Psych110 Chapter 2
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
What are the five ways of knowing?
Authority — books and experts; “so-and-so told me”
Logic — “A>B and B>C, so A>C”
Common sense — it’s obvious!
Intuition, personal experience — “I find it to be true.”
Science — an objective method to gather and evaluate information.
What are the advantages of knowing things through science?
Methodology is not specific to one area.
Collects objective evidence
Searches for general rules
Makes falsifiable statements
Adopts a skeptical, questioning attitude about claims
Remains open-minded about claims
What is a problem with information?
It is only as good as the method used to collect it, so you must evaluate the quality of the method.
What is the issue with bias?
Science should be free from bias, but sometimes scientists are biased. You must evaluate alternative explanations.
An important feature of the scientific method is that science is _____.
Tentative; it can support theories, but not prove them.
Peer Review
When knowledge or research is reviewed by the scientific community and verified through replication.
Knowledge is reviewed and verified through what process?
Replication
Since knowledge can be verified through replication, it is ___________.
Self correcting
Science only deals with ______ problems.
Solvable
Questions must be posed in a way that is ________. Hence, the way that we pose questions must be very _______.
Testable ; precise
Cherry-picking
Picking data that “works” and leaving out other, real data.
What are the eleven steps of the scientific process?
Ask a question; may be based on a theory.
