Lecture 7: Industrial minerals & Fossil fuels
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Building stones
Granite - coarse grained and hardwearing
Sandstone - quartz and feldspar
Limestone/Dolomite - CaCO3 - MgCO3
Marble - metamorphosed limestone
Slate - clays compressed during metamorphism
What are crushed rocks?
Aggregates:
largest volume hard-rock mineral commodity
building foundations and road building
easy to mine and crush but hard and inert
most countries have plentiful supply
mined openpit in quarries
Sand and gravel
concrete production and road building
weathered or abraded by glaciers from parent rock and transported by water
found in river chanels, their floodplains and alluvial fans and glacial deposits
exploited through dredging
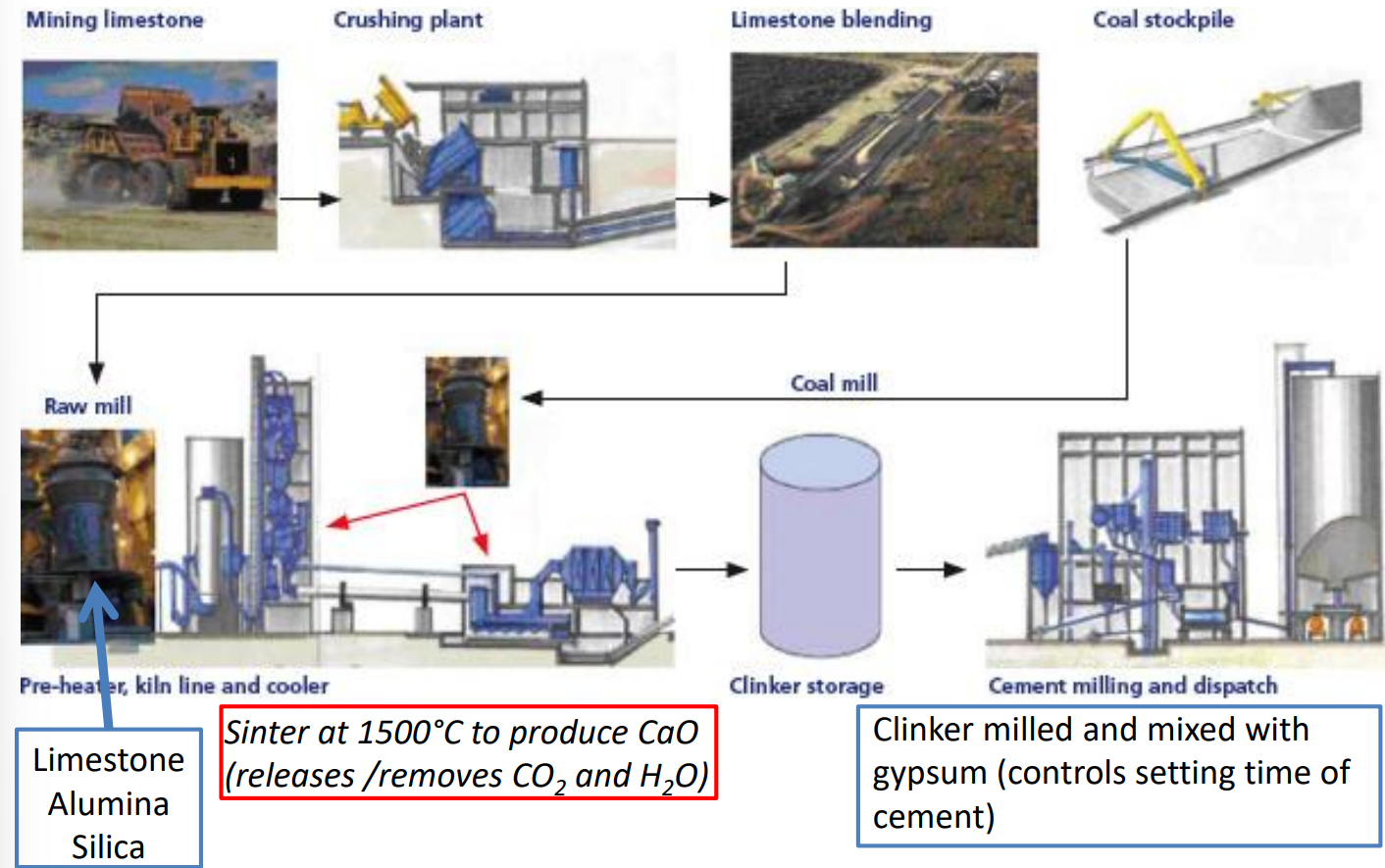
Cement
chemical binder
mixed with sand to make mortar
sand and gravel to make concrete
cement plants usually located near limestone quarries
lime, alumina, silica, gypsum
Glass
melt together minerals that can be cooled in such a way that they do not form an organised arrangement of atoms
annealed - slow cooling
Silica, soda, lime, alumina
Diamonds
Formation: dense form of carbon, hardest known material
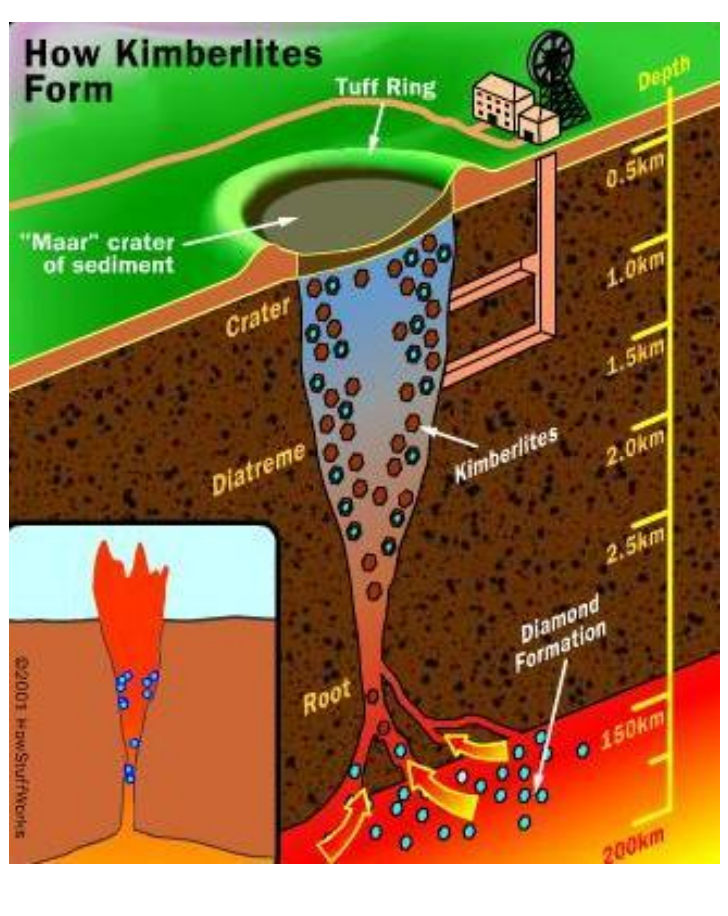
Mining: kimberlite pipes
Uses: cut, grind and polish all the modern alloys and ceramics. 80% diamonds used in industry
Diamonds: formation
form at high pressure and temp (>30kb, ~150km)
kimberlites = igneous rock highly enriched with magnesium and volatiles (CO2 and H2))
→ of those found today onlt 3% are significantly diamondiferous
→ less than 100 have been minedform pipes as magma transports diamonds to the surface
Lamproite pipes: shallower deposits
Asteroid impacts: Popigai Russia
Gold
Formation: hydrothermal and placer deposits
