(1) Muscles of the head and body
1/48
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
what are the groups of muscles of head?
1. mimetic muscles: muscles of face
2. chewing muscles: muscles of mastication.
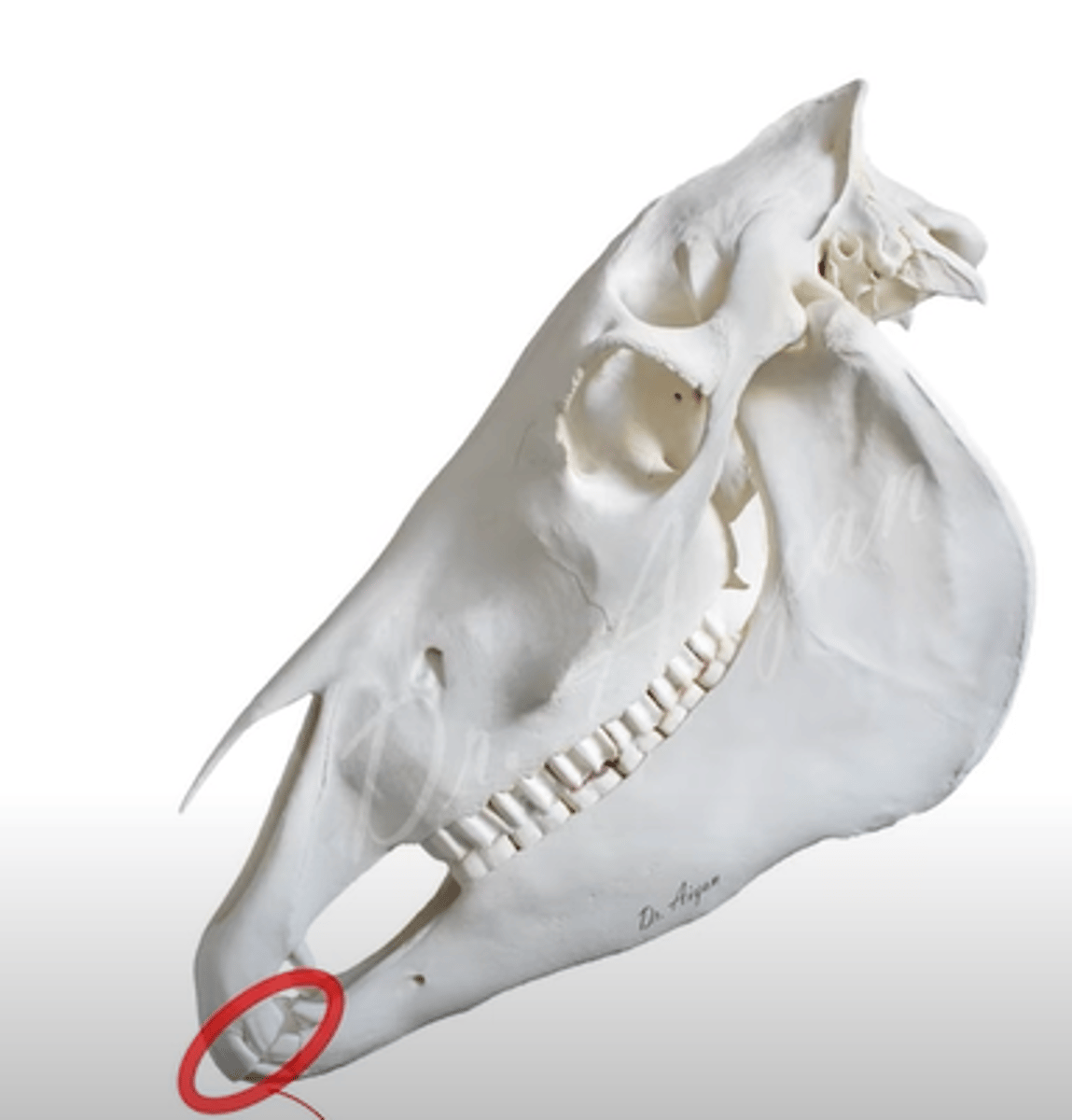
What muscle covers this area?
musculus orbicularis oris.
- mimetic muscle, which forms the base of the lips and borders the entrance into oral cavity.
what muscle covers this area? what parts does it have?
musculus buccinator, forming the base of cheek.
- consist of pars buccalis (rostrally) and pars molaris (caudomedially)
- mimetic muscle, extending bw. processes of maxilla + mandible.
- helps move food into oral cavity.
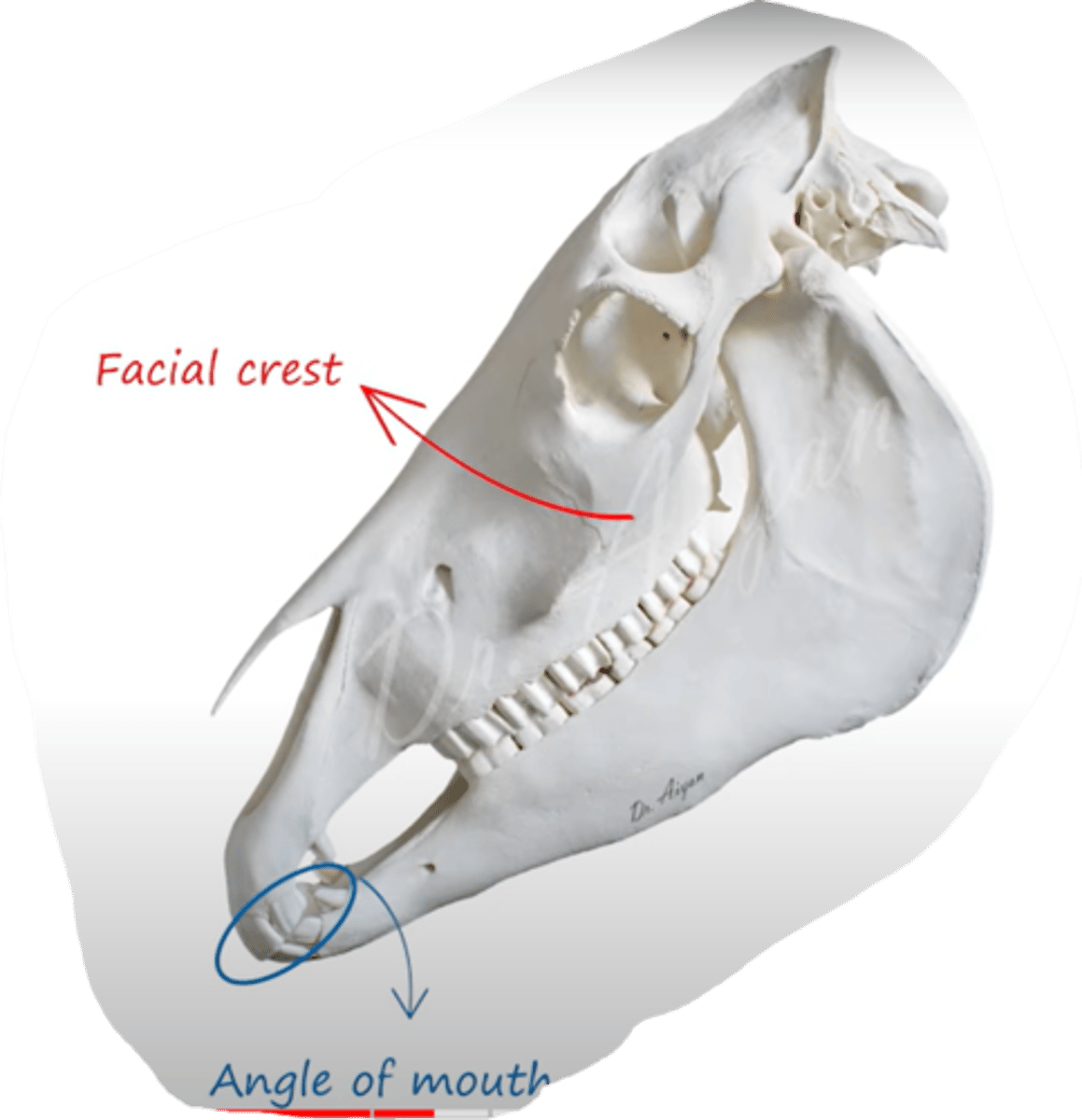
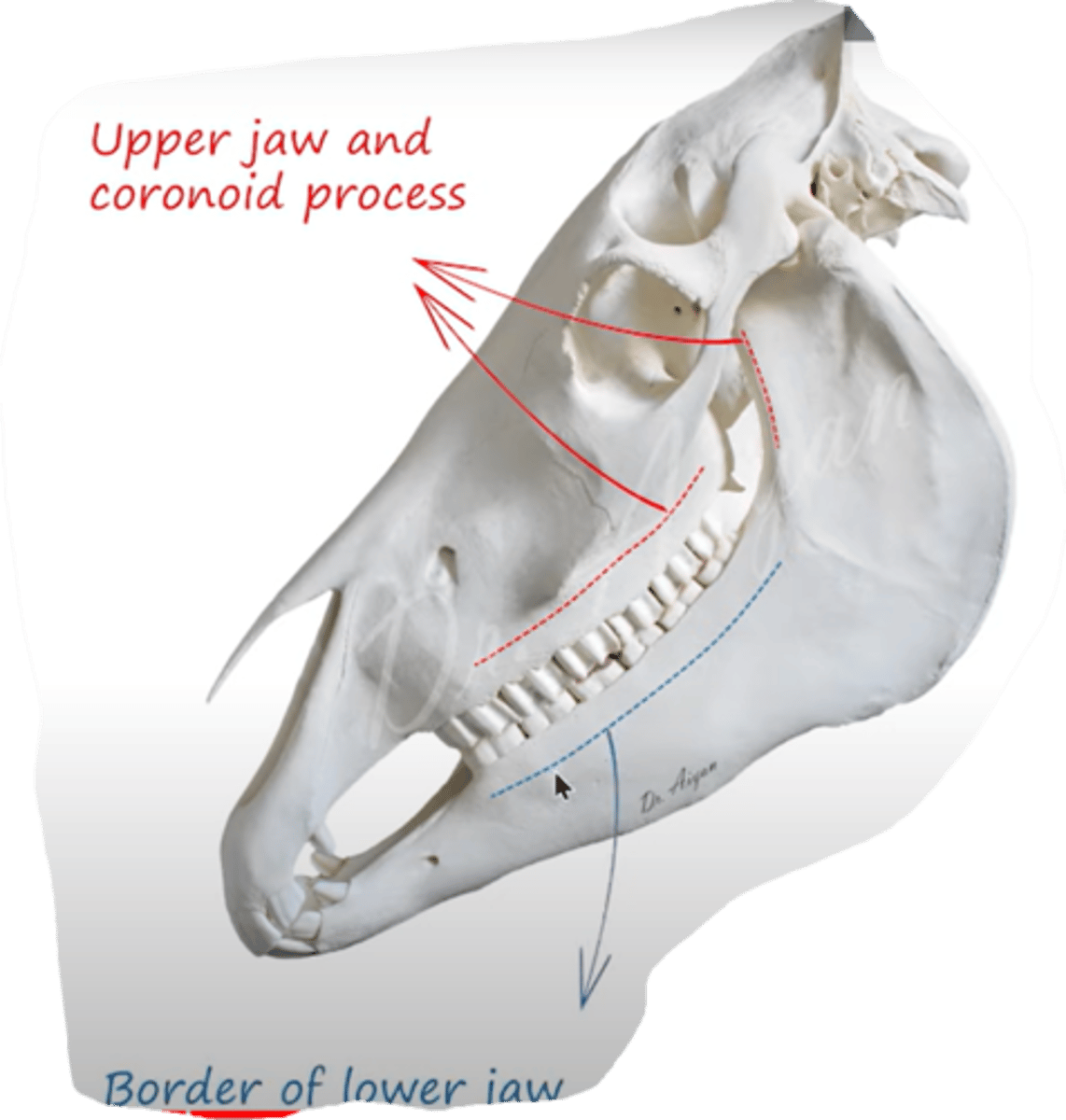
which muscle originates from crista facialis and inserts at the angle of mouth (angulus oris)?
Musculus zygomaticus.
- thin muscle, between arcus zygomaticus and angulus oris.
- mimetic muscle
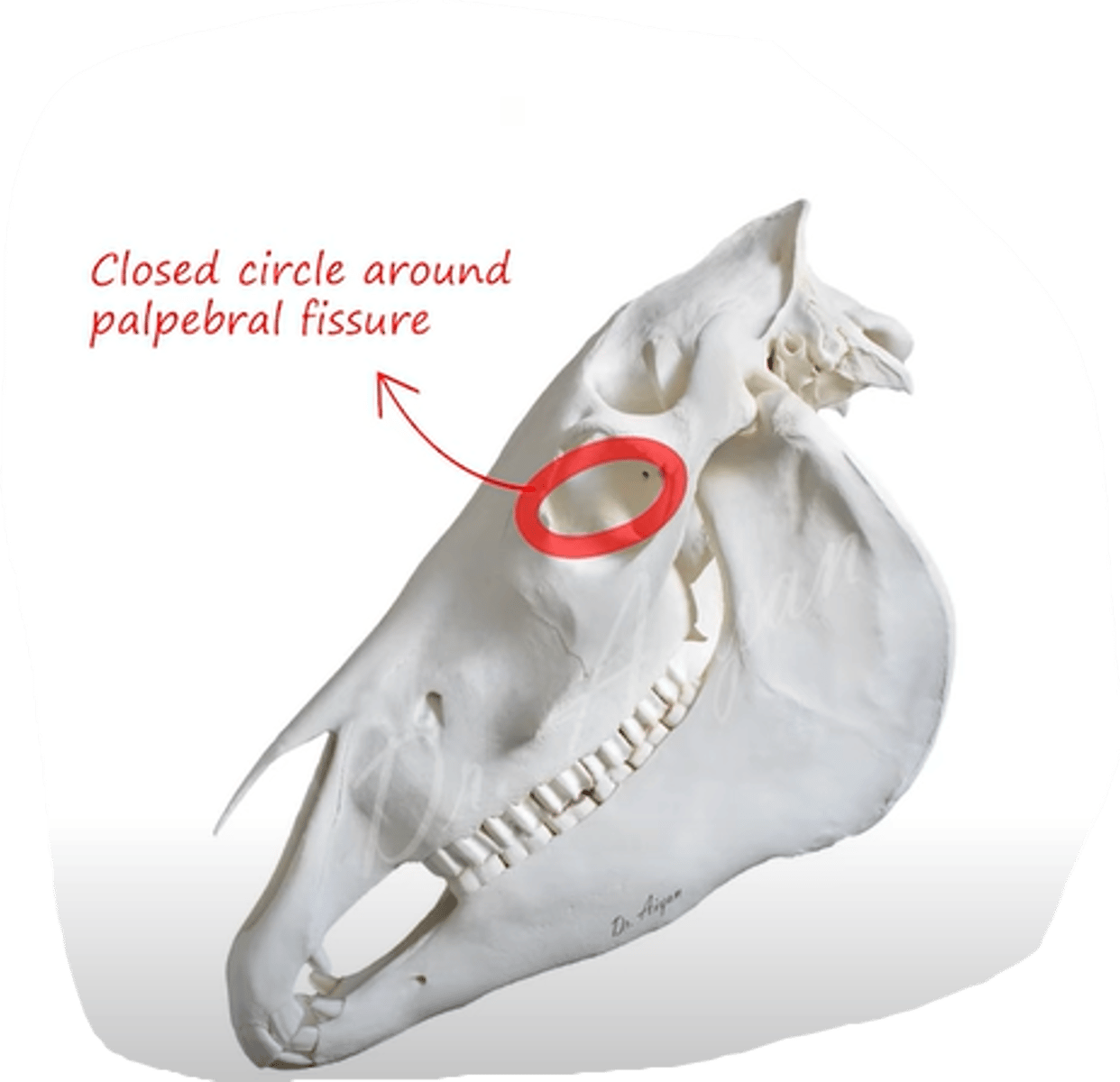
which muscle covers this area around the eyelids and inside?
Musculus orbicularis oculi.
