Basal Ganglia GT
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Fornix, mamillary bodies, cingluate gyrus, hypocampus, anterior thalamic nuclei =
memory
Parahippocampal gyrus contains
hippocampus
What is the primary function of the basal ganglia
Primary motor coordination (within muscle) center; coordinated balanced smooth motion
Overall and simplified, what is the objective of the direct pathway
wanted movement for tasks
Overall and simplified, what is the objective of the indirect pathway
inhibit unwanted movements for tasks
What is the net outome of dopamine when it is released from the subtantia nigra pars compacta to dopa-r on striatum
Dopamine will always want to end in movement. Dopamine is the lubricant of movement = greaser of the wheel
What is the “homeplate”, of the basal ganglia
motor cortex
What are the GLUTAMATE releasing structures of the BG
Motor cortex, thalmus, subthalmus
What are the GABA releasing structures of the BG
Striatum (caudate nucleus and putaman), globus pallidus medial/lateral, and substantia nlgra pars reticularis
What is the DOPAMINE releasing structure of the basal ganglia
Substantia Nigra Pars Compacta
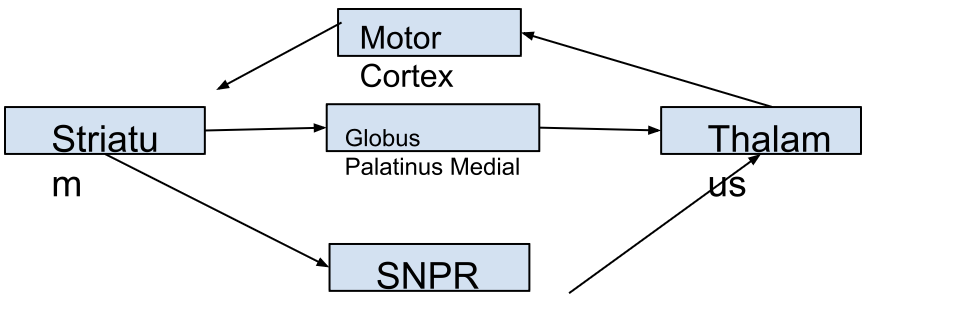
What is the ORDER the neurons run (synapse) in the DIRECT pathway
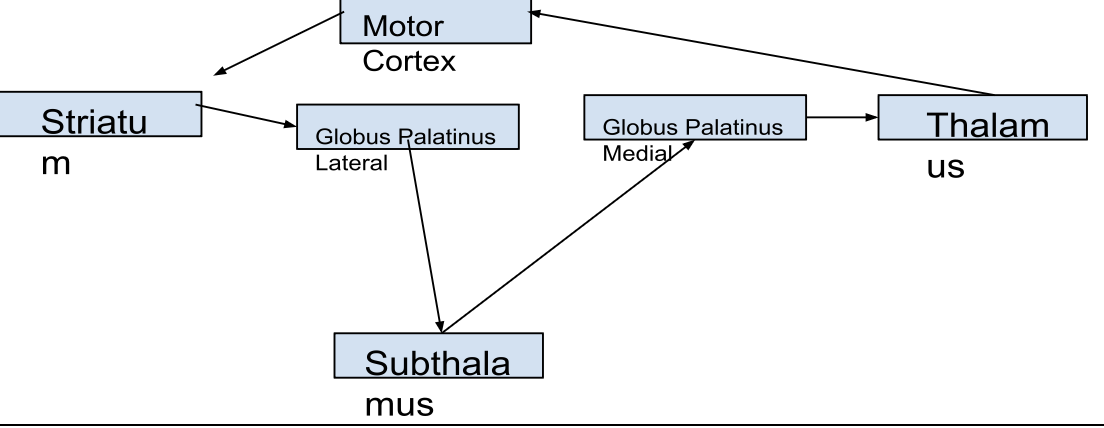
What is the ORDER the neurons run (synapse) in the INDIRECT pathway
Generally speaking, what is the BG structure that suffers degeneration with Huntington’s Disease
Striatum
Generally speaking, what is the BG structure that suffers degeneration with Parkinson’s Disease
Substantia Migra Pons Compacta
What is the effect of the motor cortex on the striatum in the DIRECT AND INDIRECT pathway
Motor cortex releases glutamate to stimulate striatum
DIRECT PATHWAY
What is the effect of the Striatum on the Globus Pallidus Medial
Inhibit Globus Pallidus with GABA
DIRECT PATHWAY
What is the effect of the Striatum on the Subst Nigra Pars Ret
Inhibit SNPR with GABA
DIRECT PATHWAY
What is the effect of the GPm and SNPR on the Thalamus
less inhibition so thalamus can secret more glutamate
DIRECT PATHWAY
What is the effect of the thalamus on the motor cortex neurons
promotes the movement
INDIRECT PATHWAY
What is the Globus lateral effect on the subthalamus of the indirect pathway?
