Brain Lesson ( Week 1 ) - Intro to Psych
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- The Brain and Behavior (Biological Bases of Behavior) - Right and Left Brain
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms

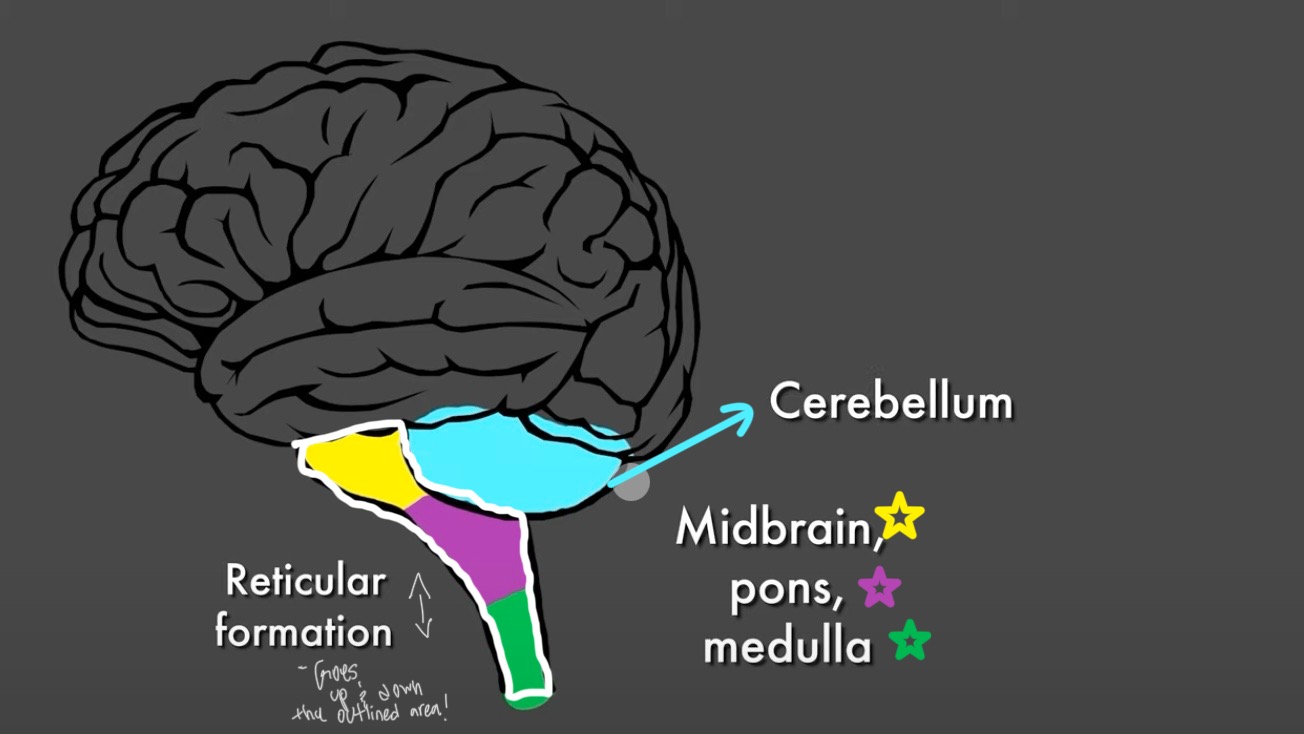
Hindbrain
Controls the most basic functions of life
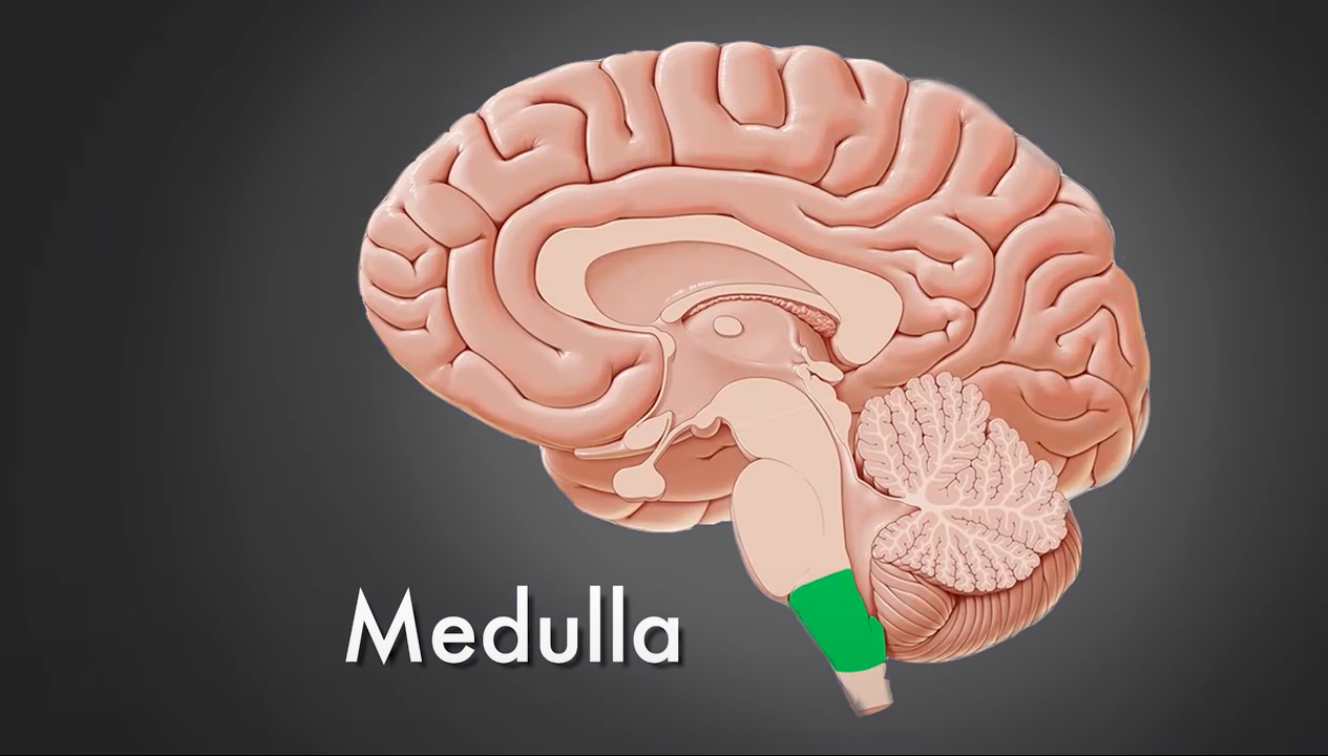
Medulla
The region of the brain that adjoins the spinal cord
Controls breathing, heart rate, and balance

Pons
Above the medulla
Controls attentiveness, and the timing of sleeping and dreaming
Damage to certain arts of the pons can put a person into a semi-permanent sleep like state
+ REM sleep may also originate in the pons
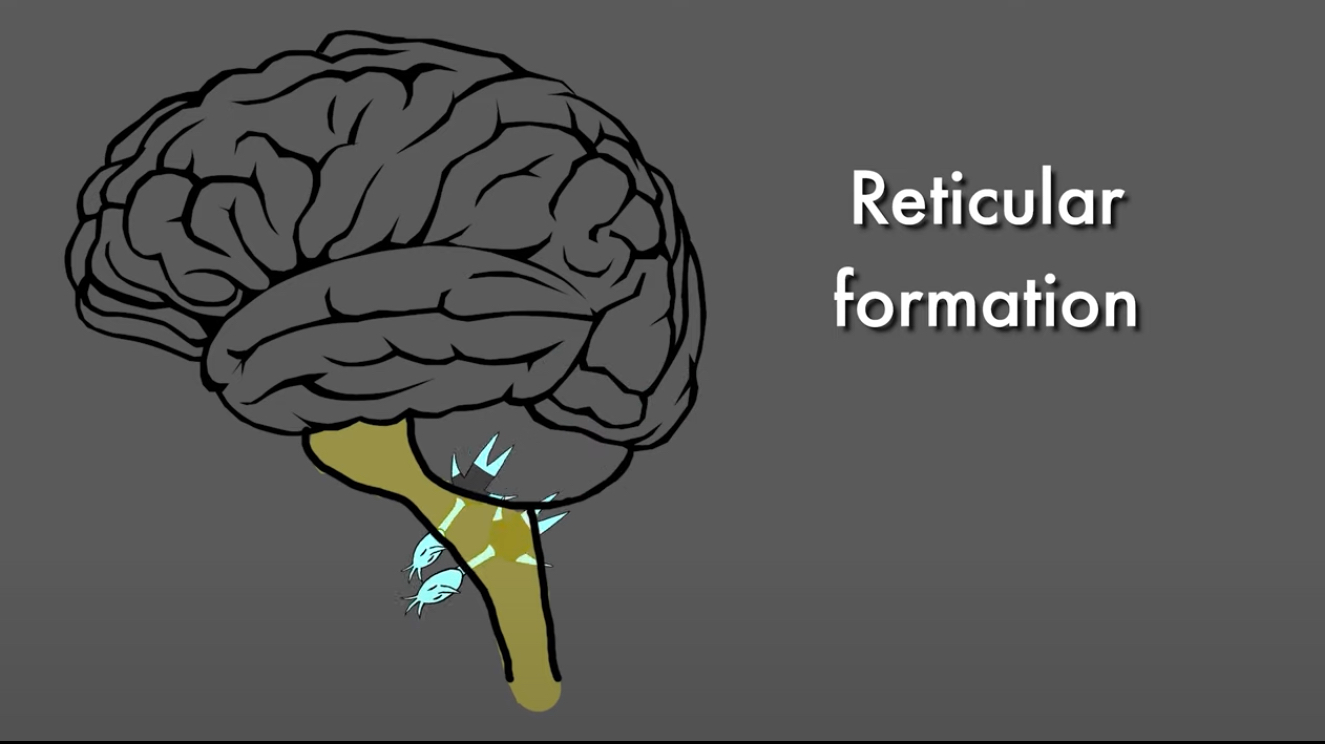
Reticular Formation
Inside the Pons and the Medulla
A network of nerves extending from the spinal cord right up through the Thalamus
