chapter 10: alkenes
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
the pi bond is much weaker/stronger than the sigma bond of a C=O, making it more easily broken
weaker
the rotation around the C=O bond is _______
restricted
whenever the two groups on each end of a C=C are different from one another, they can have two kinds of stereochemistry:
trans or trans
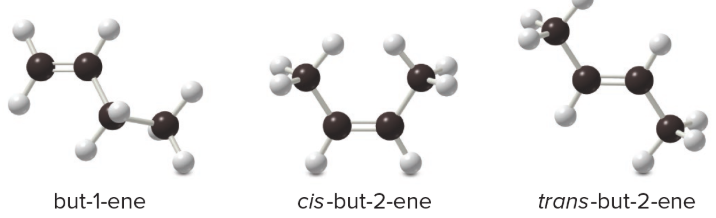
trans/cis are more stable than trans/cis
trans are more stable than cis
stability of alkenes increases as the number of r groups on the C=C increases/decreases
increases
alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons because
they have fewer than maximum number of hydrogens per carbon
C2H2n
steps to find the degree of unsaturation in a hydrocarbon
count the number of carbons and hydrogens in the given atom
compare to the alkene that matches
subtract alkene Hs from alkane Hs
divide by 2
if given the structure, add together the cyclos and double bonds
O atoms = ignore
halogens = 1 H
nitrogen = -1 H
when naming a molecule that contains a double bond and -OH, which has higher priority
the OH
alkenol
if a molecule has two double bonds, what is it called? three?
diene
triene
when naming a cycloalkene
number alkene 1 and 2 and give the first substituent the lowest number
the 1 is omitted
E/Z system
E: highest priorities are opposite of each other
Z: highest priorities are on the same side
divide the double bond in half
assign priority to substituents

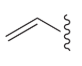
vinyl group
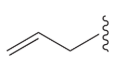
allyl group
alkenes have low/high MP and BP
low
MP and BP of alkenes increase/decrease as number of carbons increase because of increased SA
increase
alkenes are soluble/insoluble in organic solvents and soluble/insoluble in water
soluble in organic solvents
insoluble in water
most alkenes have only _____ IMF
LDFs
the cis isomer of an alkene, yields a _____ dipole , whereas in a trans isomer, the dipoles ____
small net
cancel
cis alkene is more ______, giving it a slightly higher/lower BP
polar
higher
lycopene
red pigment in tomatoes and watermelon
has 13 double bonds
antioxidant → can decrease risk of heart disease and cancer
triaclyglycerols
most abundant lipid
contains 3 ester groups
lipids are water-_______
insoluble
when a triacylglycerol is hydrolyzed it produces
glycerol and three fatty acids
saturated fatty acids have _____ double bonds in their long hydrocarbon chains, and are obtained form ______
no double bonds
animal sources
unsaturated fatty acids have ______ double bonds, and are obtained from ___
one or more
vegetable sources
double bonds in naturally occurring fatty acids have ____ configuration
Z
same side
as the number of double bonds in the fatty acid increases, the MP ______
decreases
fats have _____ MP
fats are derived from FAs having ____ double bonds
higher, solid at room temp
few
oils have ____ MP
oils are derived from FAs having ____ double bonds
lower, they are liquids at room temp
many
alkenes can be prepared from alkyl halides and alcohols via
elimination reactions
the pi bond is much weaker/stronger than the sigma bond, creating the ability for ______ reactions
weaker
addition
every reaction of alkenes involves _______, where the pi bond is _____
addition
broken
because alkenes are electron _____, they react with _______
rich
electrophiles
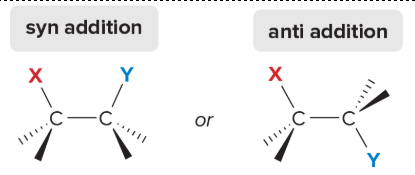
two types of addition stereochemistry
syn: same side
anti: opposite side
addition reactions are endo/exothermic
exothermic
what can be used to form alkenes
alkyl halides, tosylates, alcohols
markovnikov’s rule
in the addition of HX to an unsymmetrical alkene, the H atom bonds to the less substituted carbon
the H will go to the carbon that will produce the most stable carbocation
might only produce one product because it WONT form a 1 degree carbocation
trigonal planar atoms react with reagents from ___ directions with ____ probability
two
equal
achiral starting materials yield ____ products
racemic
the terms cis/trans refer to:
while syn/anit describe:
arrangement of groups in a particular compound
stereochemistry of a process
hydrohalogenation occurs with _________ addition of HX
syn and anti
in hydration, addition of H and OH occurs in both _______ arrangements
and carbocation formation and rearrangements can/can’t occur
syn and anti
can
halogenation forms a
vicinal dihalide
in halogenation, ____ rearrangements occur, and only _____ addition is produced
no
anti
in halogenation, halonium ions are unstable because
they produce a strained three member ring
in halogenation, the opening of bridged halonium ion intermediates resembles
the opening of epoxide rings with Nu-
steps of halogenation
addition of X+ forms unstable bridged halonium ion
nu- attack of X- occurs from backside to from trans products in anti addition
halohydrin formation
addition of electrophile X+ to form bridged halonium ion
nu- attack by H2O from backside on three-membered ring
addition of X and OH occurs in anti fashion with trans products being formed
unsymmetrical alkene: two isomers are possible but only the less substituted RX is preferred, thus the OH ends up on the more sub C
no rearrangements
NBS is a source of
Br2
hydroboration
addition of borane (BH3) to an alkene to form alkylborane
oxidation converts C-B bond to C-O bond, retention of configuration
syn addition occurs with no carbocation rearrangements
boron atom bonds to less sub carbon
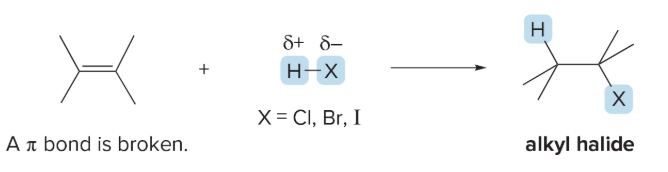
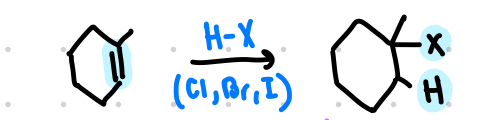
hydrohalogenation
syn and anti
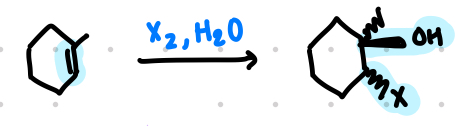
halohydrin
anti only
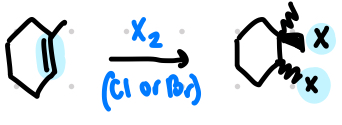
halogenation
anti only
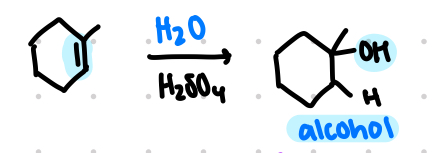
hydration
syn and anti

hydroration oxidation
syn only
bonds to less sub

E2
Sn2

E1

Sn1

E2

Sn2

sn2

e2