Releases GABA to inhibit subthalmus but in the indirect pathway it is inhibited so the subthalamus can release more glutamate
INDIRECT PATHWAY
What is the effect of the subthalamus on the GPmed
In the indirect pathway the subthalamus releases more glutamate and stimulates the globus palitus medial; subthalamus releases glutamate
INDIRECT PATHWAY
How does the GPmed affect the thalamus in the indirect pathway
In the indirect pathway the GPmed releases more GABA and inhibits the thalamus; GPmed releases GABA
What is the result of the thalamus on the motor cortex
In the indirect pathway there is less glutamate being released by the thalamus --> decresae movment of unwanted task
Where will the Dopa 1 and Dopa 2 receptors be located
on the striatum
If DOPA synapses at DOPA 1-R, what will be the result?
Movement (the striatum will increase release of GABA
If DOPA synapses on the DOPA 2-R, what will be the result?
Increase movment (the striatum with decrease GABA production) (inhibiting indirect pathway)
What is an example of a HYPOKINETIC DISORDER
Parkinson’s (decrease movement due to lack of dopamine. Can't inhibit D2 so the indirect pathway is working but it can't stimulate D1 so the direct pathways isn’t working)
What is an example of a HYPERKINETIC DISORDER
Huntington’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease = HYPOKINETIC DISORDER
How does PD affect DOPA 1-R
How does PD affect DOPA 2-R
The dopamine can't stimulate D1 so the direct pathway can't work (decreased movement); the dopamine doesn't stimulate D2 so the indirect pathway does work (increased inhibition unwanted movement)
Huntington’s Disease = HYPERKINETIC; increased unplanned/unwanted movement
What is degenerated in HD
What will be the outcome of HD on the direct pathway (at the Motor Cortex)
What will be the outcome of HD on the indirect pathway (at the Motor Cortex)
Striatum is degenerated = in the direct pathway less glutamate will act on motor cortex so less wanted movement
In the indirect pathway there is more glutamate getting to the motor cortex so an increase in unwanted movement
What is the lobe that is associated with emotional responsiveness, memory formation and emotional connection with memory, with endocrine, visceral, and somatic effectors
limbic lobe
Which gyrus will “house” the hippocampus
parahippocampal gyrus
What is the primary function of the hippocampus
memory and memory consolidation
Which aspect of the limbic lobe is closely associated with emotional memory, preparing the fight or flight reaction, fear, aggression, rage, etc
amygdala
Which structure will act as a neuronal “highway” joining the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies of the hypothalamus
fornix
What structures found in the hypothalamus thus connecting the circuit of papez (memory consolidation) to emotional and endocrine aspects of the limbic system
mammillary bodies
Which aspect of the thalamus will be most associated with the limbic system; memory formation and learning and sends neurons to the cingulate gyrus
anterior thalmic nucleus
Which aspect of the limbic system and circuit of papez will help with emotion to memory; autonomic function regulation, and emotional processing
cingulate gyrusWhat is the outcome of a lesion to the hippocampus (typically and generally, as there is so much more to this than we discuss)
What is the outcome of a lesion to the hippocampus (typically and generally, as there is so much more to this than we discuss)
Not being able to form new memory