Chapter 20: Cell Tissues, Stem Cells, and Cancer: Key Concepts and Molecular Pathways
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are the primary cell types found in tissues?
Epithelial cells embedded in extracellular matrix (ECM) along with other cell types and connective tissue.
How are cells organized within tissues?
are organized into tissues, which often assemble into organs, maintaining distinct locations and boundaries.
What is the role of stem cells in tissue maintenance?
are required for the maintenance and repair of tissues, capable of self-renewal or differentiation.
What happens when a stem cell divides?
Each daughter cell can either remain a stem cell or differentiate into a specialized cell type.
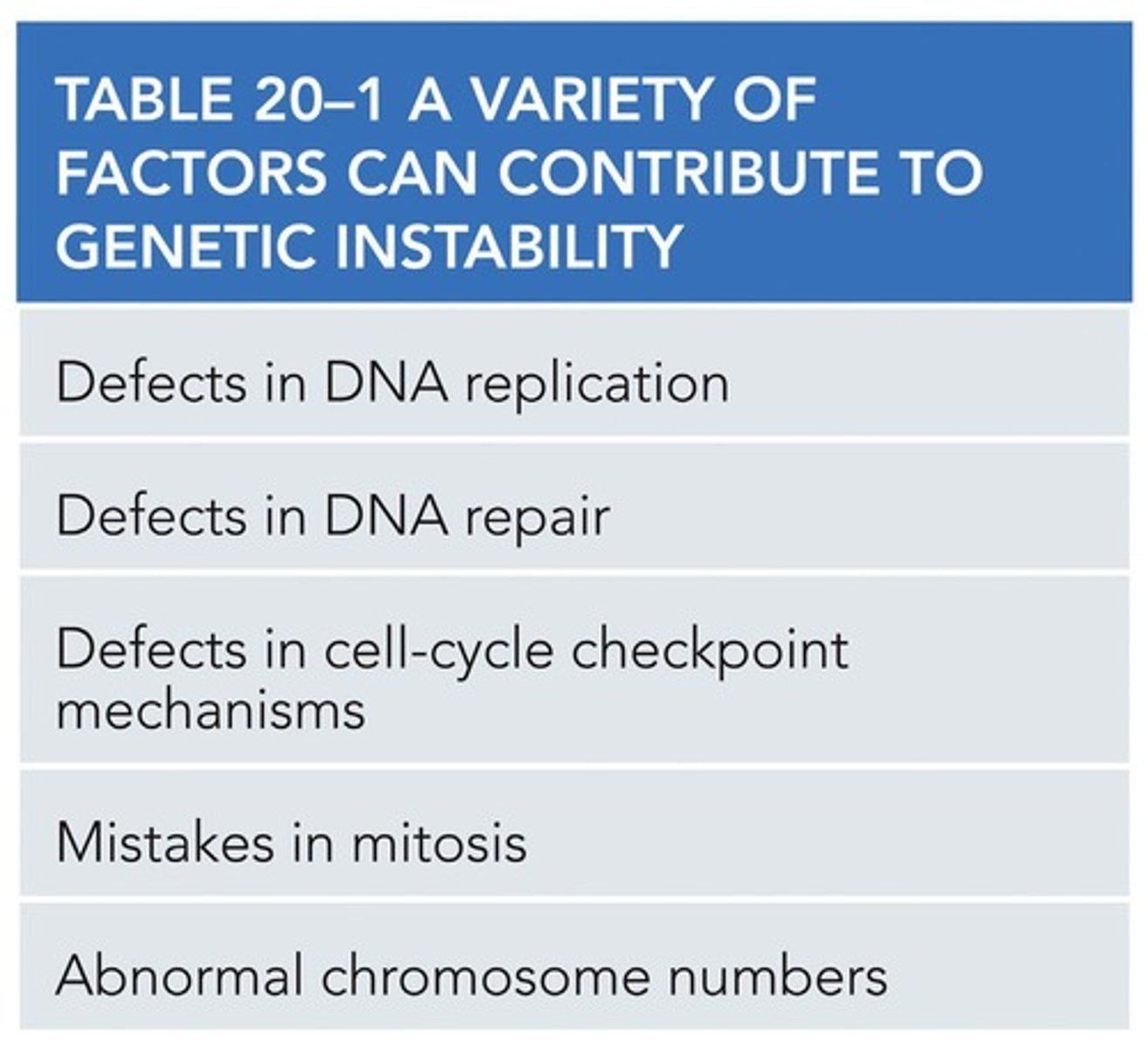
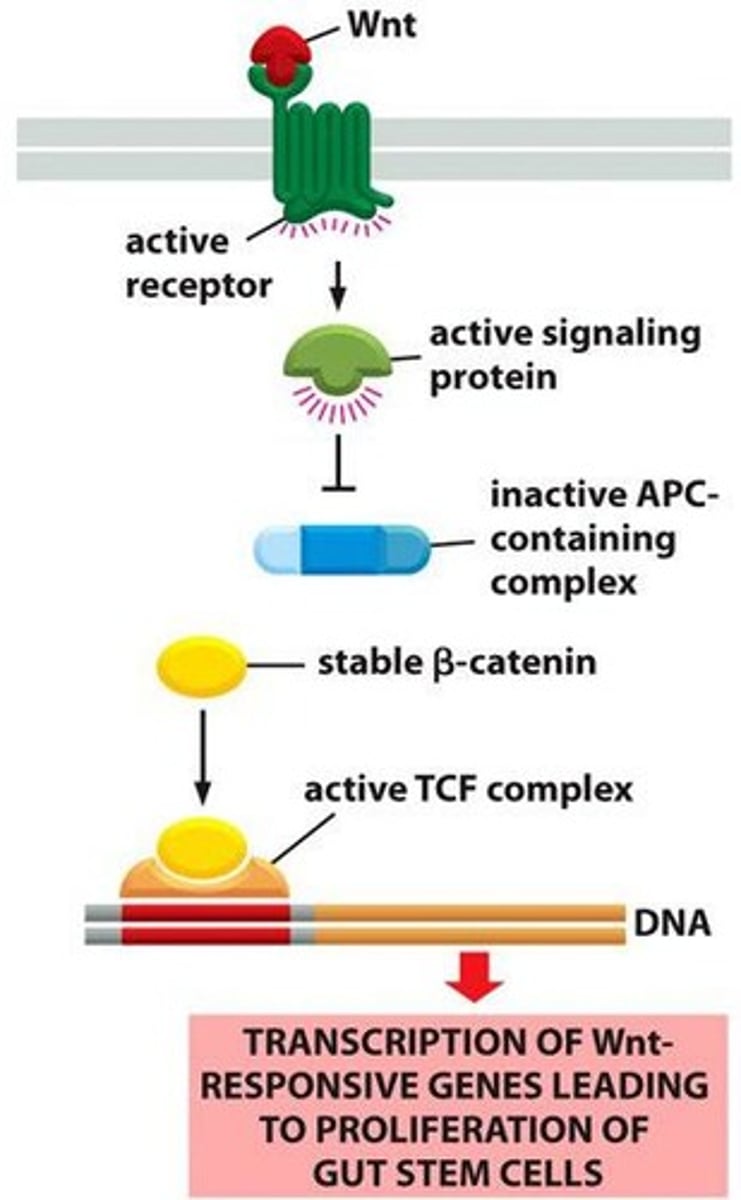
What is the significance of the Wnt signaling pathway in stem cells?
must be active to maintain stem cell fate, as shown in patients with familial colon cancer.
