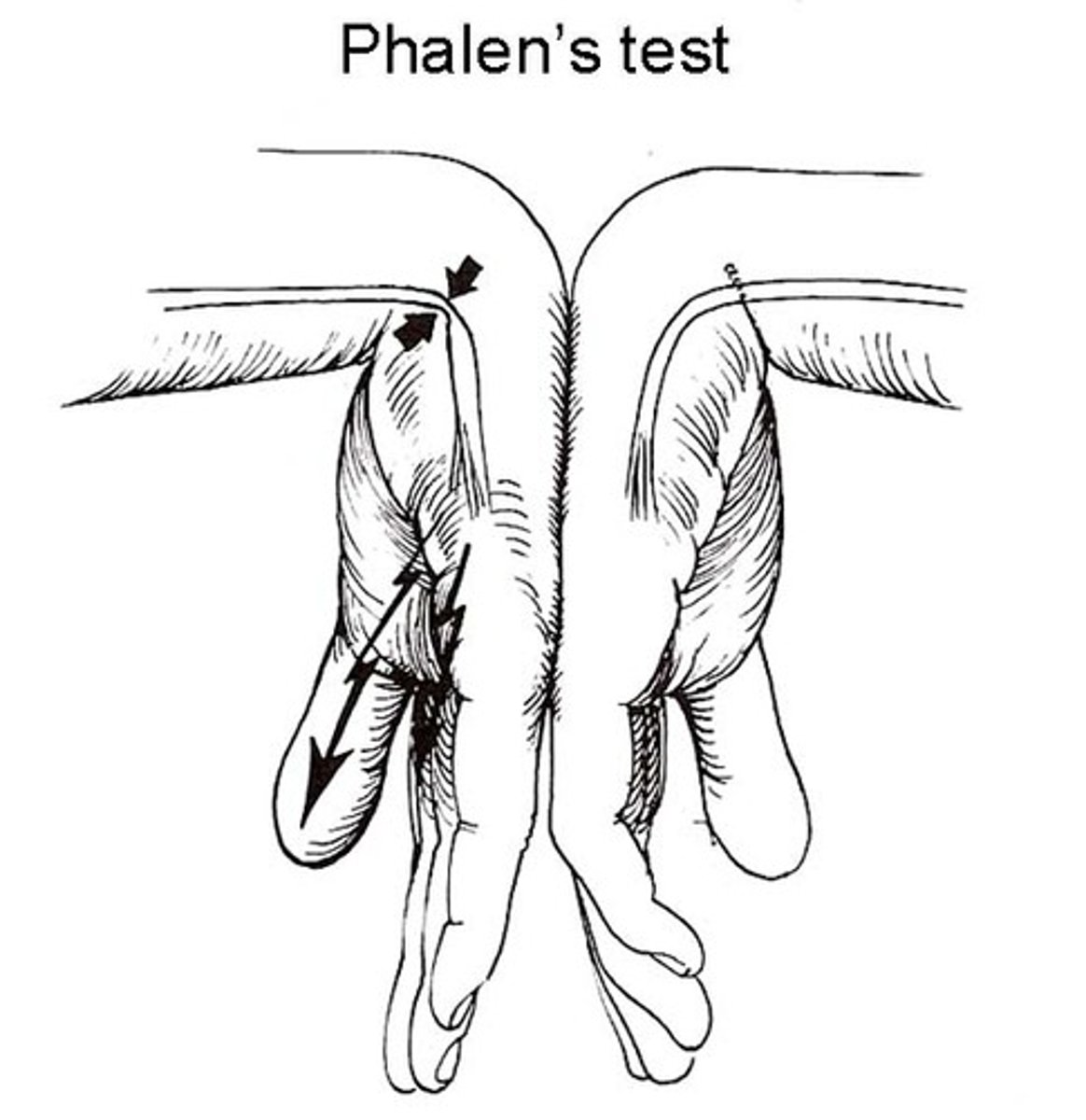
phalen's test vs tinel's sign
types of tests that ask the question: what is the minimum stimulus that the client is able to perceive?
threshold tests
types of threshold tests:
1) pinprick
2) temperature awareness
3) touch pressure
tests protective sensation
1) pinprick: sharp vs dull
2) temperature awareness: hot vs cold
sharp vs dull test
pinprick
pinprick test
Gently touch the skin with a pin & back end of pin and ask the patient whether it feels sharp or blunt
- intact
- impaired
- absent
- hyperalgesic (super pain)
temperature awareness test
- hot vs cold
- tests for protective sensation
- results = intact, impaired, absent
light touch is important for:
fine discrimination
deep touch is important for
protective sensation
touch pressure test
semmes-weinstein
tests vibration sense
tuning fork
what vibration returns first?
a) 30 hz
b) 256 hz
30 hz
if the client is able to successfully complete the 30 Hz tuning fork test, what does this mean functionally?
the client is ready for protective sensation treatment
if the client is able to successfully complete the 256 Hz tuning fork test, what does this mean functionally?
the client is ready for object recognition (discriminative touch)
if the client is not able to complete the 30 Hz tuning fork test, what does this mean functionally?
dont bother with protection sensation recovery
the nerve has not healed enough yet
transmitted though large, myelinated fibers
a) 30 hz
b) 256 hz
30
trasmitted through single quickly adapting nerve
a) 30 hz
b) 256 hz
256
loss of potential sensation in monofilament test means
they are at a big risk for injury
functional tests for touch sensation
1) static 2-point discrimination
2) moving 2-point discrimination
3) localization of touch
4) localization of moving touch
5) Moberg pick up test
6) 9 hole peg test
test that is considered the classic test of functional sensation
static 2-point discrimination
in the static 2-point discrimination, we only test what body area?
test only the finger pads
what mm do we start with in the static 2-point discrimination test?