Plays a role in autonomic functions of the body; Circulation, Respiration, Digestion, as well as Pain Modulation, Sleep, and Consciousness

Midbrain
On top of the Pons
Helps orient an organism in the environment and guide movement toward or away from stimuli
Also believed to help regulate our experience of Pain, modulate Mood, and shape Motivation

Cerebellum
Behind the Pons and Medulla ( yellow section in image)
Coordinates voluntary movements; posture and coordination , resulting in smooth and balanced muscular activity
Damage can cause problems in spatial reasoning, discriminating sounds, and integrating input received from various sensory systems
Evidence shows that it also helps use judge time, modulate our emotions, and even discriminate sounds and textures
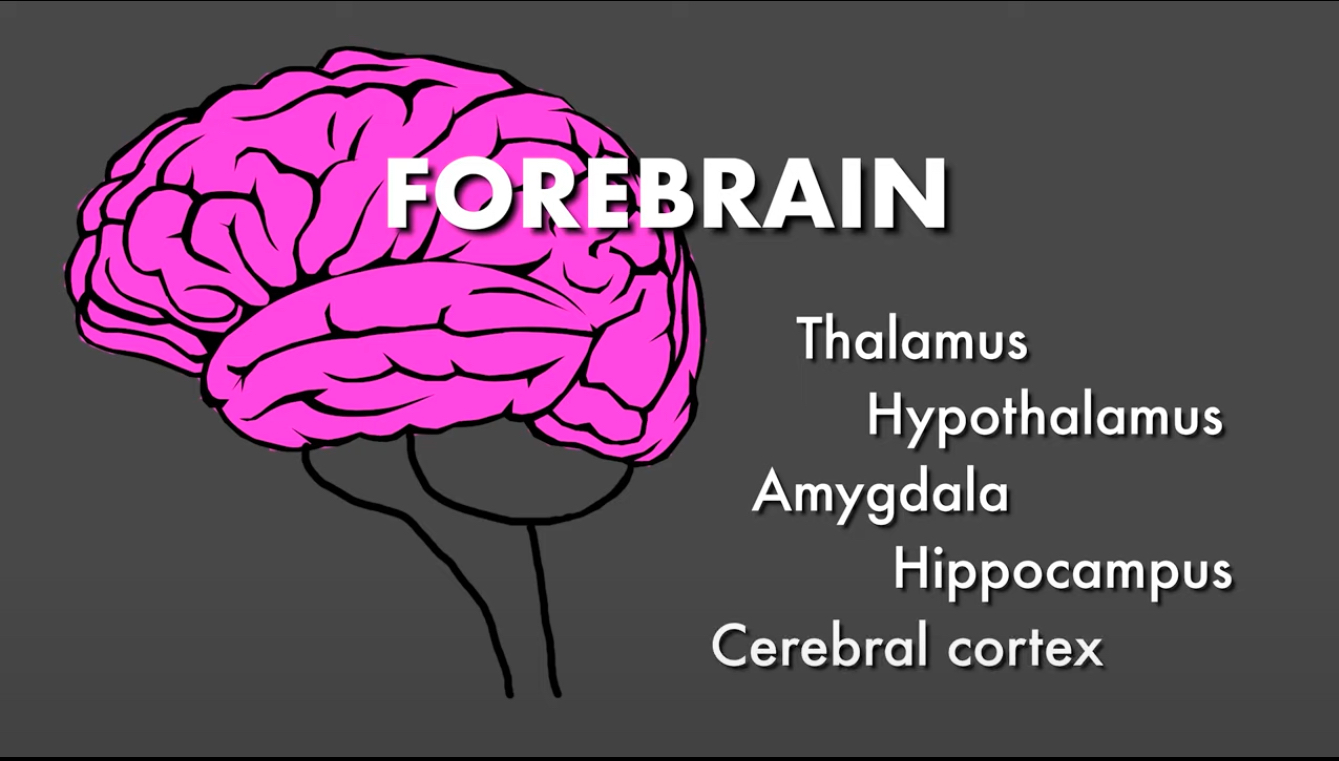
Forebrain
