Paternity Testing
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is paternity testing
DNA testing to determine who a child’s —— might be
Samples used include —-, —— cells, —— fluid, and —— cells
Latter two for baby’s DNA
father, blood, buccal, amniotic, placental
Polymorphic DNA sequences
Alleles
One of two or more nucleotide sequences that contains a variant and is found at the —— place on a ——-
Each person has —- alleles
The child will share ——- allele from the mom and —— from the dad
Markers
DNA sequence with a —- location on a chromosome
Can detect an allele of interest
Polymorphism
Presence of two or more ——- forms of a specific DNA sequence present in a population
Different versions of the allele are present in the population
same, chromosome, two, one, one, known, variant
Polymorphic DNA sequences
STR (short tandem repeats)
—— sequences that are —- throughout a DNA sequence
The —- of the repeats present varies among individuals … basis of paternity and forensic testing
VNTR (variable number tandem repeats)
—— sequences repeated throughout a DNA sequence
RFLP
Used to detect ——-
DNA sample if digested into ——— using one or more —— enzymes
The resulting fragments are then separated by —— ———
The presence of an STR or VNTR can either —— or —— restriction sites which will alter the —— and —— of fragments produced
Used to test any polymorphisms present in the father and child and compare
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism)
——— mutation in —— nucleotide
short, repeated, number longer, polymorphisms, fragments, restriction, gel electrophoresis, add, remove, number and size, point ,one
DNA based forensic testing
Compare polymorphisms between crime scene DNA and suspects to find an —— match
Southern blot test
Hybridization method used to detect a ——- DNA sequence
PCR
amplification method used to ——- a specific section of DNA
Loci
Region of DNA on a ——- that contains an allele
Random match probability
The likelihood that someone picked at random will have the same ——
Statistical comparison to see how likely a match is due to paternity/guilt rather than —- ——
exact, specific, amplify, chromosome, allele, random chance
Prenatal Paternity Testing
Can use ——- fluid and —— cells to provide baby DNA for testing
NIPP (non invasive prenatal paternity test)
Can be performed the —— trimester
Uses fetal DNA found in the —- of the pregnant mother
CVS (chorionic villus sampling)
Takes place at 10 and 13 weeks
Uses tissue from the —— and carries risk of a ——-
Amniocentesis
Takes place at 15-20 weeks
Collect amniotic fluid but carries risk of ———
amniotic, placental, first, blood, placenta, miscarriage, miscarriage
DNA based paternity testing
Requires three sources of DNA: ——(3)—-
Paternity index (PI)
relative ——- that the AF transmitted the —— ——- allele to the child at that specific locus
Inclusion
AF having the —— necessary to indicate he is likely the father
Contains all OPA’s
Exclusion
Not have any —- that could indicate the possibility of being the father
Does not contain the OPA
Obligate paternal alleles
Alleles shared between the —— and the —— that could NOT belong to the mother
maternal paternal child, probability, obligate paternal, alleles, alleles, father, child
DNA based paternity testing: Methodology
Southern Blot with probe
Uses —— specific probes to analyze the number of repeats in the polymorphism
Size of hybridized DNA correlates to # of repeats
Detects the alleles of the mother, father, and child
Can detect DNA ——-
PCR amplification of TR regions
Amplification of loci containing the ——- regions of the DNA to determine number of repeats
Separation of amplicons based on ——-
Product Band size is related to length of repeat
loci, methylation, polymorphic, size
Paternity Index (PI)
Compares the likelihood that the alleged father passed down the allele vs. the likelihood that a random man passed down the allele
Basically, determining the likelihood that the child and father matching alleles at that locus is due to —— ——-
Formula = X/Y
X = chance that the AF could transmit the —— allele
X = 1 if the AF is ——-
X = 0.5 if the AF is ——-
Y = chance a random man of the same race could have transmitted the allele
PI represents the Ratio of the two probabilities
AF is the father vs. random man is the father
Larger ratio = ——- evidence that AF is the real father
random chance obligate, homozygous, heterozygous, more
Resulting using PI, PPE, CPP, and CPI
Probability of paternity Equation
PPE = ———
A PI is calculated for EACH locus
Result is a % … must be ——- to be accurate
Cumulative Paternity Index
CPI = ———
This is a addition of the PI for each ——- tested when multiple loci are tested
Used to calculate the CPP
Cumulative Probability of Paternity
CPP = ———-
Result is a %
Representative of the probability of paternity for an AF when ALL obligate paternal alleles tested at each locus are taken into account
The more alleles matched between the father and child, the —— the probability they are the father
PI/PI+1 × 100, >99.9%, PIa + PIb + PIc, locus, CPI/CPI+1 × 100, higher
Inclusion
Conclusion that the —- is the real father
Confirmed by testing——- loci and performing —— calculations
Father must match at ——- or more loci for inclusion to be considered
AF, >20, statistical, 20
Exclusion
AF can —— be the father
AF does not match the child at ——- loci
not, 3 or more
Criteria >20
A paternity test will analyze ——- or more loci
These are locations on the chromosomes that vary in —— among individuals and are the subject of comparison between child and father
Result of >20 indicates the father and child matched at at least 20 loci
The more loci that match = the ——- the evidence of inclusion
Exclusion only needs ——- or more loci to NOT match
20, length, stronger, 3
Summary
Paternity testing is a legal —- —- ——- of a parent to a child
Applications can include ——- investigation, immigration, parentage, and clinical
Paternity testing utilizes either ——— or —— methodologies
We can determine paternity using the comparison of band ——- on southern blot or PCR
True Father should have an allele that is the same size as the OBA from the child
We can also determine paternity using the —— —— —— equation after determining the —- of a locus
If testing multiple loci we also use ——- and —— equations
The importance of paternity testing is the determine the —— of a child
chain of custody, criminal, southern blot, PCR, size, probability of paternity, PI, CPI CPP, father
Question 1: How many allele copies should the father and child share at each locus?