Formulate a hypothesis
Derive predictions to test the hypothesis
Define how to measure variables
Pick participants
Select a research method
Select a research design
Collect data
Evaluate and draw conclusions
Report findings
Refine/reformulate questions as needed
What are the five research methods?
Naturalistic observation
Case study
Survey
Correlational study
Experiment
What are the three research designs?
Within subjects
Between subjects
Mixed subjects
“R and R”
Revise and resubmit; what most researchers must do when they submit research to a journal.
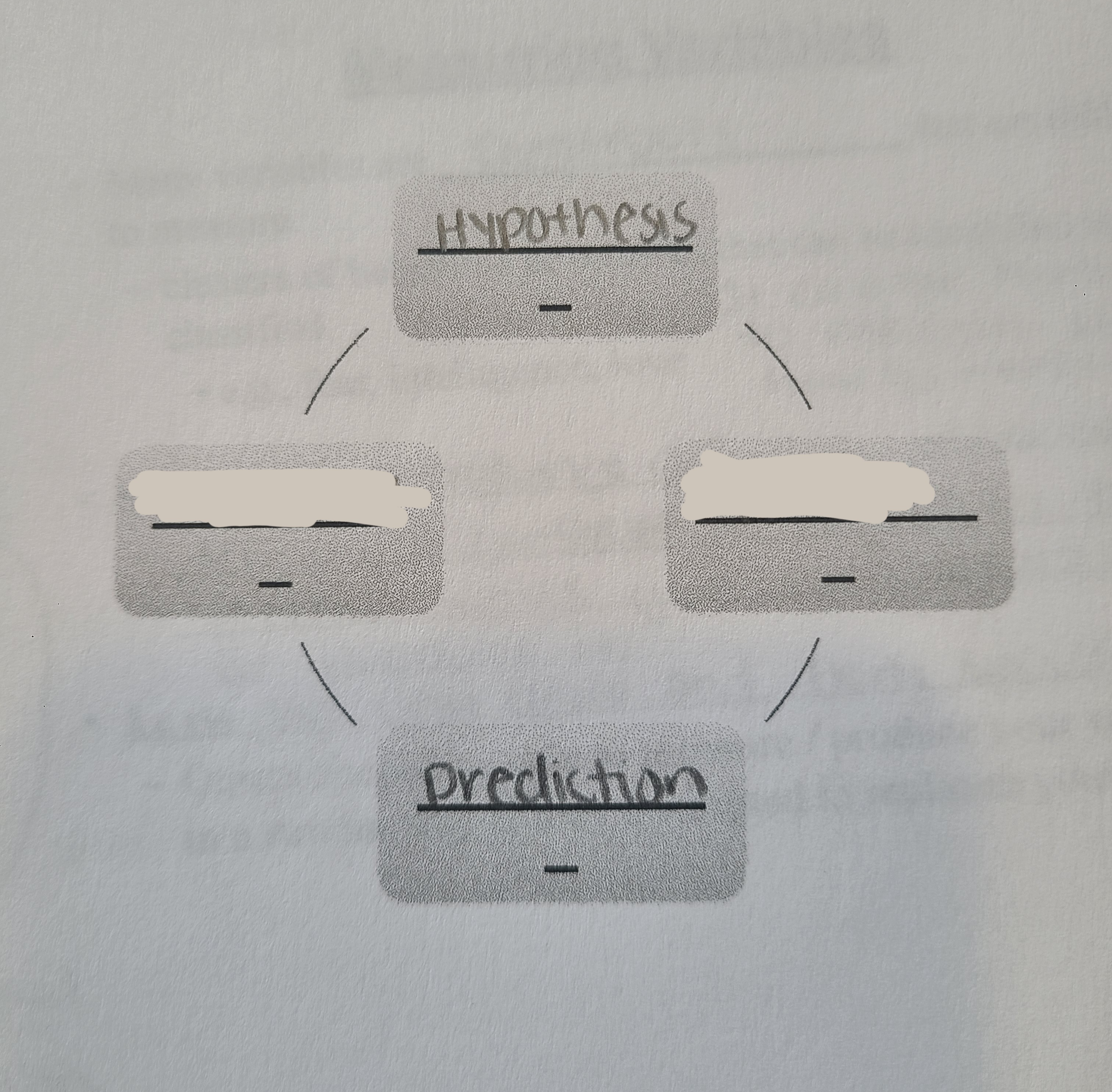
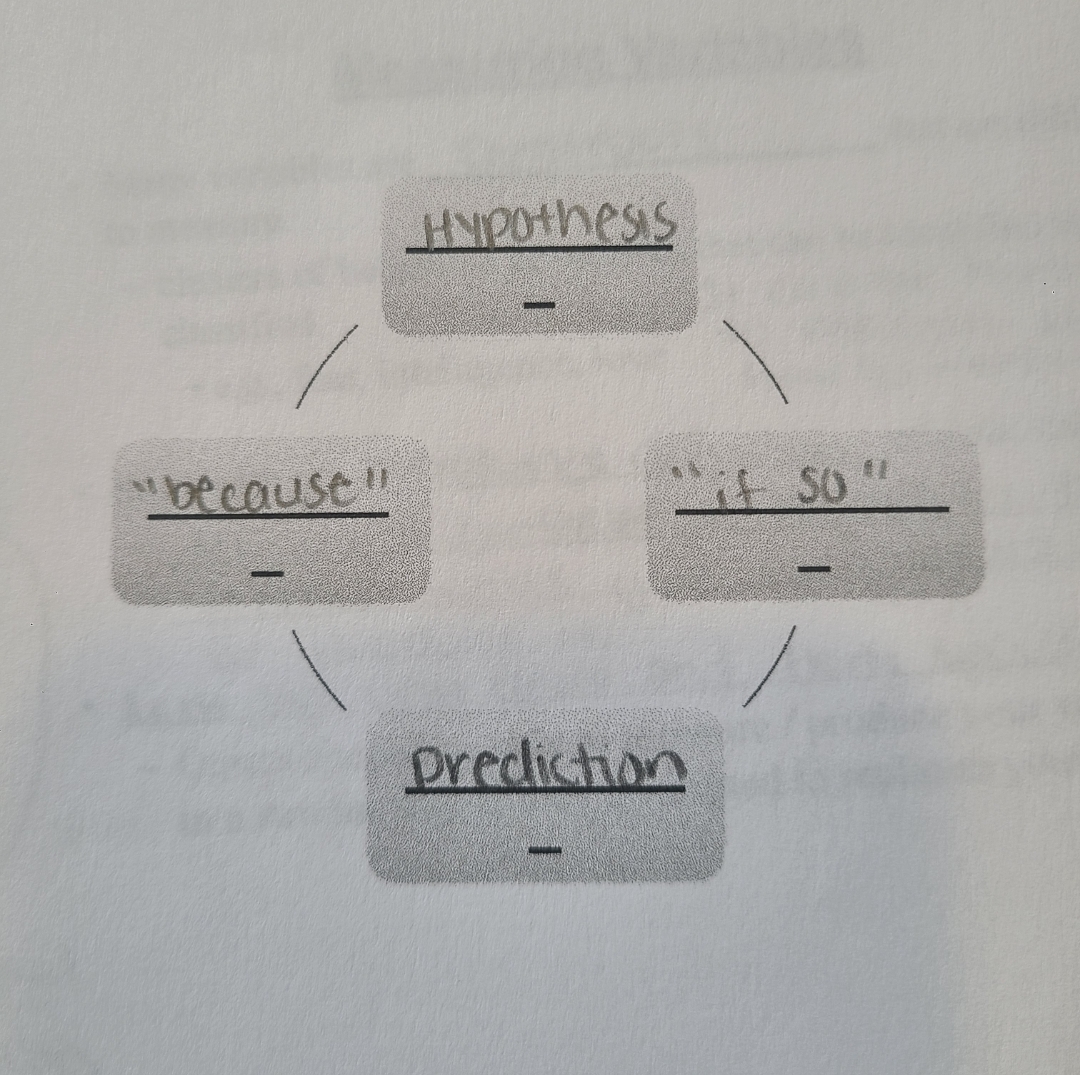
Theory
A model or framework that describes a related set of phenomena predicts future occurrences, can be falsified through empirical observation.
Hypothesis
Tentative assertions about psychology (answers why something you expect to observe will occur).
Prediction
What you expect to observe.
Parental Investment Theory
Asymmetrical parental Investment leads the lower investing sex to compete amongst each other for access to the higher investing sex, which is more discriminating.
Many variables are ________ that are difficult to measure.
Constructs
Variables
Clusters of behaviors or motives that can be identified and classified.
Operational Definition
Defining a construct in regard to the specific ways you will measure or produce it; must be very clear and very specific.
Others should be able to _________ and/or _______ your variables in a similar way if they attempted to replicate your study.
Measure and/or produce
Naturalistic Observation