Mining:
Uses: corrosion and chem resistant, most mined is still in use today. aerospace, jewellery and special alloys
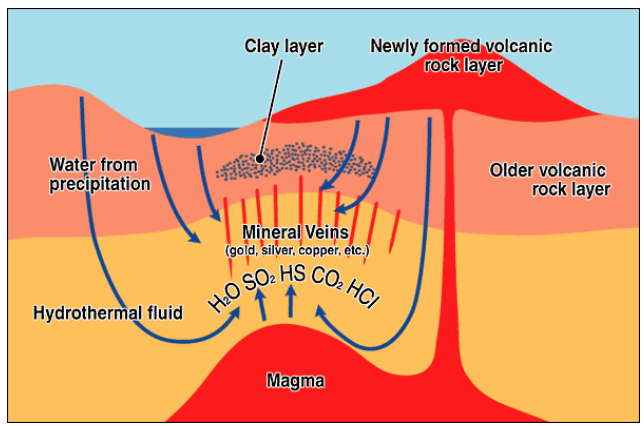
Gold: Hydrothermal deposits
hydrothermal veins associated with granitic intrustions
gold-bearing veins move along fractures in rocks
quartz+sulfide minerals
Gold: Placer deposits
weatherred out from primary deposits
concentrated through density by flowing water
created california gold rush in 1849
Gold: famous deposit
Witwatersrand deposits
south africa 1886
ancient placers
formation:
→ conglomerates laid down in shallow marine basin 2.3-2.8Ga
→ brought in by rivers from unknown primary sources in low oxygen conditions
→ associated with pyrite and uranium depositsDeepest: 3.5km
Rare Earth Elements
~169.1 ppm
form: phosphates, silicates, carbonates, oxides and halides
La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu
China produces 68.6%
Primary deposits:
Carbonatites e.g. mountain pass, usa
Alkaline igneous rocks e.g. lovozero, russia
Secondary deposits
Placer deposits e.g. IREL mineral sands, India
Ion adsorption clays e.g. South China Clay Deposits
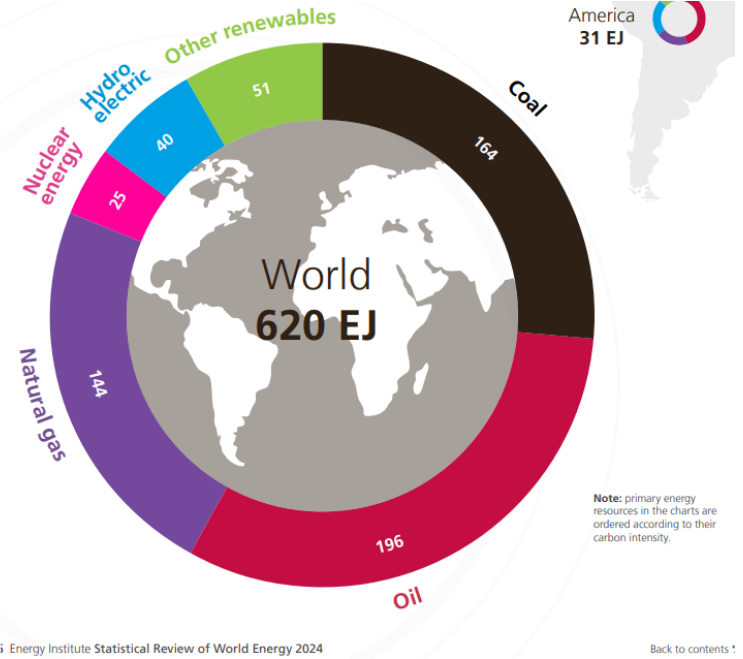
What were the key trends in global primary energy consumption in the most recent year?
Total primary energy consumption rose 2% over 2022, exceeding its 10-year average and 2019 levels. Renewables reached 14.6% of total energy (up 0.4%), and with nuclear, accounted for over 18%. Fossil fuels dropped to 81.5% of primary energy (down 0.4%).
Carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is the continuous movement of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms. Key processes include photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, ocean uptake, and fossil fuel combustion.