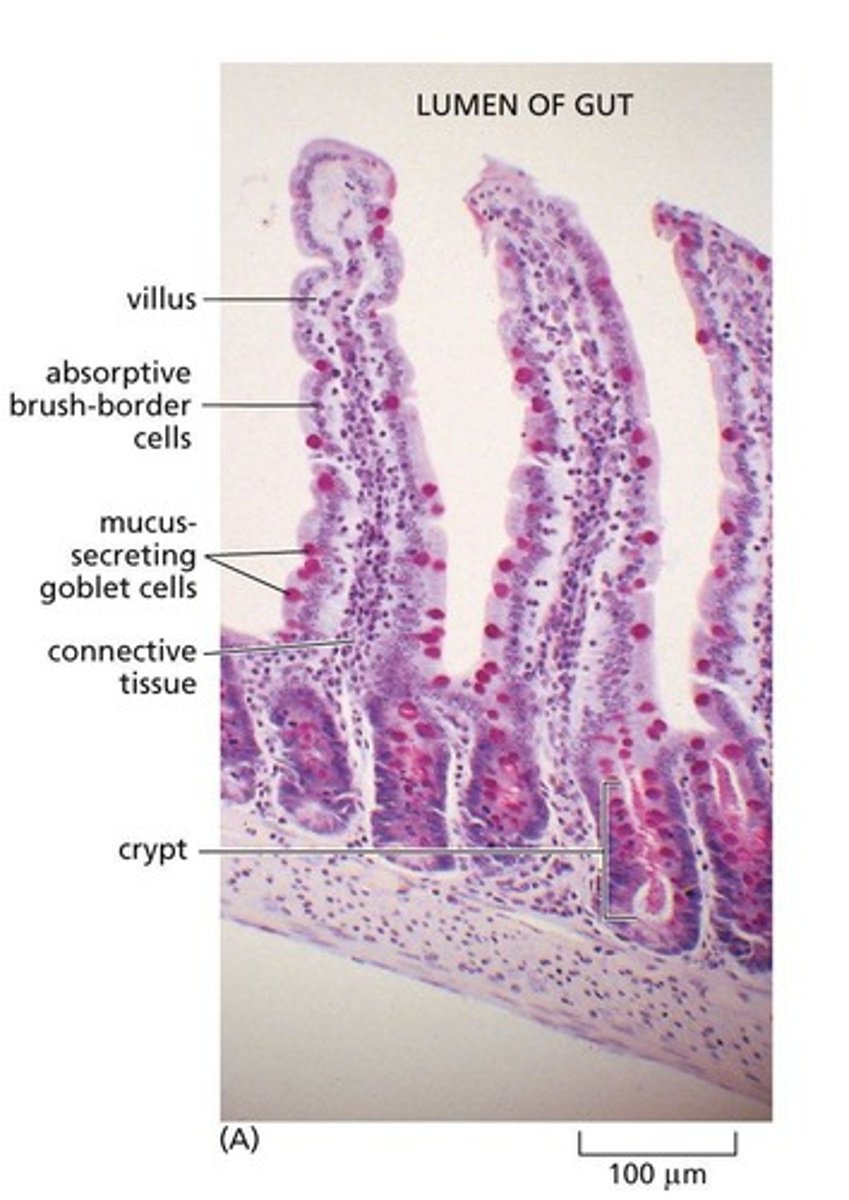
Where are intestinal stem cells located?
are located at the bottom of intestinal crypts within the connective tissue.