- muscle of eye, sphincter muiscle of palpabral fissure, consisting of deeper pars orbitalis + smaller, superficial pars palpabralis (radiates into eyelids)
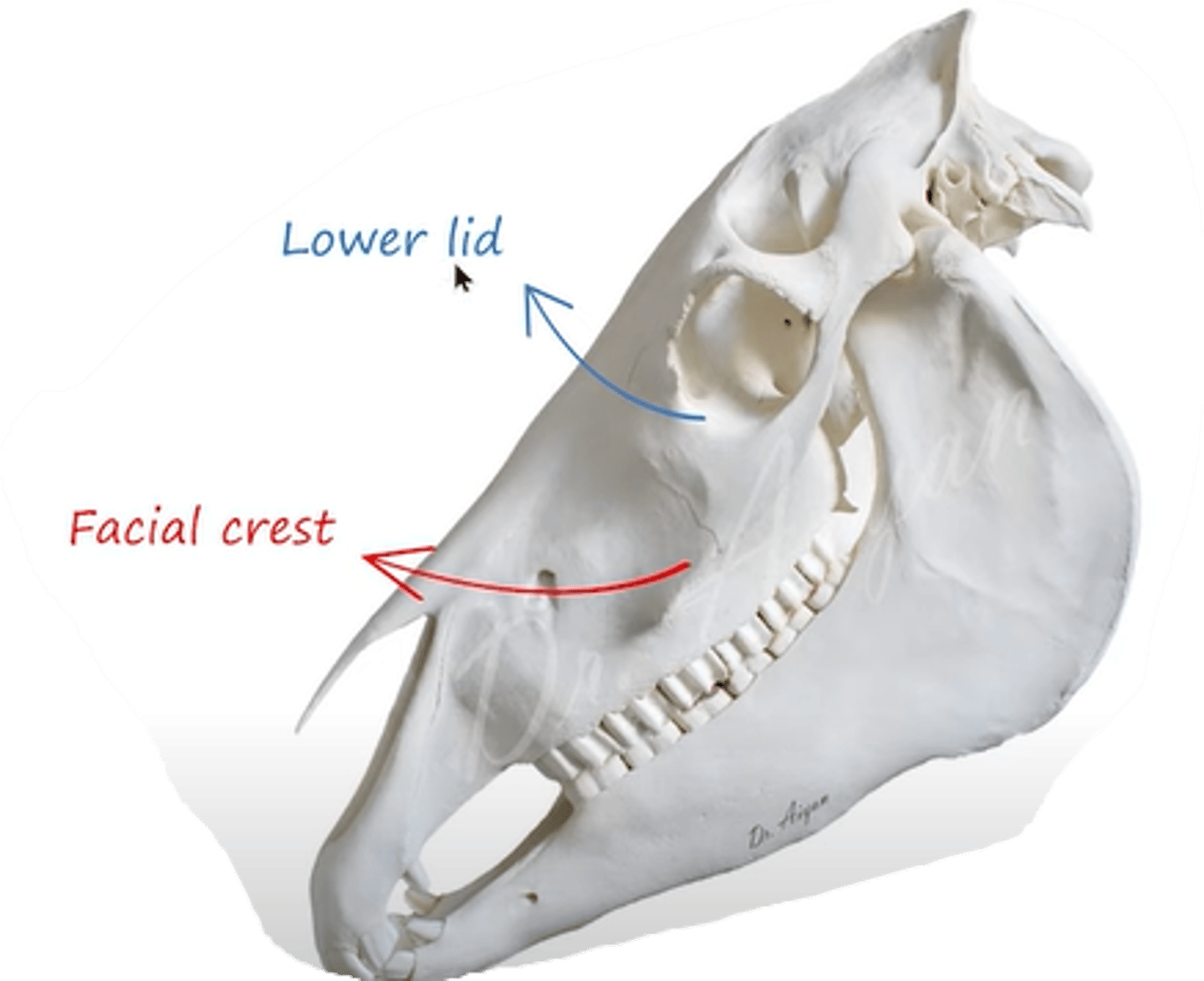
what muscle extends from crista facialis and inserts to the lower lid of eye?
musculus malaris (rostroventrally to the orbit)
- muscle of eye.
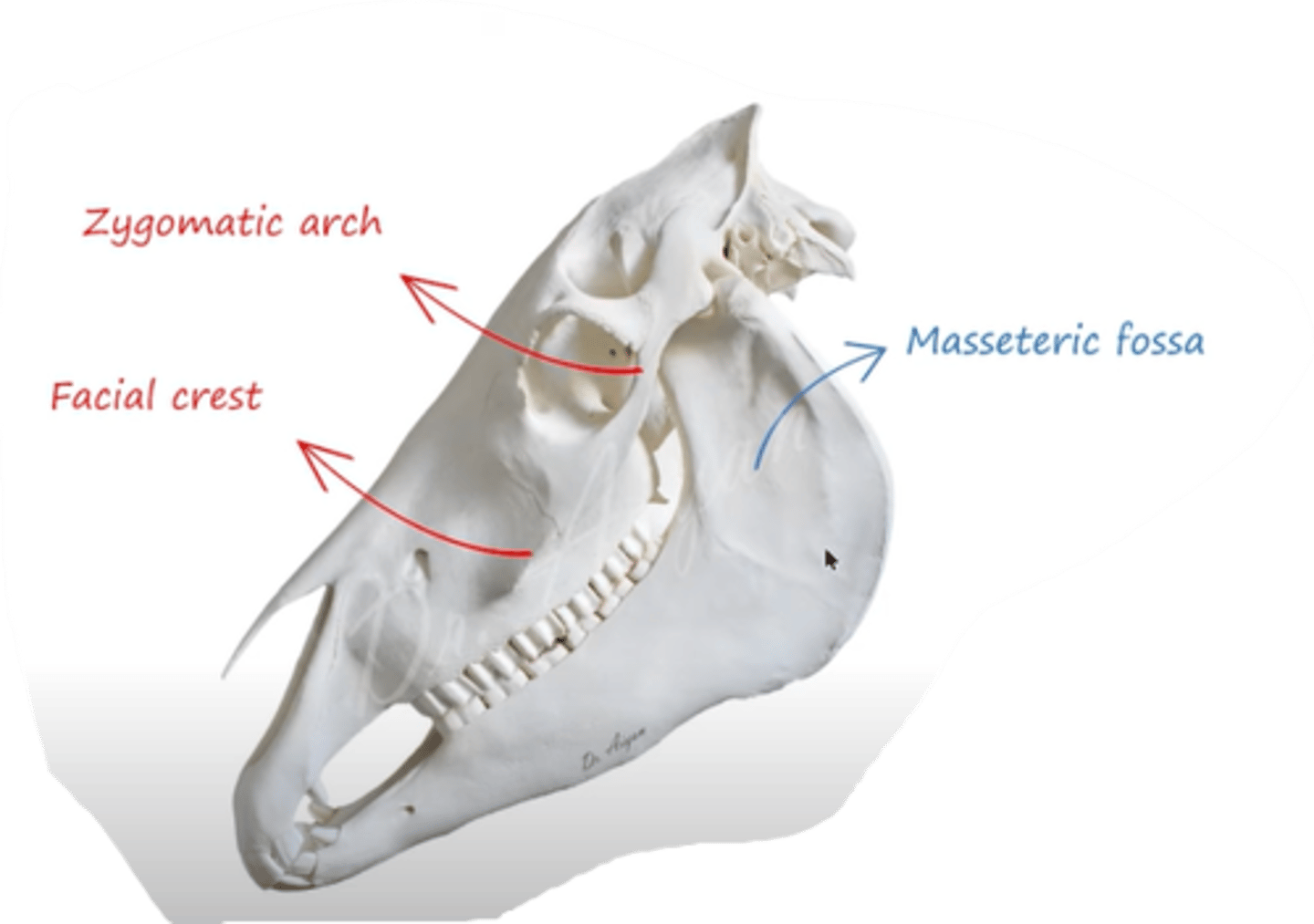
muscle that forms from arcus zygomaticus and from crista facialis, then inserts to fossa masseterica?
- what parts does it have?
musculus masseter.
chewing muscle, contracts to move the mandibula, thus helping with mastication.
main part on lateral surface of ramus mandibulae
consist of pars superficialis and pars profunda, in ca + ov also pars media.
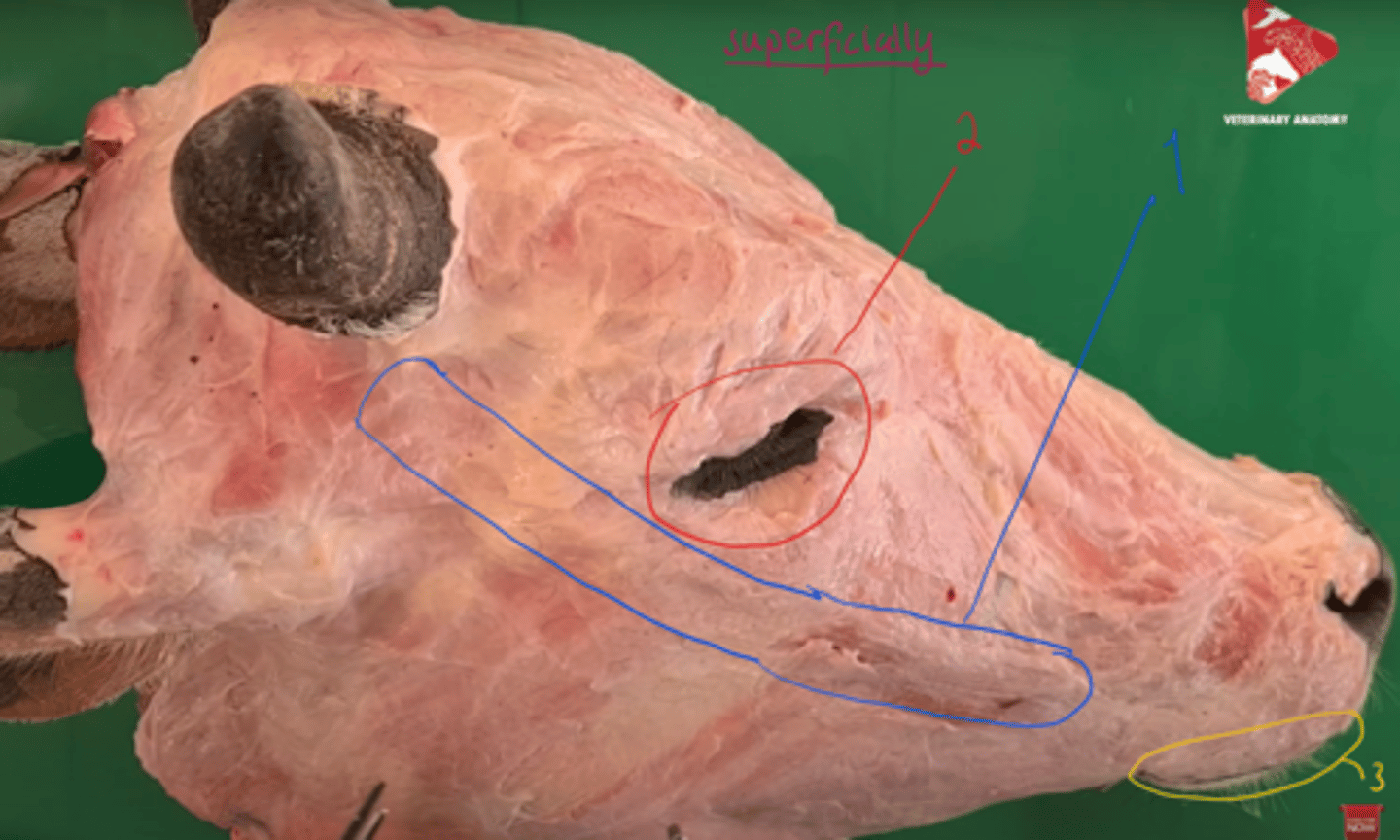
identify the muscles, seen most superficially.
1. musculus zygomaticus - mimetic
2. musculus orbicularis oculi - eye
3. musculus orbicularis oris - mimetic
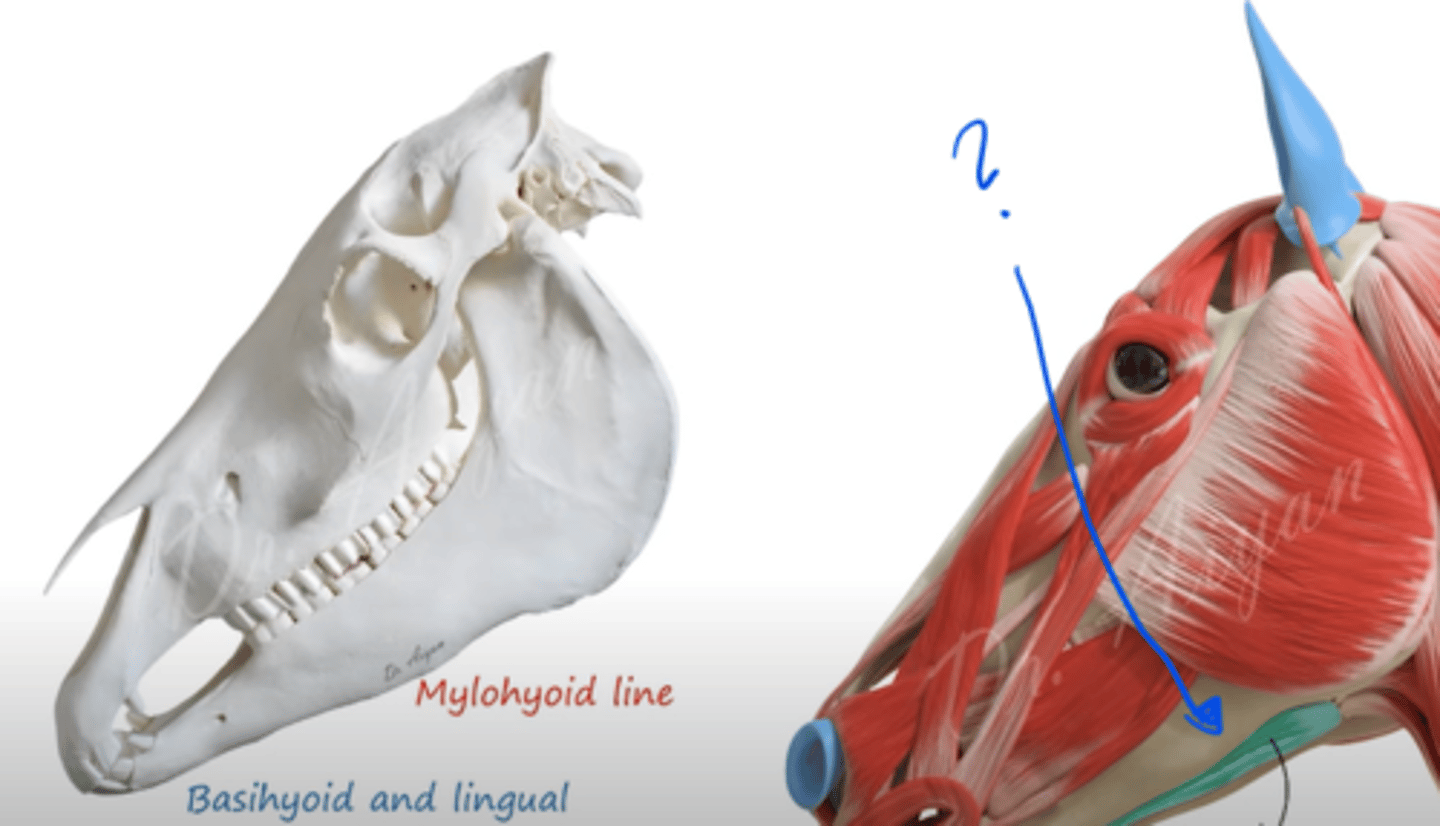
muscle that originates from the mylohyoid line (line that extends from medial surface of mandibulae) and then inserts to basihyoid and lingual process?
musculus mylohyoideus.
hyoid muscle. Forming narrow strip between the molar parts of the mandibula. Supports tongue + raises it up to palate.
divides into: pars rostralis et caudalis.
identify the muscles. - mostly overview.
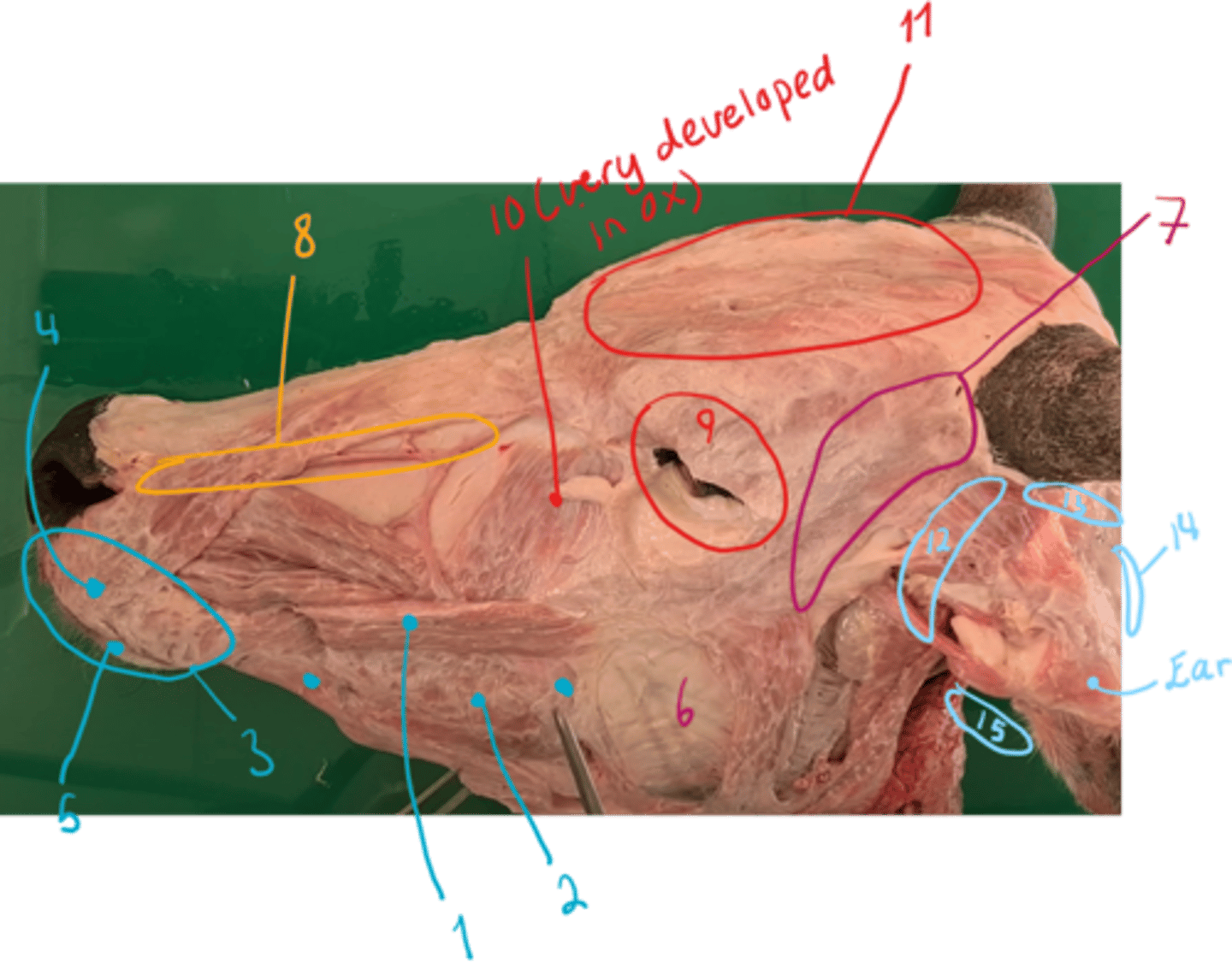
muscles of ox:
Mimetic muscles:
1. musculus zygomaticus
2. musculus buccinator: pars buccalis and pars molaris.