one
Question 2: which suspect is guilty
suspect 3
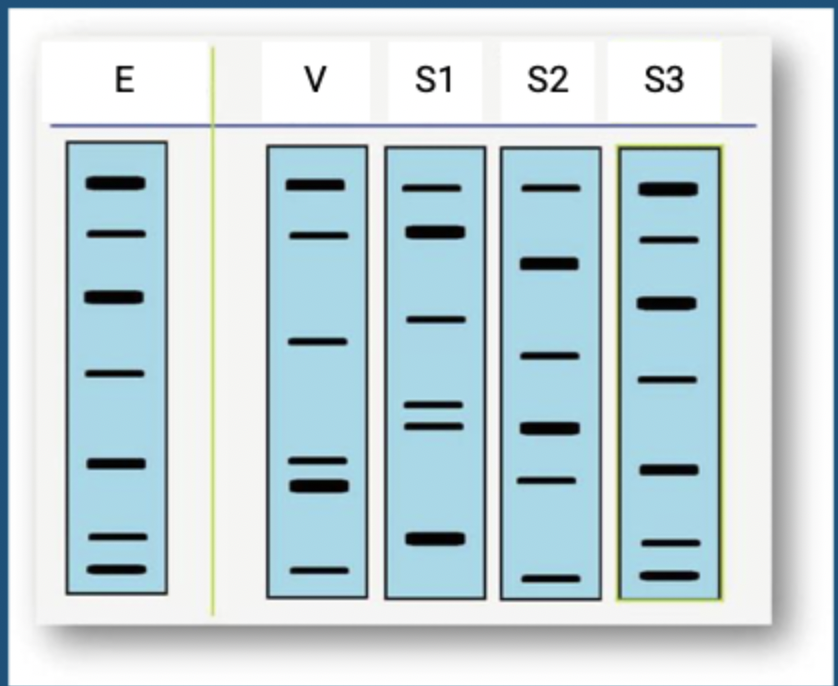
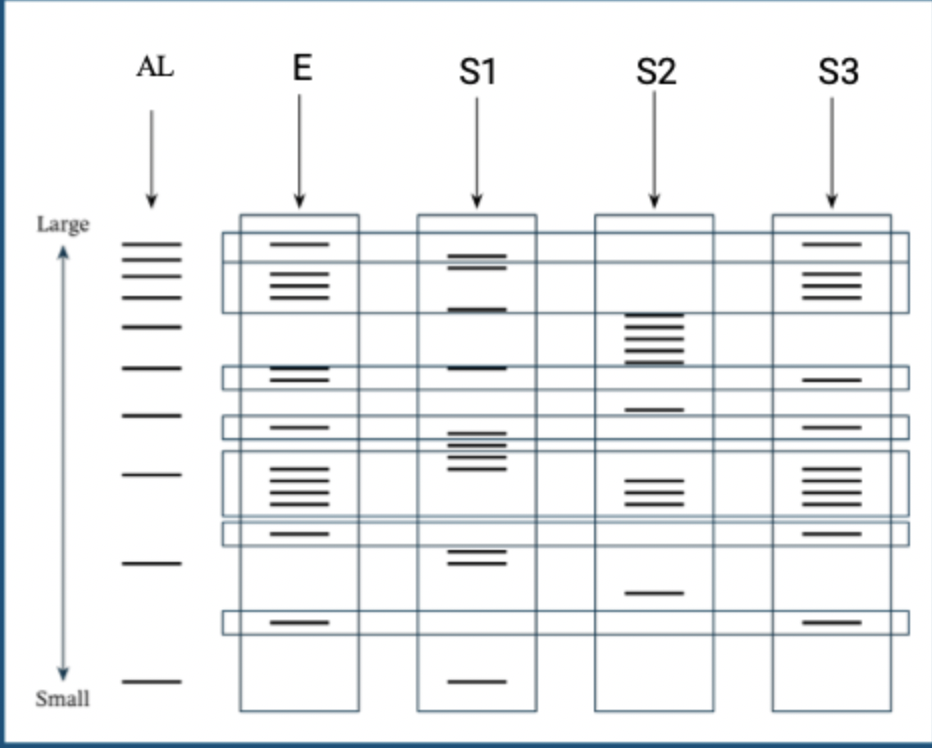
Question 3: which suspect is guilty?