made up of brain structure; Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Amygdala, Hippocampus, & Cerebral cortex
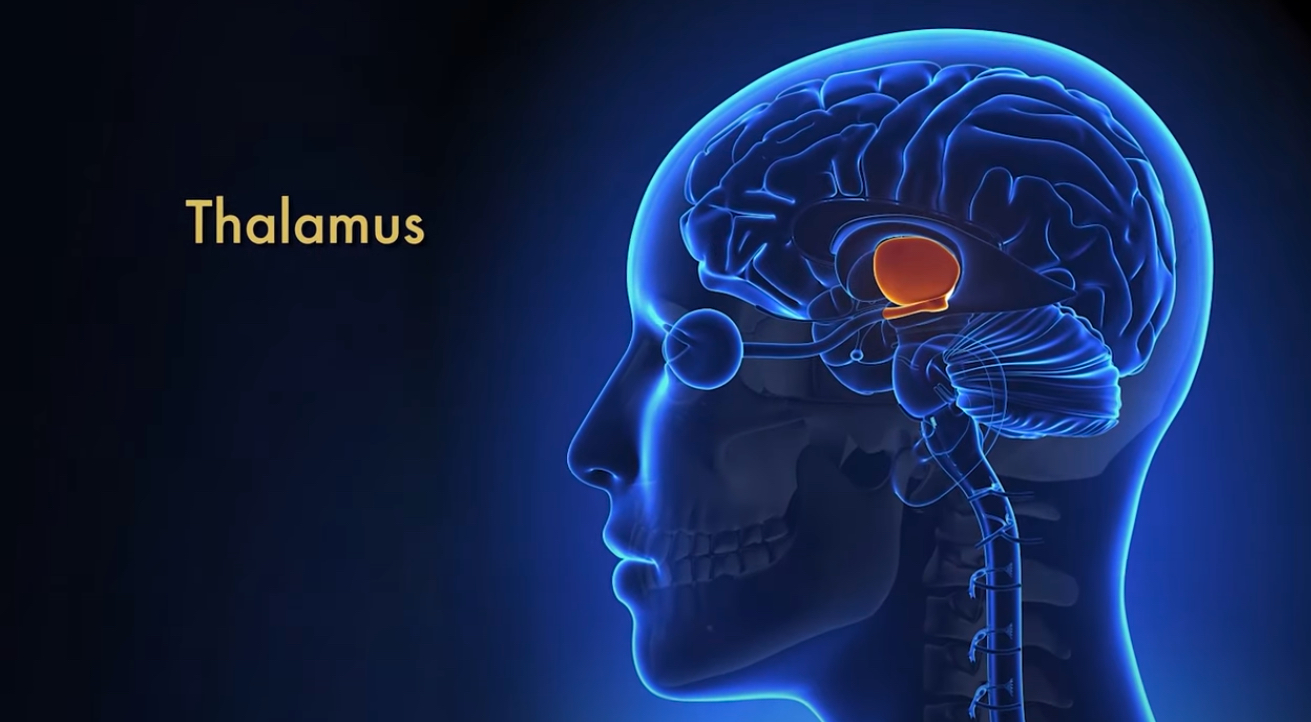
Thalamus
involved in sleep wakefulness, relay motor, and sensory signals to the cortex
Closes pathways of incoming sensations during sleep
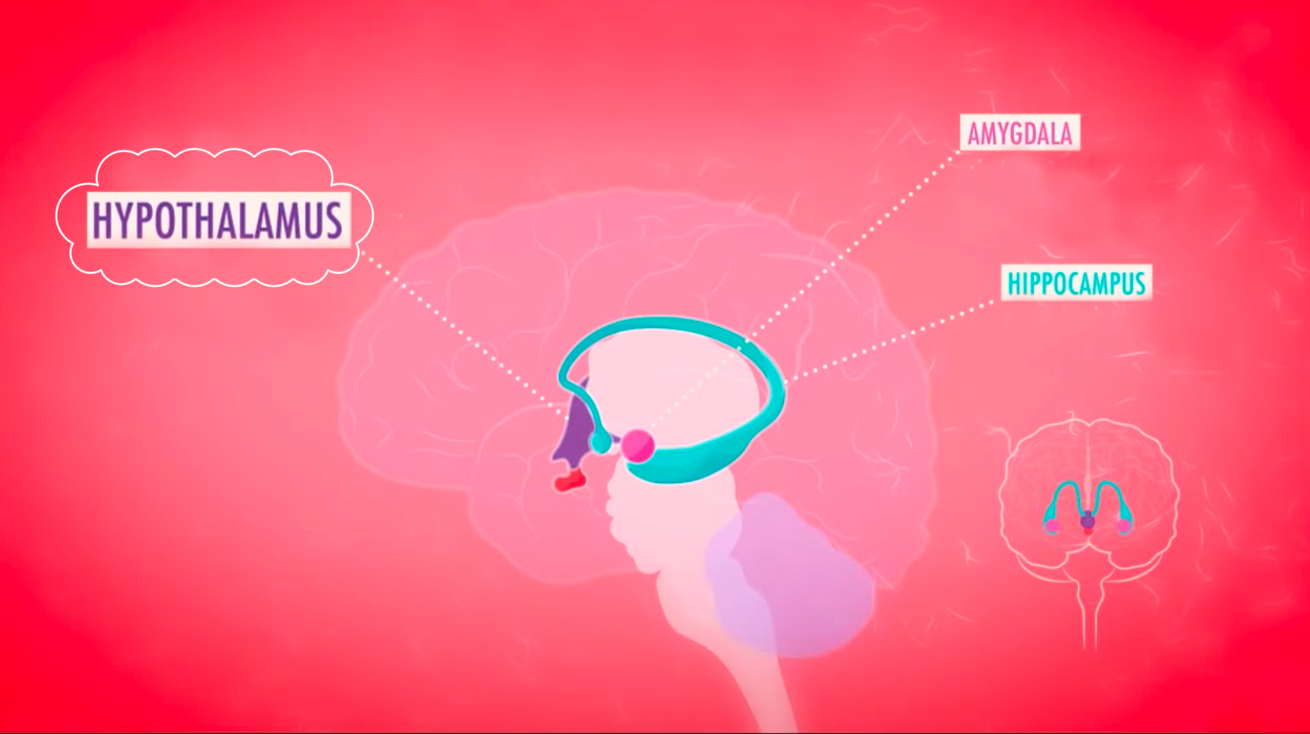
Hypothalamus
positioned underneath the Thalamus
Involved in controlling motivated behaviors; eating, drinking, and sexual activity
As well as involuntary rhythms; sleep/wake cycle, detecting when the body is too cold/hot

Amygdala
beloved to play a role in emotional response, specifically anger
Involved in determining whether a stimulus is a threat or not
Helps predict when something frightening is about to occur
Particularly active when playing video games or seeing fearful faces

Hippocampus