3. musculus orbicularis oris: forming base of lips and borders the entrance into oral cavity
4. musculus incisivus superior: directly under mucosa of upper lip.
5. musculus incisivus inferior: under mucosa of lower lip.
Chewing muscles seen:
6. musculus masseter: pars superficialis and pars profundus. Ca + sheep: pars media too.
7. musculus temporalis: in fossa temporalis. From crista temporalis, to processus coranoideus of mandible (covered by auricular muscles). Raises the mandible.
muscles of nose:
8. musculus lateralis nasi: covers the incisura nasoincisivum.
muscles of the eye:
9. musculus orbicularis oculi: in + around eyelids.
10. musculus malaris
11. musculus frontalis: covering forehead and caudal part of nose.
muscles of external ear:
12. musculi auriculares rostrales
13. musculi auriculares dorsales
14. musculi auriculares caudales
15. musculi auriculares ventrales
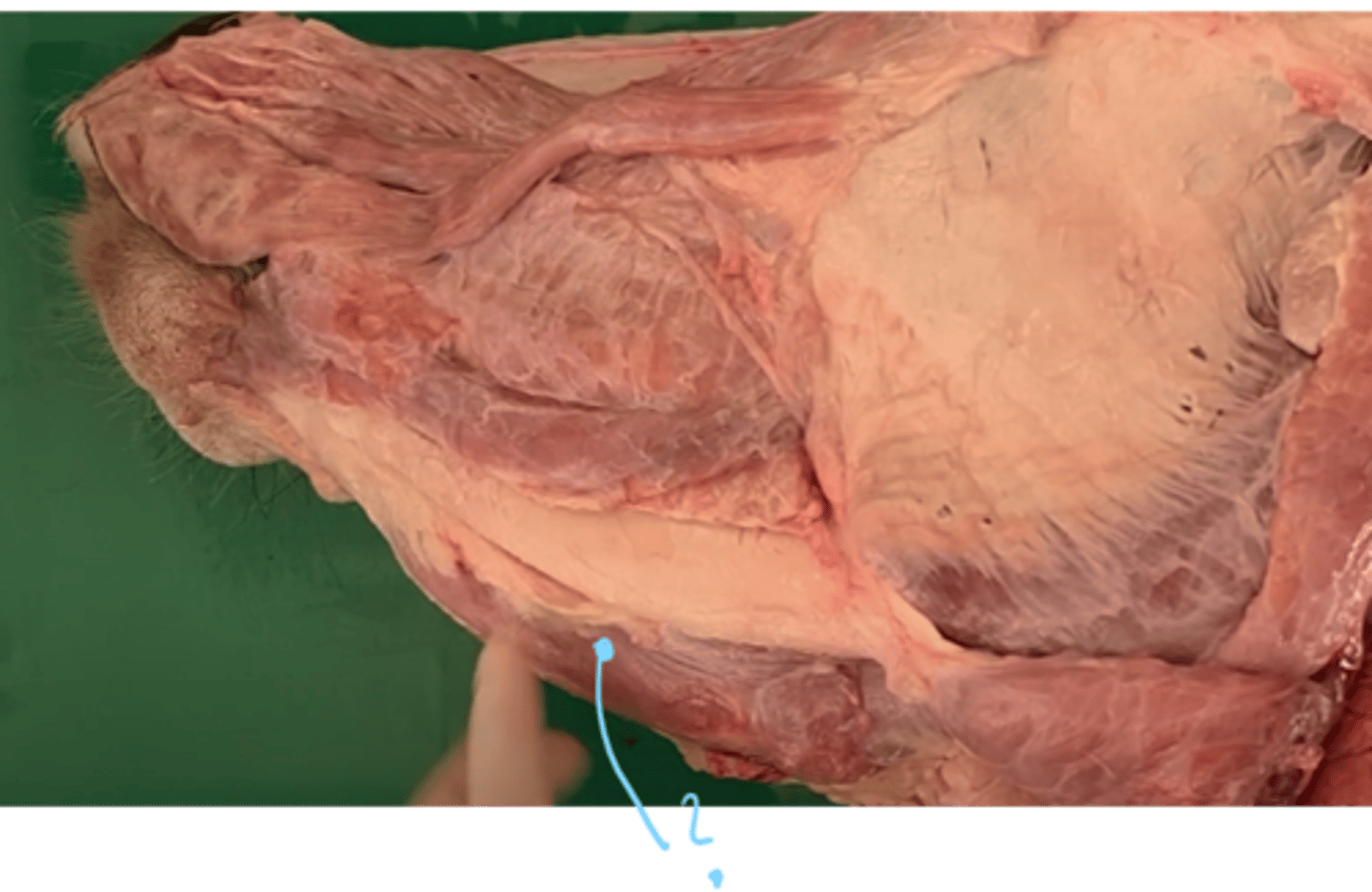
which muscle is located here in between the molar parts of the mandible?
musculus mylohyoideus
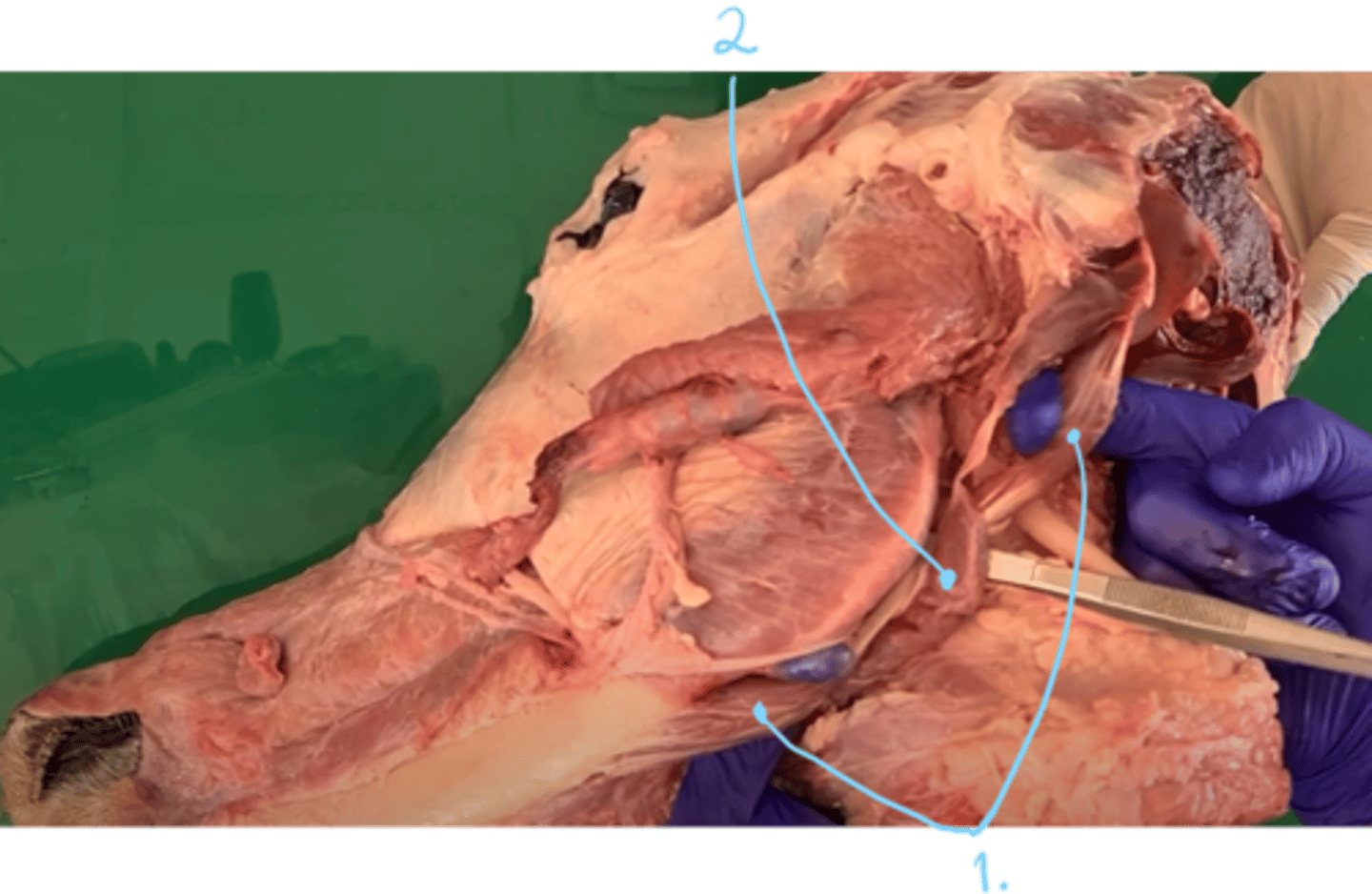
which two muscles are seen here?
- first one start on the processus paracondylaris, inserting on the medial surface of mandible.
mastication/chewing muscle:
1. Musculus digastricus - formed by venter rostralis et caudalis, connected by a round tendon. 2 parts. Role: opening oral cavity.
in eq: also has pars occipitomandibularis (lateral portion, inserts on angulus mandibulae)
muscle of intermandibular region and hyoid:
2. musculus stylohyoideus (in direction parallel to thyrohyoideum)
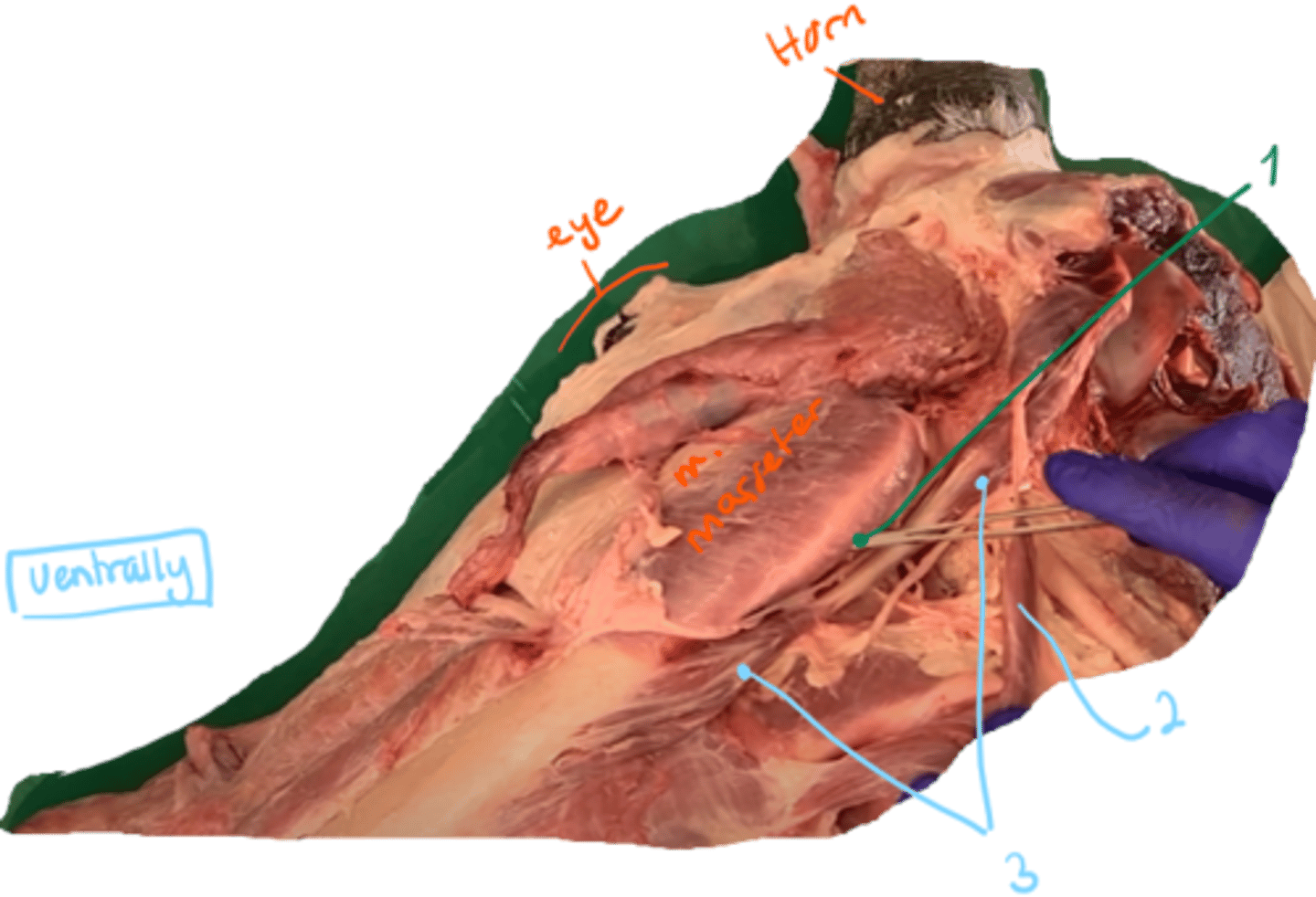
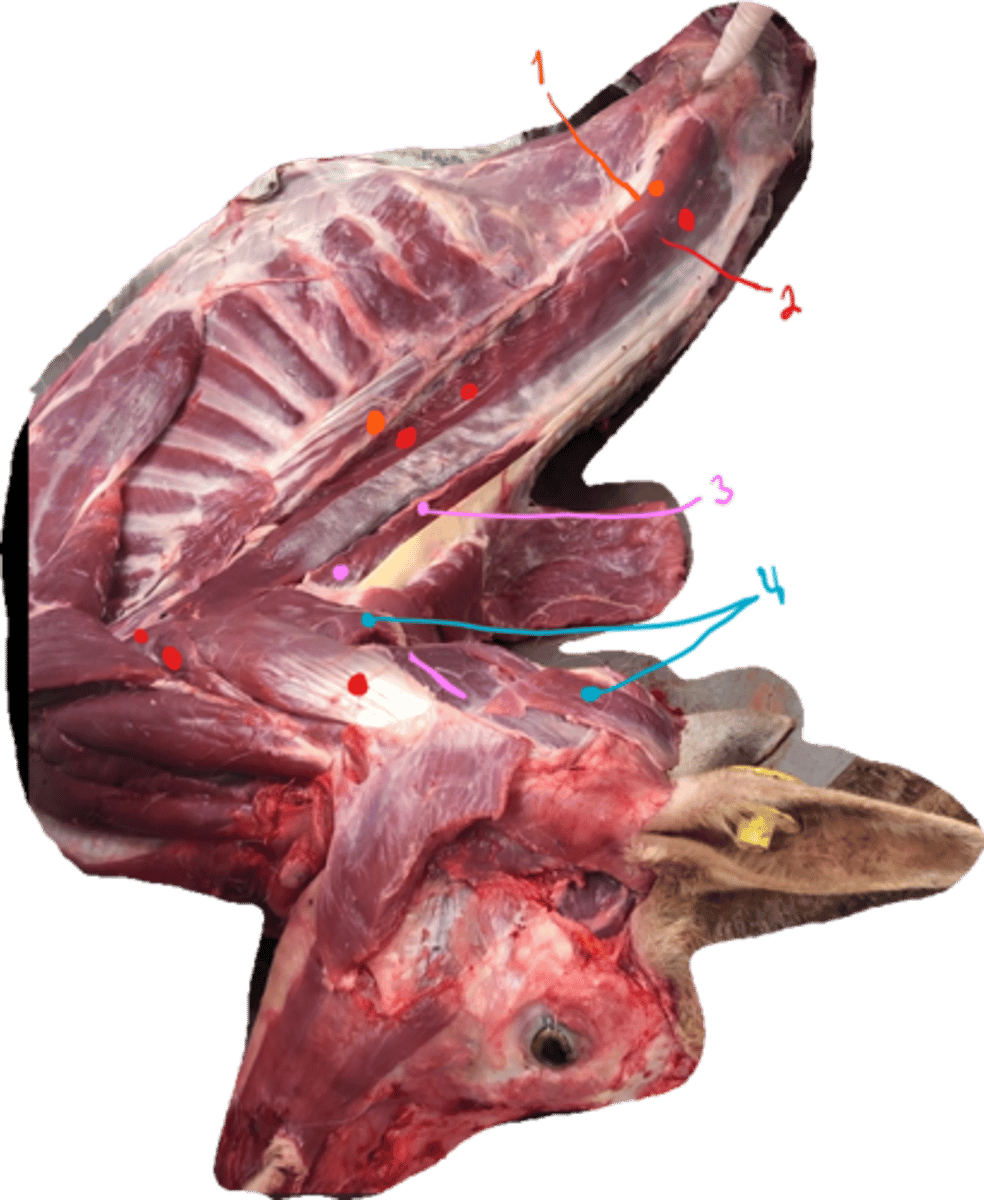
identify the muscles in the picture. what type of muscles are they?
Ventrally seen, underneath and back in the head of an ox.