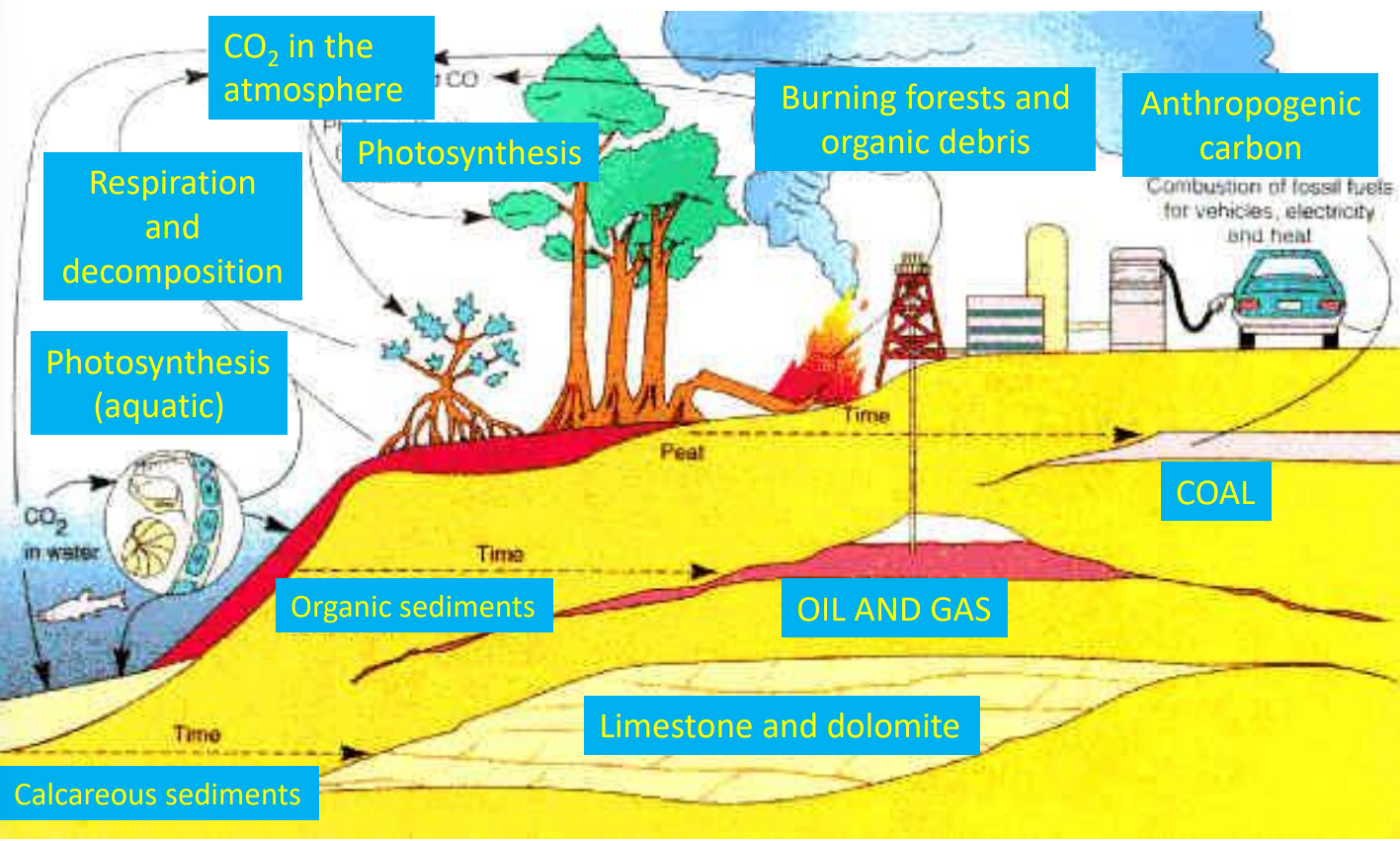
How are fossil fuels created?
created as atmospheric CO2 formed into organic matter (C, H, O)
1% est of the total organic matter is preserved through burial in sediments
How is coal formed?
dead plant matter millions of years ago form thick layer of matter
weight of laters that form ontop increases heat and pressure