Plays an important role in learning , memory, spatial orientation, and creating new memories
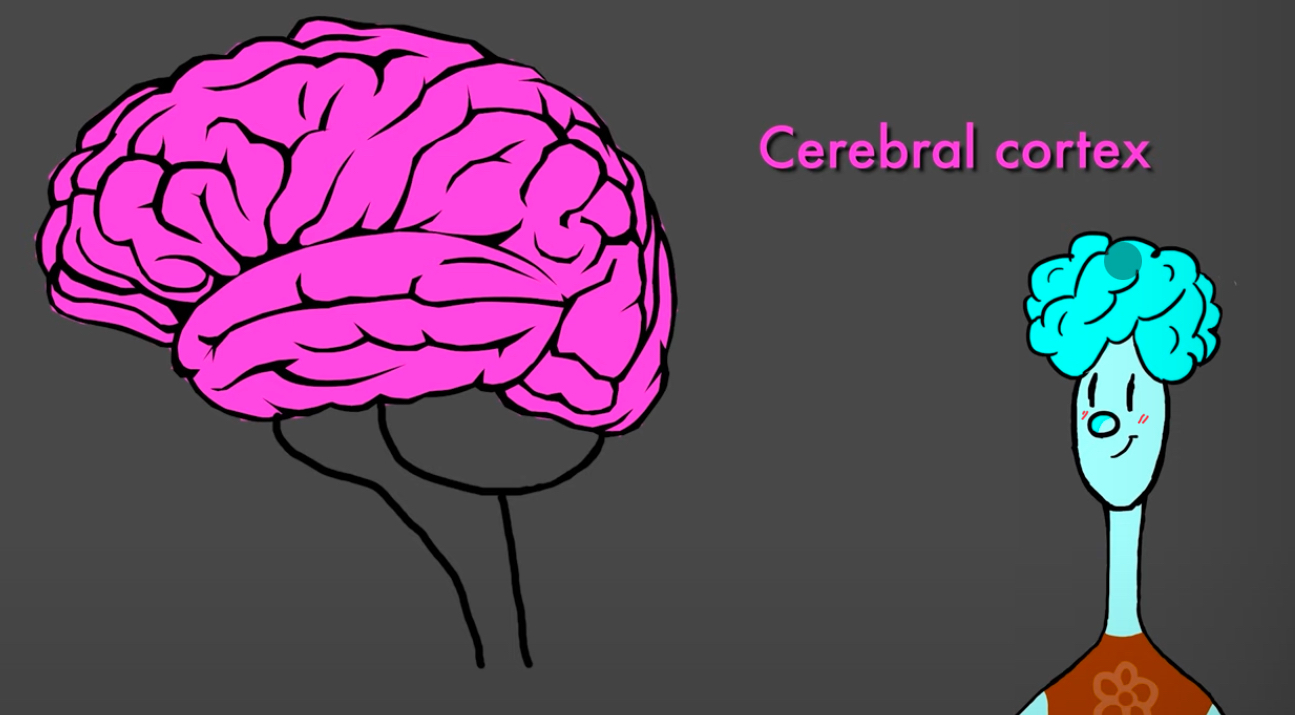
Cerebral Cortox
Is involved in every thought and perception, our ability to produce an understand language, and to construct and experience emotion
It is crucial in order to believe organize, remember, and even to hope
Structurally it is a thin on the outer surface of the brain, on average it is three millimeters thick
Makes up 80% of the human brain
Consist of a very large sheet of tissue, crumpled up into the limited space inside the skull which causes the wrinkles
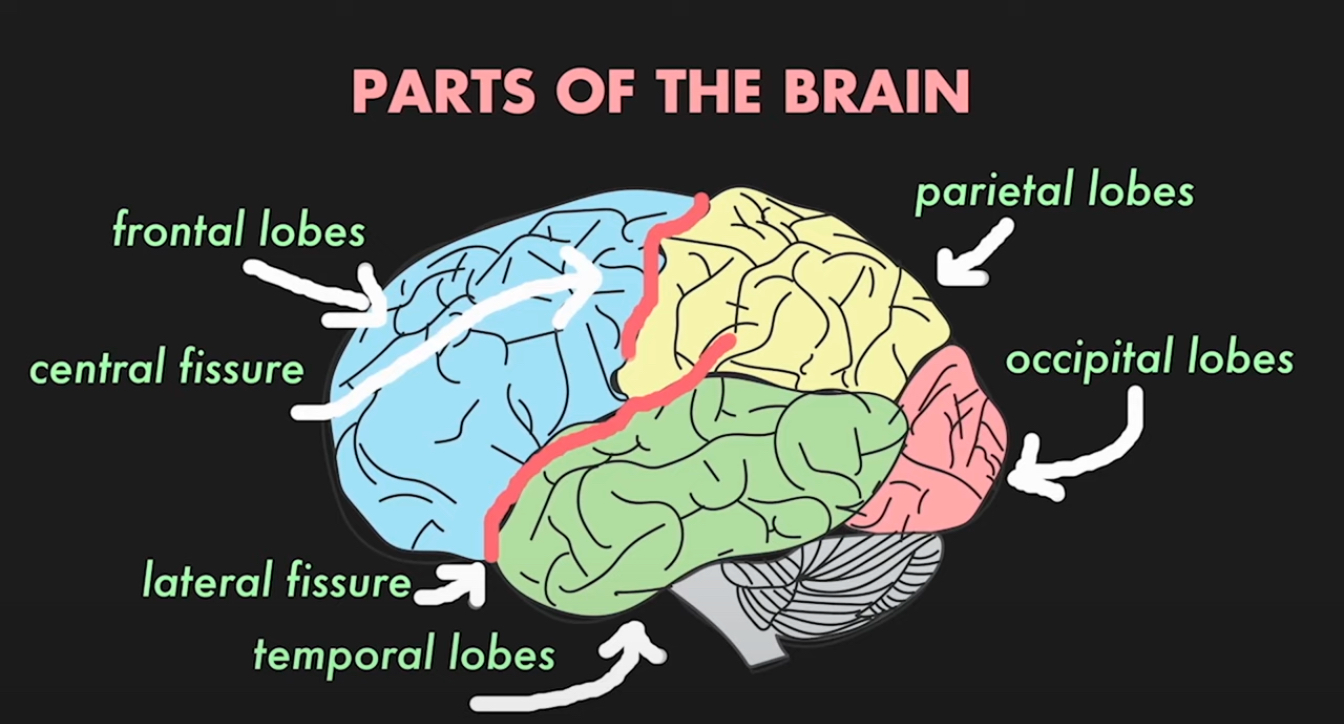
Divides into lobes

Corpus Collosum
Responsible for transmitting neural messages between both the left and right hemispheres
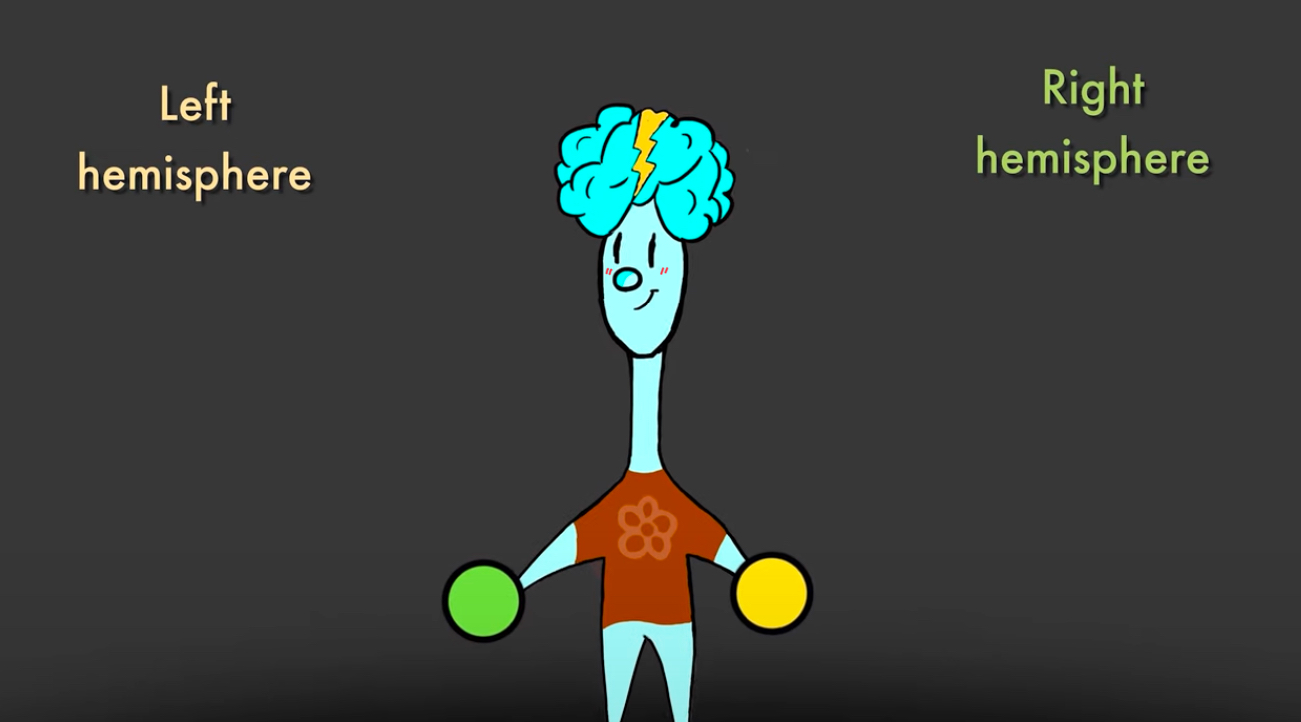
Left and Right Hemispheres