1. musculus pterygoideus medialis is seen: chewing
- Musculus pterygoideus lateralis shoild be here too, as medialis is medially to it: chewing
2. musculus stylohyoideus: hyoid muscle
3. musculus digastricus: chewing muscle
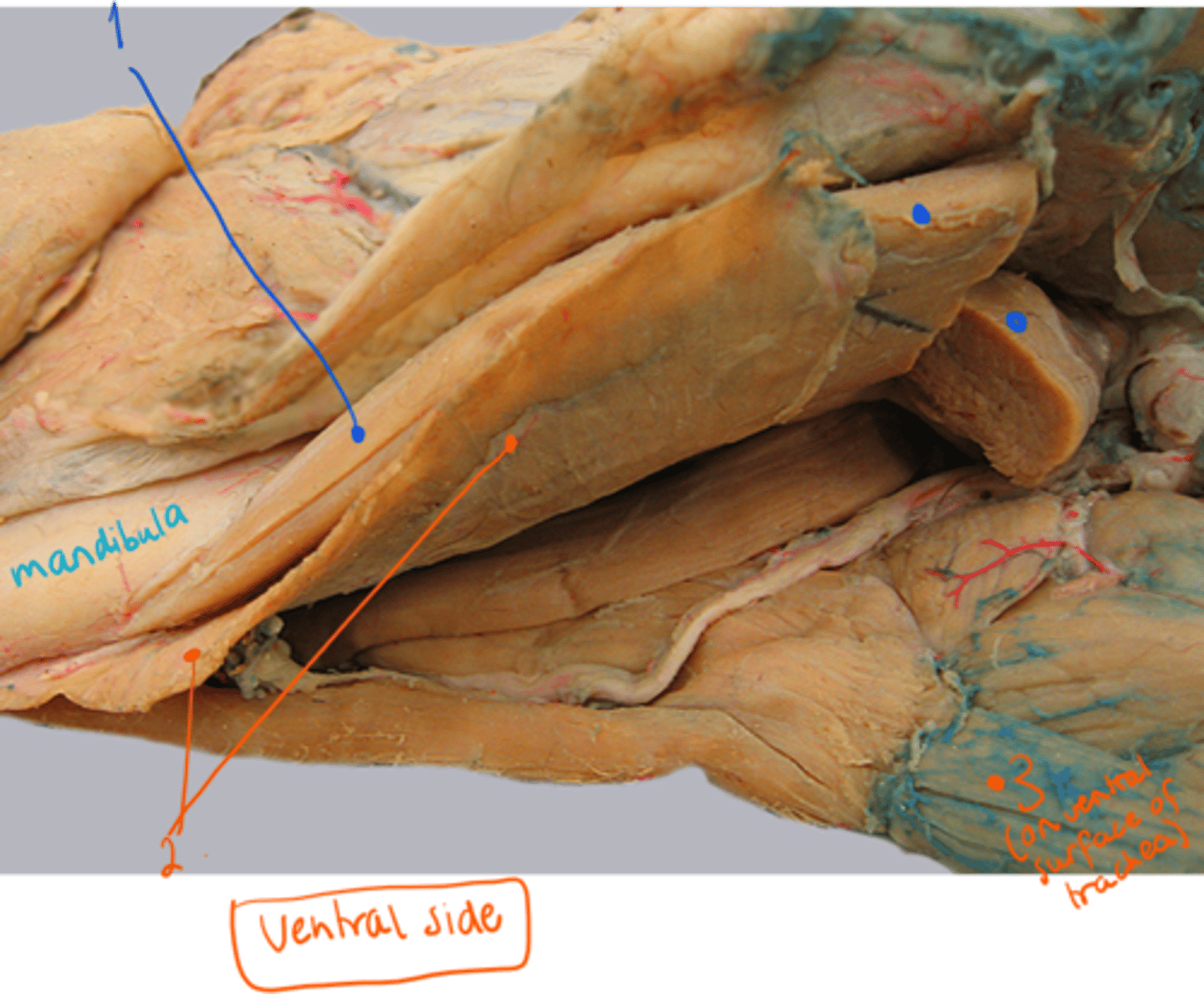
identify muscles, lying on ventral side of dog. (between mandible).
1. musculus digastricus: chewing
2. musculus mylohyoideus: hyoid muscle
3. musculus sternohyoideus: on ventral surface of trachea. Connecting hyoid with sternum, as it goes down to it, along neck.
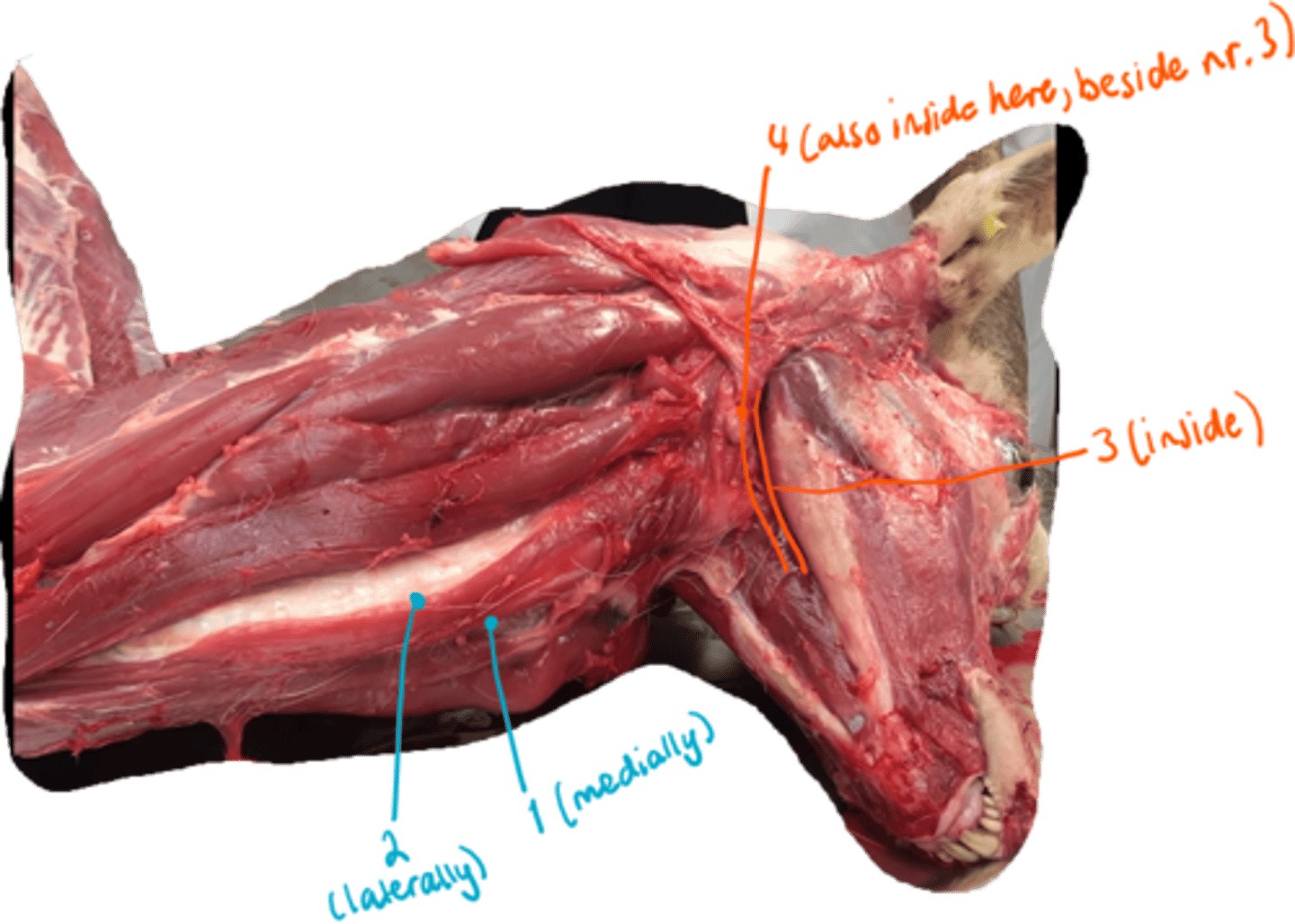
identify the 2 types of muscles here.
long hyoid muscles:
1. musculus sternohyoideus
2. musculus sternothyroideus
chewing muscles:
3. musculus pterygoideus medialis et lateralis
4. musculus digastricus
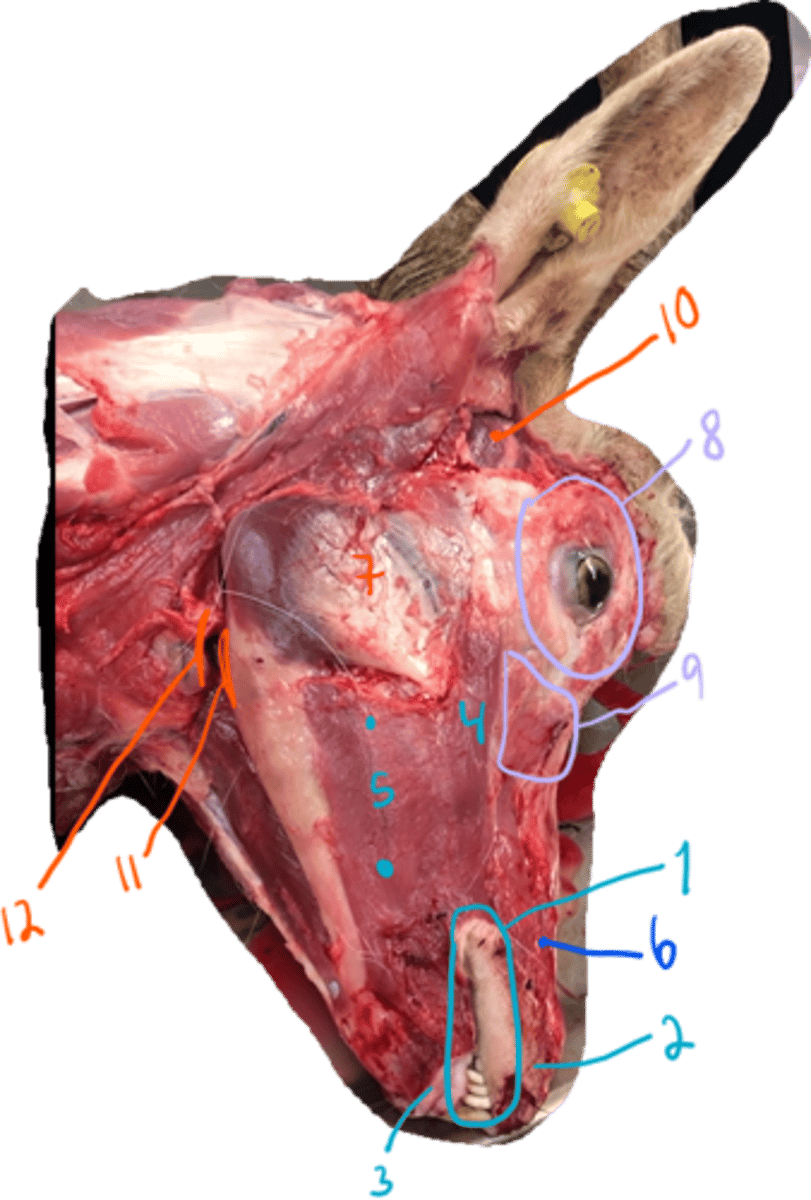
(another view)
- what are the muscles here?
mimetic muscles:
1. m. orbicularis oris
2. musculus incisivus superior
3. musculus incisivus inferior
4. musculus zygomaticus
5. m. buccinator, pars buccalis and pars molaris
nose muscle:
6. m. nasalis lateralis
chewing muscles:
7. m. masseter, pars superficialis et profundus (media in dog and sheep)
10. m. temporalis
11. m. pterygoideus med. et lateralis
12. m. digastricus
muscle of eye:
8. m. orbicularis oculi
9. m. malaris
- m. frontalis not shown.
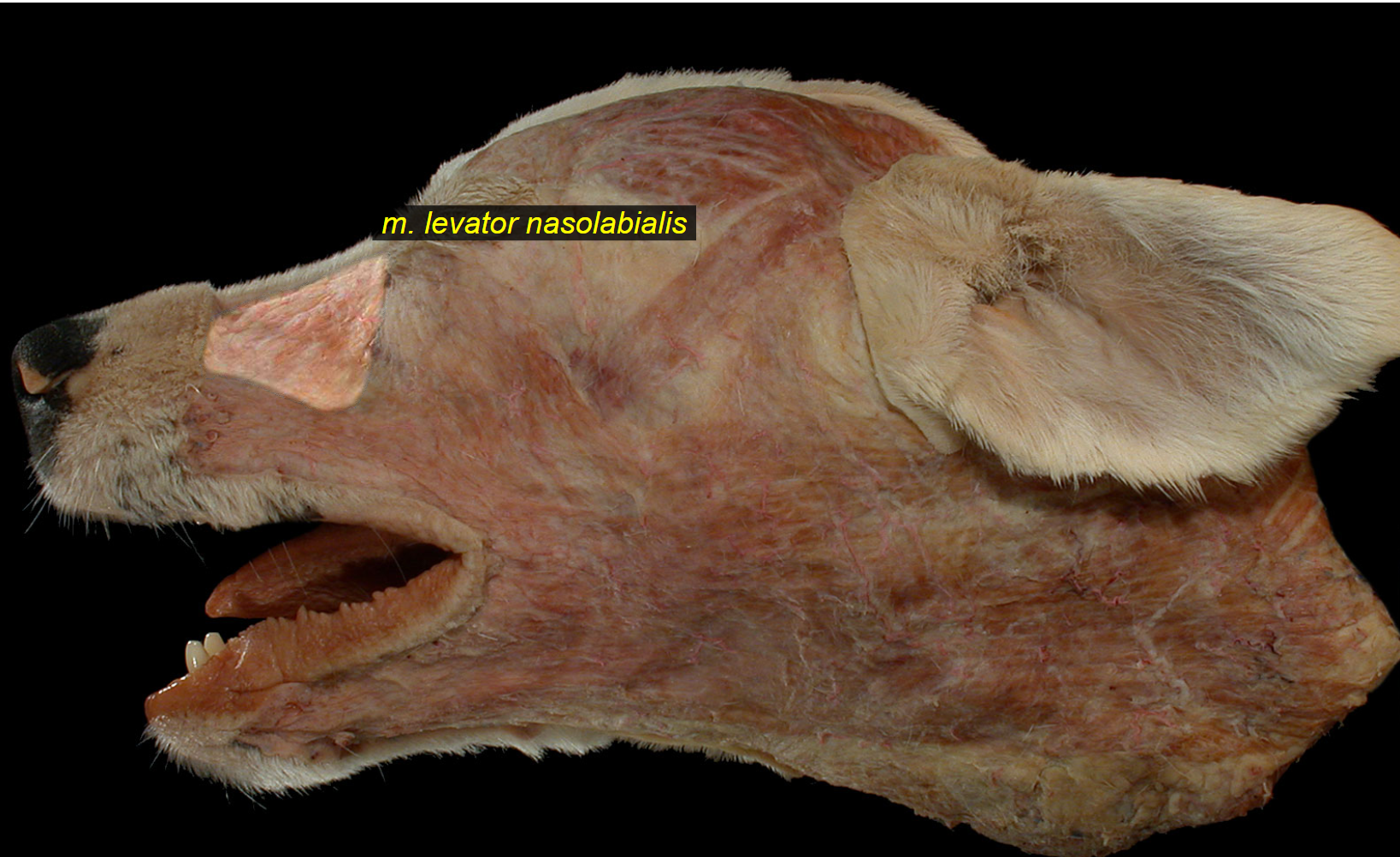
which mimetic muscle originates from fascia of frontal + nasal bone, inserting on upper part of m. orbicularis oris + lateral walls of nostrils?
new: m. levator nasolabialis - flat, thin
eq+ru: belly divides into two branches, medialis/lateralis, bw. which m. caninus passes.
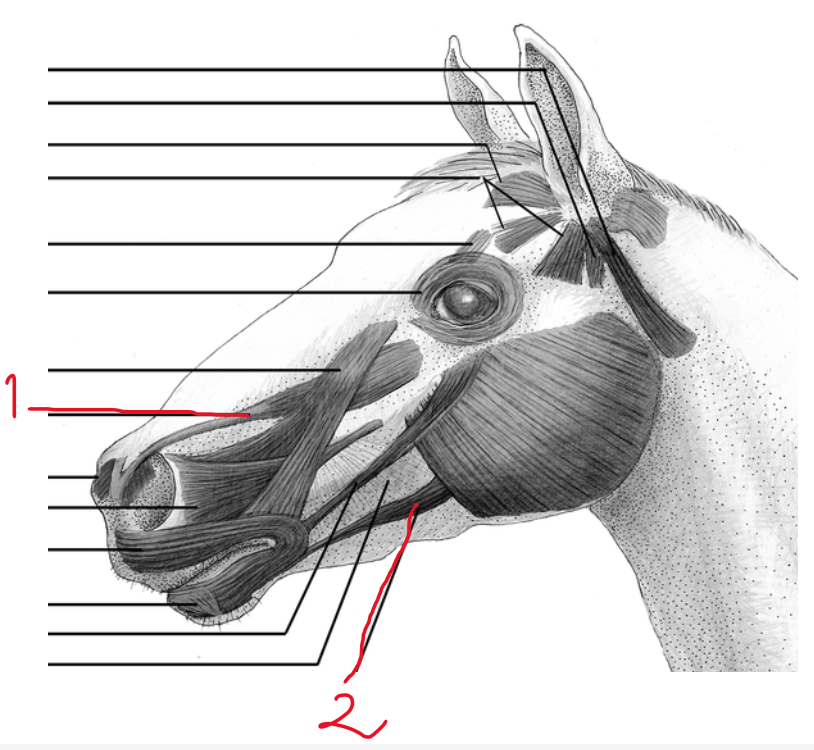
identify the two muscles:
first going from medial angle of eye, maxilla and from tuber facialis in ruminant → inserting to upper lip?
