Specific Latent Heat and Phase Changes
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is a phase of matter?
A definite region of space where all physical and chemical properties of a substance are the same.
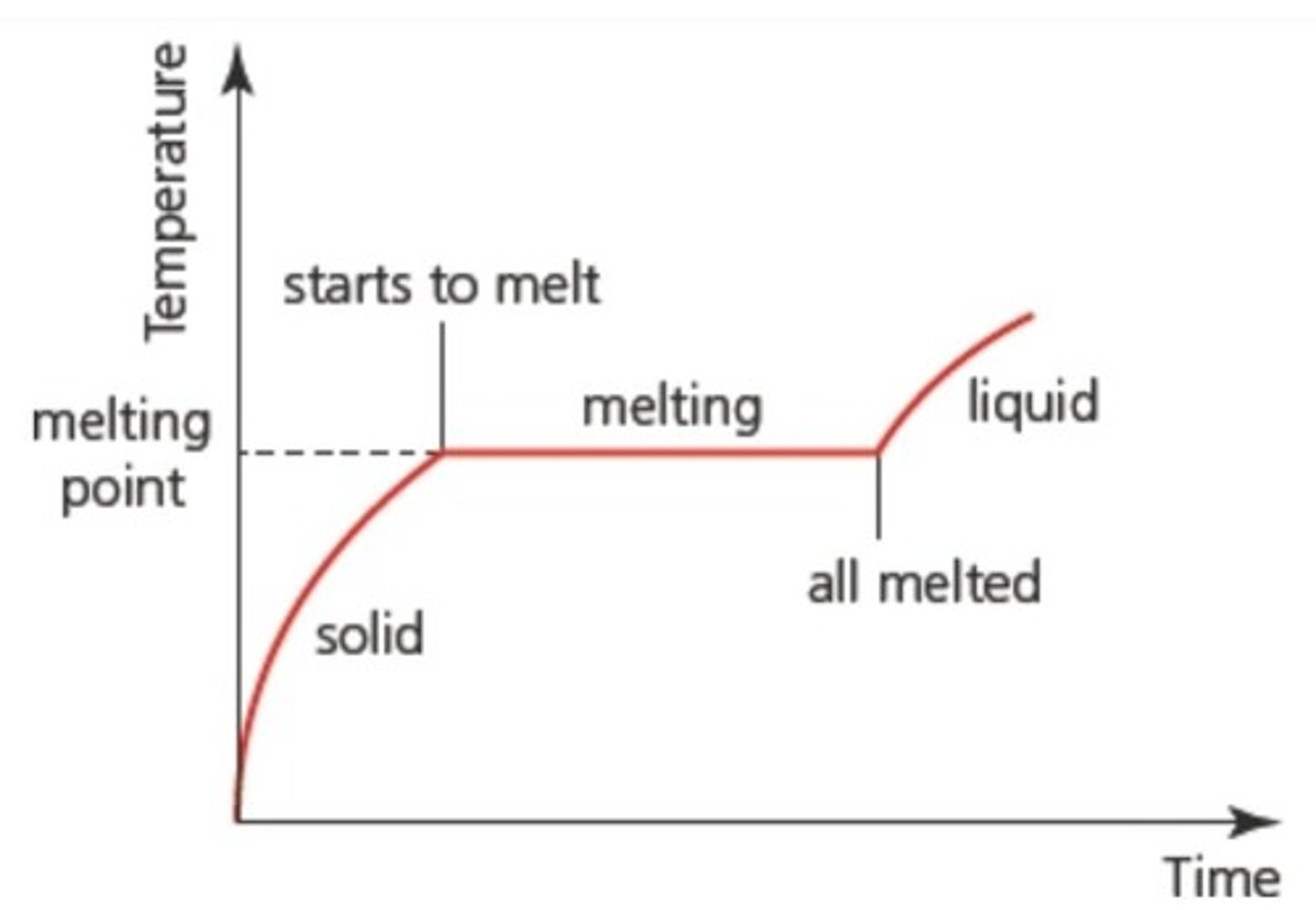
What is the melting point?
The temperature at which solids change to a liquid.