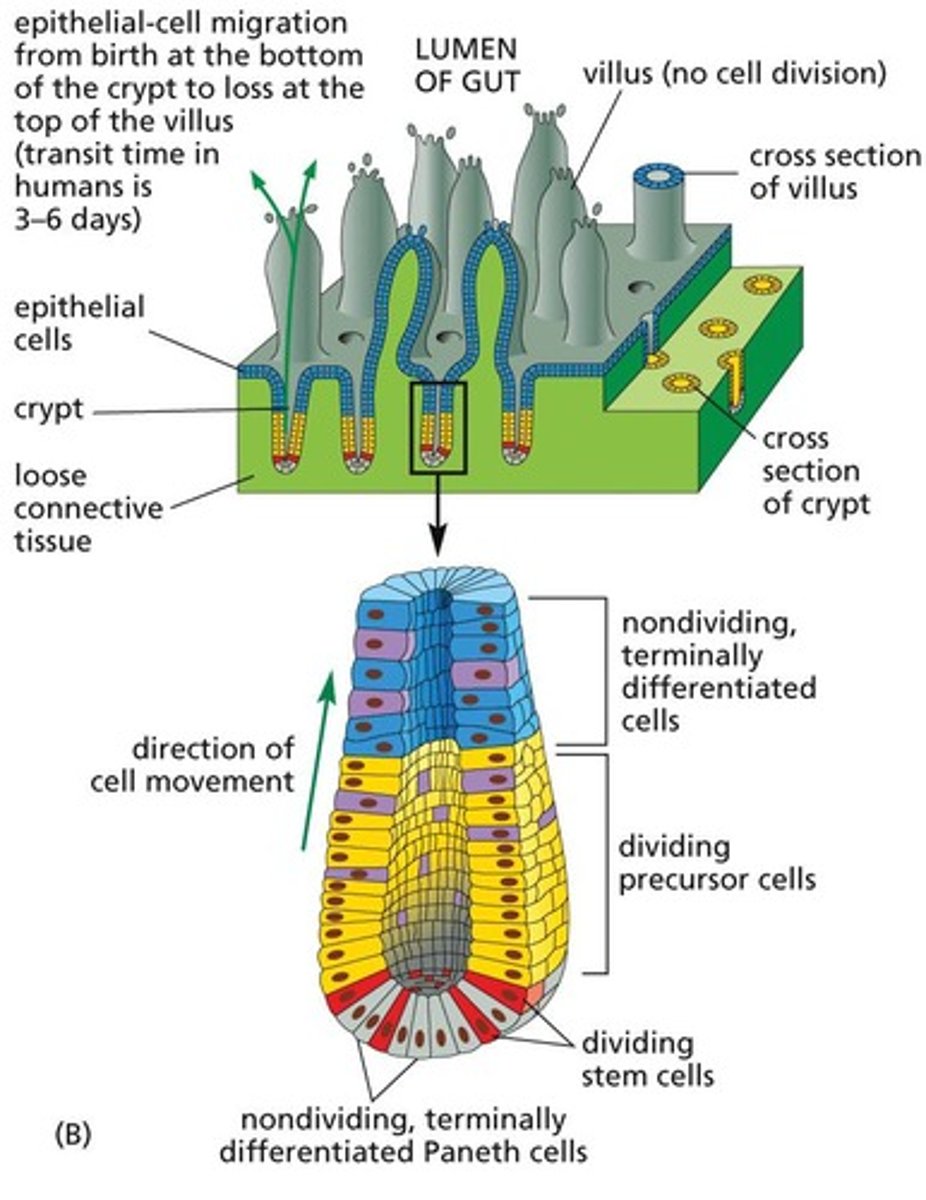
What is the process by which intestinal stem cells contribute to the epithelial layer?
They generate dividing precursor cells that undergo additional divisions before differentiating into absorptive and secretory cell types.
What are the two types of stem cells based on their differentiation potential?
Multipotent stem cells can differentiate into several cell types, while pluripotent embryonic stem cells can produce all cell types of the organism.
What is the role of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) in stem cell culture?
signals to maintain embryonic stem cells in their undifferentiated state.