The second, going from tuber maxillae in ru and processus coranoideus in eq → to lower lip?
m. levator labii superioris (strongest, from medial angle of eye, maxilla + from tuber facialis in ru → to upper lip, elevates + retracts upper lip)
m. depressor labii inferioris (not in car, from tuber maxillae in ru, processus coranoideus in eq → lower lip)
New. (mimetic)
which muscle of upper lip, is present only in su and ru, going from tuber faciale in ru or fossa canina in su → inserting on planum nasolabiale (bo) or upper lip?
m. depressor labii superioris (new) (mimetic)
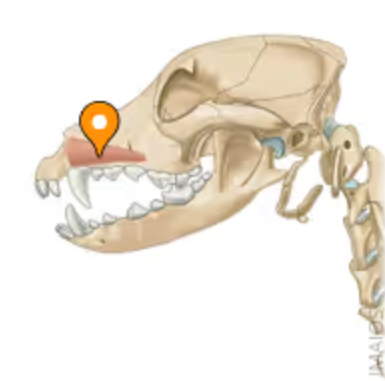
which mimetic muscle is this?
m. caninus (from maxilla close to crista facialis or tuber facialis in ru and inserting on lateral walls of nostrils) - new
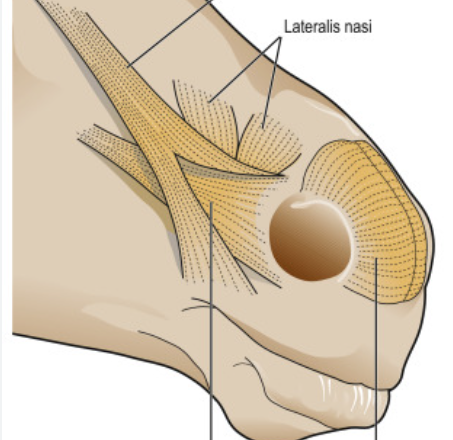
muscles of nose, short surrounding the nostrils covering the lateral walls of nose superficially, we have in addition to m. lateralis nasi?
musculus dilatator naris apicalis (seen)
m. dilatator naris medilalis (ru?)
new.
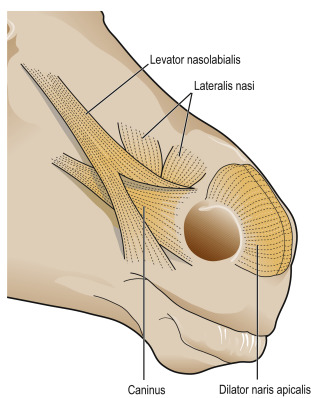
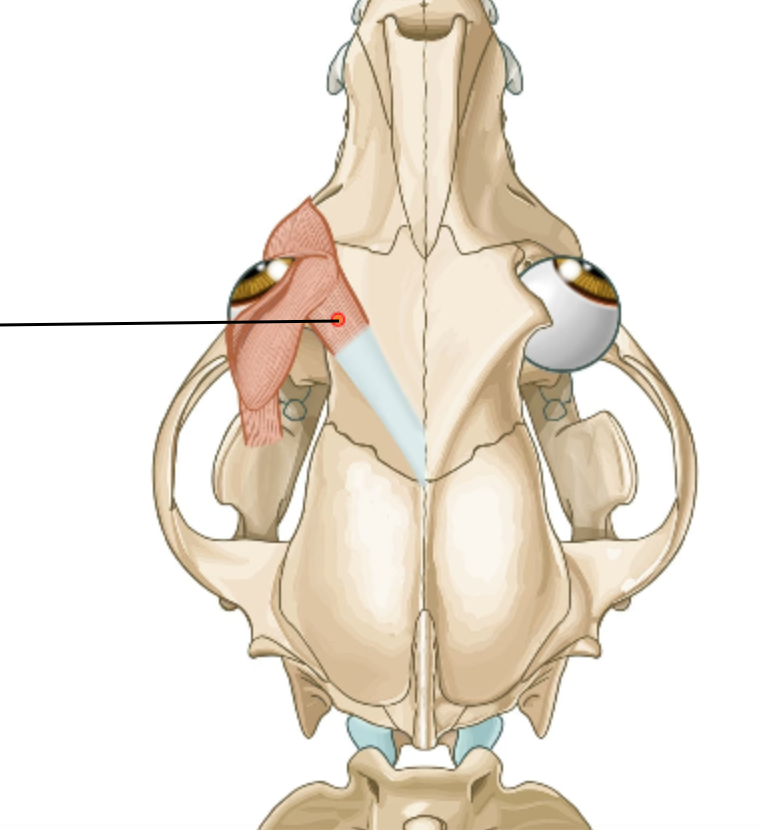
Muscle of eyelids?
m. levator anguli oculi medialis (absent in ru, instead having m. frontalis here)
which cartilage (of muscles of external ear) is situated as a triangular cartilaginous plate lying near to the m. temportalis, rostrally to the ears?
cartilago scutiformis - mm. scutulares are located around this cartilage.
which muscle lies under the tongue? originating from pars incisiva of mandible and inserts to the basihyoid?
m. geniohyoideus
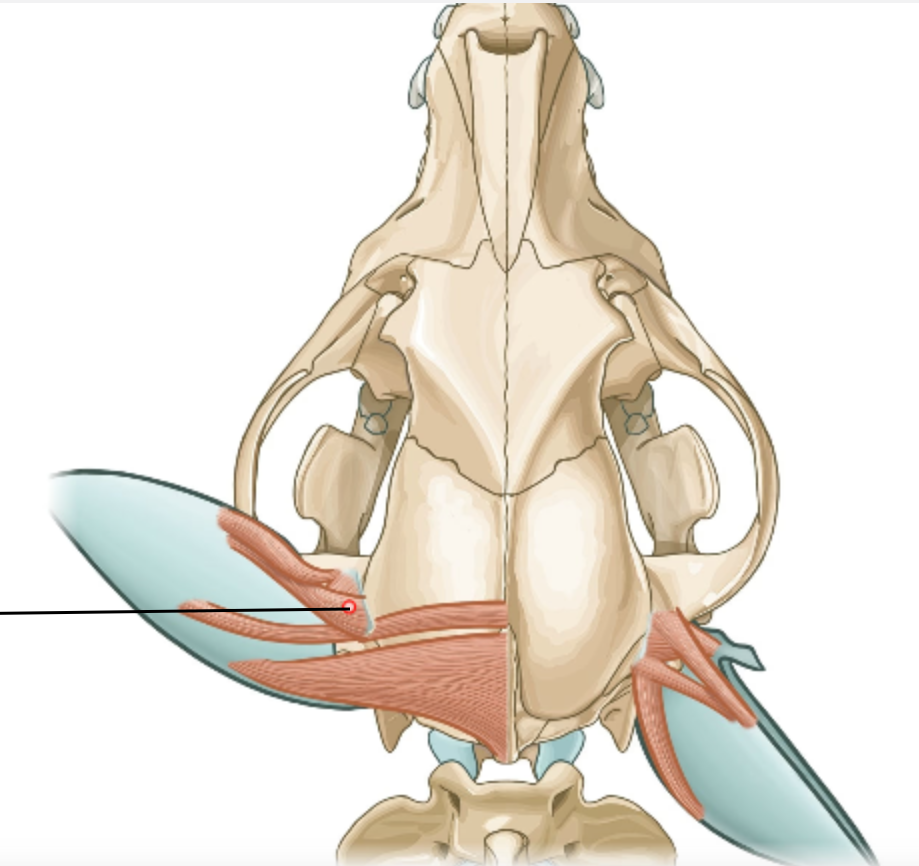
3 small short muscles that move with the hyoid bone?
m. thyrohyoideus
m. occipitohyoideus
m. ceratohyoideus
what muscle runs between the two ceratohyoids? absent in su + car.
m. hyoideus transversus
which long hyoid muscle originate from subscapular fascia near shoulder joint and inserts on basihyoid?
m. omohyoideus
what type of muscles are these? what muscle do we not see as it is too deeply located?
muscles of back.
dorsal muscles of vertebral column:
m. erector spinae:
m. iliocostalis (pars lumborum (ru +car), thoracis et cervicis (absent in car))
m. longissimus (pars lumborum, thoracis, cervicis, atlantis et capitis)
m. spinalis et semispinalis is fused in car and ru. (pars thoracic et cervicis)
while in eq + su: m. spinalis is divided into thoracic et cervicis.
m. transversospinalis:
m. splenius (flat, in the nuchal region, pars cervicis + capitis)
mm. multifidi, forming deepest layer of neck, located medially to m. spinalis.
m. semispinalis consist of which 3 parts?
Lies between the transverse + spinous processes (part of m. transversospinalis).
consist of:
m. semispinalis thoracis (not in eq + su)
m. semispinalis cervicis (not in eq + su)
In car + ru: these parts are fused with m. spinalis → m. spinalis et semispinalis thoracis et cervicis.
m. semispinalis capitis (independent in all domestic mammals, going bw. occipital bone + cervical vertebrae. In ru, su + car:
a) m. biventer cervicis
b) m. complexus
m. semispinalis capitis is divided into?
m. biventer cervicis
m. complexus
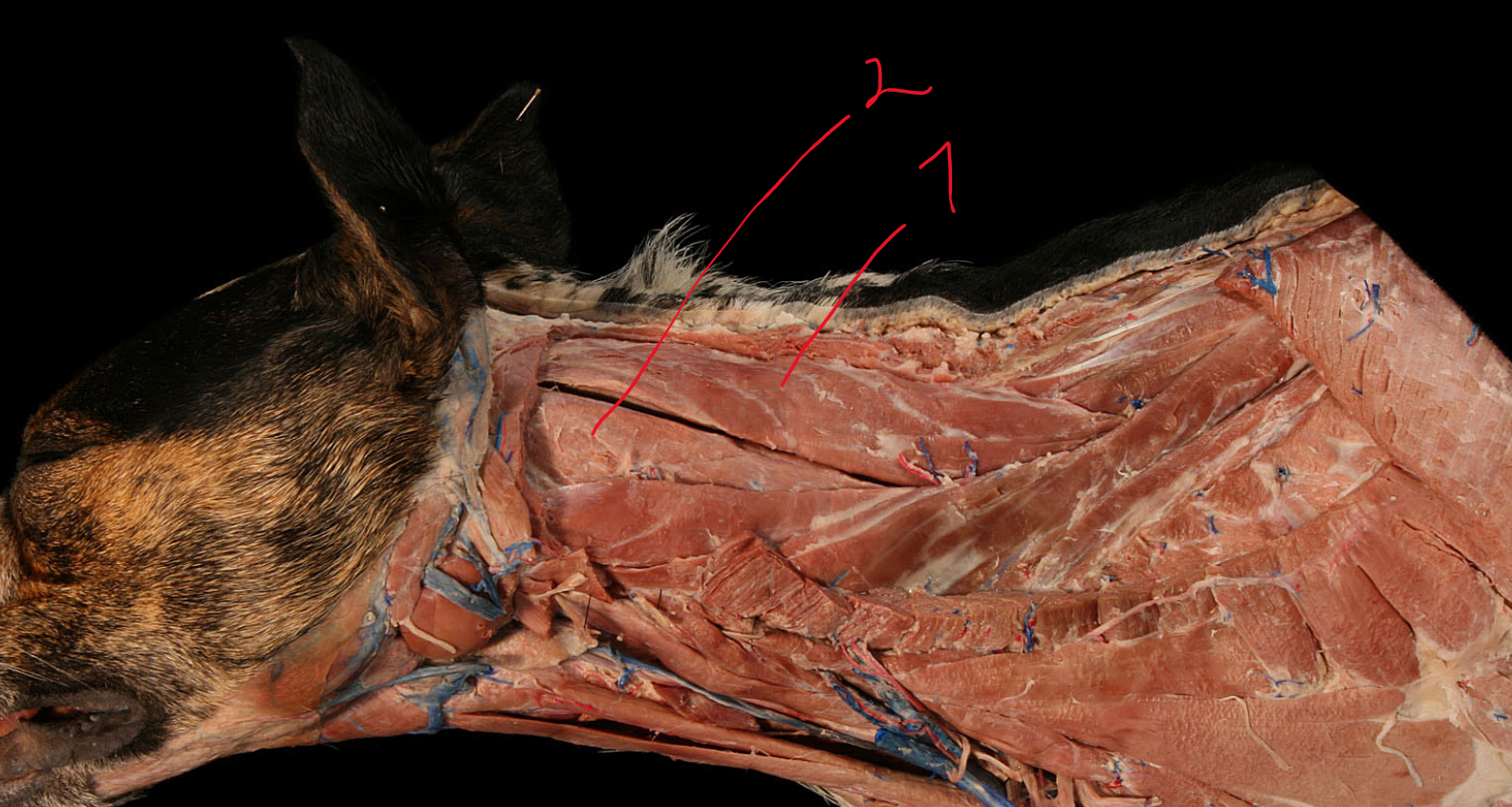
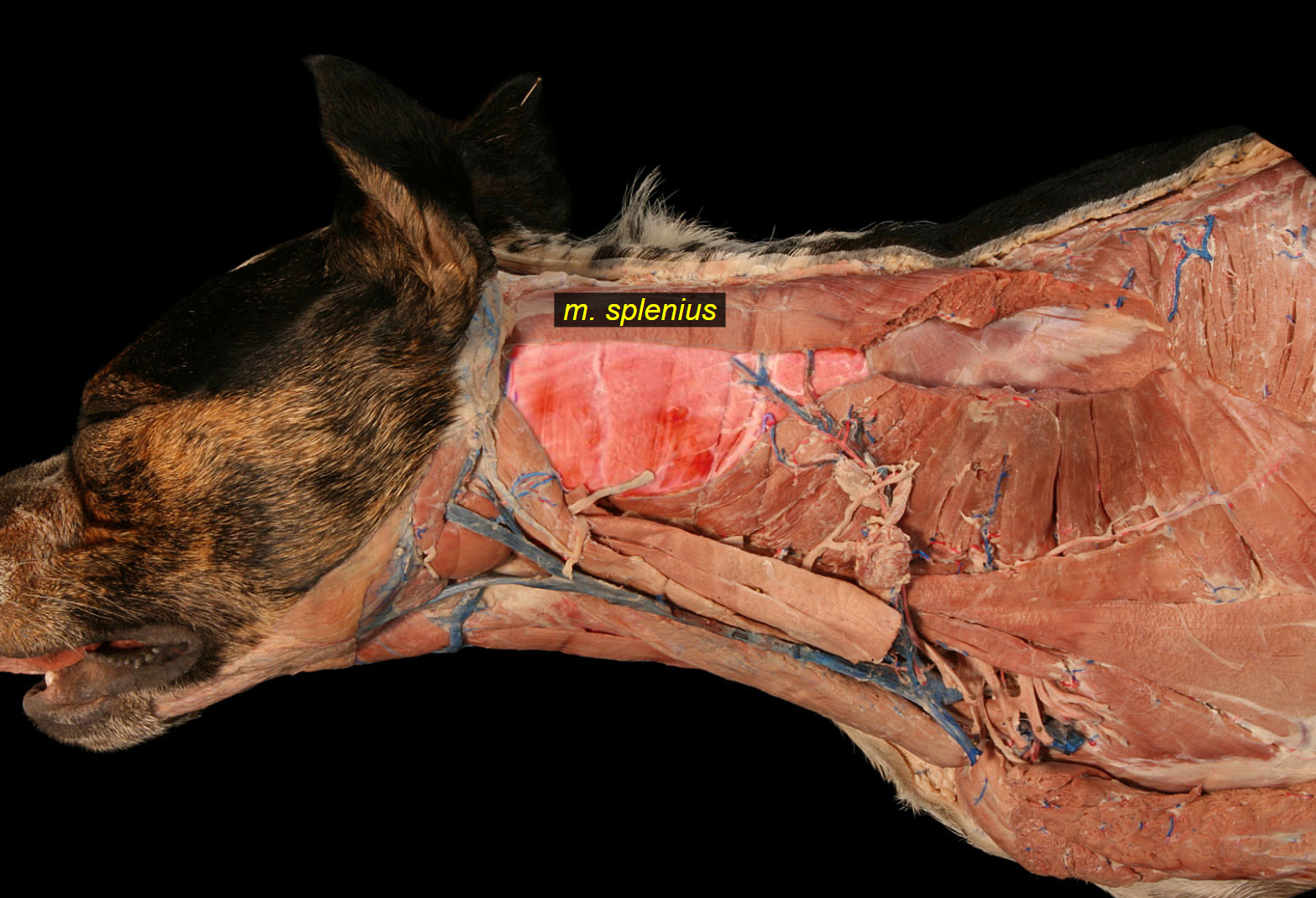
m. splenius is divided into?
flat muscle in nuchal region from withers to occipital region. Easily identified under skin - eq.