plant matter undergoes chemical and physical changes, pushing out oxygen and leaving rich hydrocarbon deposits
what are humic coal ranks?
~10% organic matter preserved during peat forming conditions, leaves behind large hydrocarbon molecules
increase in C = decrease in H and O
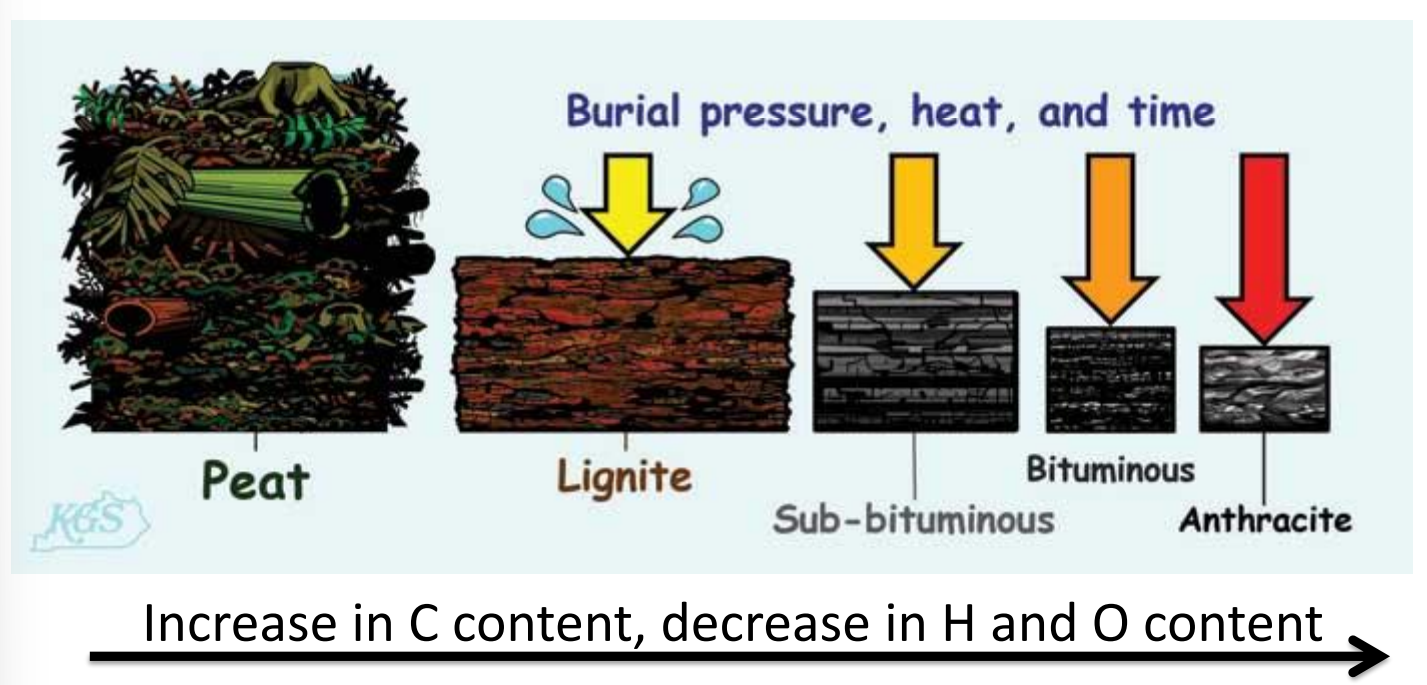
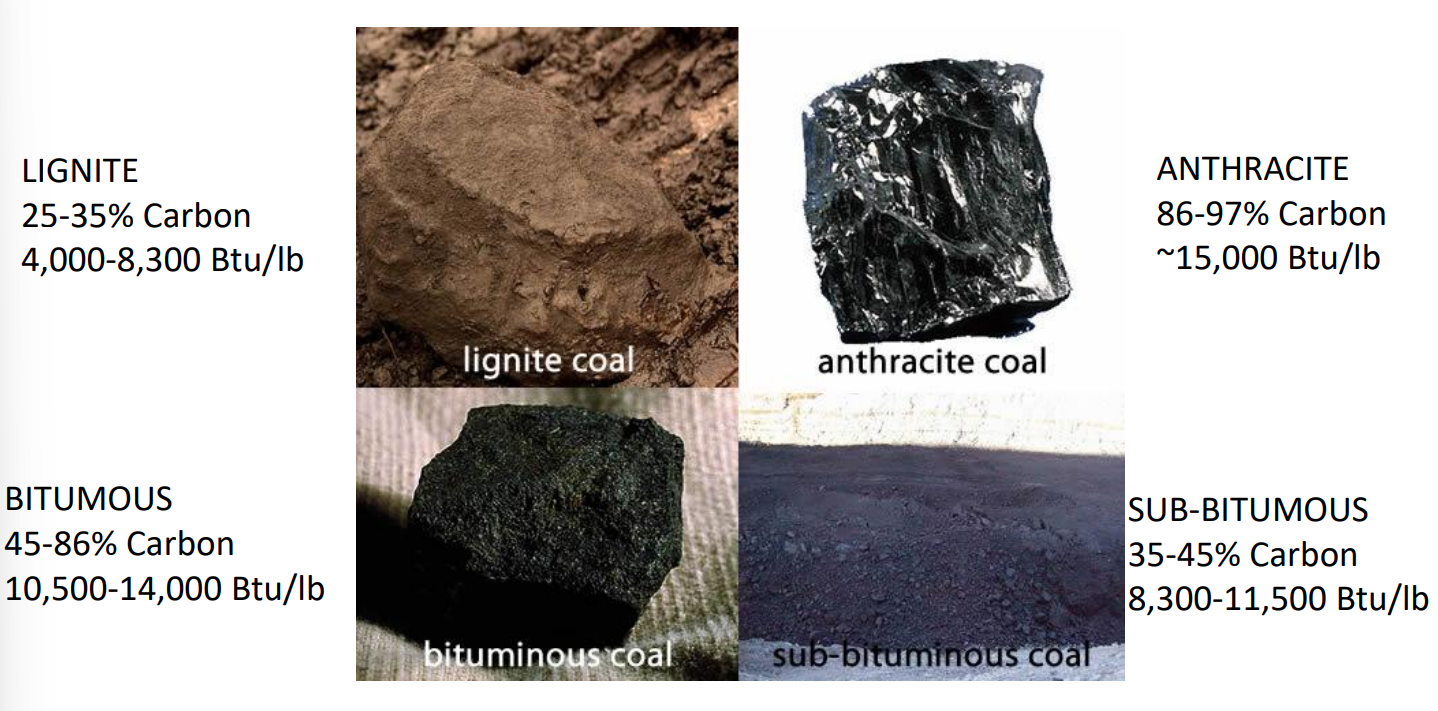
State four key different coal types.