5mm and move larger if needed
how many trials do you conduct in the static 2-point discrimination test? how many does the client need to get right?
7/10
what returns first?
1) static 2-point discrimination
2) moving 2-point discrimination
2) moving 2-point discrimination
what mm do we start with in the moving 2-point discrimination test?
8 mm
move proximal to distal
what test: touch an area and client indicates where they were touched
localization of touch
what test: touch and area and move to another and then the client indicates where you touched them
localization of moving touch
Localization of touch is an important test to perform after nerve repair because
it helps determine the client's baseline and projected functional prognosis.
Moberg pickup test (MPUT)
functional tests
placing common objects in a container
useful for median/ulnar nerve involvement
both hands with vision and then without
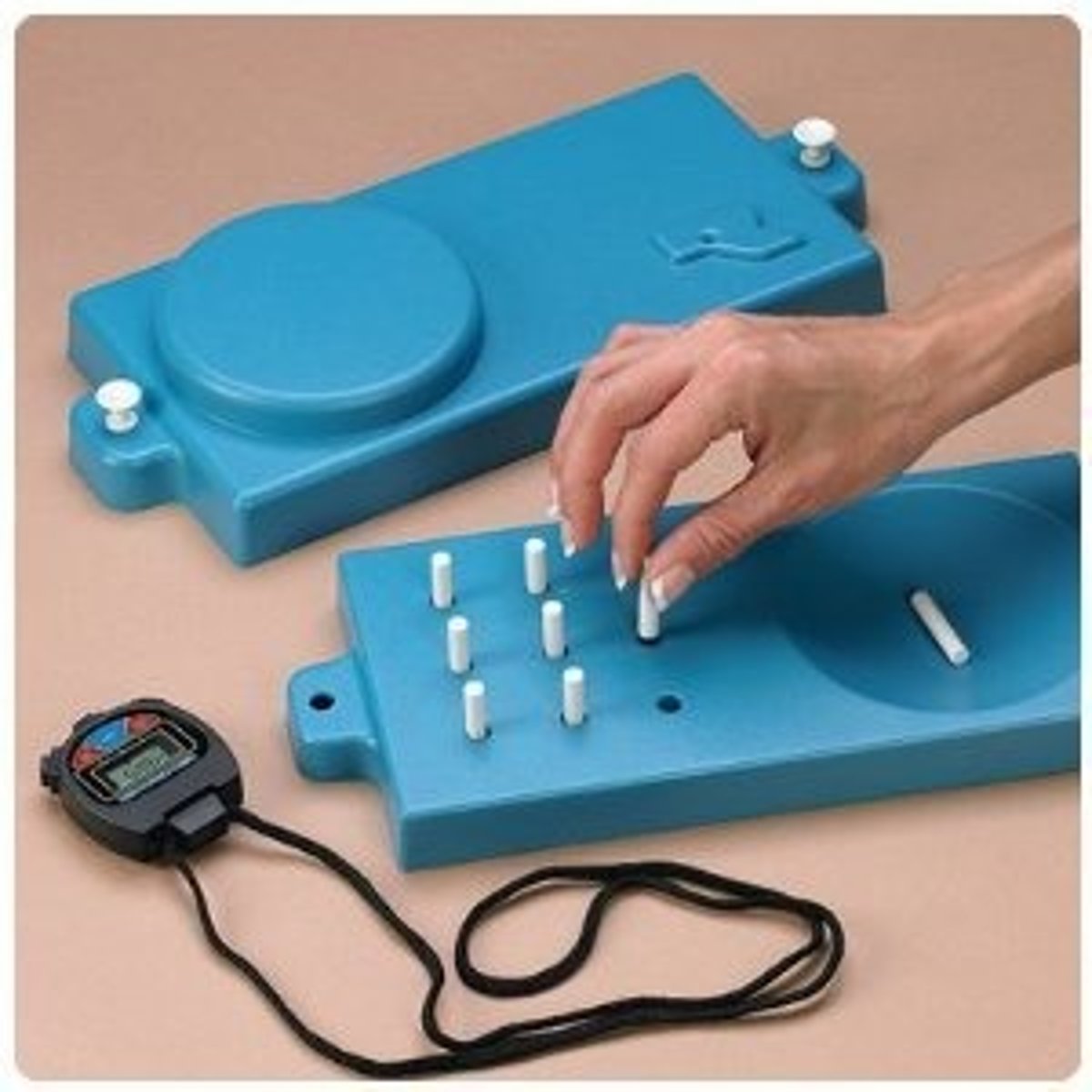
9 hole peg test
Measures finger dexterity
-the time fo each hand to place 9 pegs in a square board and remove them is the score

clients with sensory loss are either
1) hypersensitive
2) hyposensitivity
3) sensory loss
hypersensitive
normal stimulus is overbearing
hyposensitive
unable to sense normal stimulus
sensory loss
unable to discriminate sensation
tx for hypersensitivity
desensitization
grade stimulus from soft to harsh
The stimuli are upgraded to be slightly more noxious as the client's tolerance increases.
... is a decrease in a response after repeated benign stimuli.
Habituation
tx for hyposensitivity
discriminative sensory reeducation
grade stimulus from gross to fine
Discriminative sensory reeducation is graded by initially using grossly dissimilar objects, such as a spoon and a penny, and progressing over time to more similar objects, such as a dime and a penny.
sand paper vs silk
there are two types of clients who may benefit from sensory reeducation:
1) those who require reeducation to compensate for the dangers associated with sensory loss
2) those who may need to effect change on nervous systems that are either hypersensitive or more dormant.
Clients are candidates for discriminative sensory training if they
have intact protective sensation