Right controls muscle and sensory info on the left side of the body, and vice versa
damage to one side of the brain will affect the opposite side of the body
Language and calculation seems to be done on the left and spatial reasoning on he right; left=logic and right=creativity (highly statistical)
Cortical Tissue , 3 sections/functions
Sensory areas
Receives and interpret information from the eyes, ears , and other sense organs
Motor areas
control our behaviors
Association areas
Connects sensory & motor areas
Involved in many complex processes
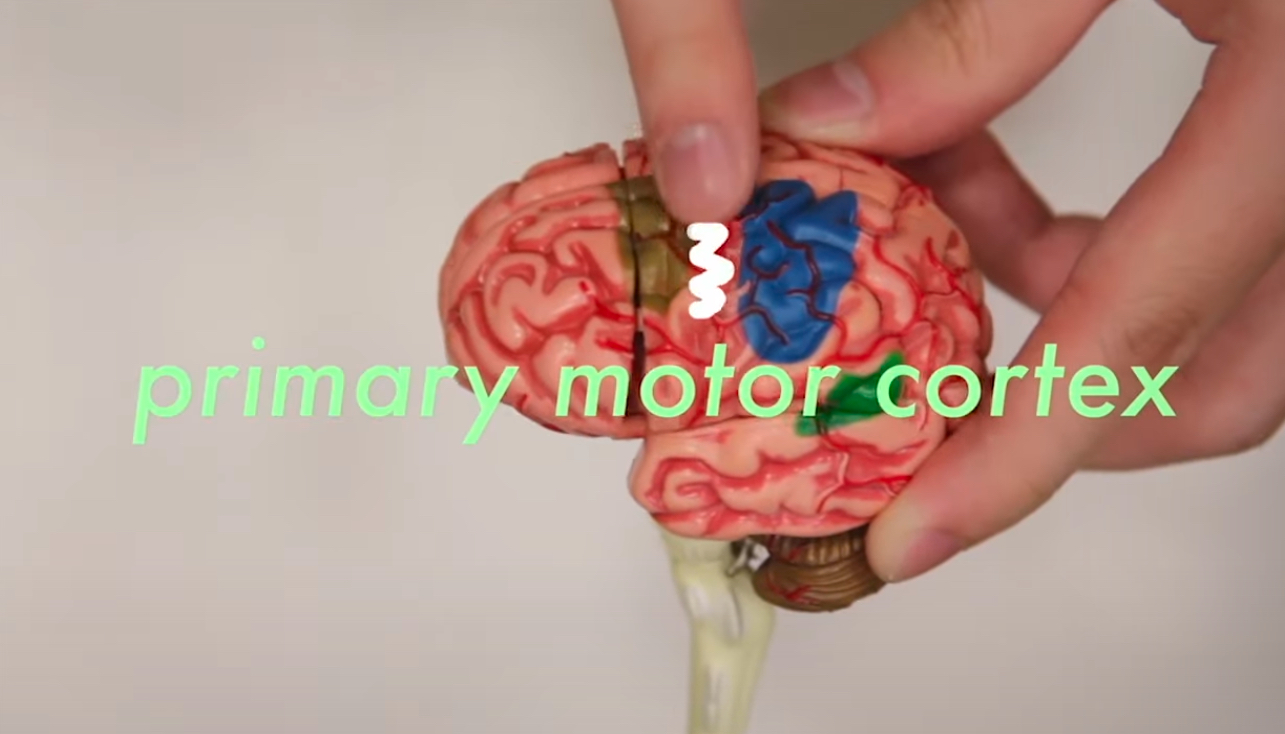
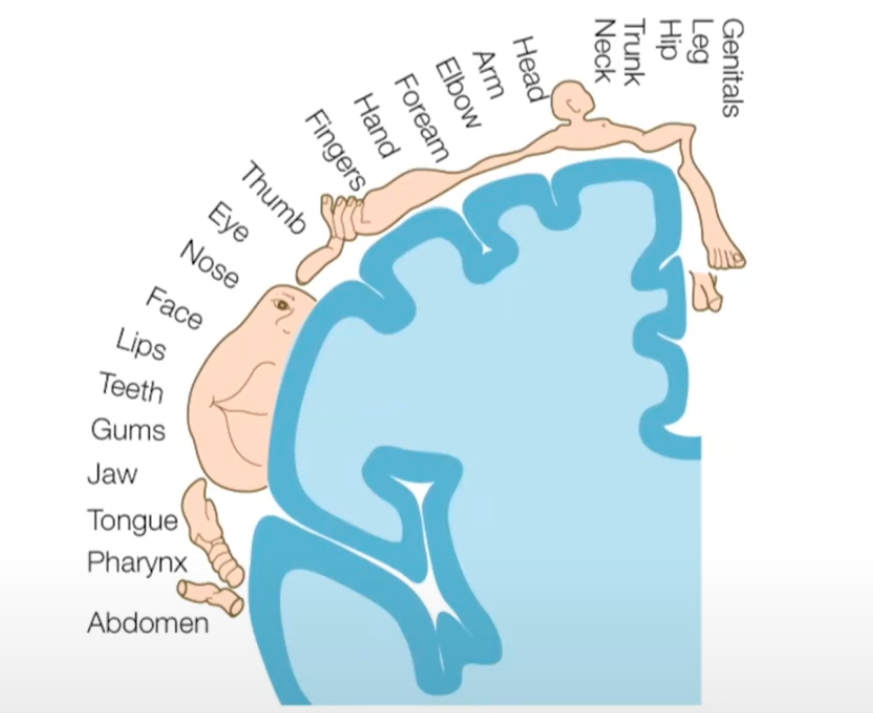
Primary Motor Cortex
Stimulating different parts of this area leads to movement of specific body parts
each portion of the primary motor cortex corresponds to a specific part of the body
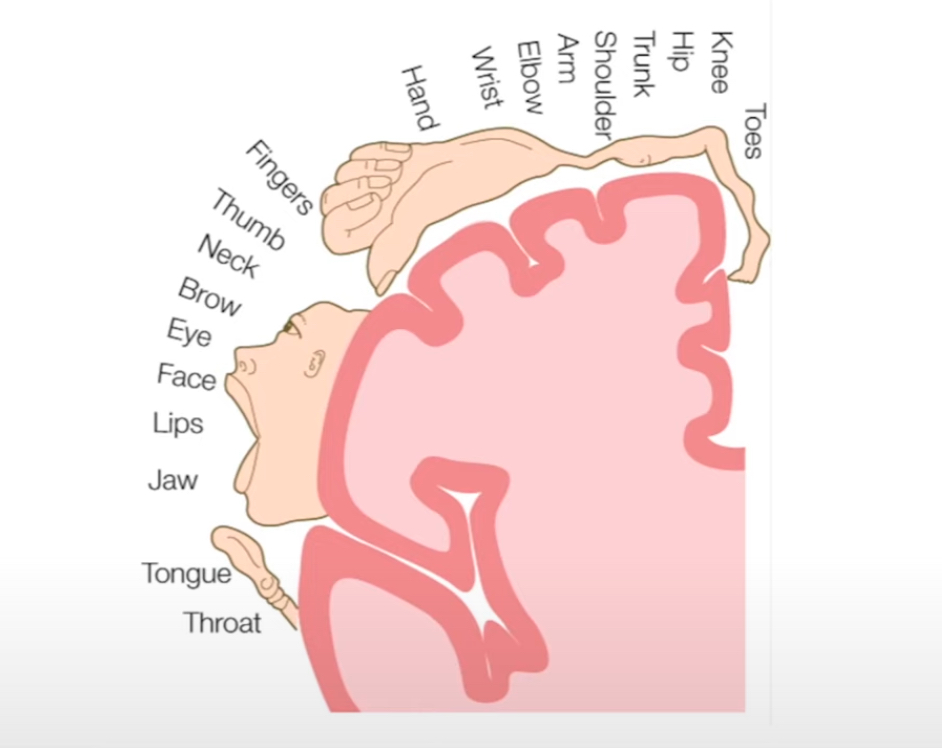
