2.2.1 rate of reaction and measuring rates of reaction
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
what happens as a chemical reaction proceeds to conc of reactants and products
concentration of reactants decreases and concentration of products increases
what is the rate of reaction
speed at which a chemical reaction takes place
what is the units of rate of reaction
mol dm-3 s-1
what is the equation for rate of reaction
change in concentration of reactants or products / change in time
draw the rate of reaction graph for conc of reactants against time and conc of products against time
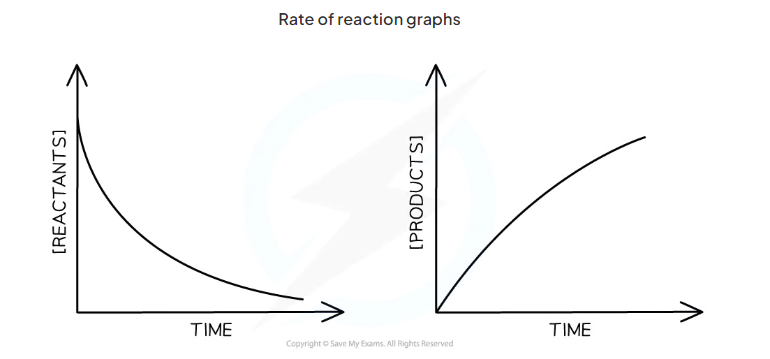
the steeper the gradient…
the faster the rate of reaction
how do we calculate the rate of reaction at a give time (instantaneous rate of reaction)
draw tangent to the curve at that time and cacluate the gradient of the tangent
how do we calculate gradient of tangent
gradient = change in y / change in x
what do we need to measure to measure the rate of reaction
how quickly the reactants are used up or how quickly the products are formed
why is the initial rate of reaction fastest
high concentration of reactant particles results in high frequency of collisions between reactant particles
why does the rate of reaction decrease with time
concentration of reactant particles decreases so decrease in frequnecy of collisions between reactant particles
what happens to the tangent when reaction is complete
tangent is horizontal
what are 3 ways of measuring rates of reaction
mass loss
gas production
colormetry
what is a colorimeter or spectrophotometer
measures the amount of light that passes through a solution
when can we use a colorimeter to measure rate of reaction
when a solution changes colour in a reaction
how does this work
light intensity that reaches a detector is measured and data plotted to show how conc of reactants or products changes with time
why can colorimetry not be used to monitor formation of coloured precipitates
light will be scattered or blocked by precipitate
what usually happens to a gas if produced in a reaction
is lost from the reaction vessel
what does this mean for the mass of the vessel
it decreases
how do we measure rate of reaction uses changes in mas
mass measured every few seconds and results plotted
what is a limitation of this method
the gas must be sufficiently dense or the change in mass is too small to measured on balance
how can we measure rates of reaction using changes in volume of gases
when gas produced, can be trapped and volume measured over time