m. splenius cervicis
m. splenius capitis
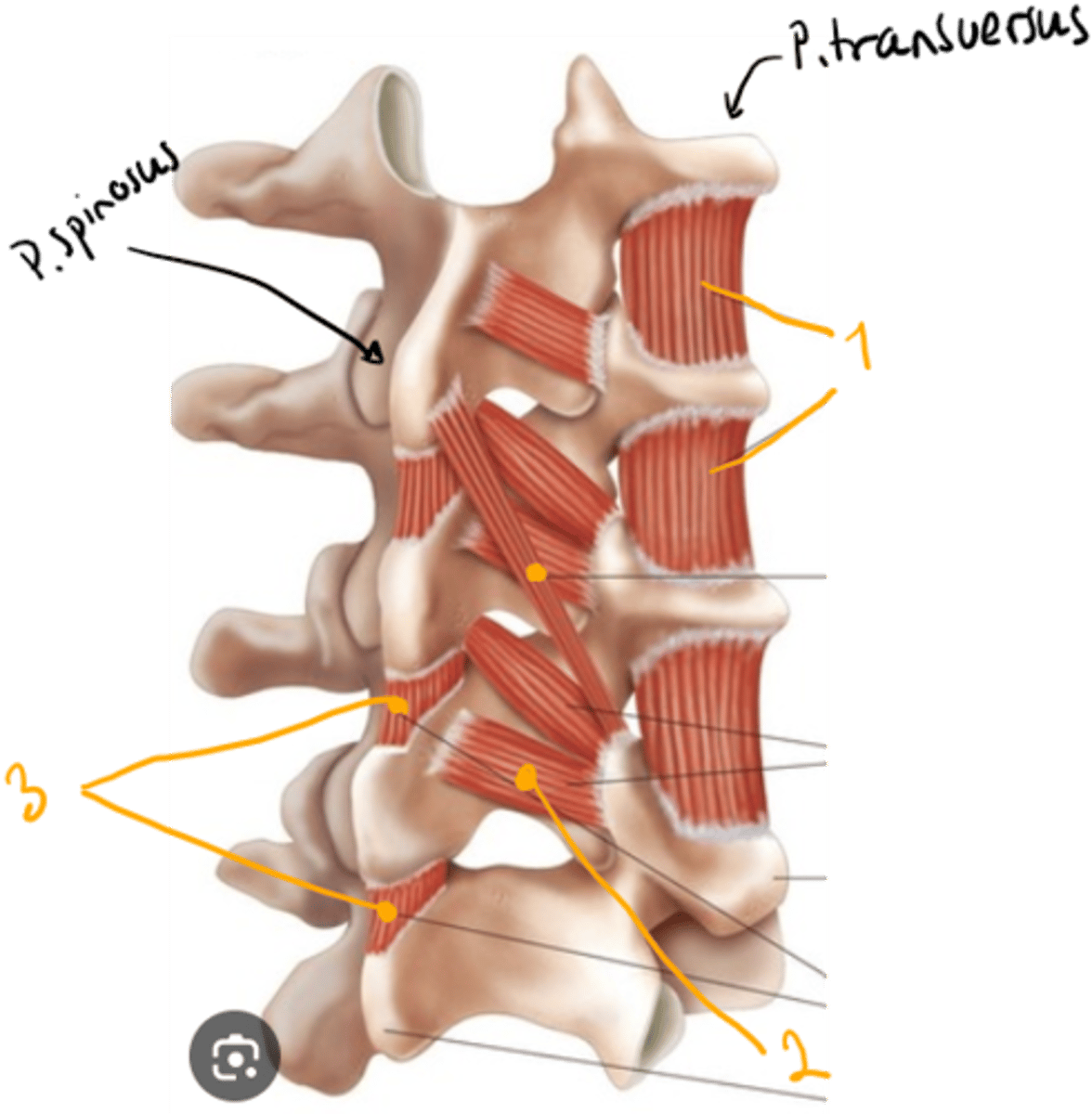
which short muscles are here?
muscle of back.
short muscles of neck and back:
1. musculi intertransversarii
- between processus transversus
2. musculi interspinales
- between processus spinosus
3. musculi rotatores
- of thoracic vertebrae, between porcessus transversus and spinosus
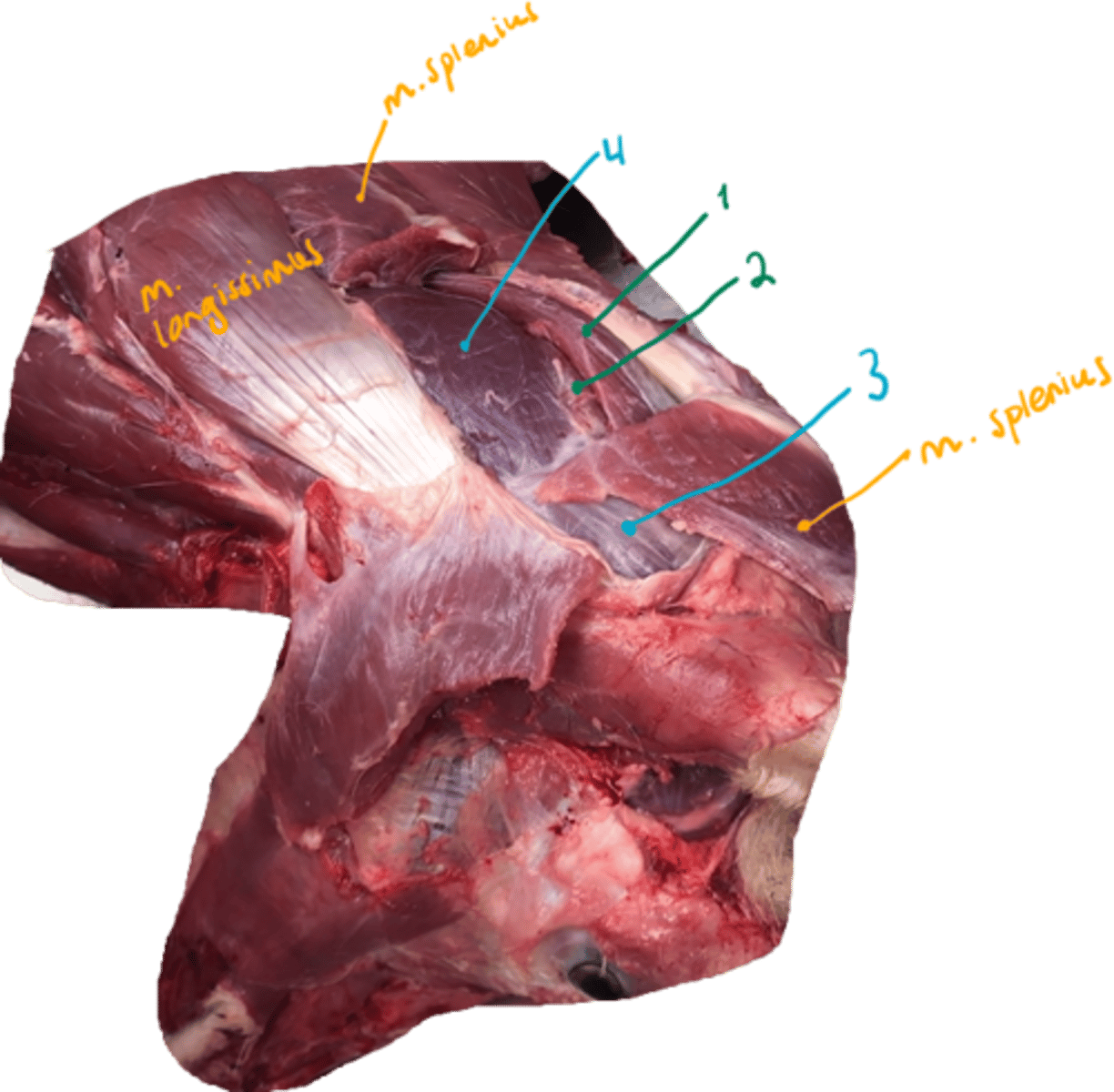
what short muscles are located here? They are located between the atlantooccipital and atlantoaxial joint.
Muscle of back.
dorsal muscles of vertebral column:
1. m. rectus capitis dorsalis major
2. et minor (minor laying underneath)
3. m. obliquus capitis cranialis
4. et caudalis.
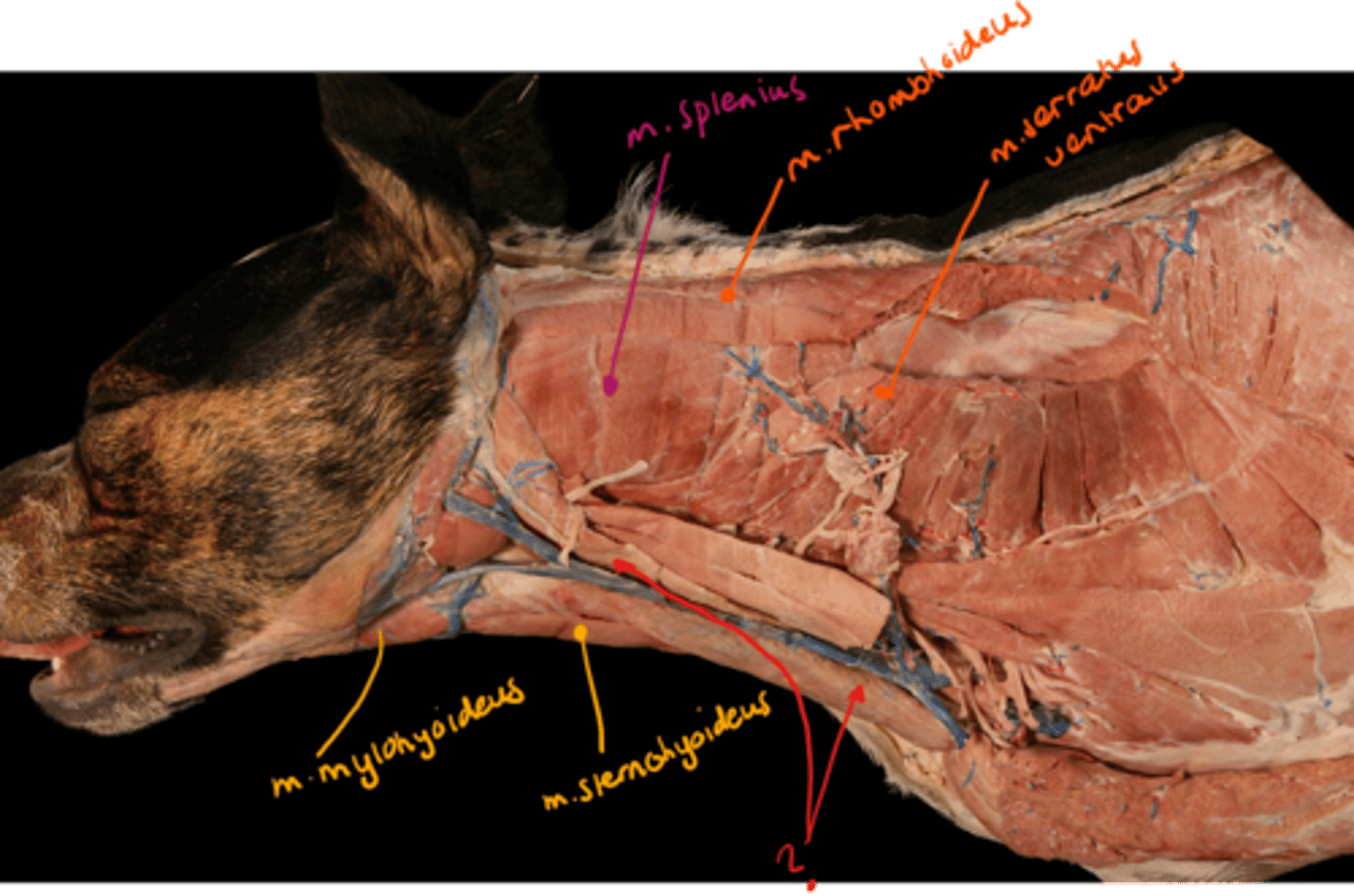
what muscle is the red arrows pointing at?
m. sternocephalicus, lying ventrally and laterally to m. brachiocephalicus, extending from manubrium sterni to head.
- pars mastoidea (bo, su and ov) and pars mandibularis (bo, eq and cap)
- pars occipitalis et mastoidea in car.
- a ventral muscle of vertebral column
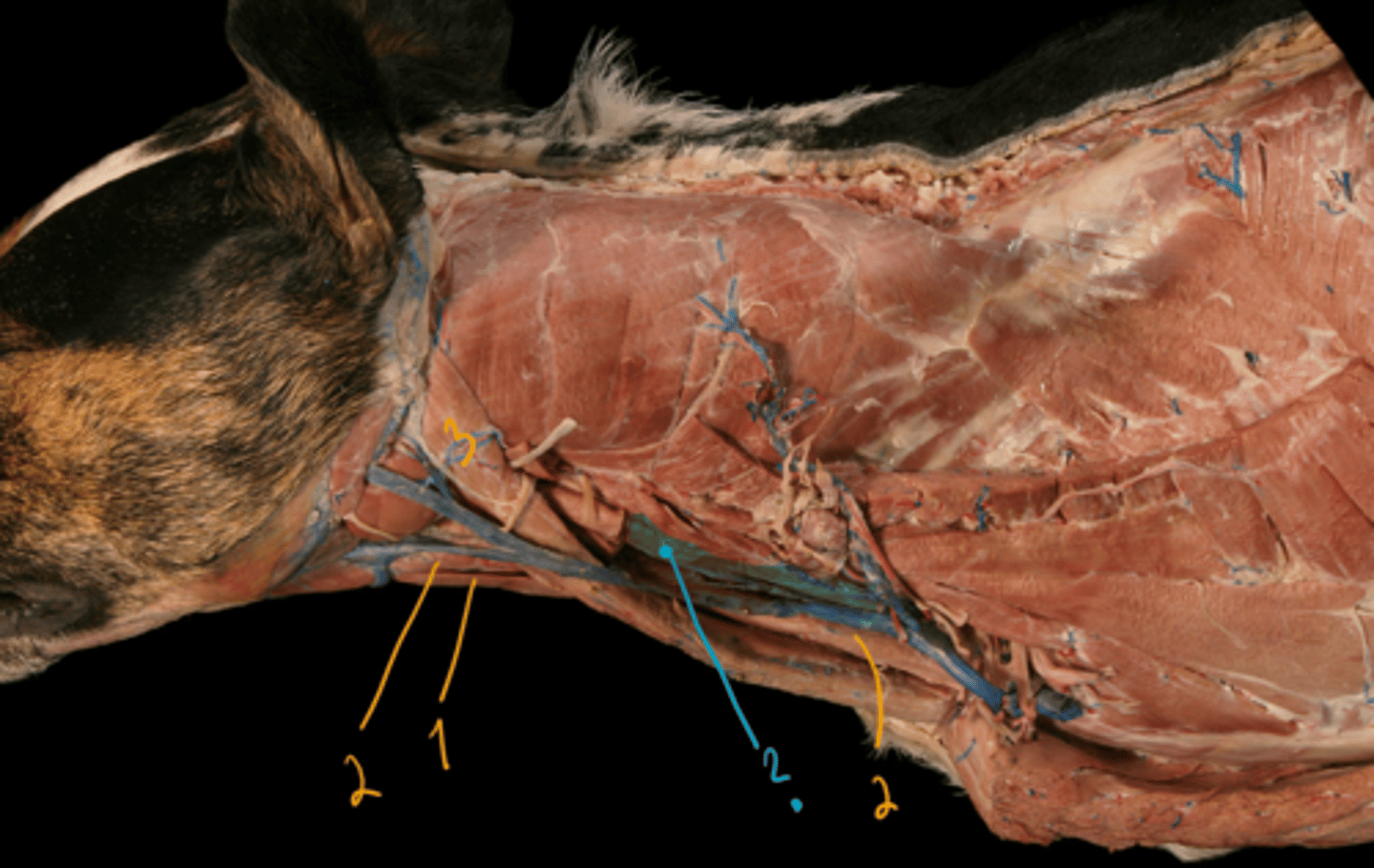
identify the blue structure.
hyoid muscles:
1. m. sternohyoideus
2. m. sternothyroideus
ventral muscles:
3. m. sternocephalicus, ventrally and laterally to brachiocephalicus
- blue: m. longus capitis, cranial continuation of m. longus colli.