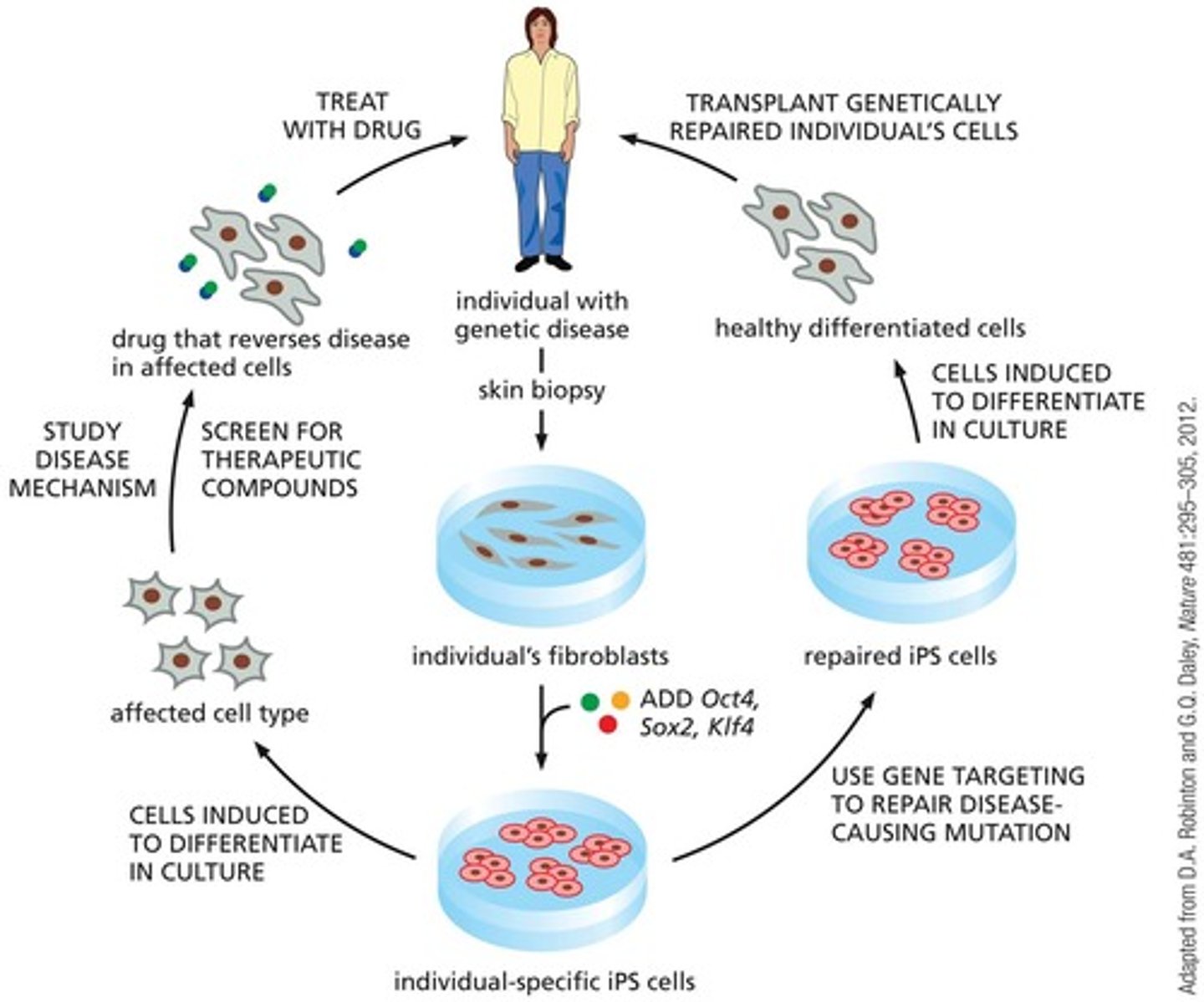
How are induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) created?
Adult somatic cells are forced to de-differentiate by exposure to specific transcription factors.