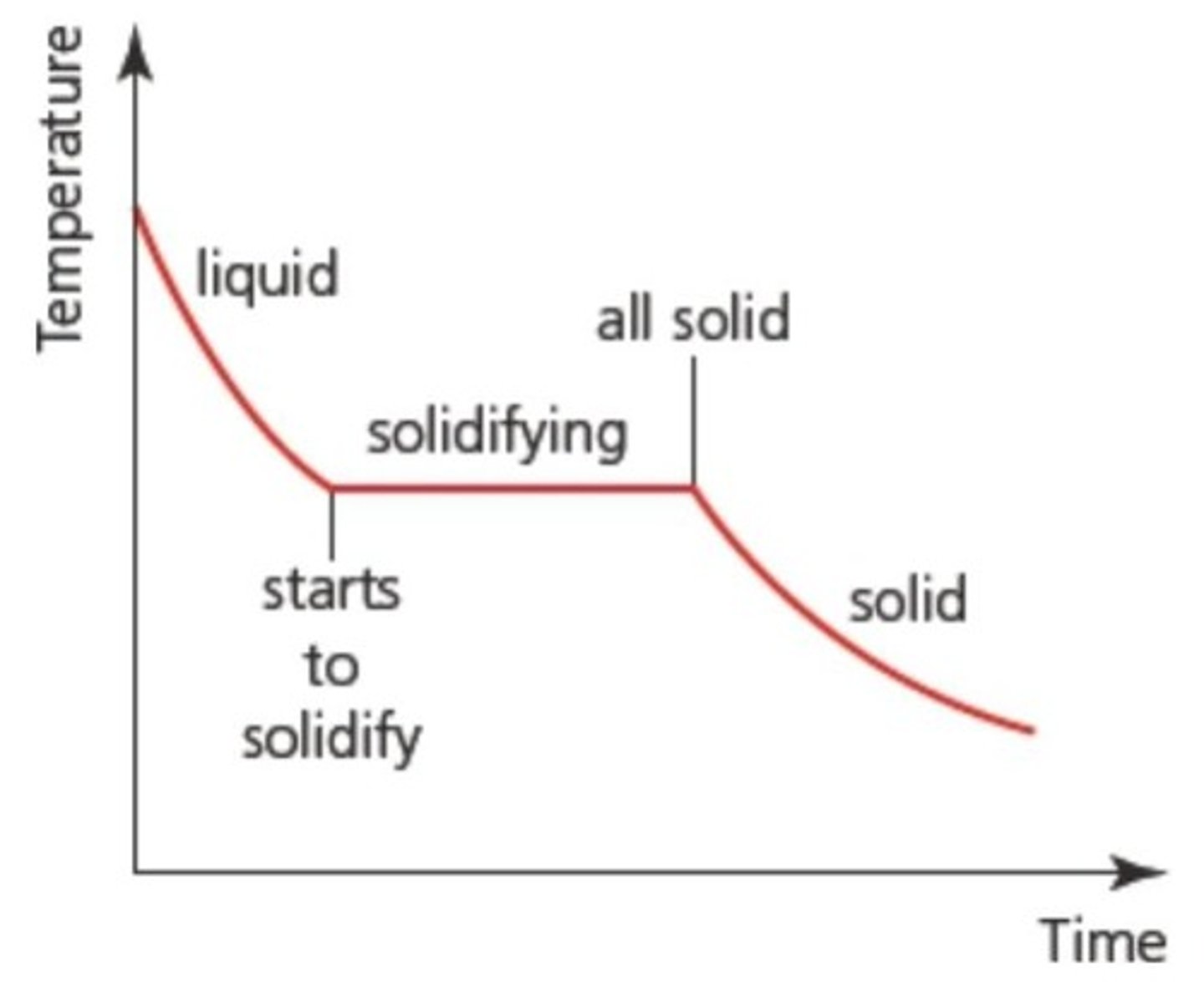
What is freezing in terms of phase change?
The process of changing from a liquid to a solid, which does not necessarily require cold temperatures.
What is fusion in the context of phase changes?
The general process of changing from solid to liquid or vice versa.
What is the difference between boiling and evaporation?
Boiling occurs throughout the liquid at a specific temperature, while evaporation occurs only at the surface and can happen at any temperature.
Why does temperature remain constant during phase changes?
Energy supplied during phase changes increases potential energy rather than kinetic energy, keeping temperature constant.
What is specific latent heat (L)?
The amount of energy per kg required to change phase without a change in temperature.
What is the specific latent heat of fusion?
The thermal energy required to change 1 kg of a substance from solid to liquid without a temperature change.
What is the specific latent heat of vaporization?
The thermal energy required to change 1 kg of a substance from liquid to gas without a temperature change.
What is the equation for thermal energy during a phase change?
Q = mL, where Q is the thermal energy, m is the mass, and L is the specific latent heat.
What is the heat of fusion for water?
3.3 x 10^5 J/kg.
What is the heat of vaporization for water?
2.3 x 10^6 J/kg.
How much energy must be removed to freeze 2.0 kg of water at 0°C?
The energy required is 2.0 kg Lfusion = 2.0 kg 3.34 x 10^5 J/kg.
How much energy is needed to vaporize 2.0 kg of water at 100°C?
The energy required is 2.0 kg Lvaporization = 2.0 kg 2.26 x 10^6 J/kg.
What happens to the average kinetic energy during phase changes?
The average kinetic energy remains constant while potential energy changes.
What is the specific heat capacity of water?
4200 J/kg·K.
What is the specific heat capacity of ice?
2100 J/kg·K.
How does the slope of a heating curve relate to specific heat capacity?
The slope is inversely proportional to specific heat capacity; steeper slopes indicate smaller values of c.
What is the relationship between latent heat and time during phase changes?
Longer phase change times indicate higher latent heat values.
What is the process of condensation?
The process of changing from gas to liquid.
What is vaporization?
The general process of changing from liquid to gas or vice versa.
What is the significance of latent heat in cooling systems?
Latent heat is utilized in processes like sweating and refrigeration to absorb or release heat without changing temperature.
What is the energy transfer equation for temperature changes?
ΔQ = mcΔT, where ΔQ is the thermal energy, m is the mass, c is specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the change in temperature.