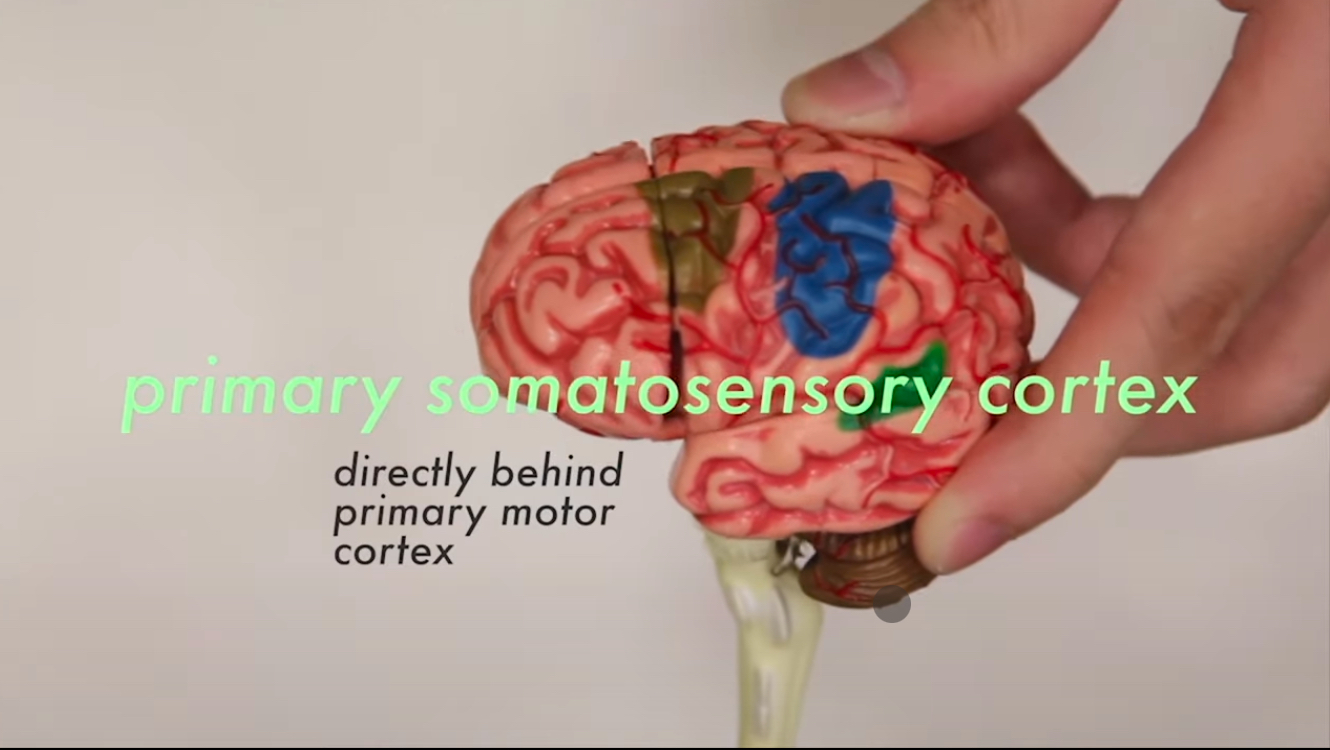
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
Is the initial receiving area for sensory info arriving from the skin senses
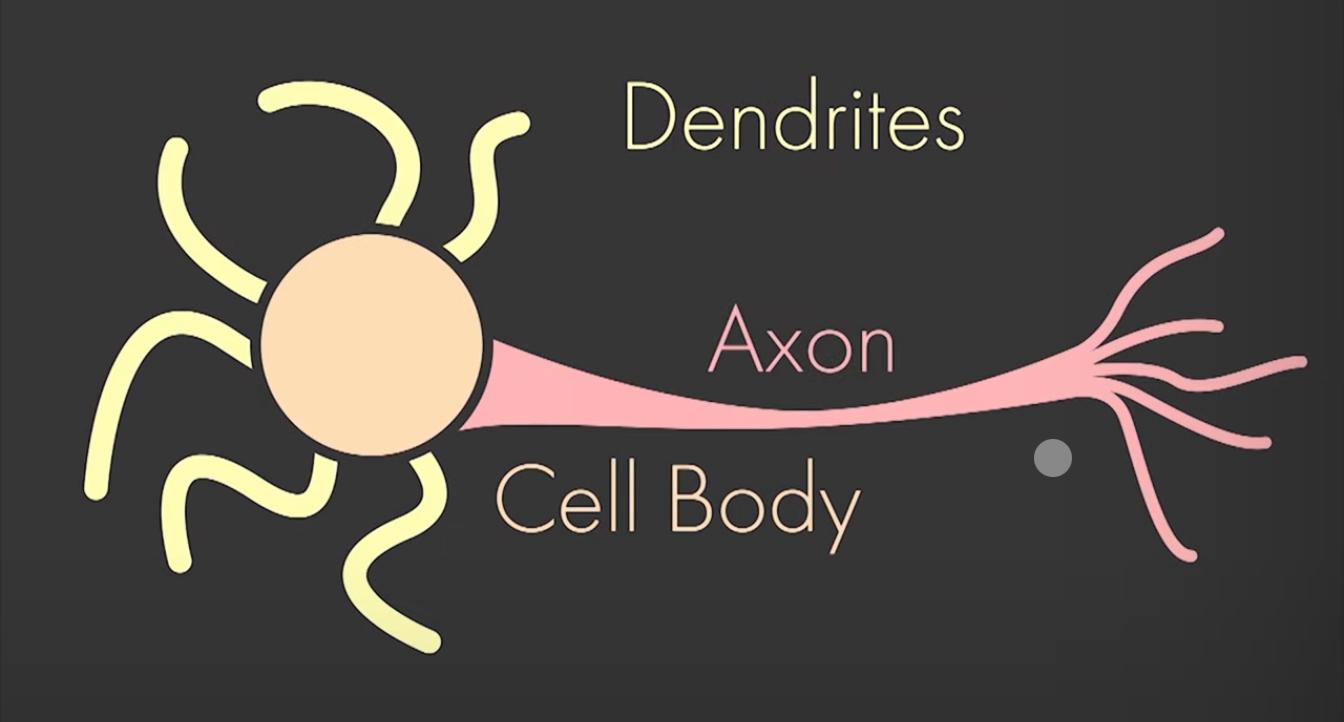
Neuron
Comes in many shapes and sizes
Dendrites : the input side, receives from other neurons
Cell Body : contains the nucleus, and all the elements needed for normal activities of these cells
Axon : is the output side, sense neuron impulses to other neurons
Glia converts glucose into lactate that feeds the neurons
Action Potential: neurons response to input, fundamental info carrier of the nervous system
Rest and Recuperation Neurotransmitters
Melatonin
Serotonin
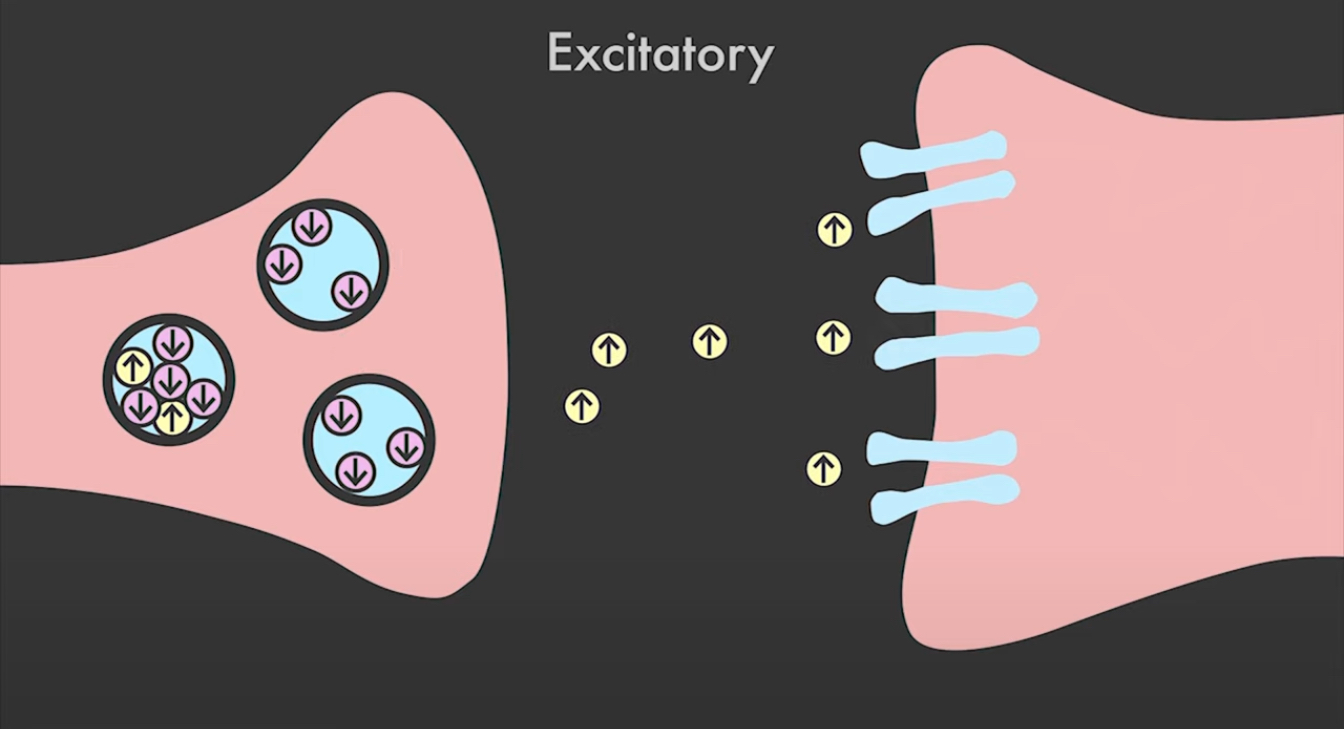
Excitatory Neurontransmitters
Acetylcholine
Glutamate
Aspartate
Noradrenaline
Histamine