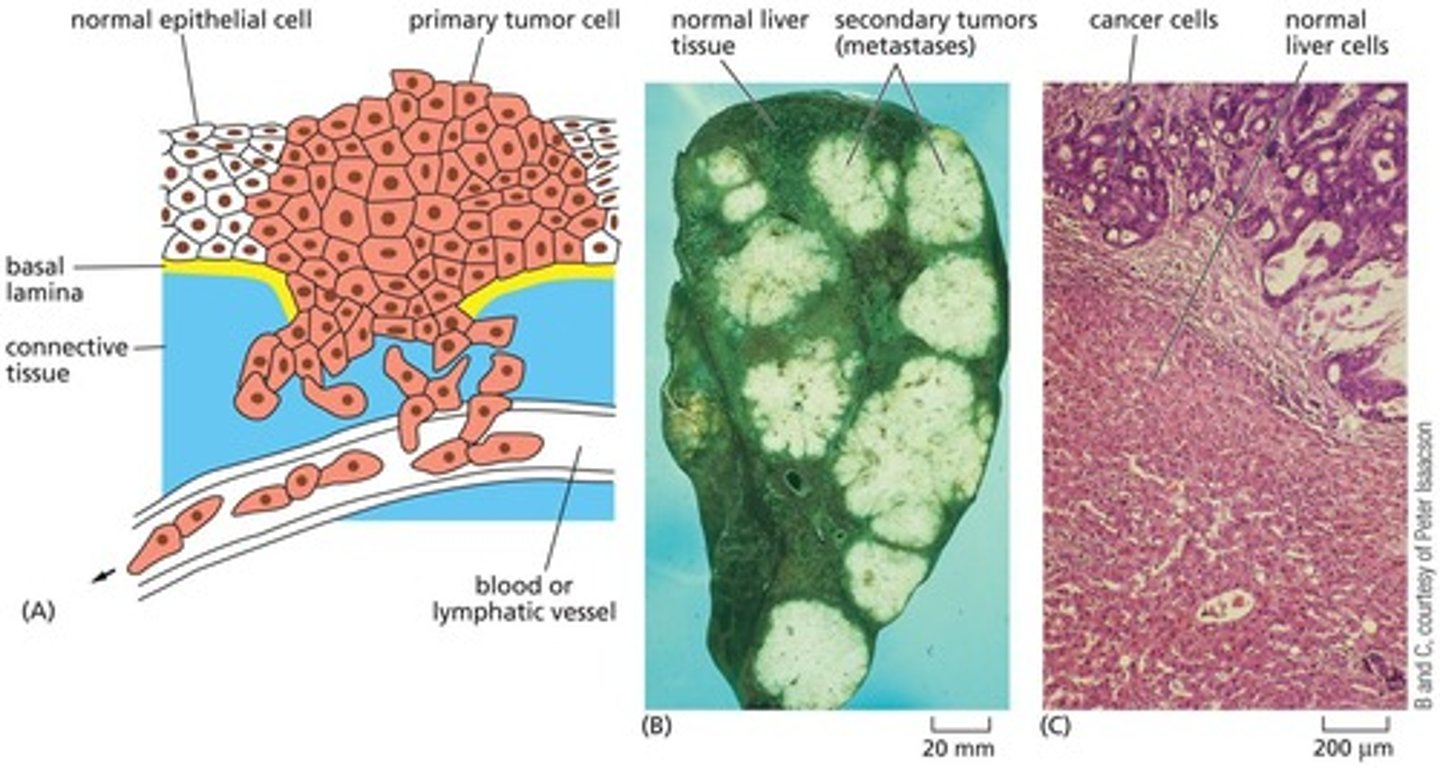
What defines cancerous cells?
are malignant and have invaded surrounding tissues, often breaking through the basal lamina.