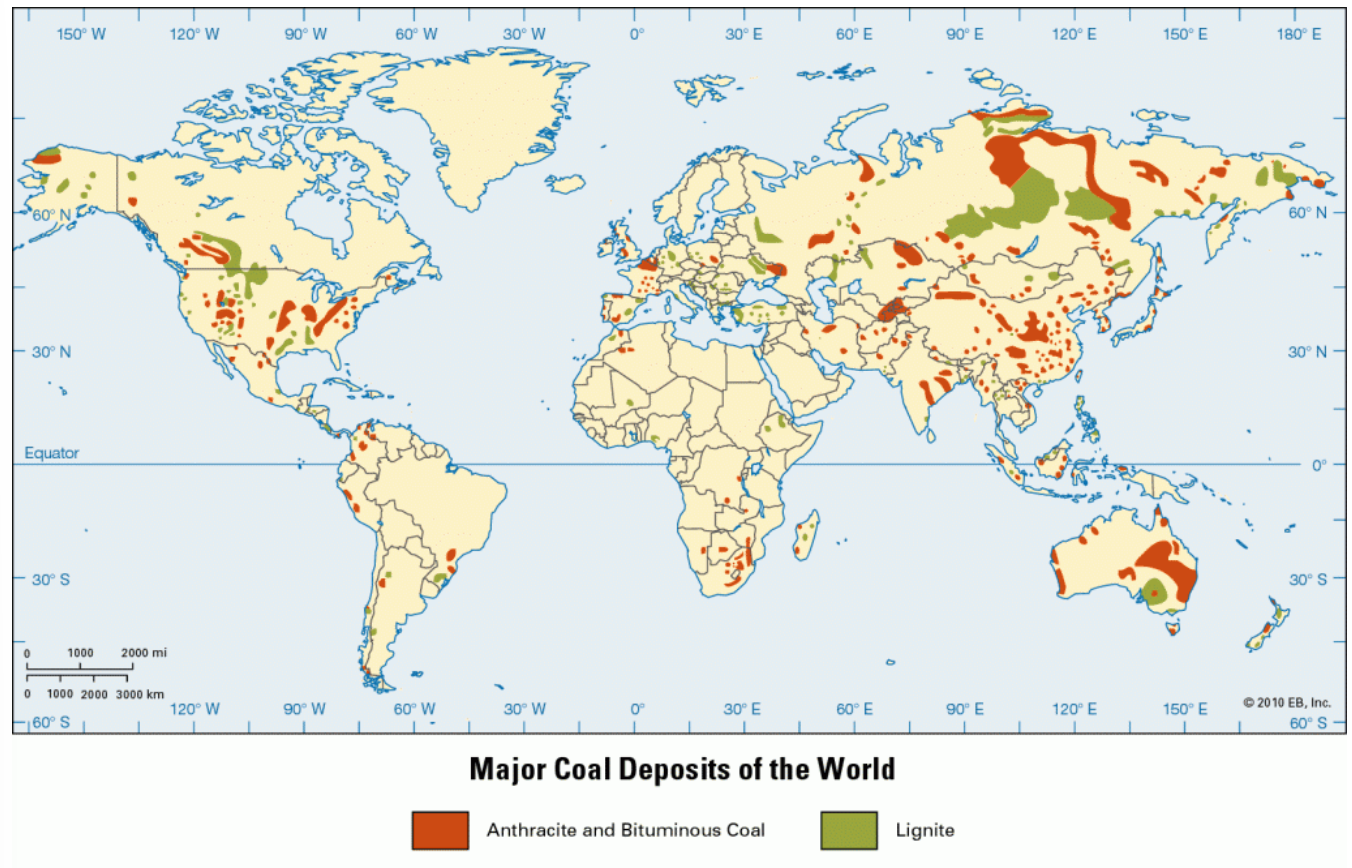
where are major coal deposits on earth?
describe how impurities cause pollution
Clay minerals and other non-combustibles = ash
Carbonate minerals e.g. Fe carbonate
NH4 N2O, NO, NO2
H2 S and FeS2 SO2
NaCl –causes corrosion in boiler plants
Trace elements e.g. Ge, As, U
How is oil and natural gas formed?
tiny organisms died and were buried on ocean floor
over time, covered by sediment and rock
over millions of years, the remains are buried deeper and deeper
heat and pressure turns them into oil and gas
describe the processes and depths at which oil and gas are formed
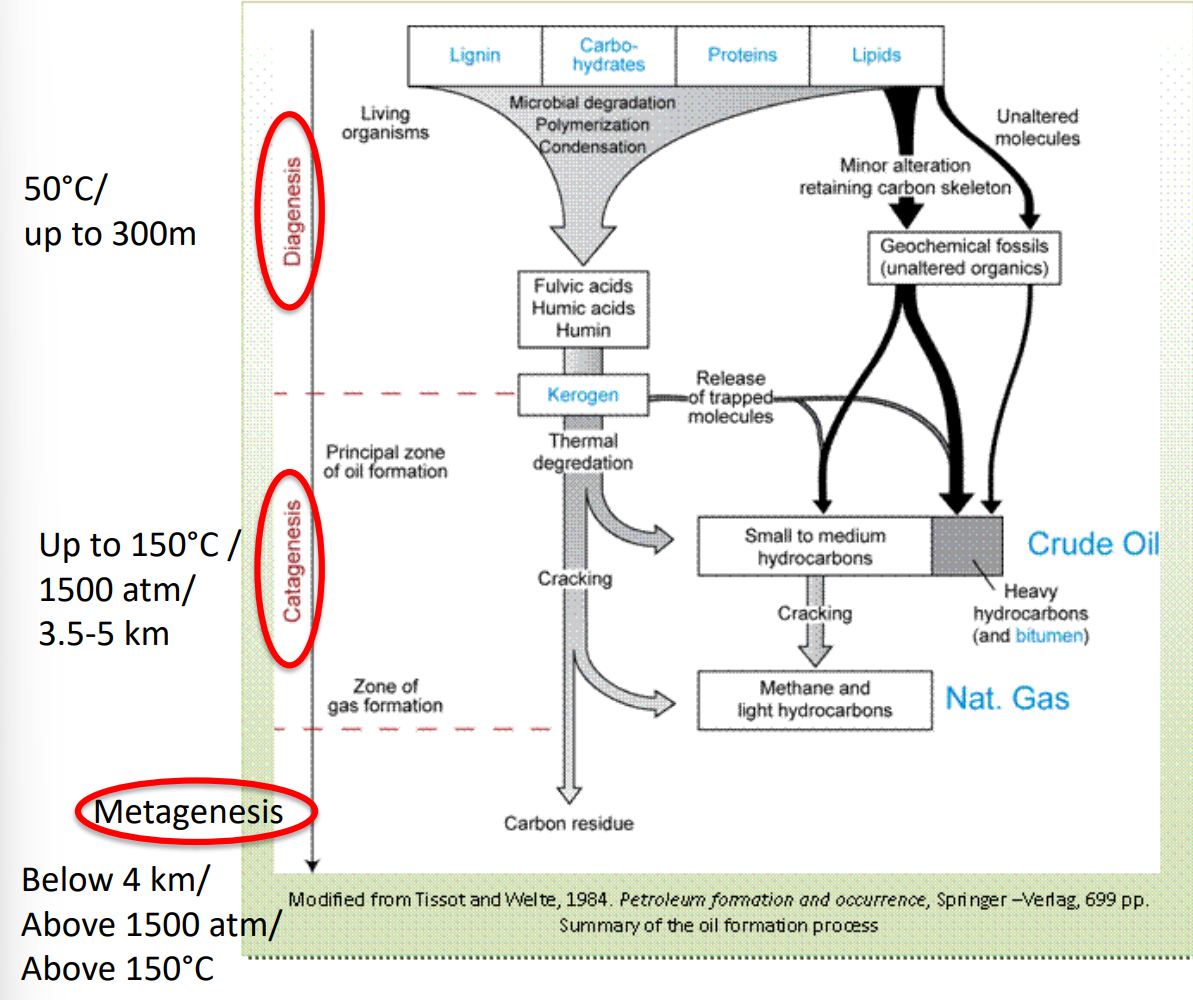
oil and gas formation with temperature
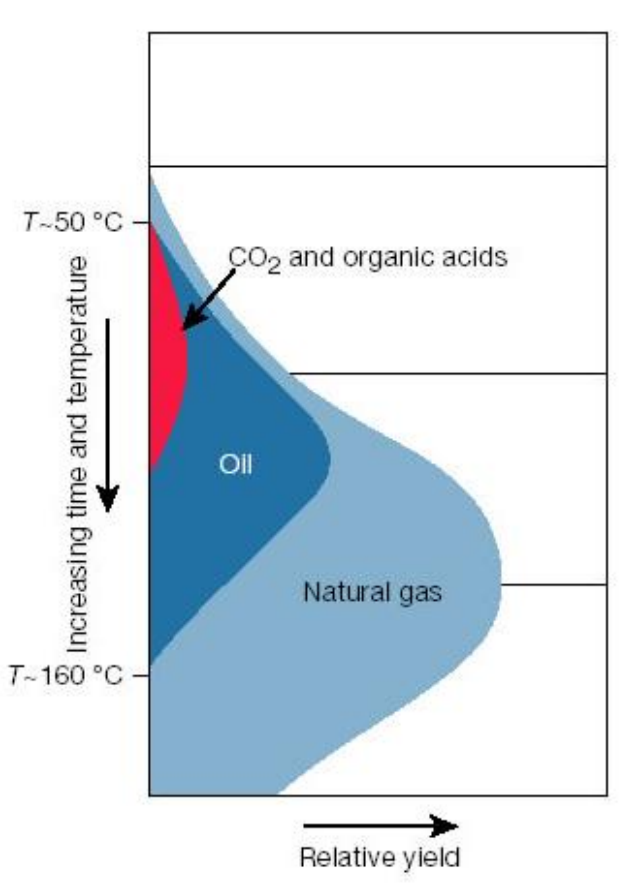
Natural gas composition
>99% methane (CH4)
minor ethane (C2H6)
propane (C3H8)
butane (C4H10)
plus CO2 H2S N2 H2 NH3
terrestrial and marine environments
Petroleum composition
mixture of numerous hydrocarbon compounds (basis for lubricants, plus >7000 organic compounds, plus “petrol”