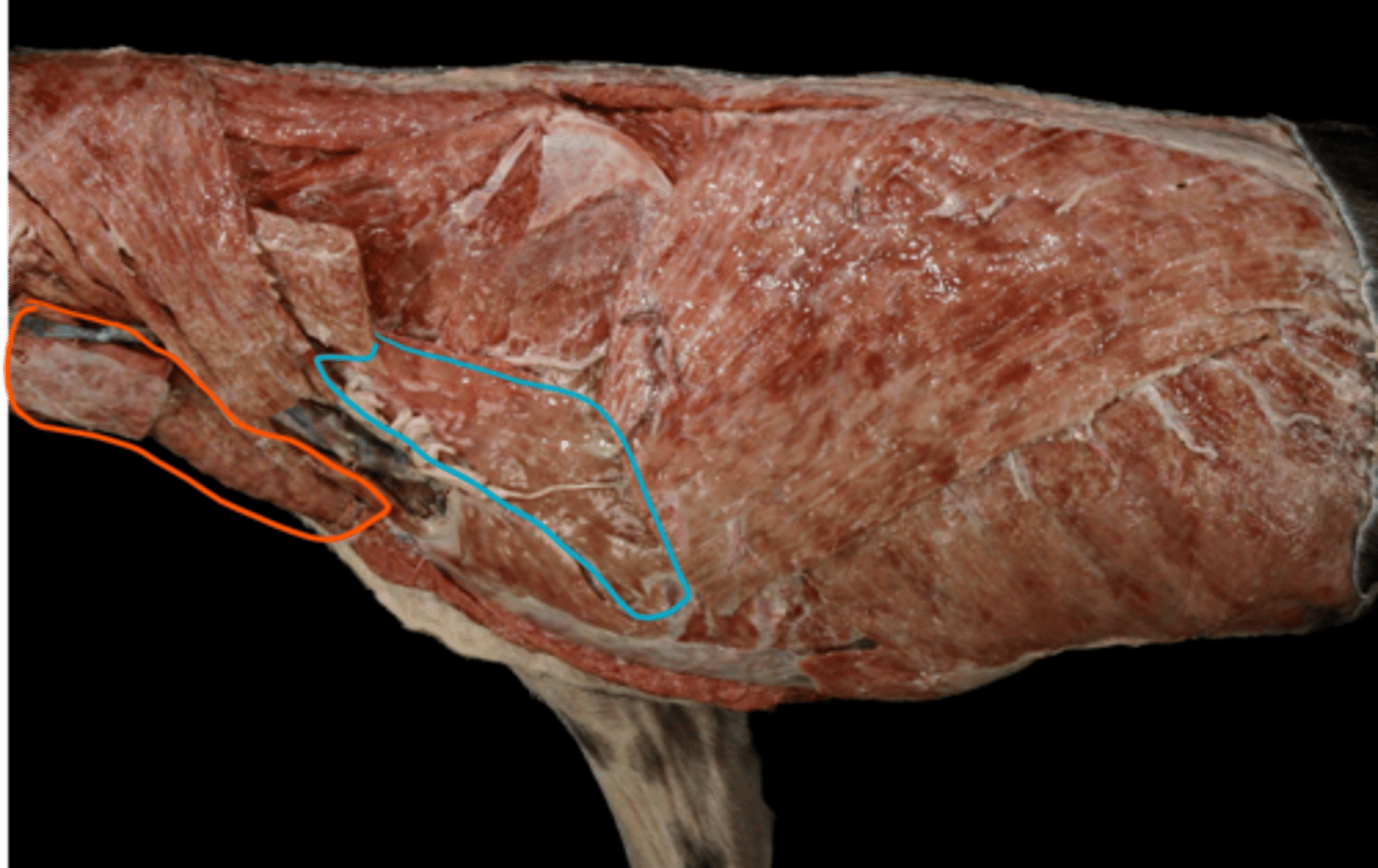
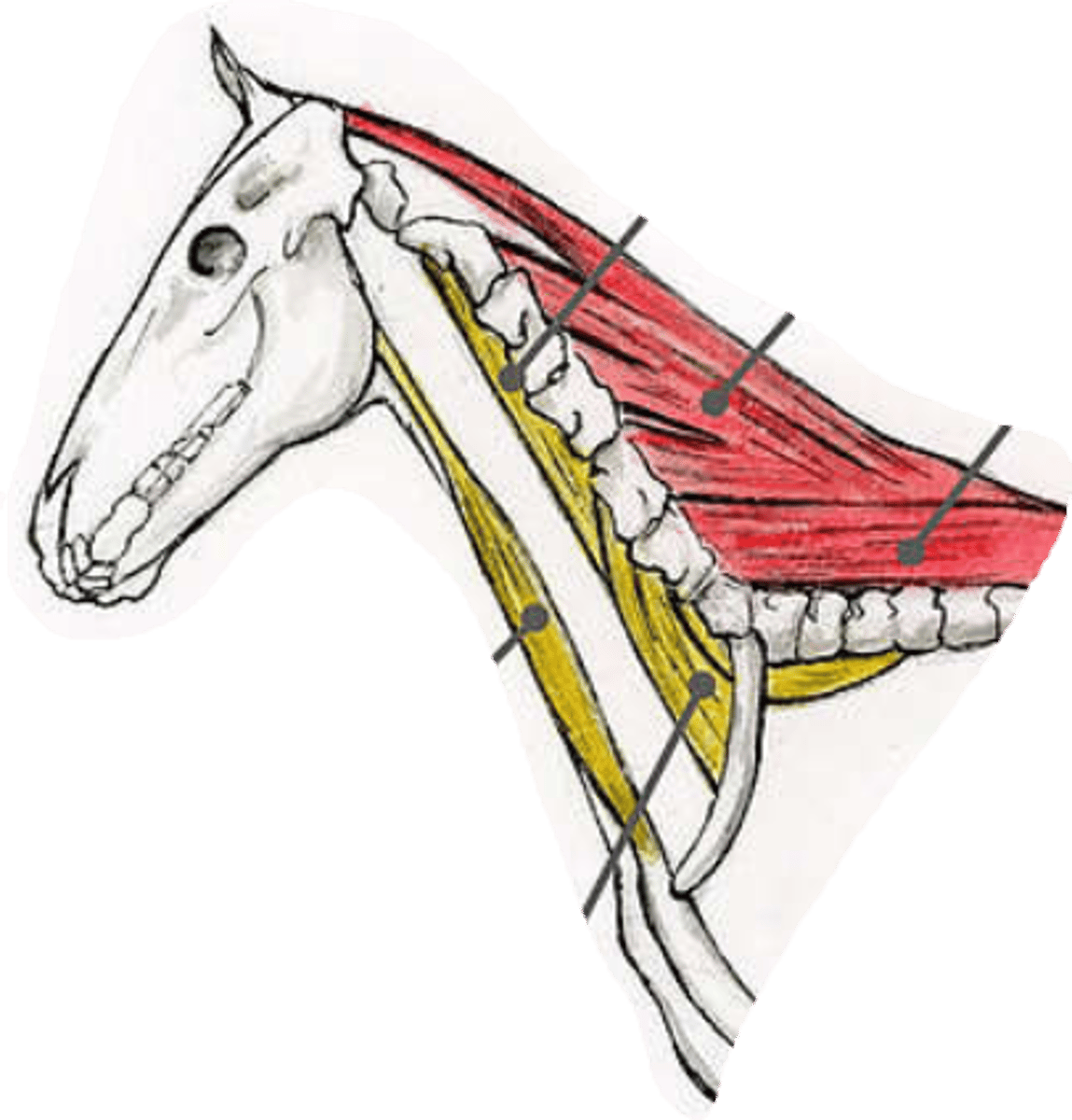
identify these ventral muscles as they are seen superficially.
blue: mm. scaleni: being between first ribs and last cervical vertebrae.
orange: m. sternocephalicus: extenting from manubrium sterni to the head.
- bo, su and ov: pars mastoidea
- bo, eq + cap: pars mandibularis
- car: pars occipitalis et mastoidea
- the big muscle dorsally of m. sternocephalicus is m. brachiocephalicus.
identify muscles. what muscle type is nr. 1?
ventral muscle of vertebral column:
1. m. longus colli, going from 6th to 8th t-vertebra, cranially continuing as m. longus capitis. (which is somewhat over the m. sternothyoroideus)
dorsal muscles of vertebral column:
2. m. longissimus thoracis
3. m. longissimus cervicis
4. m. semispinalis thoracis
5. m. iliocostalis lumborum
6. m. semispinalis cervicis
hyoid muscles:
7. m. sternohyoideus
8. m. sternothyroideus
ventral muscles of vertebral column include: (back)
- m. longus colli et capitis (from 6th to 8th T-vertebrae, ending on atlas, while capitis is the cranial continuation to occipital bone)
- mm. scaleni (between first rib and last cervical vertebra)
- m. sternocephalicus (lying ventrally and laterally to m. brachiocephalicus, from manubrium sterni to head)
- pars mastoidea + mandibularis
- car: pars occipitalis et mastoidea
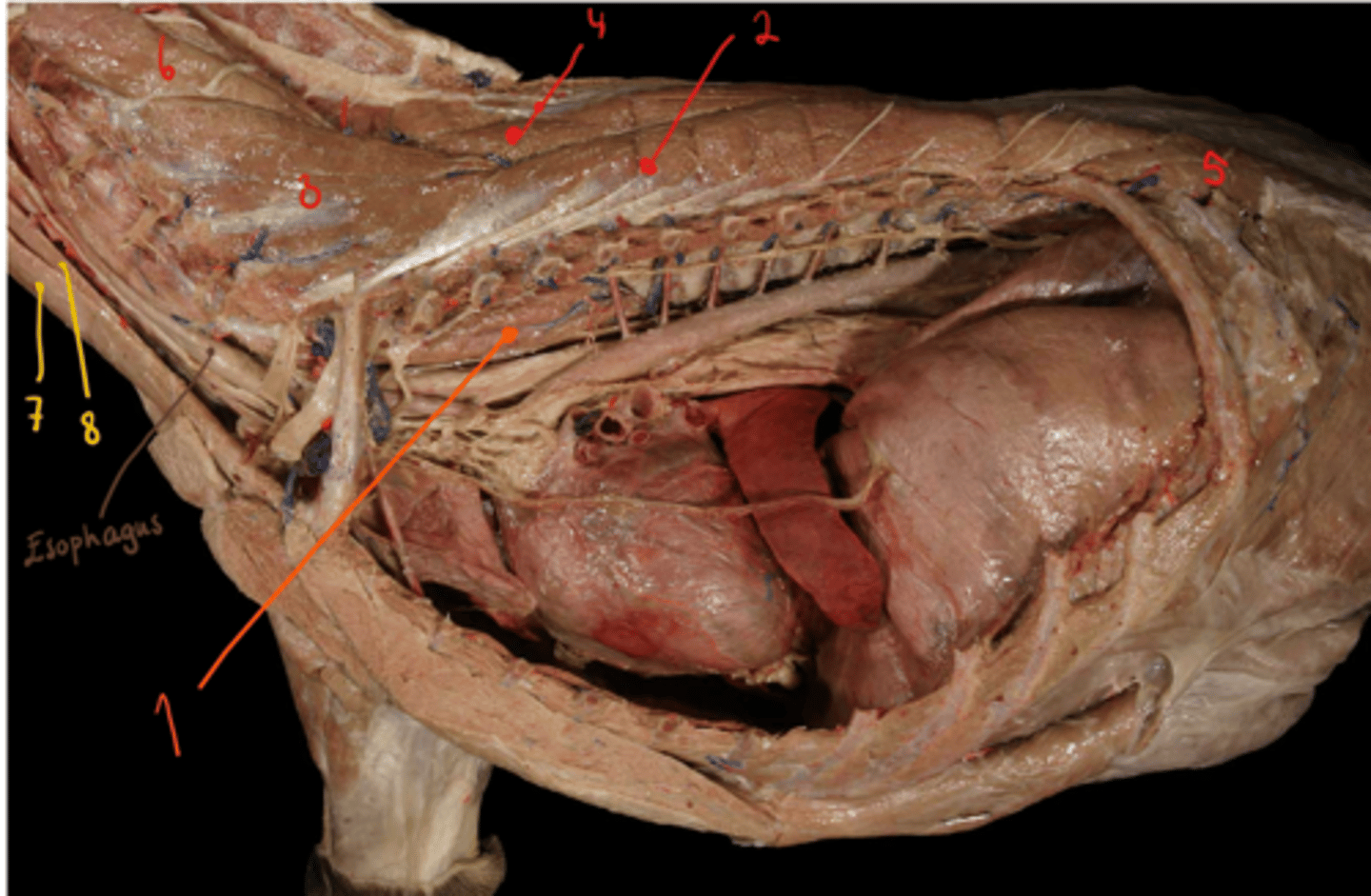
muscles of thorax include what?
- what muscles do we not see in the picture of thorax?
1. m. serratus dorsalis cranialis (covered my m. rhomboideus and m. latissimus dorsi)
2. m. serratus dorsalis caudalis (flat, caudally to the cranial one)
3. mm. intercostales externi (directed caudoventrally in the intercostal spaces)
4. mm. intercostales interni (lies under the external ones, directed cranioventrally)
5. m. rectus thoracis (thin, sheet on ventrolateral surface of thoracic wall)
6. m. transversus thoracis (transversally on dorsal surface of sternum, inside thoracic cavity)
- not seen in picture as it is internally on sternum.
7. diaphragma - separating the thoracic and abdominal cavity.
- not seen in picture.
explain the diaphragm. main parts and function.
one of the thorax muscles. It separates the thoracic and abdominal cavity. Most important muscle for inspiration.
Consist of 2 main parts:
- centrum tendinum and pars muscularis.
centrum tendinum is heart shaped consisting of crus dextrum (has an opening called foramen venae cavae) and crus sinistrum.
cupula diaphragmatis - part which projects cranially forming vertex of diaphragm.
pars muscularis: pars lumbalis (formed by crus dextrum et sinistrum, each having a pars lateralis et medialis), costalis et sternalis
what means by hiatus aorticus and hiatus espohagus?
1. A passage for aorta and thoracic duct. It is between the pars lateralis and pars medialis of crus sinistrum.
2. passage for esophagus and n. vagus. Formed by pars medialis of crus sinistrum et dextrum.
- pars costalis and pars sternalis.
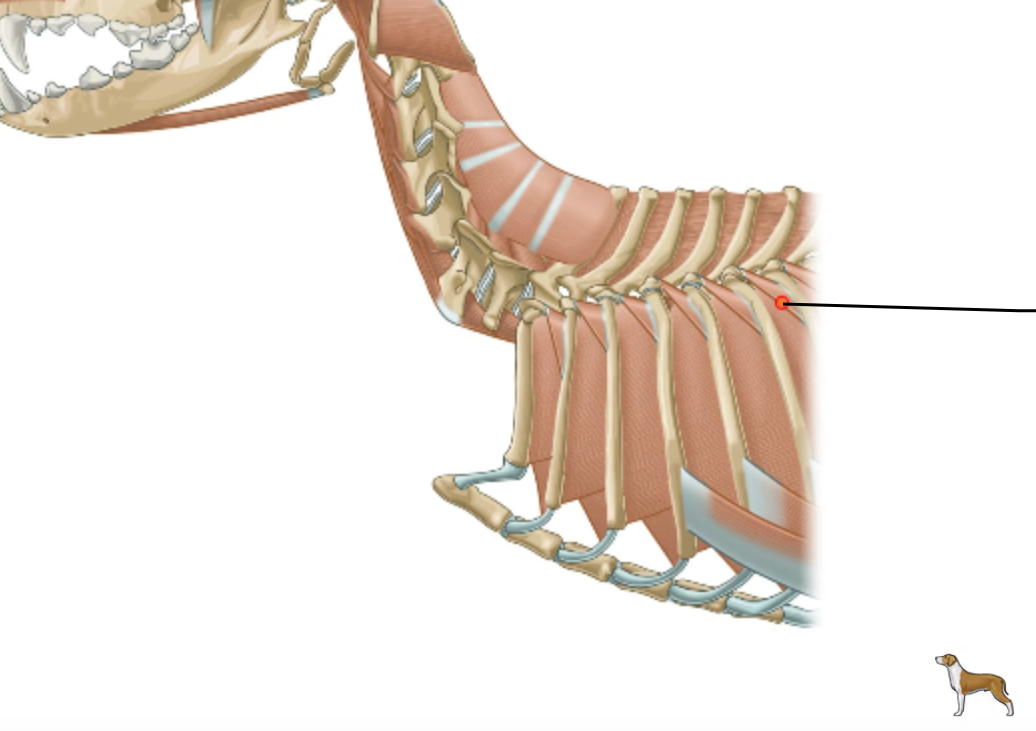
Which muscles are covered by the m. erector spinae, including series of short muscles going from the processus transversi et mamillares of thoracic vertebrae and insert on cranial border of the angle of rib?
mm. levatores costarum (function is an inspiration)
muscle of thorax
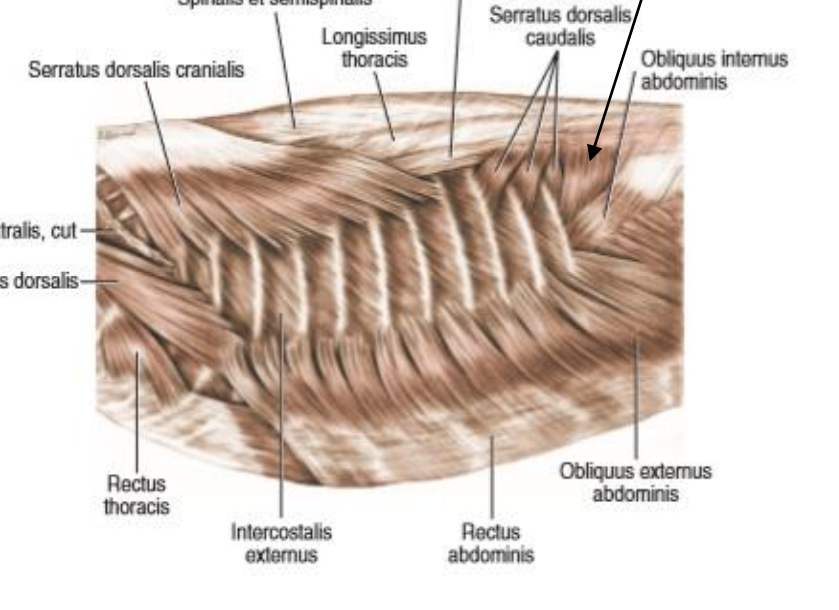
which muscle is a triangular muscle, lying between last rib and processus transversus of first lumbar vertebrae?
m. retractor costae (the black arrow)
fibres run cranioventrally and the muscle act as an expiratory muscle.