Careful monitoring and examination of what animals (including humans) do in “real world” conditions. Observations and descriptions only.
Naturalistic observation tells us what ________ happen, not ______ it happens.
Can; why
Naturalistic observation includes no __________.
Manipulation
Naturalistic observation may not be accurate. Why?
It shows what happens under observed conditions, not what typically happens.
May not generalize to others.
Case Study
Thorough observation and description of a single individual; observation and description only.
A case study can tell us what _______ happen, not _______ it happens.
can; why
In a case study and naturalistic observation, _________ is not determined
causation
Phineas Gage
A rod accidentally exploded into his brain, but he lived and recovered.
His personality changed; aggressive, anti-social, off-putting.
Possibly PTSD, Trauma, TBI, or observers annoyed him.
We ethically can’t test why he was this way.
Darwin’s observations are an example of ___________________.
Naturalistic observation
Jane Goodall is a _______.
Naturalist
Who arranged for three woman to study hominids in their natural environments?
Louis Leaky
Correlation
Tells you how well one variable predicts another variable; MUST have two measurements for each participant and one for each variable .
Correlation can only be used if there is a ______ relationship between variables.
Linear
How do you construct a graph for a correlational study?
Construct a scatter plot.
Values of variable 1 go on the x-axis (the variable that you’re predicting)
Values of variable 2 go on the Y-axis
Each person’s score is represented with a dot.