marine environments
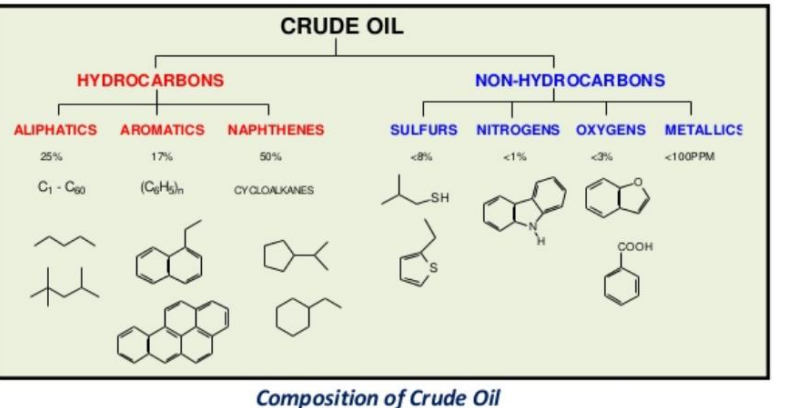
reservoir rocks and their properties
porosity: void space as opposed to solid phase within a rock. Void space may be infilled by either fluids (oil, brine, etc) or gasses (atmosphere, hydrocarbons or gas)
permeability: relative ability of a material (rock) to transmit fluids through connected pore space
→ rocks with similar porosity do not necessarily have the same permeability
What are seals?
Rocks that significantly reduce the onward migration of fluids in the subsurface
Attributes:
small pore sizes
ductile rocks (resist fracturing)
thich rock units with wide lateral extents
Mudstones, evaporites, chalk and crystalline lithologies
when did oil discovery peak?
1960s
today we consume ~4x as much as we discover
oil will not run out soon, however, good quality oil will
illustrate the accumulation of oil and gas in reservoirs
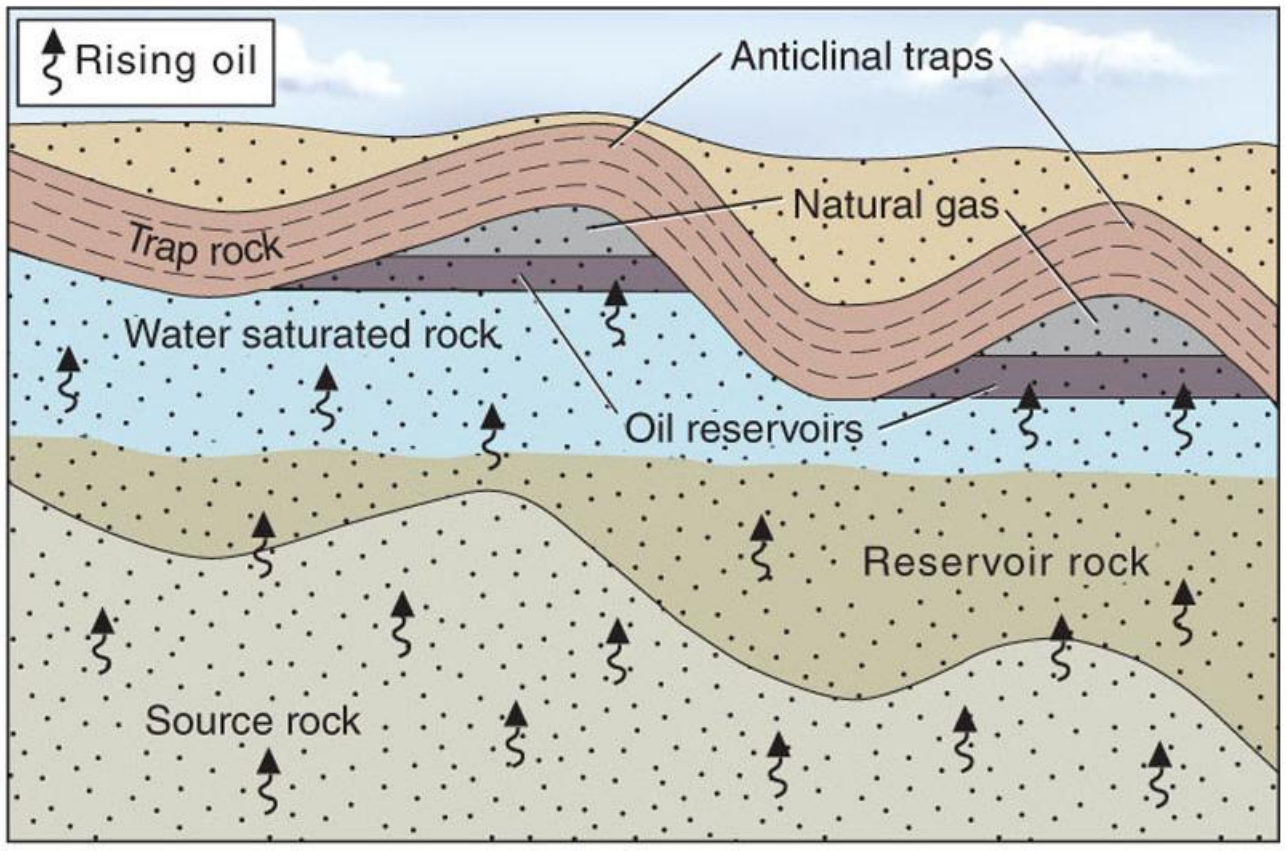
What are some examples of oil extraction?