suspect 3
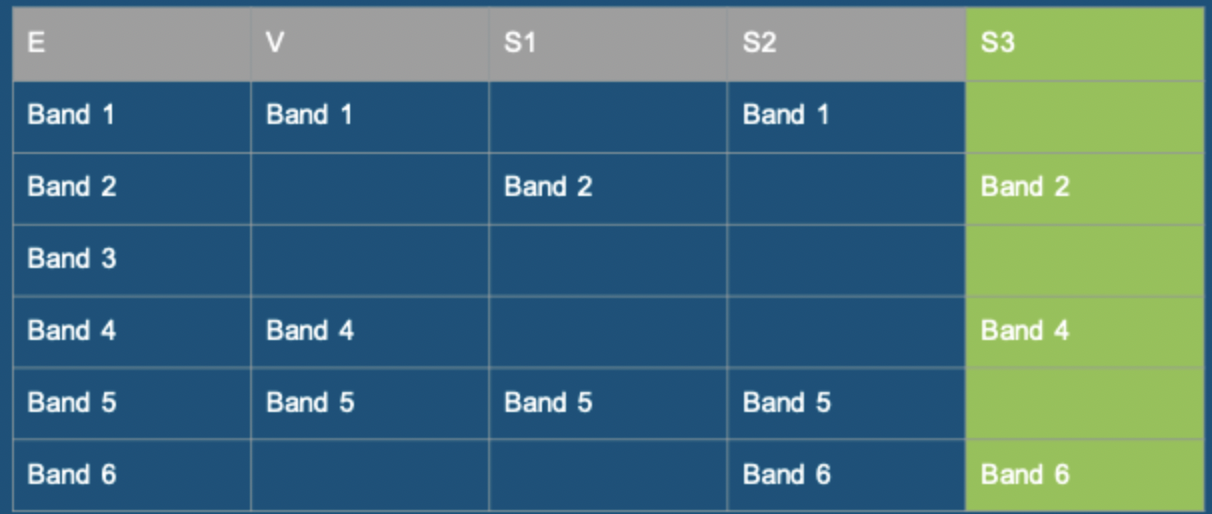
Question 4: could suspect 3 by the criminal?
no, they do not possess every band present in the evidence
Question 5: which paternity test can be performed the earliest
A. Amniocentesis
B. buccal swab
C. Noninvasive prenatal paternity test (NIPP)
D. chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
C
Question 6: which is NOT true about souther blot and PCR
A. PCR requires less genetic material than souther blot
B. PCR can be used to determine DNA methylation
C. Probes are needed for southern blot
D. Probes are needed for PCR
B
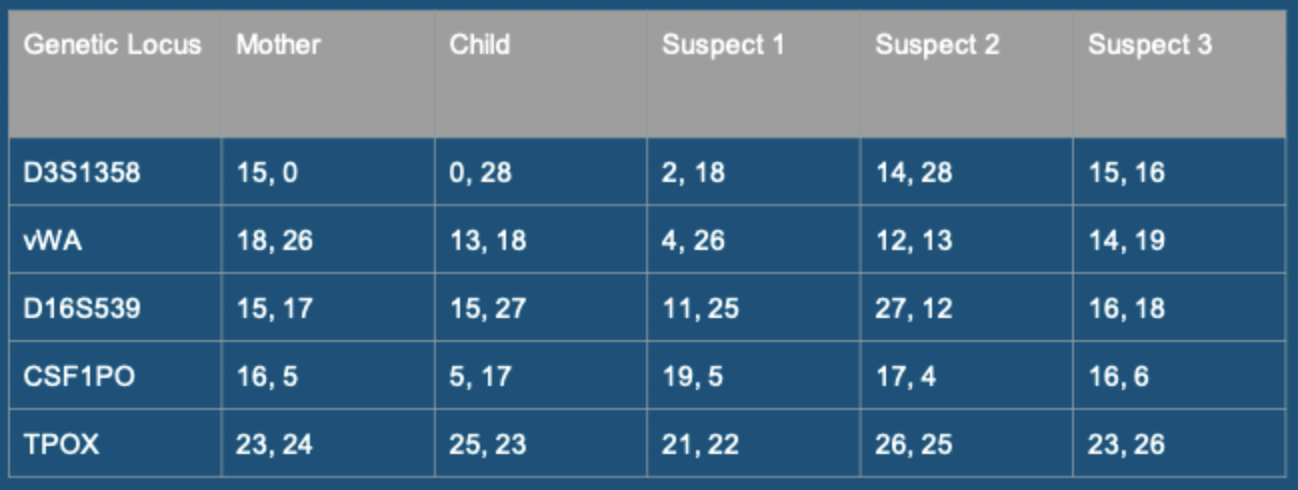
Question 7: Who is the potential father
AF 2
Question 8: can mitochondrial DNA be used for paternity testing? Why?
No, it’s passed down by the mother and is not as specific