Have excitatory affect in the neuron they increase the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential
ex; Epinephrine, Nor-epinephrine
Fight/Flight Neurotransmitters
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
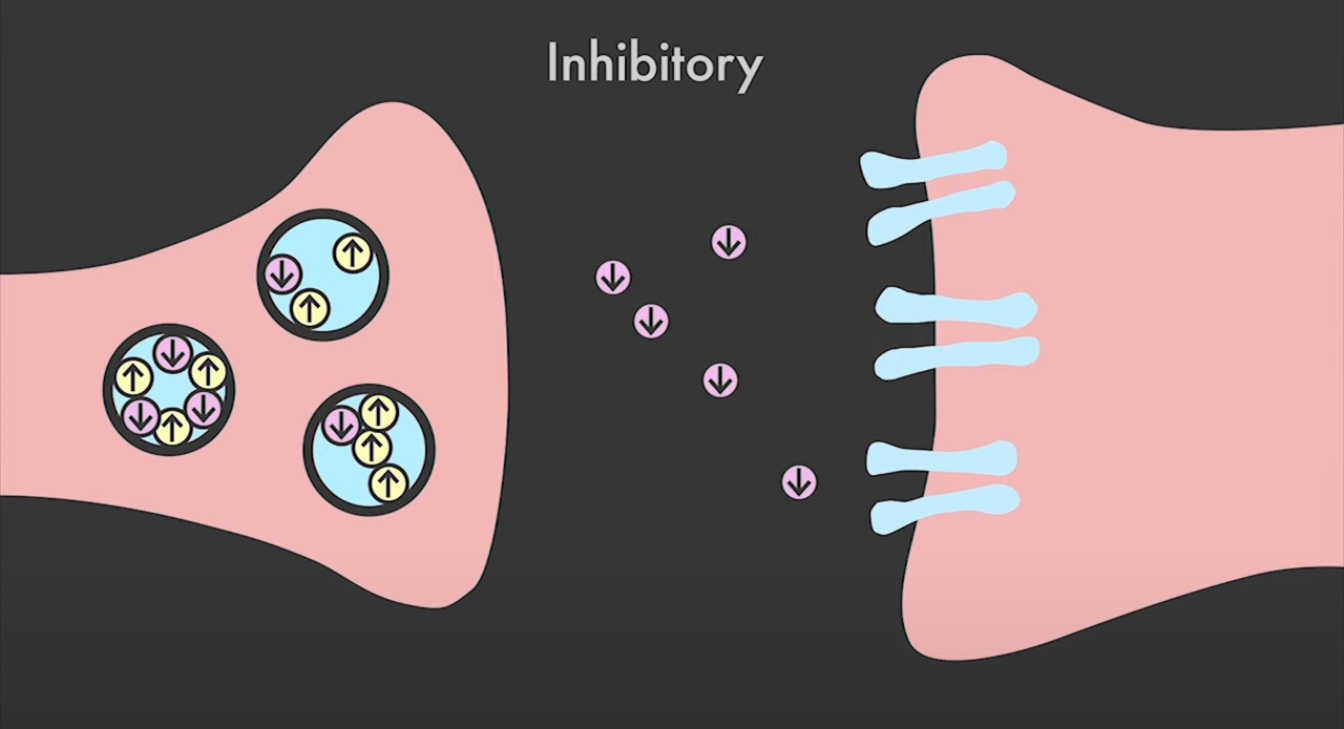
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
have an inhibitory effect on the neuron they decrease the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential - Ex; Serotonin, GABA
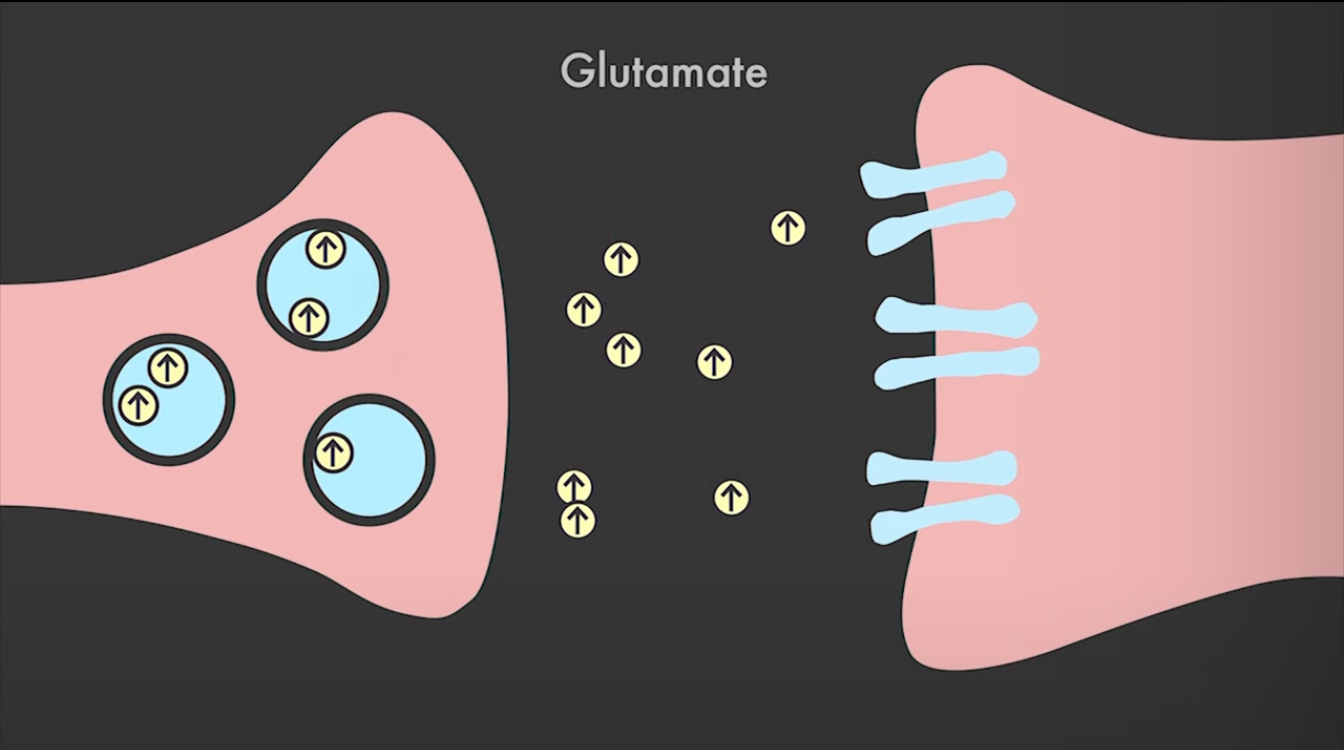
Glutamate
Rapidly excites neurons increasing the odds that they will talk with other neurons
Its real ease is associated with enhanced learning and memory
When abnormally elevated may contribute to schizophrenia and other mental disorders ; because in high doses it can be toxic damaging neural receptors by over stimulating them

GABA
Inhibits neurons by dampening neural activity
Considered an absolute work horse in our central nervous system playing critical roles in learning, memory, and sleep

Medication; aka chemicals
Agonists - Enhances ( ends up increasing the strength and duration of the transmitters affect )
Mimicking Neurotransmitters, so on their own they can activate the receptors
Blocking the Reuptake, into the pre synaptic cell
Counteracting Clean-up Enzymes, that breaks dow the transmitter after this triggered a response
Antagonist - Diminishes
Acting as Receptor “Putty”, prevent the transmitter from working by binding themselves to the synaptic receptor and blocking off the transmitter
Speeding up reuptake and others by augmenting clean up enzymes
Key Elements in Flow of a Information
selective receptor response
Different neurotransmitters provide different signals
Degeneracy- many to one
Core Systems- one to many