Primary = Gusher
Secondary = horsehead beam oil pumping unit, water injected to push it up
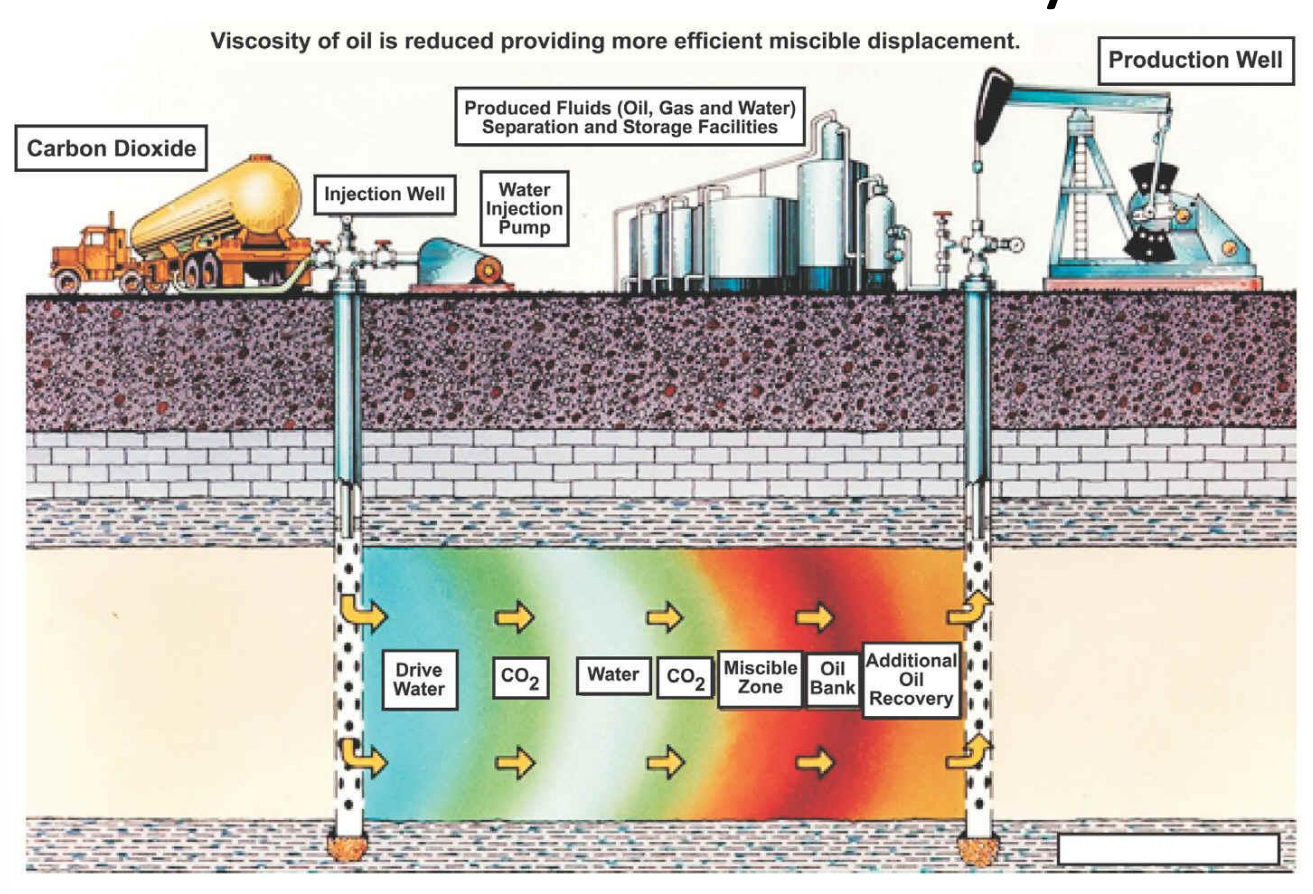
explain the enhanced oil recovery process
CO₂ EOR involves injecting carbon dioxide and water into an oil reservoir to mix with and reduce the viscosity of trapped oil, forming a miscible zone that pushes oil toward a production well for additional recovery.