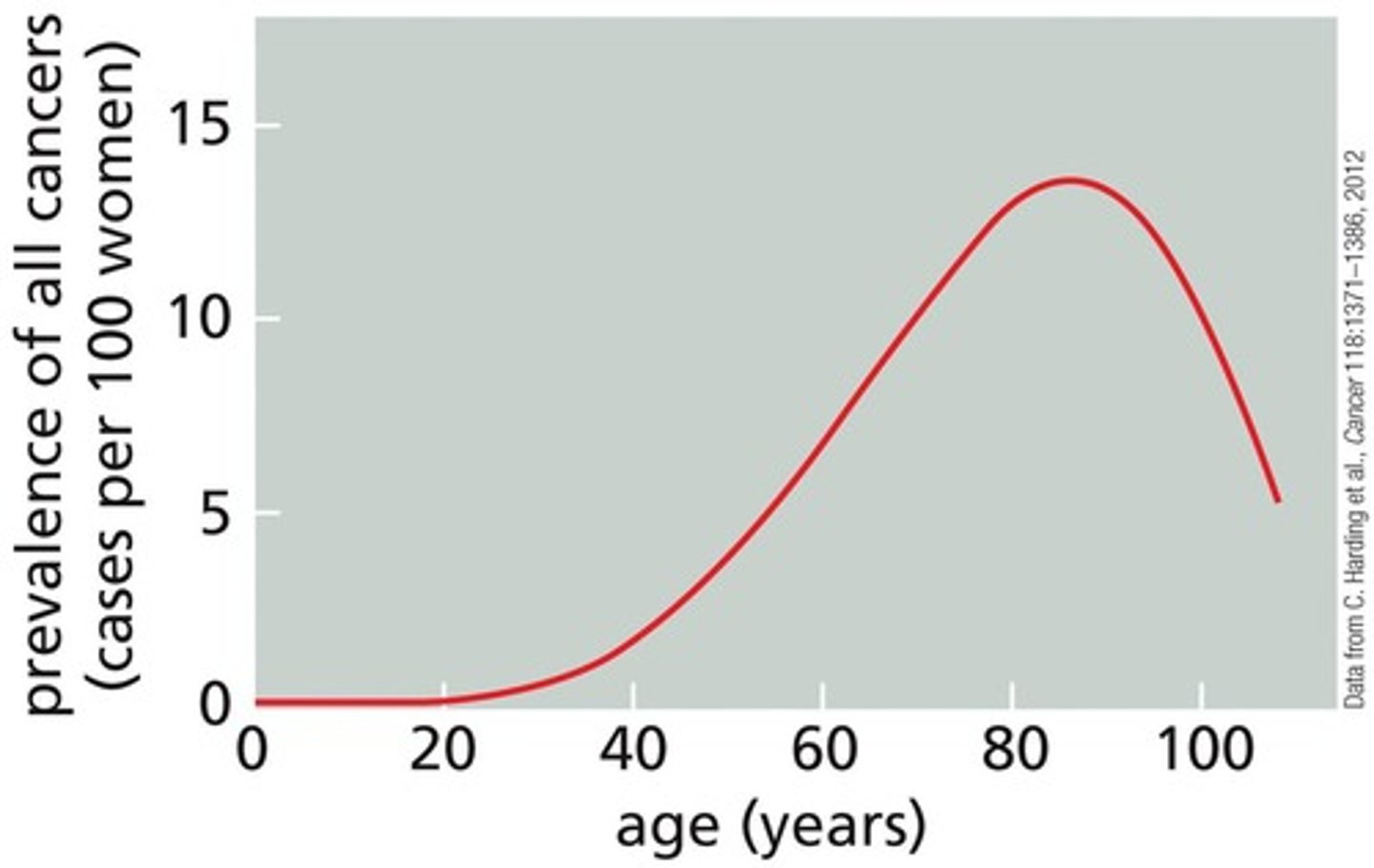
What is the relationship between age and cancer rates?
Rates of cancer increase with age due to the accumulation of mutations over time.
What are proto-oncogenes and how do they become oncogenic?
are normal genes that promote cell division; they become oncogenic through mutations that make them overactive.
What is the function of tumor-suppressor genes?
typically promote apoptosis and prevent cell division; mutations in these genes are usually recessive.
What is a common progression from a polyp to cancer?
A polyp caused by loss of both copies of the APC gene can progress to cancer through the accumulation of additional driver mutations.
What are anti-immune-checkpoint antibodies used for in cancer treatment?
They lift the inhibition on killer cells, allowing them to attack tumors.
What new properties do cells acquire as they transform into tumor cells?
Tumor cells grow and divide more than normal cells, survive without attachment, and invade neighboring tissues.
What are the therapeutic uses of embryonic stem cells?
can be used in various therapeutic processes due to their pluripotency.
How do adult stem cells differ from embryonic stem cells?
Adult stem cells are multipotent and can differentiate into a limited number of cell types, while embryonic stem cells are pluripotent.
What molecular events drive the transformation of a normal cell into a tumor cell?
Mutations in genes related to DNA replication, repair, cell-cycle checkpoints, and apoptosis signaling contribute to tumor cell transformation.