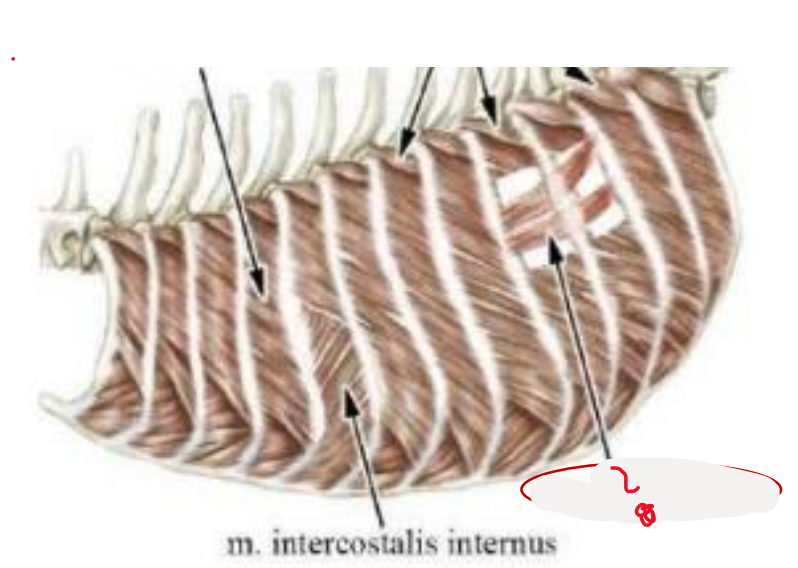
this muscle, which is located deep to the m. intercostales interna is?
mm. subcostales
in car: form three distinct muscle bundles bw. 11th and 12th rib. Acts as expiratory muscles.
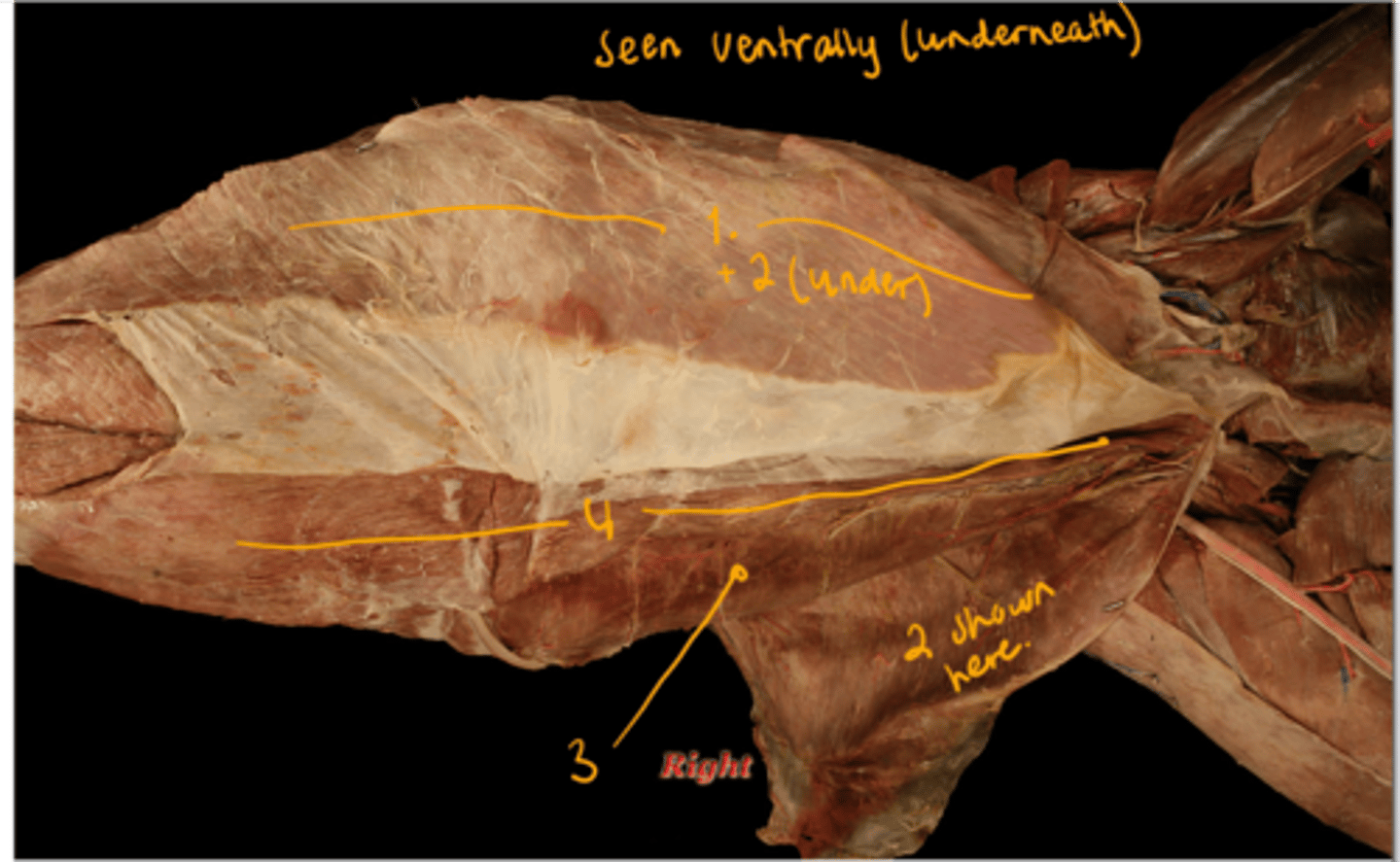
what are the muscles of abdomen? picture of dog on the underside of abdomen.
muscles of abdomen form lateral and ventral wall of belly, they are broad and flat.
m. obliquus externus abdominis (most superficially, directed caudoventrally, starting on laterally of ribs)
forms an aponeurosis, dividing into crus laterale et mediale. The anulus inguinalis superficialis.
m. obliquus internus abdominis (covered by the external one, has its muscle fibers going cranioventrally)
a) m. cremaster: muscular strip given off by the m. obliquus internus abdominis.
b) canalis inguinalis: formed by superficial and anulus inguinalis.
c) Caudal border of this muscle + lig. inguinale separates the anulus inguinalis profundus
m. transversus abdominis (in middle of abdomen, transverse direction, inserts on linea alba, expiration role)
m. rectus abdominis (muscle fibers of this has a sagittal direction, lying ventrally on abdominal wall)
divided into segments by intersectiones tendineae/tendinous intersections.
lies within vagina m. recti abdominis, is also covered ventrally by lamina externa (formed by aponeuroses of m. obliquus abdominis). Its inner surface is covered by lamina interna (formed also by aponeurosis but by m. transversus abd.)
inserts on prepubic tendon.
which ligament is extending from tuber coxae to os pubis? It separates the anulus profundus togehter with caudal borter of m. cremaster.
ligamentum inguinale, which is a part of the muscles of abdomen. A part of the m. obliquus internus abdominis.
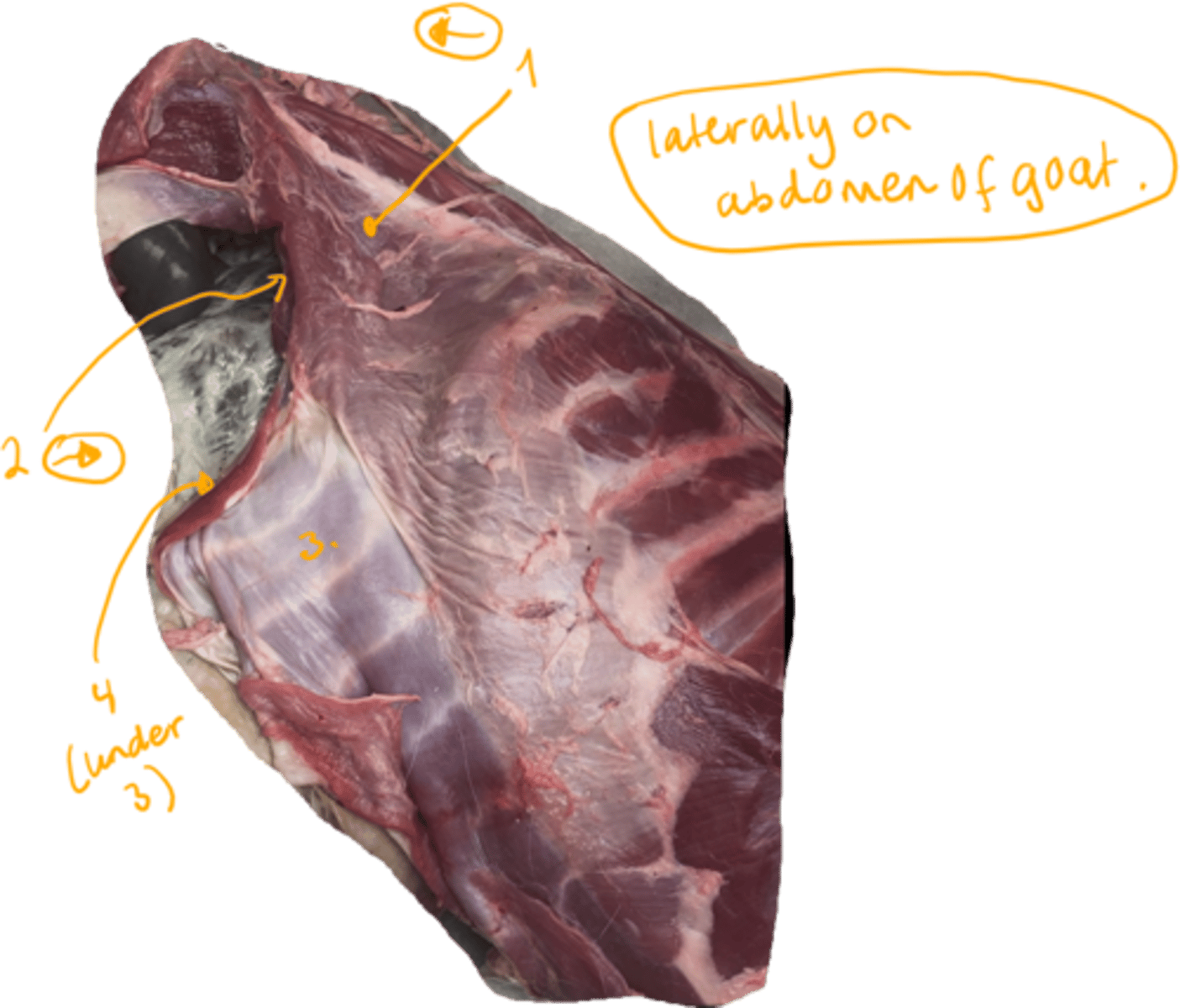

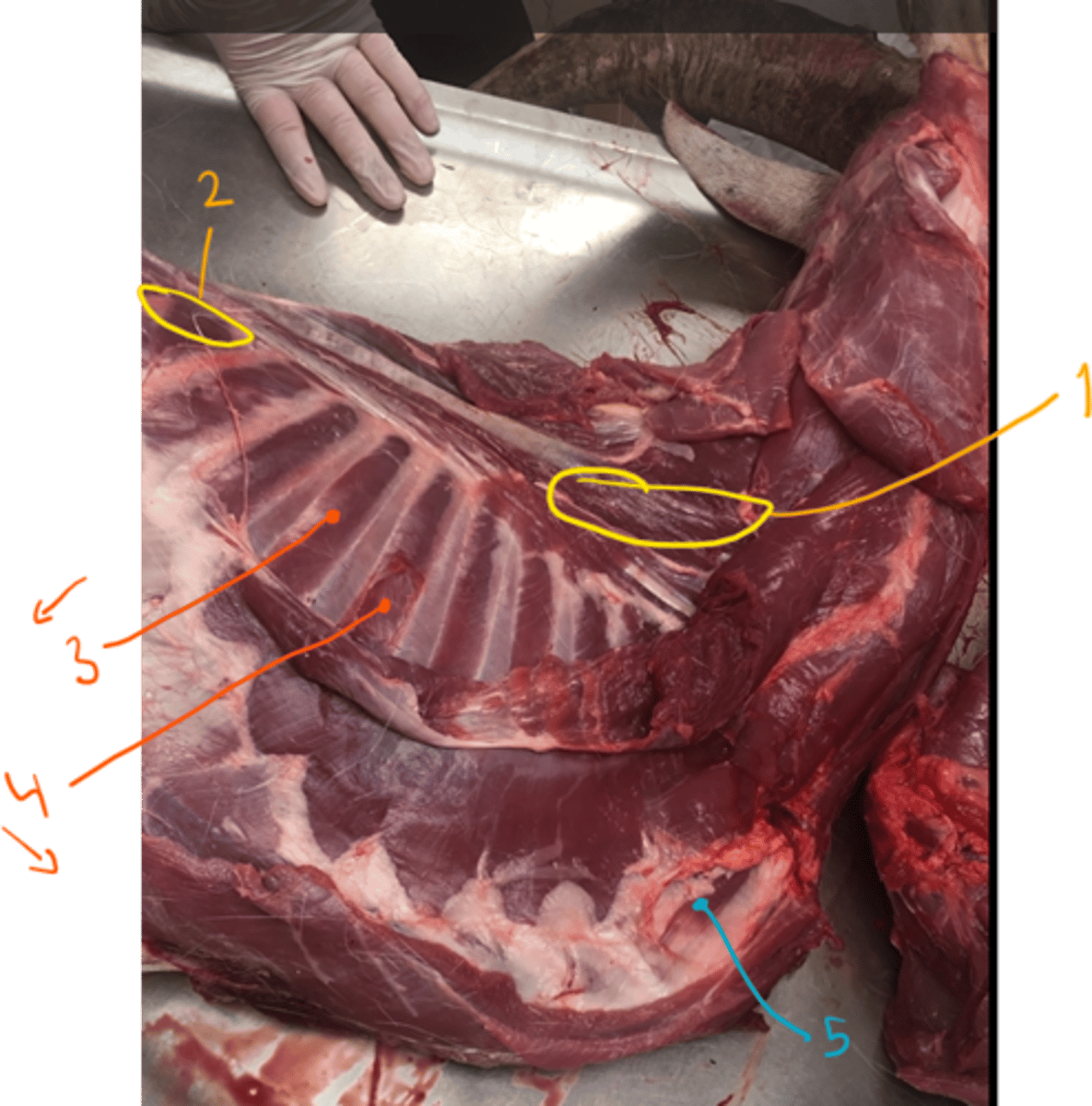
goat, show the abdominal muscles.
abdominal muscles:
1. m. obliquus externus abdominis: fibers going caudally.
2. m. obliquus internus abdominis: located underneath the external one, with fibers going cranially.
3. m. rectus abdominis which is divided into segments by the intersectiones tendineae.
4. (not seen here in picture clearly) but it is m. transversus abdomens.
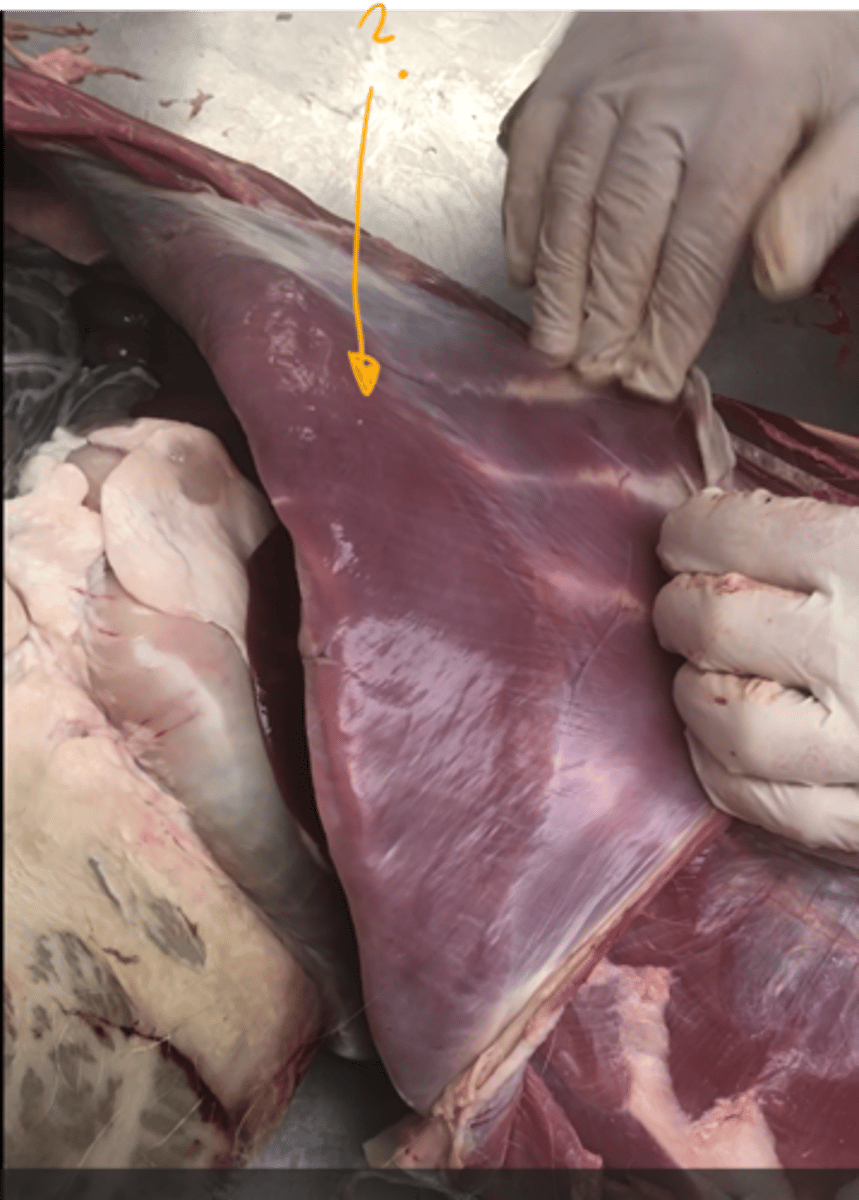
which muscle is this?
- underneath the m. rectus abdominis.
m. transversus abdominis. in the middle of abdomen with transversal direction.
muscles of tail forms?
the most caudal group of muscles of axial skeleton. they lie on the caudal vertebrae dorsally and ventrally. (MM. caudae)