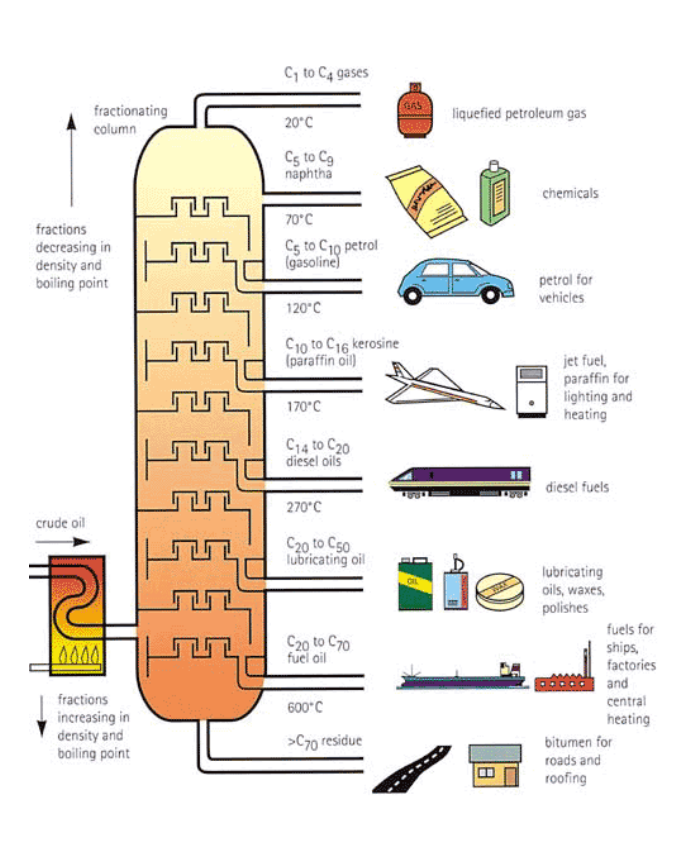
How does oil refining work?
Fractional distillation:
heating of crude oil to higher temp to condense into liquid to form useful hydrocarbons
what is natural gas composed of and how did the gas industry begin?
gas industry began with coal gas in the early 1800s
today it is dominated by natural gas → 80-99% methane with ethane, propane, butane, hydrogen and small amounts of CO2 and N2
Piped from wells to process plants - remove S, H2O, add “gas” smell - transmit via high pressure lines (24 km/h) Distant sources- liquefy by cooling (-162°C; 1/600 volume) and transport in ships
state some unconventional fossil fuels
oil based
→ oil (tar) sands
→ oil shalesGas based
→ coalbed methane
→ shale gas
Oil shales/sands
fine grained rocks - kerogen
swmps and shallow marine envs
xontains mixture of heavy hydrocarbons - can be converted to oil by heating >500C
USA and Russia
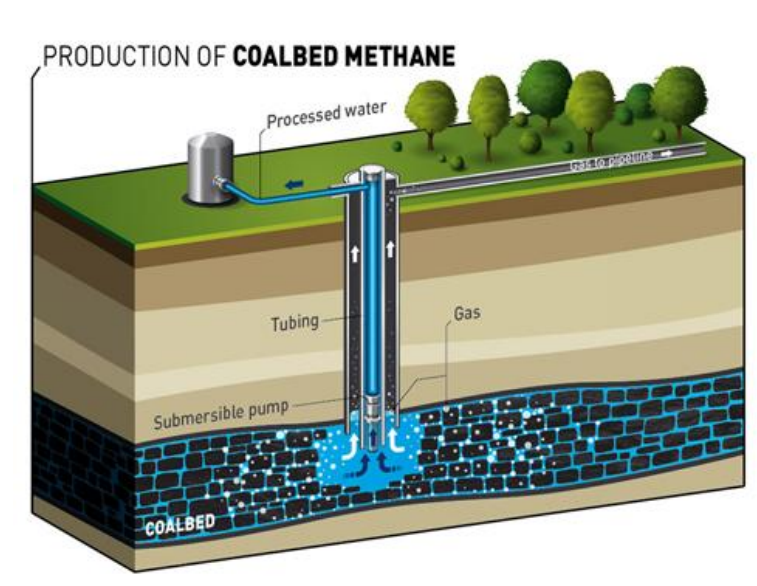
What is Coalbed methane?
CBM is extracted by releasing pressure in coal seams, by natural gas production or by pumping water
most gas is adsorbed on the surface of the coal - can contain 2-3x more gas per unit of rock volume than conventional gas deposits
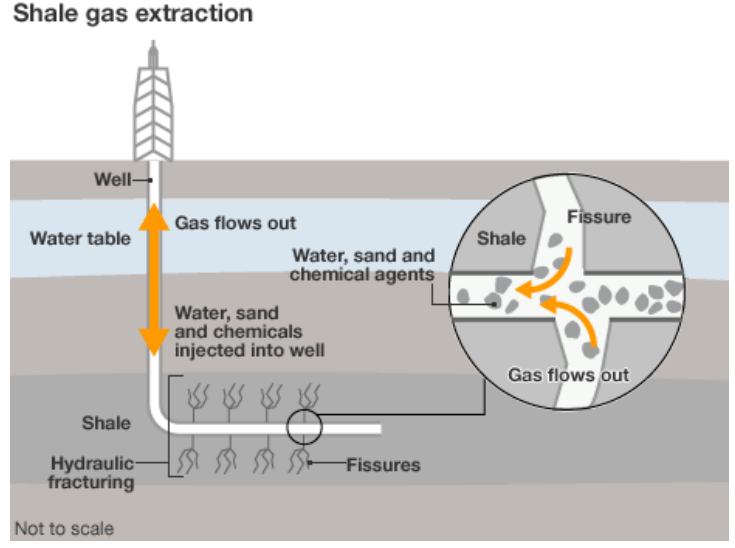
Shale gas
extracted from source rock and has naturally low permeability
gas held in frctures, pore spaces and adsorbed onto the organic material of shale
‘crack’ the rock using fracturing methods like ‘fracking’
Publication: Unextractable fossil fuels in a 1.5C world
To have a 50% chance of limiting warming to 1.5 °C, by 2050 about 60% of oil and fossil methane gas and 90% of coal must remain unextracted. Global oil and gas production must decline by 3% annually, with most regions reaching peak production within the decade.