Positive Correlation
Increases in variable X are associated with increases in variable Y; decreases in variable Y are associated with decreases in variable Y.
Negative Correlation
Increases in variable X are associated with decreases in variable Y.
No Correlation
The variables have no relationship; an increase or decrease in variable X are not associated with an increase or decrease in Y.
High scores on X show both high and low scores on Y.
Low scores on X show both high and low scores on Y.
Saying that two things are correlated isn’t enough; you must say what?
How the things are correlated, positively or negatively.
A +1 correlation indicates a ______ correlation.
Strong
A -1 correlation indicates a ______ correlation.
Weak, nonexistent
The Pearson correlation coefficient r tells you what?
The direction of a linear relationship between two variables (±)
The strength of the linear relationship between two variables (magnitude of the value)
Always between +1 and -1; the higher the absolute value — regardless of direction — the stronger the correlation is.
What are the three causal pathways for correlations?
X may cause Y
Y may cause X
Z may cause both X and Y
Third variable problem
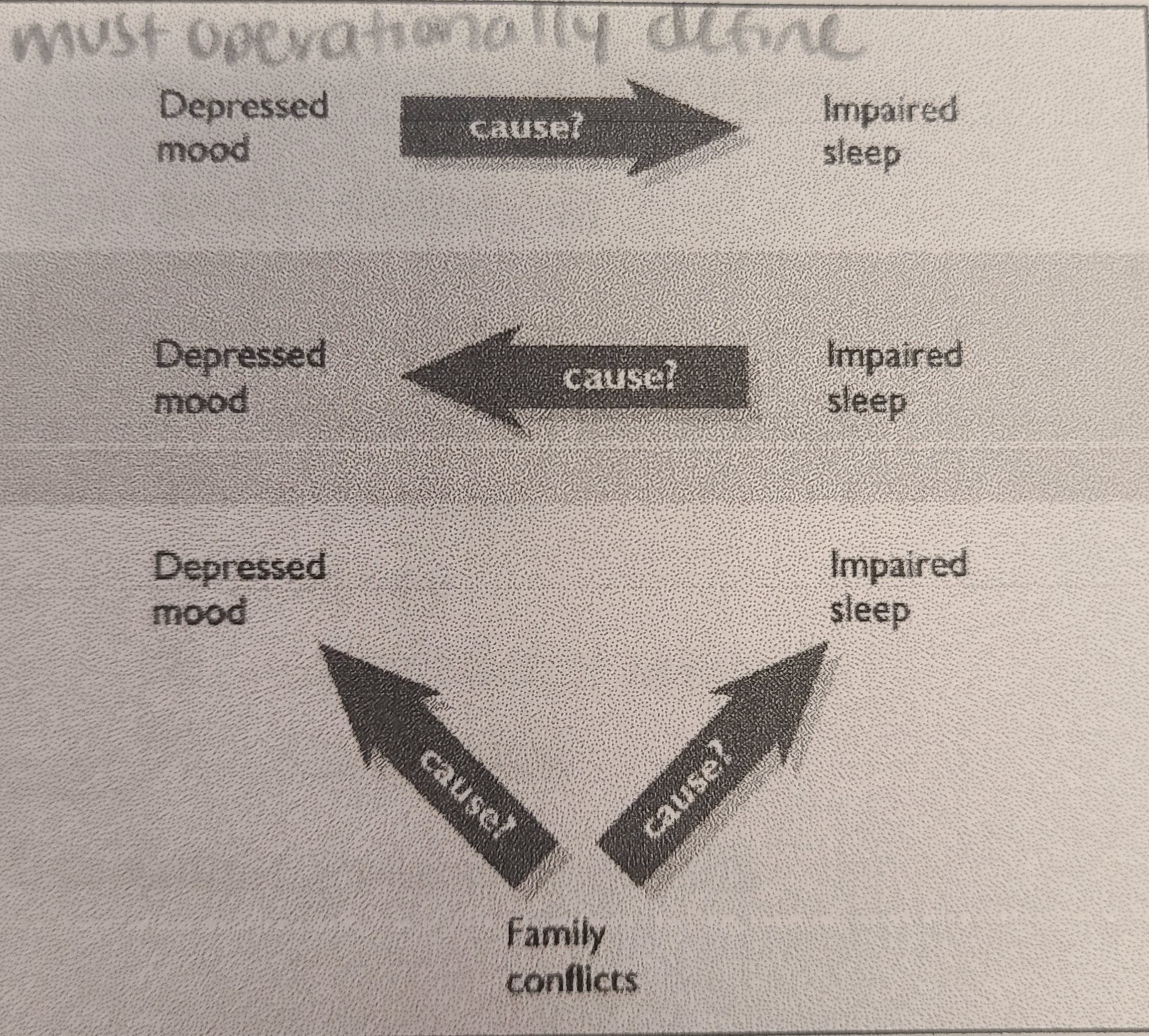
Correlation does not imply _______.
Causation
Variable
Any situation, event, or behavior that has at least two values (varies)
What are the things that a variable consists of?
Numbers or categories that vary and convey information about a well-defined entity.
Value
A possible number (or category) that a variable can have.
Score
A given person’s value on the variable.
Data
Variables and their values & scores.
Experiment
A study that manipulates a variable (the independent variable) and observes its affects on another variable (the dependent variable).
Independent Variable
What we manipulate (change) to see affects on the other variable.
Dependent Variable
What we measure
Experiments are designed to answer what is the effect of the ________ on the _________.
Independent variable on the dependent variable
Experimental Group
Comparison group; similar subjects who receive a different level of the independent variable or nothing.
Confounding Variables
A variable other than the independent variable that is linked with the independent variable that could influence the dependent variable.
A ________ variable’s affect on the dependent variable cannot be separated from the ________ variable’s affect on the dependent variable.
Confounding; independent
A confounding variable ________ with the independent variable.
Co-occurs
Sampling Bias
Occurs when some members of a population are systematically more likely to be selected in a sample than others.
Placebo Effect
When people’s expectations lead them to perceive an affect or change.
What are some reasons why there would be distortions in self-reported data?
Social accountability bias: people want to look/be perceived a certain way, so they change their answer.
If a study is not anonymous, someone may change their answer.
Experimenter Bias
A form of reactivity in which a researcher's cognitive bias causes them to subconsciously influence the participants of an experiment.
Double-blind Experiment
Both the experimenter and the participant do not know which group is which (the experimental group or the control group).
What are some flaws that could occur in research?
Sampling Bias
Placebo effects
distortions in self reported data
experimenter Bias
What are two ways to limit/prevent experimenter bias?
Use a script.
Make your experiment a double-blind experiment
Script
Following the same procedure for everything while also not knowing what group you are dealing with so that you do not affect the results.
Theory
A model or framework that describes a related set of phenomena, predicts future occurrences, can be falsified through empirical observations.
Hypothesis
Tentative assertions about our psychology; usually answers “why” something you expect to happen will occur.
Prediction
What you expect to observe; usually deduced from a hypothesis to test the hypothesis.
Who created the parental Investment Theory?
Robert Trivers
Naturalistic Fallacy
When people excuse, justify, or explain their behaviors based on evolution or genetics.
Why did Robert Trivers hypothesize women invest more in their children than men?
Men invest less because they are only needed for a few minutes to reproduce, while women carry a child for at least 9 months and may still have time after where they cannot bear children. Simply, women invest more time than men.
Be sure to _____ a comparison; for example, women are more involved in raising children than men.
Complete
What did Diane Fossey study?
Mountain gorillas that were being poached.
Participant-Observer observation
A researcher engages in the same activities as the people being observed, since the act of being